
Modeling White-matter Fiber-orientation Uncertainty for Improved
Probabilistic Tractography
Adelino R. Ferreira da Silva
Dep.
o
de Eng.
a
Electrot´ecnica, Faculdade de Ciˆencias e Tecnologia, FCT,
Universidade Nova de Lisboa, 2829-516 Caparica, Portugal
Keywords:
Probabilistic Tractography, Particle Filtering, Diffusion MRI.
Abstract:
Tractography uses fiber-orientation estimates to trace the likely paths of white-matter tracts through the brain,
in order to map brain connectivity non-invasively. In this paper, we propose a novel probabilistic framework
for modeling fiber-orientation uncertainty and improve probabilistic tractography. The main innovation in the
present formulation consists in coupling a particle filtering process with a clustered-mixture model approach to
model directional data. Mixtures of von Mises-Fisher (vMF) distributions are used to support the probabilistic
estimation of intravoxel fiber directions. The fitted parameters of the clustered vMF mixture at each voxel are
then used to estimate white-matter pathways using particle filtering techniques. The technique is validated on
simulated as well as on real human brain data experiments.
1 INTRODUCTION
White matter fiber tracking or “tractography” uses
fiber-orientation estimates to trace the likely paths of
white-matter tracts through the brain. Tractography
techniques are powerful tools to capture white mat-
ter (WM) connectivity non-invasively. Before apply-
ing tractography techniques, diffusion Magnetic Res-
onance Imaging (MRI) measurements are applied to
probe the dispersion of water molecules within tis-
sue over a time. A probability distribution on the
displacement of water molecules describes the scat-
ter pattern of molecules during the diffusion time.
Since white matter axons are tiny compared to typ-
ical MRI voxels, voxels contain hundreds of thou-
sands of axon fibers, which can adopt a wide range
of complex configurations. The simpler and most
commonly used method, Diffusion Tensor Imaging
(DTI) uses a Gaussian distribution to model the dis-
persion. DTI assumes that the diffusion scatter pat-
tern exhibits a single directional pattern, and is there-
fore unable to model multiple-directional fiber path-
ways within a voxel. Other model-based approaches,
such as the multi-tensor model (Tuch et al., 2002), or
multi-compartment models (Behrens et al., 2007; As-
saf and Basser, 2005) have been devised to account
for distinct groups of “populations” of fibers. How-
ever, model-based techniques recover but a few num-
ber of dominant fiber-orientations, and have difficulty
in discriminating common anatomical fiber configu-
rations (Seunarine and Alexander, 2009). To resolve
complex orientations, model-free methods and High
Angular Resolution Diffusion Imaging (HARDI) pro-
tocols have been developed. For instance, Q-ball
imaging (QBI) (Tuch, 2004) is one popular HARDI-
based method used to resolve fiber crossings. It re-
constructs the angular profile of the diffusion prop-
agator, commonly known as the (diffusion) orienta-
tion distribution function (ODF). The ODF exhibits
multiple local maxima in crossing regions, which are
used as fiber orientation estimates. Two more recent
model-free models are the Diffusion Spectrum Imag-
ing (DSI) (Wedeen et al., 2005), and the Generalized
q-Sampling Imaging (GQI) (Yeh et al., 2010) meth-
ods. These methods perform non-parametric recon-
structions that resolve multiple peaks in each voxel,
without requiring prior knowledge of the number of
fiber populations. Similarly to other methods for ODF
reconstruction, DSI and GQI use shell or grid sam-
pling schemes to extract information about the extent
of diffusion anisotropy, and map vector fields that rep-
resent the fiber orientations at each voxel. In contrast
to QBI, DSI and GQI are not limited to a single spher-
ical shell and a single diffusion gradient coefficient
(b-value) to characterize diffusion anisotropy.
As pointed out by (Seunarine et al., 2007; Seu-
narine and Alexander, 2009), most tractography al-
gorithms still use the basic DTI single-fiber recon-
71
R. Ferreira da Silva A..
Modeling White-matter Fiber-orientation Uncertainty for Improved Probabilistic Tractography.
DOI: 10.5220/0005069300710078
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Congress on Neurotechnology, Electronics and Informatics (NEUROTECHNIX-2014), pages 71-78
ISBN: 978-989-758-056-7
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

struction and it is not clear how to generalize them
to exploit the extra information that multiple fiber re-
constructions provide. Even when probabilistic trac-
tography is used to estimate the uncertainty of fiber-
orientations, the information used to track through
fiber configurations is limited to the principal diffu-
sion directions. For instance, in (Parker and Alexan-
der, 2003) fiber-orientations are detected by a Monte
Carlo streamline approach, and the sharpness of the
peaks are used as indicators of uncertainty. In (Seu-
narine et al., 2007), the authors have shown that the
peaks of multiple-fiber reconstructions provide useful
information that can be used to improve tractography
results. They used the Bingham distribution to model
the peak uncertainty in fiber-orientation estimates ob-
tained from the ODF. Hence, better peak shape un-
certainty estimates provided improved tractography
results. The main drawback of the above technique
is that it requires a costly and complicated calibra-
tion. The calibration procedure constructs a mapping
from two Hessian (or second derivative) eigenvalues
to Bingham parameters, using simulations on two-
tensor mixture models with known peak directions
(Seunarine et al., 2007).
The above considerations motivated us to de-
vise a probabilistic framework for modeling fiber-
orientation uncertainty and improve probabilistic
tractography. Two key ideas govern the present de-
velopment and implementation. First, we model
fiber-orientation uncertainty by using directional data
clustering to estimate white matter fiber orientations.
A clustered-mixture-model approach to model direc-
tional ODF data based on von Mises-Fisher (vMF)
distributions is used, in order to support the proba-
bilistic estimation of intravoxel fiber directions. The
generalized fractional anisotropy (GFA) (Tuch, 2004)
is applied to the reconstructed ODF in order to thresh-
old the population of acquisition directions before
clustering.
In this “clustered-vMFs” approach, each esti-
mated voxel fiber direction is associated with a com-
ponent of the fitted mixture of vMF distributions.
Hence, each voxel fiber principal direction may be
specified by the summary statistics of the estimated
vMF component in the mixture. It is worth noting
that, in opposition to (Seunarine et al., 2007), no cali-
bration is required. Fitting the mixture of von Mises-
Fisher (vMF) distributions to the clustered data, auto-
matically defines the parameters defining the statisti-
cal properties of the main peak directions. Moreover,
the number of fitted clusters automatically define the
pattern of fibers in a voxel.
The second key idea consists in using the fitted
parameters of the clustered-vMFs approach at each
voxel to guide probabilistic fiber tracking using par-
ticle filtering. Several probabilistic techniques have
been proposed in the literature to cope with direc-
tional uncertainty, partial volume effects, and errors
in fiber orientation estimates (Parker and Alexander,
2003; Zhang et al., 2009). Probabilistic methods gen-
erate multiple trajectories based on a distribution of
fiber bundles at a given seed point, in order to map the
connectionbetween the seed voxeland other voxelsof
the brain. In these techniques, Markov Chain Monte
Carlo (MCMC) methods are used to sample from
fiber orientation distributions. In order to make the
sampling stage more effective, several authors (Zhang
et al., 2009; Pontabry et al., 2013; Rowe et al., 2013)
have proposed to apply particle filtering to recursively
estimate the posterior distribution of fibers at each
propagation step. In a similar vein, in this work we
have used the Sequential Monte Carlo (SMC) frame-
work (Doucet et al., 2000) to model fiber trajectories.
The SMC algorithm propagates for each seed a cloud
of particles representing the density probability of the
fiber path passing through the seed voxel. The main
innovation in the present formulation consists in cou-
pling the particle filtering process with the clustered-
vMFs estimate outlined above.
The paper is organized as follows. Section 2
presents the underlying methodology supporting the
proposed approach, namely the particle filtering strat-
egy and the clustered-vMFs model. In Section 3 we
report on experiments applied to simulated as well as
to real brain data. The results of the proposed method-
ology are compared to those from standard streamline
approaches. Section 4 draws some conclusions and
points to future working directions.
2 METHODS
2.1 Fiber Tracking Model
In a particle filtering context, fiber tracking is formu-
lated as a non-Gaussian state space model (Doucet
and Johansen, 2011). In this model, given the prior
probability distribution that characterize the uncer-
tainty of local fiber orientations, a posterior distri-
bution of the target fiber is estimated. Given that
both the prior and the posterior distribution are non-
Gaussian, particle filtering techniques are well suited
to estimate the complex geometry of the fiber paths,
and account for directional uncertainties. In contrast,
linear filtering methods such as Kalman filtering are
often inappropriate to track complex configurations.
In a volume Ω ⊂ R
3
, a fiber trajectory can be mod-
eled as a sequence of n displacement vectors u
k
with
NEUROTECHNIX2014-InternationalCongressonNeurotechnology,ElectronicsandInformatics
72

k = 1,...,n. From a given starting point u
0
, at each
time step k, each streamline is propagated one step
from its previous location u
(i)
k−1
with a direction vec-
tor v
(i)
k
sampled from the importance density by a step
size λ, such that u
(i)
k
= u
(i)
k−1
+λv
(i)
k
. The state of a par-
ticle at time step k, x
(i)
k
, is defined by its location u
(i)
k
and direction vector v
(i)
k
.
As detailed in (Doucet and Johansen, 2011), parti-
cle filtering algorithms can be interpreted as instances
of a single generic SMC algorithm. Earlier particle
filtering algorithms, such as the popular Sequential
Importance Sampling (SIS), suffered from a degen-
eracy problem as simulation time increased: variance
of the estimates increased with time k. Degeneracy is
a key factor conditioning the application of SIS algo-
rithms. However, by introducing a re-sampling step
degeneracy can be greatly mitigated. Modern SMC
methods are a combination of SIS and resampling.
SMC methods sample sequentially from a sequence
of target probability densities π
k
(x
k
).
As outlined in Algorithm 1, by a sequence of pre-
diction, weighting and selection steps, the particle
filter provides a discrete approximation of a poste-
rior distribution p(x
k
|y
0:k
) on a time-varying param-
eter x
k
at time step k, given the observations y
0:k
for
time steps 0,1, 2,...,k, and the initial state distribu-
tion p(x
0
). At each time step k, N particles are prop-
agated by sampling from an importance distribution
π(x
(i)
k
| x
(i)
0:k−1
,y
0:k
). In the weighting stage, impor-
tance weights w
∗(i)
k
are assigned in accordance to the
likelihood p(y
k
|x
(i)
k
). The discrete approximation to
the posterior distribution p(x
k
| y
0:k
), denoted by ˜w
(i)
k
,
is computed by normalizing the importance weights
w
∗(i)
k
. Finally, a resampling step is used to remove par-
ticles with low weights and proliferate those with high
weights. Resampling may be applied at each time
step, or alternatively, it may be applied only when
the variance of the normalized weights is superior to
a pre-specified threshold. The threshold, designated
ε
ESS
in Algorithm 1, is often specified in terms of
the EffectiveSample Size (ESS) criterion (Liu, 2001),
which assesses the variability of the weights by,
ESS =
N
∑
i=1
( ˜w
(i)
k
)
2
!
(−1)
. (1)
In Algorithm 1, the importance distribution
π(x
k
| x
(i)
0:k−1
,y
0:k
) is a vMF distribution. The ini-
tial state distribution p(x
0
), is the vMF distribu-
tion parameterized by one of the components of the
clustered-vMFs estimate for the current voxel, as de-
tailed in Section 2.2. The likelihood p(y
k
|x
(i)
k
) =
(v
k
·V (u
k
)), is defined by a vMF distribution parame-
terized by the parameters of the most likely vMF clus-
ter component, for direction v
k
, at each point location
u
k
.
Input :
V Voxels’ cluster statistics
N Number of particles
ε
ESS
Resampling threshold
for particle i = 1 to N do
x
0
∼ p(x
0
)
w
∗(i)
0
=
1
N
end
for times k = 1 to K do
for particle i = 1 to N do
x
(i)
k
∼ π(x
k
| x
(i)
0:k−1
,y
0:k
)
w
∗(i)
k
= w
∗(i)
k−1
p(y
k
| x
(i)
k
)
˜w
(i)
k
=
w
∗(i)
k
∑
N
j=1
w
∗(i)
k
end
ESS =
∑
N
i=1
( ˜w
(i)
k
)
2
(−1)
if ESS < ε
ESS
then
Resample { ˜w
(i)
k
,x
(i)
k
} according to
importance weights
end
end
Algorithm 1: Sequential Monte Carlo.
In the resampling stage, the usual practice is to
attribute equal importance weights to the newly in-
troduced particles (Doucet and Johansen, 2011). The
use of equal weights helps maintaining the diversity
of the population of particles at intermediate tracking
stages, which favors the exploration of new trajecto-
ries emerging from the current state. However, this
particle filtering setting may be too rich for the res-
olution of the diffusion directions estimated at each
voxel. White matter axon radii are in the range
[0.1,10] µm, whereas MRI voxels typically have sides
in the range [1, 5] mm. Voxels therefore contain hun-
dreds of thousands of axon fibers (Seunarine and
Alexander, 2009), but the estimated principal diffu-
sion directions are typically reduced to 2 or 3 per
voxel, originating the so-called “partial volume ef-
fects” (Alexander et al., 2001). These effects in-
troduce uncertainties in anisotropy measurements at
each voxel, which influence ODF reconstruction ac-
curacy and the anatomic validity of fiber track esti-
mates. An alternative procedure, is to attribute new
importance weights according to the weights already
evolved for the population of particles. This proce-
dure helps maintainingthe selection pressure overlow
ModelingWhite-matterFiber-orientationUncertaintyforImprovedProbabilisticTractography
73

weighted particles and reduces trajectory irregulari-
ties, driving the sequence of distributions to a max-
imum a-posterior path, at the cost of particle diver-
sity. The result is a more conservative set of esti-
mated directions, and a reduced capability of the al-
gorithm for exploring very long pathways. Nonethe-
less, it may still confer realistic fiber track estimates
for brain tractography.
2.2 Clustered-vMFs Model
The fiber tracking model outlined in Section 2.1 uses
vMF distributions as sampling distributions of inter-
est. A d-dimensional unit random vector x ∈ S
d−1
is
said to have d-variate vMF distribution if its probabil-
ity density function is given by
f(x|µ,κ) = c
d
(κ)e
κµ
T
x
, (2)
where kµk = 1, κ ≥ 0 and d ≥ 2. The normalizing
constant c
d
(κ) is given by
c
d
(κ) =
κ
d/2−1
(2π)
d/2
I
d/2−1
(κ)
, (3)
where I
r
(.) represents the modified Bessel function of
the first kind and order r. The density f(x|µ,κ) is
parameterized by the mean direction µ, and the con-
centration parameter κ. The κ parameter character-
izes how strongly the unit vectors drawn according to
f(x|µ,κ) are concentrated about the mean direction
µ. Larger values of κ imply stronger concentration
about the mean direction ((Mardia and Jupp, 2000)).
The vMF distribution is unimodal for κ > 0, and is
uniform on the sphere for κ = 0.
For directional clustering estimation, we consider
a mixture of k vMF distributions (Banerjee et al.,
2005) that serves as a model for directional ODF pro-
file data, corresponding to multiple fiber orientations.
A mixture of k vMF distributions has a density given
by
f(x|Θ) =
k
∑
h=1
α
h
f
h
(x|θ
h
), (4)
where f
h
(x|θ
h
) denotes a vMF distribution with
parameter θ
h
= (µ
h
,κ
h
) for 1 ≤ h ≤ k, Θ =
{α
1
,... , α
k
,θ
1
,...,θ
k
}, and the α
h
are non-negative
and sum to 1. The Expectation Maximization (EM)
framework is used for estimating the mean and con-
centration parameters of the mixture. The clustering
algorithms proposed by (Banerjee et al., 2005) and
implemented in (Hornik and Gr¨un, 2012) were used to
fit the vMF mixture. The principal ODF profile statis-
tics are extracted directly from the estimated clusters.
The number of fibers in each voxel is automatically
estimated from the reconstructed ODF profile by the
vMF approach using the Bayesian Information Crite-
rion (BIC) criterion (Schwartz, 1979). In other words,
“BIC” is used to decide on the number of components
to select. All relevant statistical information about the
ODF orientation and multiple fiber components may
then be extracted from this fitting process.
The preceding description specifies a clustered
mixture-model approach to model directional ODF
data based on von Mises-Fisher (vMF) distributions.
In this “clustered-vMFs” approach, each estimated
voxel fiber direction is associated with a component
of the fitted mixture of vMF distributions. Hence,
each voxel fiber principal direction may be specified
by the summary statistics of the estimated vMF com-
ponent in the mixture. Based on voxel ODF recon-
structions, our method estimates intravoxel fiber di-
rections by clustering mixtures of von Mises-Fischer
distributions fitted to probabilistic distributions.
As opposed to other approaches where mixture of
vMF distributions are used to representdiffusion, e.g.,
(Rathi et al., 2009), our method works directly with
the sampled ODF distributions. Moreover, the pro-
posed clustered-vMFs statistical procedure does not
care for ODF reconstruction. The process of ODF
reconstruction is kept independent from the process
of statistical cluster estimation. The objective of the
clustered-vMFs model is to gather statistical infor-
mation in order to support robust probabilistic tracto-
graphic algorithms (Ferreira da Silva, 2012). There-
fore, multiple ODF reconstruction approaches can be
easily integrated in the proposed framework by a sim-
ple “plug-in” technique.
Before applying the clustered-vMFs approach we
need to obtain the ODF profiles at each voxel. As
pointed out in the Introduction, model-free methods
and HARDI protocols are more adequate than current
model-based methods for resolving complex orienta-
tions. Any of the model-free methods mentioned in
the Introduction, (e.g., QBI, GQI, DSI), could be used
for reconstructing ODF profiles. Starting with the raw
HARDI signal acquired on a grid of q-space, the ODF
profile is estimated at each voxel, considering a sam-
pling density of unit vectors on a unit S
2
grid or shell.
To summarize anisotropic properties of the ODF and
infer the underlying crossing patterns of the fibers we
use the GFA metric (Tuch, 2004),
GFA =
s
n
∑
n
i=1
(ψ(u
i
) − hψi)
2
(n− 1)
∑
n
i=1
ψ(u
i
)
2
, (5)
where hψi = (1/n)
∑
n
i=1
ψ(u
i
) = (1/n) is the mean
of the ODF, hui is the mean diffusion direction, and
h.i denotes the average over ψ. The GFA metric pro-
posed in (Tuch, 2004), is an extension for HARDI
protocols of the fractional anisotropy (FA) metric
NEUROTECHNIX2014-InternationalCongressonNeurotechnology,ElectronicsandInformatics
74

commonly used in diffusion tensor imaging (DTI).
When a threshold is applied to the estimated GFAs at
each voxel, the non-thresholded unit vectors provide
directional statistics information about the estimated
ODF profile.
This directional clustering procedure has several
advantages compared to traditional approaches for
orientation mapping. In fact, current best practices
perform multiple maxima extraction based on proce-
dures which are very sensitive to the local modes that
appear in the reconstructed ODFs. Signal noise and
low sampling resolution yield deformed ODF recon-
struction profiles, thus affecting accuracy and preci-
sion in multiple orientation evaluations. In contrast,
estimating orientationsfrom clustered directionaldata
is much less sensitive to local modes in the recon-
structed ODF profile. Moreover, the procedure is
more robust to noise since it estimates orientations
statistically from sampled data.
3 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
3.1 Fiber Bundle Simulation
To validate the fiber tracking model described in Sec-
tion 2 we performed simulations with synthetic fields
of diffusion profiles. Firstly, we simulated diffu-
sion profiles at each voxel by generating diffusion-
weighted signals for single and multiple fibers simula-
tions, using the method detailed in (Ferreira da Silva,
2013). Secondly, we estimated ODF profiles by ap-
plying the model-free GQI method to extract infor-
mation about the extent of diffusion anisotropy, and
map vector fields that represent the fiber orientations
at each voxel. Thirdly, the clustered-vMFs approach
was used to obtain summary statistics of the vMF
components in the mixture of von Mises-Fisher dis-
tributions. Finally, the SMC algorithm was applied to
guide probabilistic fiber tracking. The parameters of
the clustered-vMFs approach at each voxel were used
to propagate a cloud of particles, according to the fit-
ted density probability for the fiber bundle trajectory
being tracked. Based on the resampling strategy out-
lined in Section 2.1 for path tracking, we derivea map
of fiber pathways for the simulated field of diffusion
profiles.
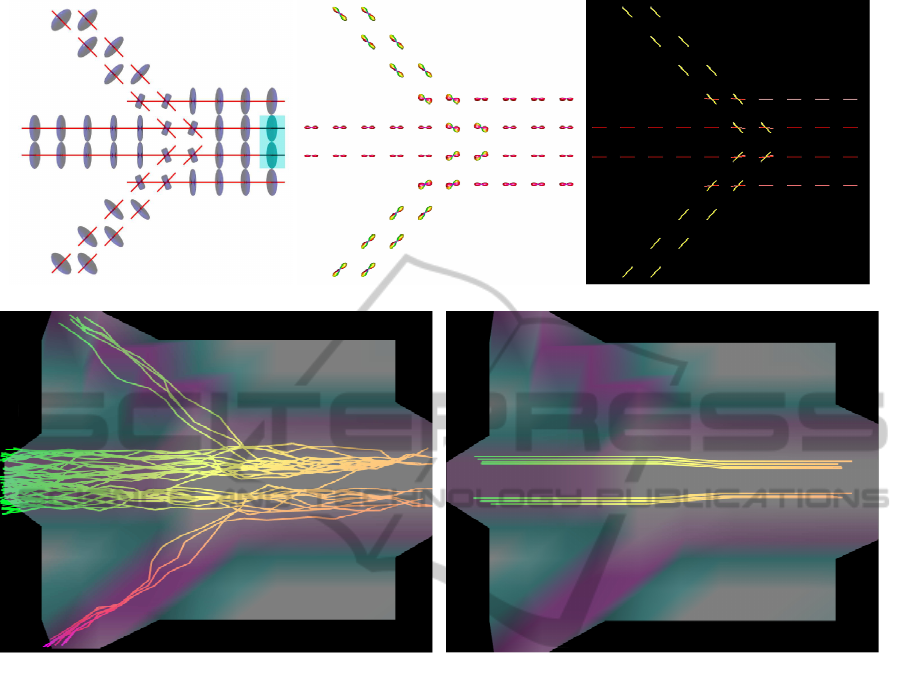
Figure 1(a) shows an example of a simulated dif-
fusion field of crossing bundles, the field of recon-
structed ODF profiles, and the field of estimated prin-
cipal directions. We specified two voxels as seed vox-
els (see the left panel of Figure 1(a)) and applied the
probabilistic SMC algorithm to obtain the tracks rep-
resented in Figure 1(b). The SMC algorithm was ap-
plied with 100 particles and 5 fibers per seed voxel.
For comparison purposes we have also applied a stan-
dard deterministic streamline tracking procedure to
the same simulation. The streamline procedure fol-
lows the tractographic approach outlined in Mori and
van Zijl (Mori and van Zijl, 2002) to map fiber tracts.
As seen in Figure 1(c), the streamline algorithm is
unable to resolve regions of crossing fiber configura-
tions. Typically a single directional path is selected in
these regions. In contrast, the probabilistic method is
able to map multiple fiber pathways in crossing fiber
regions.
3.2 Human Brain Data Experiments
In this Section we report on experiments using a DI-
COM data set provided by the “Advanced Biomedi-
cal MRI Lab, National Taiwan University Hospital”.
Specifically, we have used the data set “DSI 203-point
2mm” publicly available from
http://dsi-studio.
labsolver.org/download-images
. This data set is
from a normal 24-year-old male volunteer, and has
been provided as a demonstration data set in con-
nection with the “DSI Studio” software for diffusion
MR images analysis (Yeh et al., 2010). The data
set was obtained with an echo planar imaging dif-
fusion sequence with twice-refocused echo, dimen-
sion 96 × 96 × 60, and slice thickness 1.9 mm. Fur-
ther details on the data set specification are available
from the internet address mentioned above. We have
tested our model with the two b-tables that accompa-
nies the data set. One is a b-table for a S
2
-like grid
denoted by “dsi203
bmax4000.txt”. The other is the
b-table for the 3D-DSI sampling scheme used in the
DICOM data acquisition. This b-table has 203 points
uniformly distributed on a 3D grid limited to the vol-
ume of the unit sphere. In both tables, the b-values
range from 0 to 4000. The ODF reconstructions were
performed with 321 points uniformly distributed on
the unit S
2
hemisphere.
As for the simulation procedure outlined in Sec-
tion 3.1, we obtained estimates of the voxels’ ODF
profiles using GQI basis functions. To summarize
anisotropic properties of the ODF and infer the un-
derlying crossing patterns of the fibers we used the
GFA metric. A GFA threshold of 0.3 was applied on
the normalized ODFs, prior to vMF clustering esti-
mation. The SMC algorithm was then applied to es-
timate fiber paths. The following is a summary of
tractography results applied to two Regions Of Inter-
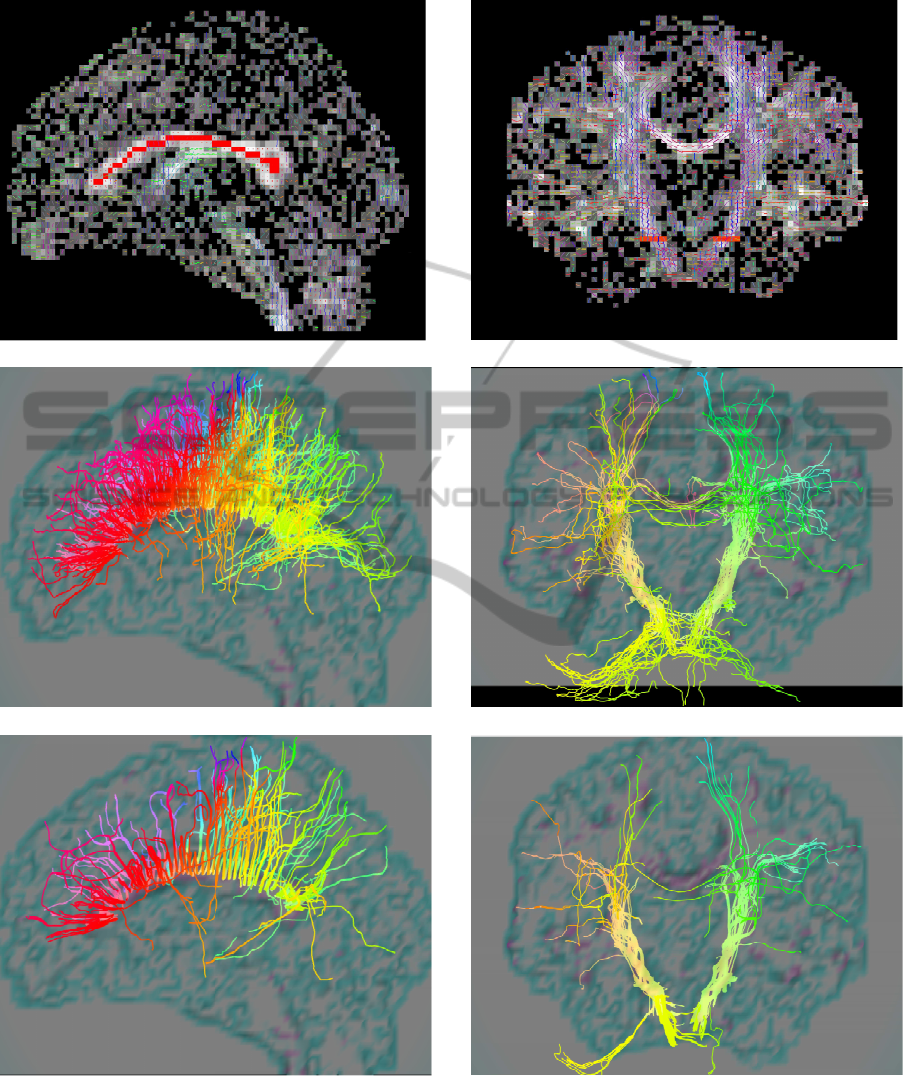
est (ROIs). For the first ROI, 43 seeds were placed
along the Corpus Callosum (CC) region in sagittal
view, as illustrated in Figure 2(a). We then applied the
clustered-vMFs method followed by SMC to track the
ModelingWhite-matterFiber-orientationUncertaintyforImprovedProbabilisticTractography
75
(a)
(b) (c)
Figure 1: (a) Simulated diffusion field with seeds marked in light-blue rectangle (left panel), field of reconstructed ODF
profiles (middle panel), and field of estimated principal directions (right panel); (b) Fiber pathways mapped using the proposed
probabilistic approach; (c) Fiber pathways mapped using a standard streamline approach.
fiber paths from each seed by propagating 150 parti-
cles, for a maximum of 300 steps. Five starting fibers
were randomly placed within each voxel for tracking
initiation. All selected principal diffusion directions
estimated for the seed voxel were tracked. Figure 2(b)
shows tractography results of the corpus callosum for
sagittal slice 48. For comparison purposes, the same
ROI and seeds were used to drive a standard determin-
istic streamline algorithm. Similarly, 5 starting fibers
were randomly placed within each voxel for tracking
initiation. The results are shown in Figure 2(c).
The second ROI used for testing was the corti-
cospinal tract (CST), which connects the spinal cord
to the cerebral motor cortex. Tractographyof the CST
is a challenging task. On the one hand, in some re-
gions of the brain other fascicles may cross with the
CST. On the other hand, the CST itself is made of sev-
eral bifurcating sub-fascicles to ensure connections
with the whole motor cortex. Unsurprisingly, stan-
dard deterministic streamline algorithms fail to map
the CST accurately, because they are unable to cope
with the complexity of bifurcating pathways. Five
seeds used placed on each side of the CST-ROI bun-
dle for coronal slice 53 as illustrated in Figure 3(a).
This figure visualizes the location of the chosen seeds,
by overlaying the GFA image with the first two main
fiber directions at each voxel for coronal slice 53. Fig-
ure 3(b) shows tractography results of the CST for
coronal slice 53 using the proposed approach. Fig-
ure 3(c) shows similar tractography results for the de-
terministic streamline algorithm.
4 CONCLUSIONS
We have presented a methodology to support im-
proved probabilistic tractography in comparison with
currently used approaches. The methodology builds
statistical inferences at each voxel based on clusters
of vMF distributions to drive sequential Monte Carlo
NEUROTECHNIX2014-InternationalCongressonNeurotechnology,ElectronicsandInformatics
76
(a)
(b)
(c)
Figure 2: Corpus Callosum tractography: a) GFA image
with seeds’ locations in red; b) Probabilistic tractography
using the proposed approach; c) Tractography using a stan-
dard streamline algorithm.
(a)
(b)
(c)
Figure 3: CST tractography: a) GFA image with seeds’ lo-
cations in red; b) Probabilistic tractography using the pro-
posed approach; c) Tractography using a standard stream-
line algorithm.
ModelingWhite-matterFiber-orientationUncertaintyforImprovedProbabilisticTractography
77

path estimates. We have shown how the improve-
ment of fiber directional estimates can benefit the
particle filtering tracking process. Moreover, by de-
coupling the two stages, statistical directional esti-
mation and probabilistic fiber tracking, the proposed
methodology is well-suited to support a wide range
of methods for ODF reconstruction. The methodol-
ogy provides a better account of white matter path-
ways in regions with complex fiber configuration than
streamline-oriented approaches. However, compar-
ing results of in vivo fiber tracking is a difficult task
in general. In the future, we intend to test the pro-
posed methodology for performing human brain con-
nectivity analysis. Connectivity networks may pro-
vide alternative validation tools for quantitative com-
parisons.
REFERENCES
Alexander, A. L., Hasan, K. M., Lazar, M., Tsuruda, J. S.,
and Parker, D. L. (2001). Analysis of Partial Vol-
ume Effects in Diffusion-Tensor MRI. Magnetic Res-
onance in Medicine, 45:770–780.
Assaf, Y. and Basser, P. J. (2005). Composite hindered and
restricted model of diffusion (CHARMED) MR imag-
ing of the human brain. NeuroImage, 27(1):48–58.
Banerjee, A., Dhillon, I. S., Ghosh, J., and Sra, S. (2005).
Clustering on the Unit Hypersphere using von Mises-
Fisher Distributions. Journal of Machine Learning
Research, 6:1345–1382.
Behrens, T. E. J., Berg, H. J., Jbabdi, S., Rushworth, M.
F. S., and Woolrich, M. W. (2007). Probabilistic dif-
fusion tractography with multiple fibre orientations:
What can we gain? NeuroImage, 34(1):144–155.
Doucet, A., Godsill, S., and Andrieu, C. (2000). On se-
quential monte carlo sampling methods for bayesian
filtering. Statistics and Computing, 10(3):197–208.
Doucet, A. and Johansen, A. M. (2011). A Tutorial on
Particle Filtering and Smoothing: Fifteen years later.
In Crisan, D. and Rozovsky, B., editors, The Oxford
Handbook of Nonlinear Filtering. Oxford University
Press.
Ferreira da Silva, A. (2012). Facing the Challenge of Es-
timating Human Brain White Matter Pathways. In
Madani, K., Kacprzyk, J., and Filipe, J., editors, Proc.
of the 4th International Joint Conference on Compu-
tational Intelligence, pages 709–714. SciTePress.
Ferreira da Silva, A. (2013). Computational Representa-
tion of White Matter Fiber Orientations. International
Journal of Biomedical Imaging, 2013. Article ID
232143.
Hornik, K. and Gr¨un, B. (2012). Mixtures of von Mises
Fisher Distributions. R package version 0.1-0.
Liu, J. S. (2001). Monte Carlo Strategies in Scientific Com-
puting. Springer Series in Statistics. Springer.
Mardia, K. V. and Jupp, P. (2000). Directional Statistics.
John Wiley and Sons Ltd., 2nd edition.
Mori, S. and van Zijl, P. C. M. (2002). Fiber tracking:
principles and strategies - a technical review. NMR
in Biomedicine, 15:468–480.
Parker, G. and Alexander, D. (2003). Probabilistic Monte
Carlo based mapping of cerebral connections utilis-
ing whole-brain crossing fiber information. In Proc.
IPMI, pages 684–695.
Pontabry, J., Rousseau, F., Oubel, E., Studholme, C., Koob,
M., and Dietemann, J.-L. (2013). Probabilistic trac-
tography using Q-ball imaging and particle filtering:
Application to adult and in-utero fetal brain studies.
Medical Image Analysis, 17(3):297–310.
Rathi, Y., Michailovich, O., Shenton, M. E., and Bouix,
S. (2009). Directional Functions for Orientation
Distribution Estimation. Medical Image Analysis,
13(3):433–444.
Rowe, M. C., Zhang, H. G., Oxtoby, N., and Alexander,
D. C. (2013). Beyond crossing fibers: Tractography
exploiting sub-voxel fibre dispersion and neighbour-
hood structure. In IPMI, pages 402–413.
Schwartz, G. (1979). Estimating the dimension of a model.
Annals of Statistics, 6:461–464.
Seunarine, K. K. and Alexander, D. C. (2009). Multiple fi-
bres: beyond the diffusion tensor. In Johansen-Berg,
H. and Behrens, T. E. J., editors, Diffusion MRI: from
quantitative measurement to in vivo neuroanatomy,
pages 56–74. Academic Press.
Seunarine, K. K., Cook, P. A., Hall, M. G., Embleton, K. V.,
Parker, G. J. M., and Alexander, D. C. (2007). Ex-
ploiting peak anisotropy for tracking through complex
structures. In Proc. 11th IEEE International Confer-
ence on Computer Vision Workshop on MMBIA, Rio
de Janeiro.
Tuch, D. S. (2004). Q-Ball Imaging. Magnetic Resonance
in Medicine, 52:1358–1372.
Tuch, D. S., Reese, T. G., Wiegell, M. R., Makris, N., Bel-
liveau, J. W., and Wedeen, V. J. (2002). High angular
resolution diffusion imaging reveals intravoxel white
matter fiber heterogeneity. Magnetic Resonance in
Medicine, 48:577–582.
Wedeen, V. J., Hagmann, P., Tseng, W.-Y. I., Reese, T. G.,
and Weisskoff, R. M. (2005). Mapping Complex
Tissue Architecture With Diffusion Spectrum Mag-
netic Resonance Imaging. Magnetic Resonance in
Medicine, 54:1377–1386.
Yeh, F.-C., Wedeen, V. J., and Tseng, W.-Y. I. (2010). Gen-
eralized q-Sampling Imaging. IEEE Transactions on
Medical Imaging, 29(9):1626–1635.
Zhang, F., Hancock, E. R., Goodlett, C., and Gerig, G.
(2009). Probabilistic white matter fiber tracking us-
ing particle filtering and von Mises-Fisher sampling.
Medical Image Analysis, 13(1):5–18.
NEUROTECHNIX2014-InternationalCongressonNeurotechnology,ElectronicsandInformatics
78
