
Should I Be Aware of the Information of Other Actors
Transversal Communication in Crisis Management
Amina Saoutal, Nada Matta and Jean-Pierre Cahier
ICD/Tech-CICO, Université de Technologie de Troyes 12 rue Marie Curie, BP. 2060,10010 Troyes Cedex, France
Keywords: Communication, Information Sharing, Awareness, Emergency Response, Crisis Management.
Abstract: In crisis management, multi-organizations are involved to deal with the events; however these services
encounter several problems that make the transversal communication and information sharing very hard,
with an ineffective mutual awareness during crisis response. Whereas, among the factors for crisis
management success, figures prominently mutual awareness and awareness information, this requires
effective interaction of the relevant information between emergency actors. But in the reality this
communication is ineffective and influences the decision making. Thus, to support emergency response,
enhance “awareness information” and transversal communication between different emergency actors, our
contribution in this paper is to understand the organizations involved in emergency response and analyse the
communication between actors. Thus we study at first, the vertical and the transversal communication in
inter/intra emergency organizations. Second, we highlight and analyse the root causes of communication
problems that actors encounter in operating level. Third, we classify by category the major information
needed in emergency response and finally, we present the dependency between awareness information and
actions achievement.
1 INTRODUCTION
Whether it is a flood, explosion in a factory,
poisoning, climatic event, fire, power failure, attack
etc…These events can produce a process of
dysfunctions and generate a crisis. To deal with
these events, several actors (professionals,
volunteers ...) from different organizations intervene
in the area to manage the crisis. Among the factors
for crisis management success, figures prominently
mutual awareness. Be aware about other activities
gives a context to own activity (Dourish and Bellotti,
1992) and it is crucial to achieve a specific task
(Schmidt, 2002; Steinmacher, 2012) in which
awareness is considered as an attribute of action (De
Souza, 2011). Achieving awareness in crisis
management requires effective inter/intra-
communication and relevant information sharing
between emergency actors (Ellis, 1991; Stanton,
2007) especially in transversal level. Not necessarily
that everyone needs to be aware of the same
information about others’ activities, but what really
matters is, the right people have the right
information at the right time to achieve an action
(Gorman et al. 2006 ; Salmon et al., 2010).
For that, to support information sharing and
awareness information, we study in this paper, the
activities of different emergency actors, we analyse
the communication in intra/inter-organizational and
we identify their roles, actions and information
needed.
2 RELATED WORK
Usually emergency actors encounter technical
problems related to the infrastructure and
transmission that affects communication, especially
in rural areas; Bowman describes a mobile
communication system to overcome this problem
(Bowman, 2006), Sharma proposed architecture of
cell-share to provide a back-channel for network
troubleshooting (Sharma, 2009) and Secretan
designs framework of ad-hoc network to share
disaster information (Secretan, 2011). Another
problem in which team member does not share
information is lack of trust. Chan has introduced two
points to boost confidence between actors: ability of
actor to send relevant information to others and
willingness to share information (Chan, 2012). Other
212
Saoutal A., Matta N. and Cahier J..
Should I Be Aware of the Information of Other Actors - Transversal Communication in Crisis Management.
DOI: 10.5220/0005077702120219
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Sharing (KMIS-2014), pages 212-219
ISBN: 978-989-758-050-5
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
problems related to the information are the quality,
the format and the quantity of information (Bui,
2000 and Ho et al., 2001).
In addition to the previous problems, we show in
this paper that emergency actors encounter other
problems related to their organization and culture.
Several studies are conducted to support the first
responders in crisis management. In order to
improve awareness among firefighters, Prasanna
proposed a prototype for information sharing that
provides awareness about the most important roles
in fire department (Prasanna, 2011). However, this
analysis is restricted to one emergency service.
Other studies were conducted on multi-agencies;
Ludwig showed and proposed semi-structure system
for the communication between actors on the site
and the control centres (Ludwig, 2013). Bui
proposed a system of GIN (Global Information
Network) to improve communication between multi-
agencies (Bui, 2000). However in these work we do
not see clearly the communication, the interaction of
information sharing and actions between different
emergency actors transversally in the operating
level. Our contribution is to complete the previous
study and make careful analysis of vertical and
transversal communication.
Thus, before supporting crisis response and
enhance communication between stakeholders, we
study at first the multi-organizations, we focus on
the communication and information sharing between
the most important emergency services vertically
and transversely. Second, we show the root causes
of communication problems that actors encounter in
sharing information. Third, we classify the
information needed in emergency response and
finally, we present the dependency between the
relevant information that an actor needs to make
decision and achieve an action.
3 EMERGENCY ACTORS IN
CRISIS RESPONSE
In this paper we study the activities, information
sharing of stakeholders and communication
problems that actors face during crisis management.
Mainly in our work, we are interested in the major
rescuers during a response: firefighters, police and
emergency medical service (EMS).
3.1 Data Gathering
We did a number of semi-structured interviews with
emergency actors from different organizations:
firefighters whose scales are different; we did two
interviews with two commanders and two others,
who are respectively column leader and group
leader, an interview with police commander and
three with specialists in emergency medical service
(EMS) at the Aube department (France) In addition
to four exercises debriefing with EMS.
We asked them to tell the most remarkable
experiences to have general idea and through the
interview, we asked pointed questions about
communication, information sharing and how they
communicate transversally with other organizations.
After examining the different interviews and
experiences, we translated data collection to models
and we highlighted the information needed by each
organization in each step, the dependency between
actions and the need for information awareness to
achieve their actions.
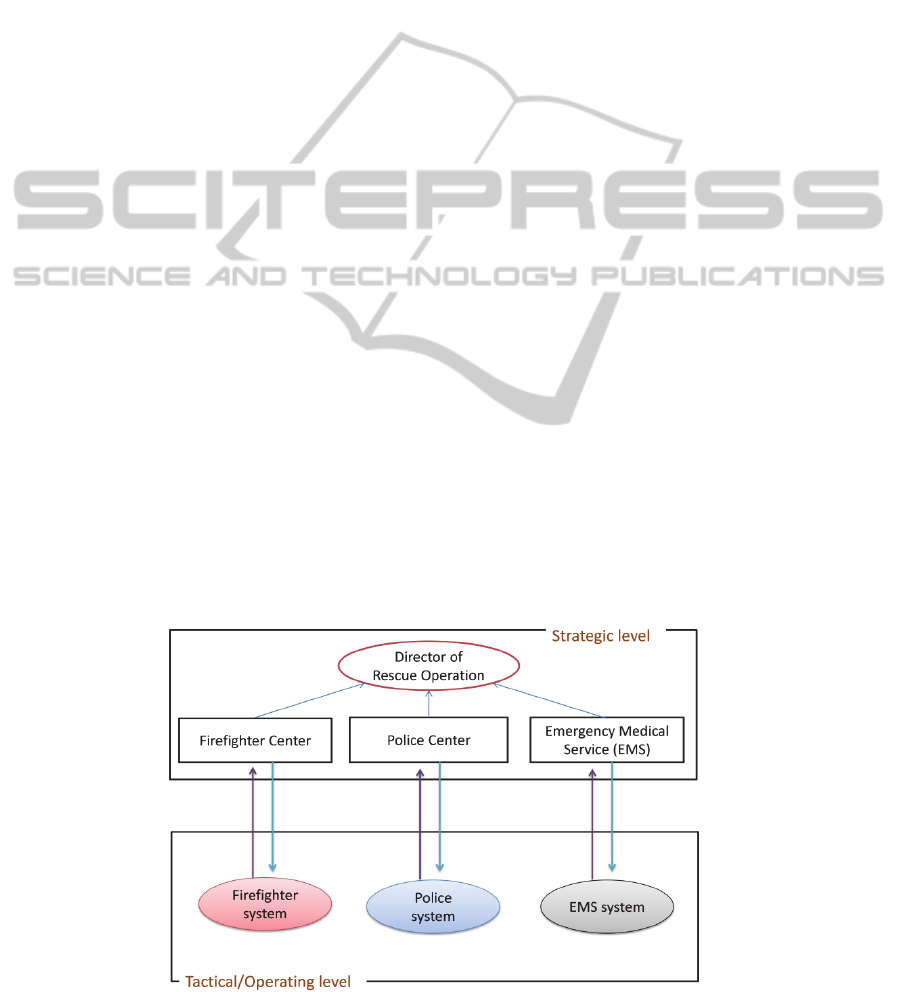
Figure 1: Organizational model in crisis management.
ShouldIBeAwareoftheInformationofOtherActors-TransversalCommunicationinCrisisManagement
213
3.2 Organizational Model
Before analysing the information sharing and
communication between actors vertically and
transversally, we show first the organizational model
to understand emergency system composition in
crisis management. In Fig.1 we will present the
model of inter-services operations, in which we
define organizational levels in the management
operation (Saoutal, 2014).
Strategic level: The major decisions are taken
in this level by the inter-ministerial
governmental / territorial / politics and
administrative crisis cell.
Tactical level: In this level the responsible of
each system, analyse the events and decides
objectives for carrying out.
4 INFORMATION SHARING IN
CRISIS MANAGEMENT
Each service has its own activity and its own
objective, the difference of goals and actions
between different actors can hind information
sharing and then influence awareness. In this
section, we show sequentially the vertical
communication and information sharing for each
service and then inter-communication between
different services.
4.1 Vertical Communication
In this part, we present the communication and
information sharing for each service and how team
member exchange message.
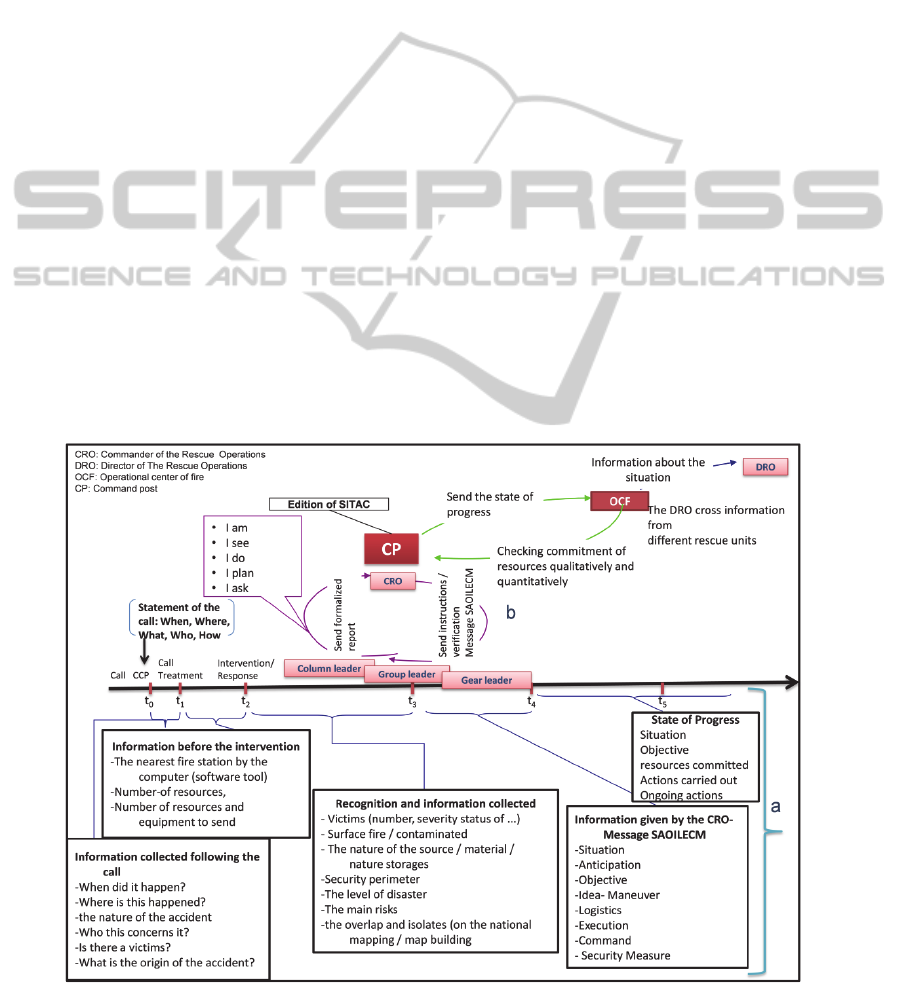
4.1.1 Firefighter
In figure 1, we show the information progress from
the beginning of event and what is the relevant
information that Firefighter service need to achieve
its objective (a). Also we show the interaction,
message exchanging and information sharing
between firefighters with different scale (b).
4.1.2 Emergency Medical Service
For Emergency Medical Service (EMS), the first
emergency post analyses the event, treats victims (a)
and transmits the information / reports to the
hospital to ask for needed emergency post and
material (b) (Sediri et al, 2013). The EMS also
transmits information to the DRO (figure 3).
Figure 2: Chronology of communication in crisis management for firefighters.
KMIS2014-InternationalConferenceonKnowledgeManagementandInformationSharing
214
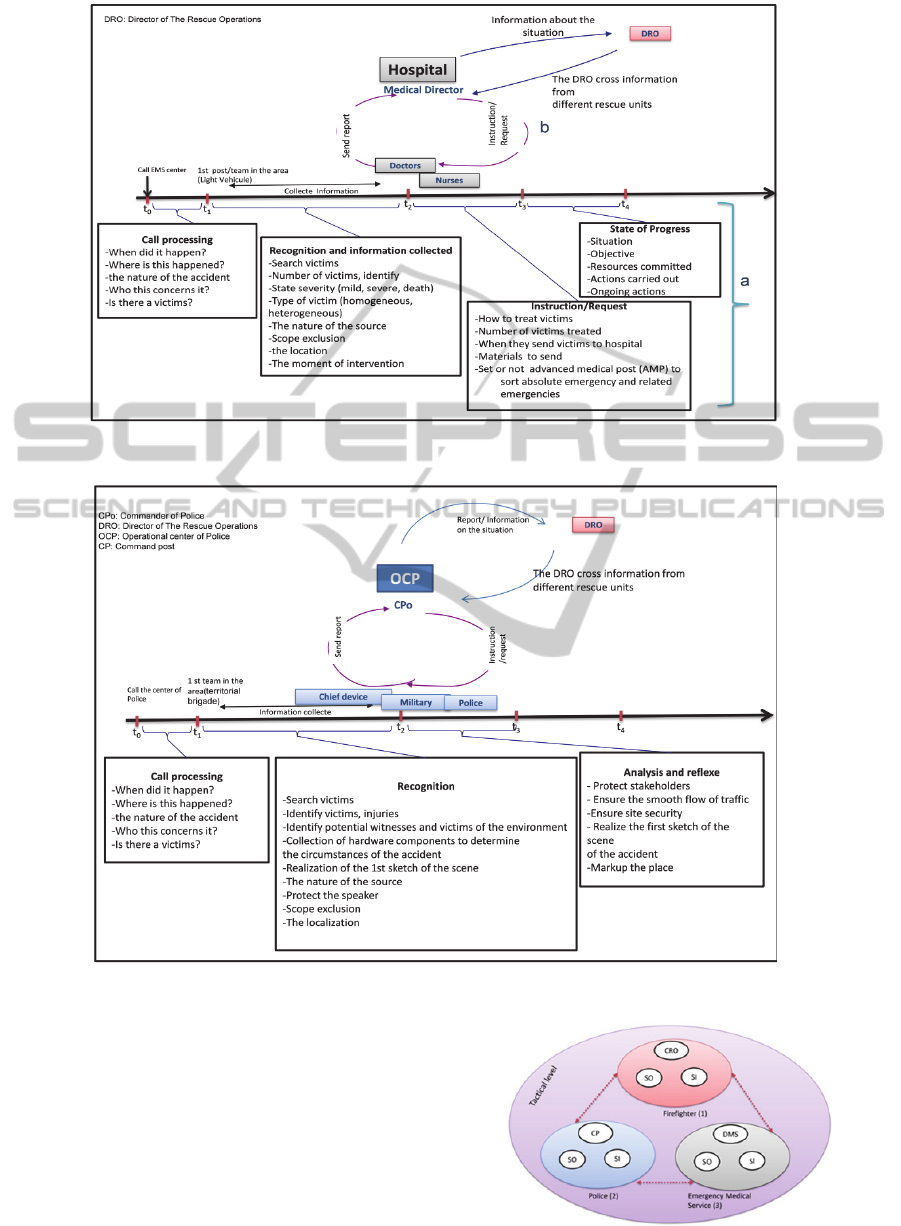
Figure 3: Chronology of communication in crisis management for EMS.
Figure 4: Chronology of communication in crisis management for police.
4.1.3 Police
In parallel the first team of police collects its specific
information: identify victims, identify witnesses,
collect material element to determine the
circumstances of accident, and determine the scope
of exclusion. Then, all this information is send to the
operational center of police.
Figure 5: Operative system in crisis management.
ShouldIBeAwareoftheInformationofOtherActors-TransversalCommunicationinCrisisManagement
215

4.2 Transversal Communication
In Fig.5, we present the model of inter-services at
operating level in crisis management; it consists of
three systems (1), (2) and (3) and each one includes
leader system, sub-system operating and sub-
information system:
CRO: Commander of the Rescue Operations is
a firefighter expert, the grade can vary
depending on the procedure, and it may be in
ascending order; from the team leader to the
site leader. His role is to ensure the success of
tactical operations close to the crisis site.
DCG: Commander of police, his role is to
ensure the site’s security.
DMS: Director of Medical Service is the
responsible for all medical decisions and
should always be in coordination with the
CRO.
SO: Subsystem Operating consists of teams and
equipment.
SI: Sub Information System, fire-fighters and
police transmit their vocal codified messages
by using a radio frequency band; the EMS
uses the radio and sometimes GSM mobile
phone to transmit photos and vocal
information.
The plan and the procedure indicate that the
commanders from different organizations (1) (2) and
(3) (Figure 5) have to communicate and share
relevant information transversally. However, in the
reality, each service works vertically with its
hierarchy with few information sharing and
interaction between different team members in this
level. However, each action to be performed may
depend on the information possessed by other actors.
5 RESULTS ANALYSIS
5.1 Transversal Information Sharing
Problems
The root causes of transversal information sharing
problem are:
Time pressure: When the actor must send
information as soon as possible to the strategic
level and waits the instruction from his
hierarchy to act, it could result more deaths
among the victims.
Self-esteem and competition: We can note that
different services are competitive in the crisis
area.
Information direction: In several times,
information is misdirected and actors do not
know to whom send or ask information.
Information type: Actors do not know exactly
which type of information is relevant for other
actors to execute their actions.
Actors distribution: We are not aware of who
is in the area or not and who will have access
to the specific area.
Different langage: Understanding message
depends on how we perceive the terminology
used by the actor transmitter. Each unit has its
terminology and uses its specific code, symbol
of message to communicate and represent
information, which is difficult to be
understandable by other units.
Different culture: Considering the multitude of
organizations involved in a crisis and the
differences of services’ culture, each unit has
its objective and priority.
The consequences of these problems are shown
when each service sends a progress report to inform
strategic level:
Impact on decision making: The director of
the rescue operations (DRO) finds different or
even contradictory information, because each
service works in its scope.
Losing time: The DRO asks services to verify
information in operational level, and when
actors do not know to whom ask or send
information.
Losing of information: When an actor delivers
information verbally to other actors verbally,
it could be loosed.
Serious damage: Several human and material
damages are generated due to the lack of
information sharing and awareness of the
overall situation.
5.2 Communication Protocol
The communication between different actors in
crisis management has three categories:
Information request: When an actor asks for
information needed to execute an action, to
follow the progress of events and to send
instruction to achieve.
Information description: the system operating
gives the situation progress and sends
description to the system leader to receive
KMIS2014-InternationalConferenceonKnowledgeManagementandInformationSharing
216
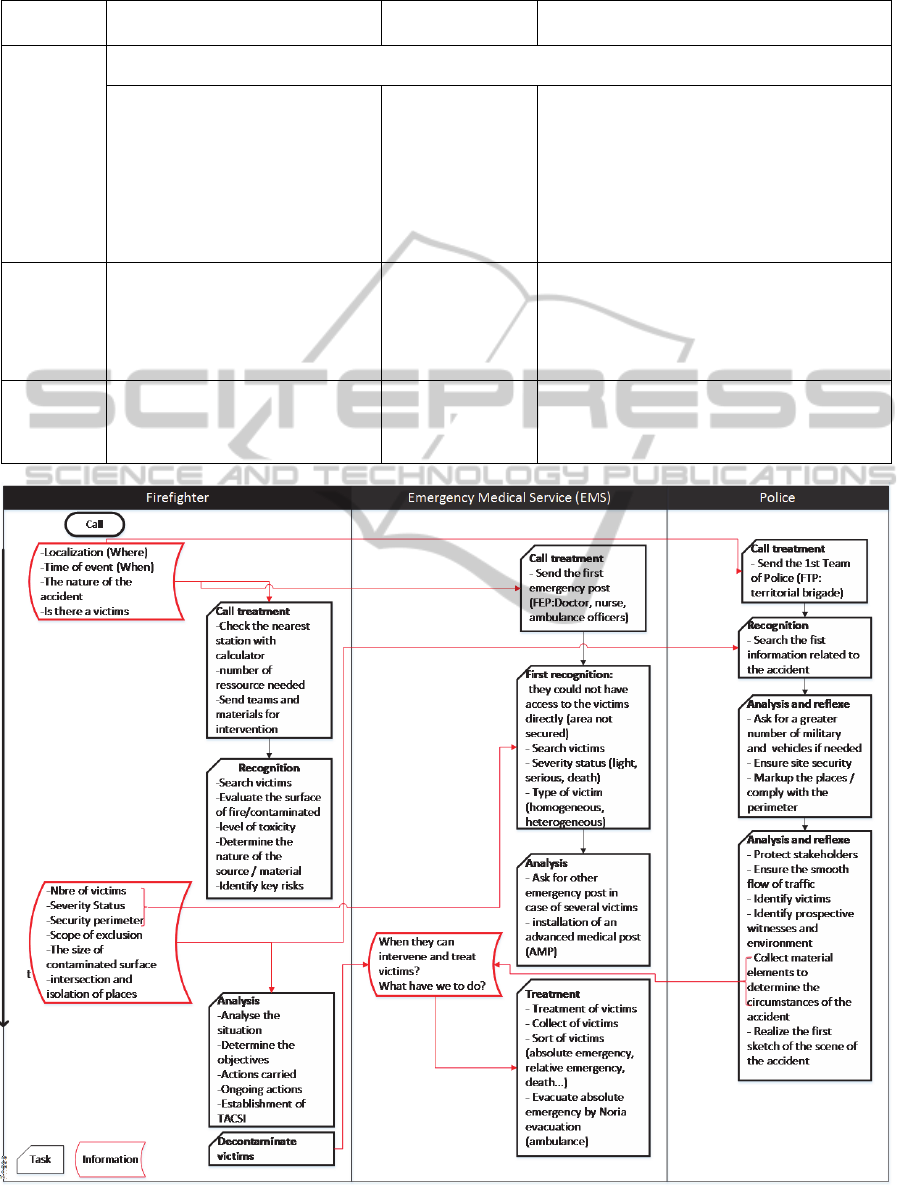
Table 1: Information related to each service in crisis management.
Information
category
Firefighter Police EMS
Request
-When did it happen? -Where is it happened? -the nature of the accident? -Who are concern person?
-Is there victims?-What is the origin of the accident?
-How to treat victims
-Who could have access to the toxic
area
-Action objectives
-Action ongoing
-Action instruction
-When they can
have access?
-Who can have
access to crisis
area?
-Ask for a number
of military and
vehicles if needed
-What they have to do?
-Number of victims (access denied in the area)?
-Severity status?
-Number of victims treated
-When they send victims to hospital
-Materials to send
-Set or not advanced medical post (AMP) to
sort absolute emergency and related
emergencies
Description
-Message SOAILECM.
-I am: Identification of actor
-I see: Describe what he sees
-I do: Describe what he is doing
-I plan: Describe what he plan to do
-I ask: Describe what he needs
-The circumstances
of the accident
-Site security
- Number of victims
-Severity status of each victim
-Type of victim (homogeneous, heterogeneous)
-The moment of intervention
Instruction
-Situation -Anticipation
-Objective -Idea- Maneuver
-Logistics -Execution
-Command - Security Measure
- Mark-up the area
-Logistics
–Manoeuvre
-Install of an advanced medical post (AMP)
-Send victims to correspond service.
-How to treat this victims
Figure 6: Information-Action dependency.
ShouldIBeAwareoftheInformationofOtherActors-TransversalCommunicationinCrisisManagement
217

instructions. The leader of each system send
report to the strategic level about the progress,
actions carried, material and resources needed
etc…
Information instructions: after receiving
information description or request, the
commander of rescue or system leader gives
instructions and order to execute and carry out
in the area.
The table 1 present the general information
related and needed by each service classified by
category.
5.3 Information-Action Dependency
On analysing the activities of different actors
through the interviews and exercises, we conclude
the interdependency between actions and
information awareness. In other words, an activity to
be performed may depend on information possessed
by others. For example, EMS could not collect and
treat victims if the firefighters haven’t determined
yet the scope of exclusion, secure the area and
decontaminate victims. Also the police could not
search the first information related to the accident
before that. Actors need an informational interaction
to execute an action. For instance, the firefighter
needs information about “victim treatment” to treat
the victim (e.g. area does not allow access to the
doctor: Toxic area), but the doctor could not deliver
the right information if he does not possess the
information about “victim severity” and his state.
Thus, it is important to share this information for
both the sender and the receiver.
6 CONCLUSIONS
On analysing the operations and experiences of
different emergency actors in crisis management, we
found problems about communication and
information sharing specially in transversal
organizations. Different services with different
cultures and priorities are invited to collaborate and
deal together with crisis; however, many problems
can hint the communication, information sharing and
impact their cooperation as consequence. In this
paper, we analyse the communication in each
service and between different services. We
emphasize the problems that influence transversal
communication between different rescuers and how
these problems can impact information awareness
and then, achievement of actions.
In our future work, we will propose a
cooperative system and common workspace between
different organizations to enhance the interaction of
relevant information by emergency actors and in
order to increase mutual awareness in crisis area to
perform actions easily and at the right time.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We thank the Champagne-Ardennes Region
(France) and all contributors of this work.
REFERENCES
Bowman, M., Graham, J.H. and Gantt, J., 2006 A Robust
and Affordable Mobile Communications System for
Emergency Management and Crisis Response. In
Fourth Annual Conference on Telecommunications &
Information Technology.
Bui T. A 2000 Framework for Designing a Global
Information Network for Multinational Humanitarian
Assistance / Disaster Relief. 2000
Chan, K., Jin-Hee Cho, and Adali, S., 2012. Composite
Trust Model for an Information Sharing Scenario.
2012 9th International Conference on Ubiquitous
Intelligence and Computing and 9th International
Conference on Autonomic and Trusted Computing,
September. Ieee, 439–46. doi:10.1109/UIC-
ATC.2012.11. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/lpdocs/
epic03/wrapper.htm?arnumber=6332033.
De Souza, C. R. B., and Redmiles, David F.. 2011. The
Awareness Network, To Whom Should I Display My
Actions? And, Whose Actions Should I Monitor?
IEEE Transactions on Software Engineering 37 (3):
325–40. doi:10.1109/TSE.2011.19. http://ieeexplore.
ieee.org/lpdocs/epic03/wrapper.htm?arnumber=57109
50.
Dourish, P., and Bellotti, V., 1992. Awareness and
Coordination in Shared Workspaces. Proceedings of
the 1992 ACM Conference on Computer-Supported
Cooperative Work - CSCW ’92. New York, New
York, USA: ACM Press, 107–14.
doi:10.1145/143457.143468. http://portal.acm.org/
citation.cfm?doid=143457.143468.
Gorman, J. C., Cooke, N. J. & Winner, J. L. 2006:
Measuring team situation awareness in decentralized
command and control environment. Ergonomics,
49(12-13), 1312-25 (2006). DOI:10.1080/
00140130600612788
Ellis, C.A. Gribbs S.J. and Rein G.L., 1991 Groupware -
some issues and experiences, Communications of the
ACM 34(1) . 38-58.
Ho, J. and Tang R. 2001. Towards an optimal resolution to
information overload: an infomediary approach. In
Proceedings of the 2001 International ACM
SIGGROUP Conference on Supporting Group Work
(GROUP '01), Clarence (Skip) Ellis and Ilze Zigurs
KMIS2014-InternationalConferenceonKnowledgeManagementandInformationSharing
218

(Eds.). ACM, New York, NY, USA, 91-96. (2001)
DOI=10.1145/500286.500302
http://doi.acm.org/10.1145/500286.500302
Ludwig, T., Reuter, C. and Pipek. V. 2013. What You See
Is What I Need : Mobile Reporting Practices in
Emergencies, no. September: 21–25.
Prasanna, R., Yang, L. & King, M. (2011). Evaluation of a
Software Prototype for Supporting Fire Emergency
Response. Proceedings of the 8th International
ISCRAM Conference – Lisbon, Portugal.
Salmon, Paul M., Neville, A. Stanton, Walker, Guy H.
Jenkins, Daniel P. and Rafferty, L.. 2010. Is It Really
Better to Share? Distributed Situation Awareness and
Its Implications for Collaborative System Design.
Theoretical Issues in Ergonomics Science 11 (1-2):
58–83. doi:10.1080/14639220903009953. http://www.
tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/14639220903009953
Saoutal A., Cahier J.-P., Matta N. (2014). Modeling the
communication between emergency actors in crisis
management. Collaboration Technologies and Systems
(CTS), International Conference (to be published).
Secretan, J. 2011. Collaborative Filtering of Spatial-
Temporal Information for Crisis Informatics. 2011
IEEE International Multi-Disciplinary Conference on
Cognitive Methods in Situation Awareness and
Decision Support (CogSIMA), February. Ieee, 292–
95. doi:10.1109/COGSIMA.2011.5753461. http://
ieeexplore.ieee.org/lpdocs/epic03/wrapper.htm?arnum
ber=5753461.
Schmidt, K. 2002. The Problem with ‘Awareness’:
Introductory Remarks on ‘Awareness in CSCW’.
Computer Supported Cooperative Work, vol. 11, no.
3, pp. 285–298.
Sediri, M, Matta, N., Dai, J., Loriette, S. and Hugerot, A.
2013. Experience Feedback Guides for Crisis
Management Using GIS. 2013 International
Conference on Collaboration Technologies and
Systems (CTS), May. Ieee, 294–99.
doi:10.1109/CTS.2013.6567244. http://ieeexplore.
ieee.org/lpdocs/epic03/wrapper.htm?arnumber=65672
44.
Sharma, A., Belding, Elizabeth M. and Perkins, Charles E.
2009. “Cell-Share: Opportunistic Use of Cellular
Uplink to Augment Rural WiFi Mesh Networks.”
2009 IEEE 70th Vehicular Technology Conference
Fall, September. Ieee, 1–5. doi:10.1109/
VETECF.2009.5379029.
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/lpdocs/epic03/wrapper.htm?
arnumber=5379029.
Stanton, N., A.,Stewart,R., Harris, D., Houghton, R. J.,
Baber, C., McMaster, R., Salmon, P. et al. 2007.
Distributed Situation Awareness in Dynamic Systems:
Theoretical Development and Application of an
Ergonomics Methodology. Ergonomics 49 (12-13):
1288–1311. doi:10.1080/00140130600612762. http://
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17008257.
ShouldIBeAwareoftheInformationofOtherActors-TransversalCommunicationinCrisisManagement
219
