
The Possibilities of Filtering Pairs of SNPs in GWAS Studies
Exploratory Study on Public Protein-interaction and Pathway Data
Matej Lexa and Stanislav Stefanic
Faculty of Informatics, Masaryk University, Botanick
´
a 68a, 60200 Brno, Czech Republic
Keywords:
GWAS, SNPs, Biological Knowledge, Databases, Genotyping, Filtering
Abstract:
Genome-wide association studies have become a standard way of discovering novel causative alleles by look-
ing for statisticaly significant associations in patient genotyping data. The present challenge for these methods
is to discover associations involving multiple interacting loci, a common phenomenon in diseases often re-
lated to epistasis. The main problem is the exponential increase in necessary computational power for every
additional interacting locus considered in association tests. Several approaches have been proposed to manage
this problem, including limiting analysis to interacting pairs and filtering SNPs according to external biolog-
ical knowledge. Here we explore the possibilities of using public protein interaction data and pathway maps
to filter out only pairs of SNPs that are likely to interact, perhaps because of epistatic mechanisms working
at the protein level. After filtering all possible pairs of SNPs by their presence in common protein-protein
interactions or proteins sharing a metabolic or signalling pathway, we calculate the possible reduction in com-
putational requirements under different scenarios. We discuss these exploratory results in the context of the
so-called ”lost heredity” and the usefulness of this approach for similar scenarios.
1 INTRODUCTION
Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have be-
come a standard way of analysing genotyping data to
discover associations between single nucleotide poly-
morphisms or similar variants and phenotype, often
representing a diagnosis or disease status or progres-
sion (Witte, 2010). The common GWAS workflow in-
cludes organizing genotyping data into an (m +1)× n
matrix with m SNPs (columns) and n individuals with
a known phenotype in one of the columns. The
data is then analyzed for statistically significant as-
sociations between the phenotype and SNP columns.
Commonly, χ
2
-test with multiple testing correction
is used to discover informative SNPs (Mantel and
Haenzel, 1959) (Huh et al., 2011). To date, 1605
GWAS studies have been deposited in GWAS Central
at http://www.gwascentral.org, reporting P-values for
almost 3 million SNP markers for the studied pheno-
types (Thorisson et al., 2009). A total of 11751 risk
SNPs have been reported from these studies (P-values
below 5.10e
−8
) in 1738 publications, as reported by
the NCBI GWAS Catalog (Hindorff et al., 2009).
There is an ongoing debate among geneticists and
other scientists about ”lost heritability”. Since only
small part of phenotypic variation is explained by sin-
gle SNPs discovered using GWAS, people have been
looking for the lost heritability (Maher, 2008), partly
for intelectual reasons and partly because it is thought
to go hand-in-hand with disease risk (Manolio et al.,
2009). One school of thought argues that it is to be
discovered in interactions between loci or SNPs (van
Steen, 2011). Most of these interactions can be de-
scribed by the well-known genetic mechanism called
epistasis.
Several approaches have been proposed to deal
with epistasis and interacting SNPs. This includes
limiting the analysis to potentialy interacting pairs
that can be predicted from simpler calculations, such
as detecting single, interaction-free SNP-phenotype
associations first (Emily et al., 2009) or limiting the
analysis to local chromosomal regions (Slavin et al.,
2011). Even though multiple loci can form an in-
teraction network, most of its properties are proba-
bly already present in pairwise interactions (Liu et al.,
2012)(Hua et al., 2012). Another approach proposes
to filter the analysed SNP combinations only for those
that (based on our biological knowledge) have a high
enough chance to interact through epistasis (Bush
et al., 2009). Such external (to the study) biologi-
cal knowledge can regard gene regulation and regu-
latory networks, metabolic and signalling pathways,
259
Lexa M. and Stefanic S..
The Possibilities of Filtering Pairs of SNPs in GWAS Studies - Exploratory Study on Public Protein-interaction and Pathway Data.
DOI: 10.5220/0004915002590264
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms (BIOINFORMATICS-2014), pages 259-264
ISBN: 978-989-758-012-3
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

protein-protein interactions, temporal or spatial co-
expression of genes, common functional categories,
such as those defined by Gene Ontology, etc. (Bush
et al., 2009).
Here we explore further the possibilities of using
public protein interaction data and pathway maps to
filter out only pairs of SNPs that can interact because
of epistatic or other unknown mechanisms working at
the protein level. After filtering all possible pairs of
SNPs by their presence in common protein-protein in-
teraction or proteins sharing a metabolic or signalling
pathway, we calculate the reduction in computational
requirements under different scenarios. Apart from
filtering by biological knowledge, an approach used
by other authors, we suggest the use of graph decon-
volution techniques, as another way to further narrow
the set of possible epistatic pairs in the data to the
most likely causative variants (Feizi et al., 2013).
2 SOFTWARE AND METHODS
2.1 Collection of Data Representing
Biological Knowledge
Biological knowledge is represented in this paper by
a set of protein-centric databases commonly used in
molecular biology to obtain information on protein-
protein interactions (DIP (Salwinski et al., 2004) ,
MINT (Licata et al., 2012)), metabolic and signalling
pathways (Wikipathways (Kelder et al., 2012)) and
biological and molecular function (Gene Ontology).
Data were downloaded in bulk text format and incor-
porated into the analysis as needed and described be-
low.
2.1.1 Protein-protein Interactions
Three databases were used as a source of protein-
protein interaction data. DIP, the Database of
Interacting Proteins (Salwinski et al., 2004)
and two MINT databases from the Molecular
INTeraction database (Licata et al., 2012). We
downloaded human data in tab25 format from DIP
(tab35/Hsapi20130707.txt, July 7, 2013) and
human binary data and complexes in mitab format
(2013-03-26-mint-human-binary.mitab26.txt,
2013-03-26-mint-human-complexes.mitab26.txt).
We used AWK scripts for selecting relevant columns
present, converting each row of the data to an SQL in-
sert statements to populate our working database. In
this manner we created tables diphuman, mint binary
and mint complexes. Further operations with this
data are described in section (2.3).
2.1.2 Metabolic and Signalling Pathways
Data for the presence of proteins and their in-
teraction in common metabolic and signalling
pathways was obtained from Wikipathways at
wikipathways.org (Kelder et al., 2012). The
human pathway data is available in the file
wikipathways data Homo sapiens.tab. Similar-
ily to the interaction data, the file was processed with
AWK scripts to generate apropriate SQL commands
for populating our database with pathway member-
ship data. After downloading wikipathway file, 13
columns were used... The next operations are de-
scribed in section (2.3).
2.2 Mapping SNP IDs to Protein IDs
To allow selection of SNP pairs (or general k-tuples
for k > 2) based on protein biological knowledge
we only considered SNPs located within coding se-
quences (this could be expanded to include poten-
tial regulatory sequences such as promoters or regula-
tory elements in introns or known trans-regulatory el-
ements further away from the respective gene). These
SNPs were then assigned to proteins coded by the se-
quence they reside in. This gives us a direct mapping
between SNP IDs (such as rs2251969, rs952094,
rs75931146, rs78394850), RefSeq gene IDs (such
as NM 003126 and protein IDs (such as Uniprot
P02549, HGNC SPTA1, RefSeq protein NP 003117 or
DIP 1020N).
Specifically, we found RefSeq gene IDs for each
protein occuring in interactions or pathways and cre-
ated a table that mapped each protein ID to a Ref-
Seq Gene ID. We used UCSC Genome Table Browser
to download SNP IDs and RefSeq coding sequence
IDs in BED format. We used BedTools ((Quinlan and
Hall, 2010)) an their region intersection and merging
capabilities to obtain clean mapping data and included
it in our mysql database.
2.3 Detecting and Counting Biologically
Relevant SNP Pairs
We used mysql operations for organizing all
data about interactions into a single table
(human interaction) where all three types of in-
teractions were included. The resulting table consists
of five columns which are ID - our internal un-
ambiguous id of interaction, Protein A - the first
interacting element participating in the interaction,
Protein B - the second interacting element, int db
- name of one of the three downloaded databases,
where interactions are described and id in db - native
BIOINFORMATICS2014-InternationalConferenceonBioinformaticsModels,MethodsandAlgorithms
260

id of the interaction in the original database named
in the previous column. This cross-reference is kept
for possible future use and was not used in this
analysis. Considering we used three different types
of data where interactions are described and each
type uses different types of protein IDs, we had to
create unambiguous ID for every protein and use this
ID in the final human interaction table in columns
Protein A and Protein B. An auxilliary table of
all proteins used in the study (human protein) was
created, where we assigned a unique ID to each
protein occuring in interactions in one of the three
tables. Duplicates occurring because of multiple
RefSeq transcripts covering the same genomic region
were eliminated usingthe UNION SQL operation
in conjunction with unique(). Finally, we used the
human protein table to merge tables diphuman,
mint binary and mint complexes into the final table
(human interaction), where all interactions are
preserved and duplicates are eliminated.
Using the data in this table, we created a table
named snp interaction which contained all interact-
ing SNP pairs that could be created from their map-
ping to two interacting proteins. This was accom-
plished with table snp2hgnc containing the mappings
between SNPs and genes in which they occur. Be-
cause the snp2hgnc table contained RefSeq gene IDs,
we had to add RefSeq IDs to the human protein
table using a web identificator translation service
from EBI. These mappings (SNP to RefSeq ID)
were then recalculated into mappings from SNPs to
each protein occuring in the human interaction table.
The snp interaction table contains the following at-
tributes: ID, SNP A and SNP B (both in the form of
dbSNP rs * IDs). This table therefore contains all po-
tentially interacting SNP pairs (based on the relevant
biological knowledge) and can be counted or read as
needed. In this paper we report some of the counts
and other relevant numbers useful in estimating the
complexity of GWAS after using the pairs for filter-
ing of SNPs or SNP pairs.
The overall relationships in this kind of data is il-
lustrated in Figure 1, showing the source of biological
knowledge and how it allows us to focus on a subset
of available SNP pairs.
2.4 Evaluation Procedures
To arrive at the main result in this study, the propor-
tion of SNP pairs that can be filtered out by consider-
ing biological knowledge, we calculated the number
of SNP pairs that can be created from the dataset as
snp × (snp − 1)/2. We also counted the number of
unique SNP pairs that fall onto proteins involved in
protein-protein interaction or that are members of a
common pathway. The percentage of the latter against
the former gave us a numerical value for the reduction
as reported in Table 1.
3 RESULTS
We collected information on two different kinds of in-
teractions between proteins in biological systems (di-
rect physical interaction and participation in a com-
mon pathway). In the context of genome-wide associ-
ation studies (GWAS) considering SNP pairs with ge-
netic or statistical interaction, we calculated the possi-
ble computational savings in stepping down from all
possible SNP pairs to only those that are supported
by some kind of biological knowledge. Only protein-
protein interaction (PPI) and pathway membership
were considered.
SNPs were evaluated in two scenarios, one using
all known human reference SNPs present in the db-
SNP 138 database (232,952,851 million altogether)
(Sherry et al., 2001), while the other only evaluated
common SNPs (as defined by the relevant UCSC Ta-
ble Browser Repeat and Variation table)(Karolchik
et al., 2004). 62,676,337 common SNPs are available
in the dbSNP 138 database (minor allele frequency of
common SNPs is > 1%). After selecting only those
SNPs that mapped to a RefSeq coding sequence in the
human genome, and removing duplicates, we counted
97,332 common SNPs and 1,590,290 general SNPs in
genes (Table 1).
3.1 Search Space Reduction After
Incorporating Biological Knowledge
3.1.1 Protein-protein Interactions
Protein-protein interactions provide many possibili-
ties for epistatic effects. Protein complexes may de-
pend on residue interactions that can sometimes ac-
cept compensatory mutations. The increased expres-
sion of one protein in a protein complex can lead to
various signals leading to increased expression of its
partners.
We counted 9419 interactions among 3033 pro-
teins in the protein-protein interaction dataset and
901659 interactions among 6513 proteins in the path-
way dataset. Each gene (coding sequences only) was
covered on average by 5.24 and 65 SNPs respectively
(Table 1). Using PPI data from DIP and MINT and
common SNPs, we were able to reduce the number
of SNP pairs to be analysed in a GWAS study only to
ThePossibilitiesofFilteringPairsofSNPsinGWASStudies-ExploratoryStudyonPublicProtein-interactionand
PathwayData
261
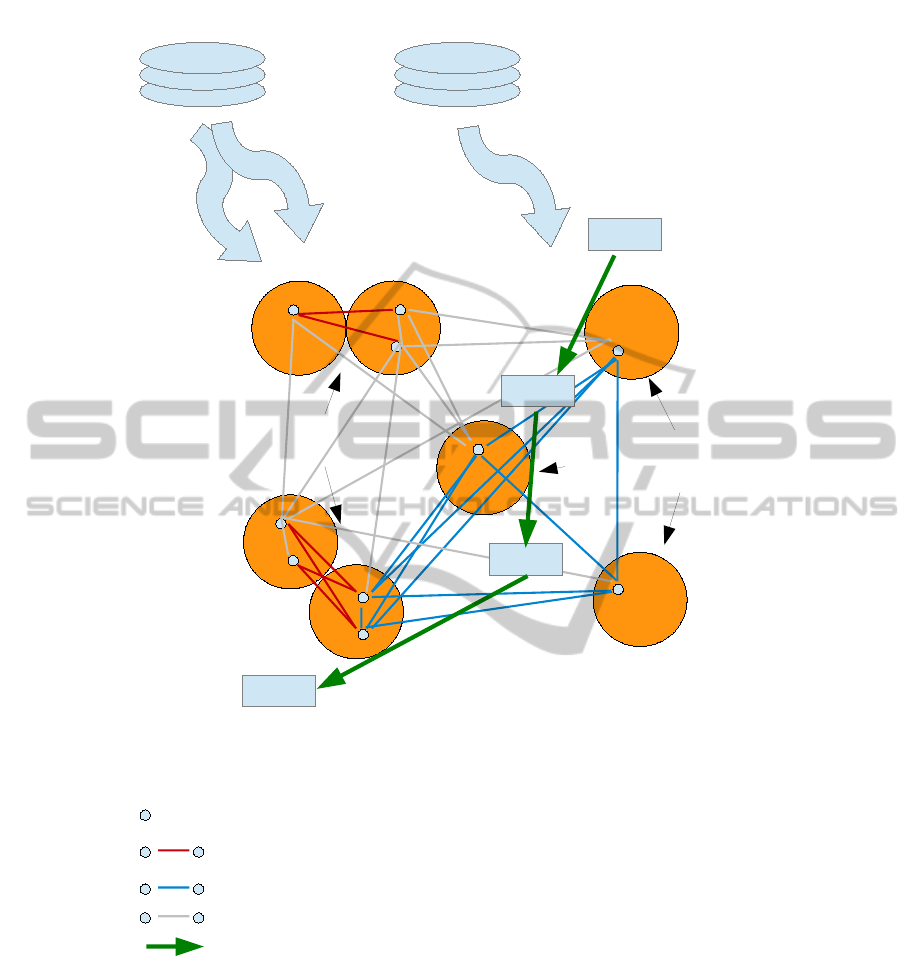
DIP, MINT Wikipathways
Interacting proteins
Pathway members
SNPs
Candidate SNP interaction (PPI-derived)
Candidate SNP interaction (pathway-derived)
SNP pairs to be filtered
Metabolic or signalling pathway
Figure 1: Relationship between different entities and types of data considered in this study. The red and green lines show
the small number of informative candidates for SNP interaction after filtration by biological knowledge from external sources
(top). Grey lines represent pairs of SNPs that will not be analyzed in a downstream GWAS analysis. To reduce clutter some
grey lines were intentionally omitted.
0.56% of the maximal possible number of pairs. Sim-
ilar reduction after filtering was obtained when con-
sidering all known SNPs.
3.1.2 Metabolic and Signalling Pathways
Pathways provide similar type of knowledge as
protein-protein interaction, but tend to form larger
network of genes/proteins. 6513 unique genes were
mapped to pathways. Their grouping was such as to
form 16622 pairwise interactions. For the purpose
of this study, any pair of proteins participating in the
same metablic pathway were deemed to potentially
interact. In a more realistic scenario, we could only
consider pairs of proteins that directly share a metabo-
lite or otherwise interact in the pathway.
BIOINFORMATICS2014-InternationalConferenceonBioinformaticsModels,MethodsandAlgorithms
262

Table 1: Numerical results of counting the processed interaction and pathway data at various stages and from different aspects.
Two sets of SNPs from dbSNP, ”SNP Common” (present in at least 1% of the population) and ”SNP All” were used in the
study. The last three columns show the filtration effect in terms of % remaining SNP pairs after the procedure. Fields marked
with asterisk (*) were prohibitively expensive to calculate and were only estimated from SNP Common data.
SNP set
Biol.knowledge
Ref gene
SNPs in set
SNP/gene
Genes in int.
SNPs in int.
SNP/int.gene
SNP pairs [mil]
Filtered [mil]
% reduction
Common
PPI 18565 97332 5.24 3033 12149 4.005 73.8 0.42 0.56
Path 18565 97332 5.24 6513 16622 2.55 138.1 7.30 5.28
All
PPI 24502 1590290 65 3033 261349 86.2 34152 133.7 0.39
Path 24502 1590290 65 6513 357572
*
54.9
*
63929
*
2344.4
*
3.67
*
Because of the bigger size of pathway maps than
the PPI network (6513/901659 v. 3033/9419 in terms
of the number of genes/gene interactions), the filtra-
tion using this criterion is bound to be less effective
and produce a higher number of potentially interact-
ing SNPs. Using pathway membership data from
Wikipathways, we were able to reduce the number of
SNP pairs to be analysed in a GWAS study only to
5.28% of the maximal possible number of pairs.
3.2 Incorporating Detected Pairs into
GWAS Workflows
While the database format was convenient for study
purposes, and while the resulting database can be eas-
ily queried for SNPs that are candidates for interac-
tion in GWAS studies, routine use of such calcula-
tions would probably benefit from a custom-coded so-
lution, with dedicated data structures created to store
marker pairs or triples, perhaps as a library that could
be linked to a GWAS analysis program.
4 DISCUSSION
We have shown that using biological knowledge from
commonly accessible biological databases can help to
identify a small subset of all possible SNP pairs, thus
reducing the computational requirements of a GWAS
analysis aiming to study marker interactions and their
association with some phenotype. While identify-
ing interacting or otherwise related proteins in pairs
helped to reduce the number of pairs to evaluate to
0.4-5% of their original unfiltered number, the effect
would be even more pronounced in case of triples
or quadruples. Filtration by biological knowledge is
definitely a viable option to prioritize SNPs prior to
analysis, as oposed to other methods prioritizing after
analysis.
It should be noted that we have not made any pro-
visions for separating SNPs that represent synony-
mous and non-synonymous mutations. Such analysis
or selection could lower the number of relevant SNPs,
resulting in further reduction in number of pairs that
must be evaluated.
It is now commonly accepted that epistasis should
be behind a significant portion of the so-called ”lost
heritability”. Many recent works, including this pa-
per, regard methods of detecting multiple interacting
SNPs in whole-genome studies and processing them
in an efficient manner. Because of the computational
complexity of evaluating k-tuples of SNPs for k >> 1,
it would be desireable to work with k as small as pos-
sible, but still be able to discover effects of larger net-
works of interacting SNPs. Liu et al. suggest such
networks could be reconstructed from detected SNP-
SNP interactions (Liu et al., 2012). However, the pair-
wise interactions could be plagued by ”phantom” in-
teractions caused by detecting indirect relationships
caused by the transitivity of interactions. Recently,
a solution to separating direct and indirect interac-
tions in networks occuring in other disciplines has
been proposed (Feizi et al., 2013). We suggest that
SNP interaction networks be reconstructed from pair-
wise data, as carried out by Liu et al.(2012) only after
the pairwise data is network-deconvoluted, resulting
in higher quality SNP networks showing only direct
interactions as edges.
ThePossibilitiesofFilteringPairsofSNPsinGWASStudies-ExploratoryStudyonPublicProtein-interactionand
PathwayData
263

5 CONCLUSIONS
In this study we explore ways to select appropriate
candidate SNP-SNP pairs for GWAS studies (for ana-
lyzing interacting SNPs), based on biological knowl-
edge. We also calculate the reduction in computa-
tional complexity that can be obtained after such pre-
filtering step. As can be seen on the contrasting ex-
amples of direct PPI and pathway membership data,
the reduction achieved by filtering is less significant
for pathway data with a wider pathway membership
compared to the more restrictive pairwise interaction.
The difference in this specific example is 10-fold. The
filtering would be even more selective in the case of
SNP triples or quadruples. This computational exer-
cise is discussed in the context of the problem of so-
called ”lost heredity” and the need to analyze possible
interactions between SNPs and their association with
certain phenotypes in GWAS analysis.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Financial support provided by the EU 7th Frame-
work Project ”THALAssaemia MOdular Stratifi-
cation System for Personalized Therapy THALA-
MOSS” (FP7-HEALTH-2012-INNOVATION-1 Col-
laborative Project; http://thalamoss.eu/index.html).
REFERENCES
Bush, W., Dudek, S., and Ritchie, M. (2009). Biofilter:
a knowledge-integration system for the multi-locus
analysis of genome-wide association studies. In Pa-
cific Symposium on Biocomputing, volume 14, pages
368–379.
Emily, M., Mailund, T., Hein, J., Schauser, L., and
Schierup, M. (2009). Using biological networks to
search for interacting loci in genome-wide association
studies. Eur J Hum Genet, 17:1231–1240.
Feizi, S., Marbach, D., Mdard, M., and Kellis, M. (2013).
Network deconvolution as a general method to dis-
tinguish direct dependencies in networks. Nature
Biotechnology, 31:726–733.
Hindorff, L., Sethupathy, P., Junkins, H., Ramos, E., Mehta,
J., Collins, F., and Manolio, T. (2009). Potential etio-
logic and functional implications of genome-wide as-
sociation loci for human diseases and traits. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA, (May 27).
Hua, L., Lin, H., Li, D., Li, L., and Liu, Z. (2012). Min-
ing functional gene modules linked with rheumatoid
arthritis using a snp-snp network. Genomics, Pro-
teomics & Bioinformatics, 10(1):23–34.
Huh, I.-S., Sohee-Oh, and Park, T. (2011). A chi-square
test for detecting multiple joint genetic variants in
genome-wide association studies. In IEEE Interna-
tional Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine
Workshop, pages 708–713.
Karolchik, D., Hinrichs, A., Furey, T., Roskin, K., Sugnet,
C., Haussler, D., and Kent, W. (2004). The ucsc ta-
ble browser data retrieval tool. Nucleic Acids Res.,
32:D493–D496.
Kelder, T., Van Iersel, M., Hanspers, K., Kutmon, M., Con-
klin, B., Evelo, C., and Pico, A. (2012). Wikipath-
ways: building research communities on biological
pathways. Nucleic Acids Res., 40:D1301–D1307.
Licata, L., Briganti, L., Peluso, D., Perfetto, L., Iannuccelli,
M., Galeota, E., Sacco, F., Palma, A., Nardozza, A.,
Santonico, E., Castagnoli, L., and Cesareni, G. (2012).
Mint, the molecular interaction database: 2012 up-
date. Nucleic Acids Res., 40:D857D861.
Liu, Y., Zhou, J., Liu, Z., Chen, L., and Ng, M. (2012). Con-
struction and analysis of genome-wide snp networks.
In IEEE 6th International Conference on Systems Bi-
ology (ISB).
Maher, B. (2008). Personal genomes: The case of the miss-
ing heritability. Nature, 456:18–21.
Manolio, T., Collins, F., and Cox, N. e. a. (2009). Finding
the missing heritability of complex diseases. Nature,
461(7265):747–753.
Mantel, N. and Haenzel, W. (1959). Statistical aspect of the
analysis of data from retrospective studies of disease.
J.Natl.Cancer Inst, 22:719–748.
Quinlan, A. and Hall, I. (2010). Bedtools: a flexible suite
of utilities for comparing genomic features. Bioinfor-
matics, 26(6):841–842.
Salwinski, L., Miller, C., Smith, A., Pettit, F., Bowie, J.,
and Eisenberg, D. (2004). The database of interact-
ing proteins: 2004 update. Nucleic Acids Research,
32(90001):D449–D451.
Sherry, S., Ward, M., Kholodov, M., Baker, J., Phan, L.,
Smigielski, E., and Sirotkin, K. (2001). dbsnp: the
ncbi database of genetic variation. Nucleic Acids Res.,
29(1):308–311.
Slavin, T., Feng, T., Schnell, A., Zhu, X., and Elston, R.
(2011). Two-marker association tests yield new dis-
ease associations for coronary artery disease and hy-
pertension. Hum Genet, 130:725–733.
Thorisson, G., Lancaster, O., Free, R., Hastings, R.,
Sarmah, P., Dash, D., Brahmachari, S., and Brookes,
A. (2009). Hgvbaseg2p: a central genetic association
database. Nucleic Acids Research, 37:D797–802.
van Steen, K. (2011). Traveling the world of gene-gene
interactions. Briefings in Bioinformatics, 13(1):1–19.
Witte, J. (2010). Genome-wide association studies and be-
yond. Annu. Rev. Public Health, 31:9–20.
BIOINFORMATICS2014-InternationalConferenceonBioinformaticsModels,MethodsandAlgorithms
264
