
The Uncertainty in the Home Health Care Assignment Problem
Afrae Errarhout
1
, Saïd Kharraja
2
and Andréa Matta
3
1
Laboratoire d’Analyse des Signaux et des Processus Industriels, Roanne, France
2
Université Jean Monnet, Saint-Etienne, France
3
Dipartimento di Meccanica, Politecnico di Milano, Milano, Italy
Keywords: Home Health Care (HHC), Assignment Problem, Continuity Care, Mixed Integer Programming,
Uncertainty.
Abstract: This paper presents an assignment problem in the home health care structures. In this problem, we search to
assign caregivers to patients during a mid-term and long-term planning horizon while considering the
caregivers’ skills and capacity. Moreover, we take into account the randomness of the patients’ demands
due to a change in their profiles or to addition of new patients through the planning horizon. As aim we
balance the caregivers’ workload and secure the continuity of the care. We use the Monte Carlo method in a
deterministic way to represent the randomness of the patients’ demand in the mixed integer programming
model we developed.
1 INTRODUCTION
The home health structures (HHC) were created in
order to reduce the hospitals charges (Jones et
al.1999). Hence, it provides medical, psychological
and social services to the patients at home among
their families. During the last decade, the importance
grow of the HHC structures allowed them to add
more complex and technical cares such as chronic
and palliative cares, home chemotherapy and
rehabilitation (Tarricone and Tsouros, 2008);
(Durand et al., 2010).
Given the standing of the HHC organization,
several studies related to the operations management
and the organization of the care delivery process
were developed. Different works could be found in
the literature, some dealing with main processes and
decisions related to home care structures for a better
understanding of the HHC operations and their
management (Matta et al. 2012) and others related to
the human resources planning such as: districting
problems (Benzarti 2012), routing and scheduling
problems (Hertz and Lahrichi, 2009) and the
assignment problems (Lanzarone et al., 2012);
(Matta et al., 2012); (Yalcindag et al., 2012); (Hertz
and Lahrichi, 2009); (Lanzarone and Matta, 2009);
(Bredström and Rönnqvist, 2008); (Punnakitikashem
et al., 2008).
This paper deals with the assignment problems in
the HHC. The works related to the assignment in the
HHC structures help the decision maker to know the
best way to allocate nurses to patients while securing
the nurses’ workload equilibrium, which insure the
cares’ quality and reduce the costs of the nurses’
tours. Each patient represents a therapeutic project
composed of different cares during his/her treatment.
However, while assigning nurses to patients, we
should take into account the nurses’ capacity. It’s
important to prevent the nurses’ overload which will
cause fatigue and stress which could be followed by
errors. Thus, workload smoothing would secure the
quality of cares and enhance patients’ satisfaction.
The HHC assignment problems present a great
uncertainty (Lanzarone and Matta, 2012; 2009). In
fact, for example, through the planning horizon,
there is a great variability in the patients’ demand; it
may be explained by the admission of new patients
or the change or evolution in patients’ profile after a
short/mid/long period of the treatment beginning.
The patients’ demand represents the risk factor in
these problems as having overloaded nurses and
adding some nurses’ tours or reducing them which
involve additional costs. Hence, we considered that
the demand prevision would help to reduce this risk.
However, although the prevision provides an
overview of the future situation, it doesn’t annihilate
the uncertainty (Kouvelis and Yu, 1997) in the
problem.
453
Errarhout A., Kharraja S. and Matta A..
The Uncertainty in the Home Health Care Assignment Problem .
DOI: 10.5220/0004905504530459
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems (ICORES-2014), pages 453-459
ISBN: 978-989-758-017-8
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

Therefore in this paper, we present an
assignment problem. We assign nurses to patient
taking into account the variability of the patient
demand due to their profile’s change or due to new
patients’ admission through the planning horizon
which ensure the care’s continuity. The objective is
to “master the overload risk” by balancing the
nurses’ workload in order to reduce the excessive
assignment. We assume that the nurses can operate
in the whole territory but we limit the number of the
districts where they can be assigned and so we
reduce their travel workload. The nurses must have
the skills required to the care they are assigned to
and there’re some care that require the presence of
two nurses, called synchronized care (Bredström &
Rönnqvist 2008).
The article is organized as follow. We introduce
in section 2 a literature review about the assignment
problems in the HHC. In section 3, we define the
problem and present the mathematical model. Then,
Section 4 reports results from computational
experiment and Section 6 concludes the paper.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
Different fields of studies deal with the assignment
problems, such as, the production systems (Bilgin
and Azizoglu, 2009), the telecommunication
networks (Dell’Amico et al., 2001), the resources
planning (Mkaouar et al., 2012), the health care
(Volgenant, 2004), etc. The assignment problem was
introduced, for the first time, in the fifties by Votaw
and Orden (1952). This problem searches to assign
one task per agent. Then in 1975, Ross and Soland
(1977) introduced the generalized assignment
problems (GAP) which allocate many tasks to set of
agents while respecting their capacity occurred.
From the GAP many other problems emerged
depending on the situation to model. The complexity
of the GAP is NP-hard (Diaz and Fernandez 2001);
(Yagiura et al., 2006); (Woodcock and Wilson,
2010) which conducted to develop many resolution
methods exact and based-heuristics approaches.
Several methods and heuristic algorithms have been
presented in the literature to solve the GAP as the
genetic algorithm (Liu et al., 2012), the Tabu search
(Diaz and Fernandez, 2001), simulated annealing
(Righini 1995), ant colony, local search (Bischoff
and Dächert, 2009) and ejection chains (Yagiura et
al., 2006). More recently, several researchers
develop hybrid heuristics (Woodcock and Wilson,
2010). These are to combine different heuristics or
combine elements of exact methods with heuristics.
In the HHC context, as mentioned previously,
there’re different works related to the human
resources planning. The districting problems
consider the territory’s repartition into districts in
order to reduce the nurses’ workload and travel
workload; Benzarti (2012) developed two
mathematical models of the districting problem. The
author considers the compactness, the care workload
balance and different patient profiles. The visits’
scheduling problem search to reduce the nurses’
travel during their visits; Ben Bachouch et al.,
(2008) developed mixed linear programming model
of vehicle routing problem with time windows to
minimize the total distance travelled by the nurses.
The assignment problem (see table 1) seeks to
allocate nurses to patients while considering their
skills and workload balance and ensure the
continuity care. Lanzarone et al., (2012) proposed
different mathematical programming models with
the aim to balance the workload of the operators
within specific categories. These models consider
the care’s continuity constraint, operator’s skills and
the districts where the patients and the operators
belong. The patients’ demands are considered either
in deterministic or stochastic way.
Hertz and Lahrichi (2009) developed two mixed
integer programming models. They solved the model
with non-linear constraints and a quadratic objective
function using a Tabu search algorithm and they
used CPLEX to solve the other linear model. By
comparing the two solution methods they confirmed
the effectiveness of the Tabu search approach. They
aim to balance the nurses’ workload within different
categories.
Yalçindag et al., (2012) coupled the assignment
and routing problems in the HHC structures. They
focused on the interaction between assignment and
routing, where the output of the assignment problem
is incorporated as an input into the routing problem,
with the assumption of one district.
Lanzarone and Matta (2012) developed a
structural policy to assign a newly admitted patient
while balancing the operators’ workload by
minimizing the cost function that penalizes the
operators’ overtime. They consider that the patients’
demands are either deterministic or stochastic.
Bertels and Fahle (2006) present a combination
of linear programming, constraints programming
and (meta) heuristics for a HHC problem that
consider the staff rostering and vehicle routing
components while minimizing transportation costs
and maximizing satisfaction of the patients and
nurses.
Lanzarone and Matta (2009) present an integer
programming model for workload balancing among
ICORES2014-InternationalConferenceonOperationsResearchandEnterpriseSystems
454
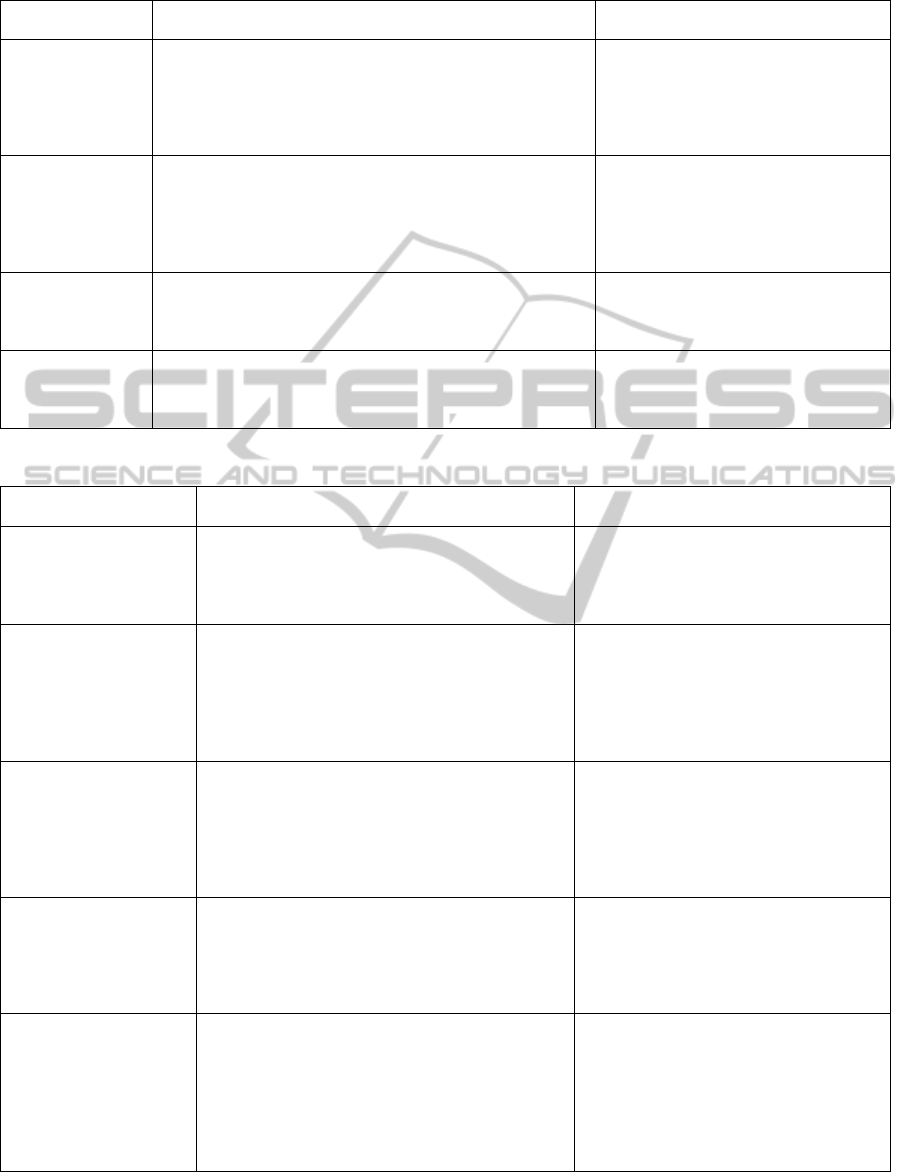
Table 1: The main literature on HHC assignment problems.
Articles Objective Constraint / Creteria
Lanzarone et al
(2012)
Allocating operators to patients
Balancing the operators’ workload (visit time)
The patients’ demands are:
deterministic or stochastic
Continuity of care
Operators’ skills
The districts where the patients and
the nurses belong
Hertz & Lahrichi
(2009)
Allocating operators to patients
Balancing the operators’ workload
Continuity of care
Visit load (the weight of each visit)
Travel load (the distance traveled)
Case load (the number of patients
assigned)
The operators’ capacity
Yalçindag et al
(2012)
Analysing the interaction between assignment problem and
routing problem
Balancing the operators’ workload (visit & travel
time)Minimizing the total distance travelled
The districts where the patients and
the nurses belong
Continuity of care
Operators’ skills
Bertels & Fahle
(2006)
Designing rosters with staff rostering and vehicle routing
components
Minimizing transportation costs
Maximizing the patients and the nurses’ preferences
Time windows
The qualification for a job
The nurses and patients’ preferences
Table 2: Literature about the risk & uncertainty in health care problems through time periods.
Articles
Objective Constraint / Creteria
Benzarti (2012)
Partitioning of the area where the HCC structure
operates into districts
The workload balance
The compactness,
The compatibility and indivisibility of
basic units
The continuity of care
Lanzarone & matta (2009)
Evaluating the Expected Value of Perfect
Information (EVPI)
Allocating operators to patients in the HHC
Balancing the operators’ workload (visit time)
Patient demand variability
Stochastic demand
Continuity of care
Operators’ skills
The districts where the patients and the
nurses belong
Sub-periods
Punnakitikashem et al.
(2008)
Assigning nurses to patients in health care
Shift (time periods)
Nurses qualification
Continuity of care
Direct care
Indirect care (e.g. updates of the patients’
condition)
Unanticipated patients
Lanzarone & Matta (2012)
Assign newly admitted patients
Balancing the operators’ care workload (visits
time)
Minimizing the operators’ overtime penalty
Continuity of care
Operators’ skills
The districts where the patients and the
nurses belong
The patients’ demands are: deterministic
or stochastic
The work presented in this
paper
Assigning nurses to patients in the HHC structures.
Balancing the nurses’ workload
Continuity of care
Uncertainty of the patients’ demand
Districts
Synchronized cares
The travel load
The nurses’ skills
The nurses’ capacity
Sub-periods
TheUncertaintyintheHomeHealthCareAssignmentProblem
455

nurses, while preserving the continuity of care. They
take into consideration the high variability of the
patient demand and they assume that the future
demand to be stochastic.
Punnakitikashem et al., (2008) develop a
stochastic integer programming model to assign
nurses to patient, they proposed the Bender’
decomposition to solve the problem and they
employed a greedy algorithm to solve the recourse
sub-problem.
The uncertainty in the future makes the
decisions’ project, in long term, difficult. Hence, the
best way to handle the uncertainty and make
decision under it, is to accept it, make strong effort
to understand it and structure it, and finally, make it
part of the decision making reasoning (Kouvelis
1997). Table 2 summarizes some works about the
risk and uncertainty in the health care field.
In this paper, we present an assignment problem
where we assign nurses to patients with the objective
is to balance the nurses’ workload in order to reduce
the excessive assignment. The nurses can operate
over the whole territory. We consider the variability
of the patients demand due to their profile’s change
or due to new patients’ admission through the
planning horizon while securing the care’s
continuity. We use the Monte Carlo method in a
deterministic way to represent the randomness of the
patients’ demand in our integer programming model.
3 MODEL DESCRIPTION
The following assignment model objective is to
balance the nurses’ workload while considering their
skills to give each care and their capacity. During
the planning horizon, the patients’ profile may
progress/regress and/or new patients may be
admitted within the HHC structure, which require a
dynamic model taking into consideration those
changes. Therefore the planning horizon is divided
to several sub-periods, weeks in our case. The
patients are characterized by the weekly number of
visits needed during their treatment, while the nurses
are defined by their weekly workload that may
change in dependency on the admission or the leave
of the patients.
The patients’ demands through the planning
horizon (sub-periods) are random, which represents
an uncertainty factor in our work and may conduct
to irrelevant results. On that account, we used a
range of estimated values instead of a single guess in
order to create more accurate model. Hence, we
choose to use the Monte Carlo simulation (Vose
2008) which tells how likely the outcomes are, so,
we can have a better understanding of the
uncertainty and the risk in the model.
Indeed, we use the Monte Carlo simulation
(Vose, 2008) in a determinist way to the mixed
integer model. Hence, we add a number of scenarios
to the model by considering randomness of the
patients’ demand for each week.
The mathematical model is presented as follow:
Decision variables:
X
1ifthenurseiisassignedtothecarej
ofthenewpatientpinthedistrictk
0otherwise
Y
1ifthenurseiisassignedto
thedistrictk
0otherwise
W
,
the nurse i workload in the week h of the scenarios
f
the difference between the nurse i and i’
workload in the week h for each scenario f.
Parameters:
m the number of nurses I = {1,.., m}
n the number of cares J = {1,…,n}.
v the total number of the patients during the
planning horizon P = {1,…, v}. This set is the
sum of the groups of patients during each week t.
z the number of districts Z = {1,…, z}
t the number of weeks in the planning horizon
T= {1,…, t}
s the number of scenarios F={1,…,s}
P
= 1, if the patient p of the district k needs the
care j during the week h for each scenarios f,
otherwise 0.
S
= 1, if the patient p of the district k needs a
care j that requires one nurse during the week h
for each scenario f.
S
= 2, if the patient p of the district k needs a
care j that requires two nurses during the week h
for each scenarios f.
N
, the limited number of district where a nurse
can be assigned.
∝
,
, the frequency of the cares of the patient p
of the district k during the week t for the
scenarios f.
q
= 1, if the nurse i has the skill to give the
ICORES2014-InternationalConferenceonOperationsResearchandEnterpriseSystems
456

care j to patient p of the district k, otherwise 0.
b
, the capacity that defines the nurse
availability.
τ ∈ [0,1] which represents the travel time ratio in
the nurses’ availability b
a
, the time required by the care j of the
patient p of the district k from the nurse i.
t
, is the average time for the care j to be
provided to patient p
M, a great constant
The mathematical formulation of the problem is
given below:
Objective functions:
The model allows balancing the workload among the
nurses in the planning horizon by minimizing the
difference between the nurses’ weekly workload.
Minimize
1
s
D
(1)
The constraints’ set:
q
X
j∈J,p∈P,k∈Z,h∈T,
f
∈
(2)
X
q
xP
i∈I,j∈J,p∈P,k∈Z,h∈T,
f
∈F
(3)
W
,
P
∝
,
a
X
i∈I,h∈T,
f
∈F
(4)
W
,
1τ
∗b
i∈I,
f
∈F
(5)
D
W
,
W
,
i∈I,i′∈I,h∈T,
f
∈F
(6)
D
W
,
W
,
i∈I,i′∈I,h∈T,
f
∈F
(7)
Y
N
i∈I
(8)
X
0i∈I,p∈P,k∈Z
(9)
∑∑
X
M
Y
i∈I,k∈Z
(10)
The constraints (2) and (3) assume respectively that
a same care can be given by one or two nurses and
that a nurse should be qualified to give the care.
Constraints (4) define the workload of each nurse
during the week t for each scenario. The constraint
(5) secures the nurses availability. Constraints (6)
and (7) define the difference between the nurses
workload to be minimized in the objective function.
Finally, constraints (8), (9) and (10) limit the
number of districts for the nurses.
4 EXPERIMENTATION AND
COMPUTATIONAL RESULTS
To test our integer programming model, we used the
optimization software ILOG CPLEX 12.5 and the
experiments were implemented on 3.39 GHz, 3GB
RAM computers.
4.1 Data Generation
Our model takes into account the uncertainty of the
patients’ demand. So, we used a real life data from
the health home care benchmarks (Howard, 1997).
We have 75 patients through the horizon planning (8
weeks) and 6 nurses. The HHC proposes 10 cares
that request a time varying from 25 to 45 minutes
and each nurse is qualified to give at least 4 types of
cares. The travel time is about τ=30% of the whole
time capacity of the nurses (each nurse works 8
hours per day and a week =5 days). The patients’
demand is represented by the frequency of the cares
they need, 3 to 8 visits per week. For each patient
the frequency may change from a week to another
over the scenarios.
In order to generate scenarios, we suppose that
the patients’ demand follow a normal distribution
(i.e. we consider the deterministic demand as the
mean and the standard deviation is represented by
the root square of the deterministic demand (Verweij
et al. 2003), see figure 1).
4.2 Computational Results
In order to test the efficiency of our model, we
generated 3 tests of random demands starting with 5
scenarios, 10 then 20 (i.e. each scenario represents a
number of the patients’ demand that was generated
from the normal distribution, see fig. 1) and we
compared their results with the results from the
deterministic demands. For all the tests the program
runs over 3 hours before running out of memory
without finding new solutions. So, we terminated the
program after 3 hours of running to get the latest
solution found. We report in the follow table the
results found for all the tests (see table 3).
TheUncertaintyintheHomeHealthCareAssignmentProblem
457

Table 3: The results of the experiments showing the average workload per scenario and per nurse, and the Minimum and
maximum workload.
Tests Avg. workload
Avg. nurses
workload
Min. workload Max. workload
5 scenarios 68725 11454 9479 12722
10 scenarios 69201 11534 11259 11618
20 scenarios 69004 11501 11286 11687
Deterministic - 11114 11080 11155
Figure 1: The normal distribution of the patients demand.
Figure 2: The nurses’ workload for the second experiment
“10 scenarios.
The results obtained by the experiments are
different from each other and we notice that these
results converge while increasing the numbers of
scenarios. So in order to get better result it’s more
appropriate to use a large number of scenarios.
These scenarios may represent the worst case, the
best case and the most likely case. Hence, we notice
that the workload from the deterministic demand to
the 5, 10 and 20 scenarios increases. Moreover, the
comparison between the results obtained by using
different scenarios and the results of the
deterministic demand shows a great difference,
which concludes that the resulting assignment is far
away from being accurate (see table 1). Furthermore,
the experiments show that the nurses’ workload is
balanced over all the scenarios (see fig. 2).
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we modeled the assignment problem in
the HHC structures. The main objective is to balance
the nurses’ workload and define the variability in the
problem that’s caused by the randomness of the
patients demand and the changes in the patients
profile every week represent an uncertainty factor.
Hence, in order to represent the variability in our
model we used the Monte Carlo method which
consists of generating a great number of scenarios
that represent the randomness of the patients’
weekly demand. We tested our mixed integer model
on CPLEX with different experiments that use a
number of scenarios and the results shows a big
difference between the test using the deterministic
demand and the ones using a random demand. This
difference illustrates the uncertainty in the
assignment problem and gives more accurate
solutions.
REFERENCES
Ben Bachouch R., Fakhfakh M., Guinet A. and Hajri-
Gabouj S. 2008. Planification de la tournée des
infirmiers dans une structure de soins à domicile.
Conférence Francophone en Gestion et Ingénierie des
Systèmes Hospitaliers (GISEH), Switzerland.
Benzarti, E. Thesis 2012. Home Health Care Operations
Management: Applying the districting approach to
Home Health Care.
Bertels, S., Fahle, T., 2006. A hybrid setup for a hybrid
scenario: combining heuristics for the home health
care problem. Computers and Operations Research
33, 2866-2890.
Bilgin, Selin and Azizoglu Meral, 2009. Operation
assignment and capacity allocation problem in
automated manufacturing systems. European Journal
of Operational Research 56, 662-676.
Bischoff, M. and Dächert K., 2009. Allocation search
methods for a generalized class of location-allocation
problems. European Journal of Operational Research
192, 793-807.
Bredström, D. and Rönnqvist M., 2008. Combined vehicle
routing and scheduling with temporal precedence and
ICORES2014-InternationalConferenceonOperationsResearchandEnterpriseSystems
458

synchronization constraints, European Journal of
Operational Research, vol 191, p19–31.
Dell’Amico, Mauro, Lodi Andrea and Martello Silvano.
2001. Efficient algorithms and codes for k-cardinality
assignment problems. Discrete Applied Mathematics
110, 25–40.
Diaz, Juan A. and Fernandez Elena, 2001. A Tabu search
heuristic for the generalized assignment problem.
European Journal of Operational Research 132, 22-
38.
Durand N., Lannelongue C. and Legrand P. 2010.
Hospitalisation à Domicile (HAD). IGAS, RAPPORT
N°RM2010-109P.
Hertz, A., Lahrichi, N., 2009. A patient assignment
algorithm for home care services. Journal of the
Operational Research Society 60, 481-495
Howard, Paula, 1997. Benchmarking Home Health Care
Data. Home Health Care Management Practice
Jones J., Wilson A., Wynn A., Jagger C., Spiers N. and
Parker G., 1999. Economic evaluation of hospital at
home versus hospital care: cost minimization analysis
of data from randomized controlled trial. British
Medical Journal, Vol N°319, p. 1547-1550.
Kouvelis, P. and Yu G., 1997. Robust Discrete
Optimization and Its Applications, Kluwer Academic
Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands.
Lanzarone, E. and Matta A., 2009. Value of Perfect
Information in Home Care Human Resource Planning
with Continuity of Care. Proceedings of the 35th
Conference on Operational Research Applied to
Health Services (ORAHS); no.17; ISBN978-90-81409-
90-2. Abstract book; 40.
Lanzarone, E. and Matta A., 2012. A cost assignment
policy for home care patients. Flex Serv Manuf J
24:465–495.
Lanzarone, E., Matta A. and Sahin E., 2012. Operations
management applied to home care services: the
problem of assigning human resources to patients.
Systems, Man and Cybernetics, Part A: Systems and
Humans, IEEE.
Linzhong, Liu, Haibo Mu, Yubo Song, Haiyan Luo,
Xiaojing Li and Fang Wu, 2012. The equilibrium
generalized assignment problem and genetic
algorithm. European Journal of Operational Research
218, 6526-6535.
Matta, A., Chahed S. and Sahin E., 2012. Modeling home
care organizations from operations management
perspective. Flex Serv Manuf J.
Mkaouar, Raoudha, Dafaoui El Mouloudi and El
Mhamedi Abderrahman, 2012. Approche de résolution
du problème d’affectation sous contraintes de
compétences et préférences.
Punnakitikashem, P., Rosenberger Jay M. and Behan D.
B., 2008. Stochastic programming for nurse
assignment. Comput Optim Appl, 40: 321–349.
Righini, Giovanni, 1995. A double annealing algorithm for
discrete location/allocation problems. European
Journal of Operational Research 86, 452-468.
Ross, G. T. and Soland R. M., 1977. Modelling Facility
Location Problems as Generalized Assignment
Problems. Management Science, 24, 345-357.
Tarricone R. and Tsouros A.D., 2008. The solid facts:
Home Care in Europe. World Health Organization.
Verweij, Bram, Shabbir Ahmed, Kleywegt Anton,
Nemhauser George, and Shapiro Alexander, 2003. The
Sample Average Approximation Method Applied to
Stochastic Routing Problems: A Computational Study.
Computational Optimization and Applications, 24:
289–333.
Volgenant, A., 2004. A note on the assignment problem
with seniority and job priority constraints. European
Journal of Operational Research 154, 330-335.
Vose, David, 2008. Risk analysis a Quantitative Guide,
3rd edition.
Votaw, D.F. and Orden A., 1952. The personnel
assignment problem. Symposium on Linear
Inequalities and Programming, SCOOP 10, US Air
Force, pp. 155–163.
Woodcock, Andrew J. and Wilson John M., 2010. A
hybrid tabu search/branch & bound approach to
solving the generalized assignment problem.
European Journal of Operational Research 207, 566-
578.
Yagiura, Mutsunori, Ibaraki Toshihide and Glover Fred,
2006. A path relinking approach with ejection chains
for the generalized assignment problem. European
Journal of Operational Research 169, 548-569.
Yalcindag, S., Matta A. and Sahin E., 2012.Operator
assignment and routing problems in home health care
services. Automation Science and Engineering
(CASE), IEEE.
TheUncertaintyintheHomeHealthCareAssignmentProblem
459
