Are Non-Standard Neural Behaviors Computationally Relevant?
Stylianos Kampakis
Department of Computer Science, University College London, London, U.K.
Keywords: Computational Power, Heterogeneous Neurons, Neural Diversity Machines, Computational Neuroscience,
Supervised Learning.
Abstract: An idea that has recently appeared in the neural network community is that networks with heterogeneous
neurons and non-standard neural behaviors can provide computational advantages. A theoretical
investigation of this idea was given by Kampakis (2013) for spiking neurons. In artificial neural networks
this idea has been recently researched through Neural Diversity Machines (Maul, 2013). However, this idea
has not been tested experimentally for spiking neural networks. This paper provides a first experimental
investigation of whether neurons with non-standard behaviors can provide computational advantages. This
is done by using a spiking neural network with a biologically realistic neuron model that is tested on a
supervised learning task. In the first experiment the network is optimized for the supervised learning task by
adjusting the parameters of the neurons in order to adapt the neural behaviors. In the second experiment, the
parameter optimization is used in order to improve the network’s performance after the weights have been
trained. The results confirm that neurons with non-standard behaviors can provide computational
advantages for a network. Further implications of this study and suggestions for future research are
discussed.
1 INTRODUCTION
Spiking neural networks have been called the third
generation of neural networks (Maass, 1997). They
have been tested on a variety of machine learning
tasks such as unsupervised (Bohte, Poutre, & Kok,
2001; Meftah, Lezoray, & Benyettou, 2010),
supervised (Ianella & Back, 2001; Bohte, Kok, &
Poutre, 2002; Ghosh-Dastidar & Adeli, 2009) and
reinforcement learning (Potjans, et al., 2009). In
many studies, the neuron model being used is
usually an integrate-and-fire neuron or some of its
variants or generalizations, like the leaky integrate-
and-fire model and the spike response model. This is
for example the case for the aforementioned studies.
However, realistic neuron models can exhibit
different behaviors, which the neural models used in
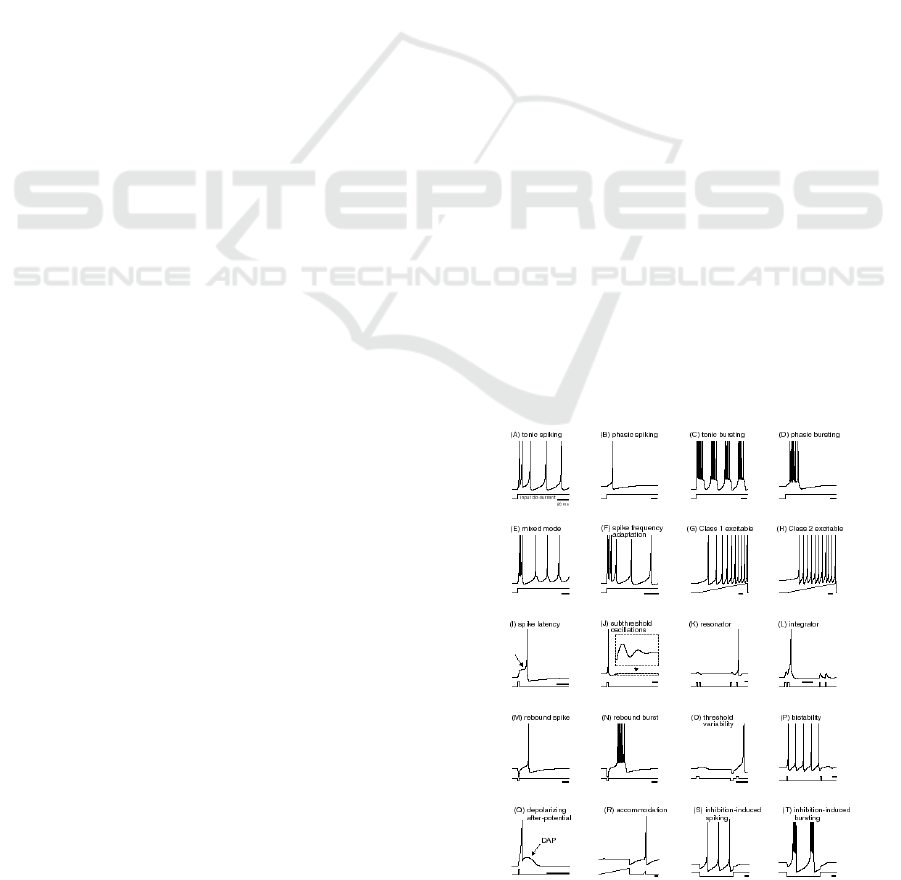
these studies cannot replicate. Izhikevich (2004)
presents 20 different neural behaviors (figure 1) that
real neurons can exhibit, while also developing a
model that can support all of these behaviors
(Izhikevich, 2003). According to this classification,
integrate-and-fire neurons are fall into the
“integrator” category.
Figure 1: Different neural behaviors exhibited by real
neurons. Electronic version of the figure and reproduction
permissions are freely available at www.izhikevich.com.
Previous researches, such as those mentioned in
the first paragraph usually just try to optimize the
32
Kampakis S..
Are Non-Standard Neural Behaviors Computationally Relevant?.
DOI: 10.5220/0005030400320037
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Neural Computation Theory and Applications (NCTA-2014), pages 32-37
ISBN: 978-989-758-054-3
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

weights of the network, and in some cases, some
other parameters, such as synaptic delays.
However, they do not optimize the behaviors of
each individual neuron. This is, of course, difficult
to do for a model of limited realism. In fact, the
integrate-and-fire model, and its variants, offer
limited flexibility with respect to the set of neural
behaviors they can exhibit. Therefore, it is difficult
to obtain computational advantages for specific tasks
(e.g. supervised learning) by trying to adapt the
neurons’ behavior.
However, it could be the case that the flexibility
of the model could help it adapt better to the task at
hand. In fact, this model was used by Kampakis
(2011) in the context of spiking neural network for a
supervised learning task. That research provided
some evidence that different neural behaviors, other
than the ones assumed by the integrate-and-fire
neuron, could be useful. More specifically, it was
demonstrated that a spiking neural network could
learn the XOR logic gate with three neurons by
using rebound spiking. This is something which
could not be achieved with simple integrators.
Kampakis (2013) looked into the issue of the
computational power of these neurons from a
theoretical perspective. This study investigated the
advantages that some specific non-standard
behaviors can offer. The study focused on
oscillators, bursting neurons and rebound spiking
neurons and demonstrated how the use of these
neurons for some particular tasks can reduce the
number of synapses or neurons used in a network.
However, a practical investigation was not pursued
in that paper. So, it remained unclear how non-
standard behaviors could actually be used in a real
setting and whether they would be useful.
Some similar ideas have emerged from other
researchers as well. Maul (2013) discussed the idea
of a “Neural Diversity Machine”. A neural diversity
machine is an artificial neural network whose
neurons can have different types of weights and
activation functions. Nodes with different activation
functions in an artificial neural network can be
thought as equivalent to neurons with different
behaviors in a spiking neural network. The
inspiration behind this idea is similar to the
inspiration behind the investigation of neurons with
non-standard behaviors. However, Neural Diversity
Machines have not been studied in the context of
more realistic neuron models.
There is further justification in the literature to
support this idea. First of all, neural diversity exists
in the brain (Moore, et al., 2010) and it has also been
suggested that it can be computationally relevant for
neural processing (Klausberger & Somogyi, 2008).
Secondly, there is evidence that artificial neural
networks whose neurons use different activation
functions can have more power (Maul, 2013).
Finally, Buzsaki et al. (2004) have shown that
biological neuronal diversification leads, both to a
reduction of the number of neurons used by a
network and to their wiring length.
The idea behind neural diversification is also
justified from the perspective of inductive bias. This
was something that was discussed by Kampakis
(2013) through the theory of “rational neural
processing”. Diverse neural behaviors possess
different inductive biases. This can make some
neural behaviors more suitable for some tasks.
Research conducted by Maul (2013) and Cohen and
Intrator (2002) has proven that this can be true for
artificial neural networks, as well.
However, while it became clear in theory
(Kampakis, 2013) that neural diversity provides
greater flexibility in spiking neurons, which can lead
to improved performance, no practical evidence of
that has been provided yet.
The goal of the research outlined in this paper is
to provide this practical evidence. The experiments
use a spiking neural network in order to test whether
diverse neural behaviors can be computationally
relevant. The network is trained on a supervised
learning task by optimizing the parameters that
control the neurons’ behavior. Experiment 1
compares a network with optimized neuron
parameters against an unoptimized network.
Experiment 2 combines the parameter optimization
with weight training in order to identify whether
parameter optimization can provide any
improvements in performance beyond weight
optimization.
The purpose of this paper is to provide some first
experimental evidence that neural diversity can be
computationally relevant for spiking neural
networks, while also connecting this evidence with
some of the recent research in the field.
2 METHODS AND MODELS
2.1 Neuron Model
This research used the Izhikevich neuron model. The
neuron model of Izhikevich (2003) is described by
the following set of equations:
0.04
5140
(1)
(2)
AreNon-StandardNeuralBehaviorsComputationallyRelevant?
33

The following condition ensures that the membrane
voltage is reset after a spike:
30,
←
←
(3)
The letters a, b, and d are dimensioneless
parameters of the model. I is the input, v is the
voltage of the neuron’s membrane, and u is the
recovery variable. The parameter c is voltage in mV.
Wang (2009) proposed an improvement over the
original model, which prohibits the membrane
voltage from reaching unrealistically high values.
This improvement was implemented in this research
as well. So, the condition from 3 changed to:
30,
←
←
30 30
30
(4)
2.2 Neural Architecture
The neural architecture used in this paper is the same
one as the one used by Kampakis (2011) for the iris
classification task and it is shown in figure 2.
Figure 2: Architecture of the network used for the
supervised learning task as it was presented in (Kampakis,
2011).
A short description of the architecture is
provided here in order to help in understanding the
paper.
The architecture consists of two layers. The first
layer consists of pairs of receptive fields with
Izhikevich neurons. The receptive fields are
comprised of Gaussian radial basis functions (hence
the name “Gauss field” in figure 2). The centers of
the receptive fields are uncovered by k-means
clustering.
The receptive fields receive the input in the form of
a real number. The output of each radial basis
function is fed into its respective input neuron. The
output of the receptive field becomes the variable
in equation 1.
The input layer is fully connected to the output
layer. The output is encoded by using a “winner-
takes-all” strategy where the first output neuron to
fire signifies the classification result.
2.3 Supervised Learning Task and
Dataset
The chosen supervised learning task is the correct
classification of the iris flowers in Fisher’s iris
dataset (Fisher, 1936). There are three iris types: Iris
setosa, Iris virginica and Iris versicolor. Each type is
represented in the dataset by 50 instances, for a total
of 150 instances.
Each instance contains four attributes: sepal
length, sepal width, petal length and petal width.
Only sepal lengh and sepal width were used, like in
(Kampakis, 2011) because the rest of the attributes
are noisy.
2.4 Neural Parameter Optimization
through Genetic Algorithms
The parameters of the network were optimized
through the use of a genetic algorithm. Parameter
search is a standard use of genetic algorithms
(Rawlins, 1991). For example, recently, Wu, Tzeng
and Lin (2009) used a genetic algorithm for
parameter optimization in a support vector
regression task. Tutkun (2009) used a real-valued
genetic algorithm for parameter search in
mathematical models. Optimization through genetic
algorithms has also been used successfully for
optimizing the parameters of neuron models to
experimental data (Taylor & Enoka, 2004; Achard &
Schutter, 2006; Keren, Peled, & Korngreen A.,
2006).
There are other choices for optimizing neuron
model parameters. A comprehensive review is
provided by Van Geit et al. (2008). Some other
choices besides meta-heuristic optimization include
hand tuning, brute force and gradient descent
methods. In practice, hand tuning is infeasible for
this case, due to the large number of tests required
for our purpose. Brute force is infeasible as well, due
to the large computational demands required.
Gradient descent methods would require us to
specify a differentiable error function. However, in
practice, this seemed to be very difficult. On the
NCTA2014-InternationalConferenceonNeuralComputationTheoryandApplications
34

other hand, genetic algorithms make no assumptions
about the problem, and provide a very nice balance
between exploitation of found solutions and
exploration of new ones.
3 EXPERIMENTAL SETUP
3.1 Experiments
This study consisted of two experiments. For the
first experiment, two networks are created. The
networks’ weights are initialized by assigning a
random set of weights sampled from the standard
normal distribution.
Then, one network is trained by using a genetic
algorithm in order to affect the parameters of each
neuron in the network individually. Affecting the
parameters changes the behavior and the response of
the neurons. The experimental hypothesis was
whether this can lead to improvements of accuracy,
therefore demonstrating that diverse neural
behaviors can be computationally relevant.
The objective function being optimized was the
training accuracy on the supervised learning task.
The training and testing is done by using 10-fold
cross-validation. The training accuracy is recorded
as the percentage of correct classifications across the
data that were used for training, and the testing
accuracy is recorded as the percentage of correct
classifications for the fold that was not used in the
training.
In order to identify whether affecting the
parameters of the neurons can lead to improvements
over the accuracy, the network was tested for 25
rounds of 10-fold cross validation against the
network with random (unoptimized) weights.
In the second experiment the network is trained
through a two-step optimization procedure. The
network’s weights are first trained using a genetic
algorithm. Then, the neurons’ parameters are
optimized by using the genetic algorithm from the
first experiment in order to improve the accuracy
even further. The second experiment is used in order
to examine whether parameter optimization can
offer advantages in addition to standard training over
the weights of the network.
It could be the case that any potential
improvements in accuracy in the first experiment
might not be significant when compared to standard
training that optimizes the weights only. Therefore,
this experiment was devised in order to explore
whether parameter optimization can be
computationally relevant when used in conjunction
with standard weight training, or whether any
advantages vanish. For that case, as for the first
experiment, the procedure was repeated for 25
rounds of 10-fold cross validation and the objective
function was the training accuracy.
For the second experiment the weights are
optimized through the use of a genetic algorithm.
The genetic algorithm used for optimizing the
weights had the exact same configuration as the one
in (Kampakis, 2011): two populations that ranged
from 50–100 members each, with crossover ratio 0.6
and 1 elite. The algorithm terminated after 150
generations had passed.
3.2 Parameter Optimization
After the weight optimization, a genetic algorithm is
used in both experiments in order to optimize over
the parameters of every neuron in the network,
without affecting the weights.
The algorithm optimizes all the parameters of
each neuron (a, b, c and d). The size of each
individual in the population was 36 (this is equal to
the sum of the number of neurons times 4). The
manipulation of these parameters allows the neurons
to exhibit many different behaviors, which were
shown in figure 1.
The tweaking of these parameters not only
affects the general behavior, but can also affect
details within each behavior, such as the frequency
of bursting, or the threshold of a neuron (Izhikevich
E. M., 2006).
The genetic algorithms were executed by using
the genetic algorithm toolbox of Matlab version
2011Rb. The default settings were used except for
the following parameters: The population was set to
75 and the crossover rate was changed from the
default of 0.8 to 0.6. This allowed a greater
exploration of the parameter space, which seemed to
improve the results in the pilot runs. The number of
generations was set to 50. The upper and lower
bounds of the variables were set to the interval [-
100; 100]. The type of mutation was Gaussian and
the selection method was stochastic uniform.
The optimization stopped as soon as the genetic
algorithm reached the upper limit of generations.
The parameters of the neurons and the architecture
were the same as the ones used by Kampakis (2011).
4 RESULTS
Table 1 presents the results of the first experiment.
The first and the third columns present the results for
AreNon-StandardNeuralBehaviorsComputationallyRelevant?
35

the optimized network. The third and fourth columns
present the results from the unoptimized network.
The first row presents the mean across all runs.
Table 1: Results of the optimization procedure and the
unoptimized neural network.
Training
accuracy
Test
accuracy
Random
Training
Random
Test
M
ean 67.8 60.5% 52.3% 52.28%
Std 15.2% 3.6% 11.8% 10.9%
M
ax 98.5% 97.0% 88.9% 28.4%
M
in 55.2% 46.7% 22.2% 7.8%
Table 2 demonstrates the results of the second
experiment. The table shows the comparison
between simple weight training (first two columns)
and the two-step optimization procedure (last two
columns). A Wilcoxon signed rank test for the null
hypothesis that the medians of the two populations
are unequal has a p-value of 0.0252.
Table 2: Comparison between weight training and the two
step optimization procedure.
Weight
(train)
Weight
(test)
Two-step
(train)
Two-step
(test)
Mean 97.0% 96% 97.7% 97.3%
Std 1.2% 1.9% 0.6% 2.3%
Table 3 shows a comparison with other algorithms
published in the literature. The comparisons include
SpikeProp (Bohte, et al., 2002), SWAT (Wade, et
al., 2008) and MuSpiNN (Ghosh-Dastidar & Adeli,
2009). The reported scores are all mean averages of
the accuracy for the iris classification task.
Table 3: Comparison with other algorithms.
Algorithm Neurons
Training
accuracy
Test
accuracy
SpikeProp 63 97.4% 96.1%
SWAT 208 97.3% 94.7%
MuSpiNN 17 Not reported 94.5%
Two-step 9 97.7% 97.3%
5 DISCUSSION
From the first experiment it is clear that the
parameter optimization leads to improvements in
performance over a randomly initialized network.
The difference between the trained network in both
the training accuracy and the test accuracy and the
random network is quite prominent. The optimized
network manages to generalize, obtaining a
performance that is clearly better than what would
be expected at random.
From the comparison between simple weight
training and the two-step optimization procedure it
seems that the parameter optimization can lead to
further improvements in the accuracy after the
network’s weights have been trained. Furthermore,
the two-step optimization’s accuracy is comparable
to other results reported in the literature, but it uses
fewer neurons.
Therefore, it seems that optimizing the neural
behavior of each neuron individually can provide
improvements in accuracy that might not be
achievable by using weight optimization alone.
6 CONCLUSIONS
This paper provided evidence that parameter
optimization for a biologically plausible neuron
model is a feasible strategy to improve the
performance of a supervised learning task. This was
done in alignment with recent research that has
promoted the idea that neural networks (biological,
spiking and artificial) with heterogeneous neurons
and non-standard behaviors might possess increased
computational power. This study provided additional
evidence for this idea by showing that it holds true
for spiking neural networks, as well.
This study provides evidence that biologically
simple neuron models, such as the integrate-and-fire
model, might offer limited computational
capabilities compared to more biologically realistic
neuron models. Furthermore, the study provided
evidence that biologically realistic features in neuron
models can be computationally relevant and that
they might provide feasible targets for an
optimization procedure when considering specific
tasks, such as supervised learning.
A question worth investigating is whether
additional improvements in performance could be
gained by adding more components that are
biologically relevant. A possible choice, for
example, could be to implement more realistic
synaptic dynamics. Furthermore, future research
could try to test other coding schemes for this
network and indicate whether different coding
schemes could provide advantages for different
tasks.
Also, many other issues remain open, such as,
how to connect the results for the spiking neural
networks with artificial neural networks and
biological networks. Some further issues include the
creation of a mathematical theory that can link these
different results in neural networks and, also, an
NCTA2014-InternationalConferenceonNeuralComputationTheoryandApplications
36

investigation of how these results could be applied
in a real setting. Finally, future research could focus
on developing a training algorithm that takes into
account neural diversity.
REFERENCES
Achard, P. & Schutter, E. D., 2006. Complex parameter
landscape for a complex neuron model. PLoS
Computational Biology, 2(7).
Bohte, S., Kok, J. & Poutre, H. L., 2002. Error
backpropagationin temporally encoded networks
ofspiking neurons.. Neurocomputing, Volume 48, pp.
17-37.
Bohte, S. M., Poutre, H. L. & Kok, J. N., 2001.
Unsupervised clustering with spiking neurons by
sparse temporal coding and multi-layer RBF networks.
IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, Volume XX.
Buzsaki, G., Geisler, C., Henze, D. A. & Wang, X. J.,
2004. Interneuron diversity series: circuit complexity
and axon wiring economy of cortical interneurons.
Trends in Neurosciences, 27(4), p. 186–193.
Cohen, S. & Intrator, N., 2002. A hybrid projection-based
and radial basis function architecture: initial values
and global optimisation. Pattern Analysis and
Applications, 5(2), pp. 113-120.
Fisher, R. A., 1936. The use of multiple measurements in
taxonomic problems. Annals of Eugenics, pp. 179-188.
Ghosh-Dastidar, S. & Adeli, H., 2009. A new supervised
learning algorithm for multiple spiking neural
networks with application in epilepsy and seizure
detection. Neural Networks, Volume 22.
Ianella, N. & Back, A. D., 2001. A spiking neural network
architecture for nonlinear function approximation.
Neural Networks, 14(2001), pp. 933-939.
Izhikevich, E., 2003. Simple model of spiking neurons.
IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 14(6).
Izhikevich, E. M., 2004. Which model to use for cortical
spiking neurons?. IEEE Transactions on Neural
Networks, 15(5), pp. 1063-1070.
Izhikevich, E. M., 2006. Dynamical Systems in
Neuroscience: The Geometry of Excitability and
Bursting. s.l.:MIT Press.
Kampakis, S., 2011. Improved Izhikevich neurons for
spiking neural networks. Journal of Soft Computing.
Kampakis, S., 2013 (under review). ReSpiN: A
Supervised Training Algorithm for Rebound Spiking
Neurons. Journal of Soft Computing.
Kampakis, S., 2013. Investigating the computational
power of spiking neurons with non-standard
behaviors. Neural Networks, Volume 43, pp. 41-54.
Keren, N., Peled, N. & Korngreen A., 2006. Constraining
compartmental models using multiple voltage
recordings and genetic algorithms. Journal of
Neurophysiology, pp. 3730-3742.
Klausberger, T. & Somogyi, P., 2008. Neuronal diversity
and temporal dynamics: the unity of hippocampal
circuit operations. Science, 321(5885), pp. 53-57.
Maass, W., 1997. Networks of spiking neurons: the third
generation of spiking neural networks. Neural
Networks, 10(9), pp. 1659-1671.
Maul, T., 2013 (in press, accepted manuscript). Early
experiments with neural diversity machines.
Meftah, B., Lezoray, O. & Benyettou, A., 2010.
Segmentation and edge detection based on spiking
neural network model. Neural Processing Letters,
32(2), pp. 131-146.
Moore, C. I., Carlen, M., Knoblich, U. & Cardin, J. A.,
2010. Neocortical interneurons: from diversity,
strength. Cell, 142(2), pp. 189-193.
Potjans, W., Morrison, A. & Diesmann, M., 2009. A
spiking neural network model of an actor-critic
learning agent. Neural Computation, 21(2), pp. 301-
339.
Rawlins, G. J. E. ed., 1991. Foundations of Genetic
Algorithms (FOGA 1). s.l.:Morgan Kaufmann.
Taylor, A. M. & Enoka, R. M., 2004. Optimization of
input patterns and neuronal properties to evoke motor
neuron synchronization. Journal of Computational
Neuroscience, 16(2), pp. 139-157.
Tutkun, N., 2009. Parameter estimation in mathematical
models using the real coded genetic algorithms. Expert
Systems with Applications, 36(2), pp. 3342-3345.
Valko, M., Marques, N. C. & Castellani, M., 2005.
Evolutionary feature selection for spiking neural
network pattern classifiers. Covilha, IEEE, pp. 181 -
187.
Van Geit, W., De Schutter, E. & Achard, P., 2008.
Automated neuron model optimization techniques: a
review. Biological Cybernetics, Volume 99, pp. 241-
251.
Wade, J. J., McDaid, L. J., Santos, J. A. & Sayers, H. M.,
2008. SWAT: An unsupervised SNN training algorithm
for classification problems. Hong Kong, IEEE, pp.
2648 - 2655.
Wang, H., 2009. Improvement of Izhikevich’s neuronal
and neural network model. Wuhan, China, IEEE.
Wu, C.-H., Tzeng, G.-H. & Lin, R.-H., 2009. A novel
hybrid genetic algorithm for kernel function and
parameter optimization in support vector regression.
Expert Systems with Applications, 36(3), pp. 4725-
4735.
AreNon-StandardNeuralBehaviorsComputationallyRelevant?
37
