
Harmonicity of the Movement as a Measure of Apraxic Behaviour
in Stroke Survivors
Marta Bieńkiewicz
1
, Philipp Gulde
1
,
Georg Goldenberg
2
and Joachim Hermsdörfer
1
1
Technische Universität München, Lehrstuhl für Bewegungswissenschaft,
Uptown München-Campus D Georg-Brauchle-Ring 60/62 D-80992 München, Germany
2
Städtisches Klinikum München, Klinik für Neuropsychologie, Englschalkinger Straße 77, 81-925 München, Germany
Keywords: Apraxia, Smoothness of Movement, Harmonicity, Kinematic Patterns, Stroke Rehabiliation.
Abstract: Due to the brain damage caused by stroke, apraxic patients suffer from tool use impairment, and sequencing
actions during daily tasks (ADL). Patients fail to use tools in a purposeful manner, often adopting an
inappropriate speed of the movement and a disrupted movement path (Laimgruber et al., 2005). The core of
this symptom lies in the compromised ability to access the appropriate motor program relevant to the task
goal (Hermsdörfer et al., 2006). Although many studies have explored kinematic and spatial features of
apraxia both in object and non-object related motor tasks, there is a niche in the research to provide a
spatiotemporal biomarker for this behaviour. We propose a novel approach based on dynamical systems
framework (Bootsma et al., 2004), looking into the temporal and spatial components of movements.
Preliminary data shows that this measure has a potential to encapsulate the disrupted motor behaviour in
those patients. We put forward a circular-fit based model to quantify deviations from the regular movement
pattern. The application of this study is to create a measure of motor behaviour to be implemented in the
autonomous assistance system (CogWatch) that could facilitate performance of ADL both in the clinical and
home-based setting.
1 INTRODUCTION
The cerebrovascular accident (CVA), whether it is
caused by bleeding or ischemia, causes a permanent
damage of brain tissue. Stroke survivors suffer from
a range of disruptions in motor circuitry such as
spasticity or loss of control over limb
(paresis/plegia). In addition, stroke can cause
sensory deficits as well as language comprehension
and production problems. The main focus of this
paper is apraxia disorder, which describes a
compromised ability of CVA patients to use objects
in an accurate, goal directed manner and in turn,
carry out ADL (Goldenberg et al., 1996). In this
study, we propose a novel quantitative approach for
capturing subtle differences in motor control on the
spatiotemporal dimension between patient group and
healthy elderly.
2 BACKGROUND
The CogWatch (www.cogwatch.eu) project is
designed to create an autonomous assistance system
to aid ADL independence in stroke cohort. The
primary scope of the project is addressing patients
who suffer from impaired ability to use everyday
tools, due to left brain damage (Bieńkiewicz et al.,
2013; Hermsdörfer et al., 2013). That means
inability to access previously mastered knowledge
about action execution, despite a preserved ability to
integrate sensory information from the environment
and execute smooth movement in a goal directed
manner (De Renzi et al., 1982).
The incidence of persistent signs of apraxia in
the population of CVA patients is estimated to be
approximately 24% of all stroke survivors
(Bickerton et al., 2012). The difficulty with the use
of tools is a source of frustration for patients, as it
directly increases the need for the help from
caregivers during ADL. This loss of independence
compounds the problems associated with CVA and
makes the consequences of apraxia more debilitating
(Hanna-Plady et al., 2003). One of the on-going
strands of the project is to identify spatiotemporal
patterns emerging during the production of ADL in
295
Bie
´
nkiewicz M., Gulde P., Goldenberg G. and Hermsdörfer J..
Harmonicity of the Movement as a Measure of Apraxic Behaviour in Stroke Survivors.
DOI: 10.5220/0004913802950300
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing (BIOSIGNALS-2014), pages 295-300
ISBN: 978-989-758-011-6
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

this group of patients for the purpose of monitoring
online task performance, progress of recovery and
feed in automatized action recognition algorithms
(Hughes et al., 2013).
2.1 Apraxia Non-kinematic Features
The most widely accepted definition of apraxia
describes it as neurological sign of brain damage,
behaviourally observed as the inability to perform
skilled, well-learned motor acts (rothi et al., 1997).
As previously mentioned, this deficit cannot be
however explained by shortfall of motor or sensory
brain functions caused by stroke (figure 1). For
example, features of apraxia are independent from
the loss of motor function of the limb (paresis or
spasticity) or partial loss of visual field (hemianopia)
or compromised visual attention (visual neglect)
(petreska et al. 2007; goldenberg et al., 2007).
Figure 1: Illustration of the conceptual underpinnings of
the apraxic behaviour. Despite preserved ability to execute
movement and sensory system being functional, patients
have difficulty accessing the motor concepts relevant to
the action goal.
For example, problems with the object use are
present when the task is performed with the non-
affected limb (in the case of right handed
participants with left brain damage, problems with
motor features are present when the task is
performed with the left hand). However, the
problems with daily activities can be enhanced by
these deficits, but are regarded as separate symptoms
from the compromised functionality of motor
schemas. Detailed descriptions of apraxia refer to
three subcategories of symptoms affecting both
object related and non-object related performance
(Petreska et al., 2007; De Renzi et al., 1982, Jason et
al., 1983). This classification refers to the transitive
(object manipulation actions, e.g. using a hammer to
put a nail into wooden board) or non-transitive (such
as gestures, imitation and pantomime) (Goldenberg
& Hagmann, 1997). The non-transitive movements
involve gesture production and recognition for the
meaningful gestures (such as waving goodbye) and
non-meaningful ones (such as copying finger or
hand postures) (Goldenberg et al., 1996). These two
different subtypes of apraxia are usually described in
the body of research as separate – conceptual
apraxia and ideomotor apraxia respectively
(Goldenberg, 2003). The problems with smooth
performance of the task are referred in the literature
as a third category, which is limb apraxia. Limb
apraxia is defined as disruption of kinematic pattern
of the movement, with preserved gesture and tool
knowledge (Petreska et al., 2007). Those subtypes
however, although differentiated as separate
symptoms of apraxic behaviour, often coincide. In
addition to apraxia Action Disorganisation
Syndrome is distinguished in many other
neurological disorders apart from stroke and
regarded as difficulty with sequencing of the motor
acts (Cooper et al., 2005). That means performing
the action in an efficient and organised manner,
despite preserved tool knowledge. The distinction
between ADS and apraxia is however still widely
discussed in the body of literature.
Due to apraxia and ADS, patients are prone to
conceptual, spatial and temporal errors during daily
activities that can lead to potential health and safety
issues (e.g., grasping the knife by the sharp end,
pouring boiling water onto the kitchen desktop).
Common errors include problems with sequencing
in multistep actions (e.g., action or ingredient
addition, omission, anticipation and perseveration
errors) along with conceptual errors (e.g., misuse of
objects, object substitution, hesitation, toying and
mislocation) (Petreska et al., 2007). The cognitive
aspect of apraxia (i.e., the loss of knowledge how
the action is performed) is often accompanied by
changes in the kinematic pattern of the movement in
the unimpaired hand. During the pantomime and
gesture production, patients show irregularities
usually in the direction of the movement, amplitude,
speed and spatial position. Therefore, pantomime
performance is one of the hallmarks in the
neuropsychological examination of patients, due to
its high sensitivity. Some patients might not exhibit
a difficulty with the tool use, but fail to pantomime
the performance. The plausible explanation for this
phenomenon is that the priopioceptive information
from grasping the tool provides additional
sensorimotor input, which reinforces the selection of
the appropriate motor schema (Hermsdörfer et al.,
2006). The kinematic characteristics of apraxia
syndrome will be further discussed in the following
section.
2.2 Apraxia Spatio-temporal Features
There are several studies looking into the kinematic
BIOSIGNALS2014-InternationalConferenceonBio-inspiredSystemsandSignalProcessing
296

hallmarks of apraxic tool use. Unlike the studies
using video-based approach in assessment of apraxia
(Schwartz et al., 1995), or neuropsychological
batteries in assessment of ADL in CVA patients
(Vanbellingen et al., 2011; Graessel et al., 2009),
research using motion capture recordings allows one
to measure the subtle differences in the motor
control. In the seminal study by Laimgruber et al.
(2005), several variables were distinguished as
sensitive measures of the differences between
spatiotemporal features of task performance between
the CVA patients and elderly controls in a
pantomime task of taking a sip of water from a glass.
Those variables were: movement time, peak
velocity, deceleration phase and grip aperture.
Deficits in the speed of the movement were also
shown in other tasks such as the pantomime of
sawing (Hermsdörfer et al., 2006) and pantomime
and use of a hammer (Hermsdörfer et al., 2012). In a
scooping motion task involving CVA patients with
left brain damage, another study has reported
deficits in the amplitude of the movement and
reduced hand roll (Hermsdörfer et al., 2012). In
addition Clark et al. (1994) have demonstrated
imprecise plane of motion and trajectory shape in
the pantomime and tool use of a knife when slicing a
piece of bread, along with the impaired coupling in
the hand velocity and trajectory shape. This was also
shown by Poizner et al. (1995) in the same task
scenario, which highlights the impaired joint
coordination in a slicing movement. The disruptions
in the kinematic features of the movement are linked
to its more observable features such as perplexity,
indicating a difficulty with accessing the appropriate
motor plan (Hermsdörfer et al., 2006).
Other studies looking at goal-directed movement
without tool use, such as pointing task, have
reported impaired reaction times, acceleration
deficits and prolonged movement times in the task
performance by apraxic individuals (Fisk &
Goodale, 1988; Hermsdörfer et al., 1999;
Hermsdörfer et al., 2003; Haaland & Harrington,
1994). In grasping movements, impaired prehension
and awkward hand rotation were noted as spatial
features of kinematic impairments in patients
(Hermsdörfer et al., 1999; Tretriluxana et al,. 2009).
2.3 Smoothness of Movement
Differences in the movement organisation in terms
of spatiotemporal characteristics are usually limited
to the presented above approaches, taking into
consideration velocity and acceleration profiles,
movement times and movement path. In this study,
we focus on the movements that are naturally
cyclical in both spatial and temporal dimensions
(sawing, hammering and circular toothbrushing). We
have chosen this particular task, due to the plethora
of research investigating the oscillatory arm
movements in healthy adults. Bootsma, Fernandez
and Mottet (2004) have demonstrated that self-paced
cyclical arm movements performed back and forth
between two targets are normally represented by
velocity curves that resemble a repetitive sinusoid
oscillation over time. This natural harmonicity of the
movement can be represented by circular shaped
phase planes, when the velocity of the movement is
plotted against position. This can be plotted as a
semi-circle on either side of the x/y/z axis,
representing one pointing movement. The
assumption is that the more phase plane deviates
from a regular circular shape, the less harmonic the
movement. Lower harmonicity of the movement can
implies a less natural the pace of the movement or a
lesser degree of control (Bootsma et al., 2004).
2.4 Research Aims
The purpose of this research is to explore the
feasibility of new biomarkers based on the
harmonicity measure to capture the apraxic features
in the movement.
3 METHODS
3.1 Experimental Design
In the study 20 healthy elderly, age-matched with
patients will be tested. All of the healthy participants
are to be right handed, 10 will be tested with right
hand, 10 with the left hand. In the clinical group, 10
patients will be tested that suffered from first CVA,
affecting primarily areas in the left brain
hemisphere.
Control and patient groups will be tested under
two modes of execution:
A. Actual action execution
B. Pantomime with action object visible
Three daily tasks will be tested:
i) Sawing a piece of wood
ii) Hammering
iii) Toothbrushing
Each of those conditions will have two trials of
repetition and the experimental design will be
counterbalanced using Latin Squares. The practice
trial will include a task of pouring a glass of water
HarmonicityoftheMovementasaMeasureofApraxicBehaviourinStrokeSurvivors
297
from a jug (pantomime versus tool use). Motor
performance will be recorded using passive marker
setup and Qualisys Motion Capture system.
Pantomime and tool use in addition will be assessed
using the Goldenberg & Hagmann (1998) 2 point
scale. The following kinematic variables will be
analysed alongside: movement time, peak velocity,
movement path, frequency of the movement,
number of acceleration zerocrossings (jerks),
deceleration phase, grip aperture and orientation.
Number of errors committed and kinematic features
of the movement will be compared across conditions
for each patient and groups between patients and
age-matched controls.
3.2 Phase Portraits and Circular Fit
Matlab script (Mathworks, 2012) was developed to
provide the derivates of spatiotemporal positional
data and create phase plot data. The algorithm was
based on the Bootsma et al. (2004) study looking
into the harmonicity of aiming movement. We have
adopted the approach proposed by the authors and
normalised for Aω – peak velocity of an ‘idealised’
harmonic movement at given amplitude and
movement time and for the amplitude of the
movement. This can be mathematically expressed
as:
Aω=(A* π)/(MT*2) (1)
where A denotes distance travelled and MT
movement time.
To create a mathematical fit for the phase plot
data we applied the ‘Taubin’ method of curve and
surface fitting (1991) and incorporated it into Matlab
script. This method is based on a geometric-fitting
approach and minimization of the approximate mean
square distance:
∑
∑
(2)
Where x
i
and y
i
refer to consecutive points from the
phase plot data for each trial.
3.3 Squared Error as Candidate
Measure of Harmonicity
For the purpose of calculating the deviations from
the harmonic movement pattern, we have adopted
squared error approach as a preliminary outcome
measure. Each stroke of the movement and reversal
in a trial will be normalised according to the
procedure listed in the 3.2 and further centralised
with respect to the origin of the fit. Subsequently a
squared error will be calculated between each data
point of the velocity/position data and the closest
point demarked by radius from the fitted circle. The
median value will be extracted for each trial and
condition for each participant.
Those values will be compared across patients
and healthy elderly controls.
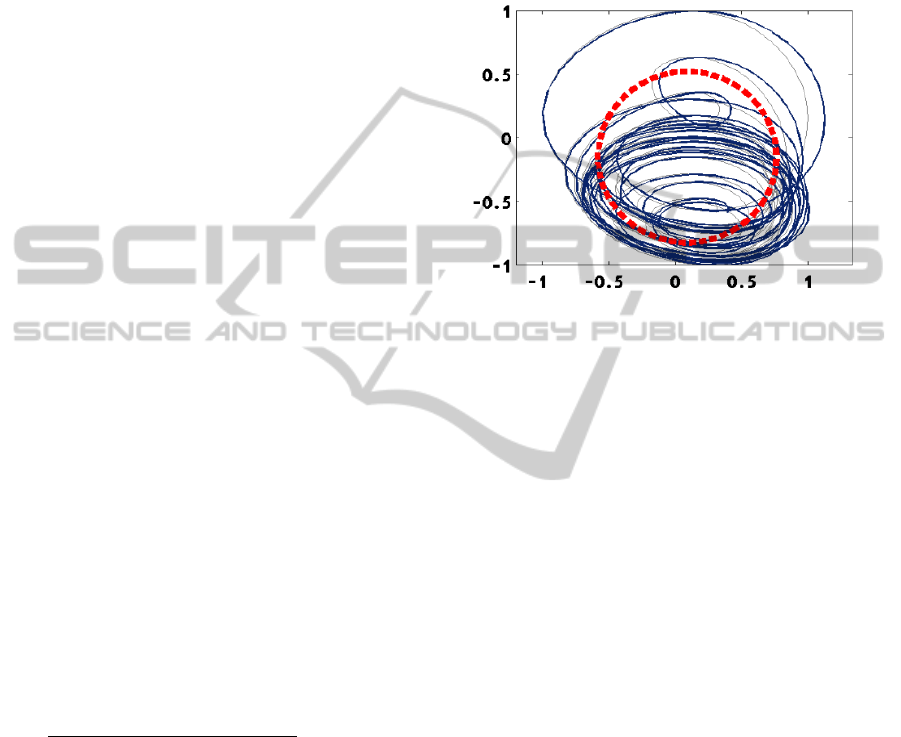
Figure 2: Illustration of how squared error measure is
calculated based on the normalised phase plot data and
fitted circle based on Taubin method. Black arrow depicts
the 2-D distance between the fitted circle radius point and
velocity/position data (red point). For each stroke of the
movement and reversal, velocity/position data is
centralised with respect to the origin of the fitted circular
shape. The dashed red line represents a circular fit
modelled to the positional data.
4 PRELIMINARY RESULTS
Preliminary data analysis provides an optimistic
outlook for the method. So far 9 patient data were
analysed along with the data from 16 healthy elderly
subjects (10 tested on the right hand and 6 on the left
hand). Graphical representation of the sample data
are visualised in Figure 3. We have observed
increased variability in terms of velocity/positional
data in the group of apraxic patients in comparison
to healthy elderly.
As illustrated on the Figure 3, preliminary data
shows that in patients showing features of apraxia,
we observe a disrupted pattern of harmonicity of the
movement, when represented as phase plots. In
addition, a difference in the surface fitting will be
taken as a mean difference between the centralised
movement cycle and fitted circle. In the preliminary
data inspection other measures also revealed
differences between patients and age matched
controls, such as movement frequency, amplitude
and movement path ratio (x/y/z to xyz).
BIOSIGNALS2014-InternationalConferenceonBio-inspiredSystemsandSignalProcessing
298

Figure 3: An example of normalised phase planes showing
relation between the velocity of the movement against the
position on the main movement axis (respectively z, y, x)
from preliminary data analysis. Each row illustrates
performance in the pantomime mode on the tasks:
hammering, sawing and tooth brushing. Left panel depicts
movement organisation of the apraxic individual (CVA in
August 2012, 12 months prior to data collection). In the
right side panel, control data for age and sex matched
volunteer.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The work on this line of CogWatch project is in
progress and requires detailed analysis to identify
differences between selected CVA patients that
show apraxic behaviour and healthy elderly
performance. On the basis of the data collected in
this study, a new measure might emerge that will
feed into the development of the rehabilitation
approach for those patients. This parsimonious
approach to kinematic analysis might provide a
novel insight into understanding the kinematic
consequences of apraxia. The long term goal is to
use harmonicity of movement as the biomarker for
non-motor execution related disruptions in the
performance of ADL that require cyclical
movements. Authors are not aware of any kinematic
biomarkers specific to apraxia being identified in a
body of research. In this paper, we have argued that
using the harmonicity measure might allow one to
encapsulate many features of apraxic behaviour on
the spatiotemporal dimension such as: movement
amplitude, movement path, frequency of the
movement, speed and acceleration profiles. The
purpose of application of harmonicity measure in
CogWatch is to compare how different
interventions, based on supplementary sensory
information, influence motor behaviour in patients
with apraxia and monitor the progress of recovery.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was funded by the EU STREP Project
CogWatch (FP7-ICT- 288912). Authors would like
thank to the Klinikum Bogenhausen patients and
staff members for participation in the research and
student assistants: Johannes Pflüger, Andrea
Schlegel, Anna Voitl and Saskia Steinl for the help
with running the experimental sessions.
REFERENCES
Bickerton, W., Riddoch, J., Samson, D., Balani,A., Mistry,
B., & Humphreys, G., (2012). Systematic assessment
of apraxia and functional predictions from the
Birmingham Cognitive Screen, Journal of neurology,
neurosurgery & psychiatry with practical neurology,
83 (5), 513-52.
Bieńkiewicz, M., Goldenberg, G., Cogollor, J., Ferre, M.,
Hughes, C., Hermsdörfer, J. (2013).Use of Biological
Motion based Cues and Ecological Sounds in the
Neurorehabilitation of Apraxia. HEALTHINF 2013.
Bootsma, R., Fernandez, L., & Mottet, D. (2004). Behind
Fitts’ law: kinematic patterns in goal-directed
movements, International Journal of Human-
Computer Studies, 61 (6), 811-821.
Clark, M.A., Merians, A.S., Kothari, A., Poizner, H.,
Macauley, B., Rothi, L.J.G. and Heilman, K.M. (1994)
Spatial planning deficits in limb apraxia. Brain, 117:
1093–1106.
Cooper, R. P.; Schwartz, M.; Yule, P. & Shallice, T.
(2005). The simulation of action disorganisation in
complex activities of daily living. Cognitive
Neuropsychology 22 (8) 959-1004.
De Renzi, E., Faglioni, P., & Sorgato, P. (1982) Modality
specific and supramodal mechanisms of apraxia.
Fisk, J., & Goodale, M. A. (1998), The effects of
unilateral brain damage on visually guided reaching:
hemispheric differences in the nature of the
deficit. Experimental Brain Research,72, 425–35.
Goldenberg, G. (2003) Apraxia and beyond: life and work
of Hugo Liepmann. Cortex, 39(3): 509–524.
Goldenberg, G., Hermsdörfer, J., Glindemann, R., Rorden,
C., & Karnath, H. O. (2007). Pantomime of tool use
depends on integrity of left inferior frontal cortex.
Cerebral Cortex, 17, 2769-2776.
HAMMERING
SAWING
TOOTHBRUSHING
CVA_MALE (AGE 54) CONTROL_MALE (AGE 55)
HarmonicityoftheMovementasaMeasureofApraxicBehaviourinStrokeSurvivors
299

Goldenberg, G. and Hagmann, S. (1997) The meaning of
meaningless gestures: a study of visuo-imitative
apraxia. Neuropsychologia, 35(3): 333–341.
Goldenberg, G., & Hagmann, S. (1998) Therapy of
activities of daily living in patients with apraxia.
Neuropsychological Rehabilitation, 8(2), 123–41.
Goldenberg, G., Hermsdörfer, J., & Spatt, J. (1996).
Ideomotor apraxia and cerebral dominance for motor
control. Cognitive Brain Research, 3, 95-100.
Graessel, E., Viegas, R., Stemmer, R., Küchly, B.,
Kornhuber, J. & Donath, C., (2009). The Erlangen
Test of Activities of Daily Living: first results on
reliability and validity of a short performance test to
measure fundamental activities of daily living in
dementia patients. International Psychogeriatrics, 21,
103-112.
Haaland, K.Y., Harrington, D.L., (1994). Limb-
sequencing deficits after left but not right hemisphere
damage. Brain and Cognition, 24, 104-22.
Hanna-Pladdy, B., Heilman, K.M., & Foundas, A.L.
(2003) Ecological implications of ideomotor apraxia:
evidence from physical activities of daily living.
Neurology, 60, 487–490.
Hermsdörfer, J., Mai, N., Spatt, J., Marquardt, C.,
Veltkamp, R., & Goldenberg, G. (1996) Kinematic
analysis of movement imitation in apraxia, Brain, 119,
1575-1586.
Hermsdörfer, J., Ullrich, S., Marquardt, C., Goldenberg,
G., & Mai, N. (1999). Prehension with the ipsilesional
hand after unilateral brain damage. Cortex, 35, 139-
161.
Hermsdörfer, J., Blankenfeld, H., & Goldenberg, G.
(2003). The dependence of ipsilesional aiming deficits
on task demands, lesioned hemisphere, and apraxia.
Neuropsychologia, 41, 1628-1643.
Hermsdörfer, J., Hentze, S., & Goldenberg, G. (2006)
Spatial and kinematic features of apraxic movement
depend on the mode of execution. Neuropsychologia,
44, 1642–1652.
Hermsdörfer, J., Li, Y., Randerath, J., Roby-Brami, A., &
Goldenberg, G. (2012). Tool use kinematics across
different modes of execution. Implications for action
representation and apraxia. Cortex, in press.
Hermsdörfer, J., Bieńkiewicz, M., Cogollor, J., Russel,
M., Baptiste, E., Parekh, M., Wing, A., Ferre, M.,
Hughes, C., (2013). CogWatch - Automated
Assistance and Rehabilitation of Stroke-Induced
Action Disorders in the Home Environment. HCI (17):
343-350 .
Hughes, C., Baber, C., Bieńkiewicz, M., Hermsdörfer, J.
(2013). Application of Human Error Identification
(HEI) Techniques to Cognitive Rehabilitation in
Stroke Patients with Limb Apraxia. HCI (8) , 463-471.
Jason, G. W. (1983). Hemispheric asymmetries in motor
function: Left hemisphere specialization for memory
but not performance. Neuropsychologia, 21 (1), 35-45.
Laimgruber, K., Goldenberg, G., & Hermsdörfer, J. (2005)
Manual and hemispheric asymmetries in the execution
of actual and pantomimed prehension,
Neuropsychologia, 43(5), 682-692.
MATLAB and Statistics Toolbox Release 2012b, The
MathWorks, Inc., Natick, Massachusetts, United
States.
Petreska, B., Adriani, M., Blanke, O. & Billard,
A. (2007) Apraxia: a review. In C. von Hofsten (Ed.).
From Action to Cognition. Progress in Brain Research.
Elsevier. Amsterdam. Vol. 164, pp. 61-83.
Poizner, H., Clark, M.A., Merians, A.S., Macauley, B.,
Rothi, L.J.G. and Heilman, K.M. (1995) Joint
,coordination deficits in limb apraxia. Brain, 118: 227–
242.
Schwartz, M. F., Montgomery, M. W., Fitzpatrick-
desalme, E. J., Ochipa, C., Coslett, H. B., & Mayer, N.
H. (1995). Analysis of a disorder of everyday action.
Cognitive Neuropsychology, 12, 863-892.
Taubin, G. (1991). Estimation Of Planar Curves, Surfaces
And Nonplanar Space Curves Defined By Implicit
Equations, With Applications To Edge And Range
Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. PAMI, 13, 1115-
1138.
Tretriluxana, J., Gordon, J., Fisher, B. E., & Winstein, C.
J. (2009). Hemisphere specific impairments in reach-
to-grasp control after stroke: effects of object size.
Neurorehabilitation and Neural Repair, 23, 679-691.
Vanbellingen, T., Kersten, B., Van de Winckel, A.,
Bellion, M., et al. (2011). A new bedside test of
gestures in stroke: the apraxia screen of TULIA
(AST). Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and
Psychiatry 82(4), 389-92.
BIOSIGNALS2014-InternationalConferenceonBio-inspiredSystemsandSignalProcessing
300
