
On the Impact of the Clipping Techniques on the
Performance of Optical OFDM
Jo˜ao Guerreiro
1,2
, Rui Dinis
1,2
and Paulo Montezuma
1,3
1
DEE, FCT, Universidade Nova de Lisboa, Monte de Caparica, Portugal
2
IT, Instituto de Telecomunicac¸˜oes, Lisboa, Portugal
3
UNINOVA, Monte de Caparica, Portugal
Keywords:
OFDM (Orthogonal Division Multiplexing), Optical Communications, Asymmetric Clipping, Nonlinear
Distortion Effects.
Abstract:
Recently, OFDM modulations are being considered for both optical fiber and wireless optical communications,
specially due to their efficiency to combat the inter-symbol interference. Between the modifications of the
standard OFDM that meet the requirements of the incoherent OFDM optical communications such as the ones
that consider intensity modulation/direct detection, the asymmetric clipping optical OFDM and the DC biased
optical OFDM techniques are the most popular but both involve an asymmetric clipping operation. Therefore,
due to the high sensitivity of OFDM signals to nonlinearities, the nonlinear distortion effects introduced by
the asymmetric clipping in the form of in and out-band-distortion should not be neglected. In fact, in order
to address the performance of such systems, these distortion effects must be accurately characterized. In
this work, by making use of a Gaussian approximation, we study analytically the impact of the asymmetric
clipping in the performance of optical OFDM techniques by deriving theoretical expressions for the power
spectral density and for the distortion at the subcarrier level, which is a key step to understand the potential
performance of these systems.
1 INTRODUCTION
Employed in many wired and wireless communica-
tions standards specially due to their facility to com-
bat the inter-symbol interference (ISI), their simple
equalization processes and their ease of implementa-
tion, OFDM modulations (Cimini, 1985) have been
also recently considered to support optical communi-
cations (Armstrong, 2009). However, in optical wire-
less communications (OWC) that consider incoherent
OFDM systems (with intensity modulation/direct de-
tection IM/DD) some aspects of the typical OFDM
techniques must be changed, since the OFDM sig-
nal is used to modulate the transmitted light and, for
this reason, must be real and unipolar. There are two
well-established techniques to transform a conven-
tional OFDM signal into a real and positivesignal: the
DC biased optical OFDM (DCO-OFDM) (Carruthers
and Kahn, 1996) where a DC-bias is added to the orig-
inal OFDM signal and the residual negative part of
the signal is clipped and the asymmetric clipping op-
tical OFDM (ACO-OFDM) (Armstrong and Lowery,
2006) where the original OFDM signal is deliberately
clipped at zero. While the former doesn’t present a
good power efficiency, the latter is shown to be power
efficient and has been target of recent research (Arm-
strong and Schmidt, 2008)(Dimitrovand Haas, 2010).
However, both techniques involve the use of clipping
operations.
One of the major OFDM weaknesses is the large
envelope fluctuations of their signals that lead to
the existence of a high peak-to-average power ratio
(PAPR) and, consequently, high sensitivity to nonlin-
ear devices. Therefore, a clipping operation in the
transmission chain will lead to existence of nonlin-
ear distortion effects in the transmitted signals and,
for this reason, it is important to evaluate its impact
on the performance.
Under the assumption that the OFDM signal
presents a large number of subcarriers and using the
central limit theorem the OFDM signal can be seen
as a Gaussian random process. Making use of this
approximation, a nonlinearly distorted OFDM signal
can be divided in two uncorrelated terms: one that
is proportional to the input signal and another that
concentrates the nonlinear distortion effects (Rowe,
51
Guerreiro J., Dinis R. and Montezuma P..
On the Impact of the Clipping Techniques on the Performance of Optical OFDM.
DOI: 10.5220/0005032500510055
In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Optical Communication Systems (OPTICS-2014), pages 51-55
ISBN: 978-989-758-044-4
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

Oversampling
{S
k
}
Asym. Clipping
IDFT
{S
T x
k
}
{s
n
}
DFT
{y
n
}
{Y
k
}
Figure 1: Considered OFDM transmission chain.
1982). In the literature, there are several works that
employ statistical methods to derive closed-forms so-
lutions for the output PSD of the nonlinearly distorted
signal but they are mainly focused in odd nonlinear
characteristics (Dinis and Gusmao, 2004)(Ara´ujo and
Dinis, 2010). The asymmetrical clipping employed in
DCO-OFDM and in the ACO-OFDM is not an odd
function and, for this reason, its analysis is different.
In this work we study the influence of an asym-
metric clipping in optical OFDM transmissions by us-
ing a statistical approach that makes use of a Gaussian
approximation. In order to access the performance of
such systems, we derive theoretical expressions for
the PSD at the nonlinearity output and we analyze
both the in-band and out-band distortion introduced
by this nonlinearity.
2 SYSTEM
CHARACTERIZATION
In Fig. 1 it is represented the considered OFDM trans-
mission chain.
In each OFDM frame, a data sequence {S
Tx
k
;k =
0,1,..., N − 1} composed by N complex sym-
bols from a given constellation (as for instance
a quaternary phase shift keying (QPSK) constella-
tion) is transmitted. The transmitted symbols are
equiprobable, i.e., E[S
Tx
k
] = 0, and uncorrelated, i.e.,
E[S
Tx
k
S
Tx
∗
k
] = 2E[|S
Tx
k
|
2
]δ
k,k
′
, where δ
k,k
′
is the Kro-
necker delta. Moreover, as the OFDM signal modu-
lates the transmitted light, its time-domain samples
must be real and positive. To avoid the existence
of complex samples at the inverse discrete Fourier
transform (IDFT) output, the data vector {S
Tx
k
;k =
0,1,..., N −1} is constrained to have Hermitian sym-
metry, i.e.,
S
Tx
k
=
0, k = 0,N/2
S
Tx
N−k
= S
Tx
∗
k
, otherwise.
(1)
We also considered an oversampling operation with
oversampling factor M, performed through the addi-
tion of M(N −1) idle subcarriers at the useful band
edges. Thus, the final block that represents the signal
to be transmitted is {S
k
;k = 0,1,...,MN −1}. In this
condition, the IDFT output is represented by {s
n
;n =
0,1,..., MN −1} = IDFT{S
k
;k = 0,1,...,MN −1},
with the n
th
sample given by
s
n
=
1
MN
MN−1
∑
k=0
S
k
exp
j2π
kn
MN
, (2)
and Im(s
n
) = 0 ∀n. The autocorrelation between
the time-domain samples can be expressed as
R
s,n−n
′
= E[s
n
s
∗
n
′
]
=
1
(MN)
2
MN−1
∑
k=0
E[|S
k
|
2
]exp
−j2π
k(n−n
′
)
MN
.
(3)
Moreover, the autocorrelation and the
power spectral density (PSD) form a Fourier
pair, i.e., {R
s,n−n
′
;n,n
′
= 0,1,...,MN − 1} =
1
MN
IDFT{G
S,k
;k = 0,1,...,MN − 1}, and
E[S
k
S
∗
k
′
] = MNG
S,k
. To assure the positivity of
the time-domain samples {s
n
;n = 0,1,... ,MN −1},
we consider an asymmetric clipping operation. This
operation is represented by the following nonlinear
function
f(x) =
x, x > −s
M
−s
M
, x ≤ −s
M
.
(4)
where s
M
is the clipping level. In Fig. 2 it is de-
picted the nonlinear function that models the asym-
metric clipping considering several clipping levels.
x
f (x)
−2.5 − 2 − 1.5 − 1 − 0.5
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5
−0.5
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
Figure 2: Asymmetric clipping considering different values
of s
M
.
Throughout this work we considered that s
M
<
0 which is the typical scenario of the DCO-OFDM
schemes. In these conditions a DC component must
be added to the clipped signal in order to assure that
OPTICS2014-InternationalConferenceonOpticalCommunicationSystems
52
the samples are positive. In the case of the ACO-
OFDM schemes the clipping is made with s
M
= 0
and there is no need for a DC-bias. For modeling
purposes, when the number of subcarriers is large
(let’s say that N ≥ 32), the time-domain samples of
an OFDM signal are Gaussian distributed and can be
modeled by s whose the probability density function
(PDF) is
p(s) =
1
√
2πσ
2
exp
−
s
2
2σ
2
, (5)
where σ
2
is the variance of s. Thanks to the Gaus-
sian nature of OFDM signals, the Bussgang theorem
(Rowe, 1982) can be used. This theorem states that
a nonlinearly distorted signal is given by the sum of
two uncorrelated components: a scaled replica of the
input signal and a term that concentrates the nonlin-
ear distortion effects. Therefore, the n
th
time-domain
sample at the nonlinearity output can be described as
y
n
= f(s
n
) = αs
n
+ d
n
, (6)
where α is a relation between the cross-correlation
between the input and the output signals of the non-
linearity and autocorrelation of the input signal
α =
E[s
n
y
n
]
E[|s
n
|]
2
=
E[s
n
y
n
]
σ
2
, (7)
and {d
n
;n = 0, 1, ...,MN −1} represents the distor-
tion term. In the frequency domain, the output is
{Y
k
;k = 0,1,... ,MN −1} and for the k
th
subcarrier
we have
Y
k
= αS
k
+ D
k
, (8)
where {D
k
;k = 0, 1,... , MN −1} is the distortion in-
troduced in the k
th
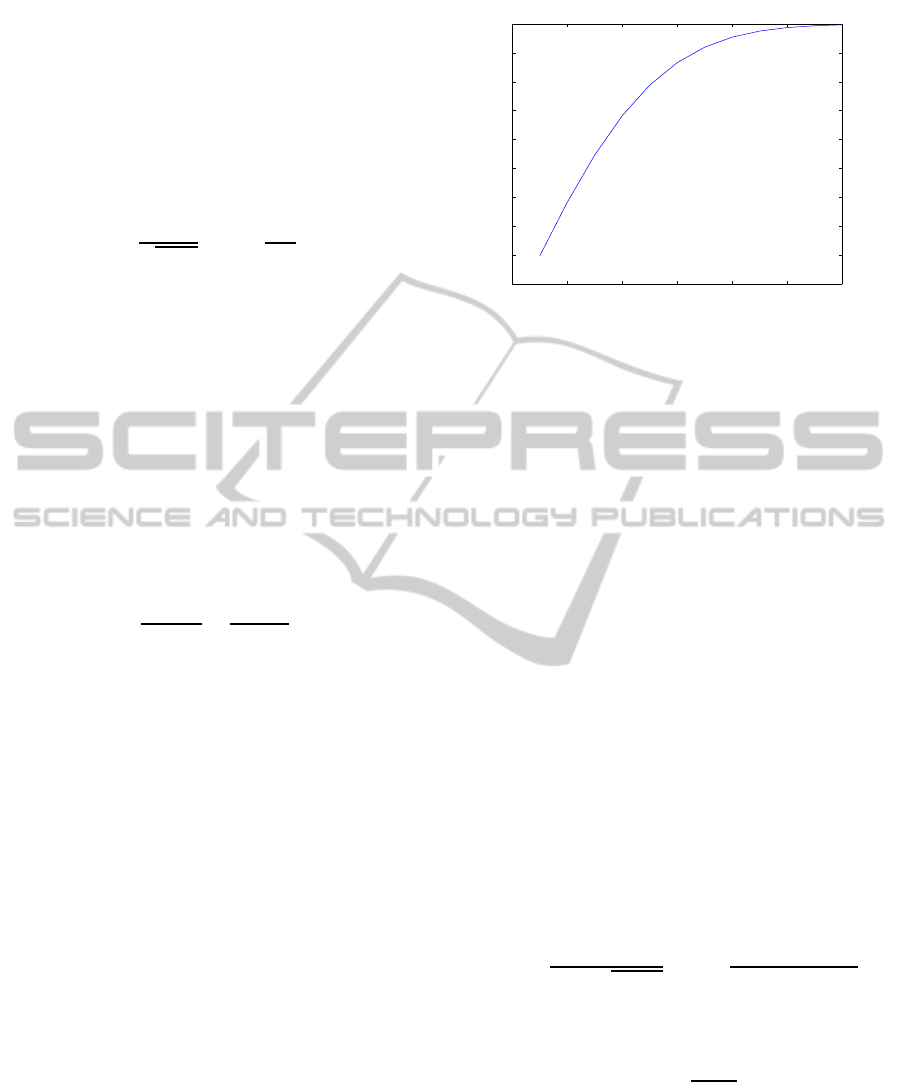
subcarrier. In Fig. 3 it is shown
the evolution of α with the clipping level. In fact,
throughout this work we consider a normalized clip-
ping level s
M
/σ since we are working with random
signals and the clipping level must be related to their
standard deviation σ.
As s
M
/σ increases, it is less likely that the sam-
ples of the OFDM signal enter in the nonlinear region
and the value of α tends to the unity (when α = 1, no
nonlinear distortion effects are introduced).
3 OUTPUT AUTOCORRELATION
FOR MEMORYLESS
NONLINEARITIES
In this section, in order to obtain the average PSD of
a nonlinearly distorted random process we study its
autocorrelation function, since it forms a Fourier pair
s
M
/σ
α
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3
0.55
0.6
0.65
0.7
0.75
0.8
0.85
0.9
0.95
1
Figure 3: Evolution of α with the normalized clipping level
s
M
/σ.
with the PSD. Although the output autocorrelation for
memoryless nonlinearities with Gaussian inputs were
already studied in (Dinis and Gusmao, 2004)(Ara´ujo
and Dinis, 2010), these works only consider nonlin-
earities with odd characteristics, which is not the case
of the asymmetrical clipping function characterized
in (4). Our aim is to derive the autocorrelation of an
OFDM signal that is submitted to this type of nonlin-
earities by making use of its Gaussian nature. Let us
start by expressing the autocorrelation at the input of
the nonlinearity. Due to the stationarity of the ran-
dom process that models the OFDM signal, the auto-
correlation only depends on the time lag between the
observation moments, τ, and we can write
R
s
(τ) = E[s
1
s
2
] =
+∞
Z
−∞
+∞
Z
−∞
s
1
s
2
p(s
1
,s
2
)ds
1
ds
2
, (9)
where s
1
and s
2
are two random variables resulting
from the observation of the random process at t = 0
and t = τ, respectively. The variance of these random
variables is σ
2
and their joint PDF is given by
p(s
1
,s
2
) =
1
2πσ
2
p
1−ρ
2
exp
−
s
2
1
+ s
2
2
−2ρs
1
s
2
2σ
2
(1−ρ
2
)
,
(10)
where ρ is their correlation that is defined as
ρ = ρ(τ) =
R
s
(τ)
R
s
(0)
. (11)
At the nonlinearity output the autocorrelation is
given by
R
y
(τ) = E[ f(s
1
) f(s
2
)]
=
+∞
Z
−∞
+∞
Z
−∞
f(s
1
) f(s
2
)p(s
1
,s
2
)ds
1
ds
2
. (12)
OntheImpactoftheClippingTechniquesonthePerformanceofOpticalOFDM
53

However, it can be shown that the joint PDF of s
1
and
s
2
can be expressed as a function of their marginal
densities and the Hermite polynomials as
p(s
1
,s
2
) = p(s
1
)p(s
2
)
+∞
∑
m=0
ρ
m
2
m
m!
H
m
s
1
√
2σ
H
m
s
2
√
2σ
,
(13)
which allows us to rewrite (12) as
R
y
(τ) =
+∞
Z
−∞
+∞
Z
−∞
f(s
1
) f(s
2
)p(s
1
)p(s
2
)
+∞
∑
m=0
ρ
m
2
m
m!
×
H
m
s
1
√
2σ
H
m
s
2
√
2σ
ds
1
ds
2
. (14)
In addition, as f(s
1
) = f(s
2
) = f(s), p(s
1
) = p(s
2
) =
p(s) and H
m
s
1
√
2σ
= H
m
s
2
√
2σ
= H
m
s
√
2σ
we can
rewrite the output autocorrelation as
R
y
(τ) =
+∞
∑
m=0
ρ
m
2
m
m!
+∞
Z
−∞
f(s)p(s)H
m
s
√
2σ
ds
2
. (15)
By defining P
m
as the power of the intermodulation product
of order m
P
m
=
1
2
m
m!
+∞
Z
−∞
f(s)p(s)H
m
s
√
2σ
ds
2
, (16)
we can rewrite (15) as
R
y
(τ) =
+∞
∑
m=0
ρ
m
P
m
=
+∞
∑
m=0
R
s
(τ)
σ
2
m
P
m
. (17)
With the average PSD of the output given by G
y
( f) =
DFT(R
y
(τ)).
4 PERFORMANCE RESULTS
In this section we present a set of results to demon-
strate the accuracy of the proposed analytical expres-
sion for the autocorrelation of a nonlinearly distorted
signal. In Fig. 4 it is shown the PSD of the nonlin-
earity output {G
Y,k
;k = 0,1, . . . , MN −1} both theo-
retically and by simulation using the fact that G
Y,k
=
E[|Y
k
|
2
]/MN. We considered two oversampling fac-
tors M = 8 and M = 4, N = 512 data subcarriers,
m = 40 and s
M
/σ = 1.0. From the figure, we note
that regardless of the oversampling factor, the accu-
racy of the theoretical expression for the PSD is very
high. As P
0
6= 0 there is a peak in the subcarrier in the
middle of the spectrum (k = 0), since a DC compo-
nent is introduced by the nonlinearity.
G
Y,k
(dB)
k/N
−2 − 1.5 − 1 −0.5
0 0.5 1 1.5 2
−70
−60
−50
−40
−30
−20
G
Y,k
(dB)
k/N
−4 −3 −2 −1
0 1 2 3 4
−100
−80
−60
−40
−20
: Simulation
: Simulation
M = 8
M = 4
: Theory
: Theory
Figure 4: PSD of the nonlinearity output considering M = 4
(top figure) and M = 4 (bottom figure).
In Fig. 5 it is shown the PSD of the distortion
term {G
D,k
;k = 0,1,...,MN −1} obtained both the-
oretically (considering the contribution m intermodu-
lation products except the one associated to the use-
ful term, where m = 1) and by simulation considering
that G
D,k
= E[|D
k
|
2
]/MN. We also considered that
M = 4, N = 512 data subcarriers and s
M
/σ = 1.0.
k/N
PSD (dB)
−2 −1.5 − 1 − 0.5
0 0.5 1 1.5 2
−70
−65
−60
−55
−50
−45
−40
−35
−30
−25
−20
: Simulation
· · · · · · · : Theory (m = 10)
− − −− : Theory (m = 5)
: Theory (m = 30)
Figure 5: PSD of the distortion component obtained both
theoretically and by simulation considering different values
of m.
From the figure we can note that the results are
very accurate with errors near 0 dB specially when
we consider a large number of intermodulation prod-
ucts (m = 30). Regarding the performance evalua-
tion, we can compute the signal-to-interference ra-
tio (SIR). This ratio gives an indication of the perfor-
mance losses at the subcarrier level that are associated
with the in-band distortion introduced by the nonlin-
earity. The SIR for k
th
subcarrier is defined as
SIR
k
= α
2
E[|S
k
|
2
]
E[|D
k
|
2
]
. (18)
OPTICS2014-InternationalConferenceonOpticalCommunicationSystems
54
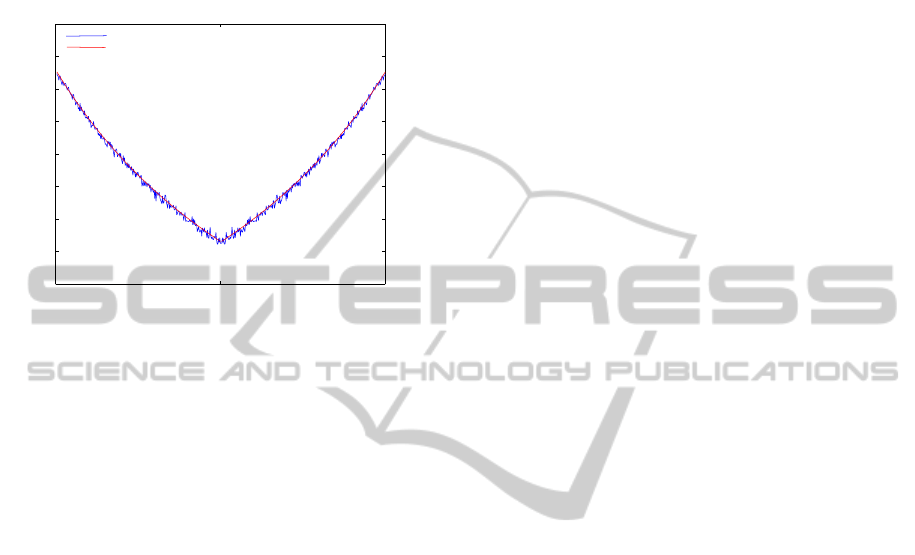
In Fig. 6 it is shown the SIR computed both theoreti-
cally and by simulation considering M = 4, N = 512
data subcarriers, s
M
/σ = 1.0 and m = 40. As the
SIR is dependent on the average PSD of the distor-
tion component, its accuracy is as high as the one of
the Fig. 5 when m is high.
SIR (dB)
k/N
−0.5
0 0.5
12
12.5
13
13.5
14
14.5
15
15.5
16
: Simulation
: Theory
Figure 6: Evolution of the SIR obtained both theoretically
and by simulation.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper we considered incoherent optical OFDM
systems that have a nonlinear operation in their trans-
mission chain. It is presented an analytical method
based on a statistical approach that can be used to
characterize the distortion levels at the subcarrier
level and, consequently, be used to access their per-
formance. The analytical method is validated by a set
of simulation results that demonstrate its high accu-
racy.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This paper was partially supported by FCT un-
der the projects PEst-OE/EEI/LA0008/2013
(pluriannual founding and HETNET), GALNC
EXPL/EEI-TEL/1582/2013, DISRUPTIVE
EXCL/EEI-ELC/0261/2012 and the grant
SFRH/BD/90997/2012).
REFERENCES
Ara´ujo, T. and Dinis, R. (2010). Analytical evaluation of
nonlinear effects on ofdma signals. IEEE Transac-
tions on Wireless Communications, 9:3472–3479.
Armstrong, J. (2009). Ofdm for optical communications.
IEEE Journal of Lightwave Technology, 27:189–204.
Armstrong, J. and Lowery, A. J. (2006). Power efficient
optical ofdm. IEEE Electronic Letters, 42:370–372.
Armstrong, J. and Schmidt, J. (2008). Comparison of asym-
metrically clipped optical ofdm anddc-biased optical
ofdm in awgn. IEEE Communication Letters, 12:343–
345.
Carruthers, J. B. and Kahn, J. M. (1996). Multiple-
subcarrier modulation for wireless infrared communi-
cation. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communi-
cations, 14:538–546.
Cimini, L. (1985). Analysis and simulation of a digital mo-
bile channel using orthogonal frequency division mul-
tiplexing. IEEE Transactions on Communications,
33:665–675.
Dimitrov, S. and Haas, H. (2010). On the clipping noise in
an aco-ofdm optical wireless communication system.
IEEE GLOBECOM’10.
Dinis, R. and Gusmao, A. (2004). A class of nonlinear sig-
nal processing schemes for bandwidth-efficient ofdm
transmission with low envelope fluctuation. IEEE
Transactions on Communications, 52:2009–2018.
Rowe, H. (1982). Memoryless nonlinearities with gaussian
input: elementary results. IEEE Communication Let-
ters, 61:1519–1526.
OntheImpactoftheClippingTechniquesonthePerformanceofOpticalOFDM
55
