
Secure Protocol for Financial Transactions Using Smartphones - SPFT
Formally Proved by AVISPA
Shizra Sultan, Abdul Ghafoor Abbasi, Awais Shibli and Ali Nasir
Department of Computing,School of Electrical Engineering & Computer Sciences,
National University of Science and Technology, Islamabad, Pakistan
Keywords: Financial Protocol, Smartphones, Secure Payment Protocol, Formal Verification, AVISPA.
Abstract: Smartphones are overpowering the IT world by rising as a prerequisite for other technologies. Emerging
technology paradigms such as Cloud computing, web data services, online banking and many others are
revamping them as compatibility to smartphones. Banking is a vital and critical need in daily life. It
involves routine financial transactions among sellers, buyers and third parties. Several payment protocols
are designed for mobile platforms which involve hardware tokens, PIN, credit cards, ATMs etc. for secure
transactions. Many of them are not properly verified and have hidden flaws .Numerous vulnerabilities have
been found in existing solutions which raise a big question about the defense capability of smartphones to
protect user’s data. In this paper we propose a secure payment protocol for smartphones without using any
hardware token. It implicates bank as a transparent entity and users rely on a payment gateway to mark a
successful transaction. Suggested protocol uses symmetric keys, Digital certificates X.509, and two-factor
authentication to make a secure financial deal. To prove the secrecy and authentication properties of the
protocol we have formally verified it by AVISPA.
1 INTRODUCTION
Over the years technology has covered every aspect
of human life and has transformed into a utility. Aim
of technology is to facilitate humans as much as
possible so it’s moving towards integrating real life
critical areas such as education, health, finance and
many others with emerging technologies (Chang,
2012). There has been so much overlapping among
various fields of IT that one cannot clearly
demarcate the boundary of any technology. So now
when we talk about throughput, efficiency and
security of any system we just can’t look at one
component, we have to take in account the share of
all modules involved in a finished product (Isaac,
2007). We need to utilize different technologies in a
way that they combine to give a better product. For
example online banking on Smart phones; both
mentioned technologies have benefits and problems
of their own so we efficiently incorporate both to
gain as much throughput as we can. On one hand it
benefits the users; and on the other hand there have
been evil elements involved which provide a greater
harm by exploiting the vulnerabilities of such
systems. Financial indiscretion in e-commerce is
becoming a major concern for individual users as
well as for the organizations worldwide. Cyber
criminals are gradually launching well-organized
and effective attacks by exploiting the vulnerabilities
in existing architectures (Ahamad, 2012).Taking in
account all the above facts, there is a need of a
secure e-commerce solution which does not only
facilitate users’ financial needs but also fulfils the
security parameters compulsory in any transaction.
To do that we have to accommodate many different
problems like mobility and ease of access for users
so we suggest a financial solution based on smart
phones (Kungpisdan,2004).Conventional financial
solution lack extensibility, openness, privacy, and
cost effectiveness (Liu, 2005). We realize that Smart
phones are prone to attacks too so if we want to use
them for financial transactions, we need a highly
efficient and secure design (Hamid, 2012)
For large multi-national organizations there are a
lot of business transactions within & outside the
organization which requires hardware tokens, PIN or
access codes to acquire the resource (Avalle, 2014).
What if personal information of an employee is
stolen or one of the insiders tries to exploit the
system weaknesses like stolen card information or
387
Sultan S., Abbasi A., Shibli A. and Nasir A..
Secure Protocol for Financial Transactions Using Smartphones - SPFT - Formally Proved by AVISPA.
DOI: 10.5220/0005059903870392
In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Security and Cryptography (SECRYPT-2014), pages 387-392
ISBN: 978-989-758-045-1
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

mobile devices. So why not make the whole
organization transactions and resources strictly need
to know basis and anonymous (Vilmos, 2003) which
are highly secure and easy to use. So we recommend
a financial solution that does not require hardware
tokens or physical presence and is based on smart
phones focusing on close networks.
We propose a Secure Protocol for Financial
Transactions SPFT- based on smart phones. All
transactions are performed by smartphone and a user
does not have to carry cash or cards. Entities
involved in a process are; Client-C, Merchant-M,
Bank- B, Payment Gateway– PG.SPFT ensures
privacy, authentication and integrity of all entities,
provides anonymity and mechanism to resolve
disputes and is formally tested before
implementation. And to achieve that we have used
low cryptographic operations, less reliance on banks,
an honest payment gateway, Digital Certificate &
time stamping (
Xueming,2009). Formal techniques
are an efficient way to verify the security
specifications of a system. We have formalized the
authentication and secrecy properties of our protocol
(Avalle, 2014). We have verified the protocol by an
automated verification tool AVISPA.
The paper is organized as follow: Section 2
deliberates the related work. Section 3 discusses our
contribution which is a proposed protocol. Section 4
verifies the protocol via AVISPA, Section 5
accomplishes the conclusion and future work and
Section 6 states the references
2 RELATED WORK
Several protocols have been offered in past few
years for outfitting the need of payments via mobile
devices or smartphone. Significant ones are given
below: In (Kungpisdan, 2004) they addressed the
limitations of mobile devices i.e., lower
computational power & less storage space so they
proposed a secure account based mobile payment
protocol. Protocol is composed of two sub protocols,
one is merchant registration and other is called
payment protocol. In former client is registered to
merchant and its issuer while merchant gets
registered to payment gateway, in later client and
merchant communicate order and transaction details
and share with the payment gateway. Party
authentication, Transaction privacy & Transaction
integrity is ensured by credit card info, symmetric
key and MAC respectively. Third parties are a
necessary evil in financial services; they pose
privacy threats and unsolved repudiation conflicts,
(Liu, 2005) authors have suggested that with the
introduction of time stamping server and data center
this can be resolved. If all-inclusive confirmations
route via data center and all transactions carry a
signature time stamp then non-repudiation can be
achieved while privacy is achieved by reserving the
user info at user payment processor and doesn’t
travel with the transaction messages. Most of the
protocols work on a principle that all entities in a
system have internet access all the time so (T´ellez,
2007) designed a new protocol which caters the
problem when merchant can’t directly connect with
the client. Finance is always linked with banks so
they have complete control over all transactions
(Vilmos, 2003) but it can be shifted to different
entities like mobile network operators MNO for
better performance. Proposed solution (SEMOPS) is
built on credit push concept, Merchant provides
customer with specific data that can identify the
merchant & particular transaction, and client
remains anonymous throughout the process.
Customer receives the data combines with his
information authorizes it and sends to the payment
processor (can be bank or MNO). In current state
SEMOPS uses a large number of computations
which consumes a lot of mobile’s resources so
(Hamid, 2012) presents a light & secure mobile
payment system based on SEMOPS. In SIP
enhanced SEMOPS, SIP sessions are established
between associated parties to isolate different
communications between respective entities and for
signing they have used ECC (elliptic curve
cryptography) instead of RSA accomplishing higher
security with smaller key size. They have used PIN,
nonce & OTPs for mutual authentication, session
keys for privacy, PKI for integrity & non-
repudiation. Now after studying different approaches
(Xueming, 2009) logical approach will be to merge
the developments into one framework that will be
beneficial in developing a new mobile payment
method which will be more secure, flexible and
convenient assuring anonymity, non-repudiation,
confidentiality & integrity. (Avalle, 2014) Formal
methods are an effective way to verify system
specification, and are being largely used for the
verification of security protocols.
Formal methods are going towards computational
model for verifying different protocols for which
many tools are available like CryptoVerif, Athena,
TAPS, ProVerif, FDR, AVISPA etc. We have
chosen AVISPA due to its adaptability to verify
different security parameters like secrecy,
authentication, proof of origin and accountability.
SECRYPT2014-InternationalConferenceonSecurityandCryptography
388
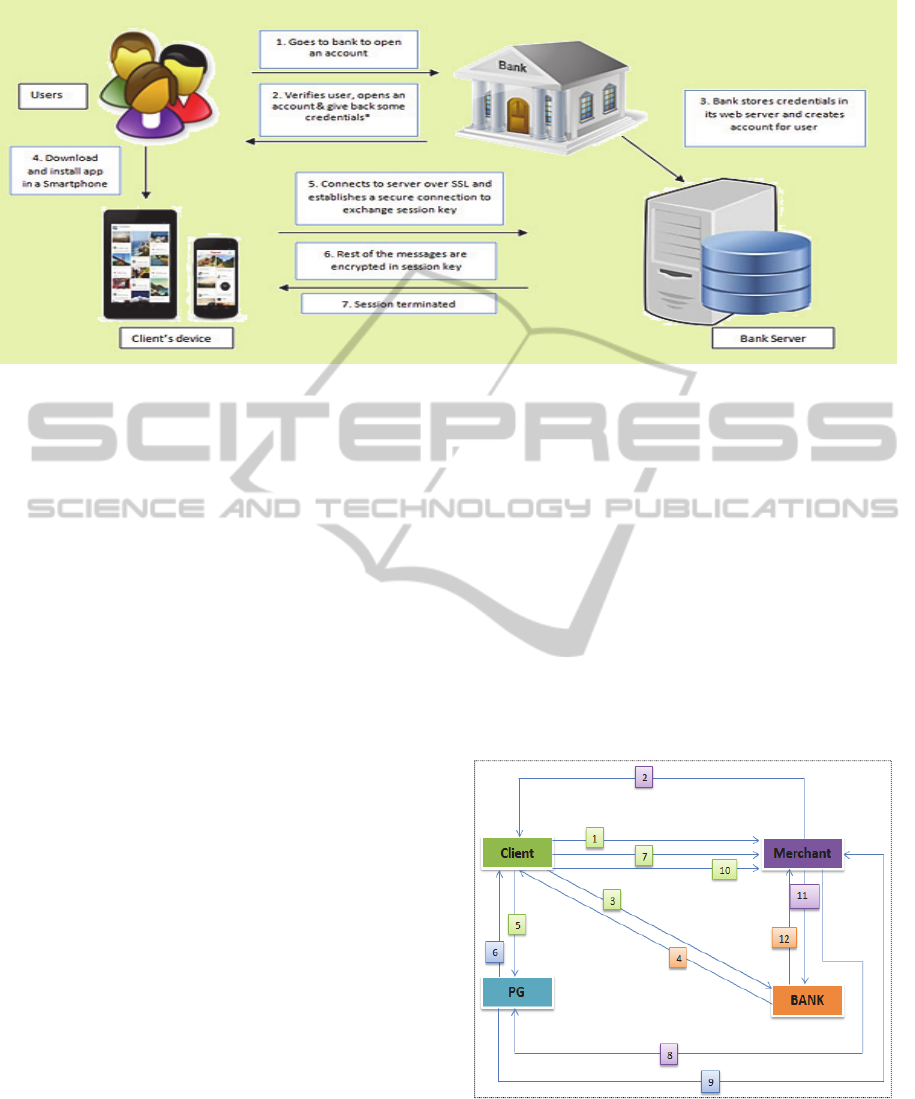
Figure 1: Architecture Diagram - SPFT.
3 OUR CONTRIBUTION
SPFT is a smartphone based payment system for
close network. Now -a- days smart phones have
become a daily life necessity, there are all those
applications which have made phones a single unit
to handle most of the chores like utility bills, online
financial transactions e.g., what we propose is to
make it more convenient that it eliminates the use of
paper money in a close environment (cafeteria bills,
buying/selling, pays) like big organizations. An
application that can control daily life small or big
transactions just with few clicks and does not have
to keep trail of paper money on daily basis. The
protocol is based on conventional actors’ i.e.,
customer, merchant, payment gateway & a financial
intuition. What is different is the kind of access
these parties have with each other, bank is always
thought to be a close system, in this protocol it’s not.
All parties will be completely transparent; there will
be no transaction trails and anonymity will be
preserved.
3.1 Proposed Solution
The proposed protocol comprises of following steps:
1) All users (customer & merchants) get
registered with the financial institution. Users
get their usernames & passwords to access the
service along with a unique master key shared
with bank and every user
2) User logs in to the system, views the multi-
merchant multi services and choses a service
he wants to avail and puts an order request to
merchant. Every service has unique ID (e.g.
café: 01, printer: 02) and then further every
item has a unique ID (tea: 02, coffee: 04) etc.
3) Merchant receives the requests and reserves
the order and replies to user with a vending-
token. The vending token has item and price
info (not item id)encrypted with sessionKey
CM
while an additional token for bank which only
has price info signed by banks public key and
then merchant private key user will 1
st
peel of
merchant’s seal and verifies the hash which
will prove that it came from the merchant
Figure 2: Flow Diagram.
4) User accesses his bank account, requests the
money equivalent to {Price} amount form the
account. {Price} passed to bank is signed by
bank’s public key
SecureProtocolforFinancialTransactionsUsingSmartphones-SPFT-FormallyProvedbyAVISPA
389

5) Bank checks 1
st
if user is legit and requested
funds are available then it generates a
purchase- ticket and reserves that money from
the users account and sends a sms/email
confirmation to user.
6) Bank sends the ticket to client enveloped in a
session key
7) Client with an addition of session key sends to
payment gateway to envelope it with two keys
i.e. two man rule and payment gateway
generates a new ticket which is in actual the
old ticket locked by two keys and signs the
original ticket. Bank deducts money from the
account and keeps with him for safe keeping so
conflicts don’t occur, bank cant access this
money until its authorized by payment gateway
8) Payment gateway replies user with TICKET2,
PIN enveloped in Client’s public key so only
client can access it and a hash of PIN signed by
payment gateway to check if it is authentic or
not
9) Client sends a TOKEN and TICKET2 to
merchant enveloped in a session Key shared
between merchant and client
10) Merchant then sends a TICKET ID to payment
gateway to request for OTP related to this ID
11) Payment gateway replies user with a TICKET
ID, OTP encrypted by Merchant’s public key
so only he can access it, hash of PIN and OTP
both signed by payment for verification and all
above are enveloped in a message encrypted
by a session key
12) Client sends TICKET ID and PIN relative to
that ID encrypted in merchant’s public key and
whole enveloped with session key
13) Merchant unlocks the ticket2 from OTP and
then by the PIN sent to him by the client after
receiving product
14) Bank transfers the amount reserved by token to
merchant’s account and sends merchant a
conformation message
3.2 Notation Scheme
For conventional actors C- client, M- merchant, B-
bank and PG-payment gateway is used while for
public key
PB
prefix and for private key
PR
is used
Table 1: Notation table followed in protocol.
Symbols Definition
TransactionID
Unique ID for specific transaction
ItemID
Unique ID for specific item
provided by related service
ServiceID
Unique ID for specific service
provided by merchant
TOKEN
Token ID, Item (description +
price)
HASH1
sha256(TransactionID, ItemInfo,
Price)
HASH2 sha256 (PIN)
HASH3 sha256 (OTP)
HASH4
sha256({Digital money} B
PU
)
TICKET1
TICKET ID, {Digital money} B
PU
,
[HASH4] B
PR
,
timestamp
TICKET2
TICKETID,{{Digital money} B
PU
}PIN}OTP, timestamp
MasterKey
Master key shared between two
entities
sessionKey
Session key shared between two
entities
CM
shared between client & merchant
CB
shared between client & bank
MB
shared between bank & merchant
CT
shared between client & ticket
checker/payment gateway
ItemInfo
Item description + its price
3.3 Protocol in Alice-Bob Notation
Registration process:
A. U B:{name, email ID, Cell No, DoB ,
username} B
PU
B. B U:{userID, password ,MasterKey
CB
}
Payment process:
1. C M : {TransactionID, ServiceID ,ItemID,
n1 , sessionKey
CM
} M
PU
2. M C : {TransactionID ,TOKEN,
{Price}B
PU
, [Hash1]M
PR
} sessionKey
CM
3. C B : { userID, password, {Price}B
PU,
sessionKey
CB
} MasterKey
CB
4. B C : { TICKET1} sessionKey
CB
5. C PG: { TICKET1, sessionKey
CT
} PG
PU
6. PG C : { TICKET2, {PIN} C
PU,
[HASH2]
PG
PR
} sessionKey
CT
7. C M : {TOKEN ,TICKET2 } sessionKey
CM
8. M PG: { TICKETID, sessionKey
MT
} PG
PU
9. PG M: { TICKETID ,{OTP} M
PU,
[HASH3]PG
PR,
[HASH2] PG
PR
} sessionKey
MT
SECRYPT2014-InternationalConferenceonSecurityandCryptography
390

10. C M: { TICKETID, [PIN] M
PU
}
sessionKey
CM
11. M B : {TICKET1} MasterKey
MB
B M : { TICKETID, Conform Message} 12.
M
PU
4 ANALYSIS USING AVISPA
It is an automation tool to validate security
protocols. Protocols that need to be verified against
properties like (secrecy, authentication, proof of
origin etc.) are written in a specification language
HLPSL. AVISPA at back-end works on principles
of formal methods like model checking to achieve
security goals and exemplify threat models. It covers
four back-end practices; OFMC (on the fly model-
checker), CL-AtSe (attack searcher), SATMC (SAT
model checker) and TA4MC (automata based
protocol analyser). We have tested the proposed
protocol with first two techniques
4.1 Program Code
Code written in HLPSL (modelling language for
AVISPA) will be provided on request
4.2 Attacks
There are three major concerns for any protocol
when seen from the security perspective, Secrecy,
authentication and integrity. We have analysed the
protocols from these three viewpoints in AVISPA
4.2.1 Secrecy
Most important parameter in financial transaction is
the secrecy of transaction details and privacy of
user’s personal information. In our protocol we have
put secrecy check on critical points when modelling
in AVISPA e.g.
I. secret(SessionKeyCM',purchase_order,{C,
M})
II. secret(SessionKeyCB',sessioncb, {C,B})
III. secret(SessionKeyCP,sessioncp, {C,P})
IV. secret(OTP,otp, {C,P})
These are some security goals written in AVISPA
format to check if the session keys and OTP are
secure or they have been compromised during the
protocol. They have all given SAFE results which
means there is no information leakage
4.2.2 Authentication
Authentication is a property which ensures that both
parties are what they are posing to be; actually it is
to develop a trust to communicate with each other.
Assuming that digital certificates haven’t been
compromised when any party digitally signs
something it assures that the certain thing belongs to
that party. In code below hash messages have been
digitally signed to confirm authentication and proof
of origin e.g.
I. RCV({TICKETID'.{DigMoney'}_inv(Sign
K_B)}_SessionKeyCB')
II. RCV({(TOKENID.ItemInfo.Price).(TICKE
TID'.{{{DigMoney'}_inv(SignK_B)}_PIN'
}_OTP').h(PIN)}_SessionKeyCM)
In above code statements message parameter {
Digital Money} is digitally signed by Bank’s private
key, which shows that certain message came from
Bank that can be verified by decrypting the message
by bank’s public key
4.2.3 Integrity
This property ensures that data has not been altered
or destroyed, and mostly its proved by the use of
hashes. In our protocol we have attached a digitally
signed hash of a message with itself to certify the
integrity of message itself. e.g.
I. SND({TransID'.(TOKENID'.ItemInfo.{Pric
e}_SignK_B).{h(TransID'.Price.ItemInfo
)}_inv(SignK_M)}_SessionKeyCM')
II. SND({(TOKENID.ItemInfo.Price).(TICKE
TID'.{{{DigMoney'}_inv(SignK_B)}_PIN'
}_OTP').h(PIN)}_SessionKeyCM)
In first message hash of (TransID +Price
+ItemInfo) is digitally signed by merchant public
key, now if anyone tries to alter the ID or price in
any of the message, this hash won’t be equal to the
hash calculated of the alter values which will show
that data in transition has been tempered with and
that transaction will be dropped
4.3 Results
Results of two AVISPA back-end formal methods
on above protocol is as follow
4.3.1 OFMC
OFMC practices several symbolic techniques to
symbolize the state-space. OFMC is used to prove
the falsification of protocols by finding efficient
SecureProtocolforFinancialTransactionsUsingSmartphones-SPFT-FormallyProvedbyAVISPA
391

attacks on them and also for the verification. i.e., for
proving the protocol correct in certain situations for
bounded number of sessions. Output generated by
OFMC for SPFT in AVISPA is as follow:
% OFMC GOAL - as specified
BACKEND OFMC
STATISTICS
parseTime: 0.00s
searchTime: 0.53s
visitedNodes: 73 nodes
depth: 14 plies
4.3.2 ATSE
It’s a constraint based attack searcher works on the
principle of reducing redundant data. It translates the
protocol in such specific language which can be
useful to effectively find attacks on protocol. Output
of our protocol is:
GOAL As Specified
BACKEND CL-AtSe
STATISTICS
Analysed : 55 states
Reachable: 20 states
Translation: 0.13 seconds
Computation: 0.00 seconds
5 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
We have suggested a radical secure payment
protocol to make daily life transactions easy and
secure for users, where client and merchant does not
need to blindly rely on financial service providers.
Each entity has a part of whole transaction; all
entities need to put their part to make an effective
transaction. Client’s identity is hidden from
merchant and bank does not need to know what is
bought. Client places a request with merchant and
requests bank to reserve money for specific deal
after it is routed to the payment gateway to look over
the transaction and locks the digital money by two-
factor authentication and authorizes both parties to
complete the transaction. After conformation by
both client and merchant, funds are transferred to the
merchant’s account. It fulfills all the security
parameters required in a payment protocol like
secrecy, authentication and conflict resolution and to
prove this we have formally tested the code by
AVISPA.
For future work we will modify the protocol
involving two different banks and formally prove it
by Model checking to draw the comparison and to
employ it in a cloud environment. As an end result,
we state that suggested protocol is flexible and
extensible to all environments. Besides it also
ensures the secrecy of personal information as well
as the anonymity of user
REFERENCES
Kungpisdan, S., Srinivasan, B., and Dung Le. P., 2004. “A
Secure Account-Based Mobile Payment Protocol” In
(ITCC’04), Proceedings of the International
Conference on Information Technology: Coding and
Computing
Liu, J., Liao, J., Zhu, X., 2005. “A System Model and
Protocol for Mobile Payment” .In (ICEBE’05),
Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on
e-Business Engineering
T´ellez, J., Camara, J., 2007. “An Anonymous Account-
Based Mobile Payment Protocol for a Restricted
Connectivity Scenario” In (DEXA’03), 18th
International Workshop on Database and Expert
Systems Applications
Vilmos, A., Karnouskos, S., 2003. “SEMOPS: Design of
a new payment service” In 14
th
international
workshop on Database & Expert Systems Applications
Abdel-Hamid, A., Badway, O., Aboud, M., 2012.
“SEMOPS+SIP+ECC: Enhanced secure mobile
payments” In (INFOS2012), 8
th
international
conference on Informatics & systems
Xueming, W., Nan, C., 2009. “Research of security
mobile payment protocol in communication restriction
scenarios”. In international conference on
computational intelligence & security
Chang, C., Yang.J., Chang,k., 2012. "An Efficient and
Flexible Mobile Payment Protocol”. In (ICGEC
’12) Genetic and Evolutionary Computing (ICGEC),
2012 Sixth International Conference
Ahamad, S., Sastry, N., Udgata, K., 2012. "Enhanced
Mobile SET Protocol with Formal Verification”. In
(ICCCT ‘12), Third International Conference of
Computer and Communication Technology
Isaac, J., Camara, J, 2007. "An Anonymous Account-Based
Mobile Payment Protocol for a Restricted
Connectivity Scenario," In (DEXA '07) Database and
Expert Systems Applications
Avalle, M., Pironti, A., Sisto, R., 2014. "Formal
verification of security protocol implementations: a
survey". Journal of Formal Aspects of Computing
Volume 26, Issue 1, pp 99-123 2014
Secure Electronic Transaction (SET) Protocol,
http://www.isaca.org/Journal/Past-
Issues/2000/Volume-6/Pages/Secure-Electronic-
Transaction-SET-Protocol.aspx
SECRYPT2014-InternationalConferenceonSecurityandCryptography
392
