
Cooperative Knowledge Discovery in Design Projects
Xinghang Dai
1
, Nada Matta
1
and Guillaume Ducellier
2
1
Tech-cico, University of Technology of Troyes, 12 Rue Marie Curie, 10010 Troyes, France
2
LASMIS, University of Technology of Troyes, 12 Rue Marie Curie, 10010 Troyes, France
Keywords: Knowledge Management, Semantic Networks, Classification, Concurrent Design Project Management,
Project Memory.
Abstract: As concurrent design has changed the landscape of design project management, knowledge management
method is introduced in this field to enhance learning in an organization. However, new challenges arise for
knowledge management in concurrent design projects: knowledge has changed from domain expert
knowledge to organizational cooperative knowledge; simple knowledge conceptualization is not sufficient
to represent interactions between concepts. Therefore, aims for these challenges, a new cooperative
knowledge discovery method based on semantic networks by classification on concept interactions is
proposed.
1 INTRODUCTION
A cooperative activity is generally defined as an
activity of several actors having a given goal
(Schmidt et al, 1992). Three dimensions must be
studied in this type on activity: communication,
coordination and collaborative decision-making
(Zacklad, 2003). A number of works on CSCW
analyzed these dimensions and several techniques
have been defined in order to give supports to
cooperative activity. We mention for instance
Workflow, Groupware tools (Khoshafian et al,
1995), design-rationale approaches (Buckingham
Shum, 1997), etc.
Our study concerns knowledge management for
cooperative activity. We attempt to deal with the
question which kind of knowledge exists in
cooperative activity and how can we represent them
to reuse it.
Recent knowledge management research has
proposed community of practices and story telling to
enhance knowledge sharing in an organization.
Experience shows that the success of these
techniques depend on the dynamic of animation in
these communities. Our work is based on knowledge
engineering approaches in which knowledge
structuring is considered as a very important
principle. We believe that learning from experience
requires two fundamental elements: reasoning
strategies (also called behavior laws) (Newell, 1982)
and production context of these strategies (Ducellier
et al, 2013). “The learning content is context
specific, and it implies discovery of what is to be
done when and how according to the specific
organizations routines” (Easterby-Smith et al, 2003).
These two elements are especially important for
cooperative knowledge representation.
This paper will begin with laying our research
background by an introduction on cooperative
knowledge and design project knowledge. Then the
concept “project memory” will be illustrated. Finally
a cooperative knowledge discovery model (CKD)
will be proposed to classify knowledge rules for
cooperative activities. This method will be
elaborated on design project memory, followed by
classification rule propositions and an example.
2 RESEARCH BACKGROUND
First of all, we are going to introduce the concept
cooperative knowledge. Secondly, the concept
cooperative knowledge will be put into design
project field to outline the characteristics of design
project knowledge. Thirdly, the concept project
memory will be proposed to represent the
knowledge in design projects.
2.1 Cooperative Knowledge
Cooperative knowledge is defined as knowledge
27
Matta X., Matta N. and Ducellier G..
Cooperative Knowledge Discovery in Design Projects.
DOI: 10.5220/0005033100270035
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Sharing (KMIS-2014), pages 27-35
ISBN: 978-989-758-050-5
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

produced in cooperative activities (Ducellier et al,
2013). Representing this knowledge leads to
consider the three aspects of cooperative activity:
coordination, communication and cooperative
decision-making. Ontology has always been
considered as a strong knowledge representation
method. Ontology is a description of shared
concepts. It consists of term, definitions, axioms,
and taxonomy. It facilitates knowledge
comprehension and knowledge sharing by setting
the standard knowledge structure (Gruber, 1995)
(Fensel, 2000). Domain knowledge ontology has
developed very fast, it has already been successfully
implemented in expert systems, IS etc. However, no
attempts have been made to construct cooperative
knowledge ontology. Due to the characteristics of
cooperative knowledge that we talked above,
components of cooperative knowledge ontology
shouldn’t be simple concept of entity; they should be
actions between concepts that represent interactions
between concepts. We defined cooperative activity
ontology as follow:
Figure 1: Cooperative knowledge ontology.
2.2 Design Project Knowledge
Design activities have gone through some major
changes during the past five decades. With the use
of IT tools in design projects and the more and more
complex features of design product, design project
tends to be multi-organizational, multi-disciplinary
(Pahl et al, 2007) (Ducellier, 2008). Moreover, with
the emergence of concurrent engineering design,
design project no longer follows a linear
management model, but a parallel one that calls for
more communication, collaboration and
coordination in project organization.
2.2.1 Design Domain Knowledge and
Cooperative Knowledge
Both domain knowledge and cooperative knowledge
are produced in design project. Past researches have
progressed a lot on design domain knowledge
management, but cooperative knowledge produced
in design projects is different from design domain
knowledge:
The nature of knowledge is different: The
domain knowledge is related to a field and
contains routines and strategies developed
individually from experiences, which involve
a number of experiments. The cooperative
knowledge is related to several fields, i.e.
several teams (of several companies) and in
several disciplines collaborates to carry out a
project. So there is a collective and
organizational dimension to consider in
cooperative knowledge. Representing domain
knowledge consists in representing the
problem solving (concepts and strategies)
(Castillo et al, 2005). On the contrary,
emphasizing knowledge in cooperative
activity aims at showing organization,
negotiation and cooperative decision-making
(Djaiz et al, 2006). Otherwise, knowledge
observed in a corporative constitutes examples
to be structured in order to extract strategies.
Capturing of knowledge is different: The
realization of a project in a company implies
several actors, if not also other groups and
companies. For example, in concurrent
engineering, several teams of several
companies from several disciplines
collaborate to carry out a design project. The
several teams are regarded as Co-partners who
share the decision-makings during the
realization of the project. This type of
organization is in general dissolved at the end
of the project (Matta et al, 2001). In this type
of organization, the knowledge produced
during the realization of the project has a
collective dimension that is in general volatile.
The documents produced in a project are not
sufficient to keep track of this knowledge. In
most of the cases, even the project manager
cannot explain it accurately. This dynamic
character of knowledge is due to the
cooperative problem solving where various
ideas are confronted to reach a solution. So
acquisition of knowledge by interviewing
experts or from documents is not sufficient to
show different aspects of the projects,
especially negotiation (Bekhti et al, 2003).
Traceability and direct knowledge capturing
are needed to acquire knowledge from this
type of organization.
KMIS2014-InternationalConferenceonKnowledgeManagementandInformationSharing
28
2.2.2 Project Memory
For the same object, people with different
background can give different interpretations;
concept alters according to different context.
Knowledge engineering approaches based on
semantic network, ontology, logic etc. has been
developed for knowledge representation. As for
design project, we have to focus on design rationale
representation as well as its interaction with other
parts of a project. In other words, a global
representation of all design projects modules as well
as interactions between them are needed for design
project. We should represent specially:
1. The design rationale (negotiation, argumentation
and cooperative decision making)
2. The organization of the project (actors, skills,
roles, tasks, etc.)
3. The consequences of problem solving (evolution
of the artefact)
4. The context of the project (rules, techniques,
resource, etc.)
We called the structure representing this type of
knowledge project memory (Matta et al, 2013).
From the knowledge structure proposed by project
memory, we want to focus on knowledge that is
produced during cooperative activities in a project.
3 CKD FOR DESIGN PROJECT
The principle of CDK method is to classify similar
concept schemas of cooperative activities to identify
certain repetitive ones as routines with a weight
factor that indicates their importance. Classification
can be defined as the process in which ideas and
objects are recognized, differentiated, and
understood, classification algorithms are used in
biology, documentation, etc. (Cohen et al, 2005). A
routine is defined as a recursive interaction schema
of cooperative activity concepts. The weight factor
is defined as percentage of recurrence of a routine
among past similar project events. Therefore, the
result of classification will be an ensemble of
interactions between cooperative activity concepts.
This result routine can be considered as a knowledge
rule for cooperative actors to learn from, and future
cooperative activities should pay attention to past
knowledge rules.
A semantic network graph enable knowledge
engineers to communicate with domain experts in
language and notations that avoid the jargon of AI
and computer science (Sowa, 2000). Our
representation of project memory is based on a
general semantic network of four modules, and then
four modules are represented in sub-networks.
Ontological hierarchy of concepts may be necessary
for generalization. The ontological hierarchy of
concept should be constructed according to a
specific context, it is important to show different
categories of concept as part of representation of
project context.
Machine learning methods are frequently used to
classify a concept automatically in a quantitative
manner. However, design project interaction
schemas are usually not voluminous and quite
distinctive; design project information are highly
structured in a computer-aided design environment.
Therefore it is not necessary to use powerful
machine learning algorithms for concept
classification, detailed CKD classification method
will be illustrated in section 3.3.
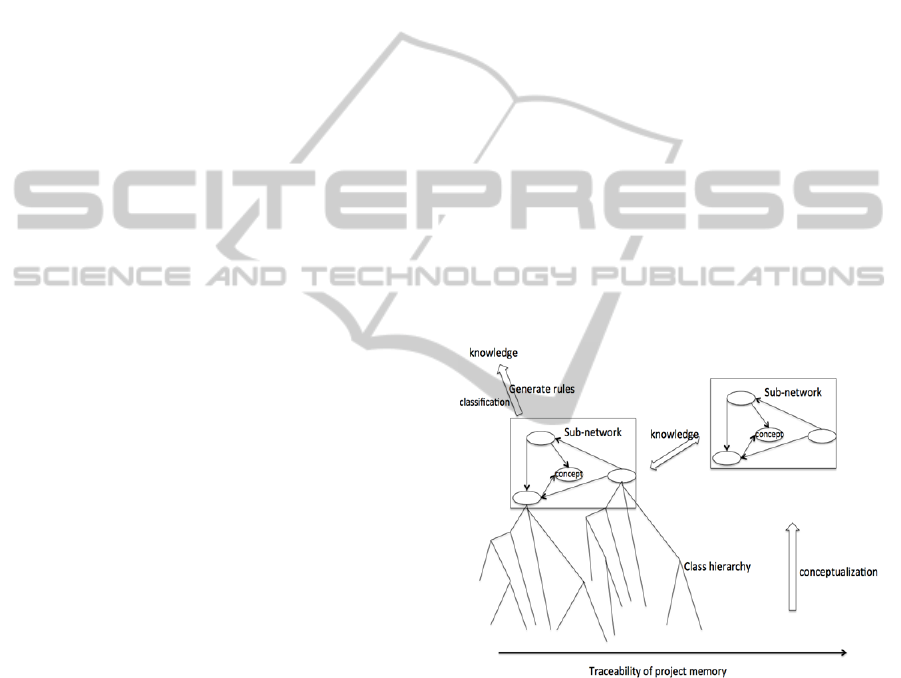
In order to apply CDK in design projects, we
have to begin with project trace from the beginning
to the end of projects. Then, project trace will be
conceptualized and fit into project memory structure.
Finally, CDK method will be applied on certain
interaction schema to find routines.
Figure 2: CDK for project memory.
3.1 Project Memory Structure
Section 2 has introduced “project memory” that list
the four essential parts of design project. The goal of
project memory is to enhance learning from
expertise and past project experience (Matta et al,
2001). Current representation approaches emphasize
on organizing and structuring project information
and expect users to learn from them. The problem is
that human can only learn from others by matching
to one’s own experience, and the knowledge level or
even knowledge context between expert and learner
CooperativeKnowledgeDiscoveryinDesignProjects
29
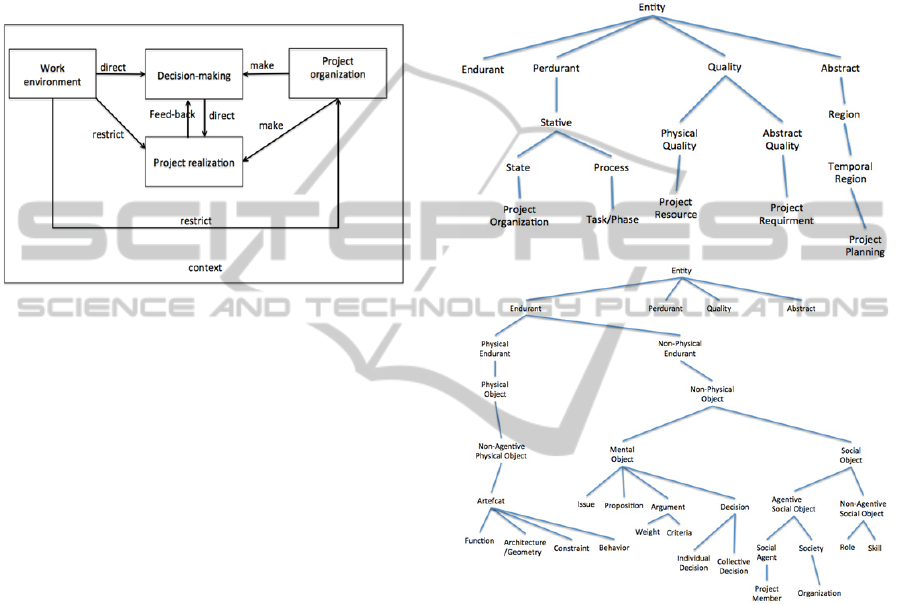
are always not the same. Traditional knowledge
engineering method usually doesn’t take project
context into consideration (e.g. IBIS, QOC), or they
neglect the interaction between different project
modules (e.g. CommonKADS, DRCS). Therefore,
instead of a single best classification system that
suits everyone, everywhere (Miksa, 1998), we have
to come up with classification models suited within
specific contexts (Mai, 2004).
Figure 3: Project memory structure.
Firstly, project memory has to be decomposed
into smaller modules in order to show project
memory in different perspective with different
context to provide a better learning angle. The
general semantic network of project memory (Figure
3) is decomposed into 4 sub-networks:
Decision-making process: this part represents
the core activity of design project, which helps
designers to learn from negotiation and
decision-making experience.
Project organization makes decision: this part
represents interaction between organization
and decision, which provides an
organizational view of decision-making.
Project organization realizes project: this part
represents arrangement of task and project
team organization, which focuses learning on
project management.
Decision-making and project realization: this
part represents the mutual influence between
decision and project realization, which reveals
part of work environment and background.
Secondly, in each project memory module, a
sub-network is built with concepts and relations.
These project memory concepts are identified based
on the research on engineering design and
knowledge representation method for design
activities (Pahl et al, 2007) (Klein, 1993) (Schreiber,
1994) (Conklin, 1988). These concepts are
employed and rearranged to represent the elements
in project memory. Foundational ontologies serve as
a starting point for building new domain and
application ontologies, provide a reference point for
different ontological approaches and create a
framework for analysing, harmonizing and
integrating existing ontologies and metadata (Mika
et al, 2004). The project memory concepts are
aligned with the general Dolce ontology as in figure
4.
Figure 4: Project memory concepts aligned with dolce
ontology.
Lastly, CDK will be used to classify interaction
schemas in or between sub-networks. The next
section will introduce each sub-network.
3.2 Semantic Networks of Project
Memory Modules
Based on these concepts, we are going to build our
sub-networks to represent especially interactions
between concepts in order to show the cooperative
knowledge.
The first part of project memory is design
rational; decision-making process is one of the most
important parts in project memory. It contains
negotiation process, decision and arguments that can
reveal decision-making context. Concepts that are
KMIS2014-InternationalConferenceonKnowledgeManagementandInformationSharing
30
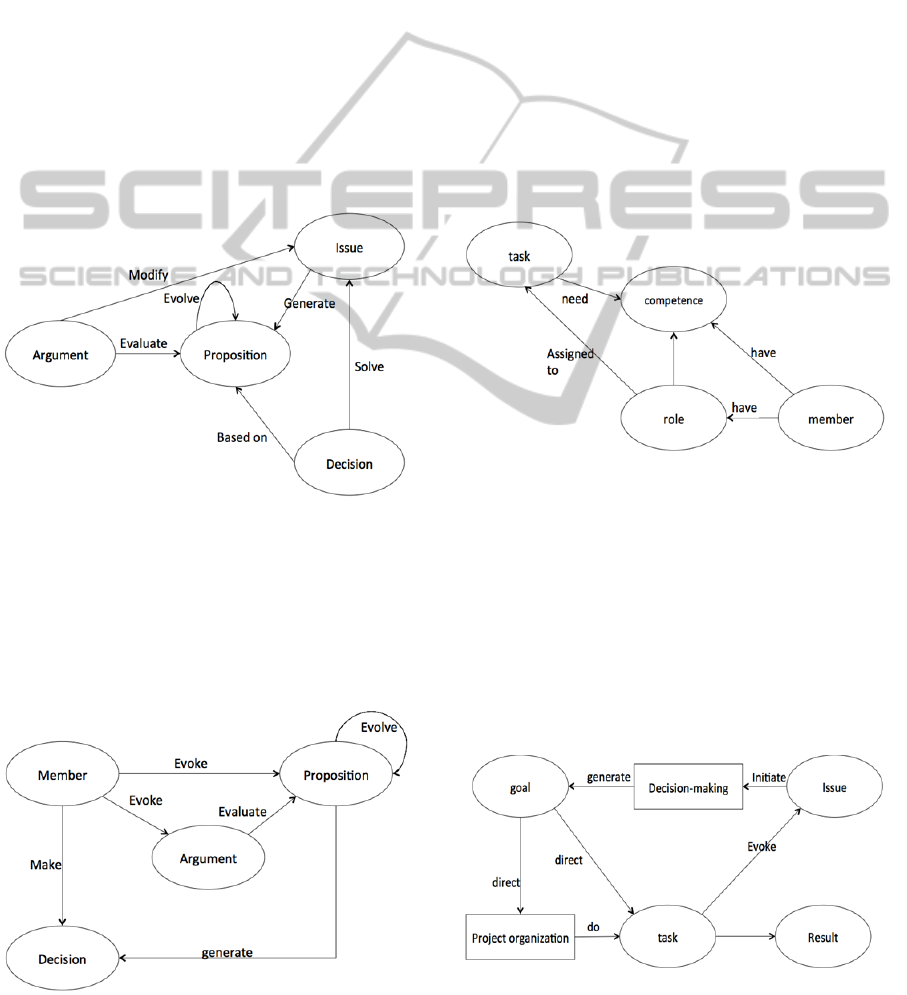
identified in a decision-making process are: issue,
proposition, argument and decision. Issue is the
major question or problem that we need to address,
it can be about product design, organization
arrangement or project realization etc.; proposition is
solution proposed to solve issue by project team
member; argument evaluates the proposition by
supporting or objecting it, which can push proposal
to evolve into another version (Conklin, 1988),
(Moran et al, 1996), (Buckinghum, 1997); argument
can also aims at issue which can possibly modify the
specification of the issue. Propositions are
considered to be possible solutions for issue, and
arguments are supposed to explain the reason why.
Decision is made by selecting some of the
propositions for the issue and setting up a goal for
next step of project realization. Figure 5 shows the
decision-making process sub-network.
Figure 5: Decision-making process.
One of the most important and useful knowledge
that we want to represent is the context of design
rationale (Moran et al, 1996). This sub-network
shows an interaction schema of concepts in decision-
making process. Moreover, other project memory
modules can also have mutual influences with
Figure 6: Project organization making decision.
decision-making process module. Therefore, we
connect decision-making to project realization to
show consequences of decision and connect
decision-making to project organization to reveal an
organizational influence.
In the sub-network above (figure 6), we want to
find a concept that serves as a bridge to connect
project organization and decision-making process.
So the concept “member” is introduced into
decision-making sub-network to add an
organizational dimension into decision-making
process. Member is an important concept of project
organization that links to competence, role and task.
This sub-network (figure 7) offers a learning
perspective on project realization with an
organizational dimension. Il presents us the
interaction schema between task and project
organization. Task is linked to two important
attributes of project member: competence and role.
Figure 7: Project organization realizing task.
At last, we want to represent the triangle between
task, decision and issue in order to show a mutual
influence of task arrangement and decision-making
process. A decision sets up a goal for a task; another
issue can be evoked during a task, which initiate
another decision-making process. The triangle ends
by achieving the final result of a task. During a
product design, the result of a task can be a new
version of a product, and the version of product
evolves between decision-making meeting and tasks.
Figure 8: Mutual influence of decision-making and project
realization.
CooperativeKnowledgeDiscoveryinDesignProjects
31
3.3 Propositions of Classification Views
The ability to extract general information from
example sets is a fundamental characteristic of
knowledge acquisition. Machine learning technique
is now a hot topic at present, it can figure out how to
perform important tasks by generalizing from
examples. One of the most mature and widely used
algorithms is classification (Domingos, 2012).
However, as we mentioned above, due to the
particular characteristics of design project
information, present machine learning techniques
are not suitable for design project memory
classification. We studied four major categories of
machine learning algorithms: statistical methods,
decision tree, rule based methods and artificial
neural network (Dietterich, 1997) (Goodman et al,
1992) (King et al, 1995). These methods are not
considered for two reasons: 1). Classification
process is not transparent to human interpretation.
2). A large recursive training set is needed for
classification. The advantage of our classification
model in project memory is that it is guided by
semantic networks that indicate knowledge rules
resided in interaction schemas. Therefore, according
to these semantic networks, we classify interaction
schemas instead of concepts. The amount of
repetitive interaction schemas is significantly fewer
compared to a concept; a large set of instances can
be conceptualized into one class, while the
probability of similar interaction schemas between
concepts is much less. Additionally, the learning
process will not ignore non-recursive schemas; on
the contrary, they will be put aside as explorative
attempts with an explanation.
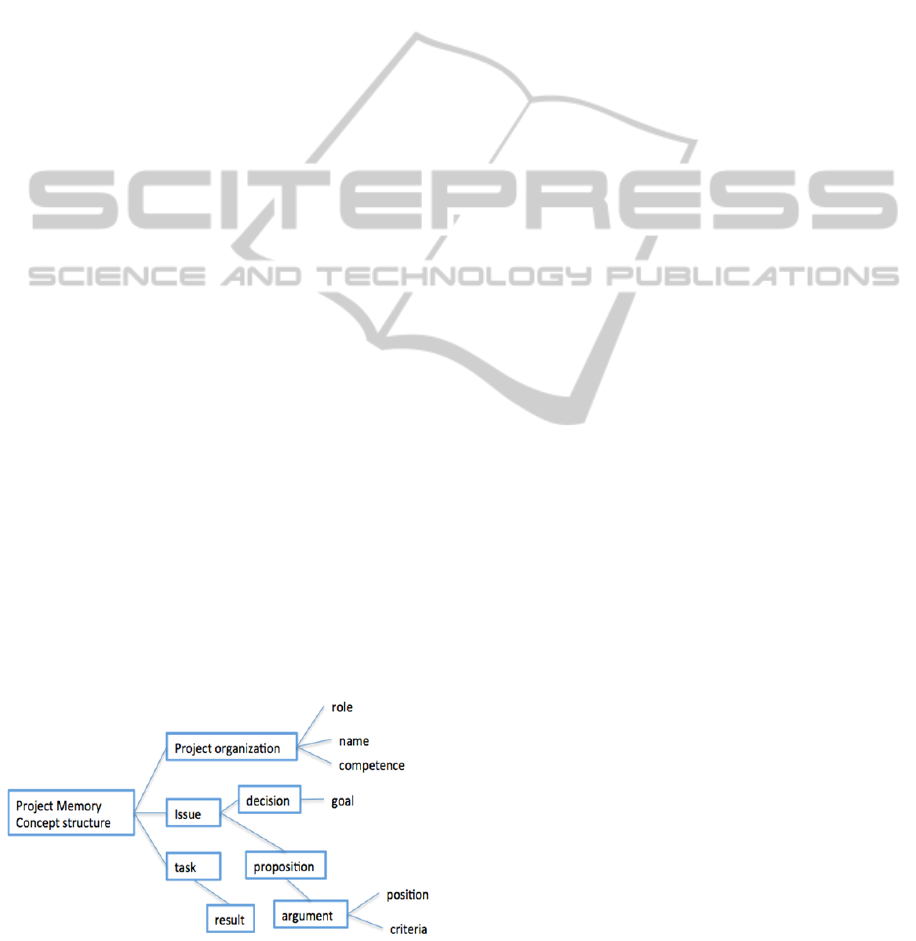
Two tablet applications have been developed to
capture project traces. They can register meeting
information and generate XML files (Matta et al,
2013). Project information will be structured
according to a XML schema as follow:
Figure 9: XML schema of project memory structure.
<xs:element name="member">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="role"
type="xs:string" />
<xs:element name="competence"
type="xs:string" />
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="issue">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="decision"
type="xs:string">
<xs:element name="proposition">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="argument">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="criteria"
type="xs:string" />
<xs:element name="position"
type="xs:int" />
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="task">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="result"
type="xs:string" />
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
Then project information will be classified
according to different views to extract knowledge
rules. Here we propose three classification views:
1. Problem-solving view: at a specific project
phase, we can classify decision-making process
for one particular issue. Solutions that are
repetitive will be classified as essential
solutions, the solutions that are distinctive will
be considered as explorative attempt with its
precondition as an explanation.
If (decision(d
1
) ∧ … ∧ decision(d
n
)) ∧
issue(i
i
) ⇒ decision(d’) ∧ issue(i
i
), then
decision(d′ )∧ issue(i
i
)⇒essential(e
i
)∧
issue(i
i
)
2. Cooperation view: an important subject that we
tried to study in our model is cooperation. This
classification view allows us to verify whether
there are parallel tasks that involve cooperative
design or regular meetings concerning whole
project team. Projects that are not undertaken
concurrently can lead to unsatisfactory results,
e.g. solution duplication or excess of project
constraint. This rule will reveal the influence of
KMIS2014-InternationalConferenceonKnowledgeManagementandInformationSharing
32
concurrent design on project result.
If ∃(issue(i) ∧ entire_team(m)) ∧
∃(task(t
1
) ∧ … ∧ task(t
n
)),then
∃cooperation(m)
3. Management view: this classification view will
focus on project organization influence on
different project memory modules. For
example, we can classify project realization
with an organizational dimension to examine
how project organization arrangement can
influence project realization.
A weight factor that indicates recurrence rate
will be attributed to each classification result to
show the importance of this result. The three aspects
proposed above are the most interesting and
practical classification views that we find so far,
however we do not exclude the possibility that more
useful classification views exist. In the next section,
CKD according to these three views will be applied
to two example projects.
4 EXAMPLE AND RESULT
Two software design projects were undertaken by
two teams in the year 2012 and 2013. The group
members are students majored in computer science
or mechanic design. The goal of the project is to
design a tablet application, which proposes solutions
for product maintenance; it should allow a
technician to access and modify PLM and ERP
information in order to facilitate information flow in
supply chain. MMreport and MMrecord were
employed to keep track of meetings from the
beginning to the end of the project, they can be
downloaded in APPstore for free. XML documents
were generated by these two applications. We
analysed these XML documents as well as other
documents (email, forum discussion and result)
according to the XML schema proposed in section
3.3. Next we are going to demonstrate three rules
extracted by comparison between these two projects.
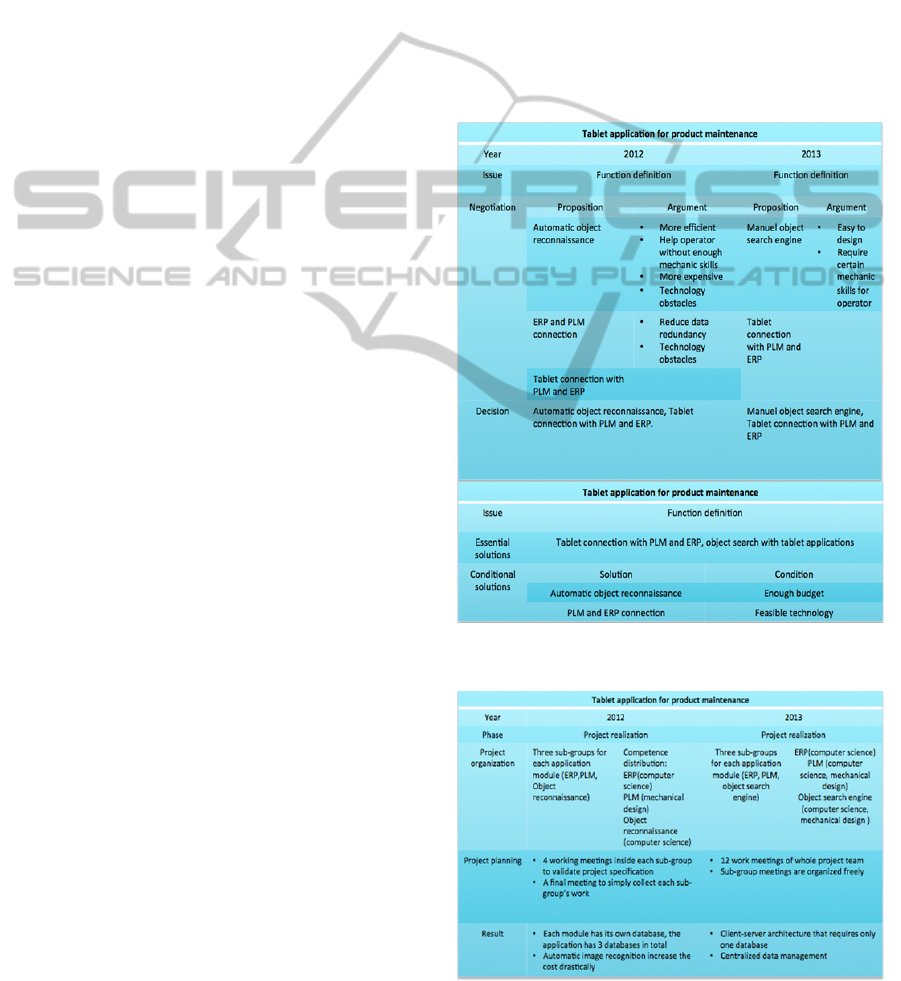
A problem-solving rule on the issue “function
definition” can be extracted by comparing the
decision-making process on this issue of both
projects. We classify repetitive solutions as essential
solutions for the issue function definition, and
distinctive solutions as explorative cases with a
precondition. The detailed classification is shown in
figure 10.
Cooperation rules on this project can be
extracted by classifying project planning, which is
represented by the sub-network decision-making
process and project realization. If there are tasks
concern module integration and regular meetings on
project specification of whole project team, then this
project is undertaken concurrently. If no meetings
are held with the whole group or no integration task
is assigned to more than one sub-group, then this
project is considered failed at concurrent design.
We can see from the project information 2012, four
meetings were held inside each sub-group and only
one final meeting involved the entire project group,
but the issue of the final meeting was “collecting
each group’s work”, which means no integration
issue was dealt with. Apparently in the project 2012,
design activities were not organized concurrently,
which leads to the result “database duplication” and
“expensive project cost”.
Figure 10: Problem-solving rule classification on issue
“function definition”.
Figure 11: Project planning with organizational
dimension.
CooperativeKnowledgeDiscoveryinDesignProjects
33

Linear project planning leads to bad communication
between different sub-group designers, which result
in poor integration design. From the management
point of view, we can further this classification by
adding an organizational dimension to project
planning. These two classification is shown in figure
11.
By comparing these two project organizations,
we can see that in the project team 2012,
competence was distributed homogenously for each
group, members were divided into computer science
group and mechanical design group; whereas
competence was paired in the project team 2013,
computer science and mechanical design both exist
in each sub-group. From this classification view, we
may draw the conclusion that if designers with
different skills are assigned to the same task, project
tends to be carried out more concurrently, which
leads to a more satisfactory result.
Extraction of these rules are all guided by
comparison of structured information according to
different project views, rules may change as more
project information will be captured. CDK
classification will progress in a cumulative manner.
5 CONCLUSION AND
PERSPECTIVE
This paper presented our research work on
cooperative knowledge, especially on how to
discovery cooperative knowledge in order to reuse
them. A CKD method was proposed for this purpose
in design project field. It is a knowledge
classification guided by semantic network schemas.
Instead of classifying domain expert knowledge,
interaction schemas between concepts were
classified; it allows us to put each important concept
in its interactive context. A CKD classification is
semantically expressive and comprehensible by
users. Therefore, it is up to users to choose which
classification view to use for knowledge extraction.
We tested CKD method on two example projects,
which shows that cooperative knowledge can be
extracted by interaction schema classification, more
importantly, the knowledge rules extracted can be
quite useful for learning purpose.
No classification can be argued to be a
representation of the true structure of knowledge, the
design project knowledge classification showed in
this paper is a application field of CKD method,
class conceptualization, semantic network structure
and knowledge classification views are strictly
linked to design project context. In other words, a
CKD classification model should be built according
to application domain features. In order to enrich
this application, we will try to formalize
classification rules with programming languages and
test our model on more complicated projects.
REFERENCES
Bekhti, S., Matta, N., 2003. "Project memory: An
approach of modelling and reusing the context and the
design rationale", Proc. of IJCAI, Vol. 3.
Buckingham Shum S., 1997. Representing Hard-to-
Formalise, Contextualised, Multidisciplinary,
Organisational Knowledge, in AAI Spring Symposium
on Artificial Intelligence in Knowledge Management,
pp. 9–16.
Castillo-Navetty, O., Matta, N., 2005. "Definition of a
practical learning system," Information Technology
Based Higher Education and Training, 2005. ITHET
2005. 6th International Conference on vol., no.,
pp.T4A/1,T4A/6, 7-9.
Cohen, H., Lefebvre, C., eds, 2005. “Handbook of
categorization in cognitive science”, Vol.4, No.9.1,
Elsevier, Amsterdam.
Conklin, J., Begeman, M. L., 1988. “gIBIS: a hypertext
tool for exploratory policy discussion,” ACM
Transactions on Information Systems, vol. 6., pp. 303–
331.
Dietterich, T.G., 1997. "Machine-learning research", AI
magazine, Vol.18, No.4, pp 97.
Djaiz, C., Matta, N., 2006. "Project situations aggregation
to identify cooperative problem solving strategies." In
Knowledge-Based Intelligent Information and
Engineering Systems, pp. 687-697. Springer Berlin
Heidelberg.
Domingos P., 2012. “A few useful things to know about
machine learning,” Commun. ACM, vol. 55, no. 10, p.
78.
Ducellier, G., Matta, N., Charlot, Y., and Tribouillois, F.,
2013. "Traceability and structuring of cooperative
Knowledge in design using PLM."International
Journal of Knowledge Management Research and
Practices 11, no. 4 pp: 20.
Ducellier, G., 2008. Thèse aux plateformes PLM, Univ.
Troyes, France, 2008.
Easterby-Smith, M. P. V, Lyles, M., 2003. “The Blackwell
Handbook of Organizational Learning and Knowledge
Management.,” Adm. Sci. Q., vol. 48, p. 676.
Fensel, D., 2000. "Ontologies: A silver bullet for
Knowledge Management and Electronic-Commerce."
Berlin: Spring-Verlag.
Goodman, R.M., Smyth, P., 1992. "An information
theoretic approach to rule induction from databases,"
Knowledge and Data Engineering, IEEE transactions,
Vol.4, No. 4 , pp 301-316.
Gruber, T.R., 1995. "Toward principles for the design of
ontologies used for knowledge sharing?", International
KMIS2014-InternationalConferenceonKnowledgeManagementandInformationSharing
34

journal of human-computer studies, Vol.43, No.5, pp
907-928.
Khoshafian, S., Buckiewicz, M., 1995. Introduction to
Groupware, Workflow and Workgroup Computing.
John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, NY, USA.
King, R.D., Cao, F., Sutherland, A., 1995. "Statlog:
comparison of classification algorithms on large real-
world problems", Applied Artificial Intelligence an
International Journal, Vol.9, No.3, pp289-333.
Klein, M., 1993. “Capturing design rationale in concurrent
engineering teams,” Computer , Calif., vol. 26, no. 1,
pp. 39–47.
Mai, J., 2004. "Classification in context: relativity, reality,
and representation", Knowledge organization, Vol.31,
No.1, pp 39-48.
Matta, N. Ducellier, G., 2013. “An approach to keep track
of project knowledge in design,” Proc. IC3K/KMIS,
5th International Conference on Knowledge
Management and Information Sharing, Vilamoura
Algarve, Portugal.
Matta, N., Ribière, M., Corby, O., Lewkowicz, M.,
Zacklad, M., 2001. “ Project Memory in Design,” in
Industrial Knolwedge Management, London Springer,
pp. 147-162.
Mika, P., Oberle, D., Gangemi, A., Sabou, M., 2004.
"Foundations for service ontologies: aligning OWL-S
to dolce." WWW pp. 563-572.
Miksa, F., 1998. “The DDC, the universe of knowledge,
and the post-modern library”, NY: Forest Press,
Albany.
Moran, T.P., Carroll, J.M., eds, 1996. Design rationale:
concepts, techniques, and use, Routledge, US.
Newell, A., 1982. "The knowledge level." Artificial
intelligence 18, no. 1 pp: 87-127.
Pahl, G., Beitz, W., Feldhusen, J., Grote, K.H., 2007.
Engineering design: a systematic approach, pp.1-617.
Schmidt, K., Bannon, L., 1992. Taking CSCW seriously,
Computer Supported Cooperative Work (CSCW) 1,
pp. 7-40.
Schreiber, G., Wielinga, B., 1994. Van de Velde W.,
Anjewierden A., “CML: The CommonKADS
Conceptual Modelling Language”, Proceedings of
EKAW'94, Lecture Notes in AI N.867, L.Steels, G.
Schreiber, W.Van de Velde (Eds), Bonn:
SpringerVerlag, pp 1-25.
Sowa, J.F., 2000. Knowledge representation: logical,
philosophical, and computational foundations,
Brooks/Cole, Pacific Grove.
Zacklad, M., 2003. Communities of action: a cognitive
and social approach to the design of CSCW systems.
In Proceedings of the 2003 international ACM
SIGGROUP conference on Supporting group work,
pp. 190-197.
CooperativeKnowledgeDiscoveryinDesignProjects
35
