
DMQEA: Dual Multiobjective Quantum-inspired Evolutionary
Algorithm
Si-Jung Ryu
1
, Jong-Hwan Kim
1
and Ki-Baek Lee
2
1
Department of Electrical Engineering, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, Daejeon 305-701, Korea
2
Department of Electric Engineering, Kwangwoon University, Seoul 139-701, Korea
Keywords:
Multiobjective evolutionary Algorithm, Quantum-inspired evolutionary algorithm, Preference-based evolu-
tionary Algorithm.
Abstract:
This paper proposes dual multiobjective quantum-inspired evolutionary algorithm (DMQEA) with the dual-
stage of dominance check by introducing secondary objectives in addition to primary objectives. The sec-
ondary objectives are to maximize global evaluation values and crowding distances of the solutions in the
external global population obtained for the primary objectives and the previous archive obtained from the sec-
ondary objectives-based nondominated sorting. By employing the secondary objectives for sorting the solu-
tions in each generation, DMQEA can induce the balanced exploration of the solutions in terms of user’s pref-
erence and diversity to generate preferable and diverse nondominated solutions in the archive. To demonstrate
the effectiveness of the proposed DMQEA, empirical comparisons with MQEA, MQEA-PS, and NSGA-II are
carried out for benchmark functions.
1 INTRODUCTION
Multiobjective evolutionary algorithms (MOEAs) are
designed to solve multiobjective optimization prob-
lems to get Pareto-optimal solutions while maintain-
ing as diverse a distribution as possible. These are
well-known two goals, proximity to Pareto-optimal
front and diversity preservation, in ideal multiobjec-
tive optimization. Much research has been conducted
to enhance the solution quality and diversity (Lau-
manns et al., 2002; Cui et al., 2001; Bosman and
Thierens, 2003; Kim et al., 2009; Deb et al., 2002;
Lee and Kim, 2012).
The other issue is how to select a preferable so-
lution among the widely distributed solutions in the
Pareto-optimal front for the application of the real
world problem. To solve this issue, preference-based
solution selection algorithm (PSSA) was proposed
(Kim et al., 2012). It selects a solution considering
user’s preference for each objective, which is repre-
sented by the fuzzy measures. In PSSA, global eval-
uation value of a candidate solution is calculated by
the fuzzy integral of the partial evaluation values with
respect to the fuzzy measures. The solution with the
highest global evaluation value is selected out of the
candidate solutions.
Based on PSSA, multiobjective quantum-inspired
evolutionary algorithm with preference-based selec-
tion (MQEA-PS) was proposed (Kim et al., 2012).
In each archive generation process, MQEA-PS em-
ploys PSSA in MQEA for preference-based sorting
for the solutions in the external global population and
the previous archive. It means that the nondominated
solutions in the archive are obtained by preference-
based sorting instead of dominance-based sorting,
whereas the internal subpopulations are sorted by fast
nondominated sorting. In this way, the solutions that
reflect user’s preference for each objective can be ob-
tained in the archive. Furthermore, for considering
the diversity of the solutions as well as user’s prefer-
ence, crowding distance sorting after the preference-
based sorting in the archive generation process is de-
veloped (Ryu et al., 2012). However, the solutions are
lack of the proximity to the Pareto front.
In this paper, we propose dual multiobjective
quantum-inspired evolutionary algorithm (DMQEA)
by introducing secondary objectivesin addition to pri-
mary objectives that are given objectives in the prob-
lem. The proposed DMQEA has the dual-stage of
dominance check respectively for the primary and
secondary objectives. In the first stage, the domi-
nated solutions with respect to primary objectives are
culled out by primary objectives-based nondominated
sorting (PONS). In the second stage, nondominated
207
Ryu S., Kim J. and Lee K..
DMQEA: Dual Multiobjective Quantum-inspired Evolutionary Algorithm.
DOI: 10.5220/0005071802070214
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Evolutionary Computation Theory and Applications (ECTA-2014), pages 207-214
ISBN: 978-989-758-052-9
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

sorting is applied for the secondary objectives for
the generation of archive, which is called secondary
objectives-based nondominated sorting (SONS). The
secondary objectives are to maximize global eval-
uation values and crowding distances of the solu-
tions in the previous archive and the external global
population obtained for the primary objectives. The
archive consists of first-tier solutions obtained from
the SONS.
By employing SONS in each generation, DMQEA
can induce the balanced exploration of the solutions
in terms of user’s preference and diversity to pro-
duce preferable and diverse nondominated solutions
in the archive. The effectiveness of the proposed
DMQEA is demonstrated through statistical com-
parisons with MQEA, MQEA-PS, and NSGA-II for
benchmark functions. The experimental results con-
firm that the proposed DMQEA generates the so-
lutions with larger hypervolume while maintaining
user’s preference compared to the existing two algo-
rithms, MQEA and MQEA-PS.
The rest of this paper is organized as fol-
lows: quantum-inspired evolutionary algorithm
(QEA), preference-based solution selection algorithm
(PSSA), and crowding distance are briefly described
in Section II. Section III proposes dual multiobjective
evolutionary algorithm (DMQEA). The experimental
results are presented in Section IV and concluding re-
marks follow in Section V.
2 PRELIMINARIES
2.1 QEA
Quantum-inspired evolutionary algorithm (QEA) is
an evolutionary algorithm, which employs the prob-
abilistic mechanism inspired by the concept and prin-
ciples of quantum computing, such as a quantum bit
and superposition of states (Han and Kim, 2002; Han
and Kim, 2004). Building block of classical digital
computer is represented by two binary states, ‘0’ or
‘1’, which is a finite set of discrete and stable state. In
contrast, QEA utilizes a novel representation, called a
Q-bit representation, for the probabilistic representa-
tion that is based on the concept of qubits in quantum
computing (Hey, 1999). Quantum system enables the
superposition of such state as follows:
α|0i+ β|1i (1)
where α and β are the complex numbers satisfying
|α|
2
+ |β|
2
= 1.
Qubit is shown in Fig. 1, which can be illustrated
as a unit vector on the two dimensional space as fol-
!
!
"!
" #
!
!
"
"
!
" #
!
Figure 1: Qubit described in two-dimensional space.
lows:
α
β
(2)
where |α|
2
+ |β|
2
= 1. Q-bit individual is defined as a
string of Q-bits as follows:
q
t
j
=
α
t
j,m−1
α
t
j,m−2
··· α
t
j,0
β
t
j,m−1
β
t
j,m−2
··· β
t
j,0
(3)
where m is the string length of Q-bit individual, and
j = 1,2,...,n for the population size n. The population
of Q-bit individuals at generation t is represented as
follows:
Q(t) = {q
t
1
,q
t
2
,··· ,q
t
n
}. (4)
Since Q-bit individual represents the linear super-
position of all possible states probabilistically, vari-
ous individuals are generated during the evolution-
ary process. The procedure of QEA and the over-
all structure for single-objective optimization prob-
lems are described in (Han and Kim, 2002). To solve
multiobjective optimization problems, multiobjective
quantum-inspired evolutionary algorithm (MQEA) is
also developed (Kim et al., 2006).
2.2 PSSA
Preference-based solution selection algorithm
(PSSA) selects a solution among the obtained non-
dominated solutions considering user’s preference
(Kim et al., 2012). The nondominated solutions
cannot be directly compared against each other, and
therefore a multicriteria decision making (MCDM)
algorithm is required to evaluate them. In PSSA,
the global evaluation value of a candidate solution is
calculated by the fuzzy integral, as an MCDM algo-
rithm, of the partial evaluation values with respect to
the fuzzy measures. The fuzzy measures represent
the degrees of consideration for objectives, and
the partial evaluation value indicates a normalized
objective function value. Overall procedure of global
evaluation is summarized in Algorithm 1. Each step
ECTA2014-InternationalConferenceonEvolutionaryComputationTheoryandApplications
208

in the algorithm is briefly described in the following
and detail procedure of global evaluation is described
in (Kim et al., 2012). 1. Calculate λ-fuzzy Measures
Objectives are defined as criteria in multi-
objective problem. λ-fuzzy measure represents the
degree of consideration for each criterion. To get the
values of λ-fuzzy measures, a pairwise comparison
matrix (P) is initially defined by user for represent-
ing preference degrees between criteria. Secondly,
the normalized weights of P are calculated by adding
each value in the row of the pairwise comparison ma-
trix and dividing it by the total sum of the values in
the row. Lastly, λ-fuzzy measures are obtained using
the normalized weights (Bajwa et al., 2008).
2. Compute Global Evaluation Value
First, the value of partial evaluation of each solu-
tion is calculated by normalizing the objective func-
tion value to 1. Global evaluation of each and every
solution is performed by the Choquet fuzzy integral
of the partial evaluation values with respect to the λ-
fuzzy measures, which are obtained from the previous
steps.
Algorithm 1: Procedure of global evaluation.
• l: No. of the solutions
• m: No. of the objectives
• C: A set of objectives C = {c
1
,c
2
,...,c
m
}
• P: A power set of C
• f
j
(x
k
): j-th Objective value of x
k
• h
j
(x
k
): j-th partial evaluation value of x
k
• e(x
k
): Global evaluation value of x
k
—————————————————————
1. Calculate λ-fuzzy measures g’s of P(C)
1: Make a pairwise comparison matrix P
2: Calculate normalized weights of
3: Calculate λ-fuzzy measures of P(C).
2. Compute global evaluation value e
1: for k = 1 to l do
2: for j = 1 to m do
3: h
j
(x
k
) = Normalize(f
j
(x
k
))
4: end for
5: end for
6: for k = 1 to l do
7: e(x
k
) =
R
h◦g
8: end for
2.3 Crowding Distance
The crowding distance estimates the density of solu-
tions surrounding a particular solution in the popu-
lation (Deb et al., 2002). The crowding distance is
aimed to uniformly select the solutions in the front,
making the solutions in the most dense areas less
likely to be selected. The crowding distance is de-
fined by the average distance of the closest points on
either side of the point for each objective. Therefore,
the crowding distance is inversely proportional to the
density of solutions. Boundary points for each objec-
tive have the maximum crowding distance, and they
are always selected. Calculation of crowding distance
is described in Algorithm 2.
Algorithm 2: Crowding distance assignment.
• l: No. of the solutions
• m: No. of the objectives
• f
j
(x
k
): j-th objective value of x
k
• x
k
.CD: Crowding distance of the solution x
k
—————————————————————
1. Initialization
1: for k = 1 to l do
2: x
k
.CD = 0
3: end for
2. Calculate the crowding distances
1: for j = 1 to m do
2: for k = 1 to l do
3: Calculate the objective value f
j
(x
k
)
4: end for
5: Sort the solutions using objective value
f
j
(x
k
), x
k
= sort(x
k
)
6: x
1
.CD = x
l
.CD = ∞
7: for k = 2 to l −1 do
8: x
k
.CD = x
k
.CD+ |f
j
(x
k+1
) − f
j
(x
k−1
)|
9: end for
10: end for
3 DMQEA
Dual multiobjective quantum-inspired evolutionary
algorithm (DMQEA) has the dual-stage of domi-
nance check for the primary and secondary objec-
tives. Primary objectives are the given objectives of
the problem. The secondary objectives are to maxi-
mize both the global evaluation values and crowding
distances of the solutions in the external global pop-
ulation obtained for the primary objectives and the
DMQEA:DualMultiobjectiveQuantum-inspiredEvolutionaryAlgorithm
209
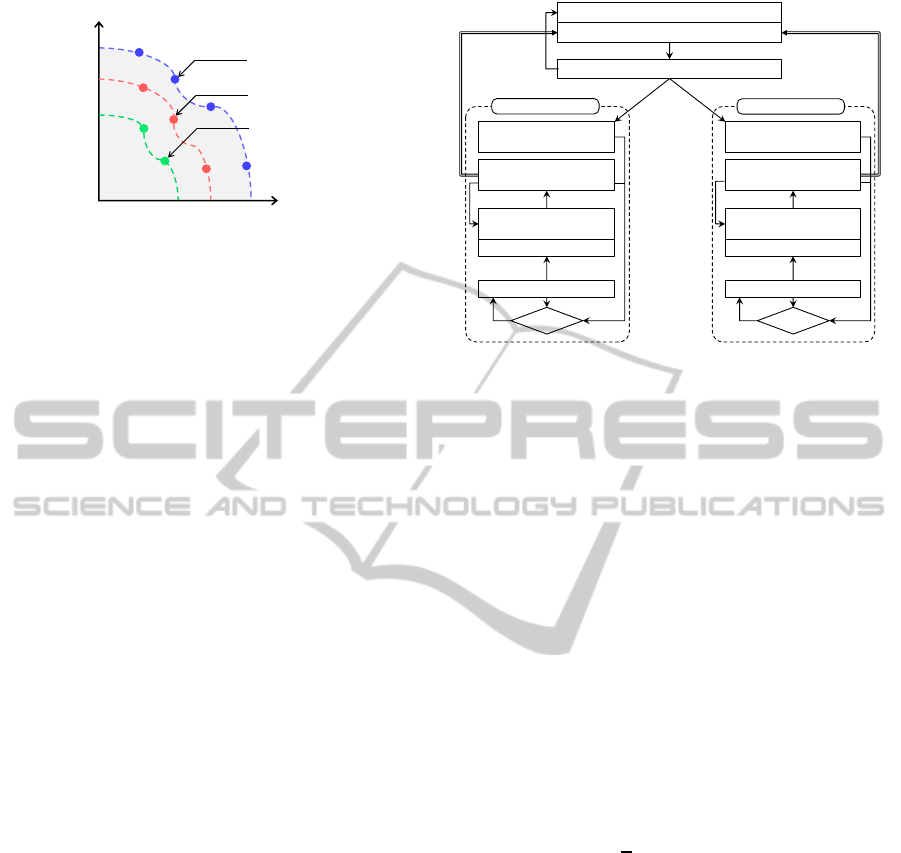
Crowding distance
Solution in tier 1
Solution in tier 2
Solution in tier 3
Global evaluation value
Figure 2: Secondary objectives-based nondominated sort-
ing.
previous archive. In each archive generation process,
the secondary objectives are employed for sorting
the solutions, which is called secondary objectives-
based nondominated sorting (SONS). By the pro-
posed SONS, the archive stores first-tier solutions.
3.1 SONS
SONS is to sort the solutions with the secondary ob-
jectives for maximizing the global evaluation value
(GEval) and crowding distance (CD). The SONS is
performed for the solutions in the external global pop-
ulation obtained for the primary objectives and the
previous archive. It means that in DMQEA, the solu-
tions are sorted by SONS that checks the dominance
relationship with respect to GEval and CD. By SONS,
the solutions that are not dominated by any other so-
lutions could be obtained as first-tier solutions that are
stored in the archive.
The proposed SONS is depicted in Fig. 2. GEval
and CD of every solution in the external global pop-
ulation and the previous archive are calculated as ex-
plained in the previous section. Note that the global
evaluation value of a solution is calculated by the
fuzzy integral of the partial evaluation values with re-
spect to the fuzzy measures representing the user’s
preference for objectives. The solutions with higher
values of GEval and CD are better in terms of user’s
preference and diversity. For example, in the figure,
blue points are classified as first-tier solutions to be
stored in the archive. The solutions in lower tiers are
discarded because they are dominated by the first-tier
solutions.
3.2 Procedure of DMQEA
In an archive generation process, MQEA employs
dominance-basedsorting for primary objectivesof the
solutions in the external global population and the
previous archive. Most of them are nondominated by
the other solutions because primary objectives-based
Previous archive ( − 1)
SONS
Reference
subpopulation
()
Previous higher-tier
subpopulation
( − 1)
Binary subpopulation
()
Q-bit subpopulation
()
Q-gate
1
st
subpopulation
PONS
Update
Multiple
observations
Reference
subpopulation
()
Previous higher-tier
subpopulation
( − 1)
Binary subpopulation
()
Higher-tier
subpopulation
()
Q-bit subpopulation
()
Q-gate
s
th
subpopulation
Update
Multiple
observations
Global population ()
Global
random migration
. . .
Archive ()
Higher-tier
subpopulation
()
PONS
Figure 3: Overall procedure of DMQEA, where PONS: Pri-
mary objectives-based nondominated sorting, SONS: Sec-
ondary objectives-based nondominated sorting.
nondominated sorting (PONS) or fast nondominated
sorting is already performed in each subpopulation. It
means that the dominance-based sorting for the pri-
mary objectives might be an ineffective operation in
selecting solutions to be stored in the archive. In-
deed, in experiments, the external global population
almost consists of nondominated solutions. To solve
this problem, DMQEA employs SONS in the archive
generation process. By SONS, each solution is clas-
sified into the corresponding tier and the solutions in
the first tier are stored in the archive. These are used
for reference solutions through the global random mi-
gration process. The overall procedure of DMQEA is
summarized in Algorithm 3, and depicted in Fig. 3.
Each step is described in detail in the following.
1. Initialize Q
k
(t) and Generate Archive A(t)
Q
k
(0) including q
0
j
, which consists of α
0
ji
and β
0
ji
, is
initialized with 1/
√
2, where i = 0,1,...,m − 1, j =
1,2,...,n, and k = 1, 2,...,s. Note that m is the string
length of Q-bit individual, n is the subpopulation size,
and s is the number of subpopulations. It means that
one Q-bit individual, q
0
j
, represents the linear super-
position of all possible states with same probabil-
ity. Binary solutions in P
k
(0) are produced by mul-
tiple observing the states of Q
k
(0), where P
k
(0) =
{x
0
1
,x
0
2
,...,x
0
n
} and x
0
j
= {x
0
j,m−1
,x
0
j,m−2
,...,x
0
j0
}, j =
1,2,...,n. A bit of one binary solution, x
0
ji
, has a value
either ‘0’ or ‘1’ according to the probability either
|α
0
ji
|
2
or |β
0
ji
|
2
, where i = 0,1, ..., m−1, j = 1,2,...,n,
as follows:
x
0
ji
=
0 if rand[0,1] ≥ |β
0
ji
|
2
1 if rand[0,1] < |β
0
ji
|
2
.
(5)
Multiple observation is performed on each and
ECTA2014-InternationalConferenceonEvolutionaryComputationTheoryandApplications
210

Algorithm 3: Procedure of DMQEA.
• P
k
(t) = {x
t
1
,x
t
2
,...,x
t
n
}
• x
t
j
= {x
t
j,m−1
,x
t
j,m−2
,...,x
t
j0
}
• Q
k
(t) = {q
t
1
,q
t
2
,··· ,q
t
n
}
• q
t
j
=
α
t
j,m−1
α
t
j,m−2
··· α
t
j,0
β
t
j,m−1
β
t
j,m−2
··· β
t
j,0
• R
k
(t) = {r
t
1
,r
t
2
,...,r
t
n
}
• s = No. of subpopulations
• n = Size of subpopulation
• m = Q-bit string length
—————————————————————
1. Initialize Q
k
(t) and generate archive A(t)
1: t = 0
2: for k = 1 to s do
3: for j = 1 to n do
4: for i = 0 to m−1 do
5: α
t
ji
= β
t
ji
= 1/
√
2
6: end for
7: Make P
k
(t) by multiple observing the states
of Q
k
(t)
8: for each objective do
9: Evaluate the objective value from x
t
j
10: end for
11: Copy all solutions in P
k
(t) into P(t)
12: Store first-tier solutions of P(t) by SONS in
the archive A(t)
13: end for
14: end for
2. Generate global population P(t)
1: t = t + 1
2: for k = 1 to s do
3: for j = 1 to n do
4: Make P
k
(t) by multiple observing the states
of Q
k
(t)
5: for each objective do
6: Evaluate the objective value from x
t
j
7: end for
8: end for
9: Run PONS for P
k
(t) ∪ B
k
(t −1)
10: Store n higher-tier solutions of P
k
(t) ∪B
k
(t −1)
into B
k
(t)
11: end for
12: Store all solutions in every B
k
(t) into P(t)
3. Update archive A(t)
1: for each solution in A(t −1) ∪P(t) do
2: Evaluate GEval and CD
3: end for
4: Run SONS
5: Store the first-tier solutions into the archive A(t)
every Q-bit individual in subpopulations, q
0
j
in
Q
k
(0), k = 1,2,...,s. Each binary solution in P
k
(0)
4. Migrate and update Q
k
(t)
1: for k = 1 to s do
2: for j = 1 to n do
3: Select a solution in A(t) randomly
4: Store it into r
t
j
5: Update q
t
j
using Q-gates referring to the
solutions in r
t
j
6: end for
7: end for
5. Go back to Step 2 and repeat
is decoded to a real number if necessary, and its
objective value is calculated. All solutions in each
binary subpopulation P
k
(0) are copied to the external
global population P(0) and store first tier solutions of
P(0) by SONS in the archive A(t).
2. Generate Global Population P(t)
Binary solutions are generated by multiple obser-
vations of Q-bit individuals in Q-bit subpopulation
Q
k
(t). Each bit of binary solution x
t
jl
, l = 1,2,...,o,
where o is the observation index is obtained. x
t
j
is assigned by the best among the observed binary
solutions x
t
jl
, l = 1,2,...,o, from the multiple ob-
servations. And then, evaluation is performed to
P
k
(t), where k = 1,2,...,s. Therefore, objective
values of all solutions in each subpopulation are
obtained. The solutions in the previous higher-tier
subpopulation and the current binary subpopulation
P
k
(t) ∪ B
k
(t − 1) are sorted by PONS to select n
solutions in order from the first tier to the lower
tiers. The n higher-tier solutions form B
k
(t), where
B
k
(t) = {b
t
1
,b
t
2
,...,b
t
n
} that is to become the previous
higher-tier subpopulation in the next generation. To
update Q-bit individuals corresponding to higher-tier
subpopulation later, Q-bit subpopulation Q
k
(t) is
rearranged by replacing each q
t
j
in the subpopulation
by the Q-bit individual that has generated b
t
j
. All
higher-tier solutions in each subpopulation B
k
(t) are
copied to the external global population P(t).
3. Update Archive A(t)
Global evaluation values are calculated by the
fuzzy integral and crowding distance is also cal-
culated. The fuzzy integral reflects how much a
user prefers the solution, and crowding distance
denotes the density of the solutions. SONS with
GEval and CD for the solutions in the external global
population and the previous archive is performed.
The nondominated solutions in the first tier are stored
into the archive A(t). The size of the archive might
be different each generation.
DMQEA:DualMultiobjectiveQuantum-inspiredEvolutionaryAlgorithm
211

4. Migrate and Update Q
k
(t)
The solutions in the archive A(t) are randomly
selected n times and they are globally migrated to
each reference subpopulation R
k
(t), where R
k
(t) =
{r
t
1
,r
t
2
,...,r
t
n
}. Note that the solutions in R
k
(t) are
employed as references to update Q-bit individuals,
each of which is corresponding to the solution in the
higher-tier subpopulation. Global random migration
procedure occurs at every generation. In the update
process of Q-bit individuals, the rotation gate is em-
ployed. r
t
j
and b
t
j
in each subpopulation are compared
bit-by-bit to decide the update directions of Q-bit in-
dividuals in the rotation gate U(∆θ), which is defined
as follows:
q
t
j
= U(∆θ) ·q
t−1
j
(6)
with
U(∆θ) =
cos(∆θ) –sin(∆θ)
sin(∆θ) cos(∆θ)
where ∆θ is the rotation angle of each Q-bit as shown
in Fig. 1. Note that crossover and mutation operators
are not used in QEA.
5. Go back to Step 2 and Repeat
Go back to Step 2 and repeat until a termination
condition is satisfied.
4 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
4.1 Experimental Settings
The proposed DMQEA was compared with MQEA,
MQEA-PS, and NSGA-II. To evaluate the perfor-
mance of algorithms, we employed seven DTLZ func-
tions as benchmark functions. The number of vari-
ables for each DTLZ function was set to 9 for DTLZ1,
16 for DTLZ2 to DTLZ6, and 26 for DTLZ7. Param-
eters for DMQEA, MQEA-PS, MQEA, and NSGA-II
were equally set and given in Table 1. Belief mea-
sure (ξ = 0.25) for MQEA-PS and DMQEA was used.
As the preferred objectives, two objectives among the
five objectives in DTLZ functions were selected. The
preference degrees or the degrees of consideration for
five objectives was set as f
1
: f
2
: f
3
: f
4
: f
5
= 1 : 10 :
1 : 10 : 1. The normalized weights from the pairwise
comparison matrix were calculated as (0.0435, 0.435,
0.0435, 0.435, 0.0435).
4.2 Performance Metrics
Two performance metrics, the size of dominated
space and the diversity, were employed to evaluate
Table 1: Parameter setting of MQEA, MQEA-PS, and
DMQEA for DTLZ functions
Algorithms Parameters Values
MQEA,
MQEA-PS,
DMQEA
The population size (N = n·s) 100
No. of generations 3000
Subpopulation size(n) 25
No. of subpopulations (s) 4
No. of multiple observations 10
The rotation angle (∆θ) 0.23π
NSGA-II
The population size (N) 100
No. of generations 3000
Mutation probability 0.1
the performances of MQEA, MQEA-PS, DMQEA,
and NSGA-II (Zitzler, 1999). The size of dominated
space,
~
S , is defined by the hypervolume of the finally
obtained global population. The quality of the ob-
tained global population is high if this space is large.
The diversity,
~
D, is to evaluate the spread of nondom-
inated solutions, which is defined as follows (Li et al.,
2004):
~
D =
∑
n
k=1
( f
(max)
k
− f
(min)
k
)
q
1
|N
0
|
∑
|N
0
|
i=1
(d
i
−
¯
d)
2
(7)
where N
0
is the set of nondominated solutions, d
i
is
the minimal distance between the i-th solution and
the nearest neighbor, and
¯
d is the mean value of all
d
i
. f
(max)
k
and f
(min)
k
represent the maximum and min-
imum objective function values of the k-th objective,
respectively. A larger value means a better diversity
of the nondominated solutions.
4.3 Results
The proposed DMQEA generated the optimized so-
lutions concentrated on the selected preferred objec-
tives, f
2
and f
4
. The hypervolume and diversity of
MQEA, MQEA-PS, DMQEA, and NSGA-II are sum-
marized in Tables 2. The results in Table 2 are aver-
aged ones by repeating the simulation 50 times.
For statistical analysis, t-test was employed to sta-
tistically compare the performance metrics of algo-
rithms. The t-test is a statistical hypothesis test in
which the test statistic follows a t distribution if the
null hypothesis H
0
is supported. If the null hypothesis
H
0
is rejected, the alternative hypothesis is supported.
t-test was used to determine whether two comparison
groups were significantly different from each other.
The t-test was carried out with the two-tailed test. Ta-
bles 3 showt-value(and p-value) for the hypervolume
with MQEA, MQEA-PS, and NSGA-II.
As shown in Table 3, the proposed DMQEA had
larger hypervolume than MQEA for DTLZ1, DTLZ3,
DTLZ6, and DTLZ7. For the fair comparison of hy-
pervolume, the size of the obtained global populations
ECTA2014-InternationalConferenceonEvolutionaryComputationTheoryandApplications
212
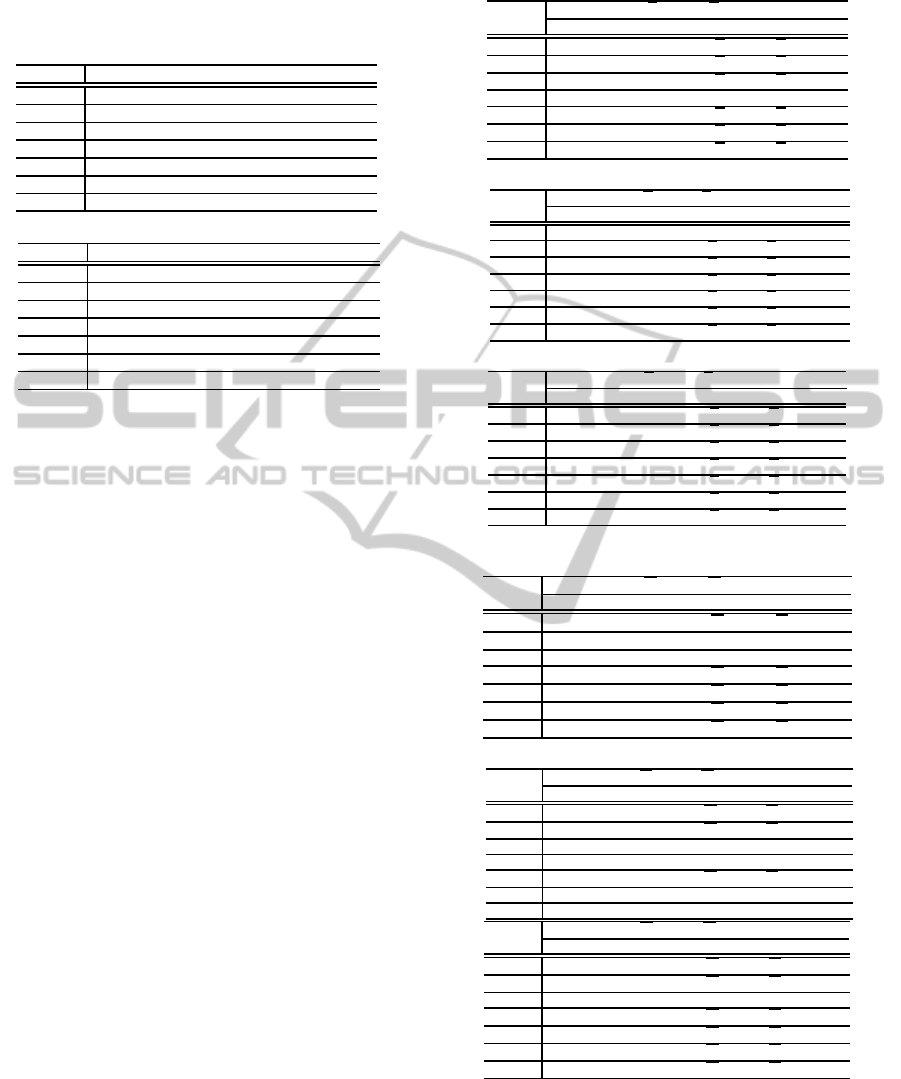
Table 2: Comparisons of hypervolume and diversity among
MQEA, MQEA-PS, and DMQEA for seven DTLZ func-
tions.
(a) Average hypervolume of nondominated solutions
Problem NSGA-II MQEA MQEA-PS DMQEA
DTLZ1 99999 99255 99740 99748
DTLZ2 99998 99796 97139 99202
DTLZ3 66773 N/A 71911 79015
DTLZ4 99999 95119 92309 94898
DTLZ5 99158 98578 95877 98388
DTLZ6 96169 67967 89411 72915
DTLZ7 63202 10907 38574 40500
(b) Average diversity of nondominated solutions
Problem NSGA-II MQEA MQEA-PS DMQEA
DTLZ1 103.95 144.99 92.13 75.99
DTLZ2 132.95 71.05 93.96 79.19
DTLZ3 104.36 55.05 60.93 52.73
DTLZ4 132.53 80.62 105.24 137.61
DTLZ5 179.29 129.39 278.32 139.29
DTLZ6 143.12 73.35 65.26 63.46
DTLZ7 164.78 115.96 136.27 135.55
for three algorithms are set to the same value. In com-
parison with MQEA-PS, DMQEA had larger hyper-
volume for all DTLZ functions except for DTLZ1 and
DTLZ6. It means DMQEA found more optimized so-
lutions close to the Pareto-optimal front. However,
in comparison with NSGA-II, DMQEA had better
performance only for DTLZ3. This is because the
proposed DMQEA generated the optimized solutions
concentrated on the selected preferred objectives, f
2
and f
4
. Due to the property of the hypervolume,
DMQEA that generates the dense solutions in a small
region has a lower value of hypervolume compared to
NSGA-II for DTLZ1, DTLZ2, DTLZ5.
Table 4 shows the result for the diversity and Ta-
ble 5 presents average objective values of preferred
solutions finally selected by PSSA among the solu-
tions obtained from MQEA-PS and DMQEA, respec-
tively. As Table 4 shows, DMQEA has a lower value
of diversity compared with MQEA, MQEA-PS, and
NSGA-II, and Table 5 shows DMQEA generated the
solutions that effectively reflect preferred objectives.
It means that DMQEA could generate the solutions
emphasized on preference objectives, f
2
, f
4
in dense
area. In other word, the proposed DMQEA could find
more optimized solutions for the preferred objectives
compared with the other algorithms.
5 CONCLUSION
In this paper, dual multiobjective quantum-inspired
evolutionary algorithm (DMQEA) was proposed by
introducing secondary objectives in addition to pri-
mary objectives. The proposed DMQEA had the
dual-stage of dominance check for the primary and
Table 3: The hypothesis test on S of the three algorithms
H
0
: S
DMQEA
−S
MQEA
= 0
t-value (p-value) Reject H
1
DTLZ1 6.731 (0.000) NO S
DMQEA
−S
MQEA
> 0
DTLZ2 -14.524 (0.000) YES S
DMQEA
−S
MQEA
< 0
DTLZ3 67.767 (0.000) YES S
DMQEA
−S
MQEA
> 0
DTLZ4 -0.557 (0.580) NO N/A
DTLZ5 -7.233 (0.000) YES S
DMQEA
−S
MQEA
< 0
DTLZ6 8.871 (0.000) YES S
DMQEA
−S
MQEA
> 0
DTLZ7 57.875 (0.000) YES S
DMQEA
−S
MQEA
> 0
H
0
: S
DMQEA
−S
MQEA-PS
= 0
t-value (p-value) Reject H
1
DTLZ1 0.252 (0.802) NO N/A
DTLZ2 15.134 (0.000) YES S
DMQEA
−S
MQEA-PS
> 0
DTLZ3 3.367 (0.001) YES S
DMQEA
−S
MQEA-PS
> 0
DTLZ4 6.287 (0.000) YES S
DMQEA
−S
MQEA-PS
> 0
DTLZ5 12.742 (0.000) YES S
DMQEA
−S
MQEA-PS
> 0
DTLZ6 -37.855 (0.000) YES S
DMQEA
−S
MQEA-PS
< 0
DTLZ7 6.709 (0.000) YES S
DMQEA
−S
MQEA-PS
> 0
H
0
: S
DMQEA
−S
NSGA-II
= 0
t-value (p-value) Reject H
1
DTLZ1 -10.460 (0.800) YES S
DMQEA
−S
NSGA-II
< 0
DTLZ2 -17.689 (0.000) YES S
DMQEA
−S
NSGA-II
< 0
DTLZ3 4.771 (0.000) YES S
DMQEA
−S
NSGA-II
> 0
DTLZ4 -25.450 (0.000) YES S
DMQEA
−S
NSGA-II
< 0
DTLZ5 -31.727 (0.000) YES S
DMQEA
−S
NSGA-II
< 0
DTLZ6 -160.96 (0.000) YES S
DMQEA
−S
NSGA-II
< 0
DTLZ7 -136.51 (0.000) YES S
DMQEA
−S
NSGA-II
< 0
Table 4: The hypothesis test on D of the three algorithms.
H
0
: D
DMQEA
−D
MQEA
= 0
t-value (p-value) Reject H
1
DTLZ1 -5.966 (0.000) YES D
DMQEA
−D
MQEA
< 0
DTLZ2 9.492 (0.000) YES D
DMQEA
−D
MQEA
> 0
DTLZ3 -0.445 (0.658) NO N/A
DTLZ4 3.794 (0.000) YES D
DMQEA
−D
MQEA
> 0
DTLZ5 3.328 (0.002) YES D
DMQEA
−D
MQEA
> 0
DTLZ6 -10.177 (0.000) YES D
DMQEA
−D
MQEA
< 0
DTLZ7 3.439 (0.001) YES D
DMQEA
−D
MQEA
> 0
H
0
: D
DMQEA
−D
MQEA-PS
= 0
t-value (p-value) Reject H
1
DTLZ1 -2.959 (0.004) YES D
DMQEA
−D
MQEA-PS
< 0
DTLZ2 -11.512 (0.000) YES D
DMQEA
−D
MQEA-PS
< 0
DTLZ3 -2.002 (0.051) NO N/A
DTLZ4 1.997 (0.051) NO N/A
DTLZ5 -9.052 (0.000) YES D
DMQEA
−D
MQEA-PS
< 0
DTLZ6 -0.644 (0.522) NO N/A
DTLZ7 -0.119 (0.906) NO N/A
H
0
: D
DMQEA
−D
NSGA-II
= 0
t-value (p-value) Reject H
1
DTLZ1 -3.871 (0.000) YES D
DMQEA
−D
NSGA-II
< 0
DTLZ2 -63.8581 (0.000) YES D
DMQEA
−D
NSGA-II
< 0
DTLZ3 1.773 (0.082) NO N/A
DTLZ4 4.527 (0.000) YES D
DMQEA
−D
NSGA-II
< 0
DTLZ5 -4.076 (0.000) YES D
DMQEA
−D
NSGA-II
< 0
DTLZ6 -65.703 (0.000) YES D
DMQEA
−D
NSGA-II
< 0
DTLZ7 -6.241 (0.000) YES D
DMQEA
−D
NSGA-II
< 0
secondary objectives. The secondary objectives are
to maximize global evaluation values and crowding
distances of the solutions. The global evaluation of
a solution was carried out by the fuzzy integral of
the partial evaluation values with respect to the fuzzy
DMQEA:DualMultiobjectiveQuantum-inspiredEvolutionaryAlgorithm
213

Table 5: The objective function values of preferred solu-
tions each selected by PSSA among the solutions obtained
from MQEA-PS and DMQEA, respectively.
(a) Average objective values of a preferred so-
lution finally selected by PSSA among the solu-
tions obtained from MQEA-PS
f
1
f
2
f
3
f
4
f
5
DTLZ1 0.0599 0.0002 0.1402 0.0002 0.4596
DTLZ2 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 1.0000
DTLZ3 0.0021 0.0002 0.0027 0.1232 5.5938
DTLZ4 1.0000 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 1.0000
DTLZ5 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 1.0000
DTLZ6 0.0002 0.0002 0.0002 0.0003 1.8851
DTLZ7 0.6302 0.0022 0.6022 0.0005 9.2351
(b) Average objective values of a preferred so-
lution finally selected by PSSA among the solu-
tions obtained from DMQEA
f
1
f
2
f
3
f
4
f
5
DTLZ1 0.0685 0.0005 0.1401 0.0005 0.5994
DTLZ2 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 1.0003
DTLZ3 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 4.4475
DTLZ4 1.0251 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 1.0000
DTLZ5 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 1.0001
DTLZ6 0.0004 0.0002 0.0004 0.0006 4.1782
DTLZ7 0.1235 0.0017 0.3517 0.0026 10.7801
measures representing user’s preference for objec-
tives. By employing the secondary objectives-based
nondominated sorting in each archive generation pro-
cess, DMQEA could generate the preferable and di-
verse solutions. For the performance comparisons
among MQEA, MQEA-PS, DMQEA, and NSGA-
II, seven DTLZ functions were used as benchmark
functions, and hypervolume and diversity were em-
ployed as performance metrics. The experimental re-
sults confirmed that the proposed DMQEA was able
to generate more optimized solutions for the preferred
objectives compared with the other algorithms.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by the Technology Innova-
tion Program, 10045252, Development of robot task
intelligence technology, funded by the Ministry of
Trade, Industry & Energy (MOTIE, Korea).
REFERENCES
Bajwa, G., Choo, E., and Wedley, W. (2008). Effectiveness
analysis of deriving priority vectors from reciprocal
pairwise comparison matrices. Asia-Pacific Journal
of Operational Research, 25(3):279–299.
Bosman, P. A. and Thierens, D. (2003). The bal-
ance between proximity and diversity in multiobjec-
tive evolutionary algorithms. evolutionary computa-
tion. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computa-
tion, 7(2):174–188.
Cui, X., Li, M., and Fang, T. (2001). Study of population di-
versity of multiobjective evolutionary algorithm based
on immune and entropy principles. In Proc. of IEEE
Congress on Evolutionary Computation, pages 1316–
1321.
Deb, K., Pratap, A., Agarwal, S., and Meyarivan, T. (2002).
A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm:
Nsga-ii. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Compu-
tation, 6(2):182–197.
Han, K.-H. and Kim, J.-H. (2002). Quantum-inspired evo-
lutionary algorithm for a class of combinatorial opti-
mization. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Com-
putation, 6(6):580–593.
Han, K.-H. and Kim, J.-H. (2004). Quantum-inspired evo-
lutionary algorithms with a new termination criterion,
hε gate, and two phase scheme. IEEE Transactions on
Evolutionary Computation, 8(2):156–169.
Hey, T. (1999). Quantum computing: an introduction. Com-
puting and Control Engineering Journal, 10(3):105–
112.
Kim, J.-H., Han, J.-H., Kim, Y.-H., Choi, S.-H., and Kim,
E.-S. (2012). Preference-based solution selection
algorithm for evolutionary multiobjective optimiza-
tion. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computa-
tion, 16(1):20–34.
Kim, J.-H., Kim, Y.-H., Choi, S.-H., and Park, I.-W.
(2009). Evolutionary multi-objective optimization in
robot soccer system for education. IEEE Computa-
tional Intelligence Magazine, 4(1):31–41.
Kim, Y.-H., Kim, J.-H., and Han, K.-H. (2006). Quantum-
inspired multiobjective evolutionary algorithm for
multiobjective 0/1 knapsack problems. In Proc. of
IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, pages
2601–2606.
Laumanns, M., Thiele, L., Deb, K., and Zitzler, E. (2002).
Combining convergence and diversity in evolutionary
multiobjective optimization. IEEE Transactions on
Evolutionary Computation, 10(3):263–282.
Lee, K.-B. and Kim, J.-H. (2012). Multiobjective particle
swarm optimization with preference-based sort and its
application to path following footstep optimization for
humanoid robots. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary
Computation, 17(6):755–766.
Li, H., Zhang, Q., Tsang, E., and Ford, J. (2004). Hy-
brid estimation of distribution algorithm for multiob-
jective knapsack problem. Evolutionary Computation
in Combinatorial Optimization, pages 145–154.
Ryu, S.-J., Lee, K.-B., and Kim, J.-H. (2012). Improved
version of a multiobjective quantum-inspired evolu-
tionary algorithm with preference-based selection. In
Proc. of IEEE World Congress on Computational In-
telligence, pages 1672–1678.
Zitzler, E. (1999). Evolutionary algorithms for multi-
objective optimization: methods and applications.
Berichte aus der Informatik, Shaker Verlag, Aachen-
Maastricht.
ECTA2014-InternationalConferenceonEvolutionaryComputationTheoryandApplications
214
