
Mining User Behavior in a Social Bookmarking System
A Delicious Friend Recommender System
Matteo Manca, Ludovico Boratto and Salvatore Carta
Dipartimento di Matematica e Informatica, Universit
`
a di Cagliari, Cagliari, Italy
Keywords:
Social Bookmarking, Friend Recommendation, Tagging System.
Abstract:
The growth of the Web 2.0 has brought to a widespread use of social media systems. In particular, social
bookmarking systems are a form of social media system that allows to tag bookmarks of interest for a user and
to share them. The increasing popularity of these systems leads to an increasing number of active users and
this implies that each user interacts with too many users (“social interaction overload”). In order to overcome
this problem, we present a friend recommender system in the social bookmarking domain. Recommendations
are produced by mining user behavior in a tagging system, analyzing the bookmarks tagged by a user and
the frequency of each used tag. Experimental results highlight that, by analyzing both the tagging and book-
marking behavior of a user, our approach is able to mine preferences in a more accurate way, with respect to
state-of-the-art approaches that consider only tags.
1 INTRODUCTION
Social media systems are defined as “web-based ser-
vices that allow individuals to (1) construct a pub-
lic or semi-public profile within a bounded system,
(2) articulate a list of other users with whom they
share a connection, and (3) view and traverse their
list of connections and those made by others within
the system” (Boyd and Ellison, 2007). Moreover, in
their 2011 tutorial (Guy and Carmel, 2011), Guy et.
al highlight that a social media system is character-
ized by: (1) a user-centered design, (2) user-generated
content (e.g., tags), and (3) social networks and online
communities.
A social bookmarking system is a form of social
media, which allows users to use keywords (tags) to
describe resources that are of interest for them, help-
ing to organize and share these resources with other
users in the network (Farooq et al., 2007). The most
widely-known example of social bookmarking sys-
tem is Delicious
1
.
In this domain, where users are connected in a so-
cial network and interact with each other, the growth
of the user population and the large amount of content
lead to the well-known “social interaction overload”
problem (Guy et al., 2013; Simon, 1971). Social in-
teraction overload is related to the excessive amount
1
http://www.delicious.com
of users and items that each user can interact with.
This leads to the scarcity of attention, which does not
allow to focus on users or items that might be inter-
esting for a user.
In order to filter information in the social media
systems domain, in the last few years the research on
recommendation has brought to the development of a
new class of systems, named social recommender sys-
tems (Ricci et al., 2011). These systems allow to face
the social interaction overload problem, by suggest-
ing users or items that users might be interested in. In
particular, user recommendation in a social domain
aims at suggesting friends (i.e., recommendations are
built for pairs of users that are likely to be interested
in each other’s content) or people to follow (i.e., rec-
ommendations are built for a user, in order to sug-
gest users that might be interesting for her/him) (Guy
et al., 2013).
Social user recommender systems can be classi-
fied into three categories:
1. Systems based on the analysis of social graphs,
which explore the set of people connected to the
target user, in order to produce recommendations.
These systems recommend either the closest users
in the graph, like friends of friends and followees
of followees (the “People you may know” fea-
ture offered by Facebook (Ratiu, 2008) is the most
widely known example of this approach), or rec-
ommend the users that have the highest probabil-
331
Manca M., Boratto L. and Carta S..
Mining User Behavior in a Social Bookmarking System - A Delicious Friend Recommender System.
DOI: 10.5220/0005000203310338
In Proceedings of 3rd International Conference on Data Management Technologies and Applications (DATA-2014), pages 331-338
ISBN: 978-989-758-035-2
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

ity to be crossed in a random walk of the social
graph (the main reference for this type of systems
is the “Who to follow” recommendation in Twit-
ter (Gupta et al., 2013)).
2. Systems that analyze the interactions of the users
with the content of the system (tags, likes, shares,
posts, etc.). In order to exploit the user interests,
these systems usually build a user profile by giv-
ing a structured form to content, thanks to the use
of metrics like TF-IDF (Term Frequency - Inverse
Document Frequency). An example of this class
of systems is presented in (Chen et al., 2009).
3. Hybrid systems, which consider both the social
graph and the interactions of the users with the
content (an example is represented by (Hannon
et al., 2010)).
It is important to notice that the recommendation
of a friend involves mutual interests and that the list
of recommended friends might be different from the
list of recommended people to follow. To the best of
the authors’ knowledge, no approach in the literature
recommends friends in a social bookmarking system.
In (Gupta et al., 2013), authors highlight that Twit-
ter is an “interest graph”, rather than a “social graph”.
A problem highlighted by the authors is that the anal-
ysis of such a graph suffers from scalability issues
and, in order to contain the complexity of the recom-
mender system, no user profile information could be
used to produce the recommendations. The definition
of interest graph can also be extended to social book-
marking systems, since a user can add as a friend or
follow another user, in order to receive her/his newly
added bookmarks.
This paper presents a friend recommender system
in the social bookmarking domain. By mining the
content of the target user, the system recommends
users that have similar interests. Given the previously
presented limitations of analyzing interest graphs and
considered the fast-growing nature of social media
systems, our recommender system makes a selective
use of the available information and does not con-
sider the graph. Moreover, it has been compared with
two reference systems, in order to evaluate the perfor-
mance in terms of precision.
Our work brings the following scientific contribu-
tions:
• for the first time in the literature, we formally de-
fine a friend recommender system that operates in
a social bookmarking system;
• we propose the first algorithm in literature that
recommends friends in this domain (other ap-
proaches in the literature recommend people to
follow but, as previously highlighted, this is a dif-
ferent research topic);
• we study how to mine content in this context, i.e.,
what information should be used to produce the
recommendations and which importance should
the different types of content have in the recom-
mender system. This is done by observing the be-
havior of users in their bookmarking activity.
The proposed system, thanks to its capability to
exploit the interests of the users and being the first
developed in this domain, puts the basis to a research
area not previously explored by the existing social
recommender systems.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows:
Section 2 presents a formalization of a social book-
marking system and of the friend recommendation
problem; Section 3 describes the details of the rec-
ommender system presented in this paper; Sec-
tion 4 illustrates the conducted experiments; Section 5
presents related work; Section 6 contains comments,
conclusions and future work.
2 FRIEND RECOMMENDATION
IN A SOCIAL BOOKMARKING
SYSTEMS
This section gives a formal definition of a social book-
marking system and of a friend recommender system
in this domain.
Definition 1. A social bookmarking system can be de-
fined as a tuple Q = {U, R, T, A,C}, where:
• U , R, and T are sets of users, resources, and tags;
• A is a ternary relation between the sets of users,
resources, and tags, i.e., A ⊆ U × R × T , whose
elements are the tag assignments of a user for a
resource;
• C is a binary relation between the users, i.e.,
C ⊆ U ×U, whose elements expresses the connec-
tion among two users. If we represent the user so-
cial relations by means of a graph, in which each
node represents a user u ∈ U and each edge c ∈ C
represents a connection among two users, we will
have an undirected edge if the users are connected
as friends and a directed edge if one user follows
the other.
Definition 2. A friend recommender system in a so-
cial bookmarking is a function f : U ×U → C, which
allows to define if, given two users u ∈ U and m ∈ U,
there is a undirected connection c ∈ C among them.
This paper aims at developing algorithms that
learn the function f , which allows to produce recom-
mendations among two users.
DATA2014-3rdInternationalConferenceonDataManagementTechnologiesandApplications
332

3 FRIEND RECOMMENDATION
BY MINING USER BEHAVIOR
3.1 System Design
The objective of our work is to build a friend recom-
mender system in the social bookmarking domain. In
its design, we considered the following aspects:
(a) As mentioned in the Introduction, the connec-
tions among users form an “interest graph”.
Therefore, exploiting user interests was crucial in
the development of the recommendations. In lit-
erature, it is known that the methods that analyze
graphs cannot exploit interests and are not scal-
able (Gupta et al., 2013). So, a solution that mines
user behavior in a social bookmarking system, in
order to derive her/his interests, is needed.
(b) Social media systems grow rapidly. This means
that the amount of content added to a social me-
dia system and the user population increase at a
fast rate. A recommender system that operates in
this context needs to build accurate profiles of the
users, which have to be up-to-date with the con-
stantly evolving preferences of the users.
(c) As (Zhou et al., 2010) highlights, the tagging ac-
tivity of the users reflects their interests. There-
fore, the tags used by a user are an important
source of information to exploit the interests of
a user.
Taking into account all these aspects, we designed
a recommender system that operates in the following
way.
Regarding point (a), we designed a system that
only analyzes the content of the users (i.e., the tagged
bookmarks). So, in order to avoid the limitations re-
lated to the graph analysis in this domain, our system
belongs to the second class presented in the Introduc-
tion, i.e., the one that analyzes the interactions of the
users with the content of the system.
Regarding point (b), in order to efficiently and
quickly update user profiles, our system computes
user similarities with low computational cost metrics,
which exploit the set of resources used by each user
and the tags used to classify them.
Regarding point (c), we embraced the theory that
user interest is reflected by the tagging activity and
we extended it, by following the intuition that users
with similar interests make a similar use of tags and
bookmark the same resources.
A detailed description of the system is presented
next.
3.2 Algorithms
Given a target user u
t
∈ U, the system recommends
the users with a high tag-based user similarity and a
high user interest. The system works in five steps:
1. Tag-based user profiling. Given the tag assign-
ments of each user, this step builds a user profile,
based on the frequencies of the tags used by a user.
2. Resource-based user profiling. Given the tag as-
signments of each user, this step builds a user pro-
file, based on the resources bookmarked by a user.
3. Tag-based similarity computation. The first met-
ric, calculated among a target user u
t
and the other
users, is based on the tag-based user profile. Pear-
son’s correlation is used to derive the similarity.
4. User interest computation. The second computed
metric is the interest of a user towards another user
and it is represented by the percentage of common
resources among them.
5. Recommendations selection. This step recom-
mends to u
t
the users with both a tag-based and
a user interest higher than a threshold value.
In the following, we will give a detailed descrip-
tion of each step.
3.2.1 Tag-based User Profiling
This step builds a user profile, based on the tags avail-
able in the tag assignments of a user, by considering
the frequency of each used tag. Given the sets defined
in Section 2, we can first consider the tag assignments
of a user u as follows:
Definition 3. Let A(u) ⊆ A, be the subset of A, whose
elements are the triples that contain a user u ∈ U, i.e.,
∀r ∈ R ∧ ∀t ∈ T, (u, r,t) ∈ A ⇒ (u, r, t) ∈ A(u).
Given a tag t, we can consider all the elements in
which the tag was assigned by user u:
Definition 4. Let A(u,t) ⊆ A(u), be the subset of A(u),
whose elements are all the triples that contain a tag
t ∈ T used by a user u ∈ U, i.e., ∀r ∈ R, (u, r,t) ∈
A(u) ⇒ (u, r,t) ∈ A(u, t).
A user can be profiled, according to her/his use
of the tags, by considering the relative frequency of
each tag, as follows:
v
ut
j
=
#A(u,t
j
)
#A(u)
(1)
Equation 1 estimates the importance of a tag t
j
∈ T
in the profile of a user u ∈ U, by defining the relative
frequency as the number of times t
j
was used, divided
by the number of tag assignments of u.
MiningUserBehaviorinaSocialBookmarkingSystem-ADeliciousFriendRecommenderSystem
333

A tag-based user profile can be implemented
by representing each user u ∈ U as a vector
−→
v
u
=
{v
u1
, v
u2
, ..., v
uk
}, where each element v
u j
is the rela-
tive frequency previously defined and k is the number
of tags in the system.
3.2.2 Resource-based User Profiling
This step builds another user profile, based on the re-
sources bookmarked by each user.
A resource-based user profile can be built by con-
sidering the fact that the user bookmarked a resource
(i.e., she/he expressed interest in it):
v
ur
j
=
1 if ∃t ∈ T | (u, r
j
,t) ∈ A(u)
0 otherwise
(2)
Eq. 2 estimates the interest of a user u in a resource
r
j
with a binary value, equal to 1 in case r
j
was book-
marked by u, and 0 otherwise.
A resource-based user profile can be implemented
by representing each user u ∈ U by means of a bi-
nary vector
−→
v
u
= {v
u1
, v
u2
, ..., v
un
}, which represents
the resources tagged by each user. Each element v
u j
is defined as previously illustrated and n is the number
of resources in the system.
3.2.3 Tag-based Similarity Computation
Since in (Zhou et al., 2010) authors highlight that the
interests of the users are reflected in their tagging ac-
tivities, our system computes the similarity among
two tag-based user profiles with the Pearson’s corre-
lation coefficient (Pearson, 1896). This metric was
chosen because, as proved by Breese et al. (Breese
et al., 1998), it is the most effective for the similarity
assessment among users.
Let (u, m) be a pair of users represented respec-
tively by vectors
−→
v
u
and
−→
v
m
. Our algorithm computes
the tag-based user similarity ts as defined in Eq. 3:
ts(u, m) =
∑
j⊂T
um
(v
ut
j
−
v
u
)(v
mt
j
− v
m
)
q
∑
j⊂T
um
(v
ut
j
− v
u
)
2
q
∑
j⊂T
um
(v
mt
j
− v
m
)
2
(3)
where T
um
represents the set of tags used by both
users u and m and values v
u
and v
m
represent, respec-
tively, the mean of the frequencies of user u and user
m. The metric compares the frequencies of all the tags
used by the considered users. The similarity values
range from 1.0, that indicates complete similarity, to
−1.0, that indicates complete dissimilarity. Negative
values are not significant to evaluate the correlation
among users (Herlocker et al., 1999), so they are dis-
carded by the task.
3.2.4 User Interest Computation
Given a pair of users (u, m), in this step we compute
two metrics based on the bookmarks tagged by the
users. The former, ui(u, m), represents the interest of
the user u towards user m, while the latter, ui(m, u),
represents the interest of the user m toward the user u.
We first consider the set of resources bookmarked
by each user.
Definition 5. Let R(u) ⊆ R be the subset of resources
used by a user u ∈ U, i.e., ∀r ∈ R, (u, r,t) ∈ A(u) ⇒
r ∈ R(u).
Then we consider the resources in common
among two users.
Definition 6. Let D(u, m) = R(u)∩R(m) be the subset
of resources bookmarked by both user u and user m.
The user interest of a user u in a user m can be
estimated as:
ui(u, m) =
#D(u, m)
#R(u)
(4)
The level of interest of a user u in a user m is es-
timated as the number of resources bookmarked by
both the users, divided by the number of resources
bookmarked by user u. This means that the inter-
est of the user m in user u depends on the number
of resources bookmarked by m (i.e., when calculating
ui(m, u), the denominator would be #R(m)).
User interest ui previously defined, can be imple-
mented, by using the two resource-based user profiles
−→
v
u
and
−→
v
m
, as follows:
ui(u, m) =
∑
n
j=1
v
ur
j
v
mr
j
∑
n
j=1
v
ur
j
∗ 100 (5)
ui(m, u) =
∑
n
j=1
v
ur
j
v
mr
j
∑
n
j=1
v
mr
j
∗ 100 (6)
where n is the total number of resources of the
system.
3.2.5 Recommendations Selection
Once the tag-based similarities and the user interests
have been computed for each pair of users, our system
choses a set of users to recommend to the target user
by selecting:
• the ones that have a tag-based user similarity
higher than a threshold value α (i.e., ts > α);
• the ones that have a user interest (at least one of
the two computed) higher than a threshold value
β (i.e., ui > β).
DATA2014-3rdInternationalConferenceonDataManagementTechnologiesandApplications
334

Definition 7. Given a target user u
t
, the candidate set
of users to recommend S(u
t
) can be defined as
S(u
t
) = {u
i
∈ U |ts(u
t
, u
i
) > α&&(ui(u
t
, u
i
) > β)k
(ui(u
i
, u
t
) > β)} (7)
4 EXPERIMENTAL
FRAMEWORK
This section presents the framework used to perform
the experiments.
4.1 Dataset and Pre-processing
Experiments were conducted on a Delicious dataset
distributed for the HetRec 2011 workshop (Cantador
et al., 2011). It contains:
• 1867 users, which represent the elements of the
set U previously defined;
• 69226 URLs, which represent the elements of the
set R previously defined;
• 53388 tags, which represent the elements of the
set T previously defined;
• 7668 bi-directional user relations, which represent
the elements of the relation C previously defined;
• 437593 tag assignments (i.e., the tuples
(user,tag,URL)), which represent the elements
of the relation A previously defined;
• 104799 bookmarks (i.e., the distinct pairs
(user,URL)), which represent the elements of the
union of the subsets R(u) previously defined.
We pre-processed the dataset, in order to remove the
users that were considered as “inactive”, i.e., the ones
that used less than 5 tags or less then 5 URLs.
4.2 Metrics
Definition 8. Let W be the total amount of rec-
ommendations produced by the system, i.e., W =
∪S(u
t
), ∀u
t
∈ U . This set represents the positive out-
comes, i.e., the sum of the true positive and the false
positive recommendations.
Definition 9. Let Z be the amount of correct recom-
mendations produced by the system, i.e., Z ⊆ W =
{(u, m)|(u, m) ∈ W ∧ (u, m) ∈ C}. So, Z represents
the subset of recommendations for which there is a
relation (i.e., a friend correlation) in the dataset. This
subset represents the true positive recommendations.
Given the previously defined two sets, we can
measure the precision of our recommender system as
the number of correct recommendations, divided by
the number of recommendations produced:
precision =
true prositive
true prositive + f alse positive
=
#Z
#W
(8)
Even if the recall metric is usually computed along
with precision, it captures a perspective that differs
from the way our system operates. We propose a
constraint-based approach that reduces the amount of
selected users, while recall measures completeness
and quantity of recommendations (Buckland and Gey,
1994). Because of the nature of the metric, it would
be misleading to compute it in order to evaluate the
accuracy of our system.
Definition 10. Let X ⊆ U be the subset of users for
which a recommendation was produced, i.e., X =
{u ∈ U|∃(u, m) ∈ W }
Definition 11. Let Y ⊆ U be the subset of users for
which a correct recommendation was produced, i.e.,
Y = {u ∈ U|∃(u, m) ∈ Z}
The percentage of users satisfied by the recom-
mendations can be computed by dividing the set of
users for which a correct recommendations was pro-
duced by the set of users for which a recommendation
was produced, as follows:
% satis f ied users =
#Y
#X
∗ 100 (9)
The two metrics evaluate the system from two
similar (but different) perspectives. In fact, precision
measures for how many couples of users a correct
recommendation was produced, while the percentage
of satisfied users measures for how many individual
users a correct recommendation was produced.
4.3 Strategy
We performed two different experiments. The first
aims to make an evaluation of the recommendations,
by measuring the precision of the system with differ-
ent threshold values. The second experiment, makes
an evaluation of the satisfied users in the produced
recommendations, given a precision value.
In order to evaluate the recommendations, we
compare our approach with a state-of-the-art policy
(Zhou et al., 2010). Zhou et al. (Zhou et al., 2010)
developed a tag-based user recommendation frame-
work and demonstrated that tags are the most effective
source of information to produce recommendations.
We compare the performance of our system with re-
spect to that of the reference one (which uses only the
tags, i.e., ui = 0), in terms of precision. Supported by
MiningUserBehaviorinaSocialBookmarkingSystem-ADeliciousFriendRecommenderSystem
335
the thesis that the use of only one source of data leads
to a better performance, we considered a second ref-
erence system, which considers only the user interest
(i.e., ts = 0).
During the analysis of the performance, we evalu-
ated all the values of the parameters α and β between
0 and 1, using a 0.1 interval.
4.4 Experiments
The details of each performed experiment and its re-
sults are now presented.
4.4.1 Evaluation of the Recommendations
Given a target user u
t
, the system builds a candidate
set, S(u
t
), of users to recommend. For each recom-
mended user u
i
∈ S(u
t
), we analyze the bi-directional
user relations in the dataset (i.e., if (u
t
, u
i
) ∈ C), to
check if there is a connection between the target user
u
t
and the recommended user u
i
(i.e., if the users are
friends). This experiment analyzes the performance
of the system in terms of precision. Given different
values of α and β, the precision of the system is cal-
culated, in order to analyze how the performance of
the system vary as the similarity between users grows.
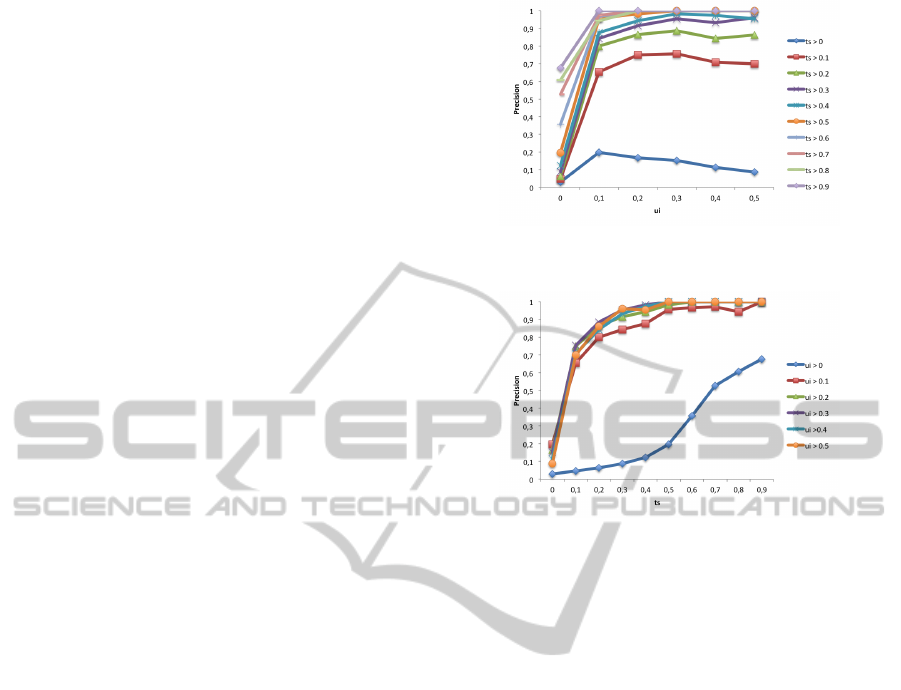
The results are illustrated in Fig. 1 and Fig. 2.
Fig. 1 shows how the precision values change with
respect to the user interest ui. The figure contains a
line for each possible value α of the tag-based user
similarity ts. We can observe that the precision val-
ues grow proportionally to the ui values. This means
that the more similar are the users (both in terms of
tag-based similarity and of user interest), the better
the system performs. However, for ui values higher
than 0.5 no user respects the constraints, so we can-
not make any recommendation.
Fig. 2 shows the same results from the tag-based
user similarity point of view. The figure presents the
precision values, with respect to the tag-based user
similarity ts; here, each line shows the results for a
given value β of the user interest ui. Also from this
perspective, the precision grows proportionally to ts.
The blue lines in Fig. 1 and Fig. 2 show the results
of the reference systems, where ts = 0 and ui = 0.
In both cases, the two metrics combined improve the
quality of the recommendations with respect to the
cases where only one is used.
4.4.2 Evaluation of the Satisfied Users
The second experiment aims at analyzing the trend of
the satisfied users, with respect to the precision val-
ues. So, for each precision value obtained in the pre-
Figure 1: Precision of the system with respect to user inter-
est ui.
Figure 2: Precision of the system with respect to tag-based
user similarity ts.
vious experiment, we computed the percentage of sat-
isfied users as shown in Eq. 9.
In order to present the results, Fig. 3 reports just a
subset of precision values. These values have been se-
lected dividing the range [0 - 1] of possible precision
values into intervals of 0.1 (i.e, [0 - 0.1), [0.1 - 0.2),
..., [0.9 - 1]) and assigning each previously computed
value of precision to the right interval. From each in-
terval, we selected the record that corresponds to the
precision value that led to the maximum percentage
of satisfied users. The reason why there are no values
for the intervals [0.2 - 0.3) and [0.4 - 0.5), is that in
the previous experiments there are no values of α and
β that led to precision values inside those intervals.
In Fig. 3 we can observe that the percentage of
satisfied users grows as the precision grows. Given
that also in the previous experiments we obtained that
the more similar the users were, the higher the preci-
sion was, we can conclude that more similar the users
are (both in terms of tag-based similarity and of user
interest), the higher is the likelihood that users are sat-
isfied by the recommendations.
These results show an interesting property of our
recommender system. In fact, even if the precision
values are split into intervals that cover the same
range (i.e., 0.1), there are two of them (i.e., [0.6−0.7)
and [0.8 − 0.9)) in which the percentage of individual
users satisfied by the recommendations significantly
increases. So, this experiment, by showing the im-
DATA2014-3rdInternationalConferenceonDataManagementTechnologiesandApplications
336
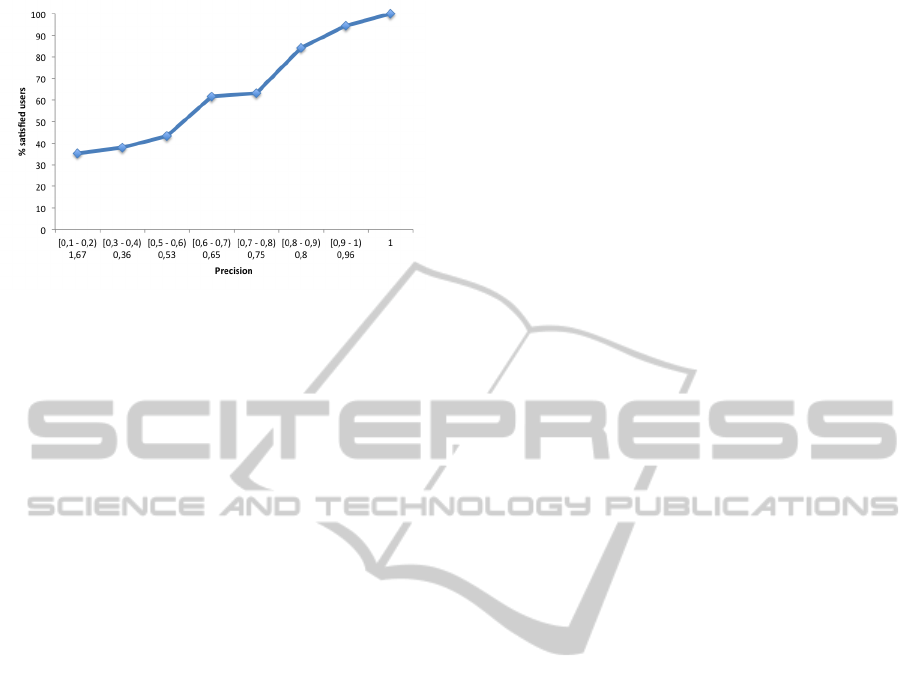
Figure 3: Percentage of satisfied users for different values
of precision.
pact of precision on individual users, is very useful in
order to tune the parameters of the system.
5 RELATED WORK
This section presents related work on user recommen-
dation in the social domain.
In (Gupta et al., 2013), Gupta et al. present Twit-
ter’s user recommendation service, which is based on
shared interests, common connections, and other re-
lated factors. The proposed system builds a graph
in which the vertices represent users and the directed
edges represent the “follow” relationship; this graph
is processed with an open source in-memory graph
processing engine, called Cassovary. Finally, recom-
mendations are built by means of a user recommenda-
tion algorithm for directed graphs, based on SALSA
(Stochastic Approach for Link-Structure Analysis).
Our proposal differs, because we make friend rec-
ommendations and, furthermore, our system does not
consider the social graph.
In (Chen et al., 2009), Chen et al. describe a
people recommender system in an enterprise social
network domain. They compare four algorithms,
two based on social relationship information and two
based on content similarity, and demonstrate that the
algorithms that use social information are stronger at
finding known contacts, while algorithms based on
content similarity are better to discover new friends.
We cannot compare with this approach, since it is ap-
plied to a delimited enterprise social network domain.
Guy et al. (Guy et al., 2009) describe a peo-
ple recommender system for the IBM Fringe so-
cial network. The system uses enterprise informa-
tion, like org chart relationships, paper and patent
co-authorship and project co-membership, which are
specific of this social network, so it is hard to compare
to them.
Hannon et al. (Hannon et al., 2010) describe
a followee recommender system for Twitter, which
is based on tweets and relationships of their social
graphs. By using this information, they build user
profiles and demonstrate how these profiles can be
used to produce recommendations. In our work, we
do not use any social connection information and fur-
thermore we recommend friends and not users to fol-
low.
In (Quercia and Capra, 2009), a recommender sys-
tem based on collocation (i.e., the position of the user)
is presented. It uses short-range technologies of mo-
bile phones, to infer the collocation and other corre-
lated information, which are the base for the recom-
mendations. In our domain we do not have such a
type of information, so we cannot compare with this
algorithm.
Zhou et al. (Zhou et al., 2010) propose a frame-
work for users’ interest modeling and interest-based
user recommendation (meant as people to follow and
not as a friend), tested on the Yahoo! Delicious
dataset. Recommendations are produced by analyz-
ing the network and fans properties. Differently from
this framework, our system produces friend recom-
mendations.
In (Brzozowski and Romero, 2011), a study about
what cues in a user’s profile, behavior, and network
are the most effective to recommend people, is pre-
sented. As previously highlighted, we are interested
in producing recommendations only based on users’
content.
Liben-Nowell and Kleinberg (Liben-Nowell and
Kleinberg, 2003) studied the user recommendation
problem as a link prediction problem. They develop
several approaches, based on metrics that analyze the
proximity of nodes in a social network, to infer the
probability of new connections among users. Experi-
ments show that the network topology is a good tool
to predict future interactions. We aim at using more
basic information and not graphs or network topolo-
gies.
In (Arru et al., 2013), Arru et al. propose a user
recommender system for Twitter, based on signal pro-
cessing techniques. The considered approach defines
a pattern-based similarity function among users and
makes use of a time dimension in the representation
of the users profile. Our system is different, because
we aim at suggesting friends while on Twitter recom-
mends “people to follow”.
MiningUserBehaviorinaSocialBookmarkingSystem-ADeliciousFriendRecommenderSystem
337

6 CONCLUSIONS
This paper presented a friend recommender system in
the social bookmarking domain. Our proposal mined
user behavior, by analyzing the resources and the tags
bookmarked by each user. The goal was to infer the
interests of the users from content, making a selec-
tive use of the available information, in order to over-
come the known limitations that a recommender sys-
tem can have in a social domain in terms of com-
plexity and scalability. As results show, our system
produces accurate recommendations by using the tags
and the bookmarks used by users.
Since a new friendship in a social bookmarking
system allows a user to be updated on the new book-
marks added by her/his friend, future work will de-
fine and analyze the novelty and the serendipity of the
bookmarks received by a user.
REFERENCES
Arru, G., Gurini, D. F., Gasparetti, F., Micarelli, A., and
Sansonetti, G. (2013). Signal-based user recom-
mendation on twitter. In 22nd International World
Wide Web Conference, WWW ’13, Companion Vol-
ume, pages 941–944. International World Wide Web
Conferences Steering Committee / ACM.
Boyd, D. M. and Ellison, N. B. (2007). Social network sites:
Definition, history, and scholarship. J. Computer-
Mediated Communication, 13(1):210–230.
Breese, J. S., Heckerman, D., and Kadie, C. (1998). Em-
pirical analysis of predictive algorithms for collabora-
tive filtering. In Proceedings of the Fourteenth confer-
ence on Uncertainty in artificial intelligence, UAI’98,
pages 43–52, San Francisco, CA, USA. Morgan Kauf-
mann Publishers Inc.
Brzozowski, M. J. and Romero, D. M. (2011). Who should
i follow? recommending people in directed social
networks. In Proceedings of the Fifth International
Conference on Weblogs and Social Media. The AAAI
Press.
Buckland, M. and Gey, F. (1994). The relationship between
recall and precision. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci., 45(1):12–19.
Cantador, I., Brusilovsky, P., and Kuflik, T. (2011). Second
workshop on information heterogeneity and fusion in
recommender systems (hetrec2011). In Proceedings
of the 2011 ACM Conference on Recommender Sys-
tems, RecSys 2011, pages 387–388. ACM.
Chen, J., Geyer, W., Dugan, C., Muller, M. J., and Guy, I.
(2009). Make new friends, but keep the old: recom-
mending people on social networking sites. In Pro-
ceedings of the 27th International Conference on Hu-
man Factors in Computing Systems, CHI 2009, pages
201–210. ACM.
Farooq, U., Kannampallil, T. G., Song, Y., Ganoe, C. H.,
Carroll, J. M., and Giles, C. L. (2007). Evaluating
tagging behavior in social bookmarking systems: met-
rics and design heuristics. In Proceedings of the 2007
International ACM SIGGROUP Conference on Sup-
porting Group Work, GROUP 2007, pages 351–360.
ACM.
Gupta, P., Goel, A., Lin, J., Sharma, A., Wang, D., and
Zadeh, R. (2013). Wtf: the who to follow service at
twitter. In 22nd International World Wide Web Confer-
ence, WWW ’13, pages 505–514. International World
Wide Web Conferences Steering Committee / ACM.
Guy, I. and Carmel, D. (2011). Social recommender sys-
tems. In Proceedings of the 20th International Con-
ference on World Wide Web, WWW 2011 (Companion
Volume), pages 283–284. ACM.
Guy, I., Chen, L., and Zhou, M. X. (2013). Introduction
to the special section on social recommender systems.
ACM TIST, 4(1):7.
Guy, I., Ronen, I., and Wilcox, E. (2009). Do you know?:
recommending people to invite into your social net-
work. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Con-
ference on Intelligent User Interfaces, pages 77–86.
ACM.
Hannon, J., Bennett, M., and Smyth, B. (2010). Rec-
ommending twitter users to follow using content and
collaborative filtering approaches. In Proceedings of
the 2010 ACM Conference on Recommender Systems,
RecSys 2010, pages 199–206. ACM.
Herlocker, J. L., Konstan, J. A., Borchers, A., and Riedl,
J. (1999). An algorithmic framework for perform-
ing collaborative filtering. In SIGIR ’99: Proceedings
of the 22nd Annual International ACM SIGIR Con-
ference on Research and Development in Information
Retrieval, pages 230–237. ACM.
Liben-Nowell, D. and Kleinberg, J. M. (2003). The link pre-
diction problem for social networks. In Proceedings
of the 2003 ACM CIKM International Conference on
Information and Knowledge Management, pages 556–
559. ACM.
Pearson, K. (1896). Mathematical contributions to the the-
ory of evolution. iii. regression, heredity and pan-
mixia. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Soci-
ety of London. Series A, Containing Papers of a Math.
or Phys. Character (1896-1934), 187:253–318.
Quercia, D. and Capra, L. (2009). Friendsensing: recom-
mending friends using mobile phones. In Proceedings
of the 2009 ACM Conference on Recommender Sys-
tems, RecSys 2009, pages 273–276. ACM.
Ratiu, F. (2008). Facebook: People you may know.
Ricci, F., Rokach, L., and Shapira, B. (2011). Introduction
to recommender systems handbook. In Recommender
Systems Handbook, pages 1–35. Springer.
Simon, H. A. (1971). Designing organizations for an infor-
mation rich world. In Computers, communications,
and the public interest, pages 37–72. Johns Hopkins
Press, Baltimore.
Zhou, T. C., Ma, H., Lyu, M. R., and King, I. (2010).
Userrec: A user recommendation framework in so-
cial tagging systems. In Proceedings of the Twenty-
Fourth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence,
AAAI 2010. AAAI Press.
DATA2014-3rdInternationalConferenceonDataManagementTechnologiesandApplications
338
