
Adaptive Oblivious Transfer with Hidden Access Policy Realizing
Disjunction
Vandana Guleria and Ratna Dutta
Department of Mathematics, Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur, Kharagpur-721302, India
Keywords:
Oblivious Transfer, Access Policy, Attribute based Encryption, Full Simulation Security Model.
Abstract:
We propose an efficient adaptive oblivious transfer protocol with hidden access policies. This scheme allows a
receiver to anonymously recover a message from a database which is protected by hidden attribute based access
policy if the receiver’s attribute set satisfies the associated access policy implicitly. The proposed scheme is
secure in the presence of malicious adversary under the q-Strong Diffie-Hellman (SDH), q-Power Decisional
Diffie-Hellman (PDDH) and Decision Bilinear Diffie-Hellman (DBDH) assumption in full-simulation security
model. The scheme covers disjunction of attributes. The proposed protocol outperforms the existing similar
schemes in terms of both communication and computation.
1 INTRODUCTION
The adaptive oblivious transfer with hidden access
policy (AOT-HAP) is a widely used primitive in cryp-
tography. It is useful whenever a large database is
queried adaptively. The database may contain some
sensitive information which the database holder wants
to make available only to selected recipients. In AOT-
HAP, each message is associated with some access
policy (AP). The AP could be attributes, roles, or
rights. It represents which combination of attributes
a receiver should have in order to access the mes-
sage. For instance, consider the medical database of
patients. Many patients do not want to reveal informa-
tion about their disease to anybody except their con-
cerned doctors. Also, sometimes doctors may want
to remain anonymous. The AOT-HAP is a solution to
such type of privacy problems.
The AOT-HAP consists of a sender, an issuer and
a set of receivers. The sender has a database of mes-
sages. Each message is associated with an access pol-
icy. The sender encrypts each message and makes the
encrypted database public, while keeping the access
policy AP of each message hidden. A receiver with
a set of attributes w interacts with the issuer to ob-
tain the attribute secret key for w and decrypts the
corresponding message. The receiver can recover the
message correctly if its attribute set w implicitly sat-
isfies the access policy AP. The AOT-HAP thus com-
pletes in two phases– initialization phase and transfer
phase. In initialization phase, the sender encrypts N
messages. In transfer phase, a receiver interacts with
sender and issuer adaptively and recovers k messages
of its choice, one message in one of the k transfer
phases. The sender does not learn which k messages
are learnt by which receiver and a receiver remains
oblivious about the N − k messages which it did not
query. Moreover, the access policies are kept hidden
in the encrypted database and a receiver learns noth-
ing about the access policy of a decrypted message
during a successful decryption.
Related Work. The oblivious transfer protocol (Ca-
menisch et al., 2007), (Green and Hohenberger, 2007)
and (Naor and Pinkas, 1999) allows receivers to ac-
cess the content of the database without putting any
restriction on who can access which message. To
introduce this property, Coull et al. (Coull et al.,
2009) and Camenisch et al. (Camenisch et al., 2009)
proposed oblivious transfer with access policy. The
sender assigned an access policy to each message.
Receivers whose attribute sets satisfy the access pol-
icy associated with a message can only recover the
message. The access policy in (Camenisch et al.,
2009) is restricted to conjunction of attributes only
(e.g a
1
∧ a
2
, where a
1
and a
2
are attributes). To ad-
dress disjunctive policy, the same message is dupli-
cated, i.e, if m is the message associated with ac-
cess policy (a
1
∧ a
2
) ∨ (a
3
∧ a
4
) then m is be en-
crypted twice– once with access policy (a
1
∧ a
2
) and
once with access policy (a
3
∧ a
4
), where a
1
,a
2
,a
3
and a
4
are attributes. To overcome this, Zhang et
al. (Zhang et al., 2010) proposed oblivious transfer
43
Guleria V. and Dutta R..
Adaptive Oblivious Transfer with Hidden Access Policy Realizing Disjunction.
DOI: 10.5220/0005016900430054
In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Security and Cryptography (SECRYPT-2014), pages 43-54
ISBN: 978-989-758-045-1
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

with access control realizing disjunction without du-
plication. However, the access policies are not hid-
den in (Camenisch et al., 2009), (Coull et al., 2009)
and (Zhang et al., 2010). Recently, (Camenisch et al.,
2012) and (Camenisch et al., 2011) proposed AOT-
HAP which are to the best of our knowledge the only
oblivious transfer protocols with hidden access poli-
cies.
Our Contribution. Motivated by the work of
(Camenisch et al., 2012) and (Camenisch et al.,
2011) which cover only conjunction of attributes,
we construct an efficient adaptive oblivious trans-
fer with hidden access policy (AOT-HAP). To the
best of our knowledge, our scheme is the first
AOT-HAP realizing disjunction of attributes. The
scheme uses ciphertext-policy attribute-based encryp-
tion (CP-ABE) of Ibraimi et al. (Ibraimi et al., 2009)
and Boneh-Boyan (BB) (Boneh and Boyen, 2004)
signature. The CP-ABE of Ibraimi et al. (Ibraimi
et al., 2009) is not policy hiding. To fit in our con-
struction, we first convert Ibraimi et al.’s protocol in
to policy hiding CP-ABE. The CP-ABE controls re-
ceivers entitled to recover the messages while policy
hiding CP-ABE hides the access policies associated
with each message together with restrictions on en-
titled receivers. The BB (Boneh and Boyen, 2004)
signature is used to check on the malicious behavior
of receivers. It helps one to verify whether the re-
ceiver has requested the same ciphertext in transfer
phase which was previously published by the sender
in initialization phase. The malicious behavior of the
sender and receivers is controlled by providing inter-
active zero-knowledge proofs (Cramer et al., 2000).
The security of the protocol is analyzed in full-
simulation model following (Camenisch et al., 2012)
and (Camenisch et al., 2011) considering the sender’s
security and the receiver’s security separately. In this
model, the simulator uses adversarial rewinding to
extract the hidden secret in zero-knowledge proofs.
Rewinding allows the simulator to rewind the adver-
sary’s state to previous computation state and start
the computation from there. The proposed proto-
col is secure under Decision Bilinear Diffie-Hellman
(DBDH), q-Strong Diffie-Hellman (SDH) (Boneh and
Boyen, 2004) and q-Power Decisional Diffie-Hellman
(PDDH) (Camenisch et al., 2007) assumption. The
receiver’s security is achieved by proving that the
sender does not learn who queries a message and
which message is being queried. The sender’s secu-
rity is analyzed by proving that a receiver– (i) learns
only one message in each transfer phase, (ii) learns
nothing about the access policies associated with the
messages and (iii) learns only those messages for
which it has the secret key associated with attributes
that satisfy the access policy of the message.
In contrast to (Camenisch et al., 2012) and (Ca-
menisch et al., 2011) which cover only conjunction
of attributes, our scheme realizes disjunction of at-
tributes as well, thereby realizing more expressive ac-
cess policies as compared to (Camenisch et al., 2012)
and (Camenisch et al., 2011). The proposed AOT-HAP
protocol outperforms significantly in terms of both
computation and communication overheads as com-
pared to (Camenisch et al., 2012) and (Camenisch
et al., 2011).
2 PRELIMINARIES
Throughout, we use the notations given in Table 1.
A function f (n) is negligible if f = o(n
−c
) for every
fixed positive constant c.
Table 1: Notations.
Symbol Description
ρ Security parameter
x
$
←− X Sample x uniformly at random from the set X
y ← Y y is the output of algorithm Y
DB Database
AP Access policy
N Database size
n Total number of receivers
m Total number of attributes
N Set of natural numbers
U = {1,2,. . .,n} Universe of receivers
X
c
≈ Y Computationally indistinguishable
ID
U
Identity of user U ∈ U
Ω = {a
1
,a
2
,. . .,a
m
} Universe of attributes
2.1 Access Structure and Satisfiability
Access structure (Beimel, 1996): Let {P
1
,P
2
,...,P
t
}
be a set of t parties. A collection A ⊆ 2
{P
1
,P
2
,...,P
t
}
is
monotone if B ∈ A and C ⊇ B implies C ∈ A,∀ B,C.
An access structure (respectively, monotone access
structure) is a collection (respectively, monotone col-
lection) A of non-empty subsets of {P
1
,P
2
,...,P
t
}, i.e,
A ⊆ 2
{P
1
,P
2
,...,P
t
}
\
/
0. The sets in A are called the au-
thorized sets, and the sets not in A are called the unau-
thorized sets.
Access tree (Goyal et al., 2006): Let Γ be a tree rep-
resenting an access structure. Each non-leaf node of
the tree represents a threshold gate, described by its
children and a threshold value. If num
x
is the number
of children of a node x and k
x
is its threshold value,
then 0 < k
x
≤ num
x
. The children of a node x are
numbered from 1 to num
x
. When k
x
= 1, threshold
gate is an OR gate and when k
x
= num
x
, it is an AND
gate. Each leaf node x of the tree is described by an
attribute and a threshold value k
x
= 1.
SECRYPT2014-InternationalConferenceonSecurityandCryptography
44

Satisfying an access tree (Goyal et al., 2006): Let
Γ be an access tree with root r. Denote by Γ
x
the
subtree of Γ rooted at the node x. Hence Γ is same
as Γ
r
. If a set of attributes w satisfies the access tree
Γ
x
, we denote it by Γ
x
(w) = 1. We compute Γ
x
(w)
recursively as follows. If x is a non-leaf node, evaluate
Γ
x
0
(w) for all children x
0
of node x. Γ
x
(w) returns 1
iff atleast k
x
children return 1. If x is a leaf node,
then Γ
x
(w) returns 1 iff att(x) ∈ w, where the function
att(x) is defined only if x is a leaf node and denotes
the attribute associated with the leaf node x in the tree.
2.2 Bilinear Pairing and Complexity
Assumptions
Bilinear Pairing: Let G
1
,G
2
and G
T
be three multi-
plicative cyclic groups of prime order p and g
1
and g
2
be generators of group G
1
and G
2
respectively. Then
the map e : G
1
×G
2
→ G
T
is bilinear if it satisfies the
following conditions:
(i) Bilinear – e(x
a
,y
b
) = e(x,y)
ab
∀ x ∈ G
1
,y ∈
G
2
,a,b ∈ Z
p
. (ii) Non-Degenerate – e(x, y) gener-
ates G
T
, ∀ x ∈ G
1
,y ∈ G
2
,x 6= 1,y 6= 1. (iii) Com-
putable – The pairing e(x,y) is computable efficiently
∀ x ∈ G
1
,y ∈ G
2
.
If G
1
= G
2
, then e is symmetric bilinear pairing. Oth-
erwise, e is asymmetric bilinear pairing. Throughout
the paper, we use symmetric bilinear pairing.
q-Strong Diffie-Hellman (SDH) assumption
(Boneh and Boyen, 2004): Let G be a multiplicative
cyclic group of prime order p with generator g. The
q-SDH assumption in G states: given (q + 1)-tuple
(g,g
x
,g
x
2
,...,g
x
q
),x ∈ Z
p
, it is hard to find a pair
(c,g
1
x+c
),c ∈ Z
p
.
The q-SDH assumption holds in generic group model
(Boneh and Boyen, 2004).
q-Power decisional Diffie-Hellman (PDDH) as-
sumption (Camenisch et al., 2007): Let G and
G
T
be multiplicative cyclic groups of prime order p
and e : G × G → G
T
be a symmetric bilinear pair-
ing. The q-PDDH assumption in (G, G
T
) states:
given (g,g
x
,g
x
2
,...,g
x
q
,H),x ∈ Z
p
,g
$
←− G
∗
,H
$
←−
G
T
, it is hard to distinguish the vector V =
(H
x
,H
x
2
,...,H
x
q
) ∈ G
q
T
from a random vector of G
q
T
.
The q-PDDH assumption holds in generic bilinear
group model.
Decision bilinear Diffie-Hellman (DBDH) assump-
tion (Ibraimi et al., 2009): Let G and G
T
be mul-
tiplicative cyclic groups of prime order p and e :
G × G → G
T
be a symmetric bilinear pairing. The
DBDH assumption in (G,G
T
) informally states that
given (g,g
a
,g
b
,g
c
),a,b,c ∈ Z
p
as input, it is hard to
distinguish e(g,g)
abc
from a random element G
T
.
2.3 Zero-Knowledge Proof of
Knowledge
A zero-knowledge proof of knowledge (Bellare and
Goldreich, 1993) is a two-party interactive protocol
between the prover and the verifier. We use the
notation of Camenisch and Stadler (Camenisch and
Stadler, 1997) for the various zero-knowledge proofs
of knowledge of discrete logarithms and proofs of va-
lidity of statements about discrete logarithms. For in-
stance,
POK{(a,b,c,d) | y
1
= g
a
h
b
∧ y
2
= g
c
h
d
} (1)
represents the zero-knowledge proof of knowledge of
integers a,b,c and d such that y
1
= g
a
h
b
and y
2
= g
c
h
d
holds, where a,b,c,d ∈ Z
p
,y
1
,y
2
,g,h ∈ G, where G
is a cyclic group of prime order p with generator g.
The convention is that the quantities in the paren-
thesis denote elements the knowledge of which are
being proved to the verifier by the prover while all
other parameters are known to the verifier. The pro-
tocol should satisfy two properties. First, it should
be proof of knowledge, i.e, the prover convinces the
verifier that it knows the integers a, b, c and d such
that y
1
= g
a
h
b
and y
2
= g
c
h
d
hold without reveal-
ing anything about the integers a,b,c and d. More
technically, a proof is said to be sound if there ex-
ists a knowledge extractor that extracts the secret val-
ues from a successful prover with all but negligible
probability. Second, it should be zero-knowledge, i.e,
the verifier does not learn anything about the inte-
gers a,b,c and d. More technically, a proof is said
to be perfect zero-knowledge if there exists a simu-
lator which without knowing secret values, yields a
distribution that cannot be distinguished from the dis-
tribution of the transcript generated by the interac-
tion with a real prover. The protocol completes in
three rounds. Let us illustrate how the prover and
the verifier interact to verify the equation 1. In the
first round, the prover picks z
1
,z
2
,z
3
,z
4
$
←− Z
p
, com-
putes y
3
= g
z
1
h
z
2
,y
4
= g
z
3
h
z
4
and sends y
3
,y
4
to the
verifier. This round computes four exponentiations in
G. In the second round, the verifier chooses a chal-
lenge r
$
←− Z
p
and gives it to the prover. In the third
round, the prover sets s
1
= z
1
+r ·a,s
2
= z
2
+r ·b,s
3
=
z
3
+r ·c,s
4
= z
4
+r ·d and sends s
1
,s
2
,s
3
,s
4
to the ver-
ifier. The verifier accepts the proof if g
s
1
h
s
2
= y
3
· y
r
1
and g
s
3
h
s
4
= y
4
· y
r
2
, otherwise, rejects the proof. This
round requires six exponentiations in G. The com-
munication complexity is 2 elements from G and 5
elements from Z
p
.
AdaptiveObliviousTransferwithHiddenAccessPolicyRealizingDisjunction
45

2.4 Formal Model and Security Notions
Communication Model: The adaptive oblivious
transfer with hidden access policy (AOT-HAP) is run
between a sender S and one or more receivers to-
gether with an issuer. The sender S holds a database
DB = ((m
1
,AP
1
),(m
2
,AP
2
),..., (m
N
,AP
N
)). Each
message m
i
in DB is associated with an access pol-
icy AP
i
,i = 1, 2, . . . , N. Each receiver R has some
attributes. The issuer generates the public key and
secret key pair to provide attribute secret keys associ-
ated with the attributes of the receivers. The AOT-HAP
completes in two phases– initialization phase and
transfer phase. In initialization phase, S encrypts each
message m
i
of DB associated with AP
i
in order to gen-
erate ciphertext database cDB = (Φ
1
,Φ
2
,...,Φ
N
).
The sender S does not embed access policies in cDB.
In transfer phase, R interacts with S and the issuer and
recovers k messages of its choice sequentially. In each
transfer phase, R has input σ
j
∈ [1,N], j = 1,2,...,k,
and recovers m
σ
j
after interacting with S and the is-
suer.
Syntactic of AOT-HAP: The AOT-HAP protocol con-
sists of three PPT algorithms Isetup, DBSetup,
DBInitialization in addition to two PPT interactive
protocols Issue and Transfer which are explained be-
low.
– Isetup: The issuer with input security parameter
ρ runs this algorithm to generate public parameters
params, public key PK
I
and secret key SK
I
. The is-
suer publishes params, PK
I
and keeps SK
I
secret to
itself.
– DBSetup: This algorithm is run by the sender S
who holds the database DB. It generates public and
secret key pair (pk
DB
,sk
DB
) for S. The sender S pub-
lishes public key pk
DB
and keeps secret key sk
DB
se-
cret to itself.
– DBInitialization: The sender S with input params,
PK
I
, pk
DB
, sk
DB
and DB runs algorithm DBIni-
tialization, where DB = ((m
1
,AP
1
),(m
2
,AP
2
),...,
(m
N
,AP
N
)), AP
i
being an access policy for mes-
sage m
i
,i = 1,2,...,N. This algorithms encrypts the
database DB in order to generate ciphertext database
cDB = (Φ
1
,Φ
2
,...,Φ
N
), where access policy AP
i
is
not embedded explicitly in the corresponding cipher-
text Φ
i
,i = 1,2,...,N. The sender S publishes cDB
and keeps AP
1
,AP
2
,...,AP
N
secret to itself.
– Issue protocol: The receiver R with input identity
ID
R
∈ U and attribute set w
ID
R
⊆ Ω interacts with the
issuer through a secure communication channel. The
issuer uses its public key PK
I
and secret key SK
I
to
generate attribute secret key ASK
w
ID
R
for R and sends
it in a secure manner to R.
– Transfer protocol: The receiver R on input ID
R
,
index σ ∈ [1,N], ciphertext Φ
σ
under access policy
AP
σ
, ASK
w
ID
R
and PK
I
interacts with S who holds
(pk
DB
,sk
DB
) for the database DB, where ASK
w
ID
R
is
the attribute secret key of R for the attribute set w
ID
R
.
By executing this protocol, R gets m
σ
if w
ID
R
satisfies
AP
σ
. Otherwise, R outputs ⊥.
The access policy in our construction is an access tree
in which leaves are attributes and internal nodes are
∧ and ∨ boolean operators. The access policy rep-
resents which combination of attributes can decrypt
the ciphertext. For instance, consider the encryption
of a ciphertext Φ with access policy AP = a
1
∧ (a
4
∨
(a
2
∧ a
3
)), where a
1
,a
2
,a
3
,a
4
are attributes. The set
w satisfying this access policy AP is either (a
1
,a
4
) or
(a
1
,a
2
,a
3
) or (a
1
,a
2
,a
3
,a
4
). The decrypter can de-
crypt Φ if it has the attribute secret key ASK
w
associ-
ated with the attribute set w.
Security Model: The security framework adapted
in this paper is in simulation-based-model following
(Camenisch et al., 2011). This model consists of a
real world and an ideal world. In the real world, par-
ties (a sender, an issuer and one or more receivers)
communicate with each other using a real protocol Π.
In this world, some of the parties may be corrupted
and remain corrupted throughout the execution of the
protocol. The corruption is static. Corrupted parties
are controlled by the real world adversary A. Honest
parties follow the protocol Π honestly. In the ideal
world, parties and ideal world adversary A
0
commu-
nicate by sending inputs to and receiving outputs from
an ideal functionality F . All the parties are honest in
the ideal world. The environment machine Z which is
always activated first is introduced to oversee the exe-
cution of F in the ideal world and the execution of the
protocol Π in the real world. It interacts freely with
A throughout the execution of the protocol Π in the
real world and with A
0
throughout the execution of F
in the ideal world. We describe below how the par-
ties communicate in both the worlds upon receiving
messages from Z.
– Real world: The sender and the issuer do not return
anything to Z, but the receiver does in the real world.
• The issuer generates the public parameters
params, public key PK
I
and secret key SK
I
by
running the algorithm Isetup. It publishes params,
PK
I
and keeps SK
I
secret to itself.
• The sender S runs the algorithm DBSetup in order
to generate public key pk
DB
and secret key sk
DB
.
It publishes pk
DB
and keeps sk
DB
secret to itself.
• The receiver R upon receiving the message (issue,
ID
R
, w
ID
R
) from Z engages in an Issue protocol
with the issuer on input ID
R
and attribute set w
ID
R
.
After completion of Issue protocol, R returns (is-
SECRYPT2014-InternationalConferenceonSecurityandCryptography
46

sue, ID
R
, b) to Z in response to the message (is-
sue, ID
R
, w
ID
R
), where b ∈ {0,1}. The random
coin b = 1 means that R has obtained the attribute
secret key ASK
w
ID
R
for attribute set w
ID
R
⊆ Ω.
Otherwise, R has failed.
• Upon receiving the message (encDB,DB), where
DB = ((m
1
,AP
1
),(m
2
,AP
2
), .. .,(m
N
,AP
N
))
from Z, S runs the DBInitialization algorithm to
generate ciphertext database cDB = (Φ
1
,Φ
2
,...,
Φ
N
) under their respective access policies
(AP
1
,AP
2
,...,AP
N
). The sender S pub-
lishes ciphertext database cDB and keeps
AP
1
,AP
2
,...,AP
N
secret to itself.
• The receiver R with identity ID
R
upon receiving the
message (transfer, ID
R
, σ) from Z engages in an
Transfer protocol with S. If the transfer succeeded,
R returns (transfer, ID
R
, m
σ
) to Z in response to
the message (transfer, ID
R
, σ). Otherwise, R re-
turns (transfer, ID
R
, ⊥) to Z
– Ideal world: All parties communicate through an
ideal functionality F in the ideal world. The honest
parties upon receiving the message (issue, ID
R
, w
ID
R
),
(encDB,DB) or (transfer, ID
R
, σ) from Z transfer it
to F . We briefly explain the behavior of F . The ideal
functionality F keeps an attribute set w
ID
R
for each
receiver R which is initially set to be empty.
• The ideal functionality F upon receiving the mes-
sage (issue, ID
R
, w
ID
R
) from R with identity ID
R
∈
U, sends (issue, ID
R
, w
ID
R
) to the issuer. The is-
suer sends back a bit c = 1 to F in response to the
message (issue, ID
R
, w
ID
R
) if the issuer success-
fully generates the attribute secret key ASK
w
ID
R
for a receiver corresponding to its attribute set
w
ID
R
. For c = 1, F sets w
ID
R
= w
ID
R
. Otherwise,
F does nothing.
• Upon receiving the message (encDB, DB)
from the sender S, where DB =
((m
1
,AP
1
),(m
2
,AP
2
),..., (m
N
,AP
N
)), F records
DB = ((m
1
,AP
1
),(m
2
,AP
2
), ...,(m
N
,AP
N
)).
• The ideal functionality F upon receiving the mes-
sage (transfer, ID
R
, σ) from R, checks whether
DB = ⊥. If DB 6= ⊥, F sends the message (trans-
fer) to S. The sender S sends back a bit d in re-
sponse to the message (transfer). If the transfer
succeeds, S sets d = 1. For d = 1, F checks if
σ ∈ [1,n] and w
ID
R
satisfies AP
σ
embedded in DB.
Then F sends m
σ
to R. Otherwise, it sends ⊥ to
R.
Let REAL
Π,Z,A
be the output of Z after interacting
with A and the parties running the protocol Π in the
real world. Also, let IDEAL
F ,Z,A
0
be the output of
Z after interacting with A
0
and parties interacting
with F in the ideal world. The task of Z is to dis-
tinguish with non-negligible probability REAL
Π,A,Z
from IDEAL
F ,A
0
,Z
. The protocol is said to be se-
cure if REAL
Π,A,Z
is computationally indistinguish-
able from IDEAL
F ,A
0
,Z
.
3 CONCRETE CONSTRUCTION
A high level description of our adaptive obliv-
ious transfer protocol with hidden access policy
(AOT-HAP) is as follows. In initialization phase,
the sender S with the database DB = ((m
1
,AP
1
),
(m
2
,AP
2
),...,(m
N
,AP
N
)) signs the index i of each
message m
i
with the BB signature to keep a check
on the malicious behavior of the receiver R. The
signed index i is moved to group G
T
as e(A
i
,h),
where A
i
is the BB signature on index i. The mes-
sage m
i
∈ G
T
is masked with signed index i and the
component B
i
= e(A
i
,h) · m
i
is encrypted using CP-
ABE of (Ibraimi et al., 2009) under the access policy
AP
i
associated with index i. The CP-ABE of B
i
is D
i
,
where D
i
= (K
(0)
i
,K
(1)
i
,K
(2)
i, j
). The access policy is not
made public. The sender S also gives zero-knowledge
proof of knowledge of exponents used in generating
ciphertext database cDB = (Φ
1
,Φ
2
,...,Φ
N
). In each
transfer phase, whenever R wants to decrypt a cipher-
text Φ
σ
j
with a set of attributes w
ID
R
, R engages in Is-
sue protocol with the issuer. The issuer generates the
attribute secret key ASK
w
ID
R
for w
ID
R
and gives it to
R. With ASK
w
ID
R
= (d
0
,d
l
∀ a
l
∈ w
ID
R
), R computes
I
σ
j
= e(K
(1)
σ
j
,d
0
) and J
σ
j
=
∏
a
l
∈w
ID
R
e
K
(2)
σ
j
,l
,d
l
and
randomizes it. To make sure that R has randomized
the ciphertext that was previously published by S, the
receiver R proves knowledge of a valid signature for
its randomized ciphertext without revealing anything.
In order to recover the message m
σ
j
, R engages in
Transfer protocol with S. Formally, our scheme works
as follows. To generate bilinear pairing, we invoke
algorithm BilinearSetup which on input security pa-
rameter ρ generates params = (p,G,G
T
,e,g), where
e : G × G → G
T
is a symmetric bilinear pairing, g is
a generator of group G and p, the order of the groups
G and G
T
, is prime, i.e params = (p,G,G
T
,e,g) ←
BilinearSetup(1
ρ
).
– Isetup: The issuer on input ρ generates params =
(p,G,G
T
,e,g) ← BilinearSetup(1
ρ
). It picks
α,t
1
,t
2
,...,t
m
$
←− Z
∗
p
and computes T
j
= g
t
j
, j =
1,2,...,m,Y = e(g,g)
α
. The public key is PK
I
=
(params,Y,T
1
,T
2
,...,T
m
) and secret key is SK
I
=
(α,t
1
,t
2
,...,t
m
). The issuer publishes PK
I
to all the
parties and keeps SK
I
secret to itself.
– DBSetup: The sender S with input params generates
AdaptiveObliviousTransferwithHiddenAccessPolicyRealizingDisjunction
47

setup parameters for the database DB. It first picks
x,β,γ
$
←− Z
∗
p
, h
$
←− G and sets y = g
x
,H = e(g,h),Z =
e(g,g)
β
,P = e(g,g)
γ
. The public key is pk
DB
=
(H,Z, P,y) and secret key is sk
DB
= (h, x, β, γ). The
sender S publishes pk
DB
to all parties and keeps sk
DB
secret to itself. The sender S gives proof of knowl-
edge POK{(h,β,γ)|H = e(g,h) ∧ Z = e(g,g)
β
∧ P =
e(g,g)
γ
} to R. Each receiver R upon receiving pk
DB
checks the correctness of pk
DB
by verifying the POK.
If it fails, R aborts the execution. Otherwise, R accepts
pk
DB
.
– DBInitialization: The sender S on input
PK
I
,params,pk
DB
,sk
DB
and DB computes ci-
phertext database cDB = (Φ
1
,Φ
2
,...,Φ
N
),
where DB =((m
1
,AP
1
), (m
2
,AP
2
), . . .,
(m
N
,AP
N
)),m
i
∈ G
T
,i = 1,2, . . . , N. Each
message m
i
is associated with access policy
AP
i
,i = 1,2,...,N. The ciphertext Φ
i
for each
message m
i
,i = 1,2,...,N, is generated by S as
follows.
1. Parse params to extract g and sk
DB
to extract x.
Generate the BB signature on index i as A
i
= g
1
x+i
.
The signature is computed to keep an eye on
the malicious activities of R. If R deviates from
the protocol specification during transfer phase, it
will get detected.
2. Compute B
i
= e(A
i
,h) · m
i
.
3. In order to hide the access policy AP
i
associated
with each message m
i
, encrypt B
i
under the access
policy AP
i
as explained below.
(a) Pick s
i
$
←− Z
p
and compute K
(0)
i
= B
i
· Y
s
i
,
K
(1)
i
= g
βs
i
, where Y = e(g,g)
α
is extracted
from PK
I
.
(b) Set the value of root node of access policy
AP
i
to be s
i
. Mark root node assigned and all
its child nodes unassigned. Let l be the number
of child nodes of root in the access tree corre-
sponding to AP
i
. For each unassigned node do
the following recursively:
(i) If the internal node is ∧ and its child nodes
are unassigned, assign a value to each unas-
signed child node by the following technique.
For each child node except the last one, assign
r
i, j
$
←− Z
∗
p
and to the last child node assign the
value s
i
−
∑
l−1
i=1
r
i, j
. Mark these nodes assigned.
(ii) If the internal node is ∨, set the value of
each child node to be s
i
and mark the node as-
signed.
(iii) Let x be a marked node with value
e
r whose
child nodes are yet to be marked. Repeat steps
(i) and (ii) by replacing root by node x and value
s
i
by
e
r.
(c) For each leaf attribute a
j
∈ AP
i
, compute
K
(2)
i, j
= T
γs
i, j
j
, where s
i, j
is the value assigned to
leaf node a
j
as in step(b). Note that
∑
a
j
∈w
s
i, j
=
s
i
for any set of attributes w satisfying the ac-
cess policy AP
i
.
(d) For a
j
/∈ AP
i
, set K
(2)
i, j
= T
γs
i, j
j
·g
z
j
, s
i, j
,z
j
$
←−
Z
∗
p
.
(e) Compute π
i
= POK{(s
i
,s
i,1
,s
i,2
,...,s
i,m
)|
Q
i
= e(g,K
(1)
i
) = Z
s
i
∧L
i,1
= g
s
i,1
∧L
i,2
= g
s
i,2
∧
... ∧ L
i,m
= g
s
i,m
}.
The encryption of B
i
is D
i
= (K
(0)
i
,K
(1)
i
,K
(2)
i, j
),
which is generated following CP-ABE of Ibraimi
et al. (Ibraimi et al., 2009) together with the zero-
knowledge proof of knowledge π
i
, j = 1,2,...,m.
4. Set F
i
= (Q
i
,L
i,1
,L
i,2
,...,L
i,m
).
5. Set ciphertext Φ
i
= (A
i
,D
i
,F
i
,π
i
).
6. The ciphertext database cDB = (Φ
1
,Φ
2
,...,Φ
N
).
The receiver R verifies the proof π
i
, and
e(A
i
,yg
i
) = e(g,g),i = 1,2,...,N, on receiving
ciphertext database cDB. If the verification holds, R
accepts cDB. Otherwise, R aborts the execution.
– Issue protocol: The Issue protocol is the in-
teraction between R and the issuer. The in-
put of R is its attribute set w
ID
R
and identity
ID
R
∈ U. The issuer picks r
ID
R
$
←− Z
∗
p
and sets
d
0
= g
α−r
ID
R
, d
l
= g
r
ID
R
·t
−l
l
∀ a
l
∈ w
ID
R
. The
attribute secret key is ASK
w
ID
R
= (d
0
,d
l
∀ a
l
∈
w
ID
R
). The issuer sends ASK
w
ID
R
to R through a
secure communication channel together with proof
of knowledge POK{(SK
I
)|(PK
I
,SK
I
) is a key pair}
= POK{(α,t
1
,t
2
,...,t
m
)|Y = e(g,g)
α
∧ T
1
= g
t
1
∧
T
2
= g
t
2
∧ . . . ∧ T
m
= g
t
m
} to R. The receiver R ver-
ifies the proof. If the verification does not hold, R
aborts the execution. Otherwise, R accepts attribute
secret key ASK
w
ID
R
.
– Transfer protocol: The pictorial view of high level
description of transfer protocol is given in Figure 1.
This protocol is the interaction between S and R. In
each of the transfer phase, R picks the index σ
j
of its
choice with attribute set w
ID
R
. The receiver R engages
in Issue protocol with the issuer in order to obtain the
attribute secret key ASK
w
ID
R
for the attribute set w
ID
R
.
On receiving ASK
w
ID
R
= (d
0
,d
l
∀a
l
∈ w
ID
R
) for w
ID
R
,
R computes I
σ
j
and J
σ
j
as follows
I
σ
j
= e(K
(1)
σ
j
,d
0
) = e(g
βs
σ
j
,g
α−r
ID
R
),
J
σ
j
=
∏
a
l
∈w
ID
R
e
K
(2)
σ
j
,l
,d
l
.
SECRYPT2014-InternationalConferenceonSecurityandCryptography
48

Sender(DB) Receiver(ID
R
)
SK
w
ID
R
= (d
0
,d
l
∀a
l
∈ w
ID
R
)
σ
j
, j = 1,2,. ..,k
Parse φ
σ
j
as (A
σ
j
,D
σ
j
,F
σ
j
,π
σ
j
)
D
σ
j
= (K
(0)
σ
j
,K
(1)
σ
j
,K
(2)
σ
j
,l
),l = 1, 2,... ,m
F
σ
j
= (Q
σ
j
,L
σ
j
,1
,L
σ
j
,2
,. . .,L
σ
j
,m
)
v
σ
j
$
←− Z
∗
p
I
σ
j
= e(K
(1)
σ
j
,d
0
)
J
σ
j
=
∏
a
l
∈w
ID
R
e
K
(2)
σ
j
,l
,d
l
V
σ
j
= A
v
σ
j
σ
j
,X
σ
j
= I
v
σ
j
σ
j
,U
σ
j
= J
v
σ
j
σ
j
V
σ
j
,X
σ
j
,U
σ
j
←−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−
POK{(σ
j
,v
σ
j
)| e(V
σ
j
,y)=e(V
σ
j
,g)
−σ
j
e(g,g)
v
σ
j
}
W
σ
j
= e(V
σ
j
,h) · X
1
β
σ
j
U
1
γ
σ
j
W
σ
j
−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−→
POK{(β,h,γ)| W
σ
j
=e(V
σ
j
,h)·X
1
β
σ
j
U
1
γ
σ
j
∧
Z = e(g, g)
β
∧ H = e(g, h) ∧ P = e(g, g)
γ
}
K
(1)
σ
j
W
1
v
σ
j
σ
j
= m
σ
j
Figure 1: Transfer Protocol.
The receiver R randomizes A
σ
j
,I
σ
j
,J
σ
j
by choosing v
σ
j
$
←−
Z
∗
p
, sets V
σ
j
= A
v
σ
j
σ
j
,X
σ
j
= I
v
σ
j
σ
j
and U
σ
j
= J
v
σ
j
σ
j
and sends
V
σ
j
,X
σ
j
,U
σ
j
to S. The receiver R also gives zero-
knowledge proof of knowledge POK{(σ
j
,v
σ
j
)| e(V
σ
j
,y) =
e(V
σ
j
,g)
−σ
j
e(g,g)
v
σ
j
} to S. On verifying the proof, S
parses its secret key sk
DB
= (β,x,h,γ), extracts β,γ and
h to generate W
σ
j
= e(V
σ
j
,h) · X
1
β
σ
j
U
1
γ
σ
j
and gives it to
R together with the zero-knowledge proof of knowledge
POK{(β,h,γ)| W
σ
j
= e(V
σ
j
,h)·X
1
β
σ
j
U
1
γ
σ
j
∧H = e(g,h)∧Z =
e(g,g)
β
∧ P = e(g,g)
γ
}. The receiver R first verifies the
proof and uses its random value v
σ
j
used to generate
V
σ
j
,I
σ
j
,J
σ
j
to recover the message m
σ
j
as follows
K
(1)
σ
j
W
1
v
σ
j
σ
j
= m
σ
j
. (2)
The receiver R adaptively runs the transfer phase for
k different indexes σ
j
, j = 1, 2,... ,k. The correctness of
equation 2 is given as
I
σ
j
= e(K
(1)
σ
j
,d
0
) = e(g
βs
σ
j
,g
α−r
ID
R
)
= e(g,g)
βs
σ
j
(α−r
ID
R
)
X
σ
j
= I
v
σ
j
σ
j
= e(g,g)
v
σ
j
βs
σ
j
(α−r
ID
R
)
J
σ
j
=
∏
a
l
∈w
ID
R
e
K
(2)
σ
j
,l
,d
l
=
∏
a
l
∈w
ID
R
e(T
γs
σ
j
,l
l
,g
r
ID
R
t
−1
l
)
=
∏
a
l
∈w
ID
R
e(g
γt
l
s
σ
j
,l
,g
r
ID
R
t
−1
l
)
= e(g,g)
γr
ID
R
∑
a
l
∈w
ID
R
s
σ
j
,l
= e(g,g)
γr
ID
R
s
σ
j
U
σ
j
= J
v
σ
j
σ
j
= e(g,g)
v
σ
j
γr
ID
R
s
σ
j
W
σ
j
= e(V
σ
j
,h) · X
1
β
σ
j
U
1
γ
σ
j
=
e(A
σ
j
,h)e(g,g)
s
σ
j
(α−r
ID
R
)
e(g,g)
r
ID
R
s
σ
j
v
σ
j
=
e(A
σ
j
,h)e(g,g)
αs
σ
j
v
σ
j
=
e(A
σ
j
,h)Y
s
σ
j
v
σ
j
as Y = e(g,g)
α
K
(1)
σ
j
W
1
v
σ
j
σ
j
=
e(A
σ
j
,h)m
σ
j
Y
s
σ
j
W
1
v
σ
j
σ
j
= m
σ
j
Note that
∑
a
l
∈w
ID
R
s
σ
j
,l
= s
σ
j
holds only when the at-
tribute set w
ID
R
satisfies the access policy AP
σ
j
. Thus
although AP
σ
j
is kept hidden from the receivers, a
receiver with a valid attribute set w
ID
R
(that satisfies
AP
σ
j
) is capable of recovering the message m
σ
j
en-
crypted under AP
σ
j
. A receiver with an attribute set
w that does not satisfy AP
σ
j
will get a random value
by decrypting Φ
σ
j
. For instance, consider the mes-
sage B
1
with the access policy AP
1
= (a
1
∧ (a
4
∨
(a
2
∧ a
3
))), i.e, σ
j
= 1. The CP-ABE of B
1
is as fol-
lows. Pick s
1
$
←− Z
p
, set K
(0)
1
= B
1
·Y
s
1
,K
(1)
1
= g
βs
1
,
K
(2)
1,1
= T
γs
1,1
1
,K
(2)
1,2
= T
γs
1,2
2
,K
(2)
1,3
= T
γs
1,3
3
,K
(2)
1,4
= T
γs
1,4
4
and K
(2)
1, j
= T
γs
1, j
j
g
z
j
,s
1, j
,z
j
$
←− Z
p
, j = 5,6,...,m. The
ciphertext D
1
= (K
(0)
1
,K
(1)
1
,K
(2)
1, j
), j = 1,2,...,m. The
values s
1,1
,s
1,2
,s
1,3
and s
1,4
used above were gener-
ated as follows. The root node of the access pol-
icy AP
1
= (a
1
∧ (a
4
∨ (a
2
∧ a
3
))) is ∧. Assign value
AdaptiveObliviousTransferwithHiddenAccessPolicyRealizingDisjunction
49

s
1
$
←− Z
p
to this node and mark this node assigned.
Mark the child nodes unassigned which are a
1
and
∨. By the step 3(b)(i) explained in DBInitialization
assign value s
1,1
= r
1,1
$
←− Z
p
to a
1
and s
1
− r
1,1
to
∨. Replace the root by node ∨ with value s
1
− r
1,1
.
By the step 3(b)(ii), assign value s
1,4
= s
1
− r
1,1
to a
4
and s
1,2
− r
1,1
to ∧. Replace the root by node ∧ with
value s
1
− r
1,1
. Following step 3(b)(i), assign value
s
1
$
←− Z
p
to a
2
and s
1
− r
1,1
− s
1,2
= s
1,3
to a
3
. Sup-
pose the attribute set w
1
= {a
1
,a
4
} is with a receiver
which clearly satisfies the access policy AP
1
. There-
fore,
∑
a
l
∈w
1
s
1,l
= s
1,1
+ s
1,4
= r
1,1
+ s
1
− r
1,1
= s
1
.
Note. The CP-ABE scheme of Ibraimi et al. (Ibraimi
et al., 2009) is not policy hiding, but in our construc-
tion we make it policy hiding using secrets β and
γ. For instance, consider the encryption of M
i
un-
der the access policy AP
i
using CP-ABE of Ibraimi
et al. (Ibraimi et al., 2009) which is (K
(0)
i
,K
(1)
i
,K
(2)
i, j
),
where
K
(0)
i
= M
i
·Y
s
i
,
K
(1)
i
= g
s
i
,
K
(2)
i, j
= T
s
i, j
j
if a
j
∈ AP
i
,
s
i, j
are taken according to step 3(b) of algorithm
DBInitialization. In order to hide the access pol-
icy AP
i
, we hide K
(1)
i
using secret β and K
(2)
i, j
us-
ing secret γ together with random K
(2)
i, j
for a
j
/∈ AP
i
.
Thereby, the encryption of M
i
in our construction is
(K
(0)
i
,K
(1)
i
,K
(2)
i, j
), where
K
(0)
i
= M
i
·Y
s
i
,
K
(1)
i
= g
βs
i
,
K
(2)
i, j
=
T
γs
i, j
j
, a
j
∈ AP
i
, s
i, j
as in 3(b)
T
γs
i, j
j
· g
z
j
, a
j
/∈ AP
i
, s
i, j
,z
j
$
←− Z
∗
p
.
A receiver is unable to decrypt M
i
using attribute se-
cret key only issued by the issuer because of the se-
crets β and γ used by the sender during encryption.
The receiver has to interact with the sender to recover
M
i
correctly. In our construction, K
(2)
i, j
is linear to m
whereas in Ibraimi et al. K
(2)
i, j
is linear to number of
attributes in AP
i
. The protocol is constructed in such
a way that a receiver will get a correct message only
if the receiver’s attribute set satisfies the access policy
associated with the message implicitly.
4 COMPARISON WITH AOT-HAP
IN (Camenisch et al., 2012) AND
(Camenisch et al., 2011)
In this section, we compare the proposed scheme with
the AOT-HAP in (Camenisch et al., 2012) and (Ca-
menisch et al., 2011) which are the only two AOT-
HAP to the best of our knowledge. The proposal
of (Camenisch et al., 2011) employed Camenisch et
al.’s (Camenisch et al., 2007) oblivious transfer, batch
Boneh-Boyan (BB) (Boneh and Boyen, 2004) signa-
ture and Camenisch-Lysyanskaya (CL) signature (Ca-
menisch and Lysyanskaya, 2004). On the contrary,
the AOT-HAP of Camenisch et al. (Camenisch et al.,
2012) relies on interactive zero-knowledge proofs
(Cramer et al., 2000), Groth-Sahai non-interactive
proofs (Groth and Sahai, 2008), the privacy friendly
signature (Abe et al., 2010) and ciphertext-policy
attribute-based encryption (CP-ABE) (Nishide et al.,
2008). We point that in (Camenisch et al., 2011),
the access policy associated with a message is of
the form AP = (c
1
,c
2
,...,c
l
), where c
i
∈ {0,1},i =
1,2,...,l. On the other hand, the access policy in (Ca-
menisch et al., 2012) is AP = (c
1
,c
2
,...,c
l
), where
c
i
∈ [1,n
i
],i = 1, 2, . . . , l. The symbol l denotes the
number of categories and n
i
is the number of possi-
ble attributes for each category. Thus each category
c
i
in (Camenisch et al., 2012) has n
i
values whereas
in (Camenisch et al., 2011) each category c
i
has only
two values. The schemes in (Camenisch et al., 2012)
and (Camenisch et al., 2011) covers only conjunction
of attributes. In contrast to (Camenisch et al., 2012)
and (Camenisch et al., 2011), our scheme employs
modified policy hiding Ibraimi et al.’s (Ibraimi et al.,
2009) CP-ABE and BB (Boneh and Boyen, 2004) sig-
nature. Our scheme allows disjunction of attributes
as well, thereby realizes more expressive access pol-
icy. On a more positive note, the proposed protocol is
significantly more efficient as compared to both (Ca-
menisch et al., 2012) and (Camenisch et al., 2011) as
illustrated in Tables 2, 3 and 4, where PO stands for
the number of pairing, EXP for the number of expo-
nentiation, l denotes the number of categories, m is
the total number of attributes, αX + βY represents α
elements from the group X and β elements from the
group Y . In (Camenisch et al., 2011), m = 2l and in
(Camenisch et al., 2012) m = n
1
+ n
2
+ ...+ n
l
. Note
that (Camenisch et al., 2012) and (Camenisch et al.,
2011) used asymmetric bilinear pairing e : G
1
×G
2
→
G
T
. The computation cost also include the cost of
verifying the proof of knowledge POK.
Ours Isetup algorithm requires the issuer to compute
m EXP in G, 1 EXP in G
T
and 1 PO to generate the
public key PK
I
, whereas (Camenisch et al., 2012) and
SECRYPT2014-InternationalConferenceonSecurityandCryptography
50
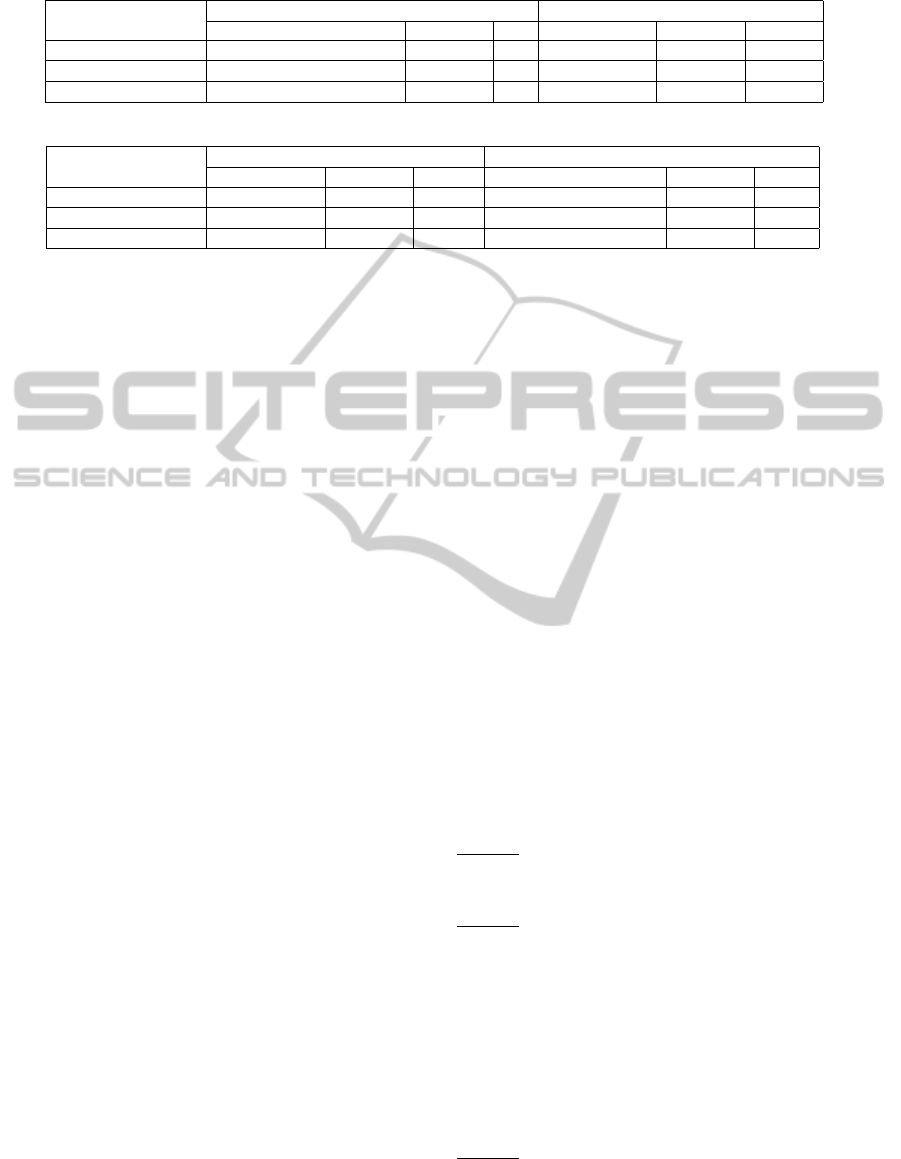
Table 2: Comparison of computation in per ciphertext generation.
AOT-HAP Sender Receiver
EXP in G
1
+ G
2
EXP in G
T
PO EXP in G
1
+ G
2
EXP in G
T
PO
(Camenisch et al., 2012) (m +4l +16)G
1
+ (4l + 10)G
2
1 – 4G
2
– 8l + 26
(Camenisch et al., 2011) (4l +7)G
1
+ (8l + 9)G
2
– 1 – 16l + 10 144l + 19
Ours (3m +2)G 3 1 (2m +1)G 2 1
Table 3: Comparison of computation in per Transfer protocol.
AOT-HAP Sender Receiver
EXP in G
1
+ G
2
EXP in G
T
PO EXP in G
1
+ G
2
EXP in G
T
PO
(Camenisch et al., 2012) 17G
1
+ 9G
2
45 41 27G
1
+ 22G
2
38 2l + 43
(Camenisch et al., 2011) (12l +104)G
1
4l + 51 18l + 20 (16l +99)G
1
+ (8l + 35)G
2
3l + 36 1
Ours – 9 4 1G 14 6
(Camenisch et al., 2011) requires (m + 6) in G
1
, 2 in
G
2
, 1 in G
T
, 3 PO and (n + 3) in G
1
, 3 in G
2
re-
spectively. Also, the sender computes 1 EXP in G, 2
EXP in G
T
and 1 PO to generate the public key pk
DB
in DBSetup algorithm while that of (Camenisch et al.,
2012) and (Camenisch et al., 2011) computes 5 in G
1
,
2 in G
2
, 2 PO and l + 3 in G
1
, 1 PO respectively.
We emphasize that our scheme computes only a con-
stant number of pairings while that of (Camenisch
et al., 2012) and (Camenisch et al., 2011) is linear to l.
Total number of exponentiations is less in our scheme
as compared to (Camenisch et al., 2012) and (Ca-
menisch et al., 2011). Communication-wise our con-
struction performs favorably over (Camenisch et al.,
2012) and (Camenisch et al., 2011). Table 4 com-
pares the communication cost in transferring one ci-
phertext. It also compares the communication over-
heads in Transfer protocol. Note that the communi-
cation cost also include the cost involved in verifying
the proof of knowledge POK.
The communication cost involved in transferring ele-
ments the from issuer to R and from R to the issuer
is significantly low as compared to (Camenisch et al.,
2012) and (Camenisch et al., 2011).
5 SECURITY ANALYSIS
Theorem 1. The adaptive oblivious transfer with hid-
den access policy (AOT-HAP) decribed in section 2.4
securely implements the AOT-HAP functionality as-
suming the hardness of the q-SDH problem in G, the
(q + 1)-PDDH problem in G and G
T
, the knapsack
problem and provided that CP-ABE is fully secure un-
der DBDH assumption, the underlying POK is sound
and perfect zero-knowledge.
Proof. The security of the protocol is analyzed by
proving indistinguishability between adversary ac-
tions in the real protocol and in an ideal scenario.
Let A be a static adversary in the real protocol. We
construct an ideal world adversary A
0
such that no
environment machine Z can distinguish with non-
negligible probability whether it is interacting with
A in the real world or with A
0
in the ideal world
in the following cases: (a) simulation when only
the receiver R is honest, (b) simulation when only
the sender S is corrupt (c) simulation when only the
receiver R is corrupt (d) simulation when only the
sender S is honest. We do not discuss the cases when
all the parties (the sender S, the receiver R and the
issuer) are honest, when all the parties are corrupt,
when only the issuer is honest and when only the is-
suer is corrupt.
We present the security proof using sequence of hy-
brid games. Let Pr[Game i] be the probability that
Z distinguishes the transcript (messages transferred
from the sender S to the receiver R and from the re-
ceiver R to the sender S) of Game i from the real exe-
cution.
(a) Simulation when the sender S and the issuer
are corrupt while the receiver R is honest. Firstly,
we simulate the interactions of real world. The adver-
sary A controls the corrupted parties (the sender and
the issuer) whereas the simulator simulates the honest
receiver R.
Game 0: The simulator S
0
simulates R and interacts
with A exactly as in the real world. So, Pr[Game 0] =
0. Therefore REAL
Π,Z,A
= Pr[Game 0].
Game 1: The simulator S
1
works same as S
0
except
that S
1
extracts secret key SK
I
= (α,t
1
,t
2
,...,t
m
)
by running the knowledge extractor of
POK{SK
I
|(PK
I
,SK
I
) is a key pair} when the is-
sue query is instructed by Z. The difference
between Game 1 and Game 0 is given by the
knowledge error of POK which is negligible pro-
vided the underlying POK is sound. Therefore,
there exists a negligible function ε
1
(ρ) such that
|Pr[Game 1] − Pr[Game 0]| ≤ ε
1
(ρ).
Game 2: This game is the same as Game 1 except
that the simulator S
2
runs the knowledge extractor
of POK{(h,β,γ)|H = e(g,h) ∧ Z = e(g,g)
β
∧ P =
e(g,g)
γ
} to extract h,β,γ from A. The difference be-
AdaptiveObliviousTransferwithHiddenAccessPolicyRealizingDisjunction
51

Table 4: Comparison in terms of communication.
AOT-HAP Per Ciphertext Per Transfer Protocol
Z
p
G
1
+ G
2
G
T
Z
p
G
1
+ G
2
G
T
(Camenisch et al., 2012) 1 (m +2l +11)G
1
+ (2l + 4)G
2
1 19 18G
1
+ 14G
2
21
(Camenisch et al., 2011) – (4l + 2)G
1
+ (4l + 5)G
2
1 (6l + 55)G
1
+ (4l + 40)G
2
4l + 7 17
Ours 2m +2 3m +2 3 8 2 8
tween Game 2 and Game 1 is the knowledge error
of POK which is negligible provided the underlying
POK is sound. Therefore, there exists a negligible
function ε
2
(ρ) such that |Pr[Game 2]−Pr[Game 1]| ≤
ε
2
(ρ).
Game 3: The simulator S
3
works same as S
2
except
that S
3
extracts the secret exponents s
i
,s
i,1
,s
i,2
,...,
s
i,m
by running the knowledge extractor of π
i
=
POK{(s
i
,s
i,1
,s
i,2
,...,s
i,m
)|Q
i
= Z
s
i
∧ L
i,1
= g
s
i,1
∧
L
i,2
= g
s
i,2
∧... ∧ L
i,m
= g
s
i,m
} when the sender S pub-
lishes ciphertext database cDB upon instructed by Z.
The difference between Game 3 and Game 2 is given
by the knowledge error of POK which is negligi-
ble provided the underlying POK is sound. There-
fore, there exists a negligible function ε
3
(ρ) such that
|Pr[Game 3] − Pr[Game 2]| ≤ ε
3
(ρ).
Game 4: The simulator S
4
works same as S
3
ex-
cept that S
4
engages in a transfer protocol with A
to learn message randomly chosen from those for
which S
4
has the necessary decryption key. The dif-
ference between Game 4 and Game 3 is negligible due
to the perfect zero-knowledgeness of the underlying
POK{(σ
j
,v
σ
j
)| e(V
σ
j
,y) = e(V
σ
j
,g)
−σ
j
e(g,g)
v
σ
j
}.
Therefore, there exists a negligible function ε
4
(ρ)
such that |Pr[Game 4] − Pr[Game 3]| ≤ ε
4
(ρ).
Now we construct the ideal world adversary A
0
with black box access to A. The adversary
A
0
incorporates all steps from Game 4. The
adversary A
0
first interacts with A to get Φ
i
,
where Φ
i
= (A
i
,D
i
,F
i
,π
i
),A
i
= g
1
x+i
,D
i
= (K
(0)
i
=
B
i
· Y
s
i
,K
(1)
i
= g
βs
i
,K
(2)
i,l
),B
i
= e(A
i
,g) · m
i
,π
i
=
POK{(s
i
,s
i,1
,s
i,2
,...,s
i,m
)|Q
i
= e(g,K
(1)
i
) = Z
s
i
∧
L
i,1
= g
s
i,1
∧ L
i,2
= g
s
i,2
∧ . . . ∧ L
i,m
= g
s
i,m
},i =
1,2,...,N,l = 1,2,...,m. The adversary A
0
simulates
the interactions of R with A for issuing decryption
key. If the decryption key is valid, A
0
sends a bit b = 1
to F , otherwise, it sends b = 0. If A
0
interacts with
A in issue protocol, A
0
extracts the secret key SK
I
=
(α,t
1
,t
2
,...,t
m
) by the running the knowledge extrac-
tor of POK{SK
I
|(PK
I
,SK
I
) is a key pair}. Upon re-
ceiving the transfer query from F , A
0
will query a
message randomly chosen from those for which A
0
has the necessary decryption key. If the transfer pro-
tocol succeeds, A
0
sends a bit b = 1 to F , otherwise,
it sends b = 0. Also A
0
runs the knowledge extrac-
tor of POK{(β,h,γ)| Z = e(g,g)
β
∧H = e(g,h) ∧ P =
e(g,g)
γ
} to extract β,h,γ from A. Now A
0
parses
SK
I
to get α and computes
K
(0)
i
e(A
i
,h)e(K
(1)
i
, g)
α
β
= m
i
as
K
(0)
i
= e(A
i
,h) · m
i
·Y
s
i
,K
(1)
i
= g
βs
i
,Y = e(g,g)
α
. The
adversary A
0
extracts attributes associated with m
i
as
follows. Let atr
i
be the set of attributes associated
with m
i
which is initially set to be empty. The adver-
sary A
0
parses F
i
as (Q
i
,L
i,1
,L
i,2
,...,L
i,m
) and checks
if K
(2)
i,l
= (L
i,l
)
γt
l
, where t
l
is extracted from SK
I
. If
so, then atr
i
= atr
i
∪{a
l
}, l = 1,2,...,m. In this way,
A
0
obtains the attribute set atr
i
associated with mes-
sage m
i
. The adversary A
0
constructs AP
i
by finding
all possible solutions of
∏
a
t
∈atr
i
(L
i,t
)
x
t
= (K
(1)
i
)
1
β
,x
t
∈ {0,1}. (3)
Note that the equation 3 can be viewed as an in-
stance of the knapsack problem as finding a solu-
tion of the equation 3 is essentially the same as find-
ing solution of
∑
t∈I
i
s
i,t
x
t
= s
i
, where x
t
∈ {0, 1},
I
i
= {t | a
t
∈ atr
i
} and s
i,t
,s
i
are extracted by
A
0
by running the knowledge extractor of π
i
em-
bedded in Φ
i
. A subset of atr
i
for which the
equation 3 holds is a clause of AP
i
and disjunct-
ing all these clauses provides the required access
policy AP
i
, where i = 1,2,. ..,N. The adversary
A
0
sends ((m
1
,AP
1
),(m
2
,AP
2
),...,(m
N
,AP
N
)) to
F for encDB. We note that A
0
provides A the
same environment as simulator S
4
provided A
0
can
solve the knapsack problem with negligible error.
So, we have IDEAL
F ,Z,A
0
= Pr[Game 4] + ε
knap
and IDEAL
F ,Z,A
0
− REAL
Π,Z,A
= |Pr[Game 4] −
[Game 0]| + ε
knap
≤ |Pr[Game 4] − [Game 3]| +
|Pr[Game 3]−[Game 2]|+|Pr[Game 2]−[Game 1]|+
|Pr[Game 1] − [Game 0]| + ε
knap
≤ ε
4
(ρ) + ε
3
(ρ) +
ε
2
(ρ) + ε
1
(ρ) + ε
knap
= ν(ρ), where ν(ρ) and ε
knap
are negligible functions. Hence IDEAL
F ,Z,A
0
c
≈
REAL
Π,Z,A
.
(b) Simulation when the sender S is corrupt while
the receiver R and the issuer are honest. In this
case the adversary A controls the corrupted sender S
whereas the simulator simulates the honest receiver
R and honest issuer. The simulation of this case is
exactly the same as Case(a) except that the simulator
itself generates the setup parameters on behalf of the
issuer, thereby knows the secret key SK
I
which the
simulator has to extract in the above case.
(c) Simulation when the sender S and the issuer
SECRYPT2014-InternationalConferenceonSecurityandCryptography
52

are honest while the receiver R is corrupt. In this
case, the adversary A controls the corrupted receiver
R and the simulator simulates the honest sender S and
honest issuer.
Game 0: This game corresponds to the real world pro-
tocol interaction in which the simulator S
0
simulates
S and honest issuer. So, Pr[Game 0] =0. Therefore
REAL
Π,Z,A
= Pr[Game 0].
Game 1: This game is same as Game 0 except that
the simulator S
1
extracts (σ
j
,v
σ
j
) by running the
knowledge extractor of POK{(σ
j
,v
σ
j
)| e(V
σ
j
,y) =
e(V
σ
j
,g)
−σ
j
e(g,g)
v
σ
j
} for each transfer phase j, j =
1,2,...,k. The difference between Game 1 and
Game 0 is the knowledge error of POK which is negli-
gible under soundness of the underlying POK. There-
fore, there exists a negligible function ε
1
(ρ) such that
|Pr[Game 1] − Pr[Game 0]| ≤ ε
1
(ρ).
Game 2: In this game, the simulator S
2
computes
c
A
σ
j
= V
1
v
σ
j
σ
j
and
\
e(g,K
(1)
σ
j
)
1
β
= X
1
βv
σ
j
σ
j
U
1
γv
σ
j
σ
j
by using
v
σ
j
which is extracted in Game 1. If the adversary A
has never requested the issuer for decryption key for
the attribute set w
ID
R
, then
\
e(g,K
(1)
σ
j
)
1
β
= e(g,K
(1)
σ
j
)
1
β
with negligible probability because we can construct
an adversary B to break the security of CP-ABE with
black box access to A. Also, if the extracted index
σ
j
/∈ {1,2,...,N}, then one can note that
c
A
σ
j
is a
forged BB signature on σ
j
. This in turn indicates
that A is able to come up with a valid BB signature
c
A
σ
j
, thereby A outputs
c
A
σ
j
as a forgery contradict-
ing the fact that the BB signature is unforgeable un-
der chosen-message attack assuming q-SDH problem
is hard (Boneh and Boyen, 2004).
Hence, there exists a negligible function ε
2
(ρ) such
that |Pr[Game 2] − Pr[Game 1]|≤ ε
2
(ρ).
Game 3: This game is the same as Game 2 except
that the simulator S
3
simulates the response W
σ
j
as
K
(1)
σ
j
m
σ
j
!
v
σ
j
and also simulates POK{(β, h, γ)| W
σ
j
=
e(V
σ
j
,h) · X
1
β
σ
j
U
1
γ
σ
j
∧ H = e(g,h) ∧ Z = e(g,g)
β
∧ P =
e(g,g)
γ
}. The difference between Game 3 and
Game 2 is negligible provided the underlying POK
has zero-knowledgeness. Therefore, there exists a
negligible function ε
3
(ρ) such that |Pr[Game 3] −
Pr[Game 2]| ≤ ε
3
(ρ).
Game 4: In this game, the simulator S
4
replaces K
(1)
σ
j
by random elements of G
T
.
Claim 1. The difference between Game 4 and Game 3
is negligible provided that the q-PDDH assumption
holds.
If the environment machine Z can distinguish be-
tween Game 4 and Game 3, we can construct a solver
B for q-PDDH assumption. The adversary B is given
an instance g
0
,g
0x
,g
0x
2
,...,g
0x
(q)
,H
0
,H
0
1
, ...,H
0
q
,g
0
$
←−
G,H
0
$
←− G
T
,x
$
←− Z
p
. The task of B is to decide
whether H
0
l
= H
0x
l
or H
0
l
are just random elements of
G
T
,l = 1, 2, . . . , q. The adversary B plays the role
of honest sender S and issuer. The adversary B uses
Z and A as subroutines. Let f (x) =
∏
q
i=1
(x + i) =
∑
q
i=0
b
i
x
i
be a polynomial of degree q, where b
i
are
coefficients of f (x). Set g = g
0 f (x)
=
∏
q
i=0
(g
0x
i
)
b
i
,
H = H
0 f (x)
and y = g
0x f (x)
=
∏
q
i=0
(g
0x
i+1
)
b
i
, Z =
e(g,g)
β
,P = e(g,g)
γ
. The adversary B sets pk
DB
=
(H,y,Z, P). Let f
i
(x) =
f (x)
x+i
=
∑
q−1
l=0
b
i,l
x
l
be a poly-
nomial of degree q − 1. The adversary B can com-
pute A
i
= g
1
x+i
= g
0
f (x)
x+i
= g
0 f
i
(x)
=
∏
q−1
l=0
(g
0x
l
)
b
i,l
and
K
(1)
i
= H
1
x+i
m
0
i
= H
0 f
i
(x)
m
0
i
=
∏
q−1
l=0
(H
0
l
)
b
i
,l
m
0
i
, where
m
0
i
= m
i
·Y
s
i
. If H
0
l
= (H
0
)
x
l
, B plays the role of sim-
ulator S
3
as in Game 3, otherwise, if H
0
l
are random
elements of G
T
, B plays the role of simulator S
4
as in
Game 4. Thus if Z can distinguish between Game 4
and Game 3, B can solve q-PDDH assumption.
Therefore, by Claim 1 there exists a negligible func-
tion ε
4
(ρ) such that |Pr[Game 4]-Pr[Game 3]| ≤
ε
4
(ρ).
We now construct the ideal world adversary A
0
with
black box access to A. The adversary A
0
incorporates
all steps from Game 4. The adversary A
0
simulta-
neously plays the role of honest sender S and honest
issuer. The adversary A
0
sets up pk
DB
on behalf of
S and PK
I
on behalf of the honest issuer. The adver-
sary A
0
generates the ciphertext Φ
i
= (A
i
,D
i
,F
i
,π
i
)
by randomly picking K
(1)
i
from G
T
,i = 1,2,...,N.
Upon receiving the message (issue, ID
R
, w
ID
R
) from
Z, A
0
sends the message to A. If A deviates from
protocol specification, A
0
outputs ⊥. Otherwise, A
requests A
0
for decryption key with attribute set w
ID
R
.
The adversary A
0
requests F for the decryption key.
If F sends the bit b = 1 to A
0
, A
0
sends the decryption
key to A. Otherwise, A
0
sends b = 0 to A.
Upon receiving the message (transfer, ID
R
, σ
j
) from
Z, A
0
sends the message to A. If A deviates from
protocol specification, A
0
outputs ⊥. Otherwise,
A
0
extracts (σ
j
,v
σ
j
) from the proof of knowledge
given by A. The adversary A
0
requests decryption
key and message m
σ
j
from F . The adversary A
0
simulates the response W
σ
j
as
K
(1)
σ
j
m
σ
j
!
v
σ
j
and sends
W
σ
j
along with the simulated zero-knowledge proof
to A. Thus the simulation provided by A
0
to A is
same as the simulator S
4
as in Game 4. So, we have
IDEAL
F ,Z,A
0
= Pr[Game 4] and IDEAL
F ,Z,A
0
−
AdaptiveObliviousTransferwithHiddenAccessPolicyRealizingDisjunction
53

REAL
Π,Z,A
= |Pr[Game 4] − [Game 0]| ≤
|Pr[Game 4] − [Game 3]| + |Pr[Game 3] −
[Game 2]||Pr[Game 2] − [Game 1]| + |Pr[Game 1] −
[Game 0]| ≤ ε
4
(ρ) + ε
3
(ρ) + ε
2
(ρ) + ε
1
(ρ) = ν(ρ),
where ν(ρ) is a negligible function. Hence
IDEAL
F ,Z,A
0
c
≈ REAL
Π,Z,A
.
(d) Simulation when the sender S is honest while
the issuer and the receiver R are corrupt. In this
case the adversary A controls the corrupted receiver R
and issuer and simulator simulates the honest sender
S. The simulation of this case is exactly the same as
Case(c) except that in this case the corrupted receivers
can obtain all the attribute secret keys they want as the
issuer is controlled by the adversary.
6 CONCLUSION
We have proposed a scheme in which the sender has
published encrypted messages which are protected
by hidden access policies. The receiver recovers the
message without revealing its identity and choice of
message to the sender. The scheme has covered
disjunction of attributes. Our construction uses ci-
phertext policy attribute based encryption and Boneh-
Boyan signature. The proposed scheme is secure
in the presence of malicious adversary under the q-
Strong Diffie-Hellman (SDH) assumption, q-Power
Decisional Diffie-Hellman (PDDH) assumption and
Decision Bilinear Diffie-Hellman (DBDH) assump-
tion in full-simulation security model. Our scheme is
computationally efficient and has low communication
overhead.
REFERENCES
Abe, M., Fuchsbauer, G., Groth, J., Haralambiev, K.,
and Ohkubo, M. (2010). Structure-preserving sig-
natures and commitments to group elements. In
CRYPTO 2010, volume 6223 of LNCS, pages 209–
236. Springer.
Beimel, A. (1996). Secure schemes for secret sharing and
key distribution. PhD thesis, PhD thesis, Israel Insti-
tute of Technology, Technion, Haifa, Israel.
Bellare, M. and Goldreich, O. (1993). On defining proofs of
knowledge. In CRYPTO 1992, volume 740 of LNCS,
pages 390–420. Springer.
Boneh, D. and Boyen, X. (2004). Short signatures without
random oracles. In EUROCRYPT 2004, LNCS, pages
56–73. Springer.
Camenisch, J., Dubovitskaya, M., Enderlein, R. R., and
Neven, G. (2012). Oblivious transfer with hidden
access control from attribute-based encryption. In
SCN 2012, volume 7485 of LNCS, pages 559–579.
Springer.
Camenisch, J., Dubovitskaya, M., and Neven, G. (2009).
Oblivious transfer with access control. In ACM 2009,
pages 131–140. ACM.
Camenisch, J., Dubovitskaya, M., Neven, G., and Za-
verucha, G. M. (2011). Oblivious transfer with hidden
access control policies. In PKC 2011, volume 6571 of
LNCS, pages 192–209. Springer.
Camenisch, J. and Lysyanskaya, A. (2004). Signature
schemes and anonymous credentials from bilinear
maps. In CRYPTO 2004, volume 3152 of LNCS, pages
56–72. Springer.
Camenisch, J., Neven, G., et al. (2007). Simulatable adap-
tive oblivious transfer. In EUROCRYPT 2007, volume
4515 of LNCS, pages 573–590. Springer.
Camenisch, J. and Stadler, M. (1997). Efficient group sig-
nature schemes for large groups. In CRYPTO 1997,
volume 1294 of LNCS, pages 410–424. Springer.
Coull, S., Green, M., and Hohenberger, S. (2009). Con-
trolling access to an oblivious database using stateful
anonymous credentials. In PKC 2009, volume 5443
of LNCS, pages 501–520. Springer.
Cramer, R., Damg
˚
ard, I., and MacKenzie, P. (2000). Effi-
cient zero-knowledge proofs of knowledge without in-
tractability assumptions. In PKC 2000, volume 1751
of LNCS, pages 354–372. Springer.
Goyal, V., Pandey, O., Sahai, A., and Waters, B. (2006).
Attribute-based encryption for fine-grained access
control of encrypted data. In ACM 2006, pages 89–
98. ACM.
Green, M. and Hohenberger, S. (2007). Blind identity-
based encryption and simulatable oblivious transfer.
In ASIACRYPT 2007, volume 4833 of LNCS, pages
265–282. Springer.
Groth, J. and Sahai, A. (2008). Efficient non-interactive
proof systems for bilinear groups. In EURO-
CRYPT 2008, volume 4965 of LNCS, pages 415–432.
Springer.
Ibraimi, L., Tang, Q., Hartel, P., and Jonker, W. (2009). Ef-
ficient and provable secure ciphertext-policy attribute-
based encryption schemes. In ISPEC 2009, volume
5451 of LNCS, pages 1–12. Springer.
Naor, M. and Pinkas, B. (1999). Oblivious transfer with
adaptive queries. In CRYPTO 1999, volume 1666 of
LNCS, pages 573–590. Springer.
Nishide, T., Yoneyama, K., and Ohta, K. (2008). Attribute-
based encryption with partially hidden encryptor-
specified access structures. In ACNS 2008, volume
5037 of LNCS, pages 111–129. Springer.
Zhang, Y., Au, M. H., Wong, D. S., Huang, Q., Mamoulis,
N., Cheung, D. W., and Yiu, S.-M. (2010). Oblivi-
ous transfer with access control: realizing disjunction
without duplication. In Pairing 2010, volume 6487 of
LNCS, pages 96–115. Springer.
SECRYPT2014-InternationalConferenceonSecurityandCryptography
54
