
Plea for Use of Intelligent Information and Communication
Technologies in Infection Surveillance and Benchmarking
by Healthcare Institutions
Walter Koller
1
, Klaus-Peter Adlassnig
2,3
, Andrea Rappelsberger
2
and Alexander Blacky
1
1
Clinical Institute of Hospital Hygiene, Medical University of Vienna and Vienna General Hospital,
Waehringer Strasse 18-20, 1090 Vienna, Austria
2
Section for Medical Expert and Knowledge-Based Systems, Center for Medical Statistics, Informatics,
and Intelligent Systems, Medical University of Vienna, Spitalgasse 23, 1090 Vienna, Austria
3
Medexter Healthcare GmbH, Borschkegasse 7/5, 1090 Vienna, Austria
Keywords: Intelligent Information and Communication Technologies in Healthcare and Medicine, Knowledge
Management, Intelligent Decision Support Systems, Surveillance of Healthcare-Associated Infections,
Hospital Benchmarking.
Abstract: Top healthcare and medicine depends on the implementation of best practice methods, which include
surveillance of and benchmarking with defined quality indicators. Using healthcare-associated infection
(HAI) surveillance as an example, we put forward arguments in favour of automated intelligent information
and communication technologies. Assessment studies with our fully automated detection and monitoring
system for HAIs not only revealed much higher precision of surveillance results and much less time
investment compared with conventional surveillance, but also a potential emerged for amendments and
adaptations regarding new input categories or new surveillance outputs desired by clinicians, administrators,
and health authorities. In this way, intelligent information and communication technologies are becoming
indispensable in building affordable “safety nets” for quality assurance and benchmarking, based on fully
automated and intelligent data and knowledge management. These in turn form the backbone of high-level
healthcare, patient safety, and error prevention.
1 INTRODUCTION
Health institutions today are confronted with
growing demands for documentation, quality
assurance, certification, and benchmarking. Many of
these tasks are performed and shared within
networks and require compliance with predefined
criteria and standards. These activities are driven by
legal, economical, best practice, and patient safety
requirements to address just a few. Having to run
such complex systems is the price for us to pay for
top healthcare, rehabilitation, and disease prevention
we are profiting from in the developed regions of the
world.
Doctors and nurses as well as other experts in
health institutions carry an increasing workload in
entering the huge amount of data required for
documentation tasks. We have to accept that these
obligations interfere with the genuine medical and
humanitarian duties we expect from caregivers, and
that such tasks contribute to the exhaustion of
medical staff. In turn, we as patients suffer from
distracted, overtired, or resigning health personnel.
All that unfolds in a climate of growing economical
and manpower restrictions.
Intelligent information and communication
technologies (ICTs) can be considered as a key
factor in overcoming this imminent deadlock of
modern health systems and in providing for high and
even better quality healthcare.
In order to achieve this goal, data generation and
documentation must comply with a few strict rules,
and ICT must be linked intelligently with the
medical documentation systems of the healthcare
institution. Redundant documentation, free text
documents, and non-coded data are detrimental. In
contrast, a strict culture of coded, concise, and
timely data entry (especially in clinical
documentation!) and a reproducible, well-
399
Koller W., Adlassnig K., Rappelsberger A. and Blacky A..
Plea for Use of Intelligent Information and Communication Technologies in Infection Surveillance and Benchmarking by Healthcare Institutions.
DOI: 10.5220/0004902303990404
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Health Informatics (HEALTHINF-2014), pages 399-404
ISBN: 978-989-758-010-9
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

documented data management combined with
modern interface technologies are considered to be
particularly promising. They allow for both effective
ICT assistance, relieve for, and higher potential of
caregivers, experts, and administrators.
We have developed and describe below an
intelligent ICT for detection and surveillance of
healthcare- associated infections (HAIs) in intensive
care medicine, called Moni (Monitoring Of
Nosocomial Infections).
2 METHODS
2.1 MONI-ICU and MONI-NICU
MONI-ICU is a clinical detection and monitoring
system for HAIs, which has been developed in
cooperation with the Vienna General Hospital
(VGH) and the Medical University of Vienna
(MUV). At present, it monitors ten intensive care
units (ICUs) for adult patients at the 2116 bed
university hospital.
MONI-NICU is the corresponding system for
neonatal intensive medicine. It monitors four
neonatal ICUs at the VGH and differs from MONI-
ICU in the effect that it uses a different knowledge
base especially developed for neonatal patients.
An early version of the MONI system is
described in Chizzali-Bonfadin et al. (1995). MONI
is a fusion of several methodologies drawn from
artificial intelligence, fuzzy set theory and logic, as
well as medical knowledge engineering (Adlassnig
et al., 2008; Adlassnig et al., 2009; Blacky et al.,
2011).
2.2 Data Sources
The MONI systems have automated access to
several data sources: Most important with regard to
patients’ day-to-day clinical, laboratory, and care
data is MONI’s access to the intensive care medical
information system ICCA, a patient data
management system (PDMS) by Philips. For the
acquisition of microbiological data, the systems are
connected to the laboratory information system
(LIS) of the hospital (MOLIS by vision4health),
established for the microbiology department.
Finally, administrative patient data from the hospital
information system (HIS) is used by both the PDMS
and the LIS to uniquely identify the patient and
hospital stay (i.s.h.med by Siemens).
2.3 Medical Knowledge Bases
Both the MONI-ICU and the MONI-NICU
knowledge bases are Arden Syntax 2.9
representations of the HAI definitions used by the
European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control
(2013), Stockholm, HAI surveillance network and
the KISS definitions issued by the German National
Center for Surveillance of Nosocomial Infections
(2013a), Berlin, respectively.
The Arden Syntax for Medical Logic Modules is
a language for encoding medical knowledge that
consists of independent modules and is maintained
and developed further by Health Level Seven (HL7)
International, a standards organization for health
data and knowledge. It was developed in order to
represent clinical knowledge in a standardized,
machine-readable but also human-readable form.
Clinical knowledge is captured in Arden Syntax
rules or procedures and can be accessed and
evaluated through a rule engine. Within the Arden
Syntax, individual rules or procedures are organized
in medical logic modules (MLMs), each of which
contains sufficient knowledge for a single medical
decision (Hripcsak, 1994); refer also to Samwald et
al. (2012) for further explanation and recent
applications.
Most data thresholds in MONI’s knowledge
bases are fuzzy, i.e., adhering to the principles of the
fuzzy set theory and logic, which were first proposed
by Zadeh (1965). An early survey on medical
diagnosis and fuzzy subsets can be found in
Adlassnig (1982). A complete extension of Arden
Syntax by fuzzy methodologies is part of the most
recent Arden Syntax, version 2.9 (Health Level
Seven, 2013).
By making thresholds fuzzy, we permit clinical
borderline cases to be evaluated in a more gradual
way than the usual binary inclusion or exclusion of a
patient with respect to a certain condition would
allow. What we formally capture here is the inherent
linguistic uncertainty of clinical terms; furthermore,
propositional uncertainty – characteristic for certain
other clinical situations – is captured by using fuzzy
logic.
2.4 Architecture and Processing
The MONI systems are implemented within an
automated, data-driven Arden Syntax framework as
described in Adlassnig and Rappelsberger (2008).
Data from the above-mentioned data sources is
downloaded overnight and stored in the systems’
HEALTHINF2014-InternationalConferenceonHealthInformatics
400

Figure 1: Data processing layers in MONI explaining the way from raw data input [of electronic bedside sensors (e.g.,
pulse, blood pressure, body temperature), from biochemical laboratory (e.g., leucocyte count, erythrocyte sedimentation
rate, C-reactive protein), from microbiology and from routine bedside data entries by ICU staff] to the required specific
outputs. HAI: healthcare associated infection, ICU: intensive care unit, NICU: neonatal intensive care unit.
data warehouse. Once the data transfer is completed,
the MLMs are executed by the Arden Syntax rule
engine. Results and reports can be accessed through
local or remote web application interfaces and
displayed in a client application or a webpage
frontend.
Data processing in MONI is a step-by-step
procedure, starting with raw data and advancing
from one knowledge level to the next, as depicted in
Figure 1.
3 RESULTS
Assessment studies on the MONI systems revealed
high precision in surveillance results (sensitivity
87%, specificity 99%, positive predictive value 96%,
and negative predictive value 95%). Using
automated surveillance systems, time spent with
surveillance could be reduced by 85% compared to
conventional surveillance methods (de Bruin et al.,
2013).
With MONI, there is no need for extra data entry
by medical or surveillance personnel. The PDMSs
collect data from automated electronic bedside
sensors (e.g.,
pulse, blood pressure, body
temperature), from biochemical laboratories (e.g.,
leucocyte count, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C-
reactive protein) as well as manual routine bedside
data entries by intensive care staff (e.g., state of
catheter insertion site). Subsequently, MONI draws
surveillance-relevant data from PDMSs and
microbiology LISs.
We pushed and succeeded in integrating the two
MONI systems fully into the information system of
our hospital. In doing so, we noticed that the interest
of our users (i.e., infection control personnel,
clinicians, study personnel) often goes in more than
one direction. For example, our intensive care
specialists for premature babies exchange their
benchmark data with the German NEO-KISS
network (German National Center for Nosocomial
Infections, 2013b) and with the international
Vermont-Oxford Network (2013).
PleaforUseofIntelligentInformationandCommunicationTechnologiesinInfectionSurveillanceandBenchmarkingby
HealthcareInstitutions
401

Austrian hospitals tend to exchange their HAI
benchmark data not only with the ECDC-affiliated
Austrian Surveillance Network ANISS (ANISS
Surveillance, 2013), but also with the German
counterpart KISS (German National Center for
Nosocomial Infections, 2013a) or with the Austrian
branch (AUQIP, 2013) of the United-States-based
International Quality Indicator Project (IQIP, 2013).
4 DISCUSSION
Having observed infection surveillance for more
than two decades, our experience is as follows:
First of all, surveillance systems depending on
manual data acquisition are laborious to establish
and to maintain, as well as vulnerable; they depend
on specifically trained and dedicated personnel and
cease to function should these people no longer be
available. Since much effort is needed to keep
manually operated surveillance systems alive, the
potential for their extension or change is rather
small.
However, in hospitals where there is a
surveillance system in place and working, user
requests and wishes to extend the system to
additional parameters or to other surveillance
networks soon arise. This reflects the growing
demand for new and more specialised benchmarking
and quality assurance networks in Austria, Europe,
and worldwide.
Secondly, in our experience, electronic PDMSs
in intensive care medicine are an important field of
application for intelligent ICT. If comprehensive
clinical, laboratory, and denominator information is
timely available from PDMSs, ICT can translate it
into the specific formats required by different
networks or applications. New or modified data
fields may be added, and more than one rule (or rule
packages) for automated expert interpretation of the
same data set may be implemented.
Two examples: MONI-NICU interprets clinical
data according to different sets of rules: NEO-KISS
and Vermont-Oxford as well as “clinical alert”
criteria, whereas MONI-ICU is designed to provide
data interpretation in accordance with ECDC as well
as KISS or CDC/NHSN (Centers for Disease
Control and Prevention, 2013a) criteria. Thus,
MONI users may share their surveillance data with
different surveillance networks nationally and
internationally.
Thirdly, surveillance systems for HAIs can be
considered as mere precursory for newer, much
more comprehensive surveillance systems. Recently,
wider entities have been introduced, e.g.,
“ventilator-associated events” instead of
“pneumonia” (Centers for Disease Control and
Prevention, 2013b) and “readmissions,
complications and deaths” which include HAIs,
timely microbiological investigation, and
appropriate antibiotic therapy (Centers for Medicare
& Medicaid Services, 2013).
Figure 2 gives a system view with emphasis on
the various outcomes: surveillance results and alerts,
reporting, and benchmarking.
Arguments against this approach:
Some people are suspicious that ICT is
importing “Big Brother” methods and “NSA
strategies” into health care systems. In fact,
protected ICT systems (not only of healthcare
institutions) themselves are endangered by computer
hackers. Much is to be done against fraudulent
intrusion and loss of confidentiality.
Others warn against dependency on ICT
systems: Some medical experts express their
concerns to be challenged or even ruled out by an
advanced computer system. Vanishing individual
capacity and expertise in understanding what is
behind ICT output may be deemed to pave the way
into the human expert’s loss of control over medical
decisions.
Be such an opposition based on plain fear or on
reality, we must deal with it and take it seriously.
Some of it may remind us of arguments used against
steam engines, railroad, motorcars, or even forks for
eating at the time before they were being introduced
in every day life. In health and medicine, and
especially in hospitals, ICT support still pertains
mainly to hospital administration, logistics, and
billing. This contrasts with other fields, e.g.,
production of technical devices, state administration,
business, and commerce. Medical expertise for a
long time seemed to be kept protected from modern
ICT appliances. This is now changing rapidly, at
least from ICT’s side. From present medical experts
we still see a lack of appreciation for ICTs. Here we
face a field of work that cannot be accomplished by
technical devices. We can assume that the future
generation of medical experts will be much more
ready to use ICT appliances. At present, we need to
convince “digital non-natives”. This brings us back
to deal with and take serious arguments as
mentioned above.
Topics we should address: What can we provide
to safely prevent fraudulent intrusion into and loss of
confidentiality of medical ICT systems? How can
we prevent human expert’s loss of control over
medical decisions? Who could be the interpreters
HEALTHINF2014-InternationalConferenceonHealthInformatics
402
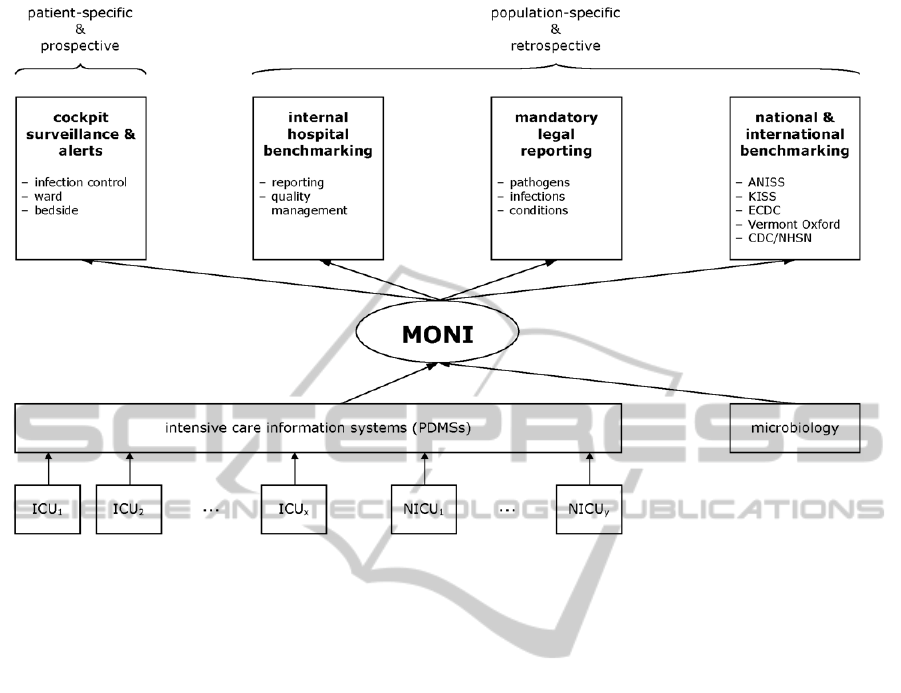
Figure 2: Position of MONI as an intelligent tool for automated processing of specified electronic clinical and laboratory
raw data into surveillance or alert information, which – if required – is outputted in appropriate formats for QM, for internal
or external benchmarking, or for mandatory legal reporting. ICU: intensive care unit for adults, NICU: neonatal ICU.
between clinical experts and ICT specialists and how
could they act successfully in bridging the relevant
perceptual gaps? And
–
one step backwards
–
how
can we accomplish acceptance of surveillance,
benchmarking, the implicated use of medical
standards, clinical criteria and defined rules even by
medical experts who are focussed on “their
individual patient with his/her specific history and
needs”?
From our own experience, we know to what
extent individual scepticism, unfamiliarity with ICT
terminology, and unwillingness to dive into the
complexity of rule-based ICT decision making can
render even powerful ICT tools useless. Still, a
significant lack of awareness of the added values
provided by surveillance, benchmarking, and related
ICT-supportable activities remains.
Finally, as stated in a recent review on electronic
surveillance for HAIs by Freeman et al. (2013) in
the Journal of Hospital Infection: “… electronic
surveillance systems should be developed to
maximize the efficacy of abundant electronic data
sources existing within hospitals;”
and furthermore: “Electronic surveillance
systems should be seen as an opportunity to enhance
current surveillance practices. Staff involved in
surveillance activities should not feel threatened by
advances in this area, but should recognize that
these methods can reduce the burdens associated
with traditional surveillance methodologies, which
will only increase as the emphasis on transparency
and public reporting causes increased demand for
more information to be reported.”
5 CONCLUSIONS
Our aim is to implement intelligent ICT systems in
health and medicine as supporting tools in an ever
growing body of knowledge that has long escaped
the mental capacity of a single human being. We
need these tools for maintaining and updating health
and medical knowledge, for comprehensively,
concisely, and timely applying this knowledge to the
medical course of a defined patient. They help us in
offering knowledgeable proposals and alerts to
caregivers and to support growing surveillance,
report, and benchmarking duties.
The MONI systems seem to be good examples
for this modern ICT approach. They include a data
warehouse for storing raw patient data, finally,
clinical events automatically inferred from these raw
patient data, and, finally, results calculated by using
PleaforUseofIntelligentInformationandCommunicationTechnologiesinInfectionSurveillanceandBenchmarkingby
HealthcareInstitutions
403

consensual clinical definitions of HAIs. They are
connected to an automated inference engine based
on fuzzified Arden Syntax, which is adopted as an
industry standard by HL7. They serve as intelligent
tools that can on the one hand be adapted to varying
or newly emerging inputs, and on the other hand to
changing output demands. In this way, they are
“living” intelligent ICT systems, responsive to
environmental changes.
REFERENCES
Adlassnig, K.-P., 1982. A survey on medical diagnosis
and fuzzy subsets. In Gupta, M.M. and Sanchez, E.
(eds.), Approximate Reasoning in Decision Analysis.
Amsterdam: North-Holland Publishing Company,
203-217.
Adlassnig, K.-P., Blacky, A., and Koller, W., 2008.
Fuzzy-based nosocomial infection control. In
Nikravesh, M., Kacprzyk, J., and Zadeh, L. (eds.),
Forging New Frontiers: Fuzzy Pioneers II. Berlin:
Springer, 343-349.
Adlassnig, K.-P. and Rappelsberger, A., 2008. Medical
knowledge packages and their integration into health-
care information systems and the World Wide Web. In
Andersen, S. K., Klein, G. O., Schulz, S., Aarts, J.,
and Mazzoleni, M. C. (eds.) eHealth Beyond the
Horizon–Get IT There. Proceedings of the 21st
International Congress of the European Federation
for Medical Informatics (MIE 2008). Studies in Health
Technology and Informatics, 136, Amsterdam: IOS
Press, 121-126.
Adlassnig, K.-P., Blacky, A., and Koller, W., 2009.
Artificial-intelligence-based hospital-acquired
infection control. In Bushko, R. (ed.) Strategy for the
Future of Health. Studies in Health Technology and
Informatics, 149, Amsterdam: IOS Press, 103-110.
ANISS Surveillance. http://www.meduniwien.ac.at/
hp/krankenhaushygiene/forschung-lehre/aniss-
surveillance/, Nov 3, 2013.
AUQIP http://www.ipg.uni-linz.ac.at/fr_leiste_proj.htm,
Nov. 3, 2013.
Blacky, A., Mandl, H., Adlassnig, K.-P., and Koller, W.,
2011. Fully automated surveillance of healthcare-
associated infections with MONI-ICU – A
breakthrough in clinical infection surveillance. Applied
Clinical Informatics, 2(3), 365-372.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2013a.
National Healthcare Safety Network (NHSN).
http://www.cdc.gov/nhsn/, Nov 4, 2013.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2013b.
National Healthcare Safety Network NHSN,
Surveillance for Ventilator-associated events.
www.cdc.gov/nhsn/acute-care-hospital/vae/, Nov 4,
2013.
Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, 2013.
Medicare.gov, The Official U.S. Government Site for
Medicare. http://www.medicare.gov/hospitalcompare/
?AspxAutoDetectCookieSupport=1, Nov 3, 2013.
Chizzali-Bonfadin, C., Adlassnig, K.-P., and Koller, W.
MONI: An intelligent database and monitoring system
for surveillance of nosocomial infections. In: Greenes,
R. A., Peterson, H. E., and Protti D. J. (eds), 1995.
MEDINFO 95. Proceedings of the Eighth World
Congress on Medical Informatics; Jul 23-27;
Vancouver, Canada. Canada: Healthcare Computing &
Communications Canada, Inc., 1684.
de Bruin, J., Adlassnig, K.-P., Blacky, A., Mandl, H.,
Fehre, K., and Koller, W., 2013. Effectiveness of an
automated surveillance system for intensive care unit-
acquired infections. Journal of the American Medical
Informatics Association, 20(2), 369-372.
European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control,
2013. http://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/Pages/home.aspx,
Nov 4, 2013.
Freeman R., Moore, L. S. P., Garcia Alvarez, L., Charlett,
A., Holmes, A., 2013. Advances in electronic
surveillance for healthcare-associated infections in the
21st Century: A systematic review. Journal of
Hospital Infection
, 84(2), 106-119.
German National Center for Surveillance of Nosocomial
Infections, 2013a. KISS (Krankenhaus-Infektions-
Surveillance-System). http://www.nrz-hygiene.de/
surveillance/kiss/, Nov 3, 2013.
German National Center for Surveillance of Nosocomial
Infections, 2013b. NEO-KISS. http://www.nrz-
hygiene.de/surveillance/kiss/neo-kiss/, Nov 3, 2013.
Health Level Seven, Inc., 2013. The Arden Syntax for
Medical Logic Systems Version 2.9, Ann Arbor, MI:
Health Level Seven Inc. http://www.hl7.org/
implement/standards/product_brief.cfm?product_id=2
90, Nov 3, 2013.
Hripcsak, G., 1994. Writing Arden Syntax Medical Logic
Modules. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 24(5),
331-363.
IQIP International Quality Indicator Project.
http://www.internationalqip.com/, Nov 3, 2013.
Samwald, M., Fehre, K., De Bruin, J., and Adlassnig, K.-
P., 2012. The Arden Syntax standard for clinical
decision support: Experiences and directions. Journal
of Biomedical Informatics, 45(4), 711-718.
Vermont-Oxford Network, 2013. http://
www.vtoxford.org/home.aspx, Nov 3, 2013.
Zadeh, L. A., 1965. Fuzzy sets. Information and Control,
8(3), 338-353.
HEALTHINF2014-InternationalConferenceonHealthInformatics
404
