
CRISTAL-iSE
Provenance Applied in Industry
Jetendr Shamdasani
1
, Andrew Branson
1
, Richard McClatchey
1
, Coralie Blanc
1
, Florent Martin
2
,
Pierre Bornand
2
, Sandra Massonnat
3
, Olivier Gattaz
3
and Patrick Emin
3
1
CCCS Research Centre, University of the West of England, Coldharbour Lane, Bristol, U.K.
2
Alpha-3i, Alpha-3i, 42 rue Rene Cassin, Rumilly, France
3
M1i, 15 route de Nanfray, 74960 Cran Gevrier, France
Keywords: Provenance, Semantic Web, Industrial Collaboration, XML, XML Schema, BPM, Resource Allocation.
Abstract: This paper presents the CRISTAL-iSE project as a framework for the management of provenance
information in industry. The project itself is a research collaboration between academia and industry. A key
factor in the project is the use of a system known as CRISTAL which is a mature system based on proven
description driven principles. A crucial element in the description driven approach is that the fact that
objects (Items) are described at runtime enabling managed systems to be both dynamic and flexible.
Another factor is the notion that all Items in CRISTAL are stored and versioned, therefore enabling a
provenance collection system. In this paper a concrete application, called Agilium, is briefly described and a
future application CIMAG-RA is presented which will harness the power of both CRISTAL and Agilium.
1 INTRODUCTION
The purpose of this position paper is to make the
case for the use of provenance (Moreau, 2010) in
industrial systems. Currently provenance gathering
systems and techniques have mostly been used
within scientific research domains such as
neuroscience (Anjum et al, 2011) or other areas of
bioinformatics (Goble, 2002). The usefulness of the
application of this technology has been discussed at
length elsewhere and is not the primary purpose of
this paper. The interested reader is directed to other
works such as (Simmhan et al, 2005). However, we
have developed a concrete application of provenance
management for industry which is discussed in this
paper. The secondary purpose of this paper is to
present the CRISTAL-iSE project.
CRISTAL-iSE (CRISTAL-iSE, 2013) is a
project about fostering collaboration between
industrial partners and academia and the
development of individual researchers in the project.
The partners involved in the project are from the
University of the West of England (UWE, Bristol,
United Kingdom, Academic), M1i (Annecy, France,
Commercial) and Alpha-3i (Rumilly, France,
Industrial). At the core of the project is a software
product known as CRISTAL (Branson et al., 2014).
This software had previously been developed at the
European Organisation for Nuclear Research
(CERN, Switzerland), in collaboration with UWE
and the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique
(CNRS, France). At the end of the project it is
foreseen that there will be three final pieces of
software developed. These will be a new open
source version of CRISTAL (UWE), a new version
of Agilium (M1i) based on this version of CRISTAL
and CIMAG-RA (Alpha-3i) which will be built upon
both the work developed by UWE and M1i.
The main concept behind CRISTAL is what is
known as a “description driven” system (Estrella,
2003). The main strength of such a “description
driven” approach is that users who develop models
of systems need only define them once to create a
usable application. CRISTAL then orchestrates the
execution of the processes defined in that model
(with the consequent capture of provenance
information). These descriptions can be modified at
runtime and can capture almost any domain; this
flexibility has been proven by its use in the
construction of the CMS ECAL (CMS, 2008) at
CERN. It has also been applied to the Business
Process Management (BPM) domain (to model
453
Shamdasani J., Branson A., McClatchey R., Blanc C., Martin F., Bornand P., Massonnat S., Gattaz O. and Emin P..
CRISTAL-iSE - Provenance Applied in Industry.
DOI: 10.5220/0004953004530458
In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS-2014), pages 453-458
ISBN: 978-989-758-029-1
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

Figure 1: The internals of a CRISTAL Item.
business-based process workflows) and the
manufacturing domain (to control manufacturing
processes) and is currently being applied to the HR
domain allowing users to modify defined processes.
Besides flexibility being a fundamental function
of the system, another area where CRISTAL excels
is the area of provenance. Provenance within the
computer science literature is defined as the source
or origin of an artefact or a piece of data. Within
CRISTAL every defined element (or Item) is stored
and versioned; therefore, nothing is ever deleted.
This allows users of the system to view older
versions of their Items (akin to Objects in Object
Orientation) at a later date and either extend or
return to a later version of an Item. A full description
of the CRISTAL provenance model is out of the
scope of this paper. Please see (Shamdasani, 2012)
for further detail and (Branson et al., 2014) for a full
description of the CRISTAL system. However, in
this section the notion of an Item is briefly
elaborated upon so that the content of this paper can
be better understood.
There follows a very brief description of Item
elements (see Figure 1) and their associations:
Workflows are complete layouts of every action
that can be performed on that Item, connected in
a directed graph that enforces the execution order
of the constituent activities.
Activities capture the parameters of each atomic
execution step, defining what data is to be
supplied and by whom. The execution is
performed by agents.
Agents are either human users or mechanical/
computational agents (via an API), which then
generate events.
Events detail each change of state of an Activity.
Completion events generate data, stored as
outcomes. From the generation of an Event
provenance information is stored.
Outcomes are XML documents resulting from
each execution (i.e. the data from completion
Events), for which viewpoints arise.
Viewpoints refer to particular versions of an
Item’s Outcome (e.g. the latest version or, in the
case of descriptions, a particular version
number).
Properties are name/value pairs that name and
type items. Properties also denormalize collected
data for more efficient querying, and
Collections enable items to be linked to each
other.
The outcome of the CRISTAL-iSE project will be a
newer, open source version of the CRISTAL Kernel,
developed and managed by UWE, a new version of
M1i’s BPM use of CRISTAL known as Agilium and
a Resource Allocation use of Agilium with
CRISTAL known as CIMAG-RA developed and
managed by Alpha-3i. As well as software outcomes
the research focus of CRISTAL-iSE is to add
Semantic and Distribution capabilities to the Kernel.
The semantic work has already begun where the
CRISTAL provenance model is being made
compliant with the Open Provenance Model (OPM)
(Moreau, 2010).
ICEIS2014-16thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
454

Figure 2: The Agilium Factory Application.
This paper is organised as follows, section 2
describes the current situation at M1i and its BPM
specific use of CRISTAL. Section 3 describes the
envisaged Alpha-3i application. Finally section 4
presents conclusions and future work by the
CRISTAL-iSE partners.
2 CRISTAL IN AGILIUM
One successful commercial application of CRISTAL
outside of CERN has been the Agilium product
(Agilium, 2013). It is currently developed and sold
to industrial and commercial clients via the M1i
company. This is a BPM orientated system which
consists of four main parts, one server application
and three user interfaces.
The Agilium Server is based on CRISTAL, but
with several domain extensions and support for
additional protocols added. The user interface (UI)
components are the Agilium Web component, the
Agilium Supervisor GUI and the Agilium Factory.
The Agilium Web is a web application based on
J2EE and running within Tomcat as the container.
This is where users can browse the currently active
jobs and different instances of business processes.
The list of jobs available to a user are constrained by
their individual roles (for example, administrator).
The web UI also allows users to complete manual
activities.
The supervisor GUI component of Agilium is
derived from the original Java Swing CRISTAL
GUI, and is used by administrators of the system to
be able to design and debug workflows and for
general system management. The key component in
Agilium is known as the Factory. The factory is a
full Eclipse based application which has a modern
UI and allows M1i’s users to create and manage
their own CRISTAL based workflows. A screenshot
of the Agilium Factory is shown in figure 2.
The major area that Agilium uses CRISTAL for
is provenance capture and recording of their BPM
process executions. Within Agilium, the provenance
model is identical to the provenance model of
CRISTAL where Events are generated and stored.
However, it is applied to the domain of BPM. As
stated previously, all models are created at runtime.
This means that all BPM workflows developed
within Agilium are stored and versioned. This
allows users to come back at a later date and view
previous versions of the BPM models, fix bugs, or
extend their previous BPM workflows.
As example of where provenance is useful for
CRISTAL-iSE-ProvenanceAppliedinIndustry
455

Agilium is a company which produces solar panels.
With this client, the production of each solar panel
can take more than a month. They also require
different versions of workflows to be stored and
accessed on site. Therefore, this client of theirs
requires that they be able to look into the past
versions of their processes and workflows. This
means that they can retrieve the history of all the
production steps for each panel, even though the
BPM workflow has evolved between the two
generations of panels.
As an example of an alteration to the fabrication
process, in the past they have modified their
production process to increase the performance level
of the solar cells. The workflows corresponding to
the production processes are modified to add or
remove activities matching an electro-deposition or
cleaning step, or alter their parameters. These
modifications are usually done at run time.
Therefore, these changes are saved and stored as
newer versions, thereby, allowing the panels using
the older versions of the workflow to continue
unhindered whereas the newer modifications can be
applied to newer solar panels in production; this is a
key strength of using CRISTAL in Agilium and
demonstrates not just the use of provenance but also
the flexibility of the system.
The inherent provenance capabilities of
CRISTAL mean that the model itself is also
versioned, allowing users to look at the production
steps for each version of the panels they have
created and to see what processes they have in
common. This also allows them to view and analyse
which processes have changed. This aspect is crucial
to their business since it allows them to look at the
evolution of the production process. The developers
at M1i chose CRISTAL as the basis for their system
since they felt that its provenance and traceability
features were key for them to create a product with a
competitive edge in the market.
3 ALPHA-3I AND CIMAG-RA
CIMAG-RA is a resource allocation and
management solution (May, 2012) which the Alpha-
3i company will market to clients as an outcome of
the CRISTAL-ISE project. This solution uses both
the Agilium component (described previous) and
CRISTAL. They require a solution which can track
and predict resource allocation to tasks over time.
There are different types of resources that have been
identified by Alpha-3i during the course of their
investigation, the different categories are: Machines
(Physical, mechanical non human entities),
Operators (Human entities that operate machines)
and Administrators (Human entities that control the
system). These resources are involved in the
completion of certain tasks. Each resource that has
to perform a task must have a correct set of
properties. Therefore there must be a matching of
properties to tasks to be completed. This is the
resource allocation problem that requires solution.
A key factor of the CIMAG-RA solution is the
requirement for provenance to influence future
scheduling. This entails the storage of CRISTAL
Events that occur on their defined Item types
(human, machines or tasks). The use of this
information will aid in optimizing customer
processes and provide useful information to
administrators. In detail, provenance is used for
different purposes:
To gauge the relevance of an allocation of a
resource to a specific task. This means storing
the experiences of a human along with the set of
tasks they have processed in the past, can help
with the decision making process. Therefore here
provenance information can be used as data
which helps users gauge the trustworthiness of
the current decision making process.
To create an audit trail or provide information to
resolve disputes. For example, in healthcare
applications, this would be data containing the
healthcare history of a single patient, the
procedures carried out on that patient and the
resources (nurses, doctor’s machines etc.)
allocated to each procedure performed on a
patient. This information must be stored in
retrievable fashion for legal or analysis purposes
(Wang et al, 2007).
To optimize non-human resource management.
For example, in the manufacturing industry,
storing and then analysing the evolution of a
machine resource can be a key factor to
determine the lifecycle of an instrument and may
aid in predicting when it will need repair or
replacement.
Another requirement of the CIMAG-RA solution is
flexibility. Indeed to meet requirements of a large
variety of clients from heterogeneous markets such
as manufacturing, medical, financial services and
others, the solution must be fully reconfigurable
without recompiling code. More precisely, resources
and tasks will be designed and modified according
to client needs or legal constraints. Therefore, a
crucial requirement is to track objects and their
provenance over time.
Many different resource management solutions
ICEIS2014-16thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
456
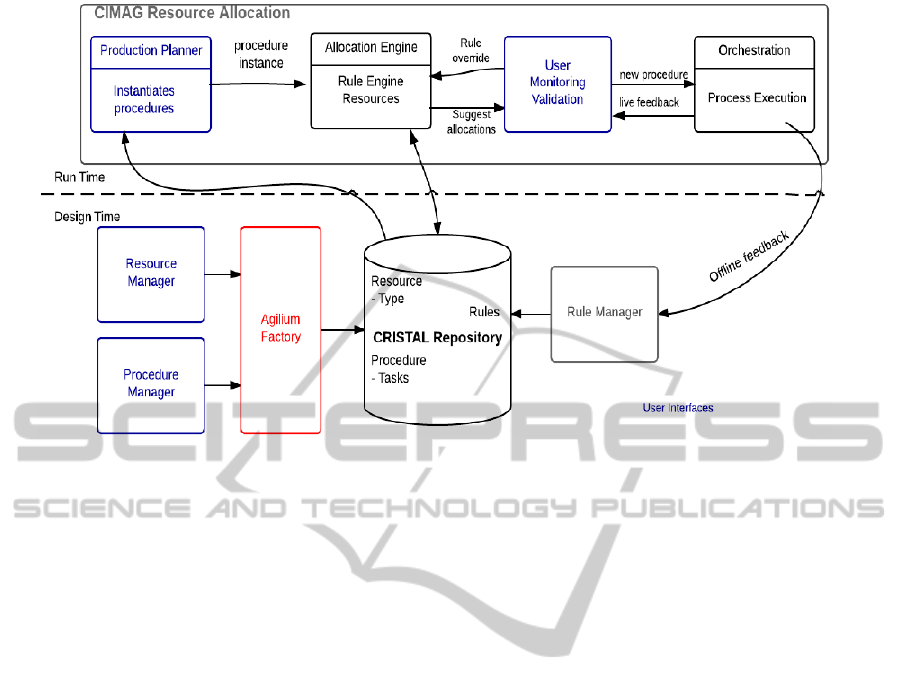
Figure 3: The CIMAG-RA Application Architecture.
exist today (Vanden Berghe, 2002 and Lombardi,
2012), however, after some investigation the
developers at Alpha-3i found that these did not fit
their needs. Mostly due to the requirements of
provenance and flexibility, described earlier as being
novelties in CRISTAL, are crucial requirements for
the CIMAG-RA software.
Figure 3, shows the architecture of CIMAG-RA
and how they use the CRISTAL kernel. It is
foreseen that Alpha-3i will implement, using
CRISTAL, a repository of procedures, i.e. a set of
tasks, and resources, where changes are tracked to
the resource and procedure management schemes
and then stored within the database of choice. From
a CRISTAL point of view, procedures, tasks and
resources are Items described by their own schema.
Such Items can evolve, thus the repository has to
manage Items that are an instance of an object
(resource, procedure and tasks) corresponding to a
schema Item regarding its version.
At design time, the Agilium factory is used to
define the resources and procedures the same way
Agilium users define their BPM Items. Concretely,
we use the Resource and Procedure Manager
components (left of figure 3) to design the schema
Items of our applications. Such schema Items are
then instantiated as resource and procedure Items
and populated using the data and constraints of the
client. For example, in the manufacturing area, a
named operator resource cannot work more than 12
hours per day and he will be on holiday from
Monday to Wednesday next week. So these and
other constraints will populate his corresponding
Item and therefore he will be matched to a
corresponding task based on other requirements.
At run time, the “Allocation Engine” component
retrieves the resources and procedures as defined at
design time, to provide an output to the planner. The
“Allocation Engine” is a specific activity that takes
inputs (resources and tasks) and processes them
using a script. Its output is the allocation of
resources to tasks and more globally procedures. As
a result, this impacts the status of resources and
procedures and consequently the content of
corresponding Items in the repository. So resources
and task Items are updated in the repository using
CRISTAL. The retrieval and update services are
represented by the double arrow between repository
and allocation engine.
Finally the output is validated by the planner and
run by the “Orchestration” module. The
Orchestration module is in charge of both executing
and monitoring the procedures regarding the
allocation model and providing feedback to planner
and the rule manager module. Regarding the
feedback from Orchestration module, the planner
can manually update the output from allocation
engine. This can also be done automatically by the
Rule manager module itself. These operations have
also an impact on the Items in repository. This
simple example illustrates the use of provenance
capture and management in the CRISTAL
empowered version of CIMAG-RA.
CRISTAL-iSE-ProvenanceAppliedinIndustry
457

4 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
This paper has introduced the CRISTAL-iSE project
and outlined its aims and objectives. The major
focus of the project is the collaboration between
academia (UWE) and industry (M1i and Alpha-3i).
During this collaboration the researchers in the
project have been able to demonstrate uses for
CRISTAL and its flexibility, particularly in the area
of provenance exploitation in commercial
applications. Thus the main research focus of the
project is the use of provenance within Industry.
One application of CRISTAL has already been
presented, where CRISTAL has been converted to a
system for BPM use M1i’s Agilium). They have
been collecting data from clients for over ten years.
A potential and new application of CRISTAL is
currently emerging with Alpha-3i’s CIMAG-RA
application. In this application, both the new
versions of Aglium and CRISTAL will be used to
create a Resource Allocation application in the
Human Resources (HR) domain.
From the large datasets that are available
already, an OPM (Open Provenance Model, Moreau
2010) compliant provenance model will be created
to foster collaboration between the wider
provenance research communities. However, this
work is currently on going and will be demonstrated
at a later date.
Currently within the project an initial
requirements gathering exercise has been completed
and initial designs have been created to move
forward with the applications that should arise from
the end of the project. These requirements have led
to a more “modular” design of the CRISTAL system
with allowing a generic core or kernel to be
available to the wider community.
From a functional point of view, the CRISTAL
kernel as is, allows the management of Items such as
process activities or tasks, workflows or procedures,
resources and scripts as defined in previous sections.
It also provides provenance capabilities and
flexibility. To fulfil the Alpha-3i requirements, we
need first to define resources based on interoperable
standards such as HR-XML and ISA 95. This
approach will ease integration with third-party
applications. We will then implement a rule based
engine to provide a logic module on top of the
kernel.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This project has been funded the Marie-Curie
Industrial and Academic Partnership Scheme (IAPP)
scheme. The authors would like to thank their home
organisations and, in particular, Becky Gooby and
Bruno Malagola for their efforts in contributing to
the project.
REFERENCES
Agilium, 2013., http://agilium.fr date accessed Dec 2013.
Anjum, A et al., 2011. Provenance Management for
Neuroimaging Workflows in neuGrid In 3PGCIC '11
Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on
P2P, Parallel, Grid, Cloud and Internet Computing.
IEEE.
Branson, A et al., 2014. CRISTAL: A Practical Study in
Designing Systems to Cope with Change, In Journal
of Information Systems. ELSEVIER.
CMS, 2008. The CMS experiment at the CERN LHC In
Journal of Instrumentation, 3:S08004. IOPSCIENCE.
CRISTAL-iSE, 2013 : http://www.cristal-ise.eu, date
accessed Dec 2013.
Estrella, F et al., 2003. Pattern Reification as the Basis for
Description-Driven Systems In Journal of Software
and System Modelling, 2(2):108–119. SPRINGER.
Goble, C,. 2002. Position statement: Musings on
Provenance, Workflow and (Semantic Web)
Annotations for Bioinformatics In Workshop on Data
Derivation and Provenance. SPRINGER.
Lombardi, M., & Milano, M. (2012). Optimal methods for
resource allocation and scheduling: a cross-
disciplinary survey In Constraints, 17(1), 51-85.
SPRINGER.
May, J et al., 2011. The surgical scheduling problem:
Current research and future opportunities In
Production and Operations Management, 20(3), 392-
405. WILEY.
Moreau, L,. 2010. The Foundations for Provenance on the
Web In Foundations and Trends in Web Science, 2(2–
3):99–241. NOW PUBLISHERS.
Simmhan, Y et al., 2005. A Survey of Data Provenance in
e-Science In SIGMOD RECORD, Vol 34, P. 31-36.
ACM.
Shamdasani, J., et al. 2012. Towards Semantic Provenance
in CRISTAL In Semantic Web in Provenance
Management Workshop (SPWM). CEUR.
Vanden Berghe, G,. 2002. An advanced model and novel
meta-heuristic solution methods to personnel
scheduling in healthcare. PhD dissertation,
UNIVERSITY OF GENT.
Wang, M et al., 2007. A time-and-value centric
provenance model and architecture for medical event
streams In Proceedings of the 1st ACM SIGMOBILE
International Workshop on Systems and Networking.
ACM.
ICEIS2014-16thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
458
