
Application of Extensible Markup Language (XML) in Medical
Research
A Bibliometrical Analysis
Thomas Ostermann, Christa Raak and Marc Malik
Institute of Integrative Medicine, Witten/Herdecke University, Gerhard-Kienle-Weg 4, Herdecke, Germany
Keywords: Extensible Markup Language, Semantic Web, XML, Bibliometric Analysis.
Abstract: One of the most innovative web standards is the Extensible Markup Language (XML) which allows
structured data storage and exchange and the creation of user defined tags for semantic processing. This
bibliometrical analysis aims at describing the application of XML in medical research. Medline/PubMed
was searched for relevant publications from 1997 to 2010 using the search term “XML” in all fields. All
articles were bibliometrically analysed with respect to their year of publication, language, keywords,
MESH-Headings, Impact factor, number of authors, number of pages. We found a total of 932 articles on
XML from 1998 to 2010 mostly published in English (n=891; 95.6%). The mean impact factor was 1.93
2.75 and increased from 1.78 3.09 before 2005 to 2.12 2.29 after 2005. Analysis of MESH headings led
to the conclusion that XML predominantly is used in lab research while clinical and health services research
only plays a minor role. As a conclusion, publications on XML impressively show that XML has become a
standard for many software-tools and is more and more recognized in handling huge amounts of data.
Applications in the field of health informatics are reasonable to expect in the future.
1 INTRODUCTION
Already in the early years of information technology
in 1988, Gorry et al. pointed out that “the technical
complexities of biomedical research almost always
demand group effort”. They also state that “groups
that wish to prosper must continually improve their
effectiveness, perhaps through the use of advanced
information technology.” (Gorry et al., 1988). They
proposed the development of a “virtual notebook”
which incorporates information resources like
MEDLINE “with user-specified rules and stored in
designated hypertext structures”. Almost at the same
time Sengupta discussed “issues of heterogeneity in
computer systems networks, databases and
presentation techniques, and the problems it creates
in developing integrated medical information
systems” (Sengupta, 1989). Both authors
recommend the development of a comprehensive
strategy to solve these problems by means of
intelligent information-sharing systems.
Up to the early 1990s, the Internet was mainly
used by academic or military institutions for
communication and file transferring when in 1993
providers were permitted to sell internet connections
to individuals. This changed the complete situation
and masses of users went “online” (Doyle et al.,
1996) and a variety of applications like internet
access for community hospital libraries (Rambo &
Fuller, 1993) or web based protein databases
(Lemkin et al., 1995) were suggested. From that
point the internet evolved dramatically and
Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP V1.0) alongside
with Hyper Text Markup Language (HTML V2.0)
as the main markup language for web pages together
with web browsers were invented and applied i.e. to
“open new possibilities for electronic publishing and
electronic journals” (Pallen, 1995).
Parallel to this development the first Working
Draft of an Extensible Markup Language (XML)
specification was published and in 1998 XML 1.0
was recommended by the World Wide Web
Consortium (W3C) (Treese, 1998).
XML documents according to the W3C “are
made up of storage units called entities, which
contain either parsed or unparsed data. Parsed data is
made up of characters, some of which form
character data, and some of which form markup.
Markup encodes a description of the document's
storage layout and logical structure. XML provides a
mechanism to impose constraints on the storage
layout and logical structure” (Bray et al., 1997).
478
Ostermann T., Raak C. and Malik M..
Application of Extensible Markup Language (XML) in Medical Research - A Bibliometrical Analysis.
DOI: 10.5220/0004911804780483
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Health Informatics (HEALTHINF-2014), pages 478-483
ISBN: 978-989-758-010-9
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
Thus, XML can be used to unite structural properties
of databases, web requirements and the demands of
end users. This is mainly done by using eXtensible
Style sheet Language Transformations (XSLT)
which includes XML oriented vocabulary for
specifying the output format of XML. Therefore
XML is often attributed as a main standard in
semantic web technology (Robu et al., 2006).
Furthermore the use of the unicode standard enables
xml documents not only to be machine- but also
human-readable (Bray et al., 2008).
Today a huge variety of XML-based applications
like RSS, SOAP have been developed and XML-
based formats have become the standard for many
software-tools like open office. In the context of
medical research, XML applications are applied in a
variety of fields ranging from lab research to
application in health services research. But also web
applications in the field of health information
libraries like semantic bibliographic search engines
make use of the potentials of XML (Ostermann et
al., 2009).
Up to now, information about these applications
has not been analysed systematically. Thus, there is
a basic need to give a bibliometric overview on the
application of XML in medical research. This article
aims at giving such an overview by analysing
articles on XML in journals listed in MEDLINE.
2 MATERIAL AND METHODS
In March 2011 Medline/PubMed was searched for
articles about XML from 1999 until 2010. To get the
broadest possible overview only “XML” was
entered as a search term for all fields. Basic
bibliometrical data from the articles found this way
was directly downloaded from PubMed by using the
csv-download option. This file included PMID,
Title, Authors, Journal, Year, language, and length
of the paper. If available official impact factors were
retrieved from the yearly Journal Citation Reports
and mapped to this data. Finally, MeSH descriptors
from the articles as well as its origin were extracted
from an xml-download and transformed and also
added to the csv-extraction sheet.
Bibliometrical analysis was performed for the
complete dataset and subdivided for the publication
year using publication year’s median as the splitting
cut point. Nominal variables were analyzed using
cross tabulations and Chi-Square-Test statistics
while metrical data was described in terms of Mean
Std.-Dev. and Median and rank test statistics. All
statistical analyses were carried out using SPSS
Version 19.
3 RESULTS
PubMed search found a total of 923 bibliographical
records from 1999 to 2010. While at the beginning
articles on XML were seldom (1999: 24 articles,
2000: 47 articles) a first peak was reached in 2003
with 102 articles. After a decrease in 2004 with only
85 articles the highest number of articles in Medline
was obtained in 2005 with a total of 109 articles.
From 2005 publication activity decreased again to a
local minimum in 2008 with only 76 articles, which
finally went up to 86 publications in 2010. With
respect to their origin, the majority of publications
came from Europe (n=440; 47.7%) closely followed
by American publications (n=337; 36.5%), while
publications from Asia (n=125; 13.5%) and
Australia (n=21; 2.3%) only play a minor role. No
publications came from Africa. In more detail, the
majority of publications was published by US-
American research groups (n=301; 32.6%, followed
by Germany (n=116;12.6%) the UK (n=102;11.1%),
France (n=49; 5.3%) and Japan (n=47; 5.1%). A
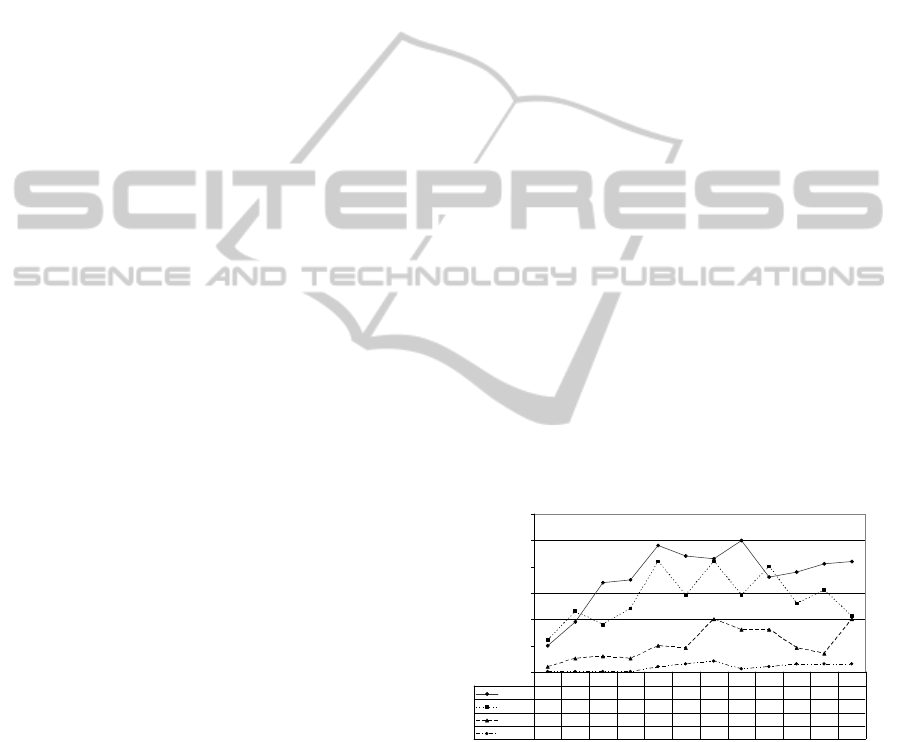
closer look at the chronological development of
percentages reveals that in the early years, American
publications ranged first but after 2000 declined and
only managed to be above Europe in 2007 (Figure
1).
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
Europe
10 19 34 35 48 44 43 50 36 38 41 42
Americ a
12 23 18 24 42 29 42 29 40 26 31 21
Asia
2 5 6 5 10 9 20 16 16 9 7 20
Aus tralia
000023412333
1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010
Figure 1: Number of publications on XML subdivided by
their origin and year of publication.
The median number of authors in all years ranged
between 3 and 4 and the number of descriptors
(keywords) ranged between 5 and 8. Number of
pages increased within the course of time from a
median of 6 before 2005 to 7.5 after 2005 (p<0.001;
Mann Whitney U-Test, Table 1).
Even more important than authors and page
numbers is the development of the impact factor and
the fields of research of publications on XML.
ApplicationofExtensibleMarkupLanguage(XML)inMedicalResearch-ABibliometricalAnalysis
479

Table 1: Sample description.
2005
> 2005 Total
# of articles
Mean per year
489
70
434
87
923
77
# of authors
Mean
Median
4.3 3.2
4
5.0 3.7
4
4.6 3.5
4
# of pages
Mean
Median
7.0 4.3
6
8.2 4.5
7.5
7.6 4.5
6
Origin
US
Asia
Europe
Australia
233 (47%)
190 (39%)
57 (12%)
9 ( 2%)
207 (47%)
147 (34%)
68 (16%)
12 ( 3%)
440 (47%)
337 (36%)
125 (14%)
21 ( 2%)
Language
English
Others
477 (98%)
12 ( 2%)
405 (93%)
29 ( 7%)
882 (96%)
41 ( 4%)
Impact factor
Mean
Median
% IF-Journals
1.8 3.1
0
47%
2.1 2.3
1.46
59%
1.9 2.8
0.69
53%
# descriptors
Mean
Median
7.6 3.9
7
6.9 4.1
7
7.3 4.0
7
Impact factor (IF) increased from a mean of 0.8
in 1999 to a mean of 2.65 in 2004 and decreased
again until 2008 where IF reached the maximum of
3.1 (both mean and median) but then decreased
again. Compared to the time before 2005 IF has
significantly increased from 1.8 3.1 to 2.1 2.3
after 2005. One reason for this development is
reflected by the percentage of journals with impact
factor which significantly (p<0.001; Chi-Square-
Test) increased from 47.0% before 2005 to 58.8%
after 2005. Figure 2 shows this development in more
detail.
A more detailed analysis with respect to the
origin of the papers also reveals that there is a small
but significant difference between publications from
Europe (Mean IF=2.00 2.76) and America (IF 2.12
2.94), which is also reflected in the course of time
(Table 2).
Again US-American publications on XML
cumulated the highest impact (300 publication with
a IF-sum of 626.47).
With the highest IF-mean per publication of 3.52
the UK cumulates to a total sum of 359.23 IF-points
from 102 articles. Only Canada has a comparable IF-
mean with 2.82 from 31 publications, while
Germany only adds 159.62 IF-points from 116
publications and Japan adds 96.72 points out of 47
publications. A more detailed analysis of the
journals XML-articles were published in reveals that
Figure 2: Boxplots of the development of Impact factor of
XML-publications within the course of time.
Table 2: Development of Impact factor subdivided by
origin and year of publication.
Europe America
Year
N
IF (MSD)
N
IF (MSD)
1999 10
1.29 2.81
12
0.53 0.88
2000 19
0.32 1.24
23
0.63 1.27
2001 34
1.08 1.43
18
0.92 1.68
2002 35
1.37 2.14
24
2.03 2.37
2003 48
2.35 5.14
42
2.00 2.61
2004 44
2.36 2.91
29
3.69 4.50
2005 43
1.96 2.48
42
2.78 4.23
2006 50
2.25 2.21
29
1.73 2.31
2007 36
1.63 2.15
40
2.07 2.62
2008 38
3.24 2.07
26
3.19 2.61
2009 41
2.36 2.44
31
2.22 2.41
2010 42
2.05 2.08
21
1.67 2.31
Total
440
2.00 2.76
337
2.12 2.94
four from the Top-10 Journals covering 254 articles
did not have an Impact factor at the time of
publication (Table 3).
In particular, the journal “Studies in health
HEALTHINF2014-InternationalConferenceonHealthInformatics
480

Table 3: Top-20 list of journals with XML-publications
and their Impact factor.
Rank Journal
N % IF Sum
1
Stud Health Technol
Inform
135 14.6 0.00
2
Bioinformatics 83 9.0 443.21
3
AMIA Annu Symp Proc 60 6.5 0.00
4
BMC Bioinformatics 52 5.6 187.74
5
Nucleic Acids Res 51 5.5 355.05
6
Int J Med Inform 33 3.6 54.82
7
Proc AMIA Symp 33 3.6 0.00
8
Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med
Biol Soc
26 2.8 0.00
9
Comput Methods
Programs Biomed
19 2.1 15.52
10
J Am Med Inform Assoc 19 2.1 50.65
11
BMC Med Inform Decis
Mak
14 1.5 8.59
12
J Med Syst 14 1.5 6.38
13
J Digit Imaging 13 1.4 13.46
14
Methods Inf Med 13 1.4 15.43
15
IEEE Trans Inf Technol
Biomed
11 1.2 16.02
16
Proteomics 11 1.2 53.48
17
J Chem Inf Model 10 1.1 33.77
18
Brief Bioinform 7 0.8 16.58
19
J Med Internet Res 7 0.8 3.59
20
Med Inform Internet Med 7 0.8 8.47
Total
618 67.0 1282.76
technology and informatics” ranks first in 7 of 12
years. Other journals however from the field of
Medical and Bioinformatics with mean impact
factors greater that three do however compensate
this resulting in a mean IF of 2.08 in the Top-20 list
of journals.
4 CONCLUSIONS
This articles aimed at summarizing the development
of publications on XML in the medical literature
from 1999-2010. Based on our findings the main
period of visibility and productivity can be identified
in the year 2004. At that time the second edition of
XML 1.1 was initially published (Bray et al., 1997).
While XML 1.1 is not widely implemented, XML
1.0 has been developed further to its fifth edition
which came out in 2008 (Bray et al., 2008). This
year denotes the second high peak in publications
and Impact factors. Although versions of XML have
changed in the course of time, its applications are
still given in knowledge transfer in the life science
(Murray-Rust, 2000) and the creation of interfaces
for related web-based information systems (Badard
and Richard, 2001). The application of XML in
Materials and Hospital Management however only
plays a minor role although Katehakis et al. (2001)
quite early have pointed out the importance of XML
for health services research: “XML provides the
appropriate technology and makes up the most
convenient vehicle towards a common format for
delivering and presenting information content.
Elaboration of the standard DTD logical structure
and related XML infrastructure will make
information personalization flexible and generic
enough to adapt to various types of users and client
devices.” In particular with the upcoming research in
individualized and personalized medicine at that
time (Ginsburg and McCarthy, 2001) XML has
managed to become a standard in clinical laboratory
procedures (Saadawi and Harrison, 2003) but its
way into patient care still seems to be far behind the
possibilities XML is offering: XML-based electronic
medical records may i.e. be used to extract
experiential clinical knowledge. Abidi & Manickam
(2002) proposed “an automated approach to generate
cases for medical case-based reasoning systems”
using XML.
Another field of application is the development
of XML-based search engines. Finding information
in the World-Wide Web is still a crucial matter in
clinical and health services research. Already in the
beginning of XML Butler reported on sophisticated
and specialized search technologies like natural
language processing to assist researchers in finding
information. Meanwhile several XML-based search
engines and tools have been developed in a variety
of fields like Complementary Medicine (Ostermann
et al., 2004), E-Health documents (Gaudinat, 2006),
Proteins and Protenomics (Keller et al., 2005).
Moreover the bibliometric analysis on XML
publications also shows a widespread use of this
technology all over the world. More than 44 nations
including Saskatchewan, Jamaica, Ecuador and
Malaysia underpin the international importance
XML has gained since 1999. However, most of the
publications origin from the main player nations in
the field of information technology namely the US,
Germany and the UK.
ApplicationofExtensibleMarkupLanguage(XML)inMedicalResearch-ABibliometricalAnalysis
481

As a limitation of this review, it has to be noted
that it only focusses on XML as one of many
concepts of the semantic web. Apart from XML
many data representation and communication
standards have been developed in the last two
decades. One of the most important standards is
given by Resource Description Frameworks (RDF).
While XML is a document format for writing and
exchanging information on the Web RDF is a model
for describing semantics and reasoning about
information on the Web (Patel-Schneider & Siméon,
2002).
Already two year earlier than Patel-Schneider
and Siméon, Decker et al. argued that semantic
interoperability should be achieved by exploiting
RDF as a metadata data model (Decker et al., 2000).
Some authors even argue that RDF will be the
universal exchange language of future healthcare
due to its self-describing structure which is easy to
generate (Booth et al., 2013). Moreover RDF might
be more powerful in “large-scale information
integration and vocabulary evolution problems”.
Although the argumentation is straight and RDF
gains more and more attention, it must be noted that
articles on RDF in contrast to XML are quite rare.
Thus, we decided to focus on XML for this current
review which does not imply a voting for XML as a
solitary standard of the semantic web.
Future development according to a recent
position paper of Baclawski & Schneider (2009), is
going to develop information infrastructures based
on Open Ontology Repositories (OOR) combining
existing ontologies with innovative information
technology architectures and standards. XML in this
vision is one but not the only leading standards that
may foster collaborative administration of
knowledge and metadata.
REFERENCES
Abidi S. S., Manickam S. Leveraging XML-based
electronic medical records to extract experiential
clinical knowledge. An automated approach to
generate cases for medical case-based reasoning
systems. Int J Med Inform. 2002;68(1-3):187-203.
Baclawski K, Schneider T. The open ontology repository
initiative: Requirements and research challenges. In:
Proceedings of Workshop on Collaborative
Construction, Management and Linking of Structured
Knowledge at the ISWC. 2009.Smith, J., 1998. The
book, The publishing company. London, 2
nd
edition.
Badard T, Richard D. Using XML for the exchange of
updating information between geographical
information systems. Computers, Environment and
Urban Systems 2001; 25(1): 17-31.
Booth D, Richards R, Dumontier M, Dowling C. Opening
Walled Gardens: RDF / Linked Data as the Universal
Exchange Language of Healthcare. Available at
http://dbooth.org/2013/mu/MU-Stage3-RFC-Simple-
Response.pdf.
Bray T, Paoli J, Sperberg-McQueen CM, Maler E,
Yergeau F. Extensible markup language (XML).
World Wide Web Journal 1997; 2(4): 27-66.
Bray T, Paoli J, Sperberg-McQueen CM, Maler E,
Yergeau F. Extensible Markup Language (XML) 1.0,
5th Edn. W3C Recommendation 26 November 2008.
Available at: http://www.w3.org/TR/REC-xml/ XML
Core Working Group, http://www.w3.org/XML/Core/
Decker S, Van Harmelen, F, Broekstra J, Erdmann M,
Fensel D, Horrocks I, Klein M, Melnik S. The
semantic web: The roles of XML and RDF. Internet
Computing, IEEE 2000, 4(5), 63-73.
Doyle D. J., Ruskin K. J., Engel T. P. The Internet and
medicine: past, present, and future. Yale J Biol Med.
1996; 69(5):429-37.
Gaudinat A, Ruch P, Joubert M, Uziel P, Strauss A,
Thonnet M, Baud RH, Spahni S, Weber P, Bonal J,
Boyer C, Fieschi M, Geissbühler A: Health search
engine with e-document analysis for reliable search
results. Int J Medical Informatics 2006; 75(1): 73-85.
Ginsburg G. S., McCarthy J. J. Personalized medicine:
revolutionizing drug discovery and patient care.
Trends Biotechnol. 2001 Dec;19(12):491-6.
Gorry G. A., Burger A. M., Chaney R. J., Long K. B.,
Tausk C. M. A Virtual Notebook for biomedical work
groups. Bull Med Libr Assoc. 1988;76(3): 256-67.
Katehakis D. G., Sfakianakis S, Tsiknakis M,
Orphanoudakis S. C., An infrastructure for Integrated
Electronic Health Record services: the role of XML
(Extensible Markup Language). J Med Internet Res.
2001 Jan-Mar; 3(1):E7.
Keller A., Eng J, Zhang N., Li X. J., Aebersold R. A
uniform proteomics MS/MS analysis platform
utilizing open XML file formats. Mol Syst Biol.
2005;1: 2005.0017.
Lemkin P. F., Orr G. A., Goldstein M. P., Creed G. J.,
Myrick J. E., Merril C. R. The Protein Disease
Database of human body fluids: II. Computer methods
and data issues. Appl Theor Electrophor.
1995;5(2):55-72.
Murray-Rust P, Rzepa HS, Wright M, Zara S. A universal
approach to web-based chemistry using XML and
CML. Chemical Communications 2000; 16: 1471-
1472.
Ostermann T, Zillmann H, Matthiessen PF. CAMbase--the
realisation of an XML-based bibliographical database
system for complementary and alternative medicine. Z
Arztl Fortbild Qualitatssich. 2004;98(6):501-7.
Ostermann T, Raak C. K., Matthiessen P. F., Büssing A,
Zillmann H. Linguistic processing and classification of
semi structured bibliographic data on complementary
medicine. Cancer Inform. 2009 Jul 6;7:159-69.
HEALTHINF2014-InternationalConferenceonHealthInformatics
482

Pallen M. Guide to the Internet. The world wide web.
BMJ. 1995;311(7019):1552-6.
Patel-Schneider P, Siméon J. The Yin/Yang web: XML
syntax and RDF semantics. Proceedings of the 11th
international conference on World Wide Web 2002,
443-453.
Rambo N, Fuller S. From bench to bedside: research and
testing of Internet resources and connections in
community hospital libraries. Proc Annu Symp
Comput Appl Med Care. 1993:549-53.
Robu I, Robu V, Thirion B. An introduction to the
Semantic Web for health sciences librarians. J Med
Libr Assoc. 2006; 94(2):198-205.
Saadawi G, Harrison J.H. Jr. XML syntax for clinical
laboratory procedure manuals. AMIA Annu Symp Proc.
2003:993.
Sengupta S. Heterogeneity in Health Care Computing
Environments. Proc Annu Symp Comput Appl Med
Care. 1989;8: 355–359.
Treese W. Putting it together: what's all the noise about
XML? Networker 1998; 2(5): 27-29.
ApplicationofExtensibleMarkupLanguage(XML)inMedicalResearch-ABibliometricalAnalysis
483
