
Integrating Semi-structured Information using Semantic
Technologies
An Evaluation of Tools and a Case Study on University Rankings Data
Alejandra Casas-Bayona and Hector G. Ceballos
Campus Monterrey, Tecnologico de Monterrey, Av. Eugenio Garza Sada 2501, 64849, Monterrey, Nuevo León, Mexico
Keywords: Semantic Technology, Ontologies, Information Integration, Information Reconciliation, Best Practices.
Abstract: Information integration is not a trivial activity. Information managers face problems like: heterogeneity (in
data, schemas, syntax and platforms), distribution and duplicity. In this paper we: 1) analyze ontology-based
methodologies that provide mediation frameworks for integrating and reconciling information from
structured data sources, and 2) propose the use of available semantic technologies for replicating such
functionality. Our aim is providing an agile method for integrating and reconciling information from semi-
structured data (spreadsheets) and determining to which extent available semantic technologies minimize
the need of ontological expertise for information integration. We present our findings and lessons learned
from a case study on university rankings data.
1 INTRODUCTION
Information has become a fundamental asset for
company’s competitiveness. Integrating information
distributed across systems and platforms in the
organization for its later analysis has become the
most important task for information managers.
Integrating information residing in distributed and
heterogeneous data sources is a well-known problem
that faces two difficult challenges: heterogeneity and
reconciliation.
Heterogeneity can be classified in four
categories: 1) structural, i.e. different schemas in
data sources; 2) syntactical, i.e. different ways of
naming the same object (catalogues); 3) systemic,
i.e. diverse platforms governed by different
authorities; and 4) semantic, i.e. different meanings
for same concept or different names for the same
concept (Buccella, Cechich, & Brisaboa, 2005). For
(Cui, Brien, & Park, 2000), resolving semantic
heterogeneity consists in identifying equivalent
concepts, no-related concepts and related concepts.
On the other hand, data reconciliation has been
classified on two levels: schema and instance
(Bakhtouchi, Jean, & Ait-ameur, 2012). Schema
reconciliation consists on finding equivalences
between tables and columns from different data
sources, i.e. it addresses structural heterogeneity,
whereas instance reconciliation consists on
identifying instances that represent the same entity
in the real world despite their multiple
representations (Zhao & Ram, 2008).
Ontologies are particularly suitable for
integrating information as long as they deal with
syntactic and semantic heterogeneity (Silvescu,
Reinoso-castillo, & Honavar, 1997). The term
ontology was introduced by Gruber in the context of
knowledge sharing as “the conceptualization of a
specification” (Gruber, 2009). This is, an ontology is
the description of concepts and relationships that an
agent or a community may use (Gruber, 2008).
Some ontology-based methodologies and
techniques for information integration have been
proposed (Buccella et al., 2005). For example, the
project MOMIS (Mediator environment for Multiple
Information Sources) allows integrating data from
structured and semi-structured data sources
(Beneventano et al., 2001). SIMS is another
mediator platform that provides access to distributed
data sources and online integration (ARENS et al.,
1993). MIRSOFT, unlike the other two approaches,
does not map entirely the origin data sources but
focuses on the minimum necessary data for
answering the integration question (Bakhtouchi et
al., 2012). These approaches support the task of data
interpretation by requiring the participation of the
domain expert at some extent and minimizing the
357
Casas-Bayona A. and Ceballos H..
Integrating Semi-structured Information using Semantic Technologies - An Evaluation of Tools and a Case Study on University Rankings Data.
DOI: 10.5220/0005004203570364
In Proceedings of 3rd International Conference on Data Management Technologies and Applications (DATA-2014), pages 357-364
ISBN: 978-989-758-035-2
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
involvement of the database administrator.
In scenarios with periodic data extraction the
cost of the required infrastructure and the time
dedicated by the expert is justified. Nevertheless, in
scenarios where an agile response is needed,
information requirements are volatile, and data is
provided by different departments in semi-structured
formats, a more agile solution is needed. Our
proposal is to use available semantic technologies
for replicating the functionality that these
approaches provide.
In section 2 we describe and analyse the facilities
provided by each approach. In section 3 we
described our approach for information integration
and our criteria for selecting semantic technologies.
In section 4 we exemplify our methodology by
integrating faculty staff information from two data
sources for a university ranking. Finally in section 5
we present a summary of lessons learned and
conclude with closing remarks in section 6.
2 RELATED WORK
Ontology-based information integration approaches
provide a solution for integrating heterogeneous
databases and semi-structured data. Some of them
additionally provide data reconciliation facilities.
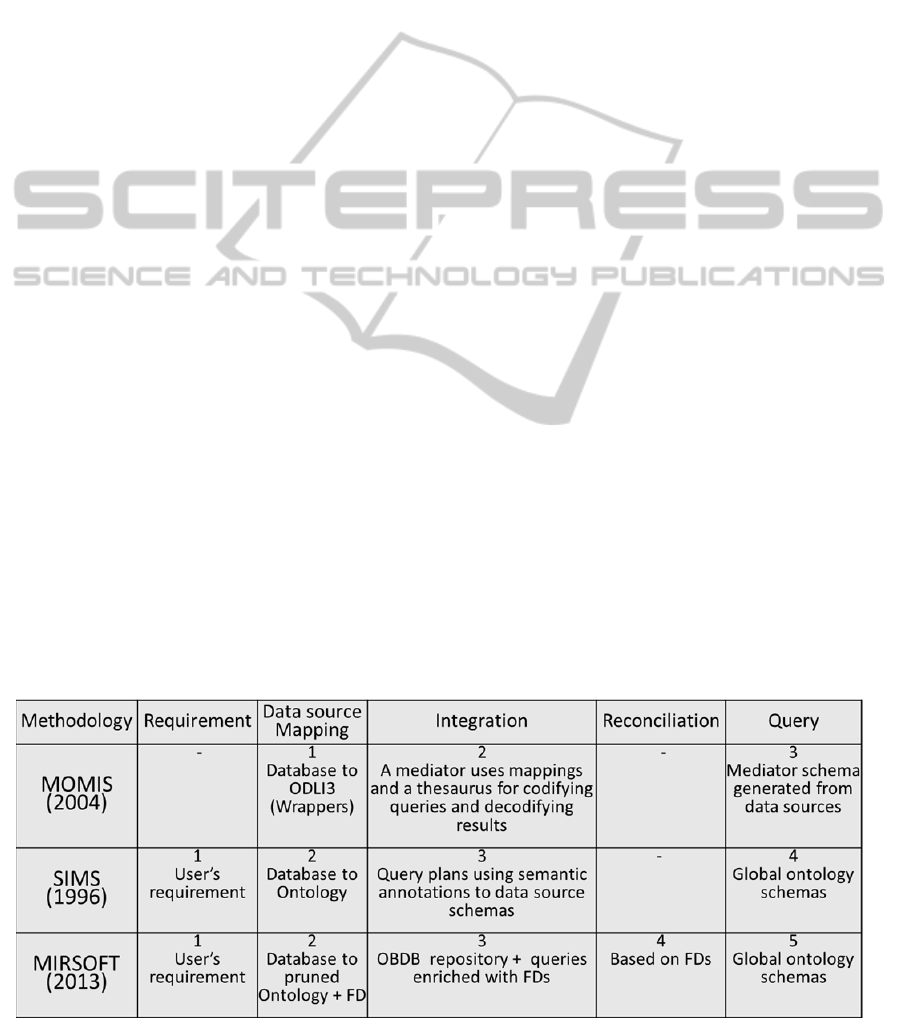
Table 1 shows a comparison of the three
analyzed methodologies found in literature related to
ontology-based information integration. For the
comparison we focused in five aspects: 1) the
original information requirement, 2) the way on
which information is mapped, 3) the way on which
integration is performed, 4) reconciliation facilities,
and 5) the schemas used for expressing queries.
Numbers in each row represent the order followed in
each methodology.
The MOMIS methodology starts in the extraction
phase where it uses a wrapper that transform the
structure of available data sources to a model OLDI3
based on Description Logics (Moreno Paredes,
2007). The integration process generates an
integrated view of the data sources (global-as-view)
through the generation of a thesaurus. Then it
performs an analysis for determining affinity
between terms and it makes clusters of similar
classes (Beneventano et al., 2001). Queries are
expressed in terms of thesaurus schemas.
SIMS, on the opposite way, was created
assuming that data sources are dynamic; hence it
starts by defining an initial question from which
proceeds to the selection of suitable data sources, in
order to minimize the cost of mapping schemas. The
integration phase starts with an expert annotating
data sources with ontology schemas and continues
enriching initial mappings with other vocabularies
automatically. SIMS elaborates query plans for
answering queries expressed in terms of the used
ontologies (Arens et al., 1996).
MIRSOFT departs from an initial user
requirement and importing mediator ontology. Then
it requires mapping data sources to mediator
schemas, as well as expressing functional
dependencies (FDs) of mapped classes, providing
ontology-based database access, also known as
OBDB or OntoDB. Before starting the mapping
stage, a selection of relevant classes and properties is
done, producing a pruned ontology. This
methodology additionally uses functional
dependencies for complementing queries and
providing reconciliation in query results
(Bakhtouchi, Bellatreche, Jean, & Ameur, 2012).
Queries are expressed and answered in terms of the
mediator ontology.
Table 1: Comparison of ontology-based methodologies for information integration.
DATA2014-3rdInternationalConferenceonDataManagementTechnologiesandApplications
358

3 INTEGRATION AND
RECONCILIATION METHOD
We evaluated the use of semantic technologies in
scenarios of periodic integration exercises where
information used for answering queries is provided
by different departments using spreadsheets with
varying formats. Heterogeneity is present in all of its
expressions: information resides in different systems
(systemic), spreadsheets have different columns
(structural), varying column names and use different
catalogues (syntactical), and the same concept is
defined distinctly in each data source (semantic).
Additionally, equivalent individuals can be found
across these data sources with contradictory
information. In this scenario, we cannot rely on
fixed structures, and mappings must be generated
cost-effectively.
Based on the aspects analyzed in previous
methodologies we propose a method suitable for this
scenario that provides ontology-based information
integration taking advantage of current Semantic
Web standards and tools. Stages of our method are
described Figure 1.
Figure 1: Information integration process.
3.1 User Requirement
We start with an initial user requirement expressed
through a global schema represented by an extension
O
G
of an existing ontology O
B
. A suitable OWL
ontology for your domain can be chosen from
ontologies repositories like Linked Open
Vocabularies
i
. A data requirement is denoted by a
class C
R
that represents a set of individuals that must
be identified and quantified across the available data
sources. Each class C
R
is declared in O
G
as subclass
of a class C
G
originally contained in O
B
in order to
make query results compatible with the original
ontology O
B
.
i http://lov.okfn.org/dataset/lov/
In this step is important to declare consistency
constraints like if two classes C
R
are disjoint, this is,
when an individual must be classified as member of
only one of these classes.
3.2 Local Ontologies
Next, each datasheet is transformed to a RDF file
where each row represents an individual of a new
class C
L
, columns represent properties of the class
and cells are property values that describe each
individual. The resulting class, properties and
individuals constitute a local ontology O
L
. Available
tools for this purpose are referenced by W3C
ii
.
3.3 Local-Global Ontology Alignments
The ontology O
G
is imported in each O
L
for
expressing the corresponding definition of each C
R
.
If the definition of C
R
only requires information of a
single data source then C
R
is defined in O
L
. If the
definition of C
R
requires information from multiple
sources its definition must be done in the integrated
ontology. The integrated ontology O
I
is a new OWL
file that imports O
D
and each O
I
.
This stage can be facilitated by ontology
mapping tools that identify semantic
correspondences between elements in two different
schemas (Zohra et al., 2011).Availabletoolsforthis
taskare referredby the Open Semantic Framework
initiative
iii
.
3.4 Reconciliation
Product of local definitions we can have multiple
individuals representing the same individual.
Reconciliation of equivalent individuals is made
declaring an OWL 2 constraint HasKey for classes
C
R
. Another alternative is declaring a SWRL rule or
using a SPARQL CONSTRUCT query that assert
statements SameIndividual for each pair of
equivalent individuals, based on functional
dependencies.
This procedure is especially important when
datasheets contain multiple rows for the same
individual that is being quantified in C
R
.
ii
http://www.w3.org/wiki/ConverterToRdf
iii
http://wiki.opensemanticframework.org/index.php/Ontol
ogy_Tools#Ontology_Mapping
IntegratingSemi-structuredInformationusingSemanticTechnologies-AnEvaluationofToolsandaCaseStudyon
UniversityRankingsData
359

3.5 Inference
Finally, a concept reasoner is used on O
I
for
classifying individuals in each C
R
. Reasoners can be
executed from the IDE of a comprehensive
framework like Protégé or Top Braid, or be executed
directly over O
I
. Another alternative is using an RDF
database with inference capabilities like Virtuoso
iv
or Stardog
v
.
In this stage, concept reasoners are used for
detecting inconsistencies between definitions and
data. In order to solve these inconsistencies, violated
constraints can be lift or inconsistent individuals can
be removed from the data set. For instance, an
individual classified in two disjoint classes will be
inconsistent and the solution will be up to the
domain expert.
3.6 Query Resolution
Finally, the domain expert identify and quantifies
individuals classified in each CR by formulating a
query over a SPARQL end-point connected to the
inferred model OI’ or by enquiring the RDF
database using the reasoning level required by
definitions. CR is quantified by a query like:
SELECT COUNT (DISTINCT (?ind))
WHERE{ ?ind a C
R
}
Figure 2 shows the inputs (O
B
, O
G
, L
1
, L
2
), the
working models (O
L1
, O
L2
, O
I
, O
I
’), and tools. Stages
of the method are numbered as well.
4 CASE STUDY
Our case study was carried out in a University that
provides statistical data to an international Ranking
organization. In this sense, the rankings department
collects information in spreadsheets from several
departments. In order to identify and classify the
university academic staff, information is collected
from both Human Resources and Academic
departments.
The integration was initially performed by a
computer science specialist with basic knowledge on
ontologies, following the use cases from (Allemang
& Hendler, 2008). After a series of integration
exercises that allowed us to evaluate available tools
we asked two other specialists in information
iv
http://virtuoso.openlinksw.com/rdf-quad-store/
v
http://stardog.com/
integration to replicate one of the integration
exercises. For this purpose we prepared two user
guides with a summary of use cases given in
(Allemang & Hendler, 2008), where OWL
constructors are classified according to integration
or reconciliation purposes. Reconciliation guide is
shown in the Appendix.
Figure 2: Datasets and Tools.
In this section we describe the results of the
evaluation of tools and in section 5 we discuss our
findings and perspectives on semantic technologies.
4.1 User Requirement
The initial requirement is given by definitions of the
ranking evaluation criteria. In our integration
exercise we identified six classes C
R
that can be used
for answering the faculty staff criteria: Faculty Staff,
Full Time Professor, Part Time Professor, Local
Professor, International Professor and Professor with
PhD. Further calculations like the Full-time
equivalent are out of the scope of the integration and
reconciliation task.
We evaluated Neon Toolkit
vi
, Protégé
vii
and
TopBraid Composer Standard Edition
viii
based on the
following criteria: 1) the usability of its interface, 2)
visualization of definitions, 3) facilities for
importing data from spreadsheets, 4) configurable
reasoning levels, and 5) facilities for exporting query
results. Additionally, our selection criteria
considered the minimization of the number of tools
used along the entire process, being TopBraid
Composer choosen for the first four stages and
Protégé for the last two.
On the other hand, we evaluated two ontologies:
vi http://neon-toolkit.org
vii http://protege.stanford.edu/
viii http://www.topquadrant.com/
Spreadsheet
co
n
ve
r
te
r
O
G
L
1
Results
OL
1
OL
2
O
B
O
I
O
I
’
Reasoner SPARQL
L
2
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
(iv)
(v)
Imported
Process (vi)
DATA2014-3rdInternationalConferenceonDataManagementTechnologiesandApplications
360

VIVO
ix
and Semantic Web for Research
Communities
x
(SWRC) as base for our global
ontology, and selected the last one because it
provides enough expressivity for our purpose and
has less and simpler schemas.
4.2 Local Ontologies
We used TopBraid Composer facilities for
transforming spreadsheet data to local ontologies,
generating a local ontology for each data source (one
class and N properties). Two local ontologies where
produced, denoted Local A (O
L-A
) and Local B (O
L-
B
) in the following. Local classes (C
L
) generated in
each local ontology are denoted Person A (C
L-A
) and
Person B (C
L-B
), respectively. Figure 2 illustrates
with an example the heterogeneity between both
data sources.
Figure 2: Example of data found in both data sources.
4.3 Local-Global Ontology Alignments
In the Global-Local ontology alignments stage we
formulated one definition for each CR per local
ontology, i.e. 12 definitions in total. Figure 3
illustrates some definitions made for OL-A and OL-
B. Prefixes G: and A: represent the ontologies OG
and OL-A respectively.
TopBraid Composer suggested mappings
between equivalent properties in O
L-A
and O
L-B
after
they were imported to the integrated ontology O
I
.
(see Figure 4). Mappings proposed by this tool were
correct and facilitated using properties defined in
local ontologies for recovering information from
both data sources (see queries in section 4.6).
G:PTProfessor A:Person A:hasContrat = {A,B,C}
(1)
G:FTProfessor A:Person A:hasContrat = {D, E, F}
(2)
G:FacultyStaff G:PTProfessor G:FTProfessor
(3)
G:FTProfessor G:PTProfessor ⊆ ⊥
(4)
G:LocalProfessor A:Person A:hasNac = ‘Mexican’
(5)
G:LocalProfessor B:Person B:hasNacionality = ‘Mex’
(6)
G:InternationalProfessor ¬ A:MexicanProfessor
(7)
Figure 3: Example of definitions in local ontologies.
ix http://www.vivoweb.org
x http://ontoware.org/swrc/
Figure 4: Equivalent classes and properties.
4.4 Reconciliation
Reconciliation was done through the assertion of
statements SameIndividual between persons with the
same employee identification number. In O
L-A
this
property is called hasId, whereas in O
L-B
the
equivalent property is named hasIdentification. This
procedure was done with a SPARQL CONSTRUCT
query.
4.5 Inference
For the reasoning stage we evaluated the reasoners
integrated in Protégé and TopBraid Composer:
FACT++, Hermit, OWLIM
xi
and Pellet.
Not a single reasoner in TopBraid Composer
could be configured for making the Closed World
Assumption (CWA), hence it was not possible to
classify individuals based on definitions like
International Professor that uses a ComplementOf
constraint. This was not the case of Hermit in
Protégé which makes the CWA by default and
correctly made this classification. The resoner that
had better performance in TopBraid Composer was
OWLIM.
Thanks to the definition of Full-time Professor
and Part-time Professor as disjoint classes it was
possible to detect inconsistencies between data
sources. Figure 4 illustrates an inconsistency of this
type, where the same professor is classified as Part-
time in O
A
(A:hasContract = A) and as Full-time in
O
B
(B:hasContract = X), given local definitions. To
solve this problem we removed the disjoint
constraint and adjusted the query for retrieving Part-
time professors as explained in next section.
4.6 Query Resolution
Information required for answering rankings
xi
http://owlim.ontotext.com/display/OWLIMv40/OWLI
M-Lite+Reasoner
IntegratingSemi-structuredInformationusingSemanticTechnologies-AnEvaluationofToolsandaCaseStudyon
UniversityRankingsData
361

questions were expressed in SPARQL through the
combination of classes C
R
. For instance, for
determining the number of Full Time International
Faculty Staff we used the intersection of Full Time
Professor and International Professor.
Given that we found professors classified as
Full-time and Part-time the query for retrieving Part-
time Professors was adjusted as follows:
SELECT COUNT (DISTINCT (?ID))
WHERE{
?prof a G:PTProfessor .
?prof A:hasID ?ID .
FILTER NOT EXISTS {?prof a G:FTProfessor.}
We also needed to adjust the query for retrieving
International professors using OWLIM. Given that it
does not support CWA, the following query asks for
faculty staff and discards local professors:
SELECT COUNT (DISTINCT (?ID))
WHERE{
?prof a G:FacultyStaff .
?prof A:hasID ?ID .
FILTER NOT EXISTS {?prof a
G:MexicanProfessor.}
5 DISCUSSION
In this section we describe the lessons learned from
tool’s maturity and the experience of non-ontologist
users with our methodology. We also identify the
advantages of ontology-based versus relational-
based integration, and delimit the reach of ontology
mapping tools in the integration process.
5.1 Lessons Learned
From the proposed method and the evaluation of
tools we get to the following conclusions.
In our scenario, an ontologist expert could
replicate most of the functionality provided by
mediator architectures described in section 2,
including reconciliation of individuals.
It was possible to represent semantically the
concepts in our case study with constructors
supported by OWL 2 profiles.
Deficiencies in inference support was remediated
through the use of SPARQL.
Inference in memory becomes unfeasible with a
relative small ammount of data (above a
thousand records with more than 30 columns).
We have to decide between preselect the
columns to use in the integration, or use a RDF
database with inference support. In the first case,
information that could be useful for further
integrations is lost, and in the second we sacrify
the facilities provided by the IDE for making
definitions and export results.
From the experience of users following our
method and the selected tools we draw the following
preliminary conclusions:
The most dificult concept to understand for
database specialists was the notion of Open
World Assumption in the construction of
definitions. Unfortunately most of the
reasoners implement this assumption and
forces the user to adopt the equally confusing
notion of negation as failure (c.f. queries in
section 4.6).
The usability of the selected tools was the best
given our evaluation and user guides prepared
for applying OWL constructors in the
integration and reconciliation stages (see
Appendix), in despite the users found hard to
understand the meaning of OWL constructors
without a previous introduction that include
notions of set theory.
Interfaces for constructing OWL definitions are
not suitable for non-experts on ontology
languages.
5.2 Ontology-based versus
Relational-based Integration
Volatile input formats in our scenario make
affordable the use of semantic technology as long as
avoids the necessity of creating fixed-data structures
(tables) that cannot be reused in subsequent
integrations.
On the other hand, the absence of common keys
between datasources requires the use of entity
resolution techniques, which have been developed
for both technologies. Nonetheless, the semantic
representation allows representing equivalences
between individuals that produce an automatic
horizontal integration once datasources are merged.
Silk is an example of a tool deviced for entity
resolution in Linked Data (Volz, et al., 2009).
Despite reasoners allow inferring information
like individual equivalences based on keys, it is
necessary to merge the information from all
datasources in a single repository or having
distributed stream reasoning. This kind of
technologies are still emerging. Stardog is an
example of it.
DATA2014-3rdInternationalConferenceonDataManagementTechnologiesandApplications
362

5.3 Ontology Mapping Tools
Ontology mapping approaches may solve the
problem of aligning local and global schemas,
avoiding (or at least reducing) the need of a non-
ontologist user to decide which OWL constructors to
use for integrating and reconciling information.
Despite local schemas may contain few
properties (datasheet columns), mapping them to
large global ontologies may be largely benefited
from the use of these tools, as ilustrated by
(Rodriguez, et al., 2011).
However, the automatic discovery of mappings
could exacerbate the problem of reasoning in large
amounts of data producing an excess of mappings
between schemas that are not used to answer the
question that motivates integration.
6 CONCLUSIONS
The need of an agile process for information
integration has become more evident in large
organizations, as much as for trivial questions as for
building indicators that involve information
managed by external organizations.
We presented a method supported by current
semantic technologies that provide information
integration of heterogeneous data sources. In
scenarios where data is provided in semi-structured
formats and varies over time, our method matches
the results obtained by other robust mediator
architectures in a cost-effective manner.
Nevertheless, information integration requires a
deep understanding of ontological representations in
order to perform a proper integration and
reconciliation, despite the facilities provided by
current tools.
Despite semantic web languages and protocols as
well as current semantic technologies are mature
enough for enabling information integration there
are still some issues that must be addressed. For
instance, by providing scalable reasoning on large
amounts of data, friendly interfaces for non-ontology
experts and configuration options for reasoners that
allows making the Closed World Assumption when
the information is complete.
Solving these problems will allow taking
advantage of ontology mapping tools for discovering
all possible alignments between local and global
schemas. Furthermore, it will be possible to select
automatically the domain ontology that better suits
(best scored matches) to a set of local schemas.
In this exercise we classified OWL constructors
according to their usage in the integration stage, but
they can be further classified according to the
heterogeneity type they address, in order to facilitate
user’s adoption.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Authors thank to Tecnologico de Monterrey and
CONACYT for sponsoring this research through
grants 0020PRY058 and CB-2011-01-167460,
respectively.
REFERENCES
Allemang, D, & Hendler, J., 2008. Semantic Web for the
Working Ontologist: Effective Modeling in RDFS and
OWL. Morgan Kaufmann.
Arens, Y., Chee, C., Hsu, C., In, H., Knoblock, C. A., &
Rey, M., 1996. Query Processing in the SIMS
Information Mediator. In Proceedings of ARPI 1996.
61–69.
Arens, Y., Chee, C. Y., Hsu, C.-N., & Craig A., K., 1993.
Retriving and Integrating Data from Multiple
Information Sources. International Journal of
Intelligent and Cooperative Information Systems, 2.
127-158.
Bakhtouchi, A., Bellatreche, L., Jean, S., & Ameur, Y. A.,
2012. MIRSOFT: mediator for integrating and
reconciling sources using ontological functional
dependencies. International Journal of Web and Grid
Services. doi:10.1504/IJWGS.2012.046731.
Beneventano, D., Bergamaschi, F., Guerra, M., & Vincini,
2001. The MOMIS approach to Information
Integration.
Beneventano, Domenico, & Bergamaschi, S., 2004. The
Momis Methodology For Integrating Heterogeneous
Data Sources. Chapter in Building the Information
Society, 19-24.
Buccella, A., Cechich, A., & Brisaboa, N. R, 2005.
Ontology-Based Data Integration Methods : A
Framework for Comparison. Revista Colombiana de
Computación, 6.
Cui, Z., Brien, P. O., & Park, A., 2000. Domain Ontology
Management Environment, In Proceedings of the 33rd
Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences.
1–9.
Gruber, T., 2009. What is Ontology? In the Encyclopedia
of Database Systems, Ling Liu and M. Tamer Özsu
(Eds.), Springer-Verlag.
Lenzerini, M., Sapienza, L., Salaria, V., & Roma, I., 2002.
Data Integration : A Theoretical Perspective. In
Proceedings of the twenty-first ACM SIGMOD-
SIGACT-SIGART symposium on Principles of
database systems. 233 - 246.
Moreno Paredes, A., 2007. Técnicas de depuración e
IntegratingSemi-structuredInformationusingSemanticTechnologies-AnEvaluationofToolsandaCaseStudyon
UniversityRankingsData
363

integración de ontologías en el ámbito empresarial.
Universidad de Sevilla.
Rodríguez-Mancha, M., Ceballos, H., Cantú, F., & Díaz-
Prado, A., 2011. Mapping relational databases through
ontology matching: a case study on information
migration. In Proceedings of the 6th International
Workshop on Ontology Matching (OM-2011). CEUR-
WS Vol-814, 244–245.
Silvescu, A., Reinoso-castillo, J., & Honavar, V., 2001.
Ontology-Driven Information Extraction and
Knowledge Acquisition from Heterogeneous ,
Distributed , Autonomous Biological Data Sources. In
Proceedings of the IJCAI-2001 Workshop on
Knowledge Discovery from Heterogeneous,
Distributed, Autonomous, Dynamic Data and
Knowledge Sources.
Volz, J., Bizer, C., Gaedke, M., & Kobilarov, G., 2009.
Discovering and Maintaining Links on the Web of
Data. In Proceedings of the 8th International Semantic
Web Conference (ISWC 2009), 650–665.
Zhao, H., & Ram, S., 2008. Entity matching across
heterogeneous data sources: An approach based on
constrained cascade generalization. Data &
Knowledge Engineering, 66(3), 368–381.
Zohra B., Angela B., Erhard R., 2011. Schema matching
and mapping. Springer.
APPENDIX
Table 2 is an example of the guide with
reconciliation operators provided to database
specialist during the integration exercise. Cases and
solutions were obained from (Allemang & Hendler,
2008). A similar table was prepared for integration
operators.
Table 2: User’s guide with OWL reconciliation operators.
DATA2014-3rdInternationalConferenceonDataManagementTechnologiesandApplications
364
