
A Cortico-Collicular Model for Multisensory Integration
Federico Giovannini
1
and Elisa Magosso
1,2
1
Health Sciences and Technologies Interdepartmental Center for Industrial Research BioEngLab,
University of Bologna, Via Venezia 52, Cesena, Italy
2
Department of Electrical, Electronic and Information Engineering “Guglielmo Marconi”,
University of Bologna, Via Venezia 52, Cesena, Italy
Keywords: Neural Network Modelling, Visual-Auditory Interactions, Multisensory Enhancement, Ventriloquism.
Abstract: Remarkable visual-auditory cross-modal phenomena occur at perceptual level: a visual stimulus enhances or
biases auditory localization in case of spatially coincident or spatially disparate stimuli. Hemianopic patients
(with one blind hemifield resulting from damage to primary visual cortex) retain visual enhancement but not
visual bias of auditory localization in the blind hemifield. Here, we propose a neural network model to
investigate which cortical and subcortical regions may be involved in these phenomena in intact and
damaged conditions. The model includes an auditory cortical area, the primary and extrastriate visual
cortices and the Superior Colliculus (a subcortical structure). Model simulations suggest that: i) Visual
enhancement of auditory localization engages two circuits (one involving the primary visual cortex and one
involving the Superior Colliculus) that act in a redundant manner. In absence of primary visual cortex
(hemianopia), enhancement still occurs thanks to the Superior Colliculus strongly activated by the spatially
coincident stimuli. ii) Visual bias of auditory localization is due to an additive contribution of the two
circuits. In hemianopia, the effect disappears as the Superior Colliculus is not sufficiently activated by the
spatially disparate stimuli. The model helps interpreting perceptual visual-auditory phenomena and their
retention or absence in brain damage conditions.
1 INTRODUCTION
Perception is a multisensory phenomenon. Everyday
environment provides us with a rich flow of
information involving various senses
simultaneously; our brain combines the different
sensory information in order to enhance detection of
events, to disambiguate conflicting situations, to
produce the most appropriate response (Stein and
Meredith, 1993; Calvert, Spence and Stein, 2004).
Knowledge of the neural mechanisms underlying
cross-modal processing is fundamental for our
understanding of human brain functions and a
plethora of different techniques (neuroanatomical
and electrophysiological in animals, behavioural and
neuroimaging in humans) has been used to this aim
(Calvert and Thesen, 2004).
A close interconnection between auditory and
visual systems has been found in a multitude of
subcortical and cortical areas. Among them, the
Superior Colliculus (SC) - a subcortical structure
involved in orientation and localization behaviour –
has been largely investigated: it receives converging
auditory and visual afferents, both from cortical and
non-cortical structures, and creates a topographically
aligned bimodal representation of the space
(Wallace, Meredith and Stein, 1993; Meredith and
Stein, 1996). Moreover, compelling evidence now
exists that even the primary visual and auditory
cortices - traditionally considered to be purely
unisensory – exhibit properties of visual-auditory
interaction (Ghazanfar and Schroeder, 2006): this
may be mediated both via feedback connections
from multisensory regions and via direct
connections between the unisensory areas (Driver
and Spence, 2000; Foxe and Schroeder, 2005).
Such numerous interconnections form the
structural basis for the remarkable visual-auditory
phenomena observed at perceptual level. In
particular, several psychophysical studies have
evidenced how visual information can affect the
perceived localization of a sound, and two main
effects have been observed in healthy subjects.
When the visual and auditory stimuli are presented
simultaneously at the same spatial position, the
15
Giovannini F. and Magosso E..
A Cortico-Collicular Model for Multisensory Integration.
DOI: 10.5220/0005023600150023
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Neural Computation Theory and Applications (NCTA-2014), pages 15-23
ISBN: 978-989-758-054-3
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

visual cue can improve auditory localization (visual
enhancement of auditory localization) (Bolognini,
Leo, Passamonti, Stein and Làdavas, 2007); the
beneficial effect of the visual stimulus is especially
evident in case of a weak (i.e., hard-to-localize)
sound. This phenomenon could mainly involve the
SC, as it is reminiscent of the response properties of
SC neurons: the response of a visual-auditory SC
neuron is enhanced by spatially coincident stimuli,
with less effective unimodal stimuli producing
greater response enhancement (a property called
inverse effectiveness) (Stein and Meredith, 1993).
When the visual and auditory stimuli are presented
together but in disparate spatial position, the visual
cue bias the auditory localization, i.e. sound location
is perceived shifted toward the visual stimulus
(visual bias of auditory localization or ventriloquism
effect) (Bertelson and Radeau, 1981; Bolognini et
al., 2007). This phenomenon may involve direct
projections from visual cortex to the auditory cortex
(Bertini, Leo, Avenanti and Làdavas, 2010).
The issue of cross-modal visual-auditory
processing is receiving growing attention with
respect to patients having hemianopia, i.e., a visual
field defect, characterized by a loss of vision in one
hemifield. It generally results from damage to visual
primary cortex (occipital lobe) on one side of the
brain, while leaving intact the SC. Studies on these
patients (Leo, Bolognini, Passamonti, Stein and
Làdavas, 2008; Passamonti, Frissen and Làdavas,
2009) have found that visual enhancement of
auditory localization – in case of spatially coincident
stimuli - is maintained in the blind hemifield,
although the patients may remain unconscious of the
visual stimulus. On the contrary, ventriloquism - in
case of spatially disparate stimuli - is not retained in
the blind hemifield. Retention of enhancement has
been hypothesized to depend on the functional
integrity of SC and of its related circuits; absence of
ventriloquism effect has been explained by the
damage of the occipital cortex that disrupts the
neural circuits underlying this effect.
Due to the multiplicity of mechanisms and
circuits involved, a comprehension of all these
aspects may benefit from the use of neural network
models. In recent years, we proposed several
neurocomputational models to investigate different
aspects of visual-auditory integration (Magosso,
Cuppini, Serino, Di Pellegrino and Ursino, 2008;
Cuppini, Magosso, Rowland, Stein and Ursino,
2012; Magosso, Cuppini and Ursino, 2012;
Magosso, Cona and Ursino, 2013; Cuppini,
Magosso, Bolognini, Vallar and Ursino, 2014). In
particular, some of those models were devoted to
investigate the properties of single neurons in the
SC, neglecting aspects of multisensory interaction in
the cortex (Magosso et al., 2008; Cuppini et al.,
2012); others focused only on visual-auditory
integration in the cortex, not including subcortical
structures (Magosso et al., 2012, Magosso et al.,
2013, Cuppini et al., 2014). Moreover, none of them
investigates the mechanisms underlying
multisensory perceptual effects in brain damaged
patients (such as hemianopic patients). Aim of the
present work is to overcome the previous limitations
by i) considering, within a single neural network
model, the interaction between cortical and
subcortical (collicular) areas in visual-auditory
processing; ii) mimicking visual enhancement and
visual bias of auditory localization in hemianopic
conditions, evidencing the differences compared to
intact conditions; iii) shading light on the
contribution of specific cortical and subcortical
circuits in the two examined visual-auditory
phenomena.
2 THE NEURAL NETWORK
MODEL
2.1 Model Description
The model includes four areas of neurons (Fig. 1),
representing: the auditory cortex (A), the primary
visual cortex (V), the extrastriate visual cortex (E),
the Superior Colliculus (SC). The external auditory
stimulus impacts on area A, which is reciprocally
connected with area SC. The external visual
stimulus targets area V (this mimics the geniculo-
striatal pathway), which communicates with area E;
the visual stimulus also impacts directly the SC (this
mimics the retino-collicular pathway). Area V and E
are also connected with SC. Finally, the two areas A
and V communicate directly via reciprocal synapses.
Each area is formed by a monodimensional array
of N (N = 181) neurons, which code for the azimuth
positions of the external space and are topologically
aligned (proximal neurons code for proximal
positions). We assumed that the head and eyes of
our hypothetical subject are fixed and maintained in
central alignment, so that the head-centered
coordinates (for auditory space coding) and the
retinotopic coordinates (for visual space coding) are
coincident. These conditions are the same adopted in
psychophysical studies investigating visual
enhancement and bias of auditory localization (Leo
et al., 2008). Azimuthal positions range between -
NCTA2014-InternationalConferenceonNeuralComputationTheoryandApplications
16

90° and +90°, and are spaced 1° apart so that both
hemifields of space are represented (one spanning
from -90° to -1°, the other from +1° to +90°, 0°
representing the central position). Finally, neurons
within each area communicate via lateral synapses.
Figure 1: Model architecture.
In the following, each neuron is referenced with a
superscript (r) indicating its area (r = A, V, E, SC)
and subscript (j) indicating its position within the
area (j = -90° ÷ +90°, i.e., its preferred azimuth
position). represents the net input of a neuron at
time and
represents its output activity.
The activity
of a generic neuron is
computed by feeding its input
through a
sigmoidal function (saturated to 1) and a first order
dynamics. To include variability in the network, the
sigmoidal function is affected by Poisson random
noise. For the sake of simplicity, we used the same
time constant and the same sigmoidal relationship
for all types of neurons.
The net input
that reaches a neuron may be
generically written as the sum of three contributions:
an external input
due to a stimulus (visual or
auditory) in the space, a lateral input
coming
from other neurons in the same area via lateral
synapses, an inter-area input
coming from
neurons in the other areas via inter-area synapses.
Hence, we can write
(1)
where each term can assume a different expression
according to the specific area. Expressions for
individual term in (1) are given below.
i) The external input - Area A, area V and area
SC receive an external input (see Fig. 1). The
external input is mimicked via a Gaussian function,
representing the result of a local stimulus spatially
filtered by the neuron receptive fields (RFs)
∙exp
2∙
,
,,
(2)
is the position at which the stimulus is centered;
=
since the same visual stimulus impacts
simultaneously on both the areas.
is related to the
width of neuron RF: we set
=
; moreover, to
simulate the higher spatial resolution of the visual
system, we assumed that
(=
) is smaller than
(Magosso et al., 2012).
represents the strength
of the stimulus (arbitrary units): since the SC
receives less fibres from the retina than the primary
visual cortex (Cowey, 2010), we set
= 0.5∙
.
Finally, the exstrastriate area (E) does not receive
any external input, hence
0,∀
(3)
ii) The lateral input - This input originates from
the lateral connections within the same area, and it is
computed as
∙
,
,,,
(4)
is the strength of the lateral synapse from a
presynaptic neuron at position k to the postsynaptic
neuron at position j, both in the same area r, and
is the activity of the presynaptic neuron. In
each area, lateral synapses are arranged according to
a Mexican hat, obtained as the difference of
excitatory and inhibitory contributions, each
mimicked as a Gaussian function. Autoexcitation
and autoinhibition are avoided in each area.
iii) The inter-area input The inter-area input
originates from inter-area synapses. For the sake of
simplicity, inter-area synapses have a one-to-one
structure (i.e., they connect neurons in spatial
register). According to Fig. 1, we have
,
∙
,
∙
,
∙
,
∙
,
∙
,
∙
,
∙
,
∙
,
∙
(5)
where
,
is a parameter indicating the strength of
connection from a neuron in area s to a neuron in
area r.
Parameter values were assigned according to the
following criteria. i) Parameters of the external
input - Standard deviations were set so that the
visual stimulus induces a narrow activation, while an
auditory stimulus induces a wider excitation
compatible with visual bias of sound location (Alais
et al. 2010). Strength of the input to area V and A
was assigned so that neuron response settles to the
lower part or central (linear) part of the sigmoidal
ACortico-CollicularModelforMultisensoryIntegration
17

static characteristic. Strength of the external visual
input to SC was assigned sufficiently low so that it is
unable to effectively activate SC in absence of
cortical input (Sparks, 1986). ii) Parameters of
individual neurons – Parameters of the sigmoidal
relationship was assigned to have a smooth
transition from silence to saturation. The dynamic
resembles that of neuron membrane (Magosso et al.,
2012). iii) Parameters of lateral intra-area synapses
– They parameters were assigned to maintain
confined activation in each area preventing
excessive spreading of excitation. iv) Parameters of
inter-area synapses – They were assigned so that : a)
an unimodal effective stimulus does not induce a
phantom activation in the areas of non-stimulated
modality; b) an unimodal effective stimulus induces
an intermediate level of activation in the SC
neurons.
2.2 Model Simulations and
Computation of Model Outcome
The model was used to simulate hemianopic
conditions. A hypothetical hemianopic patient was
simulated by silencing 80 neurons, randomly
chosen, in the hemifield +1° ÷ +90° within the
primary visual area (area V). Moreover, the spared
V neurons in this hemifield were made less sensitive
to input by modifying their sigmoidal function. We
will refer to hemifield +1° ÷ +90° as the hemianopic
field. The hemifield -1° ÷ -90° was maintained
intact; we will refer to it as intact field.
Simulations were performed by stimulating the
network with unimodal (auditory or visual) stimuli
and bimodal visual-auditory stimuli (both spatially
coincident and spatially disparate), in the intact and
hemianopic field. Stimuli were applied at the
beginning of the simulation and maintained
throughout. Each simulation lasted enough to reach
regime conditions.
To evaluate visual enhancement and visual bias
of auditory localization in the model, we calculated a
quantity representing the perceived location of the
auditory stimulus starting from the overall auditory
population activity. At the end of simulation, we
computed the average value, i.e. the barycenter (
),
and the standard deviation (
) of the population
activity in area A
∑
∙
∑
(6)
∑
∙
∑
∙
(7)
The perceived auditory location
was obtained
as:
(8)
where the barycenter metric is affected by a random
Gaussian noise (
) with null mean and standard
deviation equal to
.
Then, according to psychophysical studies, we
computed the auditory localization error
|
|
(9)
and the visual bias of auditory location
∙100
(10)
where
and
represent the actual position of the
auditory and visual stimulus, respectively.
3 RESULTS
We first present network response to unimodal
stimulation, in order to describe network behavior.
Then visual enhancement and visual bias of auditory
localization were analyzed in both hemifields.
3.1 Unimodal Stimulation
Fig. 2 shows the exemplary network response to an
unimodal visual stimulus applied in the intact field
(at position
= -40°, Fig. 2 (a)) and in the
hemianopic field (
= + 40°, Fig. 2 (b)) of a
simulated hemianopic patient. In both cases, the
strength of the stimulus is
= 16. In the intact
field, the visual stimulus is effective enough to
highly activate both the primary and extrastriate
visual areas, and to produce an intermediate
activation in the SC. Activation of both visual
cortices may correspond to conscious perception of
the visual stimulus. No phantom activation in the
auditory area is produced by a single visual stimulus.
In the hemianopic field, the visual stimulus produces
a very mild activation of spared V neurons close to
that position, while extrastriate area remains silent.
Lack of activation in these areas may reproduce
visual unawareness. The direct retino-collicular
pathway activates SC neurons just above threshold.
Fig. 3 displays the response to an unimodal
auditory stimulus; this response is the same in the
two hemifields as it does not involve the visual
pathways. A stronger (
= 17, Fig. 3 (a)) and a
weaker (
= 15, Fig. 3 (b)) auditory stimulus is
applied to the network at
= -40°. The stronger
auditory stimulus induces a high and quite confined
NCTA2014-InternationalConferenceonNeuralComputationTheoryandApplications
18

Figure 2: Unimodal visual stimulation. (a) Neuron activity
in the model areas in response to a visual stimulus of
strength
=16 applied in the intact field (
=-40°). (b)
Neuron activity in the model areas in response to a visual
stimulus of strength
=16 applied in the hemianopic.
Figure 3: Unimodal auditory stimulation. (a) Neuron
activity in the model areas in response to an auditory
stimulus of strength
=17. (b) Neuron activity in the
model areas in response to an auditory stimulus of strength
=15.
activation in the auditory cortex and activation of the
SC; this may correspond to an easy-to-localize
sound. The weaker stimulus produces a low and
spread activation in the auditory cortex, and an
extremely low activation in the SC; this may
correspond to a hard-to-localize sound. Worth
noticing that an effective auditory stimulus does not
produce any phantom activation in the visual areas.
3.2 Visual Enhancement of Auditory
Localization
The weak auditory stimulus (
= 15) has been
applied together with the visual stimulus (
= 16)
in the same spatial position, both in the intact
hemifield (
=
= - 40°) and in the hemianopic
hemifield (
=
= + 40°). Results are reported in
Fig. 4.
In the intact field (Fig.4 (a)), the bimodal
stimulation induces a strong activation in all the
areas. In particular, activation in area A is strongly
heightened and narrowed compared to unimodal
condition (compared with Fig. 3 (b)): this mimics
the perceptual enhancement of auditory localization.
Two mechanisms may contribute to such an
enhancement: i) the direct synapses between area A
and V; ii) the feedback synapses entering the
auditory neurons from the SC. In the hemianopic
field (Fig.4 (b)), combination of the two stimuli
(which - when applied separately - produce just a
minimum activation in SC) triggers SC neurons to
the maximum level. This is the consequence of the
sigmoidal activation function of the neuron: the two
stimuli together move the working point of SC
neurons along the steep central part of the sigmoid,
causing a disproportionate increase in the response
(inverse effectiveness). Strong SC activation, via the
feedback synapses, reinforces auditory activity in a
spatially selective manner; just a weak improvement
of activation in area V and E occurs that could not
be sufficient for emergence of visual awareness.
This may correspond to enhancement of auditory
localization by an “unseen” visual stimulus.
To quantify the visual enhancement of auditory
localization and to resembles the procedure adopted
in real psychophysical studies (Leo et al., 2008), ten
hemianopic patients were simulated (by randomly
silencing 80 neurons in the hemianopic field): in
each simulated patient, fifteen weak auditory
unimodal stimulations (as in Fig. 3 (b)) and fifteen
spatially coincident bimodal stimulations (as in Fig.
4) were applied at each of the following positions
±24°, ±40°, ±56°. For each stimulation, the
localization error was calculated according to (9)
and data were collapsed across positions in each
hemifield. Moreover, in order to discriminate the
role of the SC and the role of area V in the
ACortico-CollicularModelforMultisensoryIntegration
19
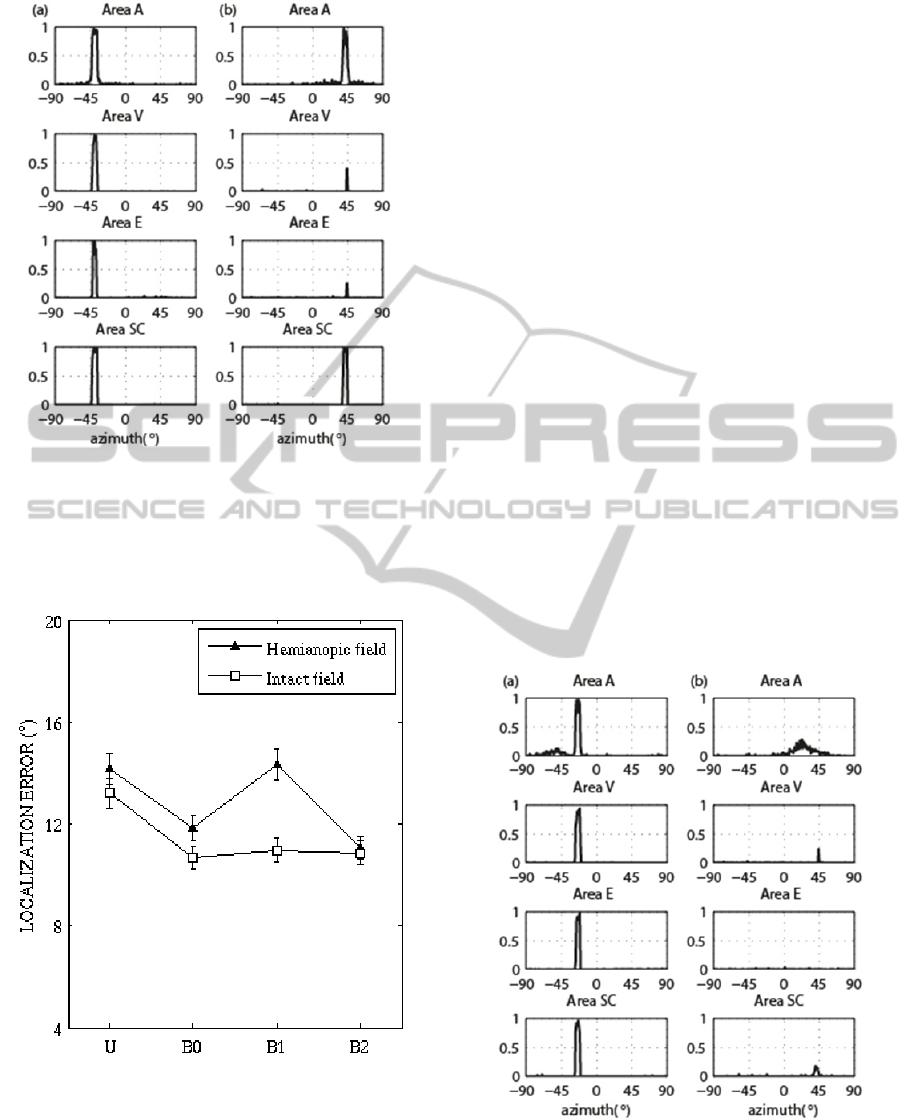
Figure 4: Bimodal spatially coincident stimulation.
Neuron activity in the model areas in response to a visual
stimulus of strength
=16 and an auditory stimulus of
strength
=15. (a) Stimuli applied in the intact field
(
=
=-40°). (b) Stimuli applied in the hemianopic field
(
=
=40°).
Figure 5: Auditory localization error. U: unimodal
auditory stimulation. B0 bimodal stimulation. B1: bimodal
stimulation with
,
,
0. B2: bimodal
stimulation with
,
,
0.
enhancement effect, in case of bimodal stimulation,
the localization error was computed in three
different conditions: with all intact synapses, by
neglecting the feedback synapses exiting the SC
(
,
,
0), by neglecting the direct visual-
auditory synapses (
,
,
0). Results are
reported in Fig. 5. Both in the intact and in the
hemianopic fields, the auditory localization error in
bimodal condition is significantly reduced with
respect to unimodal condition (in agreement with in-
vivo studies (Leo et al., 2008)). Interestingly, in the
intact field, direct visual-auditory synapses and the
SC feedback synapses play a redundant role, as their
selective elimination does not impact significantly
on error reduction. Conversely, in the hemianopic
field, the residual circuit involving the SC becomes
essential for the enhancement to occur.
3.3 Visual Bias of Auditory
Localization
Fig. 6 displays network response to the visual
stimulus and the simultaneous weak auditory
stimulus applied 16° left, in the intact field (Fig. 6
(a)) and in the hemianopic field (Fig. 6 (b)). In the
intact field, the effective visual stimulus strongly
reinforces the marginal auditory activation at the
visual stimulus position; such auditory neurons are
just above threshold and can be positively reinforced
both via the direct visual– auditory synapses and via
the feedback from the SC (strongly activated at the
Figure 6: Bimodal spatially disparate stimulation. Neuron
activity in the model areas in response to a visual stimulus
of strength
=16 and an auditory stimulus of strength
=15. (a) Stimuli applied in the intact field (
=-24,
=-40°). (b) Stimuli applied in the hemianopic field
(
=40,
=24°).
NCTA2014-InternationalConferenceonNeuralComputationTheoryandApplications
20
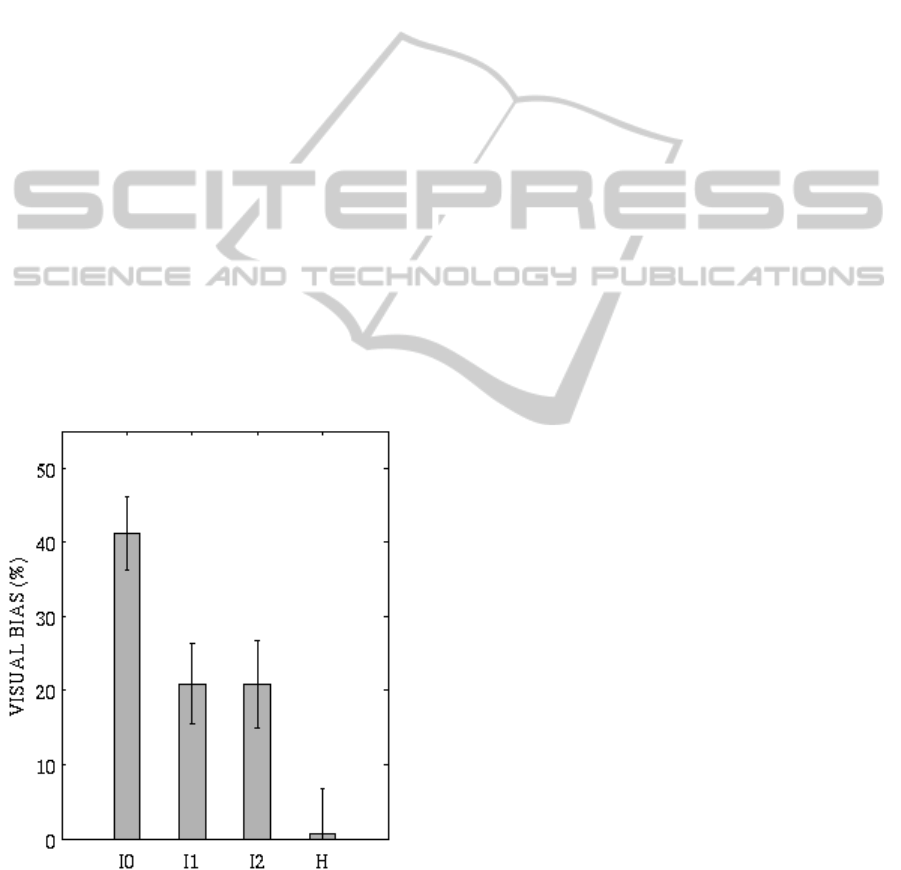
visual stimulus position). Hence, the auditory
activation is biased toward the location of the visual
stimulus. On the contrary, in the hemianopic field,
no significant alteration in the auditory activation
can be observed with respect to unimodal condition
(see Fig. 3 (b)). Worth noticing that in this case, SC
neurons are only slightly activated (by the direct
visual input) since the two weak stimuli, being
spatially disparate, do not have an enhancement
effect on the SC neurons.
To quantify the visual bias of auditory
localization - in each simulated patient – a visual
stimulus was applied (fifteen times) at each of the
following locations ±24°, ±40°, ±56°, together with
a weak auditory stimulus located 16° right or left.
For each stimulation, visual bias was computed
according to (10) and results were collapsed across
positions in each hemifield. In the intact hemifield,
simulations were performed with all intact synapses
and by selectively removing the feedback synapses
from the SC and the direct-visual auditory synapses.
Results are displayed in Fig. 7. According to in vivo
data (Leo et al., 2008), in the intact field (with all
intact synapses) visual bias is about 40% of visual-
auditory disparity; the SC feedback synapses and the
direct visual-auditory synapses cooperate in a
balanced manner to produce the effect. In the
hemianopic field, the visual bias is irrelevant.
Figure 7: Visual bias of auditory localization. I0:
stimulation within intact field. I1 stimulation within intact
field with
,
,
0. I2: stimulation within intact
field with
,
,
0. H: stimulation within
hemianopic field.
4 DISCUSSION
Here, we propose a model that considers the
interaction between cortical and subcortical
structures (i.e., the Superior Colliculus) in mediating
visual-auditory perceptual phenomena. The model
represents an extension of our previous models
(Magosso et al., 2008; Cuppini et al., 2012; Magosso
et al., 2012; Magosso et al., 2013; Cuppini et al.,
2014). Some main advancements can be highlighted.
i) The neural network includes a distinction between
the primary and the extraprimary visual cortices and
their different interactions with the SC. Such
distinction was neglected in the previous models,
while it may be important in investigating visual
deficits that selectively involve specific part of the
visual pathway. ii) The model investigates how the
interaction between cortical and subcortical circuits
may affect cortical activation and may reflect at
perceptual level. Previous models, on the contrary,
either inspected only properties of single SC
neurons, without considering perceptual effects
mediated by the cortex, or investigated perceptual
illusions by modeling only cortical areas and
neglecting the cortical-collicular communication; iii)
Previous models did not investigated multisensory
effects in brain damaged patients.
Model architecture agrees with existing
knowledge in the literature. It includes two major
visual pathways (Tong, 2003; Isa and Yoshida,
2009): one (geniculo-striatal pathway) guides most
of the projections from the retina - via the geniculus-
to the primary visual cortex, which communicates
with the extrastriate area; the other (retino-collicular
pathway) sends a smaller number of projections
from the retina directly to SC. In agreement with
several studies (Sparks, 1986; Wallace et al., 1993
Meredith and Stein, 1996; Stein and Meredith,
1993), model SC neurons receive afferents from the
visual cortical areas (areas V and E), and from the
auditory cortical area, and have visual and auditory
RF in spatial register. The property of inverse
effectiveness of real multisensory SC neurons (Stein
and Meredith, 1993) is mimicked via the non-linear
(sigmoidal) activation function. Moreover, SC area
in the model sends feedback connections to area A
and area E: according to neuroanatomical data (Isa
and Yoshida, 2009; Sparks, 1986). Finally, the
model includes direct synapses between area A and
V in agreement with evidence of direct connections
between unisensory areas (Alais, Newell and
Mamassian, 2010; Foxe and Schroeder, 2005)..
Network activation is interpreted in terms of
perceptual responses. First, we hypothesized that a
ACortico-CollicularModelforMultisensoryIntegration
21

visual stimulus is consciously perceived only in case
of simultaneous and sufficiently high activation in
both area V and E. This is in agreement with some
theories of visual awareness (Tong, 2003). Second,
we assumed that the perceived location of an
auditory stimulus is “read out” from the population
auditory activity as the barycenter of activity,
affected by a noise proportional to the dispersion of
activity around the barycenter. This provides
auditory localization error in agreement with in-vivo
data (Leo et al., 2008; Bolognini et al., 2007).
The model is used to inspect the circuits
underlying the phenomena of visual enhancement
and visual bias of auditory localization The
following speculations can be drawn from model
results. i) In intact conditions, visual enhancement of
auditory localization is mediated by two
mechanisms: the feedback synapses from the SC and
the direct visual-auditory synapses. These
mechanisms are redundant. Indeed, the spatially
coincident stimuli produce a strong activation (up to
maximum level) both in area V and in area SC: the
synapses entering auditory area from either area V
or area SC are sufficient by themselves - joined with
lateral synapses in area A - to reinforce auditory
activation up to saturation level and to narrow it.
Hence, each single mechanism is maximally
effective. ii) Such redundancy has enormous benefit
in hemianopic conditions in which area V has lost its
functionality. The residual mechanism, i.e. the
feedback from the SC, gives rise to an effect which
is comparable to that observed in intact condition
(Fig. 5). It is important to note that this strongly
depends on SC neurons robust activation, which is
the consequence of the spatial rule and the inverse
effectiveness rule implemented in the model. iii) The
retention of this effect in hemianopia occurs also in
the absence of significant activation in the visual
areas (Fig. 4 (b)), corresponding to absence of
awareness of the visual stimulus (as in vivo study
(Leo et al., 2008)). iv) In intact condition, visual bias
of auditory localization results from the additive
influence of direct visual-auditory synapses and of
the SC feedback synapses; the two mechanisms
contribute to a similar extent to the final bias. v) In
hemianopic condition, the spared SC circuit is not
able to maintain its effect: because of the spatial
disparity between the visual and auditory stimulus,
the overall input reaching the SC neurons is not
sufficient to enhance their activity.
In conclusion, the model provides insight into
the contributions of cortical and subcortical circuits
in mediating visual-auditory phenomena and
interprets the retention or absence of these
phenomena in hemianopic patients. We would like
to mention some important aspects, not considered
here, that can be the subject of future extensions. 1)
Simulation of audio-visual integration in neglect
patients. Neglect patients suffered of a visual
attentional deficit due to a lesion in the fronto-
temporal parietal areas (extraprimary areas, e.g. area
E in our model), hence residual multisensory
integration in these patients may be mediated by
different circuits compared to hemianopic patients.
2) Simulation of motivational factors (e.g. reward
expectation) on cross-modal binding. Recent studies
(Bruns, Maiworm and Röder, 2014) , indeed, have
evidenced that participant’s motivational goal
significantly influences ventriloquism effect. 3)
Simulation of gaze mechanisms. Here, we
considered only condition of fixed head and eyes
and did not simulated conditions of visual
exploration of space. Oculomotor strategies are
particularly important for visual localization in
hemianopic patients. 4) Simulation of rehabilitation
of hemianopic patients via visual-auditory
integration. Indeed, some studies (Bolognini, Rasi,
Coccia and Làdavas, 2005) have proved that
hemianopic patients, subjected to an audio-visual
stimulation training, improved visual field
exploration and visual detections.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work has been supported by the 2007-2013
Emilia-Romagna Regional Operational Programme
of the European Regional Development Fund and by
the FARB Programme Fund for Basic Research of
Alma Mater Studiorum University of Bologna.
REFERENCES
Alais, D., Newell, F.N., and Mamassian, P., 2010.
Multisensory processing in review: from physiology to
behaviour. Seeing and Perceiving, 23(1), pp.3–38.
Bertelson, P., and Radeau, M., 1981. Cross-modal bias
and perceptual fusion with auditory-visual spatial
discordance. Perception & Psychophysics, 29(6),
pp.578–584.
Bertini, C., Leo, F., Avenanti, A., and Làdavas, E., 2010.
Independent mechanisms for ventriloquism and
multisensory integration as revealed by theta-burst
stimulation. The European Journal of Neuroscience,
31(10), pp.1791–1799.
Bolognini, N., Rasi, F., Coccia, M. Làdavas, E., 2005.
Visual search improvement in hemianopic patients
NCTA2014-InternationalConferenceonNeuralComputationTheoryandApplications
22

after audio-visual stimulation. Brain, 128 (Pt.12), pp.
2830-2842.
Bolognini, N., Leo, F., Passamonti, C., Stein, B.E., and
Làdavas, E., 2007. Multisensory-mediated auditory
localization. Perception, 36(10), pp.1477–1485.
Bruns, P., Maiworm, M., Röder, B., 2014. Reward
expectation influences audiovisual spatial integration.
Attention, Perception & Psychophysics, [Epub ahead
of print].
Calvert, G., Spence, C., and Stein, B.E., 2004. The
handbook of multisensory processes. MIT Press.
Calvert, G., and Thesen, T., 2004. Multisensory
integration: methodological approaches and emerging
principles in the human brain. Journal of Physiology,
Paris, 98(1-3), pp.191–205.
Cowey, A., 2010. The blindsight saga. Experimental Brain
Research, 200(1), pp.3–24.
Cuppini, C., Magosso, E., Rowland, B., Stein, B., and
Ursino, M., 2012. Hebbian mechanisms help explain
development of multisensory integration in the
superior colliculus: a neural network model.
Biological Cybernetics, 106(11-12), pp.691–713.
Cuppini, C., Magosso, E., Bolognini, N., Vallar, G., and
Ursino, M., 2014. A neurocomputational analysis of
the sound-induced flash illusion. Neuroimage, 92,
pp.248-266.
Driver, J., and Spence, C., 2000. Multisensory perception:
beyond modularity and convergence. Current Biology,
10(20), pp.R731–735.
Foxe, J.J., and Schroeder, C.E., 2005. The case for
feedforward multisensory convergence during early
cortical processing. Neuroreport, 16(5), pp.419–423.
Ghazanfar, A.A., and Schroeder, C.E., 2006. Is neocortex
essentially multisensory? Trends in Cognitive
Sciences, 10(6), pp.278–285.
Isa, T., and Yoshida, M., 2009. Saccade control after V1
lesion revisited. Current Opinion in Neurobiology,
19(6), pp.608–614.
Leo, F., Bolognini, N., Passamonti, C., Stein, B.E., and
Làdavas, E., 2008. Cross-modal localization in
hemianopia: new insights on multisensory integration.
Brain, 131(Pt 3), pp.855–865.
Magosso, E., Cona, F., and Ursino, M., 2013. A neural
network model can explain ventriloquism aftereffect
and its generalization across sound frequencies.
BioMed Research International, 2013, p.475427.
Magosso, E., Cuppini, C., Serino, A., Di Pellegrino, G.,
and Ursino, M., 2008. A theoretical study of
multisensory integration in the superior colliculus by a
neural network model. Neural Networks, 21(6),
pp.817–829.
Magosso, E., Cuppini, C., and Ursino, M., 2012. A neural
network model of ventriloquism effect and aftereffect.
PLoS ONE, 7(8), p.e42503.
Meredith, M.A., and Stein, B.E., 1996. Spatial
determinants of multisensory integration in cat
superior colliculus neurons. Journal of
Neurophysiology
, 75(5), pp.1843–1857.
Passamonti, C., Frissen, I., and Làdavas, E., 2009. Visual
recalibration of auditory spatial perception: two
separate neural circuits for perceptual learning. The
European Journal of Neuroscience, 30(6), pp.1141–
1150.
Sparks, D.L., 1986. Translation of sensory signals into
commands for control of saccadic eye movements:
role of primate superior colliculus. Physiological
Reviews, 66(1), pp.118–171.
Stein, B.E., and Meredith, M.A., 1993. The merging of
senses. Cambridge, MA, The MIT Press.
Tong, F., 2003. Cognitive neuroscience: Primary visual
cortex and visual awareness. Nature Reviews
Neuroscience, 4(3), pp.219–229.
Wallace, M.T., Meredith, M.A., and Stein, B.E., 1993.
Converging influences from visual, auditory, and
somatosensory cortices onto output neurons of the
superior colliculus. Journal of Neurophysiology,
69(6), pp.1797–1809.
ACortico-CollicularModelforMultisensoryIntegration
23
