
Distributed ICT Architecture for Developing, Configuring and
Monitoring Mobile Embedded Healthcare Systems
Finn Overgaard Hansen
1
, Troels Fedder Jensen
1
and Jose Antonio Esparza Isasa
2
1
Aarhus University, School of Engineering, Finlandsgade 22, Aarhus, Denmark
2
Department of Engineering, Aarhus University, Finlandsgade 22, Aarhus, Denmark
Keywords:
Distributed Systems, eHealth, Mobile Health - mHealth, System Architecture, Smartphone Gateway, Embed-
ded System, Mobile Wearable System.
Abstract:
This paper presents a system architecture to support remote access to mobile embedded healthcare systems
during development and use. It describes the system architecture developed to allow remote debugging, con-
figuration and monitoring of mobile healthcare systems as well as the prototypes that have been developed
to explore the architecture. The architecture has been applied in a concrete wearable embedded healthcare
system for treatment of leg venous insufficiency through compression therapy.
1 INTRODUCTION
Distributed, mobile and wearable embedded health-
care systems give rise to many challenges both during
the development and maintenance phases. In many
situations the testing phase has to be carried out in an-
other physical location than where the development is
done, this can be caused by different reasons e.g. that
the actual systems are coupled to a given physical en-
vironment or as in our case that the testing should be
carried out on a certain location due to the placement
of testing equipment and testing experts.
The wearable embedded healthcare systems
which are target for the architecture described in this
article are safety-critical, thus requiring special atten-
tion to fault tolerance, and have a limited user in-
terface consisting of e.g. a push button and one or
more LEDs, for which reason they can be difficult to
monitor and debug during both test and maintenance
phases.
The distributed architectures described in this pa-
per are developed for the e-Stocking EU Ambient As-
sisted Living (AAL) Project. The aim of the project
is to develop an intelligent, mobile and embedded
healthcare system, an ICT-enabled medical Graded
Compression Stocking (GCS) solution (described in
section 5.1). Key features of the novel intelligent
stockings are easy application and operation, compli-
ance with individual patient’s clinical needs, and en-
hanced mobility and self-sufficiency.
This paper is structured as follows: Section 2
presents the state of the art on the topic. Section 3
yields a list of requirement for the proposed architec-
ture. Section 4 describes the architecture and scenar-
ios proposed to meet the requirements . Section 5 de-
scribes design and implementation details. Section 6
presents and discuss the results obtained. Section 7
describes future work and conclusions.
2 STATE OF THE ART
The AAL program aims to find efficient solutions to
help elderly persons maintain self-sufficiency. The
promises and challenges of AAL have been described
in (Sun et al., 2009) and (Estudillo-Valderrama et al.,
2010).
To enhance self-sufficiency of patients who wear
the ICT-enabled medical GCS, the GCSs must to be
mobile and preferably be monitorable regardless of
location. An obvious solution to this is to use a smart-
phone as a communications gateway between the
embedded system and external systems as described
in (Germano et al., 2009) and (Bialy et al., 2011),
in which the local wireless communication with the
embedded system is based on the Bluetooth stan-
dard commonly supported by smartphones. Trends
and importance of using wireless technologies in E-
Health are described in (El Khaddar et al., 2012).
Architectures for smart homes and home health-
care systems have been researched in many projects,
484
Hansen F., Jensen T. and Esparza Isasa J..
Distributed ICT Architecture for Developing, Configuring and Monitoring Mobile Embedded Healthcare Systems.
DOI: 10.5220/0004911904840489
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Health Informatics (HEALTHINF-2014), pages 484-489
ISBN: 978-989-758-010-9
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
four of which are evaluated in (Fabbricatore et al.,
2011). This has not been the focus of our current re-
search, which describes a stand-alone healthcare sys-
tem for the single medical purpose of delivering an
intelligent compression solution. Our approach could
readily be integrated with a common ICT platform in
the home for extending the possibilities of the current
solution or for integrating other patient-related health-
care measurements such as vital signs.
Extensive research has been conducted in Wire-
less Body Area Networks (WBAN), e.g. (Latr
´
e et al.,
2011), (Chin et al., 2012) and (Hansen and Tofte-
gaard, 2011), where the WBAN integrates several
sensors or actuators located on a patient which com-
municate with a wearable gateway node, such as a
smartphone. In (Yang and Gerla, 2011) they presents
a personal gateway, where a specially designed de-
vice, called a PHM-Gate, preprocesses sensor data,
as in the WBAN case, before the data is forwarded to
a smartphone acting as a gateway for external com-
munication.
To our knowledge, no research has been published
on the design and use of a distributed ICT architecture
to support the combined development, configuration
and monitoring of mobile embedded healthcare sys-
tems.
3 REQUIREMENTS FOR THE
SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE
This section lists the key requirements for the system
architecture:
R1 The system shall use a portable gateway for con-
nection to external systems
R2 The gateway shall enable mobility by support-
ing mobile internet communication to centralized
systems
R3 Communication to centralized systems shall be
over the internet
R4 The system shall have a simple user interfaces,
preferably consisting only of buttons and LEDs
R5 The system shall support remote software debug
and download
These requirements, along with others, have
formed the basis for the development of the system
architecture and scenarios presented in Section 4.
4 SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE
AND SCENARIOS
The system has four envisioned main application
scenarios: Calibration and configuration, remote
software debugging, remote software updating, and
health status monitoring. To support the implemen-
tation of these scenarios the system architecture de-
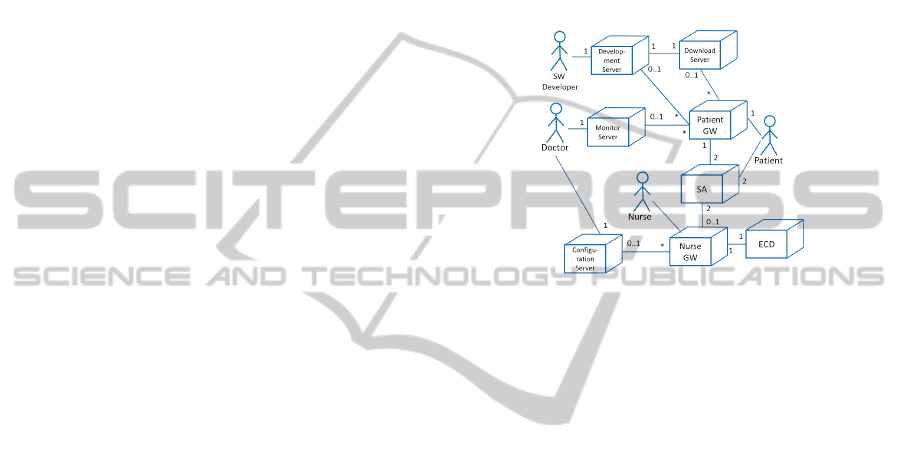
picted in the UML deployment diagram in Figure 1
has been defined.
Figure 1: System architecture.
The actors in Figure 1 are briefly described below.
Patient: The wearer of the Stocking Assembly (SA)
and recipient of compression therapy. The Patient
may interact with the Patient Gateway on a regular
basis to follow treatment progress.
Nurse: A nurse (or similarly skilled person) who is
responsible for the calibration of the configuration
of the SA to the patient through the use of a Nurse
Gateway
Doctor: A Doctor who is responsible for the com-
pression therapy. The Doctor issues the SA to the
Patient, defines configuration parameters for the
SA and remotely monitors treatment progress.
SW Developer: A skilled person responsible for the
development and continued support of software
for the SA. The SW Developer remotely de-
bugs the deployed SA software and makes new
software updates available through the Download
Server.
These actors interact with the system through a num-
ber of nodes described below.
SA: Stocking Assembly (SA): The actual stocking
worn by the Patient which administers compres-
sion to the Patient’s leg in accordance with cali-
bration parameters.
ECD: e-Stocking Calibration Device. A device used
to provide the SA with actual on-skin pressure
readings in the calibration scenarios.
DistributedICTArchitectureforDeveloping,ConfiguringandMonitoringMobileEmbeddedHealthcareSystems
485

Nurse GW: Nurse Gateway. A smartphone used by
the Nurse for calibration and configuration of the
SA for the individual patients.
Patient GW: Patient Gateway. A smartphone used
by the Patient to monitor treatment progress. Also
the gateway used for remote debugging of the SA
and the remote installation of software updates
Development server: A computer system used to
develop and debug software for the SA.
Download server: A server which publishes SA
software versions.
Monitor server: A server which makes health status
indications for specific SAs available to the Doc-
tor.
4.1 Calibration and Configuration
This subsection describes two closely related sub-
scenarios, namely calibration of the SA and config-
uration of same. The calibration scenario covers the
initial calibration session of the SA. Calibration en-
sures that the SA will deliver the correct compres-
sion to the patient’s leg regardless, within the dynamic
range of the SA, of the patient’s leg shape and size.
Periodic follow-up calibration sessions, e.g. once ev-
ery month, can be carried out to ensure that the com-
pression therapy administered to the patient’s leg is
optimal even as the patient’s leg changes size and vol-
ume, and as the elastic properties of the SA changes
over time.
To support optimal results of the compression
therapy, the compression levels applied to the pa-
tient’s leg are configured initially and can be re-
configured periodically as the treatment progresses.
The actors and nodes involved in configuration of
the SA are the Doctor (primary actor) and the Config-
uration Server (see Figure 1) who specifies the com-
pression levels of the SA’s individual compression
sections as he sees most prudent to the compression
therapy. To support his decision-making, the Doctor
may leverage results retrieved from the SAs (further
details provided in subsection 4.4). Having defined
a new configuration, the Doctor uploads this to the
Configuration Server. Configurations are stored on
the Configuration Server and retrieved during calibra-
tion (see below).
Calibration involves the Nurse (primary actor) and
Patient (secondary actor), see Figure 1, and the SA,
Nurse Gateway, ECD and Configuration Server as
nodes. Calibration is to be performed in the patient’s
home or a nursing home. When calibration shall take
place, the Patient applies the SA and the Nurse con-
nects the SA and the e-Stocking Calibration Device
(ECD) through an application running on the Nurse
Gateway. The Nurse then uses the Nurse Gateway to
retrieve configuration parameters, defined for the Pa-
tient by the Doctor, from the Configuration Server and
downloads them to the SA. Subsequently, the Nurse
commands initiation of the calibration, during which
the SA compresses the Patient’s leg to the configured
level, all the time evaluating the actual on-skin pres-
sure through communication with the ECD. When the
correct level is reached, the SA is calibrated. At this
time, the connections to and from the Nurse Gateway
can be dismantled and the SA again be left to operate
in its regular stand-alone mode.
4.2 Remote Software Debugging
In this scenario the system developers remotely re-
trieve information regarding the system’s execution,
errors occurred etc.
The actor involved in this scenario is the SW De-
veloper (primary actor) while the nodes involved are
the Patient Gateway, the SA, and the Development
Server. In this scenario, the SW Developer will ini-
tiate a debugging session with a specific remote de-
vice. The Patient Gateway is commanded to execute
a remote debugging application which will connect
to the SA and the Development Server. When con-
nected, the SA can pass debug information through
the Patient Gateway to the Development Server and
thus to the SW Developer who may then evaluate the
information. During this session, the Patient may be
required to participate, e.g. by pushing a button etc.
If this is the case, the Patient Gateway may be used
to communicate instructions directly to the Patient by
simple text messages or telephone conversation.
4.3 Remote Software Update
This scenario facilitates remote updating of the SA
software, e.g. to distribute a software update or bug
fix, both in the development, test, and deployment
phases. The actors and nodes are the same as in the
aforementioned remote debugging scenario with the
addition of the Download Server node.
When an update to the existing SA software has
been produced and properly evaluated, the SW De-
veloper may push this update to the Download Server,
thereby making it available to all SA’s deployed. At
regular intervals, e.g. once per day, the Patient Gate-
ways will establish contact to the Download Server
to check for software updates for the Patient’s SA.
If such an update is found, the Patient Gateway will
download it, request connection to the SA and initiate
the download of the updated software to the SA.
HEALTHINF2014-InternationalConferenceonHealthInformatics
486

As the SA is considered a safety-critical system,
care must be taken to ensure that the software update
which is installed in the SA is indeed functional, and a
fall-back mechanism which resorts to the last known
functional software must be in place. Several alterna-
tives exist for this purpose, of which the simplest one
is to let the Patient Gateway upload the existing soft-
ware from the SA, download the new version to the
SA and have the SA verify the software. Should veri-
fication of the new software fail, the Patient Gateway
may resort to re-downloading the previous version of
the software. Alternatively, the SA shall be equipped
with sufficient persistent memory to hold two soft-
ware versions at the same time so that the functional
software version can be present while a new software
version is downloaded and evaluated.
4.4 Health Status Monitoring
Health status monitoring refers to the monitoring - re-
mote or local - of key health status indicators emanat-
ing from the SA. This scenario can be divided into two
sub-scenarios: Local and remote health status moni-
toring.
In the local health status monitoring scenario, we
find the Patient, the Patient Gateway and the SA in-
volved. The Patient uses the Patient Gateway to es-
tablish communication with the SA. When the con-
nection is established, the Patient uses a health status
monitoring application to review health status indica-
tions, both current and historical, provided by the SA
(e.g. usage statistics) and derived treatment progress
indications. It is envisioned that the possibility to con-
tinuously monitor health status indicators will moti-
vate the patient to engage in continued treatment and
thus improve therapeutic results.
Remote monitoring covers the scenario in which
the health status indications, again both current and
historical, are monitored remotely. The participants
in this scenario are the Doctor, the Monitor Gateway,
the Patient Gateway and the SA.
The Doctor, who is responsible for the patient’s
treatment, periodically requests health status indica-
tions from the SA (e.g. leg volume) and reviews them.
This scenario will not replace the regular visits of
the Patient to the Doctor, but the data harnessed and
knowledge derived from objective health status mon-
itoring including usage statistics are believed to be a
valuable supplement, which will qualify the Doctor’s
discussion of treatment progress with the Patient. Fur-
thermore, this scenario will allow the doctor to pro-
actively adjust treatment parameters, e.g. changes in
compression configuration, thus increasing the effi-
ciency of the compression therapy. Finally, as eval-
Figure 2: The Stocking Assembly, constituting the mobile
embedded healthcare system in this study.
uation of health status indications is considered to be
much faster than as-many face-to-face visits, this sce-
nario would also allow the doctor to evaluate the treat-
ment of more Patients more often.
5 DESIGN AND
IMPLEMENTATIONS
This section presents design and implementation is-
sues for the different subsystems that compose the dif-
ferent architectures presented in the section above.
5.1 Mobile Embedded Healthcare
System
The Stocking Assembly (SA), which constitutes the
mobile embedded healthcare system in this study, is
shown in Figure 2. The SA consists of the stocking it-
self (items 1 and 2), an actuator box for supplying air
(item 3) to the compression sections and an Electronic
Control Unit (ECU) for controlling the compression
of the patient’s leg (item 4). The three individual com-
pression sections of the SA are mounted laterally to
cover the entire length of the stocking. Each compres-
sion section consists of two air chambers mounted at
same height on both sides of the leg.
By compressing the sections to different levels
the compression applied to the patient’s leg can be
graded from ankle level to just below the knee. The
compression delivered to the leg is continuously reg-
ulated through measurement of the air pressure in the
air chambers or the on-skin pressure. The compres-
sion applied is calibrated to each individual patient by
DistributedICTArchitectureforDeveloping,ConfiguringandMonitoringMobileEmbeddedHealthcareSystems
487

means of the e-Stocking Calibration Device (ECD).
The compression is managed by an object-
oriented embedded software application executing
atop an operating system on the ECU which controls
sensors, actuators, user input and other external in-
terfaces. The ECU hardware consists of an ARM
Cortex-M3-based processor implemented on a Cy-
press PSoC5 hardware platform and various periph-
erals and custom-made hardware interfaces.
5.2 e-Stocking Calibration Device
The ECD interfaces pressure sensors mounted to mea-
sure on-skin pressure and provides these measure-
ments as data to the ECU against which the SA can
calibrate the air pressure level in the compression sec-
tions. The ECD features a Bluetooth interface to com-
municate with the SA during calibration. The ECD
has been implemented using the same hardware and
software technologies as the ECU.
5.3 Smartphone as a Gateway
Both the Patient and the Nurse Gateways consist of an
Android-based smartphone device which runs a Gate-
way application. The Nurse Gateway will execute a
Gateway application which facilitates the Calibration
and Configuration scenarios described in 4. This pro-
vides bridging services when the SA and ECD should
be connected as well as the graphical user interface
for use in the calibration process. The Gateway con-
nects wirelessly to the SA and ECD, respectively, and
forwards sensor data requests and responses to the
counterpart.
The Patient Gateway application will support the
other scenarios described in Section 4 by supporting
remote debugging and downloading of software up-
dates, and by supporting system and medical diagnos-
tics data retrieval from the SA.
5.4 Wireless Communication
The ECU, ECD and Gateway make use of a
Bluetooth-based wireless communication interface.
This technology will be replaced by Bluetooth Low-
Energy (BLE or Bluetooth 4.0) in the next version of
the prototype. This technology has not been incor-
porated yet into the prototypes since the number of
smartphones supporting BLE is reduced. The incor-
poration of BLE will bring a number of advantages
to the system, of which a more simple link establish-
ment compared with Bluetooth 3.0, energy efficiency
and low latency are the most relevant ones.
5.5 Communication from Gateway to
Centralized Systems
The Gateways communicate with a number of cen-
tralized systems through the Internet. This is achieved
through the mobile internet access or a Wifi connec-
tion, both incorporated in the smartphones used for
Gateways. A design alternative is to integrate the In-
ternet access interface in the ECU. This would make it
possible to eliminate the Patient and Nurse Gateways
from the architecture and thus simplify the architec-
ture. However, this would make the SA heavier and
more power demanding, and eliminate the possibility
of having a graphical user interface for the SA on the
Gateways.
5.6 Centralized Systems
The embedded healthcare system interfaces a number
of services which can be deployed on the same or dif-
ferent servers. The services are:
Configuration Service: Allows retrieving and
changing the treatment parameters without
needing physical access to the SA.
Development Service: Allows remote debug and in-
spection of the state of the SA.
Monitoring Service: Allows remote monitoring of
health status and usage statistics.
Download Service: Allows remote deployment of
software updates to the ECU.
6 DISCUSSION AND RESULTS
At the current time, a prototype of the architecture
supporting the calibration scenario described in 4 has
been implemented and is used as an integral part of
the e-Stocking project. Furthermore, a prototype of
the remote debugging scenario is under development.
Presently, the SA-Patient Gateway interface is estab-
lished and rudimentary debugging information can be
requested remotely by transmitting raw messages to
the Patient Gateway.
Being able to remotely gauge the performance of
a safety-critical such as the e-Stocking discussed here
by evaluating a number of pre-defined parameters re-
motely while the system operates is foreseen to be of
substantial value in the development, test, and early
deployment phases in which system information may
be harnessed from the field in the event of system fail-
ure or to gauge the efficiency of e.g. recent system
updates. Such information, gathered in the field and
HEALTHINF2014-InternationalConferenceonHealthInformatics
488

made available to developers, is crucial to remove er-
rors, enhance the user experience and increase system
effectiveness.
As is the case with remote debugging, remote soft-
ware updating is believed to be of substantial benefit
to both healthcare bodies and patients, as the system
can be updated without requiring the system (and thus
the patient) to return to the doctor or nursing home.
In a longer perspective it may be beneficial to feed
the health status indications into an Electronic Patient
Record (EPR) system to fuse information harnessed
from the SA with patient information harnessed from
other sources to supplement the big picture of the
treatment of a patient. If this is the case, the archi-
tecture depicted in Figure 1 will have to be expanded
as necessary to provide access to the EPR system.
7 FUTURE WORK AND
CONCLUSIONS
On the SA, future work remains for the integration
of the remote debugging and remote software update
scenarios to enable the SA to handle debug and down-
load requests, respectively. The latter will require the
SA to be extended so that it may also receive and ver-
ify the new software prior to its use.
Work also remains to be done on the individual
Gateways, most notably in the implementation of the
common connection handling and secure protocols to
the Development, Download, Monitoring and Config-
uration Servers.
Further work is also required to provide the hu-
man actors with proper user interfaces, e.g. to allow
the Doctor to retrieve health status indications for a
specific Patient’s SAs, and to specify configuration
parameters for same.
This paper has listed the requirements of an dis-
tributed ICT architecture supporting development,
configuring and monitoring mobile healthcare sys-
tems, using the e-Stocking project as a case study.
It then described the architecture, design and imple-
mentation issues and the current status of the devel-
opment of this architecture and the e-Stocking proto-
type. Furthermore, it has described the technical chal-
lenges posed and how they were overcome, and what
work remains to be done.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research is funded by the EU Ambient Assisted
Living Joint Programme, eStockings Project under
grant agreement no. AAL-2011-4-020.
REFERENCES
Bialy, T., Kobusinski, J., Malecki, M., and Stefaniak,
K. (2011). Emeh: Extensible mobile platform for
healthcare. In Computer Science and Information
Systems (FedCSIS), 2011 Federated Conference on,
pages 355–361.
Chin, C., Crosby, G., Ghosh, T., and Murimi, R. (2012).
Advances and challenges of wireless body area net-
works for healthcare applications. In Computing, Net-
working and Communications (ICNC), 2012 Interna-
tional Conference on, pages 99–103.
El Khaddar, M., Harroud, H., Boulmalf, M., ElKoutbi, M.,
and Habbani, A. (2012). Emerging wireless technolo-
gies in e-health trends, challenges, and framework de-
sign issues. In Multimedia Computing and Systems
(ICMCS), 2012 International Conference on, pages
440–445.
Estudillo-Valderrama, M., Roa, L., Reina-Tosina, J., and
Roman-Martinez, I. (2010). Ambient assisted liv-
ing: A methodological approach. In Engineering in
Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), 2010 Annual
International Conference of the IEEE, pages 2155–
2158.
Fabbricatore, C., Zucker, M., Ziganki, S., and Karduck,
A. (2011). Towards an unified architecture for smart
home and ambient assisted living solutions: A focus
on elderly people. In Digital Ecosystems and Tech-
nologies Conference (DEST), 2011 Proceedings of the
5th IEEE International Conference on, pages 305–
311.
Germano, J., Ramalho, R., and Sousa, L. (2009). On the
design of distributed autonomous embedded systems
for biomedical applications. In Pervasive Computing
Technologies for Healthcare, 2009. PervasiveHealth
2009. 3rd International Conference on, pages 1–8.
Hansen, F. O. and Toftegaard, T. S. (2011). Requirements
and system architecture for a healthcare wireless body
area network. In Traver, V., Fred, A. L. N., Filipe, J.,
and Gamboa, H., editors, HEALTHINF, pages 193–
199. SciTePress.
Latr
´
e, B., Braem, B., Moerman, I., Blondia, C., and De-
meester, P. (2011). A survey on wireless body area
networks. Wirel. Netw., 17(1):1–18.
Sun, H., De Florio, V., Gui, N., and Blondia, C. (2009).
Promises and challenges of ambient assisted living
systems. In Information Technology: New Genera-
tions, 2009. ITNG ’09. Sixth International Conference
on, pages 1201–1207.
Yang, S. and Gerla, M. (2011). Personal gateway in mobile
health monitoring. In Pervasive Computing and Com-
munications Workshops (PERCOM Workshops), 2011
IEEE International Conference on, pages 636–641.
DistributedICTArchitectureforDeveloping,ConfiguringandMonitoringMobileEmbeddedHealthcareSystems
489
