
A Performance Evaluation Model of a Job Title using Fuzzy
Approach
Hatice Esen, Tuğçen Hatipoğlu and Ali İhsan Boyacı
Department of Industrial Engineering, Kocaeli University, Umuttepe, Kocaeli, Turkey
Keywords: Human Resources Management, Performance Evaluation, Fuzzy Logic.
Abstract: Performance evaluation is described as comparing the performance of workers and the work standards and
handling the necessary activities in a systematic way to attain these standards. What makes performance
measure a necessity is its focus on performance of personnel as an objective measure of whether the
company goes in the correct direction or not. This is because the most important problem encountered in
organizations is the difficulty in the determination of how successful the personnel are in the satisfaction of
their duties and what are their capabilities in their jobs. Besides performance evaluation is a decision
making process which involves uncertainty. To overcome the uncertainty and evaluate the workers
performance objectively, a performance evaluation model is developed of which the criteria are defined as
the fuzzy numbers and the linguistic variables. The scope of the study is to determine the performance
evaluation criteria of a purchasing specialist and weight for evaluating this job title.
1 INTRODUCTION
Human resource management is associated with a
larger productivity and efficiency, better customer
service, increased firm value, profitability and
organizational survival (Stavrou et al., 2007).
Performance evaluation, one of the most important
tools of modern human resource management, is a
crucial management process for both personnel and
organization. In performance evaluation, the aim is
to understand the current situation of an individual
and organization and react according to this
situation. As shown in a research, performance
evaluation information is used specifically in four
area; decisions demanding inter-personal
comparisons (salary determination, promotion etc.),
decisions demanding personal comparison
(feedback, personal educational need, etc.),
decisions orientated to the continuation of the
system (target determination, human force planning,
etc.) and documentation (Gürbüz and Albayrak,
2014).
What makes performance measure a necessity is
its focus on performance of personnel as an
objective measure of whether the company goes in
the correct direction or not. This is because the most
important problem encountered in organizations is
the difficulty in the determination of how successful
the personnel are in the satisfaction of their duties
and what are their capabilities in their jobs. Every
worker has different expectations from the future,
senses of duty, capabilities, knowledge and talent,
and working discipline. These differences caused by
the nature of human separate the performances of
them as well. Some personnel can completely satisfy
the duties expected from them while some can not.
Thus, managers want to know the capabilities of the
personnel under their order and their success in their
jobs. Because of that, to monitor whether the
personnel work in accordance with the targets
determined, the performance evaluation criteria are
required (Kılıç, 2011).
Performance evaluation criteria generally depend
on the individual’s characteristics, behavioral
criteria, and the results and aims about the job. But
there are two common important problems about the
criteria used to evaluate workers’ performance. First
of all, the criteria used in performance evaluation are
assumed to be related only with job. It is crucial to
define the indicators describing the aims of work
performance. There is not a universal criteria bundle.
The work analysis is the main guide to identify the
performance criteria for a certain job title. If a
criterion isn’t related with the work, then it shouldn’t
be a part of performance evaluation. Secondly, when
53
Esen H., Hatipo
˘
glu T. and Boyacı A..
A Performance Evaluation Model of a Job Title using Fuzzy Approach .
DOI: 10.5220/0005076500530060
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Fuzzy Computation Theory and Applications (FCTA-2014), pages 53-60
ISBN: 978-989-758-053-6
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

a criterion is selected to evaluate the work
performance, the measurements should be correct
and precise. In this study, a model is proposed to
identify and objectively weight the criteria for each
job position as explained above.
One of the most difficult functional areas for
evaluation is still the purchasing department. Due to
the increasing competition in the globe,
organizations are required to evaluate their internal
operations and decrease the costs by making them
excellent. One of the biggest element of cost is
purchasing spend, which is generally equal to 40–
70% of a firm’s sales volume (depending upon the
degree of vertical integration in the industry), and
thus is a source of increasing competitive advantages
(Saranga and Moser, 2010). The role of purchasing
comprises of communicating with suppliers to
decrease redundancies and increase efficiencies in
the supply chain. The strategic role of purchasing
makes it crucial to measure its performance (Easton
et al., 2002).
Due to the reasons of mentioned explanation and
understanding the model better, the criteria for
purchasing specialist position are identified and
weighted.
In the second part of the study, the methodology,
Fuzzy Analytic process, is explained. In the third
section, the proposed performance evaluation model
is detailed. The last section of the study is comprised
of the results and comments about the application.
2 FUZZY ANALYTIC
HIERARCHY PROCESS
METHOD
In Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP), a flexible
and structured methodology, complex decision
variables are structured into a hierarchical
framework to solve and analyze them (Boroushaki
and Malczewski, 2008). Human thinking and
judgment are ambiguous and it is not meaningful to
represent them with point numbers. Interval
judgments better represent them than precise value
judgments. Thus, the priority between decision
variables is decided according to the triangular fuzzy
numbers. The final priority weights are found with
synthetic extent analysis method and this is called as
fuzzy extended AHP (Chan and Kumar, 2007).
Thus, using fuzzy theory in AHP is more reasonable
and effective than classic AHP.
There are various AHP methods related to the
fuzziness, while the most popular one is Chang’s
approach. Chang established the extent analysis
method (EAM) for synthetic values of pair wise
comparisons with the use of triangular fuzzy
numbers (TFNs) (Heo et al., 2012).The triangular
fuzzy conversion scale, given in Table 1, is used in
the evaluation model of this paper.
Table 1: Triangular fuzzy scale of preference.
Relative
importance
Definition
Fuzzy
Scale
Fuzzy
Reciprocal
Scale
1
Equally
Importance
(1,1,1) (1,1,1)
3
Moderate
Importance
(1,3,5) (1/5,1/3,1)
5
Strong
Importance
(3,5,7) (1/7,1/5,1/3)
7
Demonstrated
Importance
(5,7,9) (1/9,1/7,1/5)
9
Extreme
Importance
(7,9,9) (1/9,1/9,1/7)
Let
n
xxx ,,,
21
be an object set, and
m
uuu ,,,
21
be a goal set. According to the method
of Chang’s extent analysis, each object is taken and
extent analysis for each goal, g
i
, is performed,
respectively. Therefore, m extent analysis values for
each object can be obtained, with the following
signs:
,
,…,
i = 1, 2, …, n (1)
Where all the
(j = 1, 2, …, m) are triangular
fuzzy numbers.
The steps of Chang’s extent analysis can be
given as in the following:
Step 1: The value of fuzzy synthetic extent with
respect to the ith object is defined as
∑
⨂
∑∑
(2)
To obtain
∑
, perform the fuzzy addition
operation of m extent analysis values for a particular
matrix such that
∑
∑
,
∑
,
∑
(3)
FCTA2014-InternationalConferenceonFuzzyComputationTheoryandApplications
54

and to obtain
∑∑
, perform the fuzzy
addition operation of
(j= 1,2, …,m) values such
that
∑∑
∑
,
∑
,
∑
(4)
and then compute the inverse of the vector in
equation (4) such that
∑∑
∑
,
∑
,
∑
(5)
Step 2: The degree of possibility of M
2
= (l
2
, m
2
,
u
2
) ≥ M
1
= (l
1
, m
1
, u
1
) is defined as
V (M
2
≥ M
1
) =
min
,
(6)
and can be equivalently expressed as follows:
V(M
2
≥M
1
)=hgt(M
1
∩M
2
)
=
1,
0,
(7)
where d is the ordinate of the highest intersection
point D between
and
(see figure 1).
To compare M
1
and M
2
, we need both the values
of
V(M
2
≥ M
1
) and V(M
1
≥ M
2
).
Figure 1: The intersection between M
1
and M
2.
Step 3: The degree possibility for a convex fuzzy
number to be greater than k convex fuzzy numbers
M
i
(i=1, 2, ., k) can be defined by.
V(M
≥ M
1
, M
2
, …, M
k
)= V [ (M
≥ M
1
) and
(M
≥ M
2
) and … and (M
≥ M
k
) ]
= min V(M
≥ M
İ
), i = 1, 2, …, k
(8)
Assume that
d’(A
i
) = min V(S
i
≥ S
k
).
(9)
For k = 1, 2, …, n; k ≠ i. Then the weight vector
is given by
W’ = (d’(A
1
), d’(A
2
), …, d’(A
n
))
T
;
(10)
where A
i
(i = 1, 2, …, n) are n elements.
Step 4: Via normalization, the normalized weight
vectors are
W = (d(A
1
), d(A
2
), …, d(A
n
))
T
(11)
where W is a nonfuzzy number (Kahraman et al.,
2004) .
3 PROPOSED PERFORMANCE
EVALUATION MODEL
The determination of personnel to be hired and/or
fired is a troublesome issue for many companies.
Both hiring and firing operations require a correct
measure and evaluation system. A company that has
enough and correct information about the personnel
can easily decide on a fair wage-increase policy and
the personnel to be hired. Performance evaluation
studies are crucial for these kinds of purposes as
well as in the determination of training needs and
career planning (Özdemir, 2002).
The scope of the study is to determine the
performance evaluation criteria of a purchasing
specialist and weight for evaluating this job title.
The application of the model is made at a company
in automotive supplier industry at Kocaeli. After
meeting with the executives of the company, the
boundary of the study has been determined and a
team has been created including an academic expert,
production manager, HR manager, purchase
manager, and logistics and supply manager.
First of all, the aim, importance and framework
of the study has been discussed, then the criteria
found by brainstorming has been noted in the team’s
meeting that was organized to discuss the criteria to
be used in performance measure. The criteria draft
has been evaluated again; whether they can be
measured, or they can be represented by another
criterion and whether there are any missing criteria
has been discussed. After this evaluation, the criteria
are finalized. Every criterion has been described in
APerformanceEvaluationModelofaJobTitleusingFuzzyApproach
55

detail to prevent any misunderstanding about their
meaning during their usage.
The proposed model makes the performance
evaluation by using three main criteria. These main
criteria are Decision Making and Leadership,
Communication and Relations and Technical skills.
The Decision Making and Leadership, and
Communication and Relations criteria and their sub-
criteria can be mutually used in the evaluation of all
job titles. The sub-criteria under the main criterion
of Technical skills changes according to the job title.
To make the model more understandable, the
weights used in the performance evaluation of the
job title “Purchasing Specialist” are identified. The
sub-criteria under technical skills are flexible
enough to be used for another job title. The
hierarchy belonging to the proposed performance
evaluation of “Purchasing Specialist” in the model
can be seen in Figure 2.
The decision structure has two levels;
First level (Level of determinants), determinants
of the performance evaluation are determined as
Decision Making and Leadership (DML),
Communication and Relations (CR) and Technical
Skills (TS).
Second level, this level consists of 16 sub-
criteria. Six sub-criteria about Decision Making and
Leadership are Problem solving and result
orientation (PS), Agility (AG), Adaptability (AD),
Team building and management (TB), Project
management (PM) and Strategy Elaboration (SE).
Four sub-criteria about Communication and
Relations are dealing with organization (DO),
Communication (C), International Mindset (IM) and
Interpersonal Skills (IS). Six sub-criteria about
Technical Skills are Negotiation Practice (NP),
purchasing tools practice (PT), financial awareness
(FA), Supply chain knowledge (SK), Legal
awareness (LA) and Budget management (BM). The
explanation of sub-criteria is given below:
Decision Making and Leadership:
1) Problem solving and result orientation (PS):
Ability to detect, design and implement solutions
adapted to situations and people (evaluate, diagnose)
applying QRQC (Quick Response Quality Control).
Identification and weighting of important
parameters, identification of causes, priorities and
development of solutions. Ability to achieve results
regardless of circumstances, but not at any cost.
Focus on pragmatic and practical tasks and ability to
act in the field. Willingness and ability to meet
commitments.
2) Agility (AG): Ability to combine speed and
rationality in decision making followed by the
implementation of an action plan. Ability to react to
requests and situations within the required time
constraints. Capability to manage a heavy work load
in a stressed environment and ability to deal with
urgencies.
3) Adaptability (AD): Ability to adapt easily to
different working environments. Functioning in a
matrix environment or with occasional apparently
contradictory issues. Analysis of problems from
several points of view, including the points of view
of others.
4) Team building and management (TB): Ability
to manage and coach people, to create a team spirit,
to establish (common and individual) objectives and
to assess performance and competences. Efficient
delegation of appropriate tasks. Management of
structural conflicts. Ability to select and recruit team
members. Integration of the team inside the
structure. Focus on people development. Gathering
of different personalities and mobilization of them
towards common objective.
5) Project management (PM): Ability to plan
resources in order to manage a project successfully
according to standards (quality, cost, delivery) for
customer satisfaction. Establishment of clear,
realistic timeframes for goal accomplishment.
6) Strategy Elaboration (SE): Ability to anticipate
future evolutions (helicopter view), to define vision,
objectives, strategic action plans and milestones in
order to meet objectives and to implement their
strategic plans.
Communication and Relations:
1) Dealing with organization (DO): Ability to deal
with organizational complexity, internal and external
stakeholders.
2) Communication (C): Ability “get the point
across” and to get the “buy-in” of the target
audience. Selection of the most pertinent
information, reliable sources, appropriate
population, the best medias. Definition and
organization of the content (according to different
cultures and levels) at the appropriate time.
Enhancement of information sharing and feedback.
Openness to listen to other options and to take them
into consideration. Ability to analyze complicated
situations.
FCTA2014-InternationalConferenceonFuzzyComputationTheoryandApplications
56
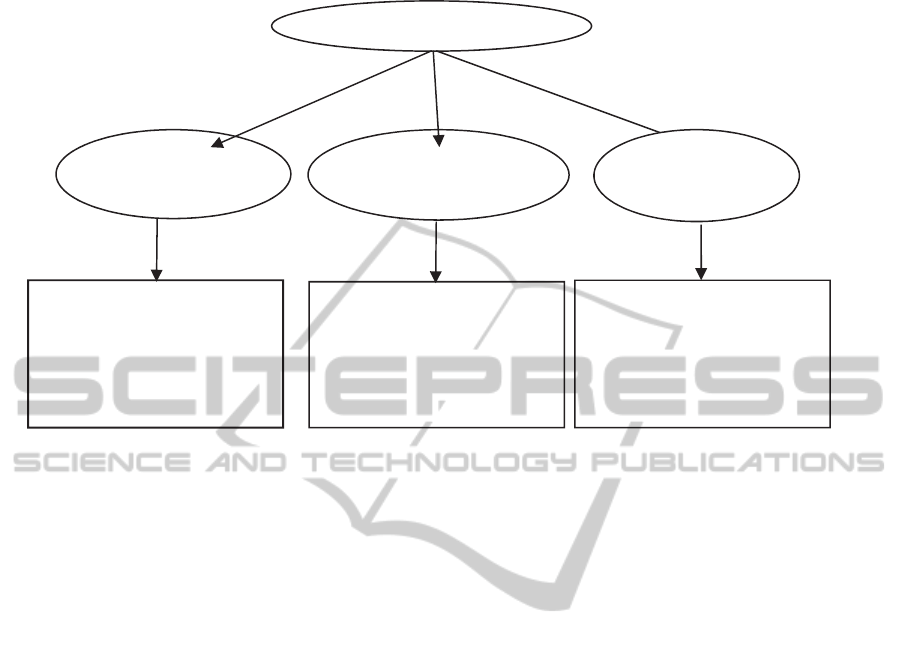
Figure 2: Hierarchies in the AHP.
3) International Mindset (IM): Ability to work
with people from different cultures. Integration of
other cultural values and systems and development
of cultural of open mindedness. Ability to think
global, act local.
4) Interpersonal Skills (IS): Ability to develop
interactive listening skills and to give constructive
reinforcement. Ability to deal with interpersonal
conflict. Ability to influence in a positive way the
work of colleagues through enthusiastic
communication.
Technical Skills:
1) Negotiation practice (NP): Ability to
prepare the negotiation strategy and tactics base on
assessment of company’s levers versus suppliers.
Knowledge of his/her limits and supplier’s decision
drivers. Ability to conduct the negotiation in a
professional manner ensuring a win-win deal.
Ability to obtain closure.
2) Purchasing tools practice (PT): Knowledge
of purchasing tools: methodology tools (commodity
matrix, system audit, process audit, initial
assessment, etc), analysis tools (market surveys,
etc), transaction tools (weekly report, EDI, MRP
system, etc)
3) Financial awareness (FA) : Understanding
of financial reports. Understanding of management
accounting and different methods to establish a price
and to evaluate the financial health of a supplier.
4) Supply chain knowledge (SK): Ability to
use supply chain knowledge to contribute to the
optimization of the supply chain together with
logistics department and supplier.
5) Legal awareness (LA): Ability to formalize
the contractual relationship in all domains
(confidentiality, development, supplies, equipment
etc). Ability to manage supplier disputes and major
crises with the help of the legal counsel. Ability to
use the law to elaborate his/her commodity strategy.
6) Budget management (BM): Ability to
evaluate all necessary resources and their costs in
order to achieve a target. Ability to manage a
budget. Evaluation and anticipation of the financial
impact of new decisions. Management of situation
changes and minimization of excess costs.
The triangular fuzzy conversion scale, given in
Table 1, is used in the evaluation model of this
study. Fuzzy pair-wise comparisons of three main
decision criteria on “Performance Evaluation” are
presented in Table 2. Then the sub-criteria are pair
wise compared in Table 3-5 respectively and
weights are calculated.
Communication
and Relations
Performance Evaluation
Decision Making
and Leadership
Technical skills
Problem solving and result
orientation
Agility
Adaptability
Team building and management
Project management
Strategy elaboration
Interpersonal skills
Dealing with organization
Communication
International mindset
Negotiation practice
Financial awareness
Supply chain knowledge
Legal awareness
Budget management
Purchasing tools practice
APerformanceEvaluationModelofaJobTitleusingFuzzyApproach
57
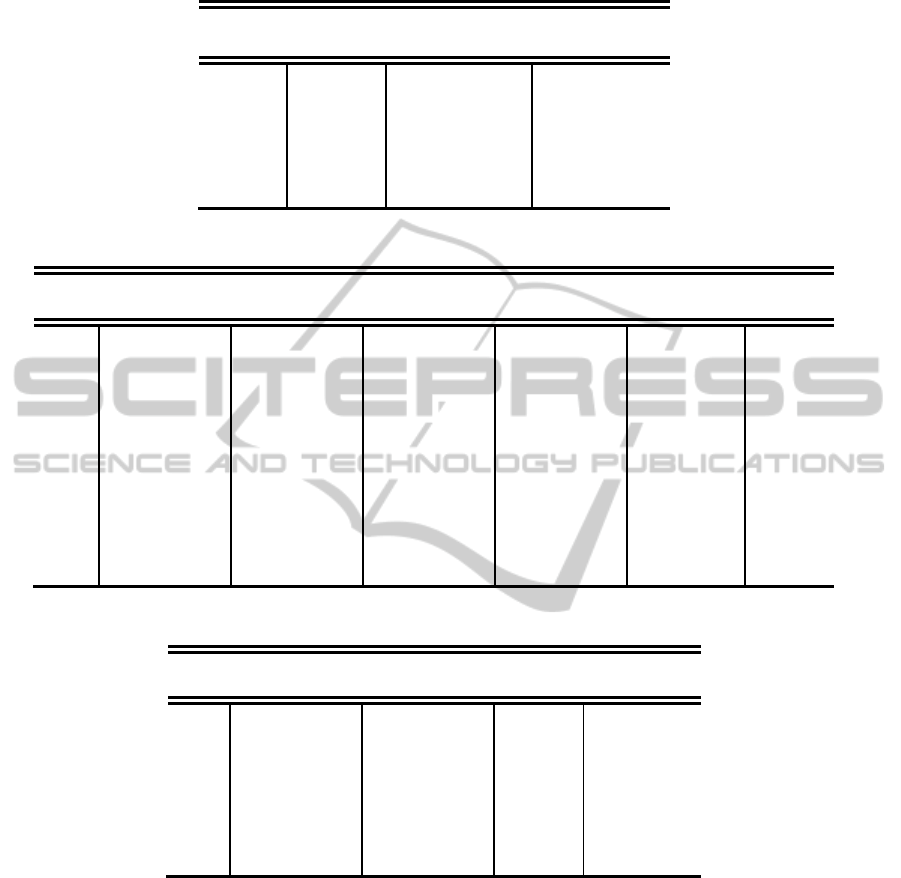
Table 2: Fuzzy linguistic preference relation decision matrix of three main criteria.
DML C TS
DML 1 1 1 1/5 1/3 1 1/7 1/5 1/3
C 1 3 5 1 1 1 1/5 1/3 1/1
TS 3 5 7 1 3 5 1 1 1
Table 3: Fuzzy linguistic preference relation decision matrix of decision making and leadership.
PS AG AD TB PM SE
PS 1 1 1 1/7 1/5 1/3 1/5 1/3 1 3 5 7 1 3 5 5 7 9
AG 3 5 7 1 1 1 1 3 5 3 5 7 3 5 7 7 9 9
AD 1 3 5 1/5 1/3 1 1 1 1 3 5 7 1 3 5 5 7 9
TB 1/7 1/5 1/3 1/7 1/5 1/3 1/7 1/5 1/3 1 1 1 1/5 1/3 1 3 5 7
PM 1/5 1/3 1 1/7 1/5 1/3 1/5 1/3 1 1 3 5 1 1 1 1 3 5
SE 1/9 1/7 1/5 1/9 1/7 1/5 1/9 1/7 1/5 1/7 1/5 1/3 1/5 1/3 1 1 1 1
Table 4: Fuzzy linguistic preference relation decision matrix of communication and relations.
DO C IM IS
DO 1 1 1 1/5 1/3 1 3 5 7 1 3 5
C 1 3 5 1 1 1 5 7 9 3 5 7
IM 1/7 1/5 1/3 1/9 1/7 1/5 1 1 1 1/5 1/3 1
IS 1/5 1/3 1 1/7 1/5 1/3 1 3 5 1 1 1
As seen in Table 2; S
DML
= (0.060, 0.103, 0.273),
S
CR
= (0.099, 0.291, 0.819) and S
TS
= (0.224, 0.605,
1.522) are calculated. Then W’ = (0.089, 0.655,
1.000) is obtained and priority weights vector of
each main criteria is W = (0.051, 0.376, 0.573)
T
.
Similarly priority weights vector of each main sub-
criteria is seen in Table 3, W = (0.2347, 0.3411,
0.2700, 0.0491, 0.1052, 0)
T
, in Table 4 W = (0.351,
0.493, 0, 0.156)
T
and in Table 5 W = (0.368, 0.291,
0.065, 0.072, 0, 0.204)
T
.
Table 6 shows overall or global importance
levels of for the main criteria and sub-
criteria.According to these results, performance
evaluation of purchasing expert is evaluated as
following:
It is further observed that the priority of the main
criteria “Technical Skills” with %57 is highest
followed by “Communication and Relations” with
%38 while “Decision Making and Leadership” is
just %5.
In case of sub criteria the priority is highest for
“Negotiation practice”, “Purchasing tools practice”
and “Budget management” respectively under
“Technical Skills” ; “Communication” and “Dealing
with organization” among “Communication and
FCTA2014-InternationalConferenceonFuzzyComputationTheoryandApplications
58

Table 5: Fuzzy linguistic preference relation decision matrix of technical skills.
NP PT FA SK LA BM
NP 1 1 1 1 3 5 3 5 7 5 7 9 7 9 9 3 5 7
PT 1/5 1/3 1 1 1 1 3 5 7 3 5 7 5 7 9 1 3 5
FA 1/7 1/5 1/3 1/7 1/5 1/3 1 1 1 1/5 1/3 1 5 7 9 1/7 1/5 1/3
SK 1/9 1/7 1/5 1/7 1/5 1/3 1 3 5 1 1 1 1 3 5 1/5 1/3 1
LA 1/9 1/9 1/7 1/9 1/7 1/5 1/9 1/7 1/5 1/5 1/3 1 1 1 1 1/7 1/5 1/3
BM 1/7 1/5 1/3 1/5 1/3 1 3 5 7 1 3 5 3 5 7 1 1 1
Table 6: Global importance levels of sub-criteria.
Global importance
of three main
criteria
Global
importance
of sub-criteria
Weights
Decision Making
and Leadership
(0.051)
PS (0.235)
0.012
AG (0.341)
0.017
AD (0.270)
0.014
TB (0.049)
0.002
PM (0.105)
0.005
SE (0)
0.000
Communication
and Relations
(0,376)
DO (0.351)
0,132
C (0.493)
0,185
IM (0)
0,000
IS (0.156)
0,059
Technical skills
(0.573)
NP (0.368)
0,211
PT (0.291)
0,167
FA (0.065)
0,037
SK (0.072)
0,041
LA (0)
0,000
BM (0.204)
0,117
relations”; “Agility”, “Adaptability” and “Problem
Solving and Result Orientation” among “Decision
Making and Leadership”.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Performance evaluation study should focus on
personnel. In organizations, performance evaluation
starts and ends with human component along with
the systems related to human. Personnel can easily
disrupt the organization’s structure when they are
incompatible with the other people in the working
environment. Thus, performance evaluation which
tries to increase the harmony of personnel with
organization has a great importance for
organizations (Boduroğlu, 2013).
Besides being the most important part of an
effective human resource management strategy,
performance evaluation is one of the most important
elements to reach the objectives of organizational
management. Performance evaluation should be
used as a tool to direct, stimulate, increase the
motivation and the trust of workers through the
organization. The most important part of the
evaluation is to make it as objective as possible.
The contributions of this study into the literature
can be summarized as follows; 1. The proposed
model can be used for other job titles in companies
by allowing flexibility in the criteria under the main
criterion of technical skills. 2. The current
performance evaluation models don’t weight the
criterion assuming that they all have the same
importance. The proposed model has such a
structure and objectivity to satisfy this lack of
current models. 3. Performance evaluation is a
decision making process which involves uncertainty.
To overcome the uncertainty and evaluate the
workers performance objectively, a performance
evaluation model is developed of which the criteria
are defined as the fuzzy numbers and the linguistic
variables.
The evaluation process of the performance can
be thought as a complex multi-criteria decision
making problem considering multiple factors and
sub factors affecting the evaluation. Fuzzy AHP
method enables decision-makers to realize a
hierarchical structure and an effective vague
APerformanceEvaluationModelofaJobTitleusingFuzzyApproach
59

assessment of main and sub factors’ weights. Hence,
we used a fuzzy approach for the evaluation of
personnel performance. By utilizing fuzzy AHP
method, the weights of sub factors are determined
subsequently.
By applying the model into a company operating
as an automotive supplier, it has been shown that the
model can be used in practice without any difficulty.
During the application, the weighing of the specific
criteria used in the performance evaluation of to
purchasing specialist has been done. The main
criteria are ordered as Technical Skills,
Communication and Relations and Decision Making
and Leadership as a result of the evaluation. The
most important sub-criteria are identified as
Negotiation practice, Communication and
Purchasing tools practice.
REFERENCES
Boduroğlu, N., 2013. Mali Müşavirler Odasında
Performans Değerlendirme Yöntemleri ve Çalışanlar
Üzerindeki Etkisi, Thesis, Beykent University.
Boroushaki, S., & Malczewski,J., 2008. Implementing an
extension of the analytical hierarchy process using
ordered weighted averaging operators with fuzzy
quantifiers in ArcGIS. Computers & Geosciences, 34,
399–410.
Chan, F.T.S., Kumar, N., 2007. Global supplier
development considering risk factors using fuzzy
extended AHP-based approach. Omega, 35 (4), 417-
431.
Easton, L., Murphy, D.J., Pearson, J.N., 2002. Purchasing
performance evaluation: with data envelopment
analysis, European Journal of Purchasing & Supply
Management, 8, 123–134.
Gürbüz, T., Albayrak, Y.E., 2014. An engineering
approach to human resources performance evaluation:
Hybrid MCDM application with interactions, Applied
Soft Computing, 21, 365-375.
Heo, E., Kim , J., Cho, S., 2012. Selecting hydrogen
production methods using fuzzy analytic hierarchy
process with opportunities, costs, and risks.
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 37, 17655
-17662.
Kahraman, C., Cebeci,U., Ruan, D., 2004. Multi-attribute
comparison of catering service companies using fuzzy
AHP: The case of Turkey. International Journal of
Production Economics, 87, 171–184.
Kılıç, S., 2011. Performans değerlendirme sisteminin
kariyer planlamasıyla ilişkisinin analizi ve bir
uygulama, Thesis, Uludağ University.
Ozdemir, M.S., 2002. Bir işletmede analitik hiyerarşi
süreci kullanılarak performans değerleme sistemi
tasarımı, Endüstri Mühendisliği Dergisi, 13(2), 2-11.
Saranga, H., Moser, R., 2010. Performance evaluation of
purchasing and supply management using value chain
DEA approach, European Journal of Operational
Research, 207, 197–205.
Stavrou, E.T., Charalambous, C., Spiliotis, S., 2007.
Human resource management and performance: A
neural network analysis, European Journal of
Operational Research, 181, 453–467.
FCTA2014-InternationalConferenceonFuzzyComputationTheoryandApplications
60
