
Encompassing Payment for Heterogeneous Travelling
Design Implications for a Virtual Currency based Payment Mechanism for
Intermodal Public Transport
Markus C. Beutel and Karl-Heinz Krempels
RWTH Aachen University, Information Systems, Ahornstr. 55, 52074 Aachen, Germany
Keywords:
Virtual Currency, Mechanism, Incentive, Public Transport, Mobility.
Abstract:
As a result of a huge offering of different traffic modes, peoples mobility behavior is more and more charac-
terized by multi- and intermodality. But this growing demand cannot be satisfied adequately yet. People have
to use numerous separated software platforms and payment schemes to get access to these modes. Whereas
some platforms already offer the access to few transport modes, an unconditional and comprehensive virtual
payment scheme for intermodal travelling is not fully developed yet.
This work examines existing virtual payment mechanisms and projects them onto the setting of the mobility
sector. First, mechanism design is determined by companies strategies, the competitive environment and the
access to the providing software platform. Basis is a scenario of an open software platform that provides
offerings of different independent market actors. Critical for developing a comprehensive mechanism is a
functional integration of (private) vehicle sharing, the consideration of specific product characteristics and
appropriate system restrictions.
1 INTRODUCTION
Innovations and technological development cause a
growing number of alternative traffic modes. For
example, electrification changes the urban landscape
by impacting modes and infrastructure. Furthermore,
peoples mobility behavior changed significantly over
the past decade. They consider and support alterna-
tive transport modes, like car or bike sharing (Rehrl
et al., 2007). People use these offerings and combine
them to heterogeneous travel chains. This issue is be-
coming more and more urgent in our society (Yogesh
Malhotra, 2000). But multi- and intermodal traveling
is still uncomfortable to realize, because of a huge
number of different software platforms, which pro-
vide access to these services.
Whereas intermodal traveling is a coherent activ-
ity for people, the software landscape to realize this
is partially divided. There are already some inten-
tions to consolidate the access to transport modes.
One the one hand, providers establish in-house plat-
forms, which offer access to their own product port-
folio. On the other hand, comprehensive access to
transport modes between different competitors is also
developing.
Table 1 shows some examples of software plat-
forms and their functionalities across the German mo-
bility sector. Common platforms, also called bro-
kers, integrate different mobility modes, combine and
present them concentrated. Across these platforms,
the range of functions varies significantly. The frame
for all following examinations is an open software
platform, which integrates the offerings of indepen-
dent market actors. In the following descriptions,
”open” means the possibility to provide services on
a platform, without discrimination by any superior in-
stance.
Within this context, the payment via virtual cur-
rencies offers highly interesting possibilities. Cash
payment is increasingly substituted through virtual
currencies (Thomas Lammer, 2006). Electronic and
mobile payments are emerging. Forecasts show a
significant rise in global mobile transactions volume
(Statista GmbH, 2013). Virtual currencies originally
are designed as loyalty programs to bound customers
to in-house services. A modified strategy is the co-
operation scheme, also defined as coalition loyalty or
cross loyalty, which describes the facilitation of loy-
alty cards at multiple, possibly competing, retailers
(Buchinger et al., 2013b).
This work gives general design implications for
an e-payment scheme for traveling via multiple trans-
305
Beutel M. and Krempels K..
Encompassing Payment for Heterogeneous Travelling - Design Implications for a Virtual Currency based Payment Mechanism for Intermodal Public
Transport.
DOI: 10.5220/0004977203050310
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Smart Grids and Green IT Systems (SMARTGREENS-2014), pages 305-310
ISBN: 978-989-758-025-3
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

Table 1: Broker Software Matrix.
Platform Moovel
1
(Daimler Mobility
Services)
DB Navigator
2
/ bahn.de
3
(Deutsche Bahn AG)
quixxit.de
4
(Deutsche Bahn
AG)
Region urban region offering national public transport offerings in Germany
Functionalities information, routing, naviga-
tion, ticketing
information, routing, naviga-
tion, assistance, ticketing
information, routing, naviga-
tion, assistance, ticketing
Modes local public transport, taxi, car
sharing, bike sharing
local public transport, taxi, car
sharing, bike sharing
local public transport, taxi,
car sharing, bike sharing (re-
duced functionalities concern-
ing flight offerings, rental cars,
ferry boats, ...)
User interfaces web service, mobile application web service, mobile application web service, mobile application
port modes within one route. Therefore, the concep-
tual basis and the general requirements of the mobil-
ity sector are described in part two. The third part
discusses the applicability of existing virtual curren-
cies on intermodal urban public transport. Thereupon,
some recommendations are stated to develop a consti-
tutive framework of a virtual currency mechanism for
intermodal travelling.
2 CONCEPTUAL BASIS
To establish a basic understanding, Figure Figure 1
defines the general scope of the context. Furthermore
it pictures the relations between stated terms and def-
initions, used in the following.
Platform
Mechanism
Provider
Ticket Product
Portfolio
Customer Services
Virtual Currency
Figure 1: Conceptual Basis.
Transactions between customers and mobility ser-
vice providers are enabled via an open software plat-
form for multimodal transport services. A Virtual
Currency (VC) is a fundamental instrument of pay-
ment, on which the constitutive mechanism relies.
The virtual currency mechanism regulates the specific
way of cash flows and transactions. Within this con-
text certain interdependencies determine the design of
each component. To develop a suitable and benefi-
cial virtual currency based mechanism for intermodal
travelling, it is essential to consider these interdepen-
dencies, especially in the mobility sector.
Because shared based transport modes are a grow-
ing part of intermodal travelling, integrating them is
desirable, but challenging. Compared to traditional
modes, car or bike sharing is distributed in a different
way. The offerings vary significantly in terms of ca-
pacity, characteristic, location and price. Therefore, it
highly depends on individual preferences. A virtual
currency based mechanism has to project these indi-
vidual preferences in an adequate way.
(Buchinger et al., 2013a) showed an inclusion of
vehicle sharing into a theoretical concept of a virtual
currency. It offers the possibility of a multimodal
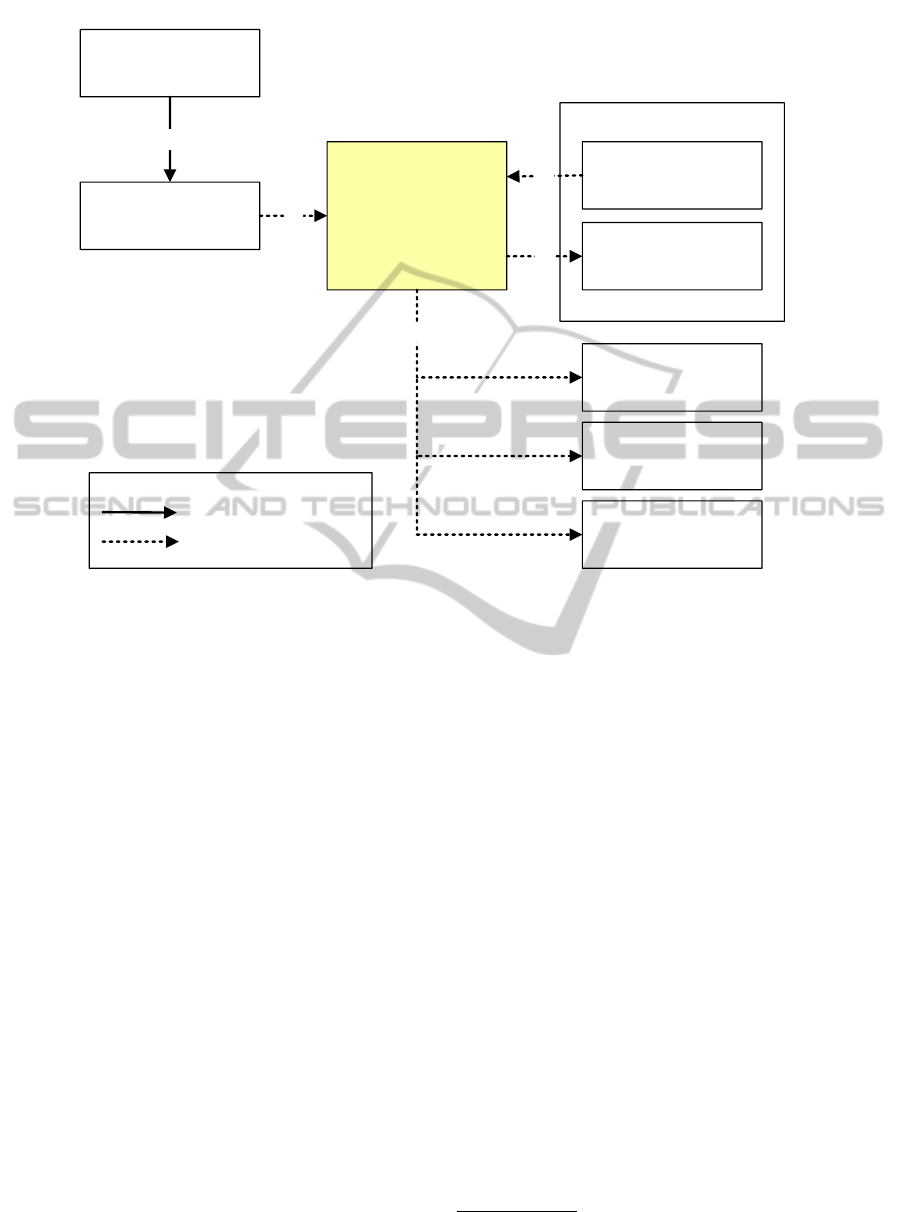
portability towards other transport modes. Figure 1
shows the systematical virtual currency flows under
consideration of vehicle sharing. All activities are
centralized in a personal digital wallet. This method
is already practiced in various virtual currency based
concepts, e.g. ClickandBuy
5
. Virtual currency funds
can be received by exchange for cash money or by
providing private vehicle capacities. Earned amounts
of private car sharing can directly be reused for trav-
ellings via other transport modes.
This primer is not solely sufficient to develop a
practicable currency scheme. Currency and in addi-
tion mechanism design are not only determined by
transport mode specifications, but also by provider’s
product portfolio conditions. Within this work, prod-
ucts are defined as tickets, which authorize customers
to use different services on certain prices. Obviously
in the mobility sector, product characteristics diverge
significantly compared to other industries. The con-
sideration of this fact is a necessary enhancement of
existing concepts. For example, some tickets have a
time limited subscription towards the usage of special
transport modes. This attribute impacts virtual cur-
rency flows substantially.
5
https://www.clickandbuy.com/DE de/home.html
SMARTGREENS2014-3rdInternationalConferenceonSmartGridsandGreenITSystems
306
PERSONAL
DIGITAL WALLET
TRAIN
VEHICLE SHARING
BUS
CUSTOMER
CAPACITY
PROVISION
CAPACITY
UTILIZATION
...
$
Virtual Currency
Management
VC
VC
VC
VC
Virtual Currency flow
Cash flow
Legend
Figure 2: Multimodal Cash Flows.
3 VIRTUAL CURRENCY
MECHANISMS IN CONTEXT
OF INTERMODAL TRAVELING
There is a large variety of loyalty concepts on vir-
tual basis. (Buchinger et al., 2013b) examined vari-
ous virtual currency schemes in detail. This constitu-
tive work, investigates especially the applicability of
existing concepts, or components of them, to urban
public transport.
3.1 Miles and More
The Miles and More program rewards customers with
miles per flight with the German airline Lufthansa.
Originally designed to raise customer loyalty towards
the German airline, the program became extended:
miles are now not only rewarded to customers, but
also sold to third parties, e.g. banks, retailers and ho-
tels. More concrete, the platform sells the ability to
reward miles to third parties. Those miles expire at
the end of a respective time period (Buchinger et al.,
2013b).
Synergy effects enhance also third party services
with additional value for the customer and for the
primer platform service. As a drawback, the system
favors a centralized service. Under certain circum-
stances cooperation between competitors is indeed
possible, however only by subordination to a general
instance and a favored service. Various mechanisms
have this feature in common, because of strategical
considerations by service providers. But this fact hin-
ders the nonrestrictive integration of private car shar-
ing and therefore it is not applicable to the reference
scenario. In contrast to this, the constraint of expos-
ing virtual currency funds is quite practicable in the
context of urban public transport. Intensifying the in-
centives of the mechanism is one possibility and also
feasible option.
3.2 Bahn.bonus
The bonus point system by the German mobility
provider Deutsche Bahn, bahn.bonus
6
, rewards cus-
tomers for travelling with different transport modes.
It refers to a multimodal offering, but is limited to in
house modes only. Bonus points can be reinvested
for travellings at discounted prices, or exchanged for
other products, e.g. suitcases. Furthermore the sys-
tem offers the possibility to classify customers into
6
http://www.bahn.de/p/view/bahncard/bahnbonus
/bahnbonus.shtml
EncompassingPaymentforHeterogeneousTravelling-DesignImplicationsforaVirtualCurrencybasedPayment
MechanismforIntermodalPublicTransport
307

levels. There is another sort of points, called status
points, which solely serve to upgrade a personal level.
This enables customers to get access to additional ser-
vices or other benefits. In other words, a personal
bonus point deposit consists of two types of bonus
points with diverging functions.
3.3 Facebook Credits
Facebook Credits support loyalty towards other ser-
vice providers, but moreover create a source of rev-
enue from the platform’s customer basis. Third party
developers are able to provide services, e.g. gaming
applications, which can be used due to the platform.
Facebook credits serve the virtual currency mecha-
nism within this specific application. Facebook’s cur-
rency is automatically converted to the currency, used
in the application. This process is not recognized by
the application users (Buchinger et al., 2013b).
Although this system is originally not operating
in the mobility sector, its characteristics can fit to
this area: the mechanism is suitable to consolidate
different services hosted by independent providers.
The key advantage is the function of keeping loyalty
towards individual third party providers sustainable.
Thereby the basic function of loyalty programs can
be maintained towards separated companies.
3.4 Auctions
The offerings of car sharing are characterized by a
large variety and complexity. People have individ-
ual and heterogeneous preferences which determine
their decisions. A functional virtual currency mecha-
nism has to be designed under consideration of these
circumstances. In this context, the fact of conflicting
preferences is critical. An auction seems to be adap-
tive to picture individual preferences and solve con-
flicts connected to them.
(Krempels, 2009) investigates different options of
solving agent preference based conflicts. The stated
auctions, where a secret bidding round occurs and the
highest bid is the winning one, are called announce-
ments. These announcement auctions can be modeled
in different forms: first, only the winner has to pay his
bid and all losing entities keep their amounts com-
pletely on their own. A second possibility is to dis-
tribute shares of the winning amount between all los-
ing entities. An increase of funds across the loosing
entities effects an improved preference conflict solv-
ing. In matters of this procedure, there a some possi-
ble variations stated. Simulation results showed that a
predefined, time based decay of money added by auc-
tions, is the most promising solution to solve these
conflicts. Diverse constraints ensure the stability of
the overall system.
Despite these simulation results, such an e-
payment concept could be problematical in terms of
broad consumer acceptance. On the one hand, using
this auction system might be less intuitive for cus-
tomers. On the other hand, the system might be too
complex to manage. In fact a simplified auction sys-
tem should be considerated.
4 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
Choosing the right design of a virtual currency based
payment mechanism overall depends on companies
strategies, the form of providing their services and the
competitive environment. The rate of discrimination
concerning a platform access determines these factors
in large part. Therefore the way of cooperation be-
tween companies to provide intermodal traveling is
essential. In this case, examinations focus on a sce-
nario, within an open software platform, which pro-
vides offerings of different entities without discrim-
ination. There are preliminary considerations about
establishing a virtual payment scheme in this spe-
cific context (Buchinger et al., 2013b). This work
advances these considerations by the following impli-
cations:
Product Portfolio Chracteristics
Central implication for designing a virtual currency
based mechanism for intermodal traveling is the con-
ceptual consideration of provider’s product portfo-
lio characteristics. Ticket products diverge signifi-
cantly from products distributed in other industries.
Many ticket products allow transport mode utilization
through time limited subscriptions. An adequate vir-
tual currency mechanism has to feature these condi-
tions in a flexible way. This characteristic also aggra-
vates the integration of vehicle sharing.
Vehicle Sharing Integration
The integration of a highly diverging modes is chal-
lenging but offers extensive value potentials. Com-
bining traditional modes with vehicle sharing means
to connect two different transaction methods alto-
gether via a virtual currency based mechanism. Fig-
ure 3 shows a conceptual mechanism integration.
Users’ personal digital wallet consists of two com-
ponents: The first components allows the unlimited
participation on transport services in a certain time,
based on a subscription agreement. Within this part,
SMARTGREENS2014-3rdInternationalConferenceonSmartGridsandGreenITSystems
308

PERSONAL DIGITAL WALLET
VEHICLE SHARING
Flexible Component
CUSTOMER
CAPACITY
PROVISION
CAPACITY
UTILIZATION
$
Virtual Currency
Management
VC
VC
VC
Virtual Currency flow
Cash flow
Legend
Constant Subscribtion Component
BUS
UTILIZATION
TRAIN
UTILIZATION
...
Figure 3: Compined Digital Wallet Scheme.
no virtual cash flows need to occur - depending on
the certain ticket conditions. The second component
includes a predefined amount of virtual coins. These
coins can be earned for providing vehicle capacities
and are reusable for car sharing or other services.
This combination allows the flexible integration of
(private) vehicle sharing. Furthermore this scheme al-
lows to model preferences via auctions. Compared to
traditional transport modes, vehicle sharing depends
substantial on specific vehicle attributes and individ-
ual customer preferences. An auction seems to be
adaptive to reflect individual preferences and solve
conflicts connected to them. In fact it could allo-
cate more efficiently with regard to these conditions.
Auctions can be constructed in diverse forms. These
forms feature different potential of preference conflict
solving, but consumer acceptance has to be consid-
ered in addition.
System Restrictions
This leads to another implication: an establishment
of mechanism restrictions. Virtual currency mech-
anism restrictions are already approved in other ar-
eas. For example expiring currencies are well adap-
tive to the mobility context. Thus incentives regu-
late customer behavior and foster the system balance.
Another adaptive restriction is a limitation of earned
amounts by providing capacities of vehicle sharing.
A concrete form is to avoid, that the earned currency
amounts exceeds a predefined starting budget. This
prevents the systematic disadvantage of other trans-
port modes.
4.1 Future Work
This investigation is intended to form a conceptual ba-
sis for a virtual currency mechanism on an open soft-
ware platform for intermodal traveling. This mecha-
nism is going to be modeled and technologically real-
ized. Refering to this, there are already some reliable
technical solutions connected to this area. For exam-
ple concerning payment APIs or virtual currencies,
which have to be considered as well. Subsequently,
the procedures are going to be evaluated to examine
the basic contributions.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was founded by German Federal Ministry
of Economics and Technology for project Mobility
Broker.
EncompassingPaymentforHeterogeneousTravelling-DesignImplicationsforaVirtualCurrencybasedPayment
MechanismforIntermodalPublicTransport
309

REFERENCES
Buchinger, U., Lindmark, S., and Braet, O. (2013a). Busi-
ness Model Scenarios for an Open Service Platform
for Multi-Modal Electric Vehicle Sharing. In Second
International Conference on Smart Systems, Devices
and Technologies (SMART 2013), number c, pages 7–
14, Roma, Italy.
Buchinger, U., Ranaivoson, H., and Ballon, P. (2013b). Vir-
tual Currency for Online Platforms - Business Model
Implications. In Proceedings of The 10th Inter-
national Conference on Electronic Business (ICE-B
2013), pages 196–206, Reykjavik, Iceland.
Krempels, K.-H. (2009). Agentenbasierte Ablaufplanung -
unter besonderer Betrachtung der pr
¨
aferenzbasierten
Diensteinsatzplanung [Agent-based Resource Planing
- Under Special Consideration of Human Resource
Planing]. Shaker Verlag GmbH.
Rehrl, K., Bruntsch, S., and Mentz, H.-J. (2007). Assisting
Multimodal Travelers: Design and Prototypical Im-
plementation of a Personal Travel Companion. IEEE
Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems,
8(1):31–42.
Statista GmbH (2013). Global mobile payment transaction
volume from 2011 to 2017.
Thomas Lammer (2006). Handbuch E-Money, E-Payment
and M-Payment. Physica-Verlag.
Yogesh Malhotra (2000). Knowledge Management and Vir-
tual Organizations. Idea Group Publishing.
SMARTGREENS2014-3rdInternationalConferenceonSmartGridsandGreenITSystems
310
