
Methods and Technologies for Wrapping
Educational Theory into Serious Games
Jacqueline Krebs and Klaus P. Jantke
Fraunhofer Institute for Digital Media Technology, Children’s Media Dept., Erich-K¨astner-Str. 1a, 99094 Erfurt, Germany
Keywords:
Game-based Learning, Serious Games, Instructional Design, Pedagogical Patterns, Critical Thinking,
Argumentation Maps, Storyboarding.
Abstract:
Although play does undoubtedly take a significant place in the development of human individuals and animals
allowing for a manifold of risk-free exploration and experiment, contemporary serious games largely fail in
meeting the high expectations of game-based learning. Educators know how to teach. Moreover, they know
how to set up conditions, including approaches to playful education, in which learners can actively engage.
In particular, experienced educators know how to adapt to a particular learner’s needs, wishes and desires.
But digital games including those named serious are computer programs. They do not know about didactics.
There is a need for methods and technologies suitable to bring educational principles and pedagogical patterns
into digital systems intended to enhance learning. The authors advocate the method of storyboarding and the
technology of storyboard interpretation to wrap educational theory into e-learning systems, in general, and
into serious games, in particular. Some comprehensive case study demonstrates the feasibility of this approach.
1 THE AUTHORS’ POSITION
Edutainment started as a serious attempt to
create computer games that taught children
different subjects. Arguably, it ended up as
a caricature of computer games and
a reactionary use of learning theory.
[ (Egenfeldt-Nielsen, 2007), p. 42 ]
Egenfeldt-Nielsen’s critical view at serious games
1
is
supported by a variety of critical studies such as, e.g.,
(Jantke, 2006) and (Jantke, 2007).
Apparently, the crux is “to get educational theory
into serious games”. This key issue is not particular
to serious games, but applies to educational media, in
general.
Latterly, some authors discuss the relevance of a
few educational approaches to game-based learning
(see, e.g., (Jin and Low, 2011), (Kirkley et al., 2011),
(Leemkuil and de Jong, 2011)). Kirkley and his co-
authors, for instance, investigate the way of getting a
five-stage learning cycle
2
of problem-based learning
perspectives (Duffy et al., 2009) realized in a certain
1
See (Sawyer and Smith, 2008) for debating the concept.
2
The topical literature is full of learning cycles ranging
from John Dewey (Dewey, 1938) to David Kolb’s Learning
Style Inventory (Kolb, 1984) to ad hoc cycles in domains
such as nursing education (Murphy et al., 2011).
serious game. The game play is discussed in much
detail, but it remains largely open how to bring the
educational theory into the digital system.
The present contribution is aimed at advocating
the authors’ following position.
Storyboarding is a methodology appropriate for
anticipating user experiences of media interaction
including game play and learning. Consequently,
storyboarding is a methodology of didactic design.
In accordance with (Jantke and Knauf, 2005),
the authors exclusively consider digital storyboards.
Digital storyboards may be easily manipulated by
computer programs for purposes such as checking
completeness and consistency, for instance.
Digital storyboards allow for going even further
as expressed by the authors’ supplementary position
to be advocated by the present paper.
Storyboards may be interpreted algorithmically.
Systems of e-learning, in general, and serious
games, in particular, may run digital storyboards
according to the educators’ specification.
The recent storyboard interpretation technology
(see (Fujima et al., 2013) and (Arnold et al., 2013))
allows for experimenting with variants of educational
principles and pedagogical patterns.
497
Krebs J. and P. Jantke K..
Methods and Technologies for Wrapping - Educational Theory into Serious Games.
DOI: 10.5220/0004955104970502
In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU-2014), pages 497-502
ISBN: 978-989-758-020-8
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

2 BACKGROUND THEORY
Educational perspectives and theories are manifold.
This position paper cannot afford any reasonable
overview. Instead, the authors confine themselves
to their application domain of critical thinking
(Bassham, 2008; Fisher, 2006; Garz et al., 1999).
There is the crucial question of how to wrap, so to
speak, the educational theory of critical thinking and
moral reasoning into some serious digital game.
2.1 Kohlberg’s Psychology
of Moral Development
Kohlberg’s substantial theory of moral development
(Kohlberg, 1984) which was inspired by Piaget’s ap-
proach (Piaget, 1932) is discussed as an example of
a theory that views conscious moral reasoning as a
central component of morality. Kohlberg’s method to
study the strength of moral judgment was quite sim-
ple. He used Piaget’s story-telling technique to tell
people stories involving moral dilemmas. He pre-
sented mainly children and adolescents dilemmas in
which different moral factors conflicted. In each case
was a choice to be considered, for example between
the rights of some authority and the needs of some
deserving individual who is being unfairly treated.
The most famous one is the Heinz dilemma: A
woman was near death from a special kind of cancer.
There was one drug that the doctors thought might
save her. It was a form of radium that a druggist in
the same town had recently discovered. The drug was
expensive to make, but the druggist was charging ten
times what the drug cost him to produce. He paid
$
200 for the radium and charged
$
2,000 for a small
dose of the drug. The sick woman’s husband, Heinz,
went to everyone he knew to borrow the money, but
he could only get together about
$
1,000, which is
half of what it cost. He told the druggist that his wife
was dying and asked him to sell it cheaper or let him
pay later. But the druggist said, “No, I discovered the
drug and I’m going to make money from it.” So Heinz
got desperate and broke into the man’s store to steal
the drug for his wife.
Kohlberg asked then a series of question, e.g.:
• Should Heinz have broken into the laboratory to
steal the drug for his wife? Why or why not?
• Would it change anything if Heinz did not love
his wife?
Kohlberg found that children from many cultures
typically move through a sequence of levels and sub-
stages, although not everyone reaches a higher level
of moral reasoning.
2.2 The Social Intuitionist Model (SIM)
& Moral Foundation Theory (MFT)
The Social Intuitionist Model of moral judgment
(Haidt, 2001) is a valuable contrast to the rational-
ist approach of Kohlberg, where moral reasoning is
described as conscious deliberation. Haidt, instead,
posits that moral judgment is mostly based on auto-
matic processes–moral intuitions–rather than on con-
scious reasoning. People engage in reasoning primar-
ily to find evidence to support their initial intuitions.
Accordingly, the SIM is seen as prequel to the MFT.
Where does morality come from? Why does
morality vary so much across cultures? Is morality
one thing, or many?
In brief, the MFT proposes that six (or more) in-
nate and universally availabale psychological systems
are the foundations of intuitive ethics (Graham et al.,
2011), (Graham et al., 2013)). These so-called moral
foundations are characterized by unique conforming
challenges, contents, triggering stimuli, virtues, and
emotions. In Western cultures issues with Harm/Care
and with Fairness/Cheating dominate. The moral
foundation Harm/Care is triggered by suffering and
distress, especially expressed by one’s own kin. It’s
accompanied by the emotion of compassion. The
Fairness/Cheating foundation deals with equality, co-
operation, and deception. It’s accompanied by the
emotions anger, guilt and gratitude. Further moral
foundations are: Loyalty/Betrayal domains regulate
group cooperation through pride and anger. It under-
lies virtues of patriotism and self-sacrifice for the
group. Whereas Authority/Subversion domains con-
trol hierarchies by recruiting the emotions respect and
fear. It underlies virtues of leadership and follower-
ship. The Sanctity/Degradation domain is referring to
food, health, and sexuality (thus conceiving the body
as sacred). This foundation is mostly accompanied by
feelings of disgust. The latest moral foundation is the
Liberty/Oppression domain and deals with feelings of
reactance and resentment of people toward those who
dominate them and restrict their liberty.
2.3 Argument Mapping
In general, argument mapping (van Gelder, 2013)
(see also (Twardy, 2004)) is described by means of
diagrams which show the structure of an argument or
of a set of arguments. Normally these are box-and-
arrow diagrams (graphs in terms of mathematics, see
section 4.4). Argument mapping is akin to other map-
ping procedures such as mind mapping and concept
mapping, but it focuses on the logical, evidential or
inferential relationships among propositions.
CSEDU2014-6thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
498

3 WRAPPING TECHNOLOGY
Quite intuitively and largely informally speaking,
assume you adopt psychological and/or pedagogical
positions to be implemented within some technology-
enhanced educational framework such as a serious
game. How do you make sure that your theory really
works, i.e. it shapes the human-system interaction?
In other words, how do you wrap, so to speak, the
educational theory in e-learning systems, in general,
and in serious games, in particular?
The authors’ ultimate answer is Storyboarding `a la
(Jantke and Knauf, 2005).
3.1 Storyboarding Human Experience
Storyboarding means the organization of experience
(Jantke and Knauf, 2005). To allow for an effec-
tive computational usage of storyboards throughout
the process of design and implementation (see, e.g.,
section 3.4), storyboards are assumed to be digital.
Conceptually, storyboards are finite, hierarchically
structured, indexed families of finite, directed graphs.
Seen as a family of graphs, every storyboard is
of the form F = {G
i
}
i∈I
, where I is any finite index
set. For simplicity, one may assume I = {1, . . . , k},
where k is any natural number indicating how many
graphs belong to F . Every individual graph G
i
is of
the form [N
i
, E
i
, sub
i
, c
i
], where, as usual N
i
and E
i
denote the nodes and the edges of G
i
, respectively.
The mapping sub
i
: N
i
→ 2
I
is assigning to every node
a set of indices telling which graphs of the collection
may be substituted for this particular node. Further,
the mapping c
i
assigns to every edge some condition
of executability
3
.
Figure 1: Illustration of Alternative Graph Substitutions.
3
Due to the lack of space, all details of logics and log-
ical reasoning are suppressed throughout the present paper.
Variants of logics in use are discussed, e.g., in (Jantke and
Arnold, 1996). Note, furthermore, that the present approach
is slightly different from (Arnold, 1996), where constraints
are not assigned to edges, butto nodes. The approach under-
lying the present paper is more expressive.
For the purpose of the present position paper, it
is sufficient to understand storyboards as collections
of graphs as exemplified in figure 1. Those nodes
which may be subject to graph substitution are called
episodes. Other nodes are called scenes. Every scene
has some meaning in the domain such as showing
some picture or playing some video, presenting some
exercise to users, running an animation, and the like.
3.2 Layered Language of Ludology
(Lenerz, 2009) discusses the description of media ex-
periences on different levels of granularity–the so-
called Layered Languages of Ludology. Similarly,
educational theory has varying levels of abstraction.
Storyboardingis an appropriatetechnologyof top-
down design beginning on high levels of abstraction.
3.3 Pedagogical Patterns
To keep it short, it is sufficient to know that the
authors take the origins such as (Alexander, 1979)
as well as modern ad hoc approaches toward the
needs of digital games research such as (Bj¨ork and
Holopainen, 2004) and (Jantke, 2012) into account.
The unprecedented strength and clarity of formal ap-
proaches such as (Angluin, 1980) is preferred due
to the intention to work with patterns algorithmically
(Jantke, 2009).
This allows for dealing with pedagogical patterns
described largely informally in everyday language (as
in (Pedagogical Patterns Advisory Board, 2012), e.g.)
more stringently using the graph-based storyboarding
approach as adopted in the present publication (see
(Jantke, 2013) for a more comprehensive study).
Pedagogical patterns are–with respect to above-
mentioned Layered Languages of Ludology–lower
level concepts. Patterns of learner activity may be
represented as “smaller” graphs for possibly multiple
usage, i.e. for substitution in different places.
3.4 The Technology of Digital
Storyboard Interpretation
The so-called Storyboard Interpretation Technology
is a very recent technological innovation published
for the first time in (Fujima et al., 2013) and (Arnold
et al., 2013). The essence of this novel approach is
to make digital storyboards immediately executable.
E-learning systems and digital games work like
interpreters–a term and an operational understanding
adopted from computer science–running, so to speak,
on the storyboard. In doing so, the system checks at
every scene how to interact with the human learner.
MethodsandTechnologiesforWrapping-EducationalTheoryintoSeriousGames
499
4 THE GAME-BASED LEARNING
CASE STUDY “CATCH 22”
This section is intended to demonstrate the authors’
positions by means of some practical application: the
serious game “Catch 22”. Wrapping technologies in-
troduced in the preceding section have been deployed
for a certain implementation surveyed in the sequel.
Educational theory is reflected by some storyboard
structures anticipating intended player experiences.
4.1 Underlying Educational Theory
Kohlberg did not ascribe moral development and
moral judgment to innate factors, but rather attributed
the transition between levels (pre-conventional, con-
ventional, post-conventional) as driven by the oppor-
tunities afforded in everyday social interactions. Al-
teration may occur as a result of everyday role tak-
ing and change of perspective fostering empathy, or it
may be driven by reflections about moral situations.
Dilemma-discussion suits perfectly to encourage crit-
ical thinking, perspective changes and moral reason-
ing skills.
Haidt’s SIM, in contrast, is understood as a social
model in that it deemphasizes the private reasoning
and emphasizes, instead, the importance of social and
cultural influences. It states that moral judgment is
a dual process, which is generally caused by quick
moral intuitions, so-called automatic evaluations, and
is followed (when needed) by slow, ex post facto
moral reasoning, so-called effortful conscious mental
activity.
According to (Haidt, 2001), the underlying SIM
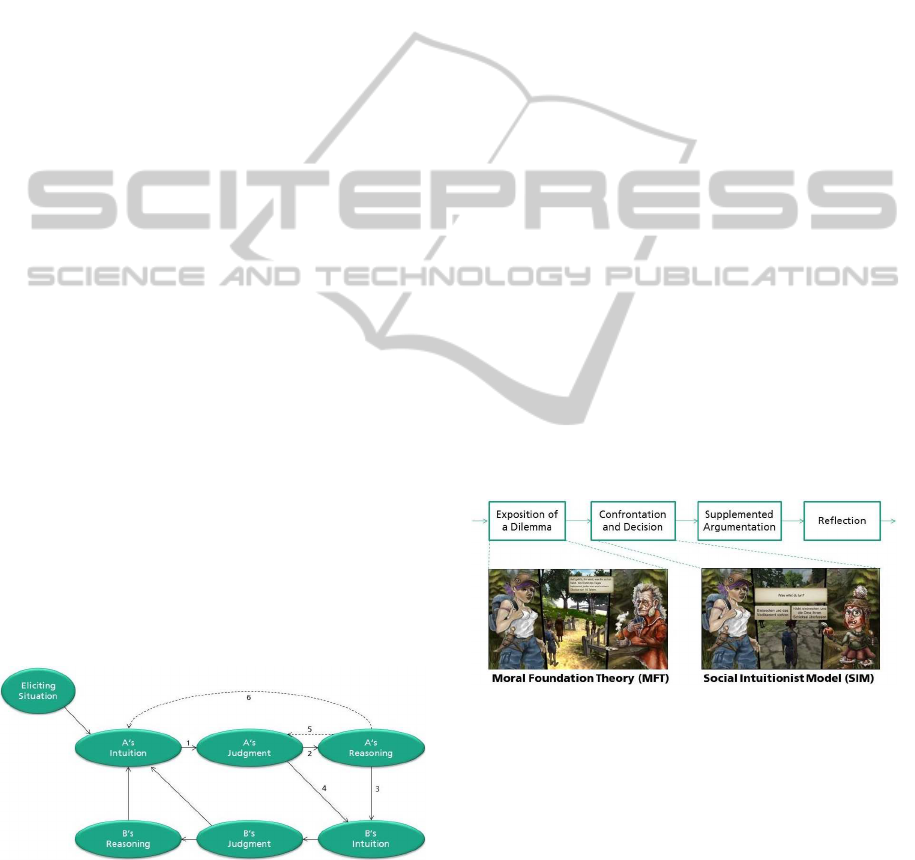
(see section 2.2) is visualized as in figure 2 below.
The numbered links, drawn for Person A only, are
Figure 2: The Social Intuitionist Model of Moral Judgment.
(1) the intuitive judgment link, (2) the post hoc rea-
soning link, (3) the reasoned persuasion link, and
(4) the social persuasion link. Two additional links
are hypothesized to occur less frequently: (5) the rea-
soned judgment link and (6) the private reflection link.
4.2 Top-level Serious Game Design
We implemented Kohlberg’s dilemma-discussion ap-
proach combined with Haidt’s SIM in a digital game
we called “Catch 22” to educate moral reasoning. For
this purpose, we designed six dilemma-situations ref-
erencing the moral foundations mentioned in sec. 2.2.
The player wanders around in a 3D-world, has to
solve quests and deals thereby with various virtual
people who involve the player in moral dilemmas.
The decision making process follows ad-hoc to the
exposition and experience of the dilemma.
Target of the game is to enhance critical think-
ing skills and to raise awareness of the complexity of
moral reasoning. For this purpose, the reasons and
objections, which count for the chosen position, are
structured and arranged in argument maps.
According to the authors’ position advocated by
means of the present paper, emphasis is put on the
question how to wrap, so to speak, Kohlberg’s and
Haidt’s theory into the digital system to be developed.
Didactic principles underlying an e-learning design
and implementation become structurally visible.
4.3 Wrapping Educational Theory
Top-down
To wrap educational theory in a serious game like
“Catch 22”, it was necessary to grapple with game
design.
Figure 3: Some Excerpt from a High Level Storyboard of
“Catch 22 ” Experience of Game Play.
If and when people play games, they have an expe-
rience. It is this experience that a game designer cares
about; because without the experience, the game is
worthless. Experiences are so much part of human
beings, they are hard to think about–even thinking
about experiences is an experience. Although every-
one is familiar with experiences, they are quite hard
to describe. You can’t see them, touch them, or hold
them; above all else you can’t really share them. So
each person’s experience of something is completely
unique, no two people can have identical experiences
of the same thing.
CSEDU2014-6thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
500
To put it straight: The digital game itself is not
the experience. The game enables the experience.
So what we do, when we are talking about wrapping
educational theory, we think about game design, we
create artifacts (sets of rules, game boards, computer
programs, ...) that are likely to create certain kinds of
experiences when human players interact with them.
As a design methodology, we deploy storyboarding
(Jantke and Knauf, 2005).
In figure 3, we imaged an extract of the high level
graph of the designed game experience in “Catch 22”.
4.4 Wrapping Educational Theory
Bottom-up
The argument mapping is embedded into game play.
Motivated after a conscious decision was made in
a dilemma-situation, it promotes clarity and insight,
more detailed and complete articulation, and more
deliberate evaluation. We use argument mapping to
help students to understand how arguments are con-
structed, and how they can enhance their reasoning
skills, by bringing visual clarity to complex issues.
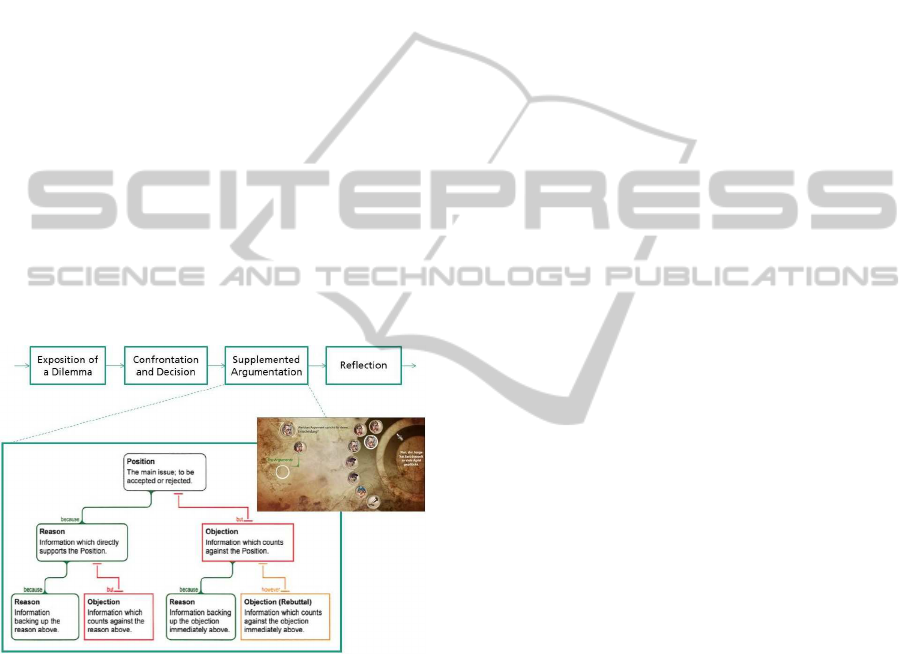
Figure 4: Expansion of an Episode by an Argument Map.
Argument mapping (van Gelder, 2013) can be
an effective way to improve general critical thinking
skills. Argument mapping can also promote rational
reasoning in complex situations and help making bet-
ter decisions in the future.
The argument mapping technique itself is simple
but it is not easy, because it is just a visual discipline
for clarifying our thinking. And clarifying our think-
ing is not easy, even with visual discipline.
To illustrate the issue presented, see figure 4, and
notice that mapping makes it clear which statements
serve as the main conclusion, which serve as reasons
to believe that conclusion, and which statements are
intended as objections to which claims.
5 CONCLUSIONS & OUTLOOK
Even nowadays, far too many systems of technology-
enhanced learning serve mostly administrational pur-
poses such as providing documents to learners
and bookkeeping by teachers. There is a rather
wide consensus that educational theory needs to be
more systematically encoded into digital systems of
technology-enhanced learning such as, for instance,
serious games.
When storyboarding `a la (Jantkeand Knauf, 2005)
is deployed as a design methodology, educational
theory may be reflected syntactically.
For illustration, have a look at the cutout of the
“Catch 22” storyboard on display in the upper part
of figure 4. The linear sequence of four episodes of
game play reflect the sequence of upper nodes in the
visualizations of Haidt’s social intuitionist model as
shown in figure 2.
To put it straight: some pedagogy becomes visible
and, therefore, the difference of varying educational
theories deployed may become visually perceivable.
This opens unprecedented options of debating
didactics and of experimenting with varying didactic
approaches.
The storyboard interpretation technology makes
those experiments operationally feasible, but it needs
some further completion to allow for systematic rou-
tine applications as sketched in (Arnold et al., 2013)
including the development of authoring tools.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors gratefully acknowledge the valuable sup-
port by many colleagues and friends, most notably
Helmut M. Niegemann supervising the first author’s
Ph.D. Thesis at the University of Erfurt, Germany, as
well as Jun Fujima and Sebastian Arnold being the
key designers and developers of the above mentioned
Storyboard Interpretation Technology.
REFERENCES
Alexander, C. (1979). A The Timeless Way of Building. New
York: Oxford University Press.
Angluin, D. (1980). Finding patterns common to a set of
strings. J. Computer and Systems Science, 21:46–62.
Arnold, O. (1996). Die Therapiesteuerungskomponente
einer wissensbasierten Systemarchitektur f¨ur Auf-
gaben der Prozeßf¨uhrung, volume 130 of DISKI.
St. Augustin: infix.
MethodsandTechnologiesforWrapping-EducationalTheoryintoSeriousGames
501

Arnold, S., Fujima, J., Karsten, A., and Simeit, H. (2013).
Adaptive behavior with user modeling and story-
boarding in serious games. In 9th International Con-
ference on Signal Image Technology & Internet-based
Systems, Dec. 2-5, 2013, Kyoto, Japan.
Bassham, G. (2008). Critical Thinking: A Student’s Intro-
duction. Boston: McGraw-Hill, 3rd edition.
Bj¨ork, S. and Holopainen, J. (2004). Patterns in Game De-
sign. Hingham, MA, USA: Charles River Media.
Dewey, J. (1938). Experience & Education. Indianapolis:
Kappa Delta Pi.
Duffy, T. M., Stinson, J., Milter, R., and Kirkley, J. (2009).
Facilitator Guidebook: Inquiry Based Learning Work-
shop. Bloomington, IN, USA: Information in Place
Inc.
Egenfeldt-Nielsen, S. (2007). Educational Potential of
Computer Games. Continuum Studies in Education.
Continuum Intl. Publ. Group.
Fisher, A. (2006). Critical Thinking: An Introduction. Cam-
bridge University Press, 8th edition.
Fujima, J., Jantke, K. P., and Arnold, S. (2013). Digital
game playing as storyboard interpretation. In Pro-
ceedings of the 5th International Games Innovation
Conference (IGIC), Vancouver, BC, Canada, Oct. 1-4,
2013, pages 64–71. IEEE Consumer Electronics Soc.
Garz, D., Oser, F., and Althof, W. (1999). Moralisches
Urteil und Handeln. Frankfurt am Main: Suhrkamp.
Graham, J., , Haidt, J., Koleva, S., Motyl, M., Iyer, R., Woj-
cik, S., and Ditto, P. H. (2013). Moral foundations the-
ory: The pragmatic validity of moral pluralism. Ad-
vances in Experential Social Psychology, 47:55–130.
Graham, J., Nosek, B. A., Haidt, J., Iyer, R., Koleva, S.,
and Ditto, P. H. (2011). Mapping the moral do-
main. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology,
101(2):366–385.
Haidt, J. (2001). The emotional dog and its rational tail: A
social intuitionist approach to moral judgement. Psy-
chological Review, 108:814–834.
Jantke, K. P. (2006). Digital games that teach: A critical
analysis. Diskussionsbeitr¨age 22, TUI IfMK.
Jantke, K. P. (2007). Serious Games – eine kritische Anal-
yse. In 11. Workshop Multimedia in Bildung und
Unternehmen “eLearning and Serious Games”, TU
Ilmenau, 20./21.09.2007, pages 7–14. TU Ilmenau,
ISSN 1436-4492.
Jantke, K. P. (2009). The pattern experience evaluation pro-
gram. In Lige¸za, A. and Nalepa, G. J., editors, Proc.
DERIS 2009: Intl. Workshop on Design, Evaluation
and Refinement of Intelligent Systems, November 28,
2009, Krak´ow, Poland, pages 70–75. AGH University
of Science and Technology.
Jantke, K. P. (2012). Patterns of game playing behav-
ior as indicators of mastery. In Ifenthaler, D., Es-
eryel, D., and Ge, X., editors, Assessment in Game-
Based Learning: Foundations, Innovations, and Per-
spectives, pages 85–103. New York, Heidelberg, Do-
drecht, London: Springer.
Jantke, K. P. (2013). Pedagogical patterns and didac-
tic memes for memetic design by educational story-
boarding. In Arnold, O., Spickermann, W., Spyratos,
N., and Tanaka, Y., editors, Webble Technology,
First Webble World Summit, WWS 2013, Erfurt, Ger-
many, June 2013, volume 372 of Communications in
Computer and Information Science, pages 143–154.
Springer.
Jantke, K. P. and Arnold, O. (1996). A modal temporal logic
and its models underlying variants of planning algo-
rithms. In Chittaro, L., Goodwin, S., Hamilton, H.,
and Montanari, A., editors, TIME–96, Intern. Work-
shop, Key West, FL, USA, May 19–20, 1996, pages
182–187. IEEE Computer Society Press.
Jantke, K. P. and Knauf, R. (2005). Didactic design through
storyboarding: Standard concepts for standard tools.
In Baltes, B. R., Edwards, L., and Galindo, F., editors,
Proc. 4th Int. Symposium on Information and Com-
munication Technologies, Cape Town, South Africa,
January 3–6, 2005, pages 20–25. Computer Science
Press, Trinity College Dublin, Ireland.
Jin, P. and Low, R. (2011). Implications of game use for
explicit instruction. In Tobias, S. and Fletcher, J. D.,
editors, Computer Games and Instruction, chapter 15,
pages 395–416. Information Age Publishing Inc.
Kirkley, J. R., Duffy, T. M., Kirkley, S. E., and Kremer,
D. L. H. (2011). Implications of constructivism for
the design and use of serious games. In Tobias, S.
and Fletcher, J. D., editors, Computer Games and
Instruction, chapter 14, pages 371–394. Information
Age Publishing Inc.
Kohlberg, L. (1984). The Psychology of Moral Develop-
ment: The Nature and Validity of Moral Stages. San
Francisco: Harper & Row.
Kolb, D. A. (1984). Experiential Learning: Experience as
the Source of Learning and Development.
Leemkuil, H. and de Jong, T. (2011). Instructional support
in games. In Tobias, S. and Fletcher, J. D., editors,
Computer Games and Instruction, chapter 13, pages
353–369. Information Age Publishing Inc.
Lenerz, C. (2009). Layered languages of ludology – Eine
Fallstudie. In Beyer, A. and Kreuzberger, G., editors,
Digitale Spiele – Herausforderung und Chance, pages
35–64. Verlag Werner H¨ulsbusch.
Murphy, S., Hartigan, I., Walshe, N., Flynn, A. V., and
O’Brien, S. (2011). Merging problem-based learning
and simulation as an innovative pedagogy in nurse ed-
ucation. Clinical Simulation in Nursing, 7:e141–e148.
Pedagogical Patterns Advisory Board, editor (2012). Ped-
agogical Patterns: Advice for Educators. Joseph
Bergin Software Tools.
Piaget, J. (1932). The Moral Judgement of the Child. Lon-
don: Keagan Paul, Trench, Turbner & Co.
Sawyer, B. and Smith, P. (2008). Serious games tax-
onomy. http://www.seriousgames.org/presentations/-
serious-games-taxonomy-2008
web.pdf.
Twardy, C. R. (2004). Argument maps improve critical
thinking. Teaching Philosophy, 27(2):95–116.
van Gelder, T. (2013). Argument mapping. In Pashler,
H., editor, Encyclopedia of the Mind. Thousand Oaks,
CA: Sage.
CSEDU2014-6thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
502
