
Evaluation of Sensor Signal Health
Using Model with Uniform Noise
Lenka Pavelkov´a and Ladislav Jirsa
Department of Adaptive Systems, Institute of Information Theory and Automation, Czech Academy of Sciences
Pod Vod´arenskou vˇeˇz´ı 4, Prague, Czech Republic
Keywords:
Industrial System Health, Sensor Signal Condition, Binomial Opinion, Bayesian Estimation, Uniform Noise,
Probabilistic Logic.
Abstract:
The paper proposes a method for evaluating a condition of a noisy sensor signal. The presented algorithm
provides a binomial opinion on the sensor signal health including uncertainty by considering (i) user given
bounds and (ii) measurement uncertainty. The obtained results can be utilised directly for a single sensor or
in a hierarchical structure describing an industrial system of interest where sensors comprise one of the basic
building block. There, each block provides a binomial opinion about its health including uncertainty. These
opinions are combined using the rules of probabilistic logic so that a single opinion on the health of the whole
monitored system is obtained.
1 INTRODUCTION
With increasing demands for safety and efficiency of
complex processes, fault detection and isolation (FDI)
becomes an important part of control systems in engi-
neering applications (Hwang et al., 2010). FDI con-
sists in binary opinion whether the system is in faulty
state and indication of location and nature of the fault.
Within an industrial plant, many possible fault
sources exist, e.g., sensors, actuators, hardware com-
ponents. These heterogeneous fault sources in-
evitably place considerable demands on related FDI.
The situation is yet more complicated due to different
possible time developments of faults as an abrupt, a
gradual or an intermittent fault. Therefore, monitor-
ing and processing of the system as a whole results
generally in a solution tailored for a particular sys-
tem, combining different probability distributions of
particular quantities of interest, either discrete of con-
tinuous, and having a high dimensionality. For appli-
cation examples, see (Isermann, 2011).
A novel dynamic hierarchical structure based on
probabilistic approach to fault detection is proposed
in (Jirsa et al., 2013; Dedecius and Ettler, 2014). In
the presented approach, the system of interest is de-
composed into blocks, representing individual phys-
ical or logical system units. For each particular
block, an opinion on its condition (health) is assessed.
Subsequently, these individual information pieces are
fused together in order to evaluate the health of the
overall system.
The paper aims at the evaluation an opinion on the
health of an above mentioned basic block. Here, the
block in question corresponds to a sensor measuring
an uncertain signal and user given signal bounds are
considered.
The paper is organised as follows. Section 2
briefly introduces the above mentioned hierarchical
structure for industrial system condition monitoring.
In Section 3, a sensor signal health using user given
requirements on this signal is defined and an binomial
opinion on this health is constructed. Afterwards, an
algorithm providing an opinion on the health of noisy
signal is proposed.
Section 4 gives an example of the health evalua-
tion of a simulated sensor signal for various types of
malfunctions.
Throughout, the transposition is marked
′
.
z
∗
denotes a set of z-values.
z
t
is the value of z at discrete-time instant
t ∈ t
∗
= {1, 2, . . . , T}, T < ∞.
The symbol f denotes probability (density) func-
tion (p(d)f) distinguished by the argument names. No
formal distinction is made among a random variable,
its realisation and a p(d)f argument.
671
Pavelkova L. and Jirsa L..
Evaluation of Sensor Signal Health Using Model with Uniform Noise.
DOI: 10.5220/0005044506710677
In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics (ICINCO-2014), pages 671-677
ISBN: 978-989-758-039-0
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

2 HIERARCHICAL CONDITION
MONITORING
A probabilistic FDI system proposed in (Jirsa et al.,
2013; Dedecius and Ettler, 2014) enables to evaluate
dynamically the industrial system health at any level
of its functional hierarchy. The investigated industrial
system is decomposed into a set of interconnected in-
dividual blocks. Each block represents an individual
physical or logical system unit (e.g. sensor, actuator,
communication line etc.).
To each particular block, an observer is assigned
that provides a below defined binomial opinion (1) on
the health of the respective block, and related uncer-
tainty.
The basic blocks are interconnected using prin-
ciples of the probabilistic logic which combines the
capability of probability theory to handle uncertainty
with the capability of deductive logic to exploit struc-
ture. In this way, a single opinion on the health of the
whole monitored system is obtained. There, a spe-
cial type of probabilistic logic called subjective logic
(SL) is utilised which allows probability values to be
expressed with degrees of uncertainty (Jøsang, 2001;
Jøsang, 2010).
In SL, the representation of uncertain probabili-
ties is based on a belief model. A subjective binomial
opinion expresses a subjective belief of a particular
subject about the truth of proposition including a de-
gree of uncertainty. For x ∈ {0, 1}, a binomial opin-
ion about the truth of proposition x = 1 is the ordered
quadruplet
ω
x
= (b, d, u, a) (1)
where
b is the belief of x being true, i.e. b = f(x = 1)
d is the belief of x being false, i.e. d = f(x = 0)
u is uncertainty, i.e., the observer is not able to decide,
a is base rate (corresponds to a prior information).
These components satisfy additivity b+ d + u = 1 and
it holds b, d, u, a ∈ [0, 1].
The expected value of b is
E
x
= b+ au . (2)
Here, we consider non-informativeprior, i.e. a = 0.5.
Note that SL provides a set of operators where
input and output arguments are in the form of bino-
mial opinions. Most of the operators correspond to
well-known operators from binary logic and proba-
bility calculus. Additional operators exist for mod-
elling special situations, such as when fusing opinions
of multiple observers.
3 SENSOR SIGNAL HEALTH
3.1 Health Definition
We focus on a basic block of the above mentioned
hierarchicaldiagnostic system that representsa sensor
signal y
t
. This signal is measured at the discrete time
instants t ∈ t
∗
= {1, . . . , T}.
A health of y
t
corresponds to how y
t
meets the
below defined bounds and it is described by the two-
valued variable H
y
H
y
∈ {0, 1} (3)
where H
y
= 1 means that y
t
is healthy and H
y
= 0 is
the opposite.
Here, we consider two-level user defined bounds
given by intervals [P
L
, P
U
], [S
L
, S
U
] where
P
L
< S
L
< S
U
< P
U
. (4)
P
L
and P
U
correspond to lower and upper physical or
safety bounds of y
t
, respectively; y
t
has to never oc-
cur outside these bounds. S
L
and S
U
are lower and up-
per soft bounds, respectively; they determine required
range where y
t
is expected to occur under usual work-
ing conditions.
Utilising the user given bounds (4), we define that
H
y
= 1 for y
t
∈ [S
L
, S
U
] (5)
H
y
= 0 for y
t
6∈ [P
L
, P
U
]
For y
t
∈ (P
L
, S
L
) ∪ (S
U
, P
U
), we are not able to decide
unequivocally about the value of H in this case.
3.2 Binomial Opinion on Health of
Deterministic Signal
Within the above described hierarchical system, an
opinion on health in the form (1) has to be assigned to
each particular basic block. For a block representing
sensor signal with user given bounds (4) and health
assignment rules (5), the values of belief b
D
and dis-
belief d
D
in (1) are unequivocal for y
t
∈ (− ∞, P
L
] ∪
[S
L
, S
U
]∪[P
U
, ∞). For y
t
∈ (P
L
, S
L
)∪(S
U
, P
U
), we has
to assign it reasonably. Here, we use the linear de-
pendence of b
D
and d
D
on the y
t
value. The lower
index D emphasizes that the value of y
t
is considered
to be deterministic. The shapes of b
D
, d
D
and u
D
are
depicted in Figure 1 and described in Table 1.
According to (1), it holds
b
D
= f(H
y
= 1) (6)
d
D
= f(H
y
= 0)
u
D
= 1− b
D
− d
D
ICINCO2014-11thInternationalConferenceonInformaticsinControl,AutomationandRobotics
672
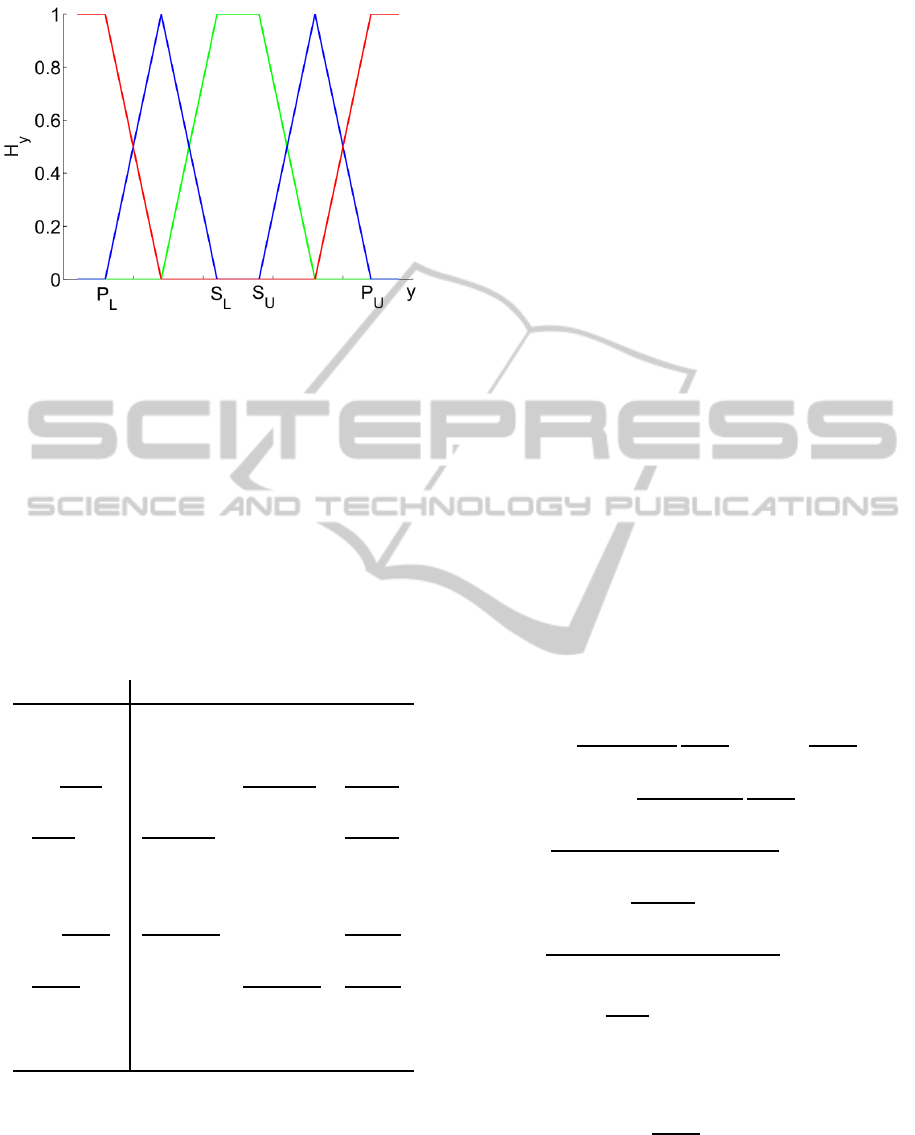
Figure 1: The course of b
D
(green), d
D
(red), u
D
(blue) (6)
for single y
t
with highlighted bounds (4).
Note that there are various ways to assign b
D
, d
D
,
u
D
in the intervals (P
L
, S
L
) and (S
U
, P
U
) depending on
user knowledge and requirements.
In reality, y
t
is not deterministic but it is often
described by a probabilistic model. Further, an
algorithm is proposed that assigns b, d, u (1) to
a probabilistic description of y
t
using the above
described courses of b
D
, d
D
, u
D
.
Table 1: Assignment of b
D
, d
D
, u
D
for deterministic signal
y
t
with user given bounds (4).
y
t
∈
b
D
= d
D
= u
D
=
(−∞, P
L
i 0 1 0
(P
L
,
P
L
+S
L
2
i
0
P
L
+S
L
−2y
t
S
L
−P
L
2y
t
−2P
L
S
L
−P
L
(
P
L
+S
L
2
, S
L
i
2y
t
−P
L
−S
L
S
L
−P
L
0
2S
L
−2y
t
S
L
−P
L
(S
L
, S
U
) 1 0 0
hS
U
,
S
U
+P
U
2
)
S
U
+P
U
−2y
t
P
U
−S
U
0
2y
t
−2S
U
P
U
−S
U
h
S
U
+P
U
2
, P
U
)
0
2y
t
−S
U
−P
U
P
U
−S
U
2P
U
−2y
t
P
U
−S
U
hP
U
, ∞) 0 1 0
3.3 Uniform Model of y
t
Considering the given hard bounds on y
t
, we use a
probabilistic model with uniformly distributed noise
for y
t
description. This model is described in detail in
(Pavelkov´a and K´arn´y, 2013).
Here, a simple version of this model, a static
model, is used for the description of a time evolution
of y
y
t
= K + e
t
(7)
where K is an unknown constant and e
t
is an uni-
form white noise e
t
, i.e. f(e
t
) = U(−r, r), r > 0. The
equivalent description y
t
by pdf is
f(y
t
) = U(K − r, K + r) = U(L,U), (8)
where L = K − r, U = K + r. To estimate parameters
K and r, Bayesian maximum a posteriori (MAP) esti-
mation of K and r on sliding window ∆ is performed.
The MAP estimation converts to a problem of linear
programming.
Note that for the purpose of signal health monitor-
ing, the static model is fully acceptable. Here, ∆ plays
the role of a forgetting. Thus, possible changes of K
from required value can be detected.
3.4 Binomial Opinion on H for
Uniformly Distributed y
t
To evaluate ω
H
for uniformly distributed y
t
, f(y
t
) =
U(L,U), and respecting the given bounds, the follow-
ing technique is used. The b, d and u in (1) are ob-
tained computing expected values of b
D
, d
D
and u
D
(given by rules in Table 1) on the interval (L,U), re-
spectively.
belief
b = E (b
D
)
U
L
=
Z
U
L
b
D
f(y
t
)dy (9)
=
Z
b
1
a
1
2y− P
L
− S
L
S
L
− P
L
1
U − L
dy+
Z
b
2
a
2
1
U − L
dy
+
Z
b
3
a
3
S
U
+ P
U
− 2y
P
U
− S
U
1
U − L
dy
=
(b
1
− a
1
)(b
1
+ a
1
− P
L
− S
L
)
(U − L)(S
L
− P
L
)
χ(b
1
> a
1
)
+
b
2
− a
2
(U − L)
χ(b
2
> a
2
)
+
(b
3
− a
3
)(S
U
+ P
U
− b
3
− a
3
)
(U − L)(P
U
− S
U
)
χ(b
3
> a
3
)
where
a
1
= max(L,
P
L
+S
L
2
)
b
1
= max(a
1
, min(S
L
,U))
a
2
= max(L, S
L
)
b
2
= max(a
2
, min(S
U
,U))
a
3
= max(L, S
U
)
b
3
= max(a
3
, min(
S
U
+P
U
2
,U))
χ(.) is an indicator function
Note that max(.) in b
i
boundaries guarantee zero
integral value (i.e. identical lower and upper
bounds) as long as this part is not included in
(L,U)
EvaluationofSensorSignalHealthUsingModelwithUniformNoise
673

disbelief
d = E (d
D
)
U
L
=
Z
U
L
d
D
f(y)dy (10)
=
Z
d
1
c
1
1
U − L
dy+
Z
d
2
c
2
P
L
+ S
L
− 2y
S
L
− P
L
1
U − L
dy
+
Z
d
3
c
3
2y− S
U
− P
U
P
U
− S
U
1
U − L
dy+
Z
d
4
c
4
1
U − L
dy
=
d
1
− c
1
(U − L)
χ(d
1
> c
1
)
+
(d
2
− c
2
)(P
L
+ S
L
− d
2
− c
2
)
(U − L)(S
L
− P
L
)
χ(d
2
> c
2
)
+
(d
3
− c
3
)(d
3
+ c
3
− S
U
− P
U
)
(U − L)(P
U
− S
U
)
χ(d
3
> c
3
)
+
d
4
− c
4
(U − L)
χ(d
4
> c
4
)
where
c
1
= L
d
1
= max(c
1
, min(P
L
,U))
c
2
= max(L, P
L
)
d
2
= max(c
2
, min(
P
L
+S
L
2
,U))
c
3
= max(L,
S
U
+P
U
2
)
d
3
= max(c
3
, min(P
U
,U))
c
4
= max(L, P
U
)
d
4
= max(c
4
,U)
uncertainty
u = E (u
D
)
U
L
=
Z
U
L
u
D
f(y)dy (11)
=
2
U − L
Z
f
1
e
1
y− P
L
S
L
− P
L
dy+
2
U − L
Z
f
2
e
2
S
L
− y
S
L
− P
L
dy
+
2
U − L
Z
f
3
e
3
y− S
U
P
U
− S
U
dy+
2
U − L
Z
f
4
e
4
P
U
− y
P
U
− S
U
dy
=
( f
1
− e
1
)( f
1
+ e
1
− 2 P
L
)
(U − L)(S
L
− P
L
)
χ( f
1
> e
1
)
+
( f
2
− e
2
)(2 S
L
− f
2
− e
2
)
(U − L)(S
L
− P
L
)
χ( f
2
> e
2
)
+
( f
3
− e
3
)( f
3
+ e
3
− 2 S
U
)
(U − L)(P
U
− S
U
)
χ( f
3
> e
3
)
+
( f
4
− e
4
)(2 P
U
− f
4
− e
4
)
(U − L)(P
U
− S
U
)
χ( f
4
> e
4
)
where
e
1
= max(L, P
L
)
f
1
= max(e
1
, min(
P
L
+S
L
2
,U))
e
2
= max(L,
P
L
+S
L
2
)
f
2
= max(e
2
, min(S
L
,U))
e
3
= max(L, S
U
)
f
3
= max(e
3
, min(
S
U
+P
U
2
,U))
e
4
= max(L,
S
U
+P
U
2
)
f
4
= max(e
4
, min(P
U
,U))
3.5 Algorithm
Here, an algorithm is summarised how to obtain an
opinion on the health of noisy signal under user given
bounds P
L
, S
L
, S
U
, P
U
Initialisation:
- set bounds (4)
- construct the b
D
, d
D
, u
D
according to Table 1
- set ∆, i.e. length of window for f(y) estimation
- set t = 0
On-line phase:
1. set t = t + 1
2. update measurements – add y
t
3. IF t > ∆, THEN remove y
t−∆−1
4. estimate L, U in (8)
5. consider parts of b
D
, d
D
, u
D
bounded by L, U
6. compute b, d and u according to (9), (10) and
(11), respectively
7. IF t < T, GO TO 1.
4 EXPERIMENTS
A series of experiments is performed to illustrate the
proposed approach. We use a simulated data. Bounds
(4) are given as follows. S
L
= 2.5, S
U
= 3.5, P
L
= 0,
P
U
= 6.
4.1 Slowly Varying Parameters
The sensor signal is simulated by the model (8) with
K varying from 3 up to 8.5, r = 0.75. The parameter
estimation is performed on the window ∆ = 25. Data
course including bounds and b, d, u assignment are
depicted in Figure 2.
4.2 Abrupt Fault
The sensor signal is simulated by the model (8) with
K changing abruptly from the value 3 up to value 6
at the time instant t = 100, r = 0.75, see the left part
of Figure 3. The parameter estimation is performed
on the window ∆ = 25. After the first fault datum
arrives, the value of b rapidly decreases but it does
not fall down completely because of the past correct
data considered within constant memorylength ∆. An
alternative is to set ∆ = 1 after b decrease. Then, ∆
is successively increased by 1 at each step up to the
original level. Figure 4 depicts both cases.
ICINCO2014-11thInternationalConferenceonInformaticsinControl,AutomationandRobotics
674

0 200 400 600 800 1000
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
time
data, bounds
0 200 400 600 800 1000
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
time
b,d,u
Figure 2: Simulation of slowly varying parameters. On the left side are depicted simulated data (blue), soft bounds (green)
and upper physical bound (red). On the right side is ω
H
assignment with b in green, d in red, u in blue.
80 100 120 140 160
2
3
4
5
6
7
time
data, bounds
80 100 120 140 160
2
4
6
8
time
data, bounds
Figure 3: Simulated data (blue) including soft bounds (green) and physical bounds (red) – abrupt fault (on the left side) and
outlier (on the right side)
80 100 120 140 160
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
time
b,d,u
80 100 120 140 160
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
time
b,d,u
Figure 4: Simulation of abrupt fault. On the left side is ω
H
assignment for constant ∆ = 25 with b in green, d in red, u in blue.
On the right side is ω
H
assignment for varying ∆ with b in green, d in red, u in blue.
4.3 One-shot Outlier
The sensor signal is simulated by the model (8) with
K = 3, r = 0.75, see the right part of Figure 3. An
outlier y
100
= 7 is simulated at the time instant t =
100. The parameter estimation is performed on the
window ∆ = 25. Similarly to previous example, an
outlier causes a rapid decrease of b. The utilisation of
EvaluationofSensorSignalHealthUsingModelwithUniformNoise
675
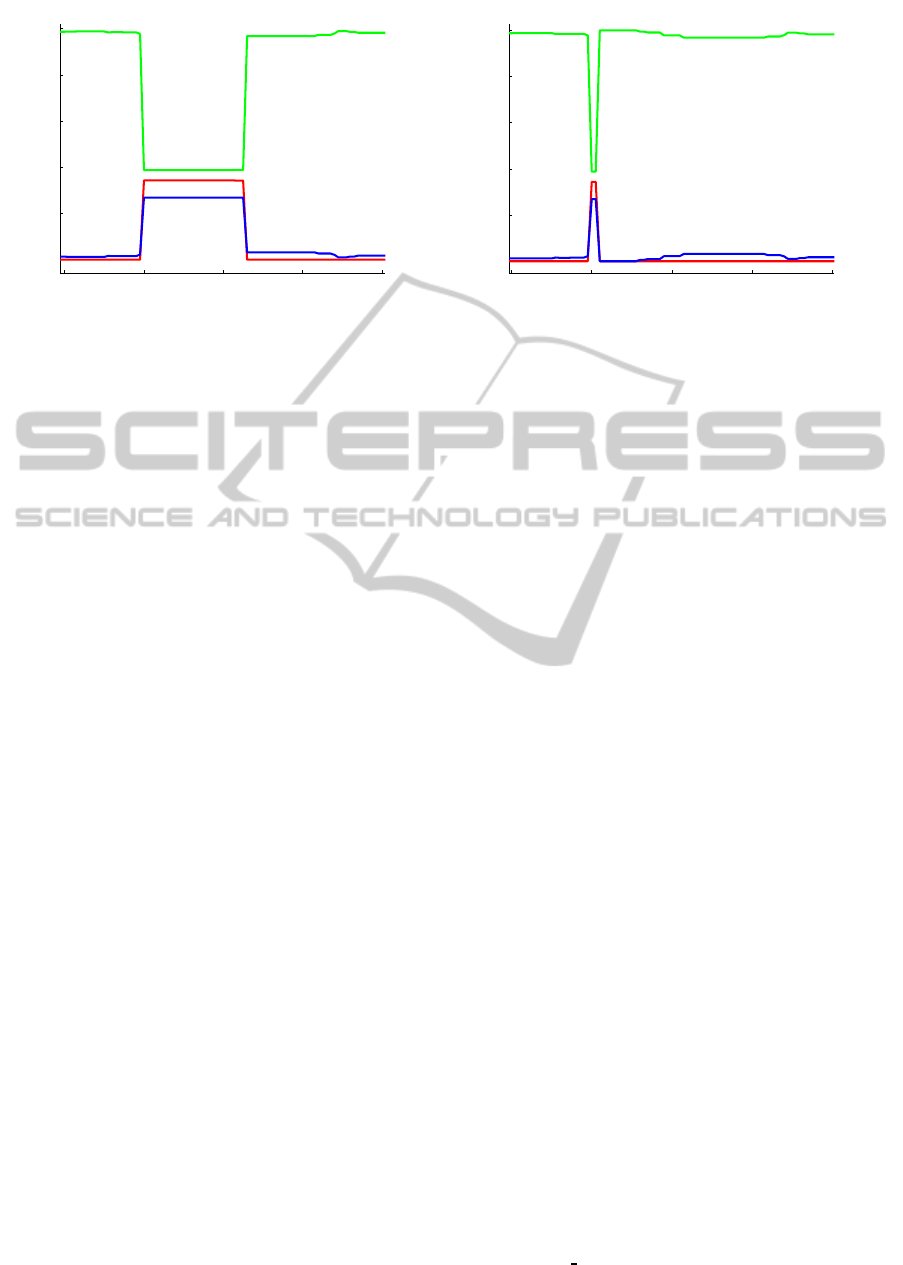
80 100 120 140 160
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
time
b,d,u
80 100 120 140 160
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
time
b,d,u
Figure 5: Simulation of an outlier. On the left side is ω
H
assignment for constant ∆ = 25 with b in green, d in red, u in blue.
On the right side is ω
H
assignment for varying ∆ with b in green, d in red, u in blue.
varying window (described in the previous example)
forwards the return to the regular state. The results
are depicted in Figure 5.
4.4 Discussion
Three frequent types of sensor signal fault were sim-
ulated. The sliding window ∆ enables to track slow
parameter changes. A higher ∆ causes the smoother
courses of b, d, u but in the case of sudden decrease
of b, the estimation algorithm cannot distinguish im-
mediately between the abrupt fault and mere outlier,
see left parts of Figures 4 and 5. Here, the setting of
∆ = 1 and its successive increasing up to the original
value improves the algorithm performance.
5 CONCLUDING REMARKS
The algorithm for assignment of a binomial opinion
on the uncertain sensor signal was developed consid-
ering user given bounds. The proposed method seems
to be effective. It enables to detect both main sensor
signal faults – abrupt and gradual.
A uniform description of involved signal leads to
simple and straightforward solution. The resulting al-
gorithm with static signal model requires only the sig-
nal bounds to be defined and a memory length to be
set. For the purpose of a sensor signal health moni-
toring, the static model is fully acceptable. Possible
changes from the required value are detected thanks
to the moving window ∆ used during the parameter
estimation.
Alternative evaluation of uncertainty using model
with Gaussian noise is proposed in (Ettler and Dede-
cius, 2014).
Further research will focus on model with alterna-
tive noise description, e.g. a trapezoidal one, that will
describe the sensor signal more precisely.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The research project is supported by the grant M
ˇ
SMT
7D12004 (E!7262 ProDisMon).
REFERENCES
Dedecius, K. and Ettler, P. (2014). Hierarchical modelling
of industrial system reliability withprobabilistic logic.
Accepted for the 11th International Conference on
Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics -
ICINCO 2014.
Ettler, P. and Dedecius, K. (2014). Quantification of infor-
mation uncertainty for the purpose of condition moni-
toring. Accepted for the 11th International Conference
on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics -
ICINCO 2014.
Hwang, I., Kim, S., Kim, Y., and Seah, C. E. (2010). A
survey of fault detection, isolation, and reconfigura-
tion methods. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems
Technology, 18(3).
Isermann, R. (2011). Fault Diagnosis Applications: Model
Based Condition Monitoring, Actuators, Drives, Ma-
chinery, Plants, Sensors, and Fault-tolerant Systems.
Springer Verlag.
Jirsa, L., Pavelkov´a, L., and Dedecius, K. (2013). Pre-
liminaries of probabilistic hierarchical fault detection.
In Preprints of the 3rd International Workshop on
Scalable Decision Making held in conjunction with
ECML/PKDD 2013, pages 1–14, Prague, Czech re-
public.
Jøsang, A. (2001). A logic for uncertain probabilities.
International Journal of Uncertainty, Fuzziness and
Knowledge-Based Systems, 9(03):279–311.
Jøsang, A. (2010). Subjective logic. Draft book
Available at: http://persons.unik.no/josang/papers/
subjective
logic.pdf.
ICINCO2014-11thInternationalConferenceonInformaticsinControl,AutomationandRobotics
676

Pavelkov´a, L. and K´arn´y, M. (2013). State and parameter
estimation of state-space model with entry-wise corre-
lated uniform noise. Int. Journal of Adaptive Control
and Signal Processing. DOI: 10.1002/acs.2438.
EvaluationofSensorSignalHealthUsingModelwithUniformNoise
677
