
Evolutionary Learning of Weighted Linear Composite Dispatching Rules
for Scheduling
Helga Ingimundardottir and Thomas Philip Runarsson
Department of Industrial Engineering, Mechanical Engineering and Computer Science, University of Iceland,
Hjardarhagi 2-6, IS-107 Reykjavik, Iceland
Keywords:
Job Shop Scheduling, Composite Dispatching Rules, Evolutionary Search.
Abstract:
A prevalent approach to solving job shop scheduling problems is to combine several relatively simple dis-
patching rules such that they may benefit each other for a given problem space. Generally, this is done in
an ad-hoc fashion, requiring expert knowledge from heuristics designers, or extensive exploration of suitable
combinations of heuristics. The approach here is to automate that selection by translating dispatching rules
into measurable features and optimising what their contribution should be via evolutionary search. The frame-
work is straight forward and easy to implement and shows promising results. Various data distributions are
investigated for both job shop and flow shop problems, as is scalability for higher dimensions. Moreover, the
study shows that the choice of objective function for evolutionary search is worth investigating. Since the
optimisation is based on minimising the expected mean of the fitness function over a large set of problem
instances which can vary within the set, then normalising the objective function can stabilise the optimisation
process away from local minima.
1 JOB SHOP SCHEDULING
The job-shop scheduling problem (JSP) deals with the
allocation of tasks of competing resources where the
goal is to optimise a single or multiple objectives –
in particular minimising a schedule’s maximum com-
pletion time, i.e., the makespan, denotedC
max
. Due to
difficulty in solving this problem, heuristics are gen-
erally applied. Perhaps the simplest approach to gen-
erating good feasible solutions for JSP is by applying
dispatching rules (DR), e.g., choosing a task corre-
sponding to longest or shortest processing time, most
or least successors, or ranked positional weight, i.e.,
sum of processing times of its predecessors. Ties are
broken in an arbitrary fashion or by another heuris-
tic rule. Combining dispatching rules for JSP is
promising, however, there is a large number of rules
to choose from, thus its combinations rely on ex-
pert knowledge or extensive trial-and-error process to
choose a suitable DR (Tay and Ho, 2008). Hence
given the diversity within the JSP paradigm, there
is no “one-rule-fits-all” for all problem instances (or
shop constraints), however single priority dispatch-
ing rules (SDR) based on job processing attributes
have proven to be effective (Haupt, 1989). The classi-
cal dispatching rules are continually used in research;
a summary of over 100 classical DRs for JSP can
be found in (Panwalkar and Iskander, 1977). How-
ever, careful combinations of such simple rules, i.e.,
composite dispatching rules (CDRs) can perform sig-
nificantly better (Jayamohan and Rajendran, 2004).
As a consequence, a linear composite of dispatching
rules for JSP was presented in (Ingimundardottir and
Runarsson, 2011b). There the goal was to learn a set
of weights, w via ordinal regression such that
h(x
j
) =
w· φ
φ
φ(x
j
)
, (1)
yields the preference estimate for dispatching job
j that corresponds to post-decision state x
j
, where
φ
φ
φ(x
j
) denotes the feature mapping (cf. Section 4). In
short, Eq. (1) is a simple linear combination of fea-
tures found using a classifier which is trained by giv-
ing more weight to instances that are preferred w.r.t.
optimality in a supervised learning fashion. As a re-
sult, the job dispatched is the following,
j
∗
= argmax
j
h(x
j
)
. (2)
A more popular approach in recent JSP litera-
ture is applying genetic algorithms (GAs) (Pinedo,
2008). However, in that case an extensive number
of schedules need to be evaluated, and even for low
59
Ingimundardottir H. and Runarsson T..
Evolutionary Learning of Weighted Linear Composite Dispatching Rules for Scheduling.
DOI: 10.5220/0005077200590067
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Evolutionary Computation Theory and Applications (ECTA-2014), pages 59-67
ISBN: 978-989-758-052-9
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

dimensional JSP, it can quickly become computation-
ally infeasible. GAs can be used directly on sched-
ules (Cheng et al., 1996; Cheng et al., 1999; Tsai
et al., 2007; Qing-dao-er ji and Wang, 2012; Ak and
Koc, 2012), however, then there are many concerns
that need to be dealt with. To begin with there are
nine encoding schemes for representing the sched-
ules (Cheng et al., 1996), in addition, special care
must be taken when applying cross-over and mutation
operators in order for schedules to still remain feasi-
ble. Moreover, in case of JSP, GAs are not adapt for
fine-tuning around optima. Luckily a subsequent lo-
cal search can mediate the optimisation (Cheng et al.,
1999).
The most predominant approach in hyper-
heuristics, a framework of creating new heuris-
tics from a set of predefined heuristics, is genetic
programming (Burke et al., 2013). Dispatching
rules based genetic algorithms (DRGA) (V´azquez-
Rodr´ıguez and Petrovic, 2009; Dhingra and Chandna,
2010; Nguyen et al., 2013) are a special case of ge-
netic programming (Koza and Poli, 2005), where GAs
are applied indirectly to JSP via dispatching rules, i.e.,
where a solution is no longer a proper schedule but a
representation of a schedule via applying certain DRs
consecutively.
There are two main viewpoints on how to ap-
proach scheduling problems, a) local level by build-
ing schedules for one problem instance at a time; and
b) global level by building schedules for all problem
instances at once. For local level construction a sim-
ple construction heuristic is applied. The schedule’s
features are collected at each dispatch iteration from
which a learning model will inspect the feature set
to discriminate which operations are preferred to oth-
ers via ordinal regression. The focus is essentially
on creating a meaningful preference set composed of
features and their ranks as the learning algorithm is
only run once to find suitable operators for the value
function. This is the approach taken in (Ingimundar-
dottir and Runarsson, 2011b). Expanding on that
work, this study will explore a global level construc-
tion viewpoint where there is no feature set collected
beforehand since the learning model is optimised di-
rectly via evolutionary search. This involves numer-
ous costly value function evaluations. In fact it in-
volves an indirect method of evaluation whether one
learning model is preferable to another, w.r.t. which
one yields a better expected mean.
2 OUTLINE
In order to formulate the relationship between prob-
lem structure and heuristic efficiency, one can utilise
Rice’s framework for algorithm selection (Rice,
1976). The framework consists of four fundamental
components, namely,
Problem Space or Instance Space P ,
set of problem instances;
Feature Space F ,
measurable properties of the instances in P ;
Algorithm Space A,
set of all algorithms under inspection;
Performance Space Y ,
the outcome for P using an algorithm from A.
For a given problem instance x ∈ P with k features
φ
φ
φ(x) = {φ
1
(x),..., φ
k
(x)} ∈ F and using algorithm
a ∈ A the performance is y = Y(a,φ
φ
φ(x)) ∈ Y , where
Y : A × F 7→ Y is the mapping for algorithm and
feature space onto the performance space. (Smith-
Miles et al., 2009; Smith-Miles and Lopes, 2011; In-
gimundardottir and Runarsson, 2012) formulate JSP
in the following manner: a) problem space P is de-
fined as the union of N problem instances consist-
ing of processing time and ordering matrices given
in Section 3; b) feature space F , which is outlined
in Section 4. Note, these are not the only possible set
of features, however, they are built on the work by (In-
gimundardottir and Runarsson, 2011b; Smith-Miles
et al., 2009) and deemed successful in capturing the
essence of a JSP data structure; c) algorithm space A
is simply the scheduling policies under consideration
and discussed in Section 5; d) performance space is
based on the resulting C
max
. Different fitness mea-
sures are investigated in Section 5.1; and e) mapping
Y is the step-by-step scheduling process.
In the context of Rice’s framework, and returning
to the aforementioned approaches to scheduling prob-
lems, then the objective is to maximise its expected
heuristic performance, i.e.,
a) Local level
max
P
′
⊂P
E [Y (a,φ
φ
φ(x))] (3)
where x ∈ P
′
and algorithm a is obtained via ordi-
nal regression based on the feature space F , i.e.,
F |
P
′
7→ A, such as the approach taken in (In-
gimundardottir and Runarsson, 2011b), and will
be used as a benchmark for the following,
b) Global level
max
a∈A
E [Y (a,φ
φ
φ(x))] (4)
ECTA2014-InternationalConferenceonEvolutionaryComputationTheoryandApplications
60

where training data x ∈ P is guided by its algo-
rithm a, i.e., A 7→ P . This will be the focus of this
study.
Note that the mappings φ
φ
φ : P 7→ F and Y : A 7→ Y are
the same for both paradigms.
The paper concludes in Section 6 with discussion
and conclusions.
3 PROBLEM SPACE
For this study synthetic JSP and its subclass, permu-
tation flow shop problem (PFSP), the scheduling task
considered here is where n jobs are scheduled on a set
of m machines, i.e., problem size n× m, subject to the
constraint that each job must follow a predefined ma-
chine order and that a machine can handle at most one
job at a time. The pair ( j, a) refers to the operation of
dispatching job j on machine a. As a result, a total of
ℓ = n· m sequential operations need to be made for a
complete schedule.
The objective is to schedule the jobs so as to
minimize the maximum completion times, C
max
, also
known as the makespan. For a mathematical formula-
tion of JSP the reader is recommended (Ingimundar-
dottir and Runarsson, 2011b).
There are two fundamental types of problem
classes: non-structured versus structured. Firstly
there are the “conventional” structured problem
classes, where problem instances are generated
stochastically by fixing the number of jobs and ma-
chines, as well as processing times are i.i.d. and sam-
pled from a discrete uniform distribution from the in-
terval I = [u
1
,u
2
], i.e., p ∼ U(u
1
,u
2
). Two differ-
ent processing time distributions are explored, namely
P
j.rnd
where I = [1, 99] and P
j.rndn
where I = [45, 55],
referred to as random and random-narrow, respec-
tively. The machine order is a random permutation
of all of the machines in the job-shop.
Analogous to P
j.rnd
and P
j.rndn
the problem
classes P
f.rnd
and P
f.rndn
, respectively, correspond to
the structured PFSP problem classes, however with a
homogeneous machine order permutation. Secondly,
there are structured problem classes of PFSP which
are modelled after real-world flow-shop manufactur-
ing namely job-correlated P
f. jc
where job processing
times are dependent on job index and independent of
machine index. Problem instances for PFSP are gen-
erated using (Watson et al., 2002) problem generator
1
.
1
Both code, written in
C++
, and problem in-
stances used in their experiments can be found at:
http://www.cs.colostate.edu/sched/generator/
Table 1: Problem space distributions used in Section 5.
Note, problem instances are synthetic and each problem
space is i.i.d. and ‘–’ denotes not available.
name size N
train
N
test
note
Permutation flow shop problem (PFSP)
P
6×5
f.rnd
6× 5 500 – random
P
6×5
f.rndn
6× 5 500 – random-narrow
P
6×5
f. jc
6× 5 500 – job-correlated
P
10×10
f.rnd
10× 10 – 500 random
P
10×10
f.rndn
10× 10 – 500 random-narrow
P
10×10
f. jc
10× 10 – 500 job-correlated
Job shop problem (JSP)
P
6×5
j.rnd
6× 5 500 – random
P
6×5
j.rndn
6× 5 500 – random-narrow
P
10×10
j.rnd
10× 10 – 500 random
P
10×10
j.rndn
10× 10 – 500 random-narrow
For each JSP and PFSP class N
train
and N
test
in-
stances were generated for training and testing, re-
spectively. Values for N are given in Table 1. Note,
difficult problem instances are not filtered out before-
hand, such as the approach in (Watson et al., 2002).
4 FEATURE SPACE
When building a complete JSP schedule, a job is
placed at the earliest available time slot for its next
machine while still fulfilling constraints that each ma-
chine can handle at most one job at a time, and jobs
need to have finished their previous machines accord-
ing to its machine order. Unfinished jobs are dis-
patched one at a time according to some heuristic. Af-
ter each dispatch the schedule’s current features are
updated. Features are used to grasp the essence of
the current state of the schedule. As seen in Table 2,
temporal scheduling features applied in this study are
given for each possible post-decision state. An exam-
ple of a schedule being built is given in Fig. 1, where
there are a total of five possible jobs that could be cho-
sen to be dispatched by some dispatching rule. These
features would serve as the input for Eq. (1).
It’s noted that some of the features directly corre-
spond to a SDR commonly used in practice. For ex-
ample, if the weights w in Eq. (1) were all zero, save
EvolutionaryLearningofWeightedLinearCompositeDispatchingRulesforScheduling
61

0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400
M
1
M
2
M
3
M
4
M
5
Time
Machine
1
1
2
3
3
3
3
3
4
4
4
4
5
5
6
12
4
5
6
Figure 1: Gantt chart of a partial JSP schedule after 15 operations: Solid boxes represent previously dispatched jobs, and
dashed boxes represent the jobs that could be scheduled next. Current C
max
denoted as dotted line.
Table 2: Feature space F for P given the resulting temporal
schedule after dispatching an operation ( j, a).
φ
φ
φ Feature description
φ
1
job j processing time
φ
2
job j start-time
φ
3
job j end-time
φ
4
when machine a is next free
φ
5
current makespan
φ
6
total work remaining for job j
φ
7
most work remaining for all jobs
φ
8
total idle time for machine a
φ
9
total idle time for all machines
φ
10
φ
9
weighted w.r.t. number of assigned tasks
φ
11
time job j had to wait
φ
12
idle time created
φ
13
total processing time for job j
for w
6
= 1, then (2) yields the job with the highest φ
6
value, i.e., equivalent to dispatching rule most work
remaining (MWR).
5 EXPERIMENTAL STUDY
The optimum makespan
2
is denoted C
opt
max
, and the
makespan obtained from the heuristic model by
C
model
max
. Since the optimal makespan varies between
problem instances the performancemeasure is the fol-
2
Optimum values are obtained by using a commercial
software package (Gurobi Optimization, Inc., 2013).
lowing,
ρ :=
C
model
max
−C
opt
max
C
opt
max
· 100% (5)
which indicates the percentage relative deviationfrom
optimality. Throughout a Kolmogorov-Smirnov test
with α = 0.05 is applied to determine statistical sig-
nificance between methodologies.
Inspired by DRGA, the approach taken in this
study is to optimise the weights w in Eq. (1) di-
rectly via evolutionary search such as covariance ma-
trix adaptation evolution strategy (CMA-ES) (Hansen
and Ostermeier, 2001). This has been proven to be a
very efficient numerical optimisation technique.
Using standard set-up of parameters of the CMA-
ES optimisation, the runtime was limited to 288 hours
on a cluster for each training set given in Section 3 and
in every case the optimisation reached its maximum
walltime.
5.1 Performance Measures
Generally, evolutionary search only needs to min-
imise the expected fitness value. However, the ap-
proach in (Ingimundardottir and Runarsson, 2011b)
was to use the known optimum to correctly label
which operations’ features were optimal when com-
pared to other possible operations. Therefore, it
would be of interest to inspect if there is any perfor-
mance edge gained by incorporating optimal labelling
in evolutionary search. Therefore, two objective func-
tions will be considered, namely,
ES
C
max
:= minE[C
max
] (6)
ES
ρ
:= minE[ρ] (7)
ECTA2014-InternationalConferenceonEvolutionaryComputationTheoryandApplications
62
0
10
20
30
j.rnd j.rndn f.rnd f.rndn f.jc
Percentage relative deviation from optimality, rho (%)
Objective function ES_Cmax ES_rho
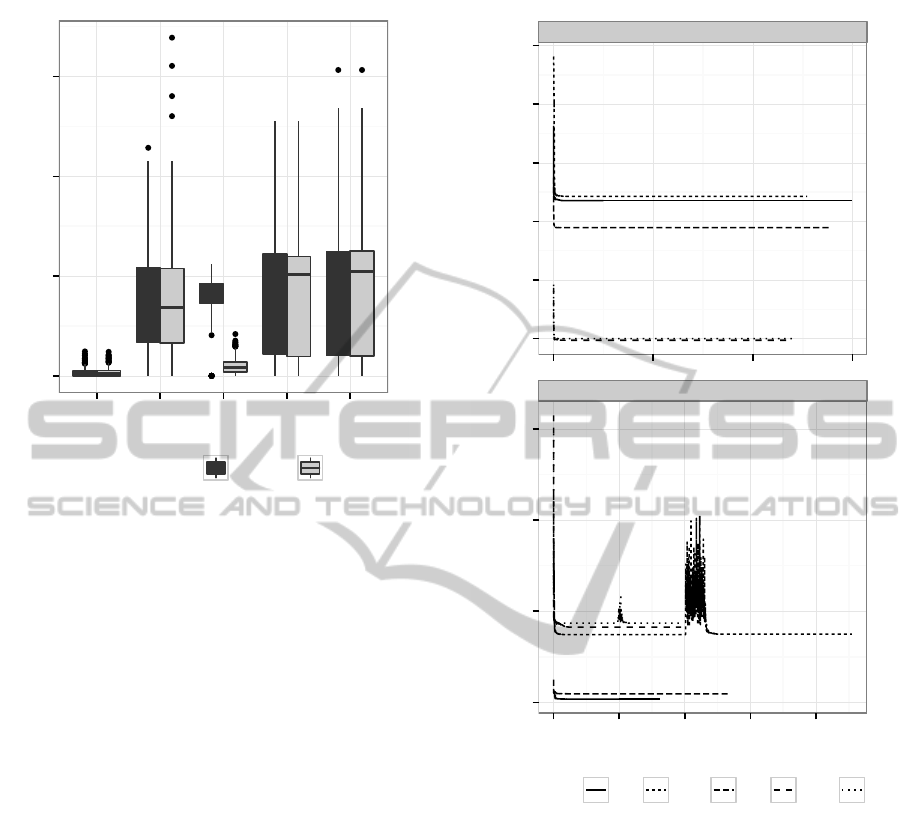
Figure 2: Box-plot of training data for percentage relative
deviation from optimality, defined by Eq. (5), when imple-
menting the final weights obtained from CMA-ES optimi-
sation, using both objective functions from Eqs. (6) and (7),
left and right, respectively.
Main statistics of the experimental run are given
in Table 3 and depicted in Fig. 3 for both approaches.
In addition, evolving decision variables, here weights
w for Eq. (1), are depicted in Fig. 4.
In order to compare the two objective functions,
the best weights reported were used for Eq. (1) on
the corresponding training data. Its box-plot of per-
centage relative deviation from optimality, defined
by Eq. (5), is depicted in Fig. 2 and Table 4 present
its main statistics; mean, median, standard deviation,
minimum and maximum values.
In the case of P
f.rndn
, Eq. (7) gave a considerably
worse results, since the optimisation got trapped in a
local minima, as the erratic evolution of the weights
in Fig. 4(a) suggest. For other problem spaces, Eq. (6)
gave slightly better results than Eq. (7). However,
there was no statistical difference between adopting
either objective function. Therefore, minimisation of
expectation of ρ, is preferred over simply using the
unscaled resulting makespan.
5.2 Problem Difficulty
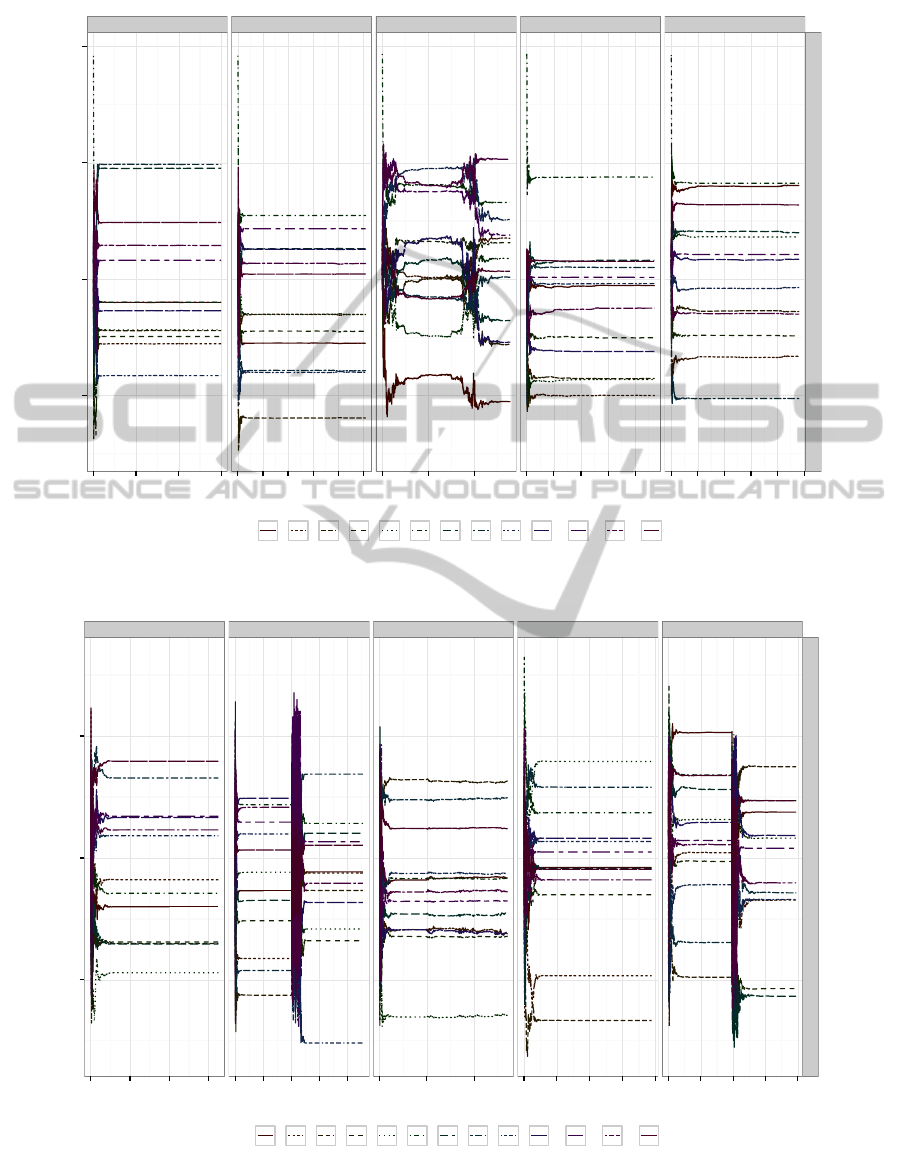
The evolution of fitness per generation from the
CMA-ES optimisation of Eq. (7) is depicted in Fig. 3.
Note, all problem spaces reached their allotted com-
putational time without converging. In fact P
f.rnd
and
ES_Cmax
ES_rho
450
500
550
600
650
700
0
10
20
30
0 2000 4000 6000
0 1000 2000 3000 4000
Generation
Fitness value
Problem
space
j.rnd j.rndn f.rnd f.rndn f.jc
Figure 3: Fitness for optimising (w.r.t. Eqs. (6) and (7)
above and below, receptively), per generation of the CMA-
ES optimisation.
P
j.rndn
needed restarting during the optimisation pro-
cess. Furthermore, the evolution of the decision vari-
ables w are depicted in Fig. 4. As one can see, the
relative contribution for each weight clearly differs
between problem spaces. Note, that in the case of
P
j.rndn
(cf. Fig. 4(b)), CMA-ES restarts around gen-
eration 1,000 and quickly converges back to its previ-
ous fitness. However, lateral relation of weights has
completely changed, implying that there are many op-
timal combinations of weights to be used. This can be
expected due to the fact some features in Table 2 are
a linear combination of others, e.g. φ
3
= φ
1
+ φ
2
.
EvolutionaryLearningofWeightedLinearCompositeDispatchingRulesforScheduling
63
j.rnd
j.rndn
f.rnd
f.rndn
f.jc
−0.5
0.0
0.5
1.0
ES_Cmax
0 2000 4000 60000 10002000300040005000 0 2000 4000 0 1000 2000 3000 4000 0 10002000300040005000
generation
weight
feature 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
(a) minimise w.r.t. Eq. (6)
j.rnd
j.rndn
f.rnd
f.rndn
f.jc
−0.5
0.0
0.5
ES_rho
0 500 1000 1500 0 1000 2000 3000 4000 0 1000 2000 0 500 1000 1500 20000 500 1000 1500 2000
generation
weight
feature 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
(b) minimise w.r.t. Eq. (7)
Figure 4: Evolution of weights of features (given in Table 2) at each generation of the CMA-ES optimisation. Note, weights
are normalised such that kwk = 1.
ECTA2014-InternationalConferenceonEvolutionaryComputationTheoryandApplications
64

Table 3: Final results for CMA-ES optimisation; total number of generations and function evaluations and its resulting fitness
value for both performance measures considered.
(a) w.r.t. Eq. (6)
P #gen #eval ES
C
max
j.rnd 4707 51788 448.612
j.rndn 4802 52833 449.942
f.rnd 5088 55979 571.394
f.rndn 5557 61138 544.764
f.jc 5984 65835 567.688
(b) w.r.t. Eq. (7)
P #gen #eval ES
ρ
j.rnd 1944 21395 8.258
j.rndn 1974 21725 8.691
f.rnd 4546 50006 7.479
f.rndn 2701 29722 0.938
f.jc 1625 17886 0.361
5.3 Scalability
As a benchmark, the linear ordinal regression
model (PREF) from (Ingimundardottir and Runars-
son, 2011b) was created. Using the weights obtained
from optimising Eq. (7) and applying them on their
6 × 5 training data. Their main statistics of Eq. (5)
are reported in Table 4 for all training sets described
in Table 1. Moreover, the best SDR from which the
features in Table 2 were inspired by, are also reported
for comparison, i.e., most work remaining (MWR)
for all JSP problem spaces, and least work remaining
(LWR) for all PFSP problem spaces.
To explore the scalability of the learning mod-
els, a similar comparison to Section 5.2 is made for
applying the learning models on their corresponding
10 × 10 testing data. Results are reported in Table 5.
Note, that only resulting C
max
is reported as the opti-
mum makespan is not known and Eq. (5) is not appli-
cable.
6 DISCUSSION AND
CONCLUSIONS
Data distributions considered in this study either var-
ied w.r.t. the processing time distributions, continuing
the preliminary experimentsin (Ingimundardottirand
Runarsson, 2011b) , or w.r.t. the job ordering permu-
tations – i.e., homogeneous machine order for PFSP
versus heterogeneousmachine order for JSP. From the
results based on 6× 5 training data given in Table 4,
it’s obvious that CMA-ES optimisation substantially
outperforms the previous PREF methods from (In-
gimundardottir and Runarsson, 2011b) for all prob-
lem spaces considered. Furthermore, the results hold
when testing on 10 × 10 (cf. Table 5), suggesting the
method is indeed scalable for higher dimensions.
Moreover, the study showed that the choice of ob-
jective function for evolutionary search is worth in-
vestigating. There was no statistical difference from
minimising the fitness function directly and its nor-
malisation w.r.t. true optimum (cf. Eqs. (6) and (7)),
save for P
f.rndn
. Implying, even though ES doesn’t
rely on optimal solutions, there are some problem
spaces where it can be of great benefit. This is due
to the fact that the problem instances can vary greatly
within the same problem space (Ingimundardottir and
Runarsson, 2012). Thus normalising the objective
function would help the evolutionary search to devi-
ate the from giving too much weight for problematic
problem instances for the greater good.
The main drawback of using evolutionary search
for learning optimal weights for Eq. (1) is how com-
putationally expensive it is to evaluate the mean ex-
pected fitness. Even for a low problem dimension
6-job 5-machine JSP, each optimisation run reached
their walltime of 288 hours without converging. Now,
6× 5 JSP requires 30 sequential operations where at
each time step there are up to 6 jobs to choose from
– i.e., its complexity is O(n
n·m
) making it computa-
tionally infeasible to apply this framework for higher
dimensions as is. However, evolutionary search only
requires the rank of the candidates and therefore it
is appropriate to retain a sufficiently accurate surro-
gate for the value function during evolution in order
to reduce the number of costly true value function
evaluations, such as the approach in (Ingimundard-
ottir and Runarsson, 2011a). This could reduce the
computational cost of the evolutionary search consid-
erably, making it feasible to conduct the experiments
from Section 5 for problems of higher dimensions,
e.g. with these adjustments it is possible to train on
10 × 10 and test on for example 14 × 14 to verify
whether scalability holds for even higher dimensions.
EvolutionaryLearningofWeightedLinearCompositeDispatchingRulesforScheduling
65
Table 4: Main statistics of percentage relative deviation
from optimality, ρ, defined by Eq. (5) for various models,
using corresponding 6× 5 training data.
(a) P
6×5
j.rnd
model mean med sd min max
ES
C
max
8.54 10 6 0 26
ES
ρ
8.26 10 6 0 26
PREF 10.18 11 7 0 30
MWR 16.48 16 9 0 45
(b) P
6×5
j.rndn
model mean med sd min max
ES
C
max
8.68 11 6 0 31
ES
ρ
8.69 11 6 0 31
PREF 10.00 11 6 0 31
MWR 14.02 13 8 0 37
(c) P
6×5
f.rnd
model mean med sd min max
ES
C
max
7.44 7 5 0 23
ES
ρ
7.48 7 5 0 34
PREF 9.87 9 7 0 38
LWR 20.05 19 10 0 71
(d) P
6×5
f.rndn
model mean med sd min max
ES
C
max
8.09 8 2 0 11
ES
ρ
0.94 1 1 0 4
PREF 2.38 2 1 0 7
LWR 2.25 2 1 0 7
(e) P
6×5
f. jc
model mean med sd min max
ES
C
max
0.33 0 0 0 2
ES
ρ
0.36 0 0 0 2
PREF 1.08 1 1 0 5
LWR 1.13 1 1 0 6
Table 5: Main statistics of C
max
for various models, using
corresponding 10× 10 test data.
(a) P
10×10
j.rnd
model mean med sd min max
ES
C
max
922.51 914 73 741 1173
ES
ρ
931.37 931 71 735 1167
PREF 1011.38 1004 82 809 1281
MWR 997.01 992 81 800 1273
(b) P
10×10
j.rndn
model mean med sd min max
ES
C
max
855.85 857 50 719 1010
ES
ρ
855.91 856 51 719 1020
PREF 899.94 898 56 769 1130
MWR 897.39 898 56 765 1088
(c) P
10×10
f.rnd
model mean med sd min max
ES
C
max
1178.73 1176 80 976 1416
ES
ρ
1181.91 1179 80 984 1404
PREF 1215.20 1212 80 1006 1450
LWR 1284.41 1286 85 1042 1495
(d) P
10×10
f.rndn
model mean med sd min max
ES
C
max
1065.48 1059 32 992 1222
ES
ρ
980.11 980 8 957 1006
PREF 987.49 988 9 958 1011
LWR 986.94 987 9 959 1010
(e) P
10×10
f. jc
model mean med sd min max
ES
C
max
1135.44 1134 286 582 1681
ES
ρ
1135.47 1134 286 582 1681
PREF 1136.02 1135 286 582 1685
LWR 1136.49 1141 287 581 1690
ECTA2014-InternationalConferenceonEvolutionaryComputationTheoryandApplications
66

REFERENCES
Ak, B. and Koc, E. (2012). A Guide for Genetic Algorithm
Based on Parallel Machine Scheduling and Flexible
Job-Shop Scheduling. Procedia - Social and Behav-
ioral Sciences, 62:817–823.
Burke, E. K., Gendreau, M., Hyde, M., Kendall, G., Ochoa,
G., Ozcan, E., and Qu, R. (2013). Hyper-heuristics:
a survey of the state of the art. Journal of the Opera-
tional Research Society, 64(12):1695–1724.
Cheng, R., Gen, M., and Tsujimura, Y. (1996). A tutorial
survey of job-shop scheduling problems using genetic
algorithmsI. Representation. Computers & Industrial
Engineering, 30(4):983–997.
Cheng, R., Gen, M., and Tsujimura, Y. (1999). A tutorial
survey of job-shop scheduling problems using genetic
algorithms, part II: hybrid genetic search strategies.
Computers & Industrial Engineering, 36(2):343–364.
Dhingra, A. and Chandna, P. (2010). A bi-criteria M-
machine SDST flow shop scheduling using modified
heuristic genetic algorithm. International Journal of
Engineering, Science and Technology, 2(5):216–225.
Gurobi Optimization, Inc. (2013). Gurobi optimization
(version 5.6.2) [software].
Hansen, N. and Ostermeier, A. (2001). Completely deran-
domized self-adaptation in evolution strategies. Evol.
Comput., 9(2):159–195.
Haupt, R. (1989). A survey of priority rule-based schedul-
ing. OR Spectrum, 11:3–16.
Ingimundardottir, H. and Runarsson, T. P. (2011a). Sam-
pling strategies in ordinal regression for surrogate as-
sisted evolutionary optimization. In Intelligent Sys-
tems Design and Applications (ISDA), 2011 11th In-
ternational Conference on, pages 1158–1163.
Ingimundardottir, H. and Runarsson, T. P. (2011b). Super-
vised learning linear priority dispatch rules for job-
shop scheduling. In Coello, C., editor, Learning
and Intelligent Optimization, volume 6683 of Lecture
Notes in Computer Science, pages 263–277. Springer,
Berlin, Heidelberg.
Ingimundardottir, H. and Runarsson, T. P. (2012). Deter-
mining the characteristic of difficult job shop schedul-
ing instances for a heuristic solution method. In
Hamadi, Y. and Schoenauer, M., editors, Learning and
Intelligent Optimization, Lecture Notes in Computer
Science, pages 408–412. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg.
Jayamohan, M. and Rajendran, C. (2004). Development
and analysis of cost-based dispatching rules for job
shop scheduling. European Journal of Operational
Research, 157(2):307–321.
Koza, J. R. and Poli, R. (2005). Genetic programming. In
Burke, E. and Kendal, G., editors, Introductory Tutori-
als in Optimization and Decision Support Techniques,
chapter 5. Springer.
Nguyen, S., Zhang, M., Johnston, M., and Tan, K. C.
(2013). Learning iterative dispatching rules for job
shop scheduling with genetic programming. The In-
ternational Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Tech-
nology.
Panwalkar, S. S. and Iskander, W. (1977). A survey of
scheduling rules. Operations Research, 25(1):45–61.
Pinedo, M. L. (2008). Scheduling: Theory, Algorithms, and
Systems. Springer Publishing Company, Incorporated,
3 edition.
Qing-dao-er ji, R. and Wang, Y. (2012). A new hybrid
genetic algorithm for job shop scheduling problem.
Computers & Operations Research, 39(10):2291–
2299.
Rice, J. R. (1976). The algorithm selection problem. Ad-
vances in Computers, 15:65–118.
Smith-Miles, K., James, R., Giffin, J., and Tu, Y. (2009).
A knowledge discovery approach to understanding re-
lationships between scheduling problem structure and
heuristic performance. In Sttzle, T., editor, Learning
and Intelligent Optimization, volume 5851 of Lecture
Notes in Computer Science, pages 89–103. Springer,
Berlin, Heidelberg.
Smith-Miles, K. and Lopes, L. (2011). Generalising algo-
rithm performance in instance space: A timetabling
case study. In Coello, C., editor, Learning and Intel-
ligent Optimization, volume 6683 of Lecture Notes in
Computer Science, pages 524–538. Springer, Berlin,
Heidelberg.
Tay, J. C. and Ho, N. B. (2008). Evolving dispatching
rules using genetic programming for solving multi-
objective flexible job-shop problems. Computers and
Industrial Engineering, 54(3):453–473.
Tsai, J.-T., Liu, T.-K., Ho, W.-H., and Chou, J.-H. (2007).
An improved genetic algorithm for job-shop schedul-
ing problems using Taguchi-based crossover. The In-
ternational Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Tech-
nology, 38(9-10):987–994.
V´azquez-Rodr´ıguez, J. A. and Petrovic, S. (2009). A new
dispatching rule based genetic algorithm for the multi-
objective job shop problem. Journal of Heuristics,
16(6):771–793.
Watson, J.-P., Barbulescu, L., Whitley, L. D., and Howe,
A. E. (2002). Contrasting structured and random
permutation flow-shop scheduling problems: Search-
space topology and algorithm performance. IN-
FORMS Journal on Computing, 14:98–123.
EvolutionaryLearningofWeightedLinearCompositeDispatchingRulesforScheduling
67
