
The Effect of Tactical Situation Display on Attack Helicopter Pilot’s
Workload
Eunghyun Lee and Yongjin Kwon
Department of Industrial Engineering, Ajou University, Suwon, Zip 443-749, South Korea
Keywords: Attack Helicopter, Flight Information, Tactical Situation Display, Workload, NASA-TLX.
Abstract: The attack helicopter performs numerous tasks, such as anti-armor operation, close air support, search and
destroy, and reconnaissance. As 71% of aviation accidents are human-caused, high workload and stress
level of pilots greatly affect their performance level. Additionally, pilots that are responsible for attack
helicopters have to work under enemy threats, which increase their stress levels. In order to decrease their
workload, we installed a TSD (Tactical Situation Display) in our helicopter simulator. Then, we analysed
the results to find out if the TSD affects the work efficiency and mental pressure of the pilots. We analysed
the task performance time and the pilot workload using the NASA-TLX with the paired sample method. The
test indicates that the additional information provided by the TSD can help reduce the pilot workload.
1 INTRODUCTION
Attack helicopters perform a wide variety of tasks,
such as target search and destroy, armed escort, and
close air support for ground troops. Due to rapidly
advancing technologies, attack helicopters are
getting more sophisticated and powerful. During
missions, attack helicopters performs the NOE (Nap
of the Earth) flight at high speed, and the decision
making process of the pilot should be quick and fast.
This could lead to the increases in their stress levels.
To help reduce the stresses, the provision of critical
flight and mission information is necessary. The
presentation of real-time, mission-critical
information to the pilot can significantly enhance the
situational awareness and the mission success rate.
In this regard, we have decided that it is imperative
to analyse the efficiency of operation and the effect
of the TSD (Tactical Situation Display). By
conducting a series of experiments with and without
the TSD, we are going to determine if it could lower
the stress levels of the pilot. In the experiments, we
measured the performance of pilots during their
search missions at the aerial warfare. We created a
situation where there’s no TSD, and the pilots have
to rely on only voice communication with a
command center. We also provided the pilots with
TSD, and the situations are compared.
2 EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE
2.1 Task Assignment
The test subjects of this study are two Ajou
University industrial engineering students. One
performed the tasks of the pilot. The other
performed the tasks of the instructor, while he was
also responsible for radio communication and
collecting data. The student pilot has been trained
before this experiment, and he is very proficient with
the helicopter simulator. The other student who is
the instructor has been also trained, so he knows the
route for each scenario and has knowledge about
radio communication.
2.2 TSD and Simulator
We performed the experiments a total of four times.
Each experiment has different air routes and is
classified into two categories; Experiment 1 is
performed only with the voice command from the
command center. Experiment 2 is performed with
the voice command and also with the TSD. We
collected the data, including the pilot TLX data, the
helicopter’s altitude and speed, the time for each
mission.
680
Lee E. and Kwon Y..
The Effect of Tactical Situation Display on Attack Helicopter Pilot’s Workload.
DOI: 10.5220/0005016606800684
In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics (ICINCO-2014), pages 680-684
ISBN: 978-989-758-040-6
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

Figure 1: TSD Screen (Command Center).
Like Figure 1, command center is able to check the
location of the helicopter anytime. The helicopter is
the blue arrow, and its route is the pink line. Also,
the white inner circle indicates the helicopter’s
0.13nm (nautical mile, approximately 240m), and
the outer circle indicates Heading. Figure 2
illustrates the attack helicopter simulator that has
been developed and installed in our university.
Figure 2: The attack helicopter simulator at Ajou
University.
2.3 NASA-TLX Data
In order to measure how much workload the pilots
feel like they have psychologically, we used the
NASA-TLX, a program invented by NASA that
measures the amount of pilot workload. This
program can be downloaded from the NASA
website. Table 1 has the detailed explanation of six
categories. After the pilot performs his task, we
evaluates for each category. The score range is 0-
100. The lower the score is, the lower amount of
workload the pilot feels.
Table 1: Categories and descriptions of NASA-TLX.
Scale Descriptions
Mental
Demand
How much mental and perceptual
activity was required? Was the task
easy or demanding, simple or complex?
Physical
Demand
How much physical activity was
required? Was the task easy or
demanding, slack or strenuous?
Temporal
Demand
How much time pressure did you feel
due to the pace at which the tasks or
task elements occurred? Was the pace
slow or rapid?
Performance
How successful were you in performing
the task? How satisfied were you with
your performance?
Effort
How irritated, stressed, and annoyed
versus content, relaxed, and complacent
did you feel during the task?
Frustration
How hard did you have to work
(mentally and physically) to accomplish
your level of performance?
2.4 Data Collection
Kangwon Province of Korea was chosen for this
experiment because it’s suitable to navigate through
and perform the reconnaissance missions. Since the
attack helicopter should not be detected by the
enemy, the moving route is set according to the
contour map. At each waypoint, the instructor gives
the pilot voice commands or voice commands with
texts. Then, the pilot communicates back to the
instructor, if he wants to confirm the information.
The pilot stays at the same altitude with a constant
speed, and performs the reconnaissance mission
according to the commands of the instructor. We
compare a scenario where the instructor only gives
voice commands and another scenario where the
instructor gives voice commands, texts, the location
of the helicopter, and the location of the enemy
using the TSD. Then, we check if these scenarios
affect the workload of the pilot. Table 2 shows four
scenarios, ICAO (International Civil Aviation
Organization) airport code and the number of
waypoints that we set for the experiments.
TheEffectofTacticalSituationDisplayonAttackHelicopterPilot'sWorkload
681
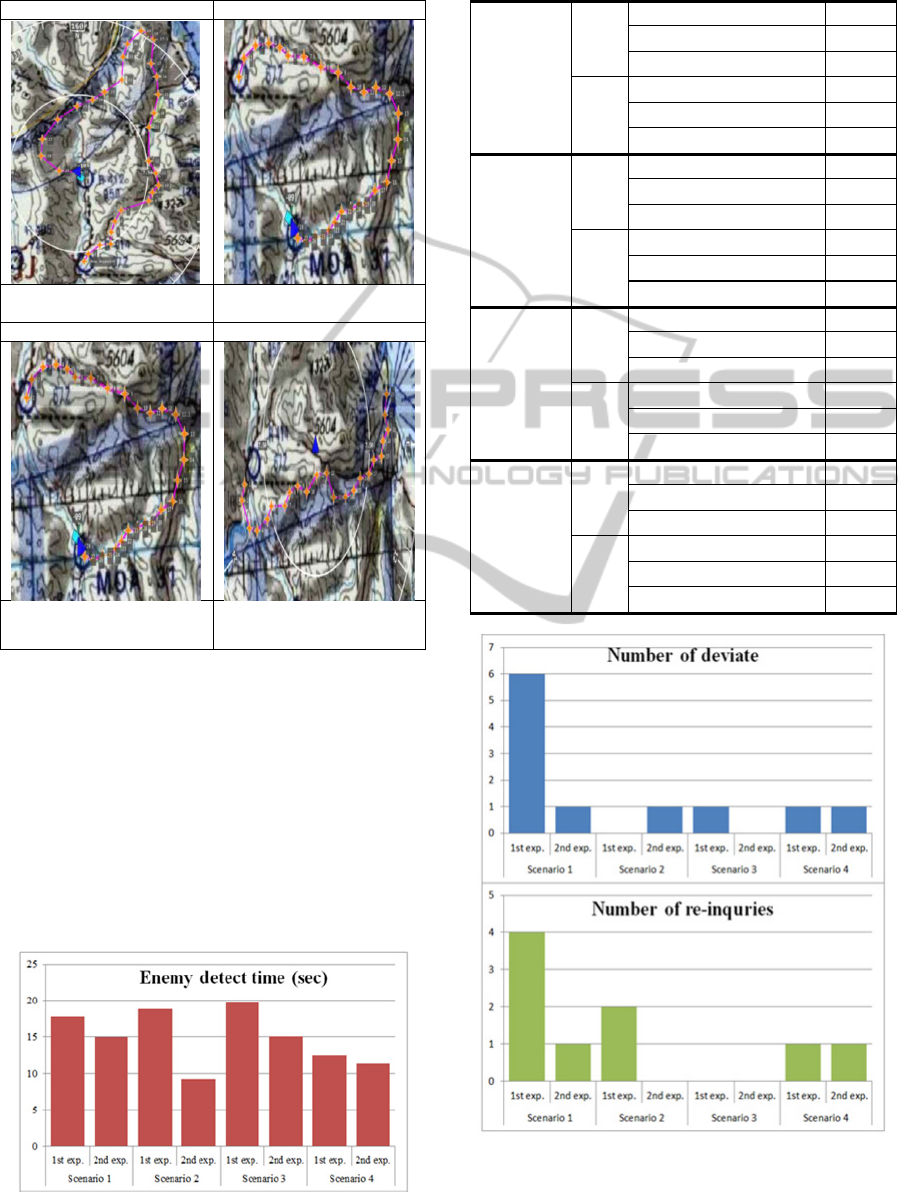
Table 2: Scenario plan maps.
Scenario 1 Scenario 2
RK43-RK44
32 Waypoints
RK43 – RKOR
29 Waypoints
Scenario 3 Scenario 4
RK43 – RKOR
36 Waypoint
RK43 – RKND
23 Waypoint
3 DATA ANALYSIS
3.1 Results
Table 3 and Figure 3 and 4 show the results of the
experiment. Essentially, when the pilot was given
more information, the time he took to find the
enemy was shorter. The command delivery was
more precise and accurate, while the pilot asked
fewer questions back to the controller.
Figure 3: Result chart (Enemy detect time).
Table 3: Results.
Scenario 1
1st
exp.
Enemy detect time 17.84
Deviate from course 6
Number of re-inquiries 4
2nd
exp.
Enemy detect time 15.02
Deviate from course 1
Number of re-inquiries 1
Scenario 2
1st
exp.
Enemy detect time 18.89
Deviate from course 0
Number of re-inquiries 2
2nd
exp.
Enemy detect time 9.27
Deviate from course 1
Number of re-inquiries 0
Scenario 3
1st
exp.
Enemy detect time 19.81
Deviate from course 1
Number of re-inquiries 0
2nd
exp.
Enemy detect time 15.11
Deviate from course 0
Number of re-inquiries 0
Scenario 4
1st
exp.
Enemy detect time 12.6
Deviate from course 1
Number of re-inquiries 1
2nd
exp.
Enemy detect time 11.34
Deviate from course 1
Number of re-inquiries 1
Figure 4: Result chart (Number of deviate and re-
inquiries).
ICINCO2014-11thInternationalConferenceonInformaticsinControl,AutomationandRobotics
682
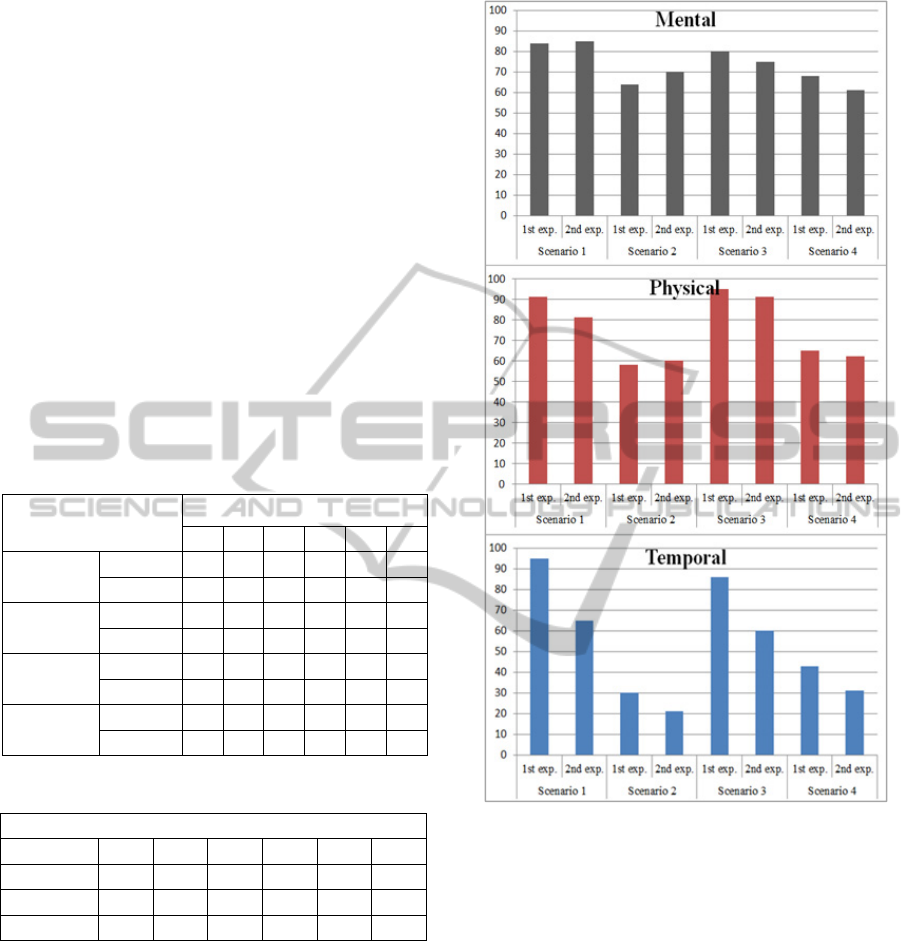
3.2 Analysis of NASA-TLX Data
Using the TLX data, we applied the paired sample
method to find out if the difference in the way of
delivering information affects the tasks. Table 4 and
Figure 5 and 6 show the TLX data, and Table 5
shows its significance levels. The values for the pilot
are significant for the Temporal, Effort, and
Frustration category, which indicate that they do
affect the pilot performance. Even when he does not
have immediate threats, the pilot is constantly under
pressure and physically stressed because he has to
check the altitude, speed, and targets. The values for
the Mental, Physical and Effort categories turned out
to be not significant. On the other hand, the values
for the Temporal, Performance, and Frustration
categories were relatively high due to the feeling of
relief he gets from accurate information delivery and
readily available information that he needs at the
moment.
Table 4: TLX Score.
Experiments
TLX Categories
M Ph T P E F
Scenario 1
1st exp. 84 91 95 25 86 20
2nd exp. 85 81 65 19 75 12
Scenario 2
1st exp. 64 58 30 24 75 10
2nd exp. 70 60 21 12 71 8
Scenario 3
1st exp. 80 95 86 36 88 12
2nd exp. 75 91 60 34 81 8
Scenario 4
1st exp. 68 65 43 12 58 25
2nd exp. 61 62 31 11 51 20
Table 5: Paired sample data.
Confidence interval of paired data
M Ph T P E F
Reliance
i
-5.7 -2.0 7.12 -0.6 3.87 1.80
Reliance
8.2 9.54 31.3 11.1 10.6 7.69
Signifi-
No No Yes No Yes Yes
4 CONCLUSIONS
When the pilot performs the scenario where various
information is given, the time he takes to detect
enemy is significantly shorter than the scenario
where only the voice command is delivered. Also,
the number of questions he asks to confirm the given
information is a lot lower. This indicates that more
information rather than simple voice commands is
more helpful for the pilot to perform his tasks better.
From the TLX analysis, the Temporal, Effort, and
Figure 5: Result charts 1 (TLX Score).
Frustration categories have significant values. It is
shown that the presence of TSD increases the
accuracy of the pilot performance and decreases the
mental pressure and stress level. According to the
NHTSA (National Highway Traffic Safety
Administration), about 71% of aviation accidents are
human caused, and about 88% of those human-
caused aviation accidents were brought on by their
low situational awareness. More research on the
TSD would lower the burden that pilots tend to feel,
while maximize the task performance ability.
TheEffectofTacticalSituationDisplayonAttackHelicopterPilot'sWorkload
683
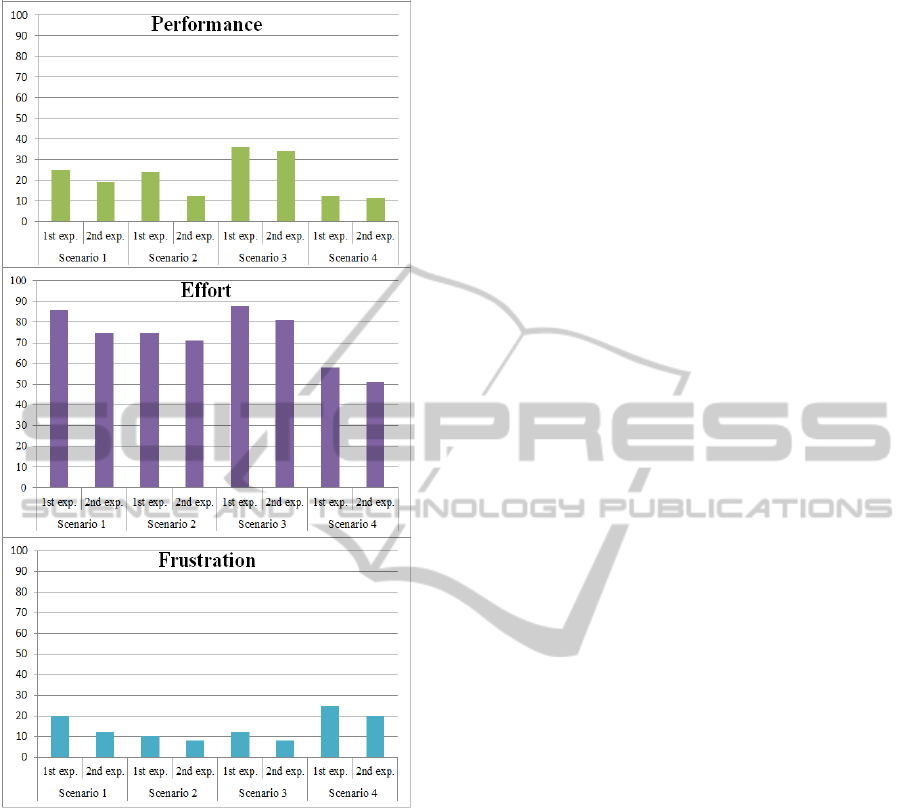
Figure 6: Result charts 2 (TLX Score).
REFERENCES
Kim Ki-Choel, Lee Jong-Sun, 2001. A Study on the Pilot
Workload Analysis in Flight Phases using the Flight
Simulator, Journal of Korean Institute of industrial
engineerings.
Woo-Sub Oh, Sung-Woo Kim, Choi Ie-Na, Jin-Suk Jang,
2005. A Study on the System Concept of KHP
Mission Equipment Package, Journal of The Korean
Society for Aeronautical and Space Sciences.
Suk-Joon Yoon, 2002. Airplane R&D simulator, Journal
of The Korean Society for Aeronautical and Space
Sciences.
Jae-Moon Lee, Chi-Young Jung, Jae-Yeong Lee, 2010.
The Combat Effectiveness Analysis of Attack
Helicopter Using Simulation and AHP, Journal of The
Korea Society for Simulation.
Jung Hoon Lee, Jun Ho Kim, Jung Yong Park, Iee Ki An,
2011. Current Status of Civil-Military Dual Use
Helicopter Development Focusing on Conversion
Case from Civil to Military Helicopter, Journal of The
Korean Society for Aeronautical and Space Sciences
Conference.
Jun-Woo Lee, Sang-Won Chae, Chil-Gee Lee, 2001.
Development of Panel Part in Flight Simulator based
on PC, Journal of The Korea Society for Simulation.
Sunh-Yun Choi, Sang-won Chae, Young-Sin Han, Chil
Gee Lee, 2002. 3D Flight Simulator for Education of
Flying Tactics, Journal of The Korea Society for
Simulation.
Tomas Schnell, Yong-Jin Kwon, Sohel Merchant, Chil
Gee Lee, 2004. Improved flight technical performance
in flight decks equipped with synthetic vision
information system displays, The international Journal
of Aviation psychology.
Jung-Hoon Lee, Byeong-Hee Chang, Hwang In-Hee,
2009. Current Status of Civil-Military Dual Use
Helicopter Development - Focusing on Conversion
Case from Military to Civil Helicopter, Current
industrial and Technological Trends in Aerospace.
Kang Byeong-Kil, 2010. Development of a Pilot
Workload Prediction Program using TAWL (Task
Analysis / Workload) Methodology, Current industrial
and Technological Trends in Aerospace.
ICINCO2014-11thInternationalConferenceonInformaticsinControl,AutomationandRobotics
684
