
Development of Concurrent Object-oriented Logic Programming
System to Intelligent Monitoring of Anomalous Human Activities
Alexei A. Morozov
1,4
, Abhishek Vaish
2
, Alexander F. Polupanov
1,4
, Vyacheslav E. Antciperov
1
,
Igor I. Lychkov
3
, Aleksandr N. Alfimtsev
3
and Vladimir V. Deviatkov
3
1
Kotel’nikov Institute of Radio Engineering and Electronics of RAS, Mokhovaya 11, Moscow, Russia
2
Indian Institute of Information Technology, Deoghat, Jhalwa, Allahabad, UP, India
3
Bauman Moscow State Technical University, Vtoraya Baumanskaya 5, Moscow, Russia
4
Moscow State University of Psychology & Education, Sretenka 29, Moscow, Russia
Keywords: Anomalous Human Activity, Intelligent Visual Surveillance, Logic Programming, Actor Prolog.
Abstract: A logic programming approach to the intelligent monitoring of anomalous human activity is considered.
The main idea of this approach is in using of a first order logic for describing abstract concepts of
anomalous human activity, i.e. brawls, sudden attack, armed attack, leaving object, loitering, pickpocketing,
personal theft, immobile person, etc. We use the Actor Prolog concurrent object-oriented logic language and
a state-of-the-art Prolog-to-Java translator for efficient implementation of logical inference on video scenes.
A logical rules generation methodology is considered in relation to the analysis of anomalous human
behaviour. The problem of creation of special built-in classes of Actor Prolog for the low-level video
processing is discussed.
1 INTRODUCTION
Human activity recognition is a rapidly growing
research area with important application domains
including security and anti-terrorist issues
(Aggarwal, 2011; Junior, 2010; Kim, 2010).
Recently logic programming was recognised as a
promising approach for dynamic visual scenes
analysis (Filippou, 2012; Shet, 2011; O'Hara, 2008;
Machot, 2011). The idea of a logic programming
approach is in usage of logical rules for description
and analysis of people activities. To approach the
problem, knowledge about object co-ordinates and
properties, scene geometry, and human body
constraints is encoded in the form of certain rules in
a logic programming language and is applied to the
output of low-level object / feature detectors. There
are several studies based on this idea. In (Filippou,
2012) a system was designed for recognition of so-
called long-term activities (such as fighting and
meeting) as temporal combinations of short-term
activities (walking, running, inactive, etc.) using a
logic programming implementation of the Event
Calculus. The ProbLog state-of-the-art probabilistic
logic programming language was used to handle the
uncertainty that occurs in human activity
recognition. An obvious merit of this approach is a
high level of abstraction in describing human
activity, but it may be too slow for the real time
video processing. Mathematical semantics of
probabilistic logical inference is also questionable.
In (Shet, 2011) an extension of predicate logic with
the bilattice formalism that permits processing of
uncertainty in the reasoning was proposed. The
VidMAP visual surveillance system that combines
real time computer vision algorithms with the Prolog
based logic programming had been announced by
the same team. S. O'Hara (O'Hara, 2008)
communicated the VERSA general-purpose
framework for defining and recognising events in
live or recorded surveillance video streams.
According to (O'Hara, 2008), VERSA provides
more advanced spatial and temporal reasoning than
VidMAP and is based on SWI-Prolog. F.A. Machot
et al. (Machot, 2011) have proposed real time
complex audio-video event detection based on
Answer Set Programming approach. The results
indicate that this solution is robust and can easily be
run on a chip.
Conventional approaches to human behaviour
recognition include low-level and high-level ones. In
this paper, we address the problem of the high-level
53
A. Morozov A., Vaish A., F. Polupanov A., E. Antciperov V., I. Lychkov I., N. Alfimtsev A. and Deviatkov V..
Development of Concurrent Object-oriented Logic Programming System to Intelligent Monitoring of Anomalous Human Activities.
DOI: 10.5220/0004929400530062
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Biomedical Electronics and Devices (BIODEVICES-2014), pages 53-62
ISBN: 978-989-758-013-0
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

semantic analysis of people activity. We use the
Actor Prolog concurrent object-oriented logic
programming language (Morozov, 1999, 2002,
2003, 2007, 2012) for implementation of the logical
inference on video scenes. The Actor Prolog system
includes a Prolog-to-Java translator that provides
means for a high-level concurrent programming and
a direct access to the low-level processing
procedures written in Java.
In the case of simple human behaviour, a set of
logic program rules can be created manually on the
basis of a priori knowledge of the particular
behaviour features, for example, speed of moving. In
the case of complex spatio-temporal behaviour, a
special methodology of generation of the logical
rules is necessary.
We have described our first experiments in the
area of human activity recognition in Section 2. The
problem of creation of special built-in classes of the
Actor Prolog logic language for the low-level video
processing is discussed in Section 3. A methodology
of logical rules generation based on a hierarchy of
fuzzy finite state automata is briefly considered in
Section 4.
2 LOGICAL ANALYSIS OF
MANUALLY MARKED VIDEOS
On the first stage of the research, we have performed
several experiments on analysis of manually marked
videos that is traditional approach in the area. The
CAVIAR data sets (Fisher, 2007) were used. The
CAVIAR data sets are annotated using the XML-
based Computer Vision Markup Language (CVML).
The structure of CVML is simple enough, so we
read it using the 'WebReceptor' built-in class of the
Actor Prolog for XML / HTML parsing. The CVML
annotations contain information about co-ordinates
of separate persons and groups of persons in videos.
So, our experiments have pursued the following
goals:
1. To check whether the Actor Prolog system is
fast enough to process videos in real time even
without performing low-level analysis.
2. To check whether there is enough information
about the positions of persons for accurate
estimation of the velocity and the acceleration
of separate personages in the video scene.
The latter issue is important because the
accurate estimation of the velocity / acceleration
opens a way for the recognition of so-called abrupt
motions of objects (Filippou, 2012). This kind of
motions is necessary for recognition of several long-
term activities (such as fighting or sudden attack),
though recognition of abrupt motions is not usually
provided by standard low-level analysing
procedures. The abrupt motions are not marked in
the CAVIAR annotations as well.
An example of abrupt motion recognition is
shown on the figure 1. A program written in Actor
Prolog uses given co-ordinates of two persons to
estimate the distance between them and the 2-nd
derivative of the co-ordinates to detect abrupt
motions of the persons.
Figure 1: An example of CAVIAR video with a case of
abrupt motions.
A logical rule describes an abnormal behaviour
(fighting) as a conjunction of two conditions:
1. Several persons have met sometime and
somewhere.
2. After that they implement abrupt motions.
The text of the logic program is not given here
for brevity. After recognition of these two
conditions, the logic programming system has
decided that there was a case of scuffle and has
indicated the fighting persons by a red rectangle (see
figure 2).
Figure 2: The logic programming system has recognised
that two persons formed a group and were fighting.
This example demonstrates a possibility of
recognition of video scenes semantics using the
BIODEVICES2014-InternationalConferenceonBiomedicalElectronicsandDevices
54

logical inference on results of the low-level
recognition of separate objects; however one can see
the following bottle-neck of the approach. Manually
defined co-ordinates of the objects were used for
estimation of their acceleration and nobody can
guarantee that automatic low-level procedures will
provide exact values of co-ordinates that are good
enough for numerical differentiation. So, the
discussion on the high-level recognition procedures
is impossible without consideration of underlying
low-level recognition methods.
The second issue of this example is whether it is
useful to separate the recognition process into
concurrent sub-processes implementing different
stages of the high-level logical inference. Working
intensity of different sub-processes is various. For
example, the differentiation of co-ordinates requires
more computational resources and another sub-
process that implements recognition of people
behaviour could wait for the results of
differentiation.
3 ADVANCED LOGIC ANALYSIS
OF VIDEO SCENES
On the next stage of the research, we have
implemented experiments on video analysis based
on the automatically extracted information about co-
ordinates and velocity of blobs in video scenes.
3.1 Implementation of Base Low-level
Video Processing Procedures
A promising approach for implementation of the
low-level recognition procedures in a logic language
is usage of the OpenCV computer vision library and
we are planning to link Actor Prolog with the
JavaCV library that is a Java interface to OpenCV.
Nevertheless, Java has enough standard tools to
solve simple image processing / recognition
problems and we have started our experiments with
pure Java.
We have created low-level Java procedures that
implement several basic recognition tasks:
1. Background subtraction;
2. Discrimination of foreground blobs;
3. Tracking of the foreground blobs over time;
4. Detection of interactions between the blobs.
The first experiments have demonstrated clearly
that the exact estimation of an object velocity was
impossible without taking into account the
interactions of objects (see figure 3), because of
edge effects of differentiation in the interaction
points.
Figure 3: A low-level procedure discriminates trajectories
(violet lines) of objects and moments of their interactions
(green circle marks and blue links).
After implementation of the object interactions
check, we have got tracks that were accurate enough
to determine whether a person is walking or running.
In the next section, we will describe an approach to
lower boundary estimation of blob velocity and
discuss its possible application to the detection of
anomalous behaviour of people.
3.2 A Fast Algorithm for Estimation of
Object Velocity
At this stage of research, we use standard method of
recovering physical co-ordinates of objects in a
scene, based on computing inverse matrix of
projective transformation by co-ordinates of 4
defining points. A well-known disadvantage of this
method is so-called ground plane assumption, that is,
one cannot compute co-ordinates of body parts that
are situated outside from a pre-defined plane.
Usually, this pre-defined plane is a ground one and
we can estimate properly the co-ordinates of person's
shoes only. Generally speaking, this problem cannot
be avoided in the framework of single camera
approach, nevertheless, our idea is in usage of object
velocity (but not co-ordinates) for the anomalous
behaviour detection and this point is exploited in the
following algorithm.
We consider simplified rectangle blobs
describing moving objects in the scene (see example
on figure 5). Co-ordinates of every corner of the
blob are recovered using the inverse matrix of the
projective transformation. Then, one compares the
co-ordinates of corresponding corners of the blob in
consecutive frames and calculates the first derivative
of their co-ordinates. The idea is that only the
corners situated in the ground plane give realistic
estimations of velocity and other corners give
DevelopmentofConcurrentObject-orientedLogicProgrammingSystemtoIntelligentMonitoringofAnomalousHuman
Activities
55
greater values, because upper parts of body visually
correspond to more distant points in the ground
plane. So, we exploit this property of projective
transformation and accept the lower boundary
estimation of object velocity as a minimal value of
velocities (V
11
, V
12
, V
21
, V
22
) of four blob corners:
V ≈ min(abs(V
11
),abs(V
12
),abs(V
21
),abs(V
22
))
Note, that the algorithm does not recover the
direction of blob movement. The precision of the
estimation of the blob velocity is not very high too,
because of the approximate nature of the algorithm.
Moreover, the automatic detection of blob shapes
often produce illegal co-ordinates of blob corners
because of common problems with shades,
obstacles, digital noise etc, and this issue is an
additional source of errors in the velocity estimation.
We have applied a median filtering to eliminate
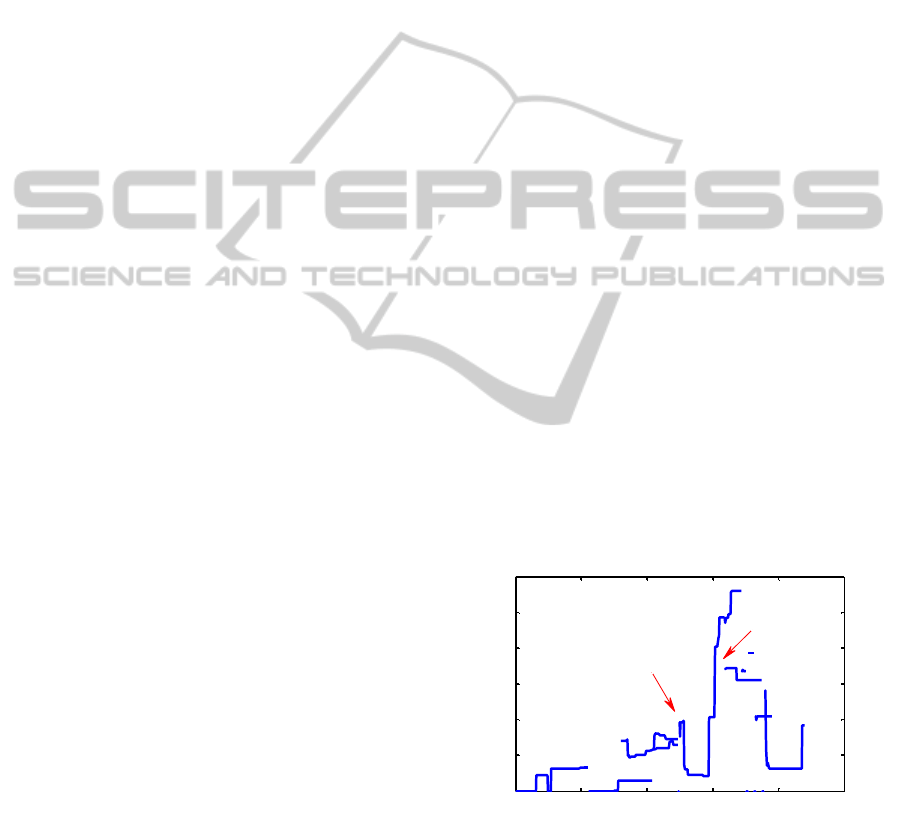
outliers in the velocity function. For instance, in the
example on figure 4, the 11 point median filter
provides an estimation of blob velocity that is good
enough for discrimination of running and walking
persons in the scene.
We have implemented this algorithm of velocity
estimation in the library of low-level methods of
image analysis of the Actor Prolog system and use it
in our experiments.
3.3 Creation of a Built-in Class of
Actor Prolog
We have developed a special built-in class of the
Actor Prolog language that uses formerly described
low-level recognition procedures. The
'ImageSubtractor' class of Actor Prolog implements
the following facilities:
1. Video frames pre-processing including 2D-
gaussian filtering, 2D-median filtering, and
background subtraction.
2. Recognition of moving blobs and creation of
Prolog data structures describing the co-
ordinates of the blobs in every moment.
3. Recognition of tracks of blob motions and
creation of Prolog data structures describing the
co-ordinates and the velocity of the blobs. The
tracks are divided into separate segments; where
segment ends there are points of interaction
between the blobs.
4. Recognition and ejection of immovable and
slowly moving objects. This feature is based on
simple fuzzy inference on the attributes of the
tracks (the co-ordinates of the tracks and the
average velocities of the blobs are considered).
5. Recognition of connected graphs of linked
tracks of blob motions and creation of Prolog
data structures describing the co-ordinates and
the velocity of the blobs.
We consider two tracks as linked ones if there
are interactions between the blobs of these tracks. In
some applications, it is useful to eject tracks of
immovable and slowly moving objects from the
graphs before further processing of the video scenes.
3.4 An Example of Anomalous
Behaviour Detection
Let us consider an example of logical inference on
video. The input of the logic program written in
Actor Prolog is the Fight_RunAway1 sample
provided by the CAVIAR team (the sequence of
JPEG files is used). The program will use no
additional information about the content of the video
scene, but only co-ordinates of 4 defining points in
the ground plane (the points are provided by
CAVIAR). The total text of the logic program is not
given here for brevity; we will discuss only the
program structure and main stages of data analysis.
The logic program creates two concurrent
processes with different priorities (see Morozov,
2003 for details about Actor Prolog model of
asynchronous concurrent computations). The first
process has higher priority and implements video
data gathering. This process reads JPEG files and
sends them to the instance of the 'ImageSubtractor'
predefined class that implements all low-level
processing of video frames. The sampling rate of the
video is 25 frames per second, so the process loads a
new JPEG file every 40 milliseconds.
0 5 10 15 20 25
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
Time [sec]
Velocity [m/sec]
Beginning of
the attack
Separation of
trajectories
Figure 4: An example of estimation of velocities of blobs
in a visual scene (see figure 3). The X-axis denotes time in
seconds and the Y-axis denotes lower boundary estimation
of blob velocities (m/sec). One can recognise walking
persons (before the beginning of the attack) and running
persons (after the separation of the trajectories of persons)
on the diagram.
BIODEVICES2014-InternationalConferenceonBiomedicalElectronicsandDevices
56

The second concurrent process implements logical
analysis of collected information and outputs results
of the analysis. The analysis of video frames
requires more computational resources, but it does
not suspend the low-level analysis, because the
second process has less priority. The analysis
includes extraction of blobs, tracking of the blobs
over time, detection of interactions between the
blobs, creation of connected graphs of linked tracks
of blobs, and estimation of average velocity of blobs
in separate segments of tracks (see figure 4). This
information is received by the logic program in a
form of Prolog terms describing the list of connected
graphs.
The 'ImageSubtractor' class uses the following
data structures for describing connected graphs of
tracks (note, that the DOMAINS, the
PREDICATES, and the CLAUSES program
sections in Actor Prolog have traditional meaning
developed in the Turbo / PDC Prolog systems):
DOMAINS:
ConnectedGraph = GraphEdge*.
GraphEdge = {
frame1: INTEGER,
x1: INTEGER,
y1: INTEGER,
frame2: INTEGER,
x2: INTEGER,
y2: INTEGER,
inputs: EdgeNumbers,
outputs: EdgeNumbers,
identifier: INTEGER,
coordinates: TrackOfBlob,
mean_velocity: REAL
}.
EdgeNumbers = EdgeNumber*.
EdgeNumber = INTEGER.
TrackOfBlob = BlobCoordinates*.
BlobCoordinates = {
frame: FrameNumber,
x: INTEGER,
y: INTEGER,
width: INTEGER,
height: INTEGER,
velocity: REAL
}.
That is, connected graph is a list of
underdetermined sets (Morozov, 1999) denoting
separate edges of the graph. Every edge is directed
and has the following attributes: numbers of front
and last frames (frame1, frame2), co-ordinates of
front and last points (x1, y1, x2, y2), a list of edge
numbers that are predecessors of the edge
(inputs), a list of edge numbers that are followers
of the edge (outputs), the identifier of
corresponding blob (an integer identifier), a
list of sets describing the co-ordinates and the
velocity of the blob in different moments of time
(coordinates), and an average velocity of the
blob in this edge of the graph (mean_velocity).
Figure 5: A logical inference has found a possible case of
sudden attack in the graph of blob trajectories. Rectangle
blobs are depicted by yellow lines, blob trajectories are
depicted by red lined, moments of interactions between
blobs are depicted by green circles and blue links.
The logic program checks the graph of tracks and
looks for the following pattern of interaction among
several persons: if two or more persons met
somewhere in the scene, and one of them has walked
(not run) before this meeting, and one of them has
run (not walked) after this meeting, the program
considers this scenario as a kind of a lam and a
probably case of a sudden attack or a theft. So, the
program alarms if this kind of sub-graph is detected
in the total graph of tracks. In this case, the program
draws all tracks of the graph under consideration in
red and outputs the "Attention!" warning in the
middle of the screen (see figure 5).
One can describe formally the concept of a lam
using defined connected graph data type.
PREDICATES:
is_a_lam(
ConnectedGraph,
ConnectedGraph,
ConnectedGraphEdge,
ConnectedGraphEdge,
ConnectedGraphEdge)
- (i,i,o,o,o);
We will define the is_a_lam (G, G, P1, E, P2)
predicate with the following arguments: G – a graph
to be analysed (the same data structure is used in the
DevelopmentofConcurrentObject-orientedLogicProgrammingSystemtoIntelligentMonitoringofAnomalousHuman
Activities
57

first and the second arguments), E – an edge of the
graph corresponding to probable incident, P1 – an
edge of the graph that is a predecessor of E, P2 – an
edge that is a follower of E. Note that G is an input
argument of the predicate and P1, E, and P2 are
output ones. Here is Actor Prolog program code with
brief explanations:
CLAUSES:
is_a_lam([E|_],G,P1,E,P2):-
E == {inputs:I,outputs:O|_},
O == [_,_|_],
walking_person(I,G,P1),
running_person(O,G,P2),!.
is_a_lam([_|Rest],G,P1,E,P2):-
is_a_lam(Rest,G,P1,E,P2).
walking_person([N|_],G,P):-
get_edge(N,G,E),
is_a_walking_person(E,G,P),!.
walking_person([_|Rest],G,P):-
walking_person(Rest,G,P).
running_person([N|_],G,P):-
get_edge(N,G,E),
is_a_running_person(E,G,P),!.
running_person([_|Rest],G,P):-
running_person(Rest,G,P).
get_edge(1,[Edge|_],Edge):-!.
get_edge(N,[_|Rest],Edge):-
N > 0,
get_edge(N-1,Rest,Edge).
In other words, the graph contains a case of a
lam if there is an edge E in the graph that has a
predecessor P1 corresponding to a walking person
and a follower P2 that corresponds to a running
person. It is requested also that E has more than one
follower (it is a case of branching in the graph).
is_a_walking_person(E,_,E):-
E == {mean_velocity:V|_},
V <= 2.0,!.
is_a_walking_person(E,G,P):-
E == {inputs:I|_},
walking_person(I,G,P).
That is, the graph edge corresponds to a walking
person if the average blob velocity in this edge is
less or equal to 2 m/sec, or the edge has a
predecessor that corresponds to a walking person.
The graph edge corresponds to a running person
if the average velocity in this edge is more or equal
to 3 m/sec, or the edge has a follower corresponding
is_a_running_person(E,_,E):-
E == {mean_velocity:V|_},
V >= 3.0,!.
is_a_running_person(E,G,P):-
E == {outputs:O|_},
running_person(O,G,P).
to a running person.
Note that aforementioned rules use plain
numerical thresholds to discriminate walking and
running persons for brevity. Better discrimination
could be provided by a kind of a fuzzy check, which
can be easily implemented using arithmetical means
of standard Prolog.
The example illustrates the possible scheme of a
logic program implementing all necessary stages of
video processing including video information
gathering, low-level image analysis, high-level
logical inference on the video scene, and reporting
the results of intelligent visual surveillance.
4 LOGICAL RULES
GENERATION
METHODOLOGY
A logical rules generation methodology based on a
hierarchy of fuzzy finite state automata was
introduced in (Devyatkov, 2005). Concepts and
notations described in (Devyatkov, 2005) should be
modified according to the specified problem domain.
Let
}|{ NttT
ii
be a discrete set of time
instances with constant intervals
ii
ttt
1
between consecutive time instances. Let
}|{],[
eses
tttttt
be a time interval T. Assume
that each 0
th
level feature (human speed and position
for our example) of each moving object
from set
},,,{
21 l
at time instance t can take on a
value
)(
0
ti
y
, },,1{
00
mi
, called feature sample.
Samples tuple
)(,),(],[
000 eses
tititti
yyY
,
},,1{
00
mi
of a single 0
th
level feature taken at
several consecutive time instances
es
tt ,, during
the
],[
es
tt time interval is called a trend.
Let us consider the following situation. Two
persons walk along perpendicular lines towards their
intersection. While person A is far from intersection,
person B slows down waiting for person A. When
person A enters intersection, person B accelerates
and runs into person A.
In order to formalise the persons' behaviour,
BIODEVICES2014-InternationalConferenceonBiomedicalElectronicsandDevices
58
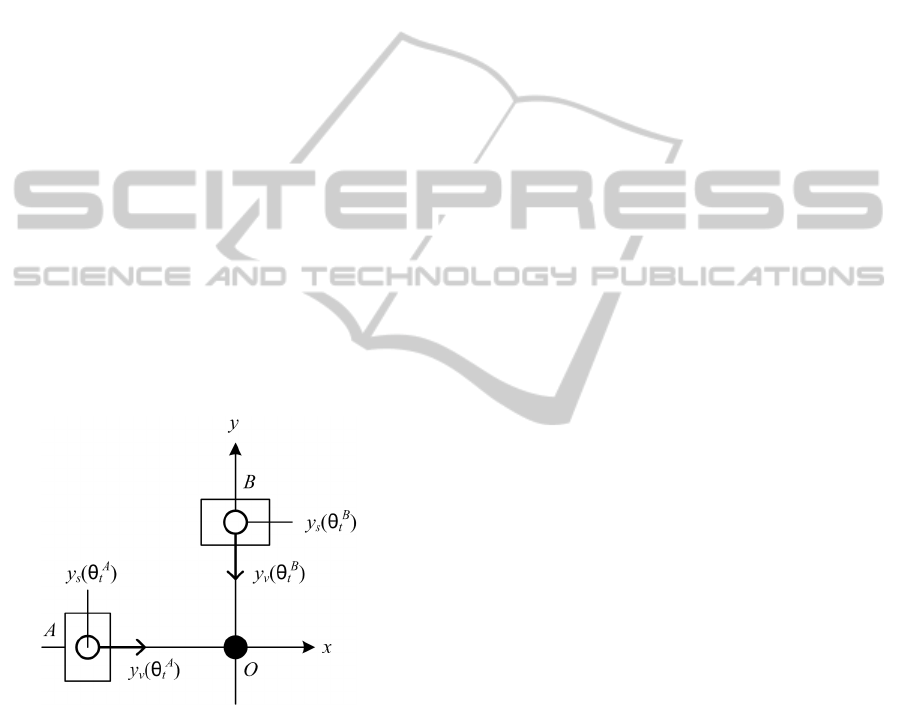
appropriate features should be specified. Let
persons A and B walk along perpendicular lines with
intersection point O. Let xOy be a rectangular co-
ordinate system such that Ox axis corresponds to the
line person A walks along, Oy axis corresponds to
the line person B walks along (figure 6). For the
purpose of simplicity, each person is considered as a
rectangle, thus the person co-ordinates are rectangle
centroid co-ordinates. Since persons move strictly
along the co-ordinate axes, the current position of
persons A and B can be determined by single co-
ordinates
)(
A
ts
y and )(
B
ts
y measured along
corresponding co-ordinate axes. The persons'
position co-ordinates
)(
A
ts
y , )(
B
ts
y are treated as
first features. The persons' speed values )(
A
tv
y ,
)(
B
tv
y are treated as second features.
One should specify observation time interval
}|{],[
eses
tttttt along with time instances
],[
esi
ttt the feature samples to be taken at. In
practice, observation time interval is determined
with some physical considerations in mind, e.g.
maximum time required for passing the observed
path segment; time instances are determined by the
surveillance equipment. Particular parameter values
assignment is outside of the scope of this paper.
Figure 6: Two persons in rectangular co-ordinate system.
Linguistic variables are specified and behaviour
template models are composed according to
(Devyatkov, 2005). Let
)(
A
position , )(
A
speed
and
)(
B
position , )(
B
speed be linguistic
variables that describe position and speed of persons
A and B. Linguistic variables
)(
A
position and
)(
B
position take on linguistic values )(
X
far ,
)(
X
near , and )(
X
inside . Linguistic variables
)(
A
speed and )(
B
speed take on linguistic values
)(
X
high and )(
X
low .
Figures 7 and 8 present fuzzy sets corresponding
to linguistic values
)(
X
far , )(
X
near , )(
X
inside
and
)(
X
high , )(
X
low .
Fuzzy sets shown on figures 7 and 8 are used to
compose first level template automata
)(
X
pos
M
,
)(
A
speed
M
and
)(
B
speed
M
that describe position and
speed of persons A and B.
Automaton
)(
X
pos
M
, shown as graph on
figure 4, determines sequence of linguistic values
[
)(
X
far , )(
X
near , )(
X
inside ] of linguistic
variable
)(
X
position . The automaton graph is
based on a chain of allowed states b
11
– b
12
– b
13
corresponding to linguistic values of the determined
sequence. b
11
is the initial state (marked with input
arrow on figure 9) and b
13
is the final state (marked
with output arrow on figure 9) of the automaton.
State transitions are specified as follows. Provided
with input linguistic value corresponding to the
current state, automaton retains its current state.
Provided with input linguistic value corresponding
to the next allowed state, the automaton moves to
that state. Automaton moves to denied state b
14
in
case of input linguistic value confronting to allowed
sequence of the automaton. Having entered the
denied state once, the automaton cannot leave this
state. Automata
)(
A
speed
M
and
)(
B
speed
M
are
presented as graphs on figures 10 and 11.
Automaton graphs are different since behaviour of
person A differs from behaviour of person B.
The second level template automaton should be
composed in order to describe joint persons'
behaviour. Let
),(
BA
condition be a linguistic
variable that takes on linguistic values
),(
BA
safe ,
),(
BA
warning , and ),(
BA
unsafe specified
with the following relations:
safe(θ
A
, θ
B
) = [pos(θ
t
A
) = far(θ
A
)] Λ
[pos(θ
t
A
) = far(θ
A
)]
(1)
warning(θ
A
, θ
B
) = ([pos(θ
t
A
) = near(θ
A
)] Λ
[speed(θ
t
B
) = high(θ
B
)]) V
([speed(θ
t
A
)=high(θ
A
)] Λ [pos(θ
t
B
)=near(θ
B
)])
(2)
unsafe(θ
A
, θ
B
) = [pos(θ
t
A
) = inside(θ
A
)] Λ
[pos(θ
t
B
) = inside(θ
B
)] (3)
DevelopmentofConcurrentObject-orientedLogicProgrammingSystemtoIntelligentMonitoringofAnomalousHuman
Activities
59
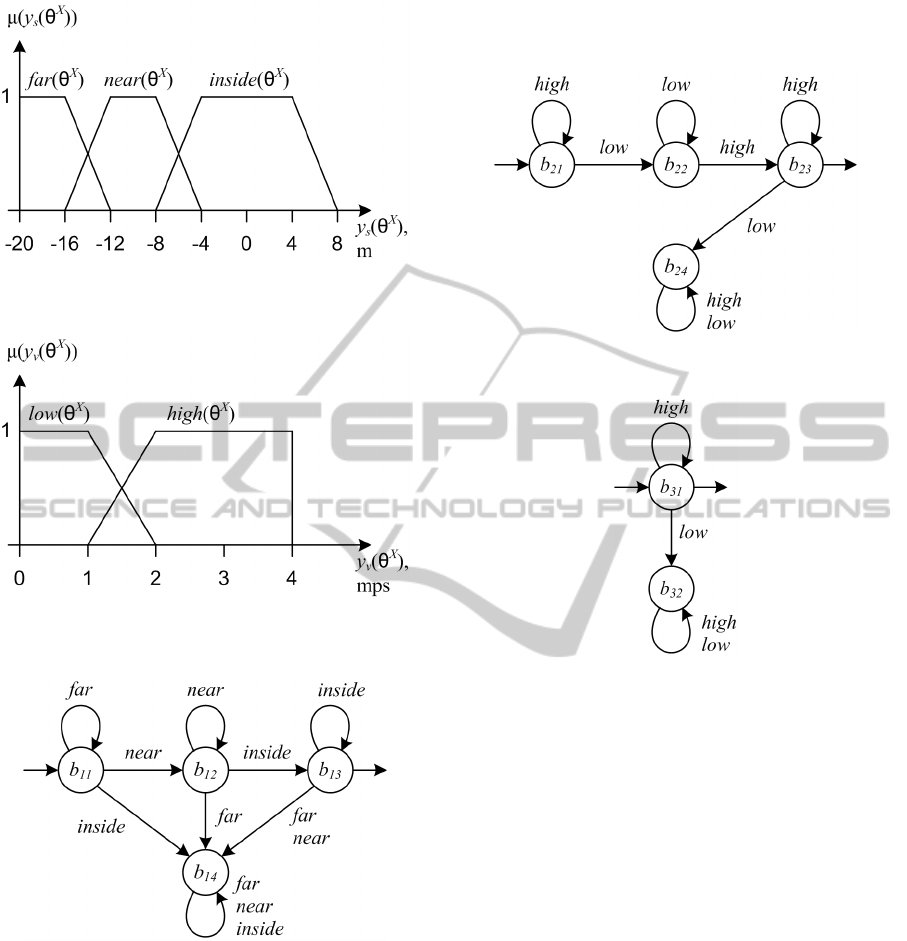
Figure 7: Fuzzy sets, corresponding to linguistic values
far(θ
X
), near(θ
X
), and inside(θ
X
).
Figure 8: Fuzzy sets, corresponding to linguistic values
low(θ
X
) and high(θ
X
).
Figure 9: First level automaton M
pos(
θ
X
)
graph.
Each linguistic value of a linguistic variable
),(
BA
condition corresponds to a composite fuzzy
set, determined on a multidimensional domain.
Domain of the composite fuzzy set is a Cartesian
product of domains of fuzzy sets involved into the
corresponding relation (Devyatkov, 2005).
According to equation (1) domain of linguistic value
),(
BA
safe is equal to
)]([)]([)],([
BABA
fardomneardomsafedom ,
where
][Edom is domain of fuzzy set E;
is
Cartesian product.
Figure 10: First level automaton M
speed(
θ
A
)
graph.
Figure 11: First level automaton M
speed(
θ
B
)
graph.
Membership function of composite fuzzy set can
be expressed through membership functions of fuzzy
sets involved into the corresponding relation
according to the following rules:
a = b Λ c → R
a
(y
b
, y
c
) = min{R
b
(y
b
), R
c
(y
c
)}
(4)
a = b V c → R
a
(y
b
, y
c
) = max{R
b
(y
b
), R
c
(y
c
)}
(5)
a = ¬b → R
a
(y
b
) = 1 – R
b
(y
b
), (6)
where a, b, c are fuzzy sets;
E
R is membership
function of fuzzy set E, determined on domain
][Edom ; ][bdomy
b
, ][cdomy
c
are feature
values from corresponding domains.
According to equation (4), membership function
of composite fuzzy set, specified on a conjunction of
two fuzzy sets, is equal to minimum value among
membership functions of its composing fuzzy sets.
Value of membership function numerically
expresses the goodness of current feature values for
a distinct linguistic value. Linguistic variable
),(
BA
condition is set to linguistic value with the
most membership function for current feature
BIODEVICES2014-InternationalConferenceonBiomedicalElectronicsandDevices
60
values.
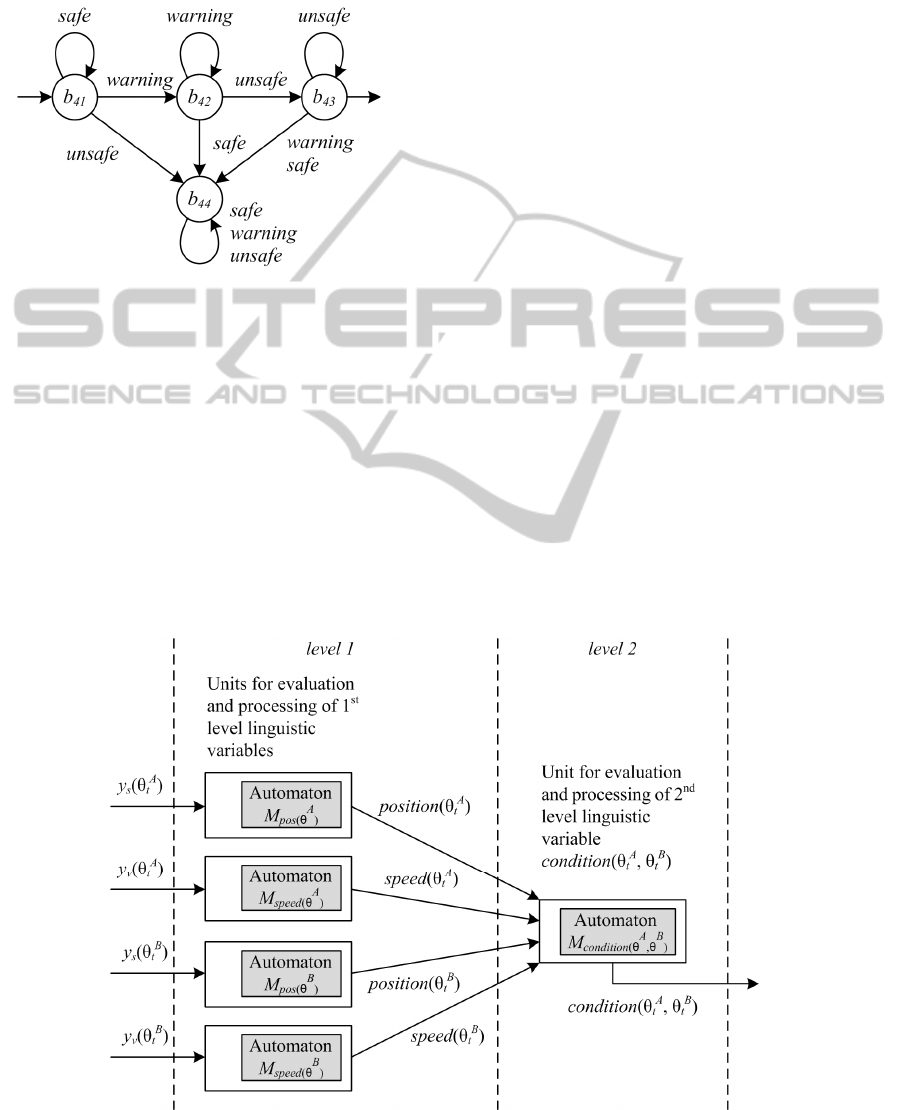
Second level template automaton
),(
BA
condition
M
that describes the joint persons' behaviour is shown
on figure 12.
Figure 12: Second level automaton M
condition(
θ
A
, θ
B
)
graph.
The computational methodology scheme is
presented on figure 13. It includes five units for
linguistic variables evaluation and processing,
arranged in two levels. Each unit compute value of
corresponding linguistic variable and inputs it to a
corresponding automaton.
Situation recognition is implemented as follows.
Initially, all first and second level automata are reset
to their initial states. Then feature samples for
consecutive time instances
],[
esi
ttt are passed by
turn into the first level units for evaluation and
processing of the first level linguistic variables. The
first level units compute values of linguistic
variables and pass them into the second level unit for
evaluation and processing of the second level
linguistic variable
),(
BA
condition . During
operation, the first and the second level automata
may change their states. Situation is recognised if all
first and second level automata have moved to their
final states after all feature samples have been
processed. Situation is not recognised if one
automaton at least has not moved to its final state.
The computational methodology scheme based
on fuzzy finite automata can easily be converted to a
logic program, using standard techniques of
transforming finite state machines into the logic
programs (Bratko, 1986).
5 CONCLUSIONS
A prospective approach for implementing the logic
programming to the problem of intelligent
monitoring of people activity is a translation from a
concurrent object-oriented logic programming
language to Java. Our study has demonstrated that
the Actor Prolog logic programming system is
suitable for this purpose and provides essential
separation of the recognition process into concurrent
sub-processes implementing different stages of high-
level analysis.
A specialised built-in class of the Actor Prolog
language implementing simple pre-processing of
Figure 13: The computational methodology scheme.
DevelopmentofConcurrentObject-orientedLogicProgrammingSystemtoIntelligentMonitoringofAnomalousHuman
Activities
61

video data and low-level analysis of video scenes
concerning the problem of intelligent monitoring of
people activity was demonstrated. We have
implemented a simple analysis of videos based on
automatically extracted information on the co-
ordinates and velocities of blobs in the video scene.
It was shown that robust recognition of abrupt
motions is impossible without accurate low-level
recognition of body parts (face, hands). This is a
subject of further studies.
An extension of the Actor Prolog logic
programming system to advanced algorithms of low-
level video processing and to investigations of new
possibilities at the level of logical analysis is
discussed. It is supposed to complete a prototype of
an open source Java library for studying logical
description and analysis of people behaviour in order
to facilitate researches in the field of intelligent
monitoring of anomalous people activity.
A logical rules generation methodology is
proposed for situation analysis in the environment of
moving objects. A formal method for representing
situations using hierarchy of fuzzy finite state
automata was considered. Future work will include
comprehensive testing of the proposed methods on
massive datasets and development of fully automatic
method for situation representation using real feature
trends.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We acknowledge a partial financial support from the
Russian Foundation for Basic Research,
No 13-07-92694, and Department of Science and
Technology, Govt. of India, No DST-RFBR P-159.
REFERENCES
Aggarwal, J. K., Ryoo, M. S. 2011. Human Activity
Analysis: A Review. ACM Computing Surveys
(CSUR), 43 (3), April.
Bratko, I. 1986. Prolog Programming for Artificial
Intelligence. Addison-Wesley Publishing Company.
Devyatkov, V. V. 2005. Multiagent hierarchical
recognition on the basis of fuzzy situation calculus.
Vestnik, Journal of the Bauman Moscow State
Technical University, Natural Science & Engineering,
2005, pp. 129-152.
Filippou, J., Artikis, A., Skarlatidis, A., Paliouras, G.
2012. A Probabilistic Logic Programming Event
Calculus. Computing Research Repository,
abs/1204.1851. [Online] Available from:
http://arxiv.org/abs/1204.1851.
Fisher, R. 2007. CAVIAR Test Case Scenarios. The EC
funded project IST 2001 37540. [Online] Available
from: http://homepages.inf.ed.ac.uk/rbf/CAVIAR/.
Junior, J., Musse, S., Jung, C. 2010. Crowd analysis using
computer vision techniques. A survey. IEEE Signal
Processing Magazine, September, pp. 66-77.
Kim, I. S., Choi, H. S., Yi, K. M., Choi, J. Y., Kong, S. G.
2010. Intelligent Visual Surveillance – A Survey.
International Journal of Control, Automation, and
Systems, 8 (5), pp. 926-939.
Machot, F. A., Kyamakya, K., Dieber, B., Rinner, B.
2011. Real Time Complex Event Detection for
Resource-Limited Multimedia Sensor Networks. In:
Workshop on Activity monitoring by multi-camera
surveillance systems (AMMCSS), pp. 468-473.
Morozov, A. A. 1999. Actor Prolog: an Object-Oriented
Language with the Classical Declarative Semantics.
In: IDL'99, Paris.
Morozov, A. A. 2002. On Semantic Link between Logic,
Object-Oriented, Functional, and Constraint
Programming. In: MultiCPL'02, Ithaca, pp. 43-57.
Morozov, A. A. 2003. Logic Object-Oriented Model of
Asynchronous Concurrent Computations. Pattern
Recognition and Image Analysis, 13 (4), pp. 640-649.
Morozov, A. A. 2003. Development and Application of
Logical Actors Mathematical Apparatus for Logic
Programming of Web Agents. In: ICLP 2003
Proceedings. Springer-Verlag, LNCS 2916,
pp. 494-495.
Morozov, A. A. 2007. Operational Approach to the
Modified Reasoning, Based on the Concept of
Repeated Proving and Logical Actors. In: CICLOPS,
Porto, pp. 1-15.
Morozov, A. A. 2007. Visual Logic Programming Method
Based on Structural Analysis and Design Technique.
In: ICLP 2007 Proceedings. Springer-Verlag, LNCS
4670, pp. 436-437.
Morozov, A. A. 2012. Actor Prolog to Java translation. In:
IIP-9, Montenegro, Budva. Moscow: Torus Press,
pp. 696-698. In Russian.
O'Hara, S. 2008. VERSA – Video event recognition for
surveillance applications. M.S. thesis, University of
Nebraska at Omaha.
Shet, V., Singh, M., Bahlmann, C., Ramesh, V., Neumann,
J., Davis, L. 2011. Predicate Logic Based Image
Grammars for Complex Pattern Recognition.
International Journal of Computer Vision, 93 (2),
June, pp. 141-161.
BIODEVICES2014-InternationalConferenceonBiomedicalElectronicsandDevices
62
