
Differential Evolution Algorithm Based Spatial
Multi-sensor Image Fusion
Veysel Aslantas and Emre Bendes
Erciyes University, Computer Engineering Faculty, 38039, Melikgazi, Kayseri, Turkey
Keywords: Multi-sensor Image Fusion, Image Quality Metrics, Differential Evolution Algorithm.
Abstract: In this paper, a new optimised region based multi-sensor image fusion method is presented. The proposed
method works on spatial domain. Differential evolution algorithm is used to optimize the contribution of the
input images to fused images based on regions. The method was compared visually and quantitatively with
Laplacian Pyramid (LP) and Shift-invariance Discrete Wavelet Transform (SiDWT) methods. Experimental
results show that the developed method outperforms other traditional methods and can effectively improve
the quality of the fused image.
1 INTRODUCTION
Because of a wide variety of imaging sensor type,
image fusion has become an important topic in
information fusion area (Aslantas and Kurban, 2009,
Zhong and Blum, 1999, Aslantas et al., 2013). For a
particular scene, images taken from different type of
sensors contain different information. While thermal
images present emitted thermal radiation of scene,
visible images contain information that is more
desirable for human visual perception. All sensors
have their own advantages and in many cases
complete representation of a scene cannot be
obtained with a single sensor. More meaningful
representation of a scene can be obtained by
transforming complementary information of
different sensors to a single image. This can be
achieved by image fusion. It is a subtopic of
information fusion and produces an image that
contains complementary information come from
images acquired by different sensors or the same
sensor with different parameters. Thus, improvement
of human visual perception is intended.
Image fusion is needed and used frequently for
different kind of areas such as medical imaging (Qu
et al., 2001), enhanced night vision (Toet et al.,
1997), concealed weapon detection (Xue et al.,
2002), extending depth of field (Aslantas and
Kurban, 2010). Accordingly, many image fusion
techniques have been developed in recent years.
They can be classified as spatial domain and
transform domain methods (Li et al., 2011). In the
former, local derivation or gradient information is
used. On the other hand, the latter are employed on
transform coefficients. Determination of valuable
information contained each image has a critical role
on the image fusion. Human visual perception is
sensitive to intensity changing like lines, edges or
texture. Multiscale transforms can efficiently
emphasize this kind of information therefore various
multiscale transforms are frequently used in image
fusion (Hu and Li, Miao et al., 2011, Lewis et al.,
2007). However, time consuming translation
operations increase computational load of these
methods. Moreover, affection of operations over the
fused image cannot be clearly predictable since the
coefficients are chanced in the transform domain and
the original pixel values of input images are not
preserved in the resulting fused image (Huang and
Jing, 2007). Contrary to transform based methods,
operations are conducted directly on the pixel values
without any transformation in the spatial domain
methods. Therefore original pixel values are
transferred to the fused image.
In most of the image fusion methods, maximum
or average of transform coefficients is utilized.
These are not sufficient in many situations, because
these types of fusion procedures are not adaptive to
information changing in the scene. Hence the
contribution of each input image to the fused image
should be varied with respect to the information
composed in them. Determining the best fused
image is an optimization problem.
718
Aslantas V. and Bendes E..
Differential Evolution Algorithm Based Spatial Multi-sensor Image Fusion.
DOI: 10.5220/0005056407180725
In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics (ICINCO-2014), pages 718-725
ISBN: 978-989-758-039-0
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

In literature, there are some image fusion
methods that employed optimization algorithms
(Mumtaz and Majid, 2008, Niu and Shen, 2006,
Raghavendra et al., 2011). In those studies, DWT is
used. However, adaptive rules have been defined for
the approximation band of DWT and choosing
maximum coefficient rule was used for the other
bands. The optimization process carried out in
approximation band for determining the optimum
contribution of each coefficient of this band, makes
the problem more complex for an optimization
algorithm. In this study, witout using any transform
method, adaptive fusion rules are determined in
spatial domain based on groups of pixels i.e.,
regions. Thus, all information on an image are taken
into account.
Rest of the paper is organized as follows. In
Section 2.1, the optimization algorithm employed
and its implementation over image fusion is
described. In Section 2.2 and Section 2.3, the
proposed method and the quality metrics are
described respectively. in Section 3, the
experimental results are presented quantitatively and
visually. Finally Section 4 concludes the paper.
2 OPTIMIZATION
BASED IMAGE FUSION
2.1 The Differential Evolution
Algorithm (DE)
The proposed method makes use of the DE
algorithm to construct a fused image in which the
regions of source images are emphasised optimally.
The DE is a well-known population based, heuristic
and evolutionary optimisation algorithm that was
proposed by Price and Storn in 1995 (Price and
Storn, March 1995). The main steps of DE are:
1. Set the initial control parameters of the DE,
2. Create initial population,
3. Mutation and crossover,
4. Selection,
5. Repeat step 3-4 until stopping conditions are
satisfied.
Before the optimization processes, some control
parameters of DE have to be determined initially
like generation size (G), population size (P), scaling
factor (F) and crossover constant (CR).
The DE starts with a population of randomly
produced P solution vectors (x) that contain
weighting factors for the segmented regions.
Mutation and crossover operators are used for
creating a new population. The former is employed
to expand the search space. At generation g
(g = 1,2,…, G), the i
th
mutant vector (v
i,g
) is
generated for each target vector by the combination
of vectors randomly chosen from the current
population as follow:
)(
,2,1,3, grgrgrgi
xxFxv
(1)
where r1, r2, and r3 are different random integer
indices selected from {1, 2, ..., P}. In order to
increase the diversity of the population, the DE
utilizes crossover operation that integrates successful
solutions from the previous generation. The
elements of the mutated vector and the elements of
the target vector are used to produce a trial vector as
follow:
randij
randij
gij
gij
gij
IjorCRrandif
IjorCRrandif
x
v
u
,
,
,,
,,
,,
(2)
where j = 1,2, ..., D; rand
j,i
ϵ [0; 1] is the random
number; CR ϵ [0; 1] is predefined crossover constant
and I
rand
ϵ [1, 2, ..., D] is a randomly chosen index.
I
rand
ensures that v
i,g+1
≠ x
i,g
Then the ‘greedy’
selection scheme is employed to decide whether or
not to include the trial vector in the population of the
next generation g + 1. If the value returned by the
objective function for the trial vector is better than or
equal to the value obtained for the target vector the
latter is replaced by the former otherwise it is
retained in the population of the next generation
Pi
otherwisex
xfufu
x
gi
gigigi
gi
,,1
)()(
,
,,,
1,
(3)
2. 2 Proposed Image Fusion Method
In this paper, a new optimization based, multi-sensor
image fusion method is proposed for mainly thermal
and optical images. These types of sensors have
been especially used in image fusion applications
like enhanced night vision and concealed weapon
detection.
Proposed method works on spatial domain and
does not include any transformation. As a
consequence, computational load of the method is
reduced according to transform based methods.
The general structure of proposed method is
given in Figure 1. The method utilises regions rather
than pixels to fuse information. Therefore, in the
first stage, region map (X
E
) computes. X
E
contains
region labels that indicate related pixels belong to a
DifferentialEvolutionAlgorithmBasedSpatialMulti-sensorImageFusion
719

Figure 1: The general structure of the proposed method.
region. Region map can be produced by employing
one of the input images (thermal or visible). Optical
cameras provide a similar vision with human eye.
However, thermal cameras provide a vision related
with the temperature which the human eye cannot
see. The main purpose of fusing thermal and visible
images is to support the visible information with the
complementary thermal information (Kun et al.,
2009). Similar objects in an environment almost
emit similar thermal radiations. The regions
corresponding to these objects are nearly viewed
homogeneously with respect to their intensity
values. To emphasize complementary information, it
is a good idea to segment the thermal image.
Accordingly, the thermal image is utilized for
producing X
E
. K-Means has been used as
segmentation algorithm in this study.
An adaptive fusion rule can be defined as in (1).
As can be seen in Figure 1, the fusion rule uses input
images (X
1
and X
2
) and region map (X
E
). For all
regions, a fusion rule is suggested by determining w
coefficients. For i
th
region w
i
coefficient has a value
between [0-1] and determines the rate of the
information transferred from the input image to
fused one. Optimization algorithm has been used to
obtain the best contribution of input images to the
fused image in the proposed method.
(i)X)
i
w((i)X
i
w(i)
B
X
2
1
1
(4)
The fused image must be evaluated by a quality
metric to attain a fitness value.
2.3 The Quality Metrics
2.3.1 Sum of the Correlation of Differences
(SCD)
Amount of information that transferred from source
images is an important measure for image fusion.
The difference between the fused image (X
F
) and
one of the source input image (X
2
) almost reveals the
information contained one in the other source image
(X
1
) and vice versa (Aslantas et al., 2013). These can
be formulated as:
(5)
The value obtained by correlating X
F1
with X
1
(or
X
F2
with X
2
) is a similarity measure between these
images. Sum of these values indicate the amount of
information shifted to the fused image from the
source images. The larger the SCD value, the better
the quality of the fused image. SCD metric
expressed as:
(6)
2.3.2 Quality of Edge (QE)
QE is one of the image quality metric that takes
input images and fusion image. Edge information is
very important to human perception. QE is a
measure of quality based on edge information
transferred from input images to fused image
(Xydeas and Petrovid, 2000). QE is calculated as:
12
21
XXX
XXX
FF
FF
),(),(
2211
XXcorrXXcorrSCD
FF
ICINCO2014-11thInternationalConferenceonInformaticsinControl,AutomationandRobotics
720

n
i
m
j
ba
n
i
m
j
bbaa
jiwjiw
jiwjikjiwjik
QE
11
11
),(),(
),(),(),(),(
(7)
where w
a
and w
b
are weighting coefficients based
on sobel edge strength of the input images, k
a
ve k
b
edge preservation coefficients.
2.3.3 Standard Deviation (SS)
Human perception is sensitive to intensity changes
and in an image, higher intensity changes cause
bigger standard deviation. SD metric is based on this
idea and calculated by using gray level values as:
n
i
m
j
)f(f(i,j)
mn
SD
11
2
1
(8)
n
i
m
j
f(i,j)
mn
f
11
1
(9)
2.3.4 Fusion Factor (FF)
Mutual information (MI) calculates shared
information by two images. MI calculated as:
ji
FR
RF
RFRF
jPiP
jiP
jiPMI
,
)()(
),(
log),(
(10)
where P
RF
is the normalized joint gray level
histogram of images R and F, P
R
and P
F
are the
normalized marginal histograms of the two images.
Fusion Factor (FF) is metric uses mutual
information. FF takes input images and fusion image
to calculate MI between input images and fusion
image. Therefore, FF can be defined as a metric that
calculate how much information transferred to fused
image from all input images. FF can be defined as:
BFAF
MIMIFF
(11)
3 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
The proposed fusion method is a region based
method. Therefore, number of region (NR) has to be
determined beforehand. In addition to this, the
parameters of the optimization algorithm described
in section 2.1, have to be set. In this paper, DE
parameters are selected as CR=0.3, F=0.3 and P=40.
SCD metric was employed during the optimization
process.
Figure 2: Images used in experiments.
In total, eight test image groups used in the
experiments are given in Figure 2 (Group, 2012,
Lewis et al., 2005). An image set consists of an
visible (v) and a thermal (t) image of the same scene.
According to application area, the image sets can be
categorized into two groups: enhanced night vision
images or concealed weapon detection. Numbers are
used for naming the source images. Numbers in the
range of [1 - 4] and [5 - 8] are signed for the night
vision images and for the concealed weapon images,
respectively. 1
st
Experimental results are shown in two groups
according to application area of input images. In
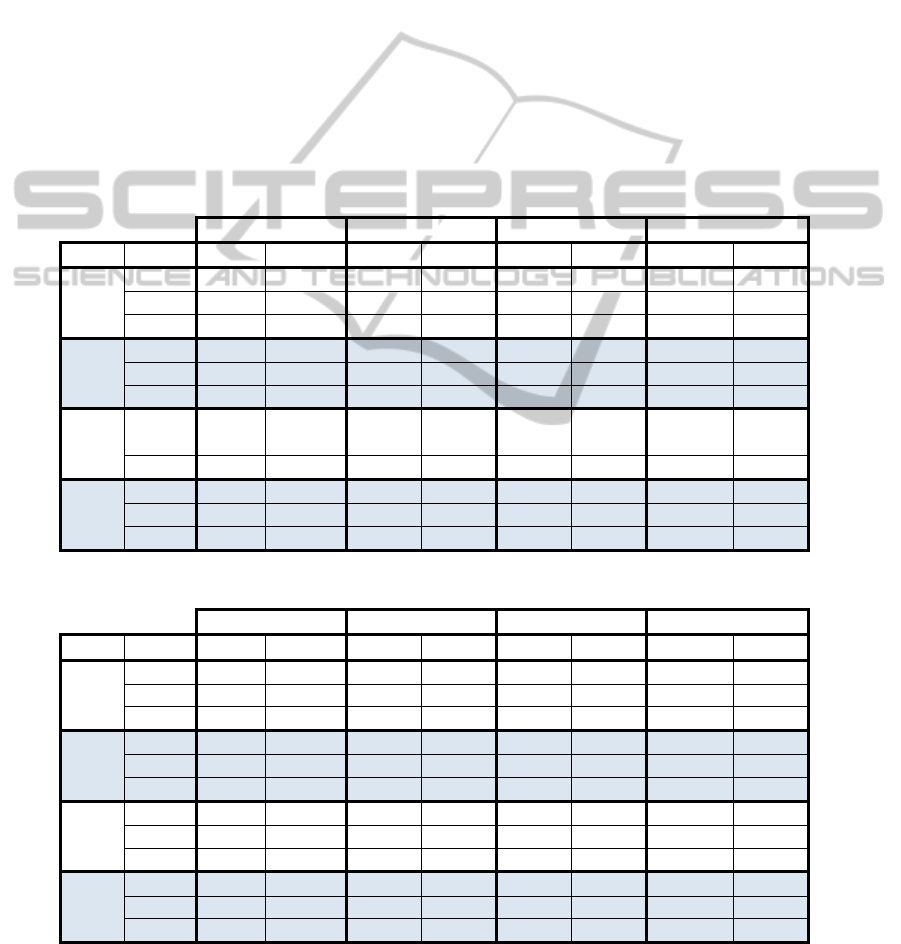
Table 1 and Table 2 quantitative results are
illustrated as mean value and standard deviation of
30 parallel optimization runs in terms of all used
quality metrics and NR. In the tables, images are
represented in the first column (I). For an image, NR
values are given in column wise and metric values
given along the rows. The higher metric values are
indicated in tables. Results for enhanced night vision
image sets can be seen in Table 1. The best results
for SCD were obtained with NR=16. On the other
hand, for the other metrics, the best results were
mostly obtained when NR is set as 4 or 8. In
addition, the same situation is occurred for
concealed weapon detection images as can be seen
from Table 2.
The proposed method is compared with LP (Burt
and Adelson, 1983) and SiDWT (Rockinger, 1997)
methods that are well known fusion methods in the
literature.
Visual results are given in Figure 3 and Figure 4.
Enhanced night vision images can be seen in
Figure 3. Especially, for image 1 and 2, the proposed
method demonstrated superior performance in visual
aspect. From analysis of the visual results of
enhanced night vision, it can be easily noticed that
DifferentialEvolutionAlgorithmBasedSpatialMulti-sensorImageFusion
721
the complementary information of the source images
successfully transferred to the fused image.
The men in the images that cannot be seen in
visible images are emphasized in fused images. In
the result of proposed method for image 2, the sign
board and the man can be more clearly perceived
than LP and SiDWT. Furthermore, the details of the
building are less affected in proposed method. For
image 1 and 3, details like leaf of trees were
noticeably transferred to fused images in the
proposed method.
Similarly, for the concealed weapon detection
images, proposed method produces remarkable
better visual results. Details of scene in visible
image are less affected; meanwhile, the gun can be
expressed in fused image. Result of the SiDWT
methods are more darkened from the others.
In Fig. 5, the proposed method, LP and SiDWT
are compared in terms of four quality metrics. In this
figure, there are four graphs for all metrics. In the
figure, the metric values are shown in vertical axis
and the images are illustrated in horizontal axis. For
SCD, FF and SD metrics, the proposed method has
superior performance as can be seen from the figure.
QE metric is a measure for transferred edge amount
from the source images. Consequently, any edge
information do not transferred causes worse QE
results. The proposed method optimise amount the
complementary information not directly edge
information. Thus, some redundant edges are
eliminated. Therefore in some images, the method
gives smaller QE metric values.
Table 1: Quantitative metric values of proposed method on enhanced night vision images.
SCD QE FF SD
I NR Mean Sd Mean Sd Mean Sd Mean Sd
1
4
1,6811 2,5E-05 0,4276 0,0002 4,6293 0,015
13,1426
0,0249
8
1,7089 5,6E-05 0,4420 0,0002
4,8687
0,02 13,0549 0,0311
16
1,7121
1,3E-04
0,4427
0,0019 4,3046 0,0924 12,6203 0,0598
2
4
1,8623 4,7E-06
0,7405
0,0002 5,8901 0,0088 32,6549 0,0265
8
1,8779 4,9E-05 0,7265 0,0009
6,0274
0,0493
33,2886
0,0557
16
1,8918
3,7E-05 0,7230 0,0012 5,9466 0,0262 32,8598 0,0664
3
4
1,6814 1,9E-04 0,6617 0,0056 5,0728 0,0403 24,7487 0,0683
8
1,7110 3,8E-04
0,6715
0,0066
5,1144
0,0494
24,8753
0,1143
16
1,7168
4,3E-04 0,6611 0,0068 5,0156 0,0547 24,7280 0,1393
4
4
1,3426 1,4E-04
0,5440
0,0001
5,9977
0,016 13,4117 0,0109
8
1,3960 4,1E-04 0,5137 0,0013 6,1987 0,0456
13,5703
0,0608
16
1,4516
2,6E-04 0,4951 0,0015 6,4637 0,032 13,3122 0,0731
Table 2: Quantitative metric values of proposed method on concealed weapon detection images.
SCD QE FF SD
I NR Mean Sd Mean Sd Mean Sd Mean Sd
5
4
1,8190 1,3E-04 0,7642 0,0004 7,2460 0,0038 21,8141 0,0041
8
1,8386 6,7E-05
0,7727
0,0007
7,2954
0,0089
21,8684
0,0086
16
1,8419
5,5E-04 0,7672 0,0024 7,1230 0,0236 21,5918 0,0353
6
4
1,7482 6,8E-05 0,6321 0,0029 5,6574 0,0334 15,5627 0,0991
8
1,7681 8,8E-05 0,6385 0,002 5,6954 0,019
16,3073
0,0727
16
1,7731
2,9E-04
0,6430
0,0037
5,7890
0,0407 16,2750 0,1086
7
4
1,5953 1,6E-04
0,4789
0,0024
6,0943
0,022
13,8252
0,0178
8
1,5959 3,2E-04 0,4597 0,0117 5,8943 0,051 13,5828 0,0876
16
1,5974
4,7E-04 0,4450 0,0219 5,8543 0,0987 13,3263 0,1569
8
4
1,9284 6,6E-07
0,6763
0,0001
7,8687
0,0058
18,4296
0,0088
8
1,9497 3,7E-06 0,6548 0,0001 7,6373 0,0025 18,0308 0,0044
16
1,9535
1,7E-05 0,6600 0,0004 7,5924 0,0061 17,8978 0,0093
ICINCO2014-11thInternationalConferenceonInformaticsinControl,AutomationandRobotics
722

Figure 3: Visual results of methods on enhanced night vision images.
Figure 4: Visual results of methods on concealed weapon detection images.
DifferentialEvolutionAlgorithmBasedSpatialMulti-sensorImageFusion
723

Figure 5: Quantitative comparison of Fusion Methods.
4 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, a new optimized region based image
fusion method is proposed in spatial domain. K-
Means is used as segmentation method, and
differential evolution algorithm is utilized in
optimization stage. Performance of the method is
compared with the classical techniques using eight
thermal and visible image sets.
The visual and the quantitative results given, the
proposed method produced better results than the
others. Especially in the night vision images, visual
results of the proposed method represent more
meaningful visual information than the others for
human perception.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by Research Fund of the
Erciyes University. Project Number: FBD-11-3801
REFERENCES
Aslantas, V., Bendes, E., Kurban, R. & Toprak, A. N.
2013. New Optimised Region-Based Multi-Scale
Image Fusion Method For Thermal And Visible
Images. Institution Of Engineering And Technology.
Aslantas, V. & Kurban, R. 2009. A Comparison Of
Criterion Functions For Fusion Of Multi-Focus Noisy
Images. Optics Communications, 282, 3231-3242.
Aslantas, V. & Kurban, R. 2010. Fusion Of Multi-Focus
Images Using Differential Evolution Algorithm.
Expert Systems With Applications, 37, 8861-8870.
Burt, P. J. & Adelson, E. H. 1983. The Laplacian Pyramid
As A Compact Image Code. Communications, Ieee
Transactions On, 31, 532-540.
Group, I. I. P. R. 2012. Image Database For Image Fusion
Applications [Online]. Kayseri: Erciyes University.
Available: Http://Ce.Erciyes.Edu.Tr/Fusiondatabase/
[Accessed].
Hu, J. & Li, S. The Multiscale Directional Bilateral Filter
And Its Application To Multisensor Image Fusion.
Information Fusion, In Press, Corrected Proof.
Huang, W. & Jing, Z. 2007. Multi-Focus Image Fusion
Using Pulse Coupled Neural Network. Pattern
Recognition Letters, 28, 1123-1132.
Kun, L., Lei, G., Huihui, L. & Jingsong, C. 2009. Fusion
Of Infrared And Visible Light Images Based On
Region Segmentation. Chinese Journal Of
Aeronautics, 22, 75-80.
Lewis, J., Nikolov, S. & Toet, L. 2005. The Multi-Sensor
Image Segmentation Data Set [Online]. Available:
Http://Www.Imagefusion.Org/Images/Mm-
Segmentations/Mm-Segmentations.Html [Accessed].
Lewis, J. J., O'callaghan, R. J., Nikolov, S. G., Bull, D. R.
& Canagarajah, N. 2007. Pixel- And Region-Based
Image Fusion With Complex Wavelets. Information
Fusion, 8, 119-130.
Li, S., Yang, B. & Hu, J. 2011. Performance Comparison
Of Different Multi-Resolution Transforms For Image
Fusion. Information Fusion, 12, 74-84.
Miao, Q., Shi, C., Xu, P., Yang, M. & Shi, Y. 2011. A
Novel Algorithm Of Image Fusion Using Shearlets.
Optics Communications, 284, 1540-1547.
Mumtaz, A. & Majid, A. Year. Genetic Algorithms And
Its Application To Image Fusion. In: Emerging
Technologies. Icet 2008. 4th International Conference
On, 18-19 Oct. 2008 2008. 6-10.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
0.8
1
1.2
1.4
1.6
1.8
2
SCD
LP SiDWT Proposed
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
0
2
4
6
8
FF
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
20
30
40
50
60
70
SD
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
QE
LP SiDWT Proposed
LP SiDWT Proposed
LP SiDWT Proposed
ICINCO2014-11thInternationalConferenceonInformaticsinControl,AutomationandRobotics
724

Niu, Y. & Shen, L. 2006. Multi-Resolution Image Fusion
Using Amopso-Ii. Intelligent Computing In Signal
Processing And Pattern Recognition. Springer Berlin /
Heidelberg.
Price, K. & Storn, R. March 1995. Differential Evolution -
A Simple And Efficient Adaptive Scheme For Global
Optimization Over Continuous Spaces. Icsi.
Qu, G. H., Zhang, D. L. & Yan, P. F. 2001. Medical
Image Fusion By Wavelet Transform Modulus
Maxima. Optics Express, 9, 184-190.
Raghavendra, R., Dorizzi, B., Rao, A. & Hemantha
Kumar, G. 2011. Particle Swarm Optimization Based
Fusion Of Near Infrared And Visible Images For
Improved Face Verification. Pattern Recognition, 44,
401-411.
Rockinger, O. Year. Image Sequence Fusion Using A
Shift-Invariant Wavelet Transform. In: Image
Processing. Proceedings., International Conference
On, 26-29 Oct 1997 1997. 288-291.
Toet, A., Ijspeert, J. K., Waxman, A. M. & Aguilar, M.
1997. Fusion Of Visible And Thermal Imagery
Improves Situational Awareness. Displays, 18, 85-95.
Xue, Z., Blum, R. S. & Li, Y. Year. Fusion Of Visual And
Ir Images For Concealed Weapon Detection. In:
Information Fusion. Proceedings Of The Fifth
International Conference On, 2002 2002. 1198-1205.
Xydeas, C. S. & Petrovid, V. 2000. Objective Image
Fusion Performance Measure. Electronics Letters 36,
308-309.
Zhong, Z. & Blum, R. S. 1999. A Categorization Of
Multiscale-Decomposition-Based Image Fusion
Schemes With A Performance Study For A Digital
Camera Application. Proceedings Of The Ieee, 87,
1315-1326.
DifferentialEvolutionAlgorithmBasedSpatialMulti-sensorImageFusion
725
