
Administration of Government Subsidies Using Contactless Bank
Cards
Aleksejs Zacepins
1
, Nikolajs Bumanis
1
and Irina Arhipova
2
1
IT Competence Centre, Lačpleša iela, Riga, Latvia
2
Ecommerce Accelerator, Skanstes 54, Riga, Latvia
Keywords: Subsidy Administration, Electronic Cards (e-Cards), Contactless Bank Cards, Public Transport Subsidies.
Abstract: Subsidization of major and minor government branches is common strategy with the aim to optimize
government funds, increase residents’ welfare and overall infrastructures’ efficiency, including public
transportation system. Within the different countries subsidization is being approached using specific
models of calculation and payment. However, most of them use the same subsidy administration approaches
– cash transfers or social services. The aim of this paper is to describe proposed improvements of transport
subsidy administration approach by implementation of e-cards for payments. It is proposed to improve
subsidy payment procedure by promoting that subsidy should be paid directly to subsidy receiver. This will
allow managing only real transactions and only subsidy receiver is interested in subsidy utilization.
Proposed approach to process the subsidy administration and payments can be realized by using existing
banking infrastructure and novel product as electronic cards.
1 INTRODUCTION
In many countries subsidy administration is an
actual problem and open question on government
level. This problem is important because in most
cases (Drevs, Tscheulin, 2014) residents’ taxes are
used for subsidy payments. Several residents groups
with ability to apply for different subsidies can be
mentioned, for example pupils, seniors, unemployed
people etc.
In Latvia subsidy administration and its payment
strategy is also widely discussed issue. In
16.02.2012 the goal (Latvian Ministry Cabinet,
2012) for Welfare Ministry to realize reform of
Latvian social assistance system was defined by the
Latvian Ministry cabinet, which states
implementation of reform by gradually transforming
assistance system from passive (subsidy social
assistance system) to active (client motivating
system). It is required to improve situation with
existing social system by providing possible biggest
added value for clients and for society overall
(Latvian Ministry Cabinet, 2012).
To start improvement of social safety system and
to grant reasonable decision making offering
optimization events for mentioned branch, in year
2013 World Bank research is carried out in Latvia
with title “Expenditure and performance
benchmarking country level, Expenditure and
performance of welfare benefits and employment
programs in Latvia” (The World Bank, 2013).
Results of this research were very significant and
together with evaluation of whole system, several
disadvantages and problems of social assistance
system, including labour market policy, State social
benefits and taxation were identified. As well main
residents risk groups were defined. As most
significant problem area in whole social safety
system, which is clarified during mentioned World
Bank research is “lack of state and government
support purposefulness and the necessity to improve
system relating to poorest residents”. Social
assistance and welfare programs are non-
contributory benefits (or services) targeted at the
poorest residents, as well at families with children,
disabled and other categories of the population who
may need income support or other help (The World
Bank, 2013).
Social assistance programs and approaches differ
across EU countries (Palme, 2013) and share spent
on cash benefits versus benefits in-kind (social
services) also differs. It can be mentioned that
Nordic countries deliver significant share of social
128
Zacepins A., Bumanis N. and Arhipova I..
Administration of Government Subsidies Using Contactless Bank Cards.
DOI: 10.5220/0004950901280132
In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS-2014), pages 128-132
ISBN: 978-989-758-029-1
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

assistance through social services compared to the
new EU member countries, like Estonia and Poland
where the majority of social assistance is provided in
form of cash transfers. During the last decade in
Latvia more than half (approximately 60 %) of
social assistance benefits were delivered as cash
transfers, and not by social services. This should be
changed in future, minimising the amount of cash
transfers. In Latvia only about one fifth of total
social protection spending is allocated to non-
contributory social assistance programs (The World
Bank, 2013).
Latvian social assistance (welfare) programs
include social assistance benefits such as benefits for
meals and food, health care benefits and transport
benefits. These benefits are meant for people
qualifying the means-tested eligibility threshold or
other eligibility criteria set by municipalities, and
being administered by municipalities.
The aim of this paper is to describe proposed
transport’s subsidy administration approach by
implementation of e-cards for payments. To improve
subsidy granting and administration procedure,
existing situation is analysed and new subsidy
administration and payment approach is proposed.
This approach improves subsidy payment procedure
by promoting that subsidy should be paid directly to
subsidy receiver. This will allow managing only real
transactions and only subsidy receiver is interested
in subsidy utilization. This approach excludes
conflicts of interests and makes more efficient
spending of subsidy funds. For new subsidy
administration approach implementation use of
existing banking infrastructure and electronic cards
is proposed.
2 ANALYSE OF GOVERNMENT
SUBSIDY ADMINISTRATION
APPROACHES
Basically the transport subsidy related literature
sources distinguishes between research neglecting
spatial location decisions and the labour-leisure
choice (Mohring, 1972; Parry, Small, 2009)
approaches disregarding spatial location decisions
but considering labour supply decisions (Wrede,
2000; Calthrop, Leuven, 2001; Richter, 2006;
Dender, 2003; Borger, Wuyts, 2009) and research
where location choice is explicitly taken into
account but labour supply is exogenously given
(Zenou, 2000; Martin, 2001; Wrede, 2001;
Brueckner, 2005; Borck, Wrede, 2009; Borck,
Wrede, 2008; Borck, Wrede, 2005; Su, DeSalvo,
2008; Wrede, 2009).
Subsidies and benefits can be administered in
different ways and using different models, thus,
creating overall problem of choosing the correct
model for administrating purpose. The existence of
different models for administrating of the same
subsidy is prevalent (Yang et al., 2010). As example,
decentralization of prescription drugs within the
Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme has two models
(Bergström, Karlberg, 2007): a population based and
a prescribed based.
Additionally, exists so called ‘Transfer of fare
revenue’, which is one of the fare compensation
measures for ‘fare-discount schemes’, which are set
by local authorities. In Japan, this scheme was
introduced from the 1970s for public bus operators
(Sakai, Shoji, 2010). Sakai and Shuji stated that
most local governments that own municipal bus
companies have implemented this scheme, but this
policy measure was aimed at improving the welfare
of senior citizens and the disabled and therefore, it is
not precisely identical to the actual subsidies. “Since
the fare discount for senior citizens and the disabled
is not stipulated by law, there are considerable
variations among local authorities regarding
concessionary fare schemes” (Sakai, Shoji, 2010).
It is known that government grants public
transport subsidies to reduce operating cost of public
transport enterprises and the individual travel cost of
public transport, therefore making decision of
choosing public transport over private more
expectable. It was stated (Yang et al., 2010) that
reducing trip expenses by public transport using
public transport subsidies will lead to private car
reduction, therefore, increasing overall volume of
public transport passengers and decreasing amount
of private cars on the roads. This scenario can be
preceded until balance between excessive trips and
public transport cost is achieved.
Nowadays in Latvia there are two main methods
or approaches for government subsidy (grant)
administration.
First subsidy administration method (see Fig.1):
residents’ subsidies are administered by service
providers (merchandisers) and subsidies (subsidy
payments) are transferred directly to service
provider’s account.
Several issues can be mentioned about such
subsidy administration method. There can be
expected mistakes in distribution of grants, because
service providers are in conflict of interests and
delays in payments for service providers. As well
service providers are interested to apply for subsidy
Administration of Government Subsidies Using Contactless Bank Cards
129
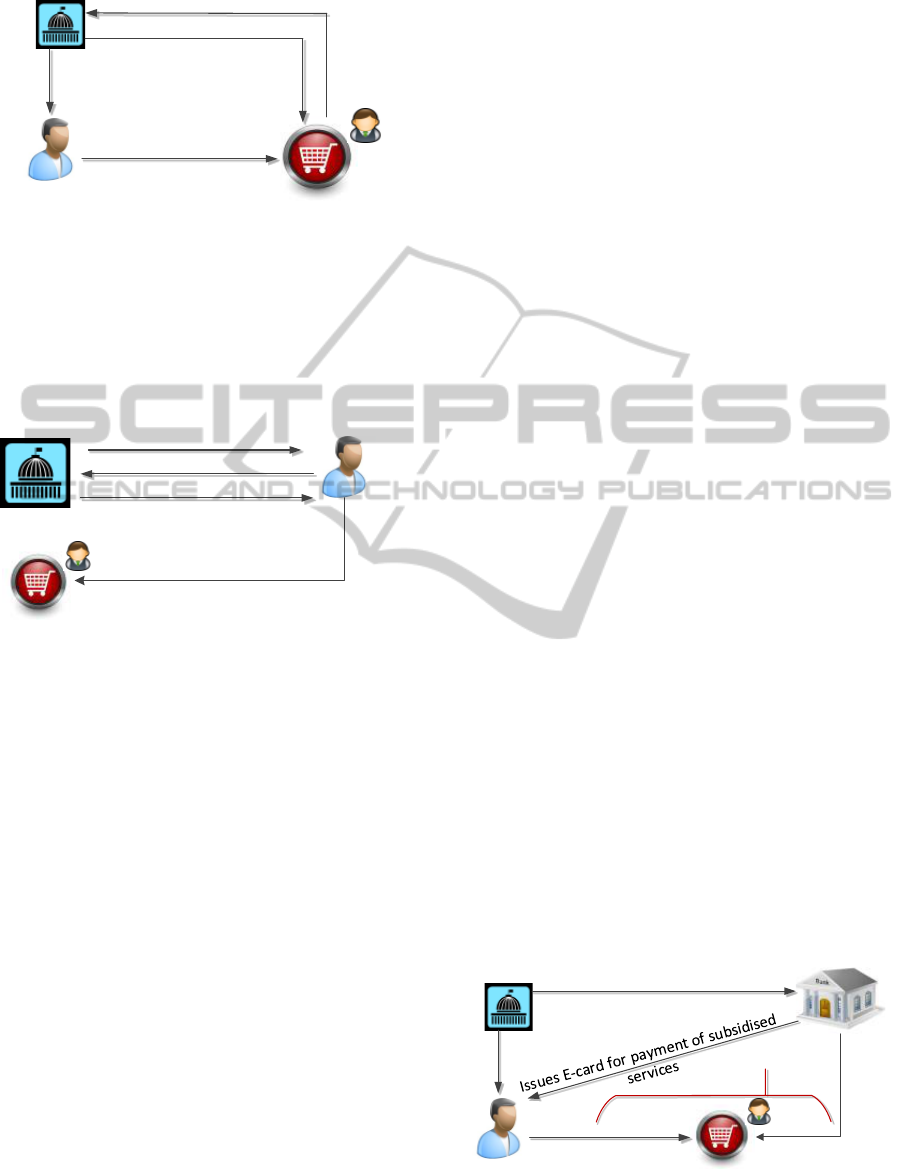
Client
(resident)
Service
provider
Government
Grants
subsidy
Applies for subsidy
payment
Pays subisdy
Pays for servce
(price - subsidy)
Figure 1: Subsidy administration by service providers.
payments as more as possible, and can do this
unfairly.
Second subsidy administration method (see
Fig.2): residents pay for service a full price and after
that provide receipts for the government institution
to receive subsidy payment.
Client
(resident)
Service
provider
Government
Grants subsidy
Pays subisdy
Applies for subsidy payment
Pays for service (full price)
Figure 2: Subsidy administration by government.
Issues of this method are that government cannot
precisely verify the subsidised deal; therefore,
service provider can unfairly create check for the
deal and client can apply for subsidy without taking
a service.
Common issue of mentioned approaches is non-
effective spending of subsidy funding.
So it is clear that it is needed to change subsidy
administration approach to grant, that subsidy will
be received directly by person whom subsidy is
granted. This approach excludes conflict situations
and makes administration of subsidy funding more
efficient. This approach guarantees that only real
service providers deals (transactions) are fixed. To
implement new subsidy administration approach is it
proposed to use cheap and fast electronic way for
payment for subsidised services or products by using
existing banking infrastructure.
3 DESCRIPTION OF PROPOSED
APPROACH FOR
GOVERNMENT SUBSIDY
ADMINISTRATION USING
CONTACTLESS BANK CARDS
It is proposed to use existing banking infrastructure
for administration of subsidies by implementation of
specific electronic cards (E-cards) for payment for
subsidised services or products. E-card is
multifunctional and personalised payment card with
additional non-contact function (including
VISA/MaterCard payment cards), where is
combined Bank payment cards functionality with
person verification and recognition functions. This
card should be issued by Bank for subsidy
administration.
Cities (governments) delegates banks to issue
contactless payment cards with established design
and with rights for residents to receive grants, but
still governments defines a list of subsidy receivers,
provides subsidy calculation scenarios and defines
list of service/product providers which can accept E-
cards for service/product payment.
Banks identify residents, open bank account for
pupils and socially unprotected residents, and issue
contactless cards in schools, in social centres and in
bank’s branches.
Pupils and socially unprotected residents pay for
subsidized products/services using banking
infrastructure.
Grants are calculated by the fact of successful
transaction, based on city defined scenario (fixed
rate, % of payment, etc.) and taking into account
defined subsidy limits (transaction count, daily
payment, monthly payment, etc.).
Bank processes payments between card’s owners
and service providers simultaneously with grant’s
payments from cities to grant’s receivers bank
account (see Fig.3).
Client
(resident)
Service
provider
Government
Grants
subsidy
Pays
subsidy
Pays for servce
with E-card (price -
subsidy)
Bank
Provides fundings for
subsidies
*Simultaneously
Figure 3: Concept of novel approach for government
subsidy administration.
ICEIS 2014 - 16th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
130

Costs for implementation of such approach for
residents are very minimal, because
issuance/cancellation of payment cards for residents
should be free of charge, calculation and
management of grants for city – free of charge,
transaction of grant’s from city’s to grant’s
receiver’s bank account is also free of charge. Costs
for the above mentioned services are included in
banking commission rate for acceptance of payment
card’s by service providers.
3.1 Possible Data Structure of Subsidy
Formulation
Subsidy provider transmits Subsidy formulation to
all Issuer banks, where Subsidy provider’s
(sub_send_name) subsidy’s receivers
(sub_rec_name) are clients (pers) of E-card’s Issuer
(issuer). Subsidy can be assigned to one or group of
persons, where Subsidy is calculated based on
specific calculation scenario (sub_scenario).
Calculation scenario is valid for specific time
interval (from_date to till_date). There is specific
limit (sub_total) of sum of assigned Subsidies for
one client. The limit is valid for specific time
interval. Subsidy’s receiver (sub_rec_name) receive
Subsidy making deals with merchant (merchant)
using E-card as payment instrument, which requires
personal ID code or card’s ID (there is possibility to
have both). IssuerID is unique for all Issuer banks,
and is listed in unified registry, maintained by Issuer
banks. Possible data structure of Subsidy
formulation is demonstrated in Figure 4:
Figure 4: Structure of Subsidy formulation.
3.2 Example of Described Novel
Subsidy Administration Approach
Described subsidy administration approach is
implemented in Latvia, in Jelgava city for
administration of subsidies for pupils. Subsidy is
granted for usage of public transportation and for
taking a meal in the school. Pupils are using specific
e-card for payment of subsidised services (see
Fig.5).
Figure 5: Example of e-card for payment of subsidised
service.
There are many benefits of implemented subsidy
administration approach:
• Additional parental control, which allows
monitoring children spending by controlling the
amount of funding on E-card.
• Maintaining of confidentiality of social status of
children and residents – everyone pays the same
amount and receive grants on their bank account.
• Service/product providers receives full price for
products/services on their bank account on the next
working day.
• Subsidies are calculated only according to actual
transaction and are transferred directly to grant’s
receiver’s bank account.
• Grants’ receivers receive information about full
price of products/services and amount of provided
grant.
• This solution is economically effective because of
direct transactions within the bank and use of
existing banking infrastructure.
• Time saving – fast service because of integration
with cash register.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Subsidization as problem on government level was
being analysed and subsidy calculation models were
introduced in many economic researches. However,
it was not stated that subsidies paid by cash transfers
can be used unfairly by private organizations.
Latvia’s transportation system was taken as
example, and solution for optimization of subsidy
administration is introduced.
In Latvia the main problem of existing subsidy
administration approach is non-effective spending of
subsidy funding. To improve the administration of
subsidies novel approach is proposed. This approach
is implemented and is practically verified in Jelgava
city in Latvia for subsidy administration of public
transportation and meals for pupils in schools.
This approach improves subsidy payment
Administration of Government Subsidies Using Contactless Bank Cards
131

procedure, by promoting that subsidy should be paid
directly to subsidy receiver. This will allow
managing only real transactions and only subsidy
receiver is interested in subsidy utilization. This
approach excludes conflicts of interests and makes
more efficient spending of subsidy funds.
Additionally to subsidy administration,
proposed approach allows better organization of
pupil’s daily life.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research is part of a project „Competence
Centre of Information and Communication
Technologies” run by IT Competence Centre,
contract No. L-KC-11-0003, co-financed by
European Regional Development Fund.
REFERENCES
Bergström, G., Karlberg, I. (2007) Decentralized
responsibility for costs of outpatient prescription
pharmaceuticals in Sweden: Assessment of models for
decentralized financing of subsidies from a. Health
Policy, Vol. 81(2-3), p. 358–367.
Borck, R., Wrede, M. (2005) Political economy of
commuting subsidies. Journal of Urban Economics,
Vol. 57, p. 478–499.
Borck, R., Wrede, M. (2008) Commuting subsidies with
two transport modes. Journal of Urban Economics,
Vol. 63, p. 841–848.
Borck, R., Wrede, M. (2009) Subsidies for intracity and
intercity commuting. Journal of Urban Economics,
Vol. 66, p. 25–32.
Borger, B. De, Wuyts, B. (2009) Commuting, transport tax
reform and the labour market: employer-paid parking
and the relative efficiency of revenue recycling
instruments. Urban Studies, Vol. 46, p. 213–233.
Brueckner, J. (2005) Transport subsidies, system choice,
and urban sprawl. Regional Science and Urban
Economics, Vol. 35, p. 715–733.
Calthrop, E., Leuven, K. (2001) On subsidising
auto0commuting! CESifo Working Paper Series 566.
Dender, K. Van (2003) Transport taxes with multiple trip
purposes. The Scandinavian Journal of Economics,
Vol. 105, p. 295–310.
Drevs, F., Tscheulin, D. (2014) Crowding-in or crowding
out: An empirical analysis on the effect of subsidies on
individual willingness-to-pay for public transportation.
Transportation Research, p. 250–261.
Latvian Ministry Cabinet (2012) Latvian government
action plan.
Martin, R. (2001) Spatial mismatch and costly suburban
commutes: Can commuting subsidies help? Urban
Studies, Vol. 38, p. 1305–1318.
Mohring, H. (1972) Optimization and scale economies in
urban bus transportation. The American Economic
Review, Vol. 62, p. 591–604.
Palme, J. (2013) Unemployment Benefits in EU Member
States. Uppsala University, Department of Economics,
Working Paper Series, Center for Labor Studies, (15),
p. 25.
Parry, I., Small, K. (2009) Should urban transit subsidies
be reduced? The American Economic Review, Vol. 99,
p. 700–724.
Richter, W. (2006) Efficiency effects of tax deductions for
work-related expenses. International Tax and Public
Finance, Vol. 13, p. 685–699.
Sakai, H., Shoji, K. (2010) The effect of governmental
subsidies and the contractual model on the publicly-
owned bus sector in Japan. Research in
Transportation Economics, Vol. 29(1), p. 60–71.
Su, Q., DeSalvo, J. (2008) The effect of transportation
subsidies on urban sprawl. Journal of Regional
Science, Vol. 48, p. 567–594.
The World Bank (2013) Expenditure and performance
benchmarking country level. Scientific research:
Latvia: “Who is unemployed, inactive or needy?
Assessing post-crisis policy options,” p. 74.
Wrede, M. (2000) Tax deductibility of commuting
expenses and leisure: On the tax treatment of time-
saving expenditure. FinanzArchiv/Public Finance
Analysis, Vol. 57, p. 216–224.
Wrede, M. (2001) Should commuting expenses be tax
deductible? A welfare analysis. Journal of Urban
Economics, Vol. 49, p. 80–99.
Wrede, M. (2009) A distortive wage tax and a
countervailing commuting subsidy. Journal of Public
Economic Theory, Vol. 11, p. 297–310.
Yang, Y., Qi, K., Qian, K., Xu, Q., Yang, L. (2010) Public
Transport Subsidies Based on Passenger Volume.
Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and
Information Technology, Vol. 10(3), p. 69–74.
Zenou, Y. (2000) Urban unemployment, agglomeration
and transportation policies. Journal of Public
Economics, Vol. 77, p. 97–133.
ICEIS 2014 - 16th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
132
