
Development of a Model based on Evaluation Considering Explicit and
Implicit Element in Multiple Criteria Decision Making
Rumiko Azuma
1
and Shinya Nozaki
2
1
Department of Social Informatics, Aoyama Gakuin University, Sagamihara, Kanagawa, Japan
2
Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, University of the Ryukyus, Okinawa, Japan
Keywords:
Decision-making Model, Implicit Evaluation, Principal Component Analysis, Analytic Hierarchy Process.
Abstract:
The Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) is a decision-making method for smoothly managing problems, cri-
teria, and alternatives. AHP can be used to respond to multiple criteria, and allows for the quantification of
subjective human judgments, as well as objective evaluations. In a classical AHP, a decision-maker derives a
list of priorities by consciously comparing criteria and alternatives in order to deriving a comprehensive evalu-
ation. However, when the number of criteria increases, the problem also becomes complicated and the subjec-
tive judgment of the decision-maker tends to be clouded by ambiguity and inconsistency. As the solution, this
study proposes a method whereby latent elements are extracted from the data given by the decision-maker, and
an evaluation is made from a different aspect based on the extracted elements. This allows for the construction
of a model in which a decision is made from both explicit and implicit elements by making a final synthesis
of the results obtained using the conventional method as well as the evaluation obtained using the method
proposed in this study. As a result, we can conclude that it is possible to make a decision that is not affected
by the ambiguity or inconsistency of the decision-maker.
1 INTRODUCTION
The analytic hierarchy process (AHP) (Saaty, 1980) is
well known as the procedure to solve multiple criteria
decision-making problems. AHP is the method which
quantifies human’s subjective judgments, and makes
a decision by combining them and system approach
in the analysis of problem. AHP is used in a variety
of multiple-choice situations such as economic prob-
lems, management problems, medical issues, energy
problems, educational problems and city planning.
When making a decision, having a large number
of various criteria and alternatives tends to compli-
cate the problem and make it impossible to arrive at
the most appropriate decision. One problem is that
the hierarchal structure becomes complicated. When
creating a hierarchal structure, it is necessary to set
independent items in the criteria. If each criterion is
not independent, it is necessary to define a multi-level
hierarchy, such as AHP inner-dependence method
(Saaty and Takizawa, 1986) or dominant AHP (Ki-
noshita and Nakanishi, 1997)(Kinoshita and Nakan-
ishi, 1998). However, even in them it is impossible to
account for all of the implicit dependencies between
the criteria at a level beneath the decision-maker’s
awareness.
Another problem is that inconsistencies may oc-
cur in choices when criteria or alternatives must be
evaluated using subjective human judgment. Ambi-
guities and inconsistencies tend to occur more often
in human judgment when the number of criteria and
alternatives increase. The work involved in making
a pairwise comparison therefore becomes unmanage-
able and consistency consequently suffers. As a re-
sult, the reliability of the final evaluation decreases,
and it is difficult to make the best decision. In order to
resolve this problem, the absolute measure method on
AHP (Saaty, 1986) has been proposed. The method
is effective in case containing too many alternatives
and can avoid the rank reversal problem. However
using the the method, the results often lose reliability
because the comparison matrix does not always have
sufficient consistency.
This study proposes a method whereby implicit
elements are extracted from the data of a decision-
maker’s judgments using principle component anal-
ysis (PCA) (Jolliffe, 2002), and new evaluation is
derived based on them. The conventional method
involves the decision-maker coming to a decision
based on explicit elements. The implicit elements ex-
271
Azuma R. and Nozaki S..
Development of a Model based on Evaluation Considering Explicit and Implicit Element in Multiple Criteria Decision Making.
DOI: 10.5220/0004905802710276
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems (ICORES-2014), pages 271-276
ISBN: 978-989-758-017-8
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

tracted by PCA are as new criteria. Then, to utilize
new criteria enables to derive new evaluation from
a different aspect. Furthermore, a final evaluation
can be made by synthesizing the explicit evaluation
and the implicit evaluation by the proposed method,
thereby constructing a decision-making model that is
not affected by ambiguity or inconsistencies of the
decision-maker.
There are researches to examine about best
method by comparing the evaluation by AHP with
the evaluation by PCA (Kim, 2006)(Wu et al., 2011).
On the other hand, there is research by which PCA
is applied to the decision-making method (Lee et al.,
2010). However, our approach is to integrate the eval-
uation by latent elements extracted by applying PCA
into AHP values which the decision-maker scored
subjectively. It is applied only to the process in which
the absolute measure method because PCA is an ef-
fective technique to normally-distributed data. Then,
our approach enables the decision-makers to achieve
clearer result.
2 BASIC CONCEPT
2.1 Analytic Hierarchy Process using
Absolute Measurement
The AHP is a technique used for dealing with prob-
lems which involve the consideration of multiple cri-
teria simultaneously. It is based on the principles
of decomposition structures, comparative judgments,
and synthesis of priorities. Comparative judgments
are necessary to perform the pairwise comparisons of
criteria and alternatives. However, in case containing
too many alternatives, it is burdensome for decision-
maker to draw pairwise comparison in alternatives.
It produces sometimes bad consistency. Saaty pro-
posed an absolute measure method on AHP to solve
the problem (Saaty, 1986). The difference between
the method and the conventional relative measure-
ment is in the procedure of scoring the alternatives
corresponding to criteria. The method is adopted that
indirect comparison. A decision-maker evaluates al-
ternatives using absolute measurement by linguistic
scales as ”very good”, ”good” and etc. The evalua-
tion value of linguistic scale is acquired by pairwise
comparison of criteria as in Table 1. Table 2 is a ex-
ample of evaluation values for linguistic scales. They
are derived from eigenvector calculated by the ratio of
a linguistic scale. In our proposal model, the absolute
measurement method is adopted.
Table 1: A example of pairwise comparison of linguistic
scale.
very good good common bad
very good 1 2 5 7
good 1/2 1 3 5
common 1/5 1/3 1 2
bad 1/7 1/5 1/2 1
Table 2: Evaluation value about Table 1.
linguistic scale weight
bad 0.120
common 0.209
good 0.569
very good 1.000
2.2 Principal Component Analysis
(PCA)
PCA is a data representation method and is a kind of
multivariate analysis. It can extract new indexes with-
out correlation from each data and analyze weight of
data in each element. Moreover, new indexes can be
extracted from a few of data set. This is achieved by
transforming to a new set of variables, the principal
components, which are uncorrelated, and which are
ordered so that the first few retain most of the varia-
tion present in all of the original data.
Suppose that matrix A is made from the result of
a questionnaire filled out by decision-maker in Figure
1, and that S
a
is a covariance matrix of A, and that
λ
k
(k = 1, 2, . .. , n) are a eigenvalue of S
a
. n is number
of questionnaire items. Suppose that λ
1
is the largest
eigenvalue, and v
1
is the corresponding eigenvector.
It can be shown that for the second,third, . . . , nth
principal component,the vectors of coefficients v
2
,v
3
,
. . . ,v
n
are the eigenvectors corresponding to λ
2
,λ
3
, .
. . , λ
n
. The vectors v
k
are principal components and
each of them is new indicator uncorrelated.
v
T
k
= ⌊v
k1
v
k2
. . . v
kn
⌋ (1)
where v
k
corresponds to kth column of new indicators
in Figure 1.
The principal component score z
ki
of ith alterna-
tive corresponding new indicator v
k
is given as
z
ki
= v
k1
a
i1
+ v
k2
a
i2
+ · ·· + v
kn
a
in
(2)
where a
in
is score of alternative A
i
corresponding cri-
terion C
n
.
ICORES2014-InternationalConferenceonOperationsResearchandEnterpriseSystems
272
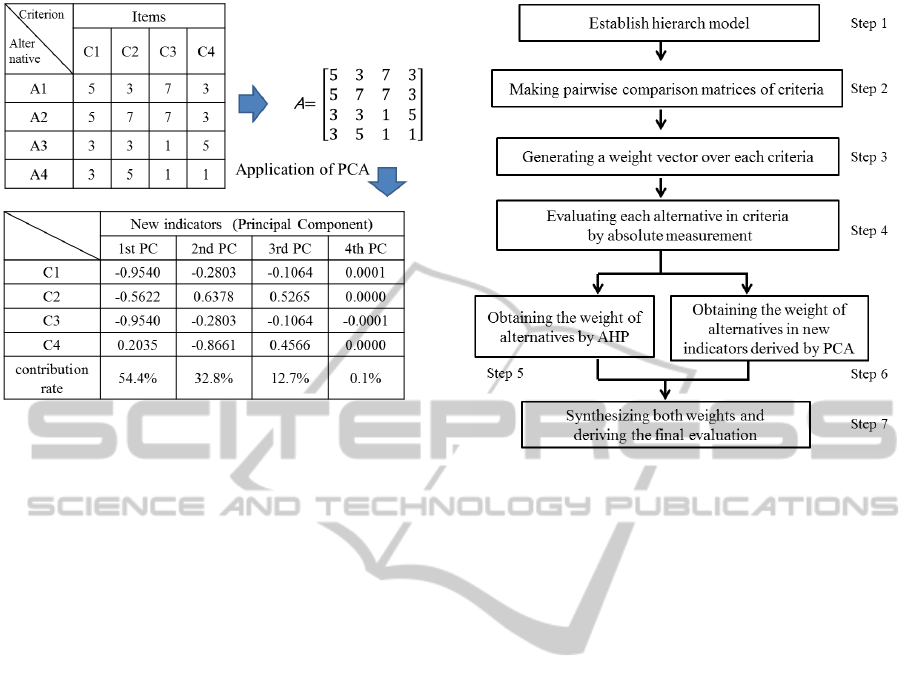
Figure 1: Example of a matrix which is made from ques-
tionnaire data and new indicators which is made from the
matrix by PCA.
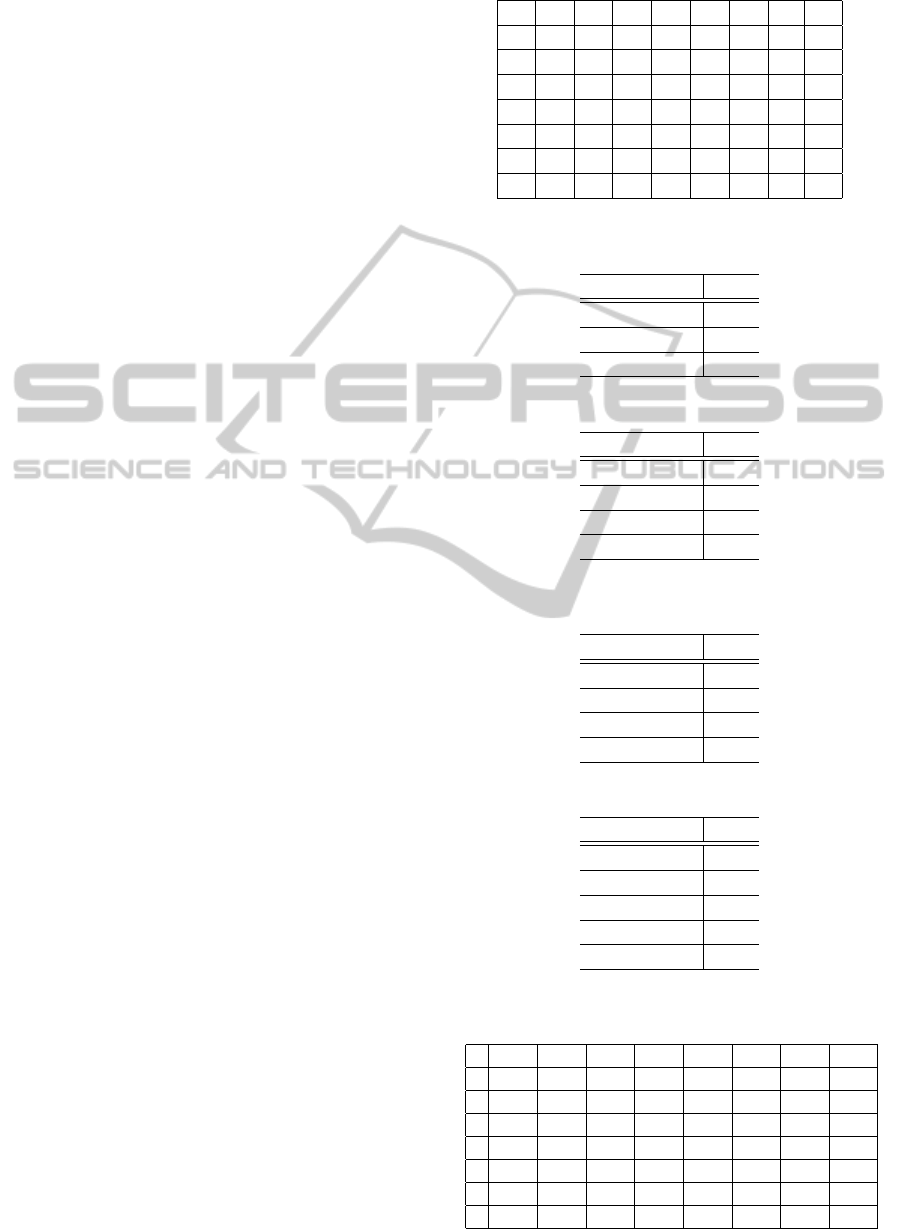
3 PROPOSED MODEL
We propose a method by adopting PCA. The pro-
posed method can extract new criteria from the abso-
lute evaluation values given by a decision-maker and
evaluate based on them. We call a result of it the eval-
uation based on implicit elements. In contrast, we call
the conventional absolute measure method on AHP
the evaluation based on explicit elements. Moreover,
we develop a new approach to derive clearer priority
by synthesizing implicit and explicit evaluation.
Figure 2 shows the flowchart of proposal model
for considering both evaluations. In Figure 2, through
Step 1 to Step 5 is the same process as the conven-
tional AHP. The evaluation X
AHP
in Step 5 is given
as
X
AHP
= Sw (3)
X
AHP
i
=
n
∑
k=1
s
ki
w
k
where matrix S consists of scores s
ki
of each alter-
native about criteria in step 4, and vector w is the
weights of criteria in Step 3. X
AHP
i
is regarded as
explicit evaluation of ith alternative..
We derive the implicit evaluation in Step 6. At
first, PCA is applied to the matrix S in order to acquire
new indicators v
1
, v
2
, . . . , v
m
. Number of new indica-
tors becomes less than half that of original criteria by
adopting until 90% of contribution rate. Moreover,
in the process of implicit evaluation, the decision-
maker does not need to be conscious of dependency
among criteria because v
k
is independent component.
Figure 2: The flowchart of proposed decision-making
model.
Next, the weight w
′
k
of each indicator v
k
as new crite-
ria is acquired by pairwise comparison. Here, vector
w
′
= (w
′
1
, w
′
2
, . . . , w
′
m
) is a weight vector of new crite-
ria. Based on Eq.(2), a vector z
k
= (z
k1
, z
k2
, . . . , z
kn
)
made up of kth principal scores is attained as
z
k
= S · v
k
(k = 1, 2, . . . , m). (4)
Finally, the priority of alternatives based on im-
plicit elements is acquired on the following Eq.(6).
X
PCA
= Zw
′
(5)
where matrix Z = (z
1
, z
2
, . . . , z
m
). The implicit eval-
uation value of ith alternative is given as
X
PCA
i
=
m
∑
k=1
z
ki
w
′
k
(6)
Final evaluation is obtained in Step 7. We define
final evaluation of ith alternative to synthesize Eq.(3)
and Eq.(6) as
X
i
= X
AHP
i
· X
PCA
i
(7)
4 APPLICATION
Suppose that a family is looking for the new house.
After visiting much real estate, eight houses remained
as possible houses for new life. We shall call them
A, B, C, D, E, F and G. A decision-maker has to
decide which house is the best. The decision-maker
DevelopmentofaModelbasedonEvaluationConsideringExplicitandImplicitElementinMultipleCriteriaDecision
Making
273
has identified the following decision criteria. Access,
Price, Safety, Comfort, Location, Width, Equipment
and Appearance (hereinafter referred to as ”Ac”, ”Pr”,
”Sa”, ”Co”, ”Lo”, ”Wi”, ”Eq” and ”Ap”). We apply
our procedure to the above mentioned example, fol-
lowing the steps in flowchart in Figure 2.
4.1 Evaluation based on Explicit
Elements
The decision-maker constructs a evaluation matrix
with respect to decision criteria in Step 2. It is per-
formed through a pairwise comparison shown in Ta-
ble 3. The values for pairwise comparison in Table 3
is scored on 9-point measurement at the same as the
conventional AHP.
In Step 3, a weight vector w of criteria is acquired
as an eigenvector for a maximum eigenvalue of the
matrix composed of Table 3, given as
w = (0.156, 0.233, 0.269, 0.138, 0.081, (8)
0.067, 0.031, 0.025)
T
.
In Step 4, the decision-maker evaluates each alter-
native about criteria. The alternatives are scored by
evaluation values acquired according to the linguistic
scales provided for each criterion as Table 4 to 7, and
not by pairwise comparison. The result is described
in Table 8.
Table 8 is regarded as matrix S and the evalua-
tion X
AHP
based on explicit elements is derived from
Eq.(3) in Step 5.
X
AHP
= Sw (9)
= (0.370, 0.458, 0.451, 0.458,
0.459, 0.327, 0.472)
T
There is little difference among priorities of B, C, D
and E in the result of explicit evaluation. Then, in
addition to the conventional method, it is necessary to
evaluate alternatives from another perspective.
4.2 Evaluation based on Implicit
Elements
According to the Step 6, we obtain an evaluation
based on implicit element by adopting PCA. The re-
sult of Table 9 is obtained by applying PCA to the data
in Table 8. The result gives us new indicators consist-
ing of principal component score. The first PC (prin-
cipal component) can be interpreted as being highly
positively related to the abundances of Ap (0.531) and
Lo (0.432), and negatively related to the abundance of
Sa (-0.455), that is, it expresses the beautiful urbane
Table 3: Pairwise comparison between each criterion.
Ac Pr Sa Co Lo Wi Eq Ap
Ac 1 1 1/3 1 3 3 5 5
Pr 1 1 1 3 5 3 5 7
Sa 3 1 1 3 5 3 5 7
Co 1 1/3 1/3 1 3 3 5 5
Lo 1/3 1/5 1/5 1/3 1 3 3 5
Wi 1/5 1/5 1/5 1/5 1/3 1/3 1 1
Ap 1/5 1/7 1/7 1/5 1/5 1/5 1 1
λ
max
= 8.606 C.I. = 0.087
Table 4: Evaluation values of criterion ”Ac”.
linguistic scale value
inconvenience 0.188
moderate 0.354
convenience 1.000
Table 5: Evaluation values of criterion ”Pr”.
linguistic scale value
low 1.000
moderate 0.464
expensive 0.208
very expensive 0.098
Table 6: Evaluation values of criteria ”Sa”,”Co”, ”Lo”,”Eq”
and ”Ap”.
linguistic scale value
very good 1.000
good 0.464
moderate 0.208
bad 0.098
Table 7: Evaluation values of criterion ”Wi”.
linguistic scale value
very large 1.000
large 0.538
moderate 0.274
narrow 0.129
very narrow 0.068
Table 8: Absolute evaluation of alternatives about each cri-
terion.
Ac Pr Sa Co Lo Wi Eq Ap
A 0.354 0.208 0.208 1.000 0.208 0.538 0.464 0.208
B 1.000 0.098 0.208 0.464 0.464 0.274 0.464 0.464
C 0.354 1.000 0.098 0.208 0.208 0.538 0.098 0.464
D 0.188 0.464 0.464 1.000 0.464 0.274 0.098 0.098
E 1.000 0.208 0.464 0.464 0.464 1.000 1.000 0.208
F 1.000 0.208 0.098 0.464 1.000 0.129 0.208 1.000
G 0.188 1.000 0.464 0.208 0.464 0.538 0.098 0.098
ICORES2014-InternationalConferenceonOperationsResearchandEnterpriseSystems
274
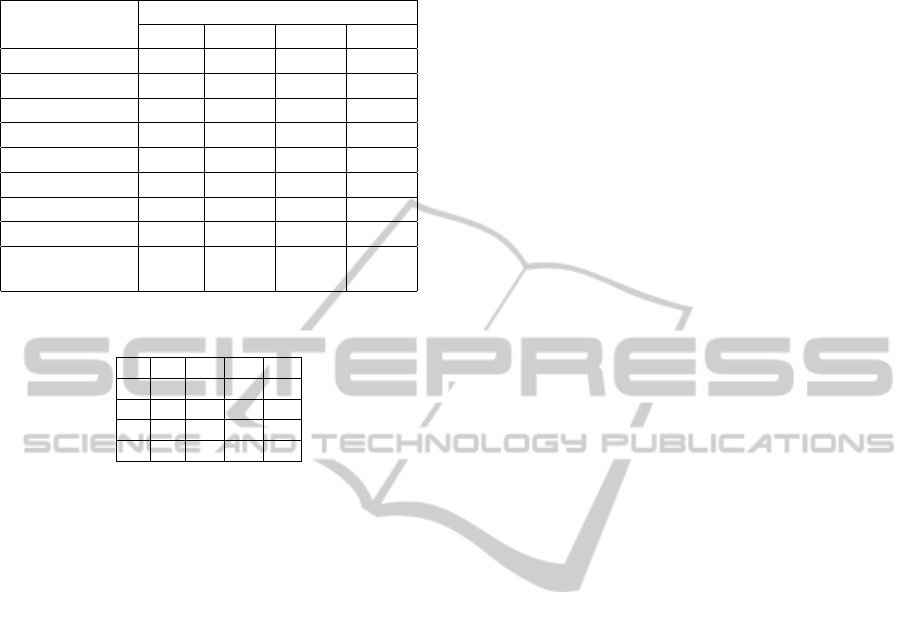
Table 9: Principal component which obtained from absolute
evaluation.
Principal Component : PC
1st PC 2nd PC 3rd PC 4th PC
Ac 0.349 0.466 0.202 -0.015
Pr -0.168 -0.541 0.343 0.156
Sa -0.455 0.167 -0.220 0.543
Co -0.162 0.182 -0.705 -0.213
Lo 0.432 0.086 -0.118 0.776
Wi -0.351 0.274 0.476 0.077
Eq -0.159 0.589 0.231 -0.080
Ap 0.531 0.010 0.052 -0.144
cumulative con-
tribution ratio
41.3% 71.2% 90.7% 97.7%
Table 10: Pairwise comparison between new criterion.
C
1
C
2
C
3
C
4
C
1
1 1/5 1/3 1/5
C
2
5 1 3 1/3
C
3
3 1/3 1 1/5
C
4
5 3 5 1
λ
max
= 4.198 C.I. = 0.066
house which is not located in safety area. The sec-
ond PC, on the other hand, is positively related to the
abundance of Eq (0.589) and Ac (0.466), and nega-
tively related to the abundance of Pr (-0.541). There-
fore, the second index means that a house is prized
convenience more than price. Similarly, the third in-
dicator is interpreted in terms of Pr, Wi and Co, as
a house which is affordable and large but inconve-
niently located. The forth indicator is characterized
by Lo (0.776) and Sa (0.543), as a house that is at
safe place and good environment. Four indicators are
identified as the following decision criteria.
• the beautiful urbane house (C
′
1
)
• the house at more convenient place (C
′
2
)
• the affordable house (C
′
3
)
• the safety house in a good environment (C
′
4
)
The decision-maker constructs a evaluation matrix
with respect to four criteria by using 9-point measure-
ment. It is shown in Table 10. The weight vector w
′
of new criteria C’ is acquired as an eigenvector for a
maximum eigenvalue of the matrix composed of Ta-
ble 10, given as
w
′
= (0.064, 0.271, 0.122, 0 .544)
T
(10)
By applying Eq.(4), the vector z
k
of principal
component scores is acquired regarding the new cri-
terion C
′
k
. Then, we obtain the implicit evaluation by
normalization of Eq.(6).
X
PCA
= (z
1
z
2
z
3
z
4
)w
′
(11)
= (0.126, 0.231, 0.052, 0.006,
0.366, 0.196, 0.022)
T
As in Step 7, the final evaluation X is obtained to
synthesize X
AHP
and X
PCA
, given as
X = (0.110, 0.251, 0.056, 0.007, (12)
0.399, 0.152, 0.025)
T
The priority of each alternative is E > B > F > A >
C > G > D.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, a decision-making model for consider-
ing both explicit and implicit element was presented.
We utilized the absolute measure method on AHP for
determining the evaluation based on explicit element.
On the other hand, we proposed the method adopting
PCA for determining the evaluation based on implicit
element.
The increase in criteria or alternatives becomes
frequently the cause of making vagueness in the
decision-maker’s judgment. In the case, we think that
our proposed procedure is effective. In the conven-
tional method, the priority of alternatives is obtained
using directly the score given by the decision-maker.
However, utilizing the score accompanied by vague
judgments directly makes the reliability of evaluation
lower. Therefore, we proposed the method which en-
ables decision-makers to evaluate based on implicit
elements extracted from the score accompanied by
vague judgments. Further, we tried to develop the
model for decision making by synthesizing explicit
evaluation and implicit evaluation. Our approach en-
ables decision-makers to achieve clearer result in de-
cision making.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by The Ministry of Edu-
cation,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology under
Grant-in-Aid for Young Scientists (B), 24700909.
REFERENCES
Jolliffe, I. T. (2002). Principal Component Analysis, Second
Edition. Springer.
DevelopmentofaModelbasedonEvaluationConsideringExplicitandImplicitElementinMultipleCriteriaDecision
Making
275

Kim, Y.-H. (2006). Study on impact mechanism for beef
cattle farming and importance of evaluating agricul-
tural information in korea using dematel, pca and ahp.
In Agricultural Information Research. Japan Society
of Agricultural Informatics.
Kinoshita, E. and Nakanishi, M. (1997). A proposal of
a new viewpoint in analytic hierarchy process. In
Journal of Infrastructure Planning and Management.
Japan Society of Civil Engineers.
Kinoshita, E. and Nakanishi, M. (1998). Proposal of new
ahp model in light of dominant relationship among al-
ternatives. In Journal of the Operations Research So-
ciety of Japan. JORSJ.
Lee, J., Kang, S., Rosenberger, J., and Kim, S. B. (2010).
A hybrid approach of goal programming for weapon
systems selection. In Computers and Industrial Engi-
neering. Elsevier.
Saaty, T. L. (1980). The Analytic Hierarchy Process.
McGraw-Hill.
Saaty, T. L. (1986). Absolute and relative measurement with
the ahp. the most livable cities in the united states. In
Socio-Economic Planning Sciences. Elsevier.
Saaty, T. L. and Takizawa, M. (1986). Dependence and in-
dependence: From linear hierarchies to nonlinear net-
works. In European Journal of Operational Research.
Elsevier.
Wu, D. S., Feng, X., and Wen, Q. Q. (2011). The research of
evaluation for growth suitability of carya cathayensis
sarg. based on pca and ahp. In Procedia Engineering.
Elsevier.
ICORES2014-InternationalConferenceonOperationsResearchandEnterpriseSystems
276
