
KEWI
A Knowledge Engineering Tool for Modelling AI Planning Tasks
Gerhard Wickler
1
, Luk
´
a
ˇ
s Chrpa
2
and Thomas Leo McCluskey
2
1
Artificial Intelligence Applications Institute, School of Informatics, University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, U.K.
2
PARK Research Group, School of Computing and Engineering, University of Huddersfield, Huddersfield, U.K.
Keywords:
Knowledge Engineering, Automated Planning.
Abstract:
This paper introduces the Knowledge Engineering Web Interface (KEWI) which primarily aims to be used for
modelling automated planning tasks in a semi-formal framework. The conceptual model used to represent the
declarative and procedural knowledge in KEWI is described formally. The model consists of three layers: a
rich ontology, a model of basic actions, and more complex methods. It is this structured conceptual model
based on the rich ontology that facilitates knowledge engineering. The focus of this paper is to show how
the central knowledge model used in KEWI differs from a model directly encoded in PDDL, the language
accepted by most existing planning engines. Specifically, the rich ontology enables a more concise and natural
style of representation. For operational use, KEWI automatically generates PDDL. Initial experiments show
that the generated PDDL can be processed by a planner without incurring significant drawbacks.
1 INTRODUCTION
Domain-independent planning has grown signifi-
cantly in recent years mainly thanks to the Interna-
tional Planning Competition (IPC). Besides many ad-
vanced planning engines, PDDL, a de-facto standard
language family for describing planning domains and
problems, has been developed. However, encoding
domain and problem models in PDDL requires a lot
of specific expertise and thus it is very challenging for
a non-expert to use planning engines in applications.
This paper concerns the use of AI planning tech-
nology in an organisation where (i) non-planning ex-
perts are required to encode knowledge (ii) the knowl-
edge base is to be used for more than one planning
and scheduling task (iii) it is maintained by several
personnel over a long period of time, and (iv) it may
have a range of potentially unanticipated uses in the
future. The first concern has been a major obstacle
to using AI-based tools which input formal represen-
tations, in that the expertise required to encode such
representations has only been possessed by planning
experts (e.g. as in NASA’s applications (Ai-Chang
et al., 2004)). The other concerns are often not cov-
ered in the planning literature: in real applications the
knowledge encoding is a valuable, general asset, and
one that requires a much richer conceptual represen-
tation than, for example is accorded by planner-input
languages such as PDDL.
As far as we are aware, very few collaborative,
domain-expert-usable, knowledge acquisition inter-
faces are available that are aimed at supporting the
harvesting of planning knowledge within a rich lan-
guage for use in a number of planning-related appli-
cations. After initial acquisition, the validation, verifi-
cation, maintenance and evolution of such knowledge
is of prime importance, as the knowledge base is a
valuable asset to an organisation.
This paper introduces the Knowledge Engineering
Web Interface (KEWI), which aims to enable the ac-
quisition and modelling of knowledge necessary for
use with automated plan generation tools. Here we
detail the theoretical aspects of KEWI, and evaluate it
using a well-understood planning domain.
2 RELATED WORK
A small number of frameworks exist that support the
formalisation of planning knowledge in shared web-
based systems. Usually, such frameworks build on
existing Web 2.0 technologies such as a wiki. A
wiki that supports procedural knowledge is available
at wikihow.com, but the knowledge remains essen-
tially informal. A system that uses a similar approach,
36
Wickler G., Chrpa L. and McCluskey T..
KEWI - A Knowledge Engineering Tool for Modelling AI Planning Tasks.
DOI: 10.5220/0005034400360047
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development (KEOD-2014), pages 36-47
ISBN: 978-989-758-049-9
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

namely, representing procedural knowledge in a wiki
is CoScripter (Leshed et al., 2008). However, their
representation is not based on AI planning and thus
does not support the automated composition of pro-
cedures. More recently, an AI-based representation
has been used in OpenVCE (Wickler et al., 2013).
There have been several attempts to create gen-
eral, user-friendly development environments for
planning domain models, but they tend to be limited
in the expressiveness of their underlying formalism.
The Graphical Interface for Planning with Objects
(GIPO) (Simpson et al., 2007) is based on object-
centred languages OCL and OCL
h
. These formal lan-
guages exploit the idea that a set of possible states of
objects are defined first, before action (operator) def-
inition (McCluskey and Kitchin, 1998). This gives
the concept of a world state consisting of a set of
states of objects, satisfying given constraints. GIPO
uses a number of consistency checks such as if the
object’s class hierarchy is consistent, object state de-
scriptions satisfy invariants, predicate structures and
action schema are mutually consistent and task speci-
fications are consistent with the domain model. Such
consistency checking guarantees that some types of
errors can be prevented, in contrast to ad-hoc meth-
ods such as hand crafting.
itSIMPLE (Vaquero et al., 2012) provides a graph-
ical environment that enables knowledge engineers to
model planning domain models by using the Unified
Modelling Language (UML). Object classes, predi-
cates, action schema are modelled by UML diagrams
allowing users to ‘visualise’ domain models which
makes the modelling process easier. itSimple incor-
porates a model checking tool based on Petri Nets that
are used to check invariants or analyse dynamic as-
pects of the domain models such as deadlocks.
The Extensible Universal Remote Operations
Planning Architecture (EUROPA) (Barreiro et al.,
2012), is an integrated platform for AI planning and
scheduling, constraint programming and optimisa-
tion. This platform is designed to handle complex
real-world problems, and the platform has been used
in some of NASA’s missions. EUROPA supports two
representation languages, NDDL and ANML (Smith
et al., 2008), however, PDDL is not supported.
Besides these tools, it is also good to mention
VIZ (Vodr
´
a
˘
zka and Chrpa, 2010), a simplistic tool
inspired by itSimple, and PDDL Studio (Plch et al.,
2012), an editor which provides users a support by,
for instance, identifying syntax errors or highlighting
components of PDDL.
In the field of Knowledge Engineering, method-
ologies have been developed which centre on the cre-
ation of a precise, declarative and detailed model of
the area of knowledge to be engineered, in contrast
to earlier expert systems approaches which appeared
to focus on the “transfer” expertise at a more super-
ficial level. This “expertise model” contains a mix
of knowledge about the “problem solving method”
needed within the application and the declarative
knowledge about the application. Often a key ratio-
nale for knowledge engineering is to create declar-
ative representations of an area to act as a for-
malised part of some requirements, making explicit
what hitherto has been implicit in code, or explicit
but in documents. Knowledge Engineering mod-
elling frameworks arose out of this, such as Com-
monKADS (Schreiber et al., 1999), which were based
on a deep modelling of an area of expertise, and em-
phasising a life-cycle of this model. The “knowledge
model” within CommonKADS, which contains a for-
mal encoding of task knowledge, such as problem
statement(s), as well as domain knowledge, is simi-
lar to the kind of knowledge captured in KEWI. Un-
like KEWI however, this model was expected to be
created by knowledge engineers rather than domain
experts and users.
2.1 AI Planning
The primary aim for KEWI is to ease the formalisa-
tion of procedural knowledge, allowing domain ex-
perts to encode their knowledge themselves, rather
than knowledge engineers having to elicit the knowl-
edge before they formalise it into a representation. We
formally describe the conceptual model which con-
sists of three layers: a rich ontology, a model of ba-
sic actions, and more complex methods. KEWI is
object-centred and allows for a richer representation
of knowledge than PDDL. It is more compact and
more expressive which means models are easier to
maintain, especially for a user who is not an expert
in AI planning. KEWI’s internal representation can
be exported to PDDL and hence standard planning en-
gines can be applied to solve planning problems mod-
elled in KEWI. We demonstrate that PDDL models
exported from KEWI are comparable to hand coded
ones.
AI planning deals with the problem of finding a
sequences of actions transforming the environment
from a given initial state to a desired goal state (Ghal-
lab et al., 2004). Actions are defined via their precon-
ditions and effects. An action is applicable in a given
state if and only if its precondition holds in that state.
Effects of an action denote how a state where the ac-
tion is applied will change. A planning domain model
consists of a set of predicates and/or fluents describ-
ing the environment and a set of actions modifying
KEWI-AKnowledgeEngineeringToolforModellingAIPlanningTasks
37

Figure 1: An architecture of KEWI.
the environment. A planning problem consists of a
planning domain model, set of objects, an initial state
and a set of goal conditions.
3 CONCEPTUAL MODEL OF
KEWI
KEWI is a tool for encoding domain knowledge
mainly by experts in the application area rather than
AI planning experts. The idea behind KEWI is to pro-
vide a user-friendly environment as well as a language
which is easier to follow, especially for users who are
not AI planning experts. A high-level architecture of
KEWI is depicted in figure 1. Encoded knowledge
can be exported into the domain and problem descrip-
tion in PDDL on which standard planning engines can
be applied. Hence, the user does not have to under-
stand, or even be aware, of any PDDL encodings.
A language in which domain knowledge is en-
coded in KEWI has three parts, which are explained
in the following subsections. First, a rich domain on-
tology is defined. The domain ontology consists of
definitions of classes of objects, hierarchies of classes
and relations between objects. Second, action types
are defined in terms of their action name, logical pre-
conditions and effects. Third, methods define ways in
which high-level task can be broken down into lower-
level activities, a so-called task network which in-
cludes explicit ordering constraints.
3.1 Ontology: Concepts, Relations and
Properties
Ontological elements are usually divided into con-
cepts and instances. Typically, the concepts are de-
fined in a planning domain whereas the instances are
defined in a planning problem. Since our focus for
KEWI is on planning domains we shall mostly deal
with concepts here.
3.1.1 Concepts
A concept is represented by a unique symbol in
KEWI. The formal definition of a concept is given
by its super-class symbol and by a set of role con-
straints that define how instances of the concept may
be related to other concepts. In KEWI, the defini-
tion of a concept also includes other, informal ele-
ments that are not used for formal reasoning. How-
ever, the knowledge engineering value of such infor-
mal elements must not be underestimated, much like
the comments in programming often are vital for code
to be understandable.
Definition 1 (KEWI Concept). A concept C in KEWI
is a pair hC
sup
, Ri, where:
• C
sup
is the direct super-concept of C and
• R is a set of role constraints of the form hr, n, C
0
i
where r is a symbolic role name, C
0
is a concept
(denoting the role filler type), and n is a range
[n
min
, n
max
] constraining the number of different
instances to play that role.
We assume that there exists a unique root con-
cept often referred to as object or thing that acts
as the implicit super-concept for those concepts that
do not have an explicit super-concept defined in the
same planing domain. Thus, a concept C may be de-
fined as h4, Ri, meaning its super concept is implicit.
This implicit super-concept has no role constraints at-
tached.
For example, in the Dock Worker Robot
(DWR) domain (Ghallab et al., 2004), the con-
cepts container and pallet could be defined with
the super-concept stackable, whereas the concept
crane could be defined as a root concept with no
super-concept (implicitly: 4). A role constraint can
be used to define that a crane can hold at most one
container as follows: hholds, [0, 1], containeri.
Since super-concepts are also concepts, we can
write a concept C as hhh4, R
n
i, . . . , R
2
i, R
1
i. Then we
can refer to all the role constraints associated with C
as R
∗
= R
n
∪ . . . ∪ R
2
∪ R
1
, that is, the role constraints
that appear in the definition of C, the role constraints
in its direct super-concept, the role constraints in its
super-concepts super-concept, etc.
The reason for introducing this simple ontology of
concepts is that we can now constrain the set of pos-
sible world states based on the role constraints. States
are defined as sets of ground, first-order atoms over
some function-free language L . This language shall
contain symbols to denote each instance of a concept
defined in the ontology (c
1
, . . . , c
L
) where the type
function τ maps each instance c
i
to its type C, a con-
cept in the ontology. The relation symbols of L are
defined through the role constraints.
Definition 2 (Relations in L ). Let hr, n, C
0
i be a role
constraint of some concept C. Then the first-order
KEOD2014-InternationalConferenceonKnowledgeEngineeringandOntologyDevelopment
38

language L that can be used to write ground atoms
in a state contains a binary relation C.r ⊆ C ×C
0
.
In what follows we shall extend the language to
include further relation symbols, but for now these
relations defined by the ontology are all the relations
that may occur in a state. The reason why the rela-
tion name is a combination of the concept and the role
is simply to disambiguate between roles of the same
name but defined in different concepts. Where all role
names are unique the concept may be omitted.
We can now define what it means for a state to be
valid with respect to an ontology defined as a set of
KEWI concepts. Essentially, for a state to be valid,
every instance mentioned in the state must respect all
the role constraints associated with the concepts to
which the instance belongs. Since role constraints are
constraints on the number of possible role fillers we
need to be able to count these.
Definition 3 (Role Fillers). Let s be a state, that is,
a set of ground atoms over objects c
1
, . . . , c
L
using
the relations in L . Let hr, n, C
0
i be a role constraint
of some concept C. Then we define vals
s
(C.r, c
i
) =
{c
f
|C.r(c
i
, c
f
) ∈ s}, c
i
∈ C, c
f
∈ C
0
, that is, the set of
all constants that play role r for c
i
in s.
Definition 4 (Valid State). Let C be a KEWI concept.
Then a state s is valid if, for any instance c
i
of C and
any role constraint hr, n, C
0
i of C or one of its (direct
and indirect) super-concepts, the number of ground
atoms a = C.r(c
i
, ∗) must be in the range [n
min
, n
max
],
i.e. n
min
≤ |vals
s
(C.r, c
i
)| ≤ n
max
.
Thus, a concept definition defines a set of role
constraints which can be interpreted as relations in a
world state. The numeric range defines how many
ground instances we may find in a valid state. This is
the core of the ontological model used in KEWI.
For example, let k1 be a crane and ca be a con-
tainer. Then a state may contain a ground atom
crane.holds(k1,ca). If a state contains this atom, it
may not contain another one using the same relation
and k1 as the first argument.
3.1.2 Relations
While the relations defined through the concepts in
KEWI provide a strong ontological underpinning for
the representation, there are often situations where
other relations are more natural, e.g. to relate more
than two concepts to each other, or where a relation
does not belong to a concept. In this case relations
can be defined by declaring number and types (con-
cepts) of the expected arguments.
Definition 5 (Relations in L ). A relation may be de-
fined by a role constraint as described above, or it
may be a relation symbol followed by an appropriate
number of constants. The signature of a relation R is
defined as C
1
× . . . × C
R
where C
i
defines the type of
the ith argument.
A valid state may contain any number of ground
instances of these relations. As long as the types of
the constants in the ground atoms agree with the sig-
nature of the relation, the state that contains this atom
may be valid.
3.1.3 Properties
In reality, we distinguish three different types of role
constraints: related classes for defining arbitrary re-
lations between concepts, related parts which can be
used to define a “part-of” hierarchy between con-
cepts, and properties which relate instances to prop-
erty values.
The first two are equivalent in the sense that they
relate objects to each other. However, properties usu-
ally relate objects to values, e.g. an object may be of
a given colour. While it often makes sense to distin-
guish all instances of a concept, this is not true for
properties. While the paint that covers one container
may not be the same paint that covers another, the
colour may be the same. To allow for the representa-
tions of properties in KEWI, we allow for the defini-
tion of properties with enumerated values.
Definition 6 (Properties). A property P is defined as
a set of constant values {p
1
, . . . , p
P
}.
It is easy to see that the above definitions relating
to role constraints and other relations can be extended
to allow properties in place of concepts and property
values in place of instances. A minor caveat is that
property values are usually defined as part of a plan-
ning domain, whereas instances are usually given in a
planning problem.
3.2 Action Types
Action types in KEWI are specified using an operator
name with typed arguments, a set of preconditions,
and a set of effects. This high-level conceptualisation
of action types is of course very common in AI plan-
ning formalisms. KEWI’s representation is closely
linked with the ontology, however. This will enable a
number of features that allow for a more concise rep-
resentation, allowing to reduce the redundancy con-
tained in many PDDL planning domains.
3.2.1 Object References
In many action representations it is necessary to in-
troduce one variable for each object that is somehow
KEWI-AKnowledgeEngineeringToolforModellingAIPlanningTasks
39

involved in the execution of an action. This variable is
declared as one of the typed arguments of the action
type. The variable can then be used in the precon-
ditions and effects to consistently refer to the same
objects and express conditions on this object.
Sometimes, an action type may need to refer to
specific constants in its preconditions or effects. In
this case, the unique symbol can be used to identify a
specific instance. In the example above, k1 was used
to refer to a crane and ca to refer to a container. In
most planning domains, operator definitions do not
refer to specific objects, but constants may be used as
values of properties.
In addition to variables and constants, KEWI also
allows a limited set of function terms to be used to
refer to objects in an action type’s preconditions and
effects. Not surprisingly, this is closely linked with
the ontology, specifically with the role constraints that
specify a maximum of one in their range.
Definition 7 (Function Terms). Let hr, n, C
0
i be a role
constraint of some concept C where n
max
= 1. Then
we shall permit the use of function terms of the form
C.r(t) in preconditions and effects, where t can again
be an arbitrary term (constant, variable, or function
term) of type C
0
.
Let s be a valid state, that is, a set of ground atoms
over objects c
1
, . . . , c
L
using the relations in L . Then
the constant represented by the function term C.r(c
i
)
is:
• c
j
if vals
s
(C.r, c
i
) = {c
j
}, or
• nothing (⊥) if vals
s
(C.r, c
i
) =
/
0.
Note that the set vals
s
(C.r, c
i
) can contain at most
one element in any valid state. If it contains an ele-
ment, this element is the value of the function term.
Otherwise a new symbol that must not be one of
the constants c
1
, . . . , c
L
will be used to denote that
the function term has no value. This new constant
nothing may also be used in preconditions as de-
scribed below.
The basic idea behind function terms is that they
allow the knowledge representation to be more con-
cise; it is no longer necessary to introduce a variable
for each object. Also, this style of representation may
be more natural, e.g. to refer to the container held by a
crane as crane.holds(k1) meaning “whatever crane
k1 holds”, where the role constraint tells us this must
be a container. As a side effect, the generation of a
fully ground planning problem could be simpler,given
the potentially reduced number of action parameters.
Interestingly, a step in this direction was already
proposed in PDDL 1, in which some variables were
declared as parameters and others as “local” variables
inside an operator. However, with no numeric con-
straints on role fillers or any other type of relation, it is
difficult to make use of such variables in a consistent
way. Similarly, state-variable representations (Jons-
son and B
¨
ackstr
¨
om, 1998) exploit the uniqueness of a
value. However, this was restricted to the case where
n
min
and n
max
both must be one.
3.2.2 Condition Types
The atomic expressions that can be used in precon-
ditions and effects can be divided into two cate-
gories. Firstly, there are the explicitly defined re-
lations. These are identical in meaning and use to
PDDL and thus, there is no need to discuss these fur-
ther. Secondly, there are the relations based on role
constraints which have the same form as such atoms
in states, except that they need not be ground.
Definition 8 (Satisfied Atoms). Let s be a valid state
over objects c
1
, . . . , c
L
. Then a ground atom a is sat-
isfied in s (denoted s |= a) if and only if:
• a is of the form C.r(c
i
, c
j
) and a ∈ s, or
• a is of the form R(c
i
1
, . . . , c
i
R
) and a ∈ s, or
• a is of the form C.r(c
i
, ⊥) and vals
s
(C.r, c
i
) =
/
0.
The first two cases are in line with the standard
semantics, whereas the the last case is new and lets us
express that no role filler for a given instance exists
in a given state. Note that the semantics of atoms that
use the symbol nothing in any other place than as a
role filler are never satisfied in any state.
The above definition can now be used to define
when an action is applicable in a state.
Definition 9 (Action Applicability). Let s be a valid
state and act be an action, i.e. a ground instance of
an action type with atomic preconditions p
1
, . . . , p
a
.
Then act is applicable in s if and only if every precon-
dition is satisfied in s: ∀p ∈ p
1
, . . . , p
a
: s |= p.
This concludes the semantics of atoms used in pre-
conditions. Atoms used in effects describe how the
state of the world changes when an action is applied.
This is usually described by the state transition func-
tion γ : S × A → S, i.e. it maps a state and an applica-
ble action to a new state. Essentially, γ modifies the
given state by deleting some atoms and adding some
others. Which atoms are deleted and which are added
depends on the effects of the action. If the action is
not applicable the function is undefined.
Definition 10 (Effect Atoms). Let s be a valid state
and act be an action that is applicable in s. Then the
successor state γ(s, a) is computed by:
1. deleting all the atoms that are declared as nega-
tive effects of the action,
2. for every positive effect C.r(c
i
, c
j
) for role con-
straint hr, n, C
0
i with n = [n
min
, 1], if C.r(c
i
, c
k
) ∈ s
delete this atom, and
KEOD2014-InternationalConferenceonKnowledgeEngineeringandOntologyDevelopment
40

3. add all the atoms that are declared as positive ef-
fects of the action.
Following this definition allows for a declaration
of actions using arbitrary relations and state-variables
that may have at most one value. The ontology, more
specifically the numeric role constraints can be used
to distinguish the two cases.
3.3 Methods
The definition of methods in KEWI is not yet finished.
As the framework is at least partially application-
driven, we may need to further refine the conceptual
framework outlined (but not fully defined) below.
The approach adopted in KEWI follows standard
HTN planning concepts: a method describes how a
larger task can be broken down in into smaller tasks
which, together, accomplish the larger task.
A method is defined by a method name with some
parameters. The name usually suggests how some-
thing is to be done and the parameters have the same
function as in action types; they are the objects that
are used or manipulated during the instantiation of a
method. Next, a method must declare the task that
is accomplished by the method. This is defined by
a task name usually describing what is to be done,
and again some parameters. For primitive tasks, the
task name will be equal to the name of an action type,
in which case no further refinement is required. For
non-primitive tasks, a method also includes a set of
subtasks. In KEWI, the ordering constraints between
subtasks are declared with the subtask, rather than as
a separate component of the method. This is simply to
aid readability without changing the expressiveness.
In addition, to these standard components, KEWI
allows the specification of high-level effects and
subgoal-subtasks. The aim here is to allow for a rep-
resentation that supports flat, PDDL-like planning do-
mains as well as hierarchical planning domains.
When a method declares that it achieves a high-
level effect, then every decomposition of this method
must result in an action sequence which will achieve
the high-level effect after the last action of the se-
quence has been completed. This could allow a plan-
ner to use a method as if it was an action in a backward
search. An alternative view is that such a method
functions as a macro action type in the domain.
A method may also include subtasks that are ef-
fectively subgoals. For example, the subtask “achieve
C.r(c
i
, c
j
)” may be used to state that at the corre-
sponding point in the subtask the condition C.r(c
i
, c
j
)
must hold in the state. The idea being that a plan-
ner may revert to flat planning (such as state-space
search) to find actions to be inserted into the plan at
this point, until the subgoal is achieved.
This mixed approach is not new and has been used
in practical planners like O-Plan (Currie and Tate,
1991). However, the semantics has not been formally
defined for this approach, something we shall attempt
in future work.
3.4 Export to PDDL
Given that most modern planners accept planning do-
mains and problems in PDDL syntax as their input,
one of the goals for KEWI was to provide a mecha-
nism that exports the knowledge in KEWI to PDDL.
Of course, this will not include the HTN methods
as PDDL does not support hierarchical planning for-
malisms.
3.4.1 Function Terms
The first construct that must be removed from
KEWI’s representation are the function terms that
may be used to refer to objects. In PDDL’s precon-
ditions and effects only variables (or symbols) may
be used to refer to objects. The following function
can be used to eliminate a function term of the form
C.r(t) that occurs in an action type O’s preconditions
or effects.
function eliminate-fterms(C.r(t), O)
if is-fterm(t) then
eliminate-fterms(t, O)
v ← get-variable(C.r(t), O)
replace every C.r(t) in O by v
The function first tests whether the argument to
the given function term is itself a function term. If
this the case, it has to be eliminated first. This guar-
antees that, for the remainder of the function t is ei-
ther a variable or a symbol. We then use the func-
tion “get-variable” to identify a suitable variable that
can replace the function term. Technically, this func-
tion may return a symbol, but the treatment is identi-
cal, which is why we shall not distinguish these cases
here. The identification of a suitable variable then
works as follows.
function get-variable(C.r(v), O)
for every positive precondition p of O do
if p = C.r(v, v
0
) then
if is-fterm(v
0
) then
eliminate-fterms(v
0
, O)
return v
0
retrieve hr, n, C
0
i from C
add new parameter v
0
of type C
0
to O
add new precondition C.r(v, v
0
) to O
return v
0
KEWI-AKnowledgeEngineeringToolforModellingAIPlanningTasks
41

This function first searches for an existing, posi-
tive precondition that identifies a value for the func-
tion. Since function terms may only be used for con-
straints that have at most one value, there can only be
at most one such precondition. If such a precondition
exists, its role filler (v
0
, a variable or a symbol) may
be used as the result. If no such precondition can be
found, the function will create a new one and add it
to the operator. To this end, a new parameter must be
added to the action type, and to know the type of the
variable we need to retrieve the role filler type from
the role constraint. In practise, we also use the type
name to generate a suitable variable name. Then a
new precondition can be added that effectively binds
the function to the role filler. And finally, the new
variable may be returned.
3.4.2 Handling nothing
The next construct that needs to be eliminated from
the KEWI representation is any precondition that uses
the role filler nothing. Note that this symbol does not
occur in states and thus cannot be bound in traditional
PDDL semantics. Simply adding this symbol to the
state is not an option since other preconditions that
require a specific value could then be unified with this
state atom. For example, if we had an explicit atom
that stated holds(k1, nothing) in our state, then the
precondition holds(?k, ?c) of the load action type
would be unifiable with this atom. An inequality pre-
condition may solve this problem, but only if the plan-
ner can correctly handle inequalities. The alternative
approach we have implemented in KEWI is described
in the following algorithm.
function eliminate-nothing(O)
for every precondition p = C.r(v, ⊥) do
replace p with C.r. ⊥ (v)
if O has an effect e = C.r(v, v
0
)
add another effect ¬C.r. ⊥ (v)
The idea behind this approach is to use a new
predicate to keep track of state-variables that have no
values in a state. This is the purpose of the new pred-
icate “C.r. ⊥”, indicating the role r of concept C has
no filler for the given argument. This is a common
approach in knowledge engineering for planning. For
example, in the classic blocks world we find a “holds”
relation for when a block is being held, and a predi-
cate “hand-empty” for when no block is held.
The algorithm above uses this technique to replace
all preconditions that have nothing as a role filler
with a different precondition that expresses the non-
existence of the role filler. To maintain this condition,
it will also be necessary to modify the effects accord-
ingly. This is done by adding the negation of this new
predicate to corresponding existing effects.
Since this is pseudo code, the algorithm actually
omits a few details, e.g. the declaration of the new
predicate in the corresponding section of the PDDL
domain, and the fact that the planning problem also
needs to be modified to account for the new predicate.
Both is fairly straight forward to implement.
3.4.3 State-variable Updates
Finally, the cases in which the value of a state-variable
is simply changed needs to be handled. The approach
we have adopted here is identical to the approach de-
scribed in (Ghallab et al., 2004). That is, when an
effect assigns a new value to a state-variable, e.g.
C.r(v, v
new
), we need to add a precondition to get the
old value, e.g. C.r(v, v
old
), and then we can use this
value in a new negative effect to retract the old value:
¬C.r(v, v
old
).
4 EVALUATION: THE DOCK
WORKER ROBOTS DOMAIN
In this section we shall describe some experiences
gained while re-engineering an existing and well un-
derstood planning domain, the dock worker robots
(DWR) domain described in (Ghallab et al., 2004).
Basically, a problem in this domain consists of a set
of locations at which containers are piled into stacks.
Cranes at these locations can move the containers
around at the same location, and robots can be used to
move containers between locations. The current state
is a given configuration of containers in piles and the
goal is usually to shift the containers to different piles.
4.1 Ontology
The original planning domain specified in PDDL de-
fines a trivial ontology that consists of just the five
types of objects that are involved in the actions as
shown in figure 2. There is hierarchy and concepts are
defined by name only. The text following a semicolon
are comments and ignored by the reasoning engine.
Apart from the lack of any intensional knowledge
about these types, this conceptualisation also does not
use a separate type for the pallets that are at the bot-
tom of each pile. In fact, a single pallet is declared as
an instance of type container in the problem files
and the same pallet is used at the bottom of every
pile. This solution works in a planning engine but is
clearly unsatisfactory from a knowledge engineering
perspective.
KEOD2014-InternationalConferenceonKnowledgeEngineeringandOntologyDevelopment
42

(:types
location ; there are several connected locations in the harbour
pile ; is attached to a location
; it holds a pallet and a stack of containers
robot ; holds at most 1 container, only 1 robot per location
crane ; belongs to a location to pickup containers
container)
Figure 2: The types declared in the original PDDL domain.
The KEWI version of the domain we have de-
veloped is shown in figure 3 is obviously much
richer. There is some hierarchical structure, e.g. the
class stackable has two sub-classes, container and
pallet. Most classes have associated role constraints
that provide an intensional definition of the class. In
addition to the types from the original domain, the
KEWI version also defines a colour property which
is there solely to illustrate the use of properties and
should be ignored by a planner. Adjacency between
locations is specified as a relation not associated with
any concept.
The use of an explicit class for pallets is the only
significant difference in the original conceptualisation
and the KEWI version of the DWR ontology. What
appears as a complication at first is actually a sim-
plification since there is no longer a need for piles.
Piles can be identified by the pallets on which they
are stacked.
When the PDDL version of the domain is gener-
ated from the KEWI environment, most of the onto-
logical information is lost, of course, as PDDL is not
sufficiently expressive for the kind of ontology KEWI
uses. However, the information is used to generate
additional relations and modify the operator specifi-
cations that are generated.
4.2 Action Types
The original PDDL specification of the DWR domain
specifies five action types:
• move: a robot moves from one location to an ad-
jacent location
• load: a crane loads the container onto a robot
• unload: a crane unloads a container from a robot
• take: a crane takes a container from a pile
• put: a crane puts the container onto a pile
All of these operators were (manually) re-encoded
in KEWI, exploiting the richer ontology and other
language features described above. The result is a
more concise representation that reduces the need for
certain explicit, but redundant parameters, precon-
ditions and effects. The generation of PDDL from
KEWI results in a specification that cannot make ref-
erence to the ontology and therefore is not as concise
as the KEWI version. In fact, as shown is table 1, it
even uses some additional parameters, preconditions
and effects.
Clearly, the KEWI version of the domain is the
most concise. The use of function terms avoids the ex-
plicit introduction of parameters. From a knowledge
engineering perspective, this means the actions can
be specified in terms of the main objects involved. A
similar construct is available in PDDL, where certain
variables are “local” and not used in the parameter
specification. However, this is not widely supported
by planners and used in few domain specifications.
The KEWI representation also uses fewer precondi-
tions and effects. This is mostly because of the use
of role constraints with nothing as their value. Thus,
both reasons for a more concise representation are di-
rectly related to the richer ontology.
Perhaps the most interesting operator to take a
closer look at is the most complex action type speci-
fied here, the put action. The original PDDL version
is shown in figure 4. The first local variable, ?else,
is a reference to the container (or pallet) that is at the
top of the pile before the action executed. Two of the
preconditions are static, two are dynamic. Interest-
ingly, the last of the preconditions, (top ?else ?p),
is not so much a logical precondition but simply a way
to bind the local variable ?else such that it may be
used in the effects. There are no negative precondi-
tions. The effects are a mixture of four positive and
two negative effects.
Compare this to the KEWI version of the same op-
erator. In the web interface, the normal view provides
many links for navigating the knowledge, whereas the
edit view shows a form with fields for different parts
of the representation are shown in figure 5. The ex-
plicit break-down in the edit view is meant to sup-
port the knowledge engineer by listing the compo-
nents available in the language.
The complete formalism specifying the action
KEWI-AKnowledgeEngineeringToolforModellingAIPlanningTasks
43

(:class agent)
(:class crane
(:super-class agent)
(:role at (:min 1) (:max 1) (:class location))
(:role holds (:max 1) (:class container)))
(:class robot
(:super-class agent)
(:role loaded-with (:max 1) (:class container))
(:property has-colour (:min 1) (:max 1) (:type colour)))
(:class location
(:role occupied-by (:max 1) (:class robot)))
(:class stackable)
(:class container
(:super-class stackable)
(:role on (:max 1) (:class stackable))
(:role piled-on (:max 1) (:class pallet))
(:property paint (:min 1) (:max 1) (:type colour)))
(:class pallet
(:super-class stackable)
(:role at (:min 1) (:max 1) (:class location))
(:role top (:min 1) (:max 1) (:class stackable)))
(:property colour
(:values ( red green blue )))
(:relation adjacent
(:arguments ( (?loc1 location) (?loc2 location) )))
Figure 3: The ontology of the DWR domain in KEWI.
Table 1: Number of parameters, preconditions and effects in the different versions of the DWR domain.
Original PDDL KEWI Generated PDDL
params precs effects params precs effects params precs effects
move 3 3 4 3 3 2 3 3 4
load 4 4 4 3 3 2 4 4 4
unload 4 4 4 3 3 2 4 4 4
take 5 6 6 2 3 4 6 7 8
put 5 4 6 3 4 4 6 7 8
(:action put
:parameters (?k - crane ?c - container ?p - pile)
:vars (?else - container ?l - location)
:precondition (and (belong ?k ?l) (attached ?p ?l)
(holding ?k ?c) (top ?else ?p))
:effect (and (in ?c ?p) (top ?c ?p) (on ?c ?else)
(not (top ?else ?p)) (not (holding ?k ?c))
(empty ?k))))
Figure 4: The original PDDL version of put.
type in KEWI is shown in figure 6. At first glance
it appears less concise, but this is simply because the
symbols are more verbose, e.g. no single letter vari-
ables are used and role constraints make the object
KEOD2014-InternationalConferenceonKnowledgeEngineeringandOntologyDevelopment
44
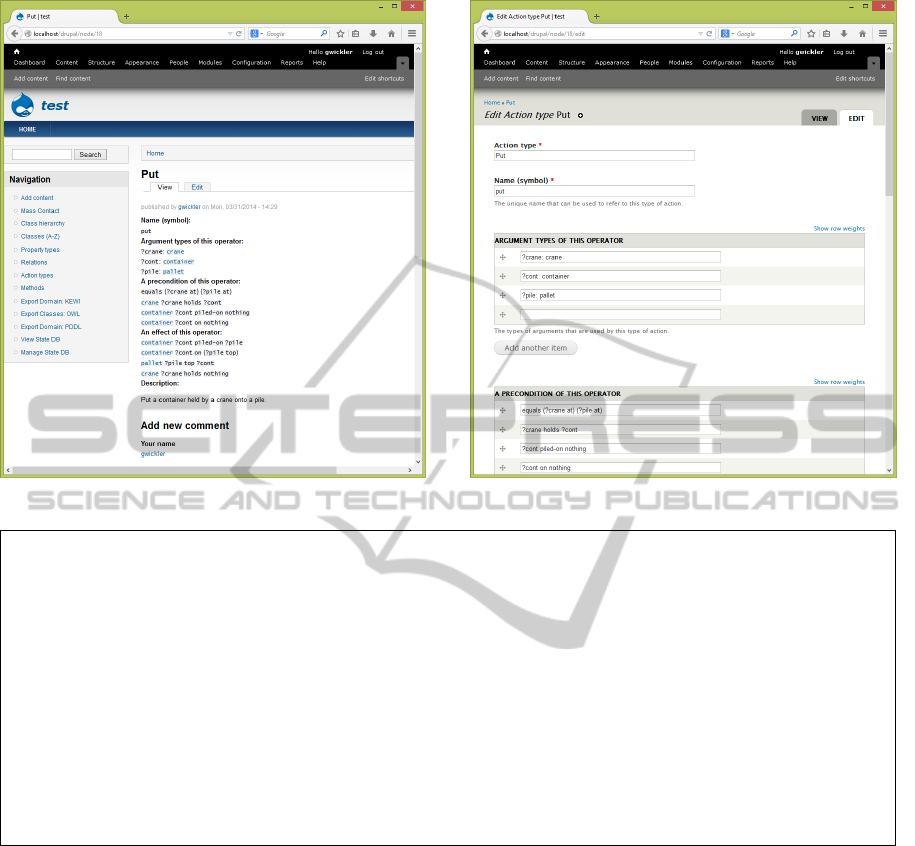
Figure 5: Different views of put in KEWI.
(:action-type put
(:arguments ( (?crane crane) (?cont container) (?pile pallet) ))
(:precondition (:and
(:relation equals ( (crane.at ?crane) (pallet.at ?pile) ))
(:constraint crane.holds ( ?crane ?cont ))
(:constraint container.piled-on ( ?cont nothing ))
(:constraint container.on ( ?cont nothing ))))
(:effect (:and
(:constraint container.piled-on ( ?cont ?pile ))
(:constraint container.on ( ?cont (pallet.top ?pile) ))
(:constraint pallet.top ( ?pile ?cont ))
(:constraint crane.holds ( ?crane nothing )))))
Figure 6: The KEWI version of put.
type explicit. None of the local variables need to be
represented in KEWI as the values they refer to can
be described with functional terms.
The first of the preconditions requires the location
of the crane and the location of the pile to be equal.
This corresponds to the first two preconditions in the
PDDL version, where the equality is implicit in the
use of the same variable. The main dynamic precondi-
tion, that the crane must hold the container, is present
in both representations. The remaining preconditions
are necessary to make the planner work in both cases,
to bind the local variable ?else or to declare the val-
ues of state-variables before execution. Normally this
is not necessary in KEWI, unless there is no previous
value (i.e. the value is nothing) which is the case
here. This could be avoided through the use of ax-
ioms, which can be declared in the KEWI ontology,
but are not currently used for reasoning. Such an ax-
iom would state that, if a container is held by a crane,
this container is not on another stackable object (con-
tainer or pallet) and that this container is not piled on
any pallet. Using axioms like this would avoid the last
two preconditions shown in the KEWI operator.
The effects of the KEWI version are fairly straight
forward. The first effect corresponds to the first ef-
fect of the original operator. The second effect cor-
responds to the third original effect, where the previ-
ously top-most container is referred to by a function
term, rather than a local variable. The third KEWI
effect corresponds directly to the second original ef-
KEWI-AKnowledgeEngineeringToolforModellingAIPlanningTasks
45

fect and the first negative effect. The use of a state-
variable makes this more concise in KEWI. The final
KEWI effect corresponds to the second negative orig-
inal effect and the final positive effect.
The final version of the put operator is the PDDL
version that is generated by KEWI. The full speci-
fication is not shown here as the additional param-
eters, preconditions and effects are just artefacts of
the translation process, and they are not very interest-
ing. For example, the equality precondition in KEWI
translates into two additional parameters and precon-
ditions, one for each function term. Then the equality
itself becomes another precondition on the two new
parameters. Clearly, there is optimisation potential,
but since this representation is not meant for human
consumption and planners should be well capable of
compiling out these redundancies, this is not some-
thing we are going to dwell on.
4.3 Planning with KEWI
More interesting is to see what a planner actually
makes of the PDDL generated by KEWI compared
to the original PDDL version. To this end, we have
taken two DWR problems
1
and adapted them to the
representation used in the generated KEWI. This has
to be done manually, which is why only two exam-
ples were used. The translation is fairly straightfor-
ward, requiring the change of all predicate names and
in one case swapping the order of the parameters. The
change from a single pallet to multiple pallets but
no piles was surprisingly trivial. The only real dif-
ference is the occupied predicate used in the origi-
nal problems. The KEWI-generated PDDL contains
a location-no-occupied-by predicate which is ef-
fectively the complement of the occupied predicate,
indicating when a location is free.
With these two problems translated (manually) it
was then possible to run a planner on them. We have
chosen the FF planning system, a robust state-space
search planner that supports all the features used in
the original as well as the generated version of the
problem. The result is shown in table 2.
The first problem is a very simple case with two
locations, one robot and six containers to be moved
to the other location. The second problem is com-
plex, involving eight locations and three robots that
need to shift more than 20 containers around the lo-
cations. The initial reachability analysis performed
by FF shows that the KEWI generated version has
more facts and actions, which means the additional
predicates give rise to some redundant information
1
See http://projects.laas.fr/planning/ for a full definition
of these problems.
that cannot be compiled away by the planner. Inter-
estingly enough, this redundant information leads to
a smaller number of states being explored for both
problems. However, processing the additional infor-
mation incurs an overhead that results in a larger over-
all search time. While this is not good news, it must
also be pointed out that the resulting plan is shorter at
least for the more complex problem. Thus, one could
argue the performance is roughly equivalent for the
original and the KEWI-generated versions.
4.4 Further Evaluation
This work is being carried out with an industrial part-
ner with significant experience in control and automa-
tion as well as simulation, and we are using a real ap-
plication of knowledge acquisition and engineering in
their area of expertise. The development of KEWI is
in fact work in progress, and its evaluation is ongo-
ing, and being done in several ways: (i) An expert
engineer from the industrial partner is using KEWI,
in parallel with the developers, to build up a knowl-
edge base of knowledge about artefacts, operations,
procedures etc. in their domain. (ii) We have created
a hand-crafted PDDL domain and problem descrip-
tions of part of the partner’s domain and for the same
problem area we have generated PDDL automatically
from a tool inside KEWI. We are in the process of
comparing the two methods and the PDDL produced.
An interface to a simulation system is being devel-
oped which will help in this aspect. (iii) We are work-
ing with another planning project in the same applica-
tion, which aims to produce natural language explana-
tions and argumentation supporting plans. In the fu-
ture we believe to combine KEWI with this work, in
order that (consistent with involving the user in model
creation) the user will be able to better validate the
planning operation.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper we have introduced KEWI, a knowledge
engineering tool for modelling planning tasks, and we
have given a formal account of parts of its structure
and tools. KEWI represents domain knowledge in an
object-centred way which is more compact and ex-
pressive than PDDL (which uses a literal-centred ap-
proach to representing domain knowledge).
As well as the usual advantages of an object-
centred approach, the use of a rich ontology with
numeric role constraints enables the use of function
terms as object references and explicit non-existence
conditions. This allows for a more concise and
KEOD2014-InternationalConferenceonKnowledgeEngineeringandOntologyDevelopment
46

Table 2: Running FF on different versions of two DWR problems.
reachable states initial plan total
facts actions searched distance length time
PDDL pb12 121 362 101 25 34 0.00
KEWI pb12 161 506 96 25 34 0.31
PDDL pb38 1453 15306 94265 104 277 2473.12
KEWI pb38 1889 21642 72565 104 235 3637.81
more natural style of representing planning knowl-
edge. Therefore, capturing and maintaining domain
knowledge in KEWI is easier, especially for users
who are not experts in automated planning.
Because most of the existing planning engines
support only PDDL, KEWI is able to export domain
knowledge into PDDL. We demonstrated that there
are no significant differences between hand-crafted
and automatically generated PDDL models. More-
over, KEWI has a user-friendly interface which is
simple enough to support domain experts in encod-
ing knowledge and it is designed to enable groups of
users to capture, store and maintain knowledge over a
period of time, thus facilitating knowledge reuse.
In future work, we plan to extend KEWI by (i) ex-
tending the representation to include numeric fluents,
time, and, eventually, continuous processes (ii) devel-
oping validation and verification methods which help
users to debug and adapt created planning domain and
problem descriptions (iii) adding automated acquisi-
tion tools which can add to KEWI’s knowledge by
inputting batch or real time data from process simula-
tions inspired by the real domain KEWI is being used
to model.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The research was funded by the UK EPSRC Au-
tonomous and Intelligent Systems Programme (grant
no. EP/J011991/1). The University of Edinburgh and
research sponsors are authorised to reproduce and dis-
tribute reprints and online copies for their purposes
notwithstanding any copyright annotation hereon.
REFERENCES
Ai-Chang, M., Bresina, J. L., Charest, L., Chase, A., jung
Hsu, J. C., J
´
onsson, A. K., Kanefsky, B., Morris,
P. H., Rajan, K., Yglesias, J., Chafin, B. G., Dias,
W. C., and Maldague, P. F. (2004). Mapgen: Mixed-
initiative planning and scheduling for the mars ex-
ploration rover mission. IEEE Intelligent Systems,
19(1):8–12.
Barreiro, J., Boyce, M., Do, M., Frank, J., Iatauro, M.,
Kichkaylo, T., Morris, P., Ong, J., Remolina, E., and
Smith, T. (2012). EUROPA: A platform for AI plan-
ning, scheduling, constraint programming, and opti-
mization. In 4th International Competition on Knowl-
edge Engineering for Planning and Scheduling (ICK-
EPS).
Currie, K. and Tate, A. (1991). O-Plan: The open planning
architeture. Artificial Intelligence, 52:49–86.
Ghallab, M., Nau, D., and Traverso, P. (2004). Automated
Planning. Morgan Kaufmann.
Jonsson, P. and B
¨
ackstr
¨
om, C. (1998). State-variable plan-
ning under structural restrictions: Algorithms and
complexity. Artificial Intelligence, 100:125–176.
Leshed, G., Haber, E. M., Matthews, T., and Lau, T. A.
(2008). Coscripter: automating & sharing how-to
knowledge in the enterprise. In CHI, pages 1719–
1728.
McCluskey, T. L. and Kitchin, D. E. (1998). A tool-
supported approach to engineering HTN planning
models. In In Proceedings of 10th IEEE International
Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence.
Plch, T., Chomut, M., Brom, C., and Bart
´
ak, R. (2012).
Inspect, edit and debug PDDL documents: Simply
and efficiently with PDDL studio. ICAPS12 System
Demonstration, page 4.
Schreiber, G., Akkermans, H., Anjewierden, A., de Hoog,
R., Shadbolt, N., de Velde, W. V., and Wielinga, B. J.
(1999). Knowledge Engineering and Management:
The CommonKADS Methodology. MIT Press, Cam-
bridge, Mass., 2nd ed. edition.
Simpson, R., Kitchin, D. E., and McCluskey, T. (2007).
Planning domain definition using gipo. Knowledge
Engineering Review, 22(2):117–134.
Smith, D. E., Frank, J., and Cushing, W. (2008). The anml
language. Proceedings of ICAPS-08.
Vaquero, T. S., Tonaco, R., Costa, G., Tonidandel, F., Silva,
J. R., and Beck, J. C. (2012). itSIMPLE4.0: Enhanc-
ing the modeling experience of planning problems.
In System Demonstration – Proceedings of the 22nd
International Conference on Automated Planning &
Scheduling (ICAPS-12).
Vodr
´
a
˘
zka, J. and Chrpa, L. (2010). Visual design of plan-
ning domains. In KEPS 2010: Workshop on Knowl-
edge Engineering for Planning and Scheduling.
Wickler, G., Tate, A., and Hansberger, J. (2013). Using
shared procedural knowledge for virtual collaboration
support in emergency response. IEEE Intelligent Sys-
tems, 28(4):9–17.
KEWI-AKnowledgeEngineeringToolforModellingAIPlanningTasks
47
