
An Ontology for Specifying and Parsing
Knowledge Representations Structures and Notations
Philippe Martin
1
and Jérémy Benard
2
1
EA2525 LIM, ESIROI I.T., University of La Réunion, F-97490 Sainte Clotilde, France
(and adjunct researcher of the School of ICT, Griffith University, Australia)
2
GTH, Logicells, 3 rue Désiré Barquisseau, 97410 Saint-Pierre, France
Keywords: Language Ontology, Meta-Modelling, Syntactic Translation, Knowledge Representation Languages.
Abstract: In its introduction, this article gives a short state of the art about ontologies of knowledge representation
languages (KRLs) and the problems caused by i) the lack of relations between these ontologies, and ii) the
lack of ontologies about notations (concrete syntaxes). For programmers, these are the difficulties of
importing, exporting or translating between KRLs; for end-users, the difficulties of adapting, extending or
mixing notations. To show how these problems can be solved, this article first shows how concepts of the
main KRL standards can be aligned and organized. Then, it shows how this KRL model ontology can be re-
used and completed by a notation ontology. Based on these two ontologies, KRLs models and notations -
and thereby parsing and generation - can be specified in a concise way that even KRL end-users can adapt.
The article gives representative examples. For these ontologies or specifications, a concise KRL notation is
introduced and used. However, the presented approach is independent of any notation and model that has at
least OWL-2 expressiveness. Thus, the results can easily be replicated. A Web address for the full
specification of the two ontologies, and for a knowledge server to test or use them, is also given.
1 INTRODUCTION
Various language models are used for knowledge
representation, retrieval and exploitation. For each
model (abstract syntax) there are also many possible
notations (concrete syntaxes). Creating a parser or an
export procedure for each knowledge representation
language (KRL; one model and/or one notation) is
time-consuming. Specifying the automatic translation
of knowledge (representations) from one KRL to
another is difficult, especially without some shared
ontology of these KRLs, hence without formal
semantic relations between their components.
Learning and understanding a KRL is also difficult
for a person. These are therefore also difficulties for
knowledge sharing. For a knowledge provider, not
being able to adapt a KRL notation, is also limiting.
There have been many works for partially
addressing these problems, except for the last one
which requires the use of a KRL notation ontology to
enable any significant adaptation.
An early major work was KIF (Knowledge
Interchange Format) (Genesereth and Fikes, 1992), a
1st-order logic based KRL - with a 2nd-order notation -
to which most KRLs could be translated to and
formalized with. Many were. To ease this, the
Ontolingua "ontology server or shared repository"
(Farquhar et al., 1997) provided a well formalized
KRL model ontology. E.g., it included a formalization
of frame-based language concepts in KIF (concepts
similar to those of OWL).
Later, with the popularization of MOF (the Meta-
Object Facility of the OMG: Object Management
Group), XML and then RDF, many language models
or ontologies were created in these three languages.
These were often simple lists of KRL components
and their structural relations. Indeed, MOF, XML and
RDF do not permit to fully define KRL components
and hence relate all of them as in Ontolingua. They
still permit to declare and use a set of KRL
components that corresponds to a certain logics with
well studied properties. Thus, the W3C provided the
different language ontologies of the OWL family
(OWL 2, 2009). With RIF-FLD, it also provided an
expressive and extensible "Framework for Logic
Dialects" (RIF-FLD, 2013). ANSI provided CL
(Common Logic, 2007), a "framework for a family of
logic-based languages" restricted to 1st-order logic.
96
Martin P. and Benard J..
An Ontology for Specifying and Parsing Knowledge Representations Structures and Notations.
DOI: 10.5220/0005082500960107
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development (KEOD-2014), pages 96-107
ISBN: 978-989-758-049-9
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

The OMG created a "Conceptual package" along with
an ontology for the "Semantics of Business
Vocabulary and Business Rules" (SBVR,
2008).These standards (RDF+OWL+RIF-FLD, CL
and MOF+SBVR) have similar or complementary
components. They are declared in their respective
XML schemas but, to our knowledge, no ontology
semantically relates them nor to concepts in Onto-
lingua. However, within the scope of each of these
standards, there are works on translating between
models or ontologies. E.g., the W3C specifies ways
to re-use RDF and OWL knowledge in RIF.
Model translation is often only a part of knowledge
translation or (re-)presentation. Indeed, there are
many existing or potential notations for KRL models
and, so far, unlike some KRL models, no notation was
represented by an ontology. Thus, no notation could
be adapted or extended by their users, except very
partially via a system of macros such as the one
usable with the C programming language. A different
parser and generator also had to be built for each
notation, except for XML-based notations (e.g,
RDF/XML: RDF in XML). The W3C proposes XSLT
for specifying syntactic translations between XML
based notations. It also proposes GRDDL for
specifying where a software agent can find "algorithms
(typically represented in XSLT)" to convert a structure
or notation to RDF/XML. Conversely, there are some
style-sheet based transformation languages and
ontologies for specifying how RDF abstract structures
can be presented, e.g., in a certain order, in bold, in a
pop-up window, etc.
: Xenon (Quan, 2005), Fresnel
(Bizer et al., 2006), OWL-PL (Brophy and Heflin,
2009) and SPARQL Template (Corby et al., 2014).
With these tools or the approach behind these tools,
each modification to a notation requires a new
template or style-sheet, and parsing is not addressed.
Supporting knowledge import/export/translation
in a generic way requires specifying KRLs with
respect to a KRL model ontology and a KRL notation
ontology. This article presents such ontologies and
gives examples of their use. To do so in a sufficiently
concise and readable way, Section 2 first introduces
FL, a concise and "visually structured" notation.
Then, using FL, it shows how the main concepts of
RIF-FLD, CL and SBVR can be related, defined and
generalized to create the above cited two ontologies.
This work required many readings of the
specifications and grammars of RIF-FLD since they
leave their underlying ontology implicit. Section 3
shows how the models and grammar of KRLs - and
thereby their parsing, presentation and translation -
can be specified based on these two ontologies. CSS-
like presentation based on syntactic or semantic
features could also be similarly specified but this is
outside the scope of this article.
The generic approach we propose to solve the
initially listed problems is independent of any
notation and any model that has at least OWL 2
expressiveness. This article focuses on presenting the
main ideas of the approach. The whole ontologies and
model+notation specifications of various KRLs, as
well as a Web server interface to test or use them, are
available at http://www.webkb.org/KRLs/. This
interface is similar to Google Translate except that the
input and output languages are KRLs and, instead of
KRL names, KRL specifications can also be given.
2 LANGUAGE ELEMENTS
To allow the display and understanding of its
numerous required illustrations, this article needs a
concise and intuitive notation for KRLs of OWL-like
expressiveness. Unfortunately, graphical notations are
not concise enough and common notations such as
those of the W3C are not sufficiently concise and
"structured" enough. Here, "structured" means that all
direct or indirect relations from an object can be (re-
)presented into a unique tree-like statement so that the
various inter-relations can readily be seen. Table 1
illustrates this by representing the same statement in
five notations: FL then UML, Turtle (or Notation3),
OWL Manchester notation and OWL Functional-style.
The way to read the content for FL is explained and
given in italics within a paragraph following the table.
The last notation is "positional relation" based.
The first four are graph-based notations: they are
composed of concept nodes and relation nodes. These
textual graph-based notations are frame-based. A
frame is a statement composed of a first "object"
(alias "node": individual or type, quantified or not)
and several links associated to it (links from/to other
objects). In this article, "link" refers to an instance of
a "binary relation type". In OWL, such a type is
instance of "owl:Property" (in FL: owl#Property).
What is not an individual is a type: relation type or
concept type (an instance of owl#Class in OWL).
In this article, the default namespace is for the
types we introduce. The names of a concept type or
individual that we introduce is a nominal expression
beginning by an uppercase letter. The name of a
relation type we introduce begins by "r_" (or "rc_" if
this is a type of link with destination a concrete term).
Thus, names not following these conventions and not
prefixed by a namespace are KRL keywords.
AnOntologyforSpecifyingandParsingKnowledgeRepresentationsStructuresandNotations
97
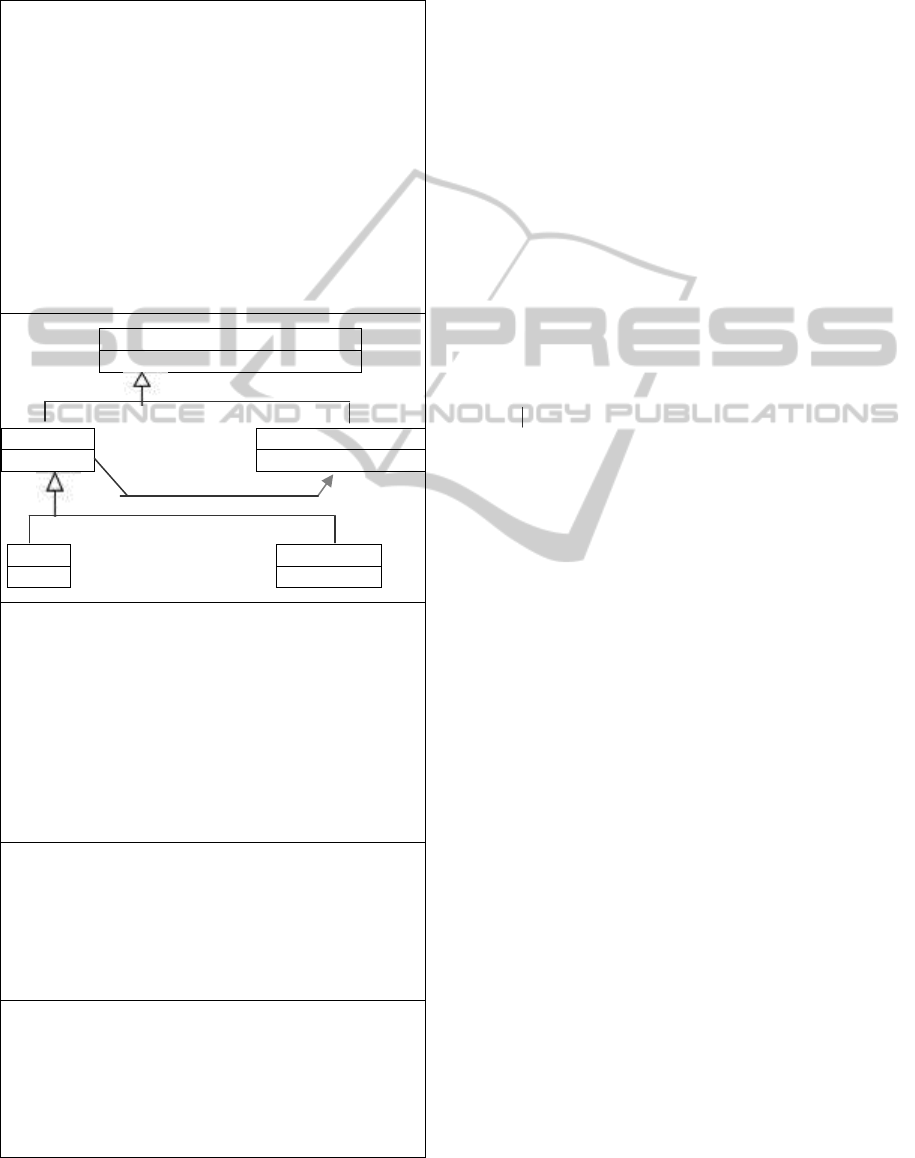
Table 1: The same statement - or set of statements (here, a set
of relations about Language_or_Language-element) - in five
different notations: FL, UML, Turtle, OWL Manchester,
OWL Functional-Style. In all other tables, FL will be used.
Language_or_Language-element //below: links defining it
= exclusion
{ (Language r_part: 1..* Language_element,
> KRL Grammar )
Language_element
};
//Notes. ">"
is an abbreviation for the "subtype" link (as in
//
some other notations). "<" is its inverse. "exclusion{...}"
//
specifies a union of disjoint types. If "T = exclusion{...}"
//
this is one subtype partition of T. If "T > exclusion{...}"
//
this is not a partition (or it is an "incomplete" one). A ","
//
separates 2 links of different types. For consecutive links
//
of the same type, this type needs not be repeated and the
//
destinations are only separated by one or several spaces.
Language_or_Language-element
Language Language-element
KRL Grammar
:Language_or_Language-element owl:equivalentClass
[ rdf:type owl:Class;
owl:unionOf ( :Language :Language_element ) ].
[ ] rdf:type owl:AllDisjointClasses; //→no shared instance
owl:members ( :Language :Language_element ).
Language rdfs:subClassOf [a owl:Restriction;
owl:onProperty : r_part;
owl:minQualifiedCardinality "1"^^xsd:nonNegativeInteger;
owl:onClass Language_element ].
KRL rdfs:subClassOf :Language.
Grammar rdfs:subClassOf :Language.
Class: Language_or_Language-element
EquivalentTo: Language or Language-element
DisjointClasses: Language, Language-element
Class: Language EquivalentTo:
r_part min 1 Language_element
Class: KRL SubClassOf: Language
Class: Grammar SubClassOf: Language
EquivalentClasses( :Language_or_Language-element
ObjectUnionOf( :Language Language-element) )
DisjointClasses(: Language :Language_element)
EquivalentClasses( :Language
ObjectMinCardinality(1 :r_part :Language_element) )
SubClassOf (:KRL : Language)
SubClassOf (:Grammar : Language)
Within nominal expressions, '_' and '-" are used
for separating words. When both are used, '-' connects
words that are more closely associated.
Since nouns are used for the introduced types, the
common convention for reading links in graph-based
KRLs can be used: links of the form "X R: Y" can
be read "X has for R Y".
If "of" is used for reversing
the direction of a link, the form "X R of: Y" can be
read "X is the R of Y". In FL, if a link is not a subtype
link (or another "link from a type"), the first node is
quantified and its default quantifier is "any", the
"forall" quantifier for definitions (in other words, the
type in the first node is defined by this link). Links
with the same first node may quantify it differently.
Indeed, in FL, the quantifiers of the source node and
destination node of each link may also be specified in
its relation node or in its destination node. This
permits FL to gather any number of statements into a
unique visually connected graph. However, in this
article, the quantifier for the first node is always "any"
and left implicit. A destination node can also be
source of links if they are encapsulated within
parenthesis. Thus, given all this and the notes at the
end of the FL content in Table 1, its first six lines can
be read: "The type Language_or_Language-element is
equivalent to its subtype partition composed of
Language_element and Language, and any instance of
Language has for (r_)part at least 1 instance of
Language_element. This last type has for subtypes (at
least) KRL and Grammar". The other tables of this
article can now be read (any new keyword will be
explained, most often via a comment next to it). In
these tables, bold characters are only for highlighting
important types and for readability purposes.
Table 2 shows how types for KRL models and
notations can be organized and inter-related. E.g.,
RIF-FLD includes RIF-BLD, both are part of the RIF
family of models, and both have a Presentation
Syntax ("PS") and an XML linearization.
Table 3 relates Language_element and some of its
direct subtypes to important top-level types, thus
adding precisions to these subtypes. Such a
specification is missing in RIF-FLD but is well
detailed in SBVR. This is why Table 3 includes many
top-level SBVR types, although indirectly: the types
with names in italics are still types that we introduce
but they have the same names as types in SBVR and
are equal to them or slight generalizations of them.
This approach is for readability reasons and flexibility:
if the SBVR authors disagree with our interpretation
of their types, only some links to SBVR types will
have to be changed, not our ontology. As illustrated
by Table 3, to complement and organize types from
other ontologies, ours had to include many new types.
r
p
art 1..*
{disjoint, complete}
KEOD2014-InternationalConferenceonKnowledgeEngineeringandOntologyDevelopment
98

Table 2: Examples of relations between KRLs.
KRL r_part: 1..* Language_element,
> exclusion { KRL_notation KRL_model },
r_grammar_head_element_type: Grouped_phrases;
KRL_notation
> (S-expression_based_notation > LISP_based_KIF)
(Function-like_based_notation
> (RIF_PS > RIF-FLD_PS RIF-BLD_PS) )
(Graph-based_notation
> (Markup_language_based_notation
> (XML_based_notation
> (RIF_XML > RIF-FLD_XML) )
(Frame_based_notation > FL JSON-LD Turtle) ) );
KRL_model
> (First-order-logic_with_sets_and_meta-statements
> (KIF_model r_model_type of: LISP-based_KIF),
r_part: 1..* First-order-logic )
(First-order-logic > (CL r_model_type of: CLIF) )
(RIF > (RIF-FLD r_model_type of: RIF-FLD_PS,
r_part: RIF-BLD )
(RIF-BLD r_model_type of: RIF-FLD_PS) )
(Graph-based_model r_model_type of: JSON-LD,
> JSON-LD_model
(RDF r_part: 1..* JSON-LD_model,
r_model_type of: JSON-LD RDF/XML),
(Frame_model_with_closed_world_assumption
> F-Logic_classic_model )
(Frame_model_with_open_world_assumption
> (Description_logic_model > OWL_model) ) );
OWL_model
> (OWL-1_model > OWL-Lite OWL-DL OWL-1-Full)
(OWL-2_model > OWL-2_EL OWL-RL OWL-2-Full),
r_part: 1..* (OWL-1-Full r_part: 1..* RDF,
r_part: 1..* OWL-DL ) )
1..* (OWL-2-Full r_part: 1..* OWL-2_EL ) );
In RIF-FLD, depending on the context, the word
"term" has different meanings. In our ontologies,
Gterm generalizes all these meanings of "term": it is
identical to Language_element and sbvr#Expression.
In RIF-FLD, an "individual term" is an abstract term
that is not a Phrase (see Table 3), although it may
refer to one. Individual_gTerm - or, simply "Iterm" -
generalizes this notion to concrete terms too. This
distinction was very useful to organize types of
language elements, especially those from the
implicit ontology of RIF-FLD (this framework uses
different vocabulary lists, including one for
signatures; in our ontology, all these terms are inter-
related). In this context, "individual" does not refer
to "something that is not a type". Since an Iterm may
refer to a Phrase, an Iterm identifier may be a Phrase
identifier. Thus, Table 3 uses the construct "near-
exclusion" instead of "exclusion".
Table 3: Situating Language_element w.r.t. other types
(note: names in italics come from SBVR).
Thing = owl#Thing, r_identifier: 0..* Individual_gTerm,
= exclusion
{ (Situation = exclusion{State Process},
r_description: 0..* Phrase )
(Entity //thing that can be involved in a situation
> exclusion
{ Spatial_entity //e.g., Square, Physical_Entity
(Non-spatial_entity //e.g., Justice, Attribute, ...
> (Description_content = Meaning,
> Proposition Question
(Concept > Noun_concept //e.g., types
(Verb_concept = Fact_type) ) )
(Description_container
> (File > RDF_file))
(Description_instrument
> (Language_or_Language-element
= exclusion
{ (Language > KRL Grammar,
r_part: 1..* Language_element )
Language_element //see below
} ) ) )
} ) };
Language_element = Gterm Expression,
r_representation of: 1 Meaning,
> near_exclusion //String is both abstract and concrete
{ (Representation > Statement,
rc_type: Concrete_term )
(Concrete_term > (Expression > Text),
> (Concrete_iTerm < Iterm) )
//see Table 7
}
near_exclusion //a reference to a phrase
is an Iterm
{ (Phrase > Statement Definition Frame) //Tables 5-6
(Individual_gTerm = Iterm, //see Table 7
> Place_holder, r_identifier of: 1 Thing )
}
near_exclusion { Positional_gTerm Frame
Gterm_with_named_arguments }
near_exclusion //subtyping these types is KRL dependent
{ (Referable_gTerm //e.g., via a variable
r_annotation: 0..* Annotation, //referable -> linkable
> (Gterm_that_cannot_be_annotated_without_link
r_annotation: 0 Annotation ) )
Non-referable_gTerm //e.g., a predefined term
};
This construct has no formal meaning (it does
not set exclusion links). It is only useful for
readability purposes. Table 3 also uses it to group
and distinguish types for abstract and concrete
terms. Indeed, a (character) string may be seen by
some persons as being both abstract and concrete.
Our ontology must be compatible with such visions
when they come at no cost.
RIF-FLD distinguishes three types of generic
structures for a Gterm that is a function or a phrase. We
dropped their RIF-related restrictions and named them
AnOntologyforSpecifyingandParsingKnowledgeRepresentationsStructuresandNotations
99

Positional_gTerm, Gterm_with_named_arguments and
Frame. Table 1 gave examples for positional and frame
terms. A term with named arguments is similar to a
frame except that, as in object-oriented languages, local
attribute names are used instead of link types (types are
global). It could be argued that a same term could be
presented in any of these three forms and hence that
these three distinctions should rather be syntactic.
However, the authors of RIF-FLD have not formalized
the equivalence/correspondence between i) "classes and
properties" ("interpreted as sets and binary relations")
and ii) "unary and binary predicates", in order to have
a "uniform syntax for the RIF component of both RIF-
OWL 2 DL and RIF-RDF/OWL 2 Full combinations"
(RIF-FLD-OWL, 2013). According to this vision, each
person re-using ontologies must decide if, for its
applications, stating such an equivalence is interesting
or not. RIF rules or a macro language such as OPPL
can certainly be used for such structural translations
(Šváb-Zamazal et al., 2012). However, to avoid
imposing this exercise to most users of our KRL model
ontology, and to avoid limiting its use for specifying
KRLs, it formalizes relations between a frame and a
Conjunction_of_links_from_a_same_source (this is
done in the last 15 lines of Table 6 plus the 3 lines
related to Half-link in Table 7; reminder: a link is - or
can also be seen as - a binary relation).
We found that a small number of link types are
sufficient for defining a structure for abstract terms and
specifying their related concrete terms. Table 4 lists and
explains the main link types. They can be seen as a
representation and extension of the signature system of
RIF-FLD. The ideas are that 1) every composite term
can be decomposed into a (possibly implicit) operator
(e.g., a predicate, a quantifier, a connective, a collection
type) and a list of parameters (alias, "parts"), and
2) many non-binary relations can be specified as links
to a collection of terms. Table 5 and the subsequent
tables use the link types of Table 4 directly or via
functions which are shortcuts for specifying such links.
This is highlighted via bold characters in those tables.
The end of Table 4 specified one of these functions. In
the tables 5 to 7, which illustrate the organization of
subtypes of Phrase and Iterm, this function is used to
define certain abstract terms as links and hence enable
to store them or present them as such when necessary.
Some of such links are used for both abstract and
concrete terms. E.g., rc_operator_name is often also
associated to an abstract term for specifying a default
name for its operator. If no such link is specified or if
"" is given as destination, the operator type name
(without its namespace identifier) is used as default
operator name.
Table 4: Main links for defining a structure for abstract
terms and specifying concrete terms.
Language_element
r_operator: 0..1 Operator , //Table 7
r_part: 0..* Gterm, //object parts or fct/relation arguments
r_parts: 1 List, //r_part destinations, sequentially ordered
r_result: 1 Gterm, //e.g., a phrase has for r_result a boolean
rc_type: Concrete_term; //rc_type is defined below
rc_link_to_concrete-term //also often from a Concrete_term
_[Gterm,Concrete_term] //signature of this relation type
> rc_begin-mark rc_separator rc_end-mark
rc_operator_begin_mark rc_operator_end_mark
rc_operator_name rc_infix-operator_position
rc_parts_begin-mark rc_parts_separator
rc_parts_end-mark rc_annotation_position; //-1: before
r_part //below are examples of its subtypes
> (r_relation_parameter
> (r_link_parameter
> (r_link_source > rdfs#domain)
(r_link_destination > rdfs#range) ) )
r_function_parameter
r_phrase_part > rdf#subject rdf#object;
r_operator > rdf#predicate; //just an example
//r_parts permits to order the parts, this is sometimes
// needed for abstract terms and this also permits to give
// a default order for presentation purposes.
r_parts _[?e,?list]
:=> [any ^(Thing r_member of: ?list) r_part of: ?e];
r_parts _[?e,?list]
:<= [any ^(Thing r_part of ?e) r_member of: ?list];
/* Notes: in FL, ":=' permits to give a full definition,
":=>" gives only "necessary conditions",
":<=" gives only "sufficient conditions",
"^(" and ")" delimit a lambda-abstraction (a construct
defining and returns a type; in OWL related KRLs,
owl#Restriction can be used),
"_(" and ")" delimit the parameters of a function call,
"_[" and "]" delimit the parameters of a definition,
".[" and "]" delimit the elements of an list,
".{" and "}" delimit the elements of a set. */
rc_type _[?t,?rct] := [any ?t rc_: 1..* ?rct];
//people who see concrete terms as specialisations of
// abstract terms can still state:
// rc_type < subtype; rc_ r_type: instance;
//in the next function signature, the variables are untyped
f_link_type _[ ?operatorName, ?linkType,
?linkSourceType, ?linkDestinationType ]
:= ^(Link rc_operator_name: ?operatorName,
r_operator: ?linkType, r_result: 1 Truth_value,
r_link_source: 1 ?linkSourceType,
r_link_destination: 1 ?linkDestination,
r_parts: .[ ?linkSource ?linkDestination] );
KEOD2014-InternationalConferenceonKnowledgeEngineeringandOntologyDevelopment
100

Table 5: Important top-level types of phrases (first row); a way to restrict this general model for KRLs (2nd row) (note:
names in italics come from RIF-FLD, names in bold italics are used in RIF-FLD signatures, bold is for highlighting).
Phrase < ^(Gterm r_operator: 1 (Relation_type > (owl#Property r_instance: r_binary_relation
) ),
r_result: 1 (Truth_value r_instance: True False Indeterminate_truth-value/*for example*/ ) ),
> (Phrase_that_is_not_referable_in_RIF-FLD //hence, phrase that cannot have an annotation in RIF-FLD
> (Annotation > cl#Comment , //"cl#' prefixes terms from Common Logics
> (Formal_annotation > (RIF_annotation r_parts: .[0..1 Constant, 0..1 Frame_or_Frame-conjuction]) )
(Annotating_phrase = f_link_type_("",r_annotation,Gterm,Annotation))
Module_directive Attribute ),
= exclusion
{ (Modularizing_phrase
> (Phrases = Grouped_phrases, r_part: 0..* Phrase, > cl#Text, //Phrases is the head element of a KRL grammar
> (Module > cl#Module cl#NamedText,
> (Document r_part: 0..1 Document_Directive 0..1 Phrases),
r_part: 0..1 (Module_parts_that_are_directives < Module,
> Module_header = f_link_type_("",r_header,Module, .[0..* Module_directive] ) )
0..1 (Module_parts_that_are_not_directives = f_link_type_("Group",r_group,Module,.[0..* Phrases],
< Module, > Module_body Group_of_phrases ),
r_parts: .[0..1 Module_header, 0..1 Module_body] ) )
(Module_directive = f_link_type_("",r_relation,Module,Thing),
> (Module_name_directive = f_link_type_("Name",r_name,Module,Name) )
(Excluded_Gterm-reference_directive = f_link_type_("",r_excluded_gTerm,Module,.[1..* Gterm_reference]) )
(Document_directive
> (Dialect_directive = f_link_type_("Dialect",r_dialect,Module,Name))
(Base_directive = f_link_type_("Base",r_base,Module,Document_locator))
(Prefix_directive = f_link_type_("Prefix",r_prefix,Module,NamespaceShortcut-DocumentLocator_pair))
(Import-or-module_directive > cl#Importation,
> (Import_directive = f_link_type_("Import",r_imported-doc,Document
,Imported_document_reference) )
(Remote_module = f_link_type_("Module",r_imported-module,Module,Remote_module_reference) )
) ) ) )
(Non-modularizing_phrase //this may include non-monotonic phrases: assertions, queries, removals
> (Formula > Positional_formula Formula_with_named_arguments > cl#Sentence Phrase_of_a_grammar,
= exclusion //the 3 following distinctions come from KIF
{ (Definition = exclusion { Non_conservative_definition Conservative_definition } )
(Sentence //fact in a world: formula assigned a truth-value in an interpretation
> Belief //the fact that someone believes in a certain thing
Axiom ) //sentence assumed to be true, from/by which others are derived
(Inference_rule> Production_rule) //like an implication but the conclusion is "true" only if/when the rule is fired
}
exclusion { Composite_formula Atomic_formula_or_reference_to_formula } ) ), //see Table 7
> Termula, //parameter for a function or atomic_formula; its subtypes are not listed in this article
};
//with the next subtype of r_part, the source ?x has some parts of type ?pt but no other parts with type the genus of ?pt
r_only_such_part_of_that_type _[?x ?pt] < r_part _(?x ?pt), //this definition requires that relations of type
:= [?x r_part: 1..* ?pt 0 ^(?t != ?pt, < (?gpt r_genus_supertype of: ?pt))]; // r_genus_supertype are set by definitions
//Thanks to this link type, our general model for KRLs and the default presentation associated to its abstract terms,
// KRLs can be defined in a very concise way. Below are examples for some abstract terms of some KRLs.
// The next section give examples for some concrete terms of some KRLs. For the Triplet_notation, nothing else is required.
RIF r_only_such_part_of_that_type: //any model of the RIF family has for part terms defined by the following lambdas:
^(Gterm_that_can_be_annotated_without_link > Phrase) ^(Grouped_phrases r_part: 0..* Document)
^(Quantification > Classic_quantification) ^(Frame > Minimal_frame) ^(Collection > List)
^(Delimited_string > Delimited_Unicode_string); //in RIF, the only "delimited strings" are "delimited Unicode strings"
RIF-BLD r_only_such_part_of_that_type: ^(Rule_conclusion > rif-bld#Formula) //these are just two examples,
^(Rule_premise > Connective_phrase_on_atomic_formulas Conjunction_phrase); // RIF-BLD has other restrictions
Triplet_notation = ^(KRL r_only_such_part_of_that_type: ^(Phrase > Link) ^(Individual_gTerm > Constant_or_variable) );
AnOntologyforSpecifyingandParsingKnowledgeRepresentationsStructuresandNotations
101

Table 6: Important types of formulas and connections between frames, links and positional formulas (note: names in italics
come from RIF-FLD, names in bold italics are used in RIF-FLD signatures, bold is for highlighting).
Composite_formula = f_relation_type_("",r_relation,.[1..* Formula]), // => r_part: 1..* Formula
> exclusion
{ (Formula_connective r_operator_type: 1 connective_operator, > cl#Boolean_sentence,
> exclusion
{ (Connective_phrase_with_1_argument = f_relation_type_("",r_unary_relation,.[1..* Formula]),
> (Negating_formula=exclusion{(Symmetric_negating_formula = f_relation_type_("Not",r_not,.[1..* Formula]))
(Negation-as-failure_formula = f_relation_type_("Naf",r_naf,.[1..* Formula]))
}))
(Connective_phrase_with_2_arguments = f_relation_type_("",r_binary_relation,.[1..* Formula]),
> (Rule = f_relation_type_(":-",r_rule_implication,.[1..* Formula]),
= exclusion{ (Inference_rule > Production_rule) (Logical_rule < Sentence, > Logical_implication) }
exclusion{ (Implication_only > Production_rule) (Logical_equivalence r_operator: r_equivalence) },
r_part: 1 (Rule_premise < Formula) 1 (Rule_conclusion < Formula) ) )
(Variable-n-ary_connective_phrase = f_relation_type_("",r_variable-ary_relation,.[1..* Formula]),
> exclusion { (Disjunction_phrase = f_relation_type_("Or",r_or,.[1..* Formula]))
(Conjunction_phrase = f_relation_type_("And",r_and,.[1..* Formula]),
> (Conjunction_of_links = f_relation_type_("And",r_and,Link),
> Frame_as_conjunction_of_links_from_a_same_source ) ) } )
} )
(Quantification = f_quantification_type_("",Quantifier,.[1 Type],Constant-or-variable,Formula),
> (Classic_quantification = f_quantification_type_("",Quantifier,.[],Variable,Formula) ) //no guard, no constant
exclusion
{ (Universal_quantification = f_quantification_type_("Forall",q_forall,.[1 Type],Constant_or_variable,Formula),
> (Classic_universal_quantification = f_quantification_type_("Forall",q_forall,.[],Variable,Formula) ) )
(Existential_quantification = f_quantification_type_("Exists",q_exists,.[1 Type],Constant_or_variable,Formula),
> (Classic_existential_quantification = f_quantification_type_("Exists",q_exists,.[],Variable,Formula) ) ) } )
};
Atomic_formula_or_reference_to_formula
> exclusion { (Formula_reference //this is also an Individual_gTerm
> exclusion { Variable_for_a_formula Reference_to_formula_in_remote_module //with the same KRL
Reference_to_externally_defined_formula } ) //not in a module and not with the same KRL
(Atomic_formula
> { Constant_for_a_formula
(Atomic_formula_that_is_not_a_constant
> near_exclusion //possible shared subtypes: subclass_or_equal, link
{ (Positional-or-name-based_formula r_operator: 1 Termula, > cl#Atomic_sentence,
> exclusion { (Positional_formula r_part: 1..* Termula)
(Name-based_formula r_part: 1..* Name-Termula_pair) } )
(Equality_formula = f_link_type_("=",r_equal,Termula,Termula), > cl#Equation)
(Class-membership = f_link_type_("#",r_type,Termula,Termula) )
(Subclass_formula = f_link_type_("##",r_supertype,Termula,Termula) )
(Frame = (Frame_as_conjunction_of_links_from_a_same_source ?f
r_frame_head: 1 Termula ?fh, r_part: (1..* Link r_link_source: ?fh) )
(Frame_as_head_and_half-links_from_head ?f
r_operator: (1 Termula ?fh r_frame_head of: ?f),
r_part: (1..* Half_link r_link_source: ?fh),
> (Minimal_frame r_part: 1..* Minimal_half-link) ) )
} )
(Binary_atomic_formula_that_is_not_a_constant
> (Link = (Link_as_positional_formula < Positional_formula,
< f_link_type_("",r_binary_relation_type,Termula,Termula),
r_part of: (1 Frame ?f r_frame_head: 1 Termula ?fh), r_link_source: ?fh )
(Link_as_frame_part r_part of: (1 Frame ?f r_frame_head: 1 Termula ?fh),
r_operator: ?fh, r_link_source: ?fh, r_link_destination: 1 Termula ?ld,
r_part: (1 Half_link r_link_source: ?fh, r_operator: ?fh, r_parts: ?ld ) ) ) )
} ) };
KEOD2014-InternationalConferenceonKnowledgeEngineeringandOntologyDevelopment
102

Table 7: Important types of "individual terms" (terms that are not phrases except for those referring to phrases) (note: names
in italics come from RIF-FLD, names in bold italics are used in RIF-FLD signatures, bold is for highlighting).
I
ndividual_gTerm //the expression "Individual term" comes from RIF-FLD
= near_exclusion
{ (Individual_concrete_term //see next sub-sections for details
> Concrete-term_for_constant_or_name Lexical-grammar_character-set Concrete_list-like_term
Concrete_list-like_term (String > (Delimited_string > Delimited_Unicode_string)) Character )
(Individual_abstract_term
> (Abstract_individual_gTerm_that_is_not_referable_in_RIF-FLD
> exclusion
{ (Operator_that_is_not_referable_in_RIF-FLD //predefined in RIF-FLD which does not rely on an ontology
> exclusion { Quantifier Connective_operator Aggregation-function_or_list_operator } )
Symbol_space_identifier //e.g., xs:decimal, rif:iri
(Name-Termula_pair r_parts: .[1 Name, 1 Termula])
(Half_link r_link_source: 1 Termula, r_operator: 1 Fterm_or_variable, r_part: 1..* Link_destination,
> (Minimal_half-link r_operator: 1 Link_type, r_part: 1 Minimal_Link_destination) ),
(Link_destination r_parts: .[0..1 Cardinality, 1 Termula], > (Minimal_link_destination r_part: 1 Termula))
} )
Fterm_or_variable Individual_abstract_term_of_a_grammar
(Operator r_type: Operator_type, > r_relation f_function Operator_that_is_not_referable_in_RIF-FLD)
(Symbol_space > rif#iri rif#local xs#string xs#integer,xs#decimal,xs#double) )
};
F
term_or_variable //cl#Term_or_sequence_marquer,
= exclusion
{ (Variable > Variable_for_a_formula) //cl#Sequence_marquer
(Fterm //cl#Term
> exclusion
{ (Gterm_reference > (Constant_gTerm = ^(Gterm r_operator: 0 Relation-or-Function_type),
= exclusion { Individual //in the classic sense of "category that is not a type"
(Predicate = Type, //cl#predicate
> rdfs#Class (Literal_or_datatype > rdfs#Literal rdfs#Datatype) ) } )
(Reference_to_external_gTerm > Gterm_locator Imported_document_reference /
* ... */) )
(Functional_term r_operator: 1 (Function_type < Type),
= exclusion { (Non-aggregate_functional_term = Expression)
(Aggregate_function_or_collection
> (Aggregate_function r_operator: 1 Aggregation-function_operator ,
r_parts: .[1 Aggregate_function_bound_list, 1 Formula] )
(Collection //e.g., rdfs#Container
= exclusion { (Unordered_collection > Set)
(Ordered_collection
> (List = f_function_type_("List",fd_list,.[1..* Ftermula]),
= exclusion { Closed_list Open-list } ) ) } ) )
} ) } ) };
C
oncrete-term_for_constant_or_name //just some examples to show that the same approach applies for concrete terms
>
(Symbol-space_name r_identifier: 1..* Symbol_space,
> exclusion { (Symbol-space_name_via_bracketed_IRI r_part: 1 IRI_reference )
(Symbol-space_name_via_compact_URI r_part: 1 Compact_URI) } ) //xs:decimal, rif:iri, ...
(Variable_name r_identifier: 1..* Variable, < ^(f_string_type_("?","","") r_part: 1 Undelimited_variable-name) )
(Constant_concrete_term r_identifier: 1..* Constant_gTerm,
> (Constant_concrete_term_without_symbol-space
> (Constant_IRI r_part: 1 IRI_reference )
(Constant_short-name_via_compact_URI r_part: 1 Compact_URI)
(Literal_or_datatype_concrete_term r_identifier of: 1..* Literal_or_datatype,
> (Double_quoted_string
< ^(f_string_type_('"','','"') r_part: 1..* f_character_type_with_escape_for_(Character,"\\",'"') ))
(Numeric_literal > (Positive_integer /^ ^(<b>f_string_type</b>_("+","","") r_part: 1..* Digit))
> (Negative_integer < ^(f_string_type_("-","","") r_part: 1..* Digit)) ) ) ) );
AnOntologyforSpecifyingandParsingKnowledgeRepresentationsStructuresandNotations
103

3 PRESENTING AND PARSING
Table 8 lists major kinds of structured concrete terms
and thus also the main presentation possibilities for
structured abstract terms (see the 14 names in italics).
Based on the five main categories for these concrete
terms (see the names in bold and not in italics), it is
easy to find the five categories of abstract terms they
correspond to, even though such links are not shown
in Table 8. We found that each of these concrete term
types can be defined with only a few types of links,
those that begin by "rc_" and that were listed in
Table 4. We defined some functions to provide
shortcuts for setting those links when defining a
particular concrete term, e.g., fc_prefix-fct-like_type.
In our ontologies, links from a type do not specify
that the given destination is the only one possible (to
do so in FL, "=>" must be used instead of '":" after the
link type name; in OWL-based models,
owl#allValuesFrom can be used). Thus, such links
represent "default" relationships: if a link from a type
T specializes a link from a supertype of T, it overrides
this inherited link. This is also true when the link type
is functional (i.e., can have only one destination) and
its destination for T does not specialize the destination
for a supertype of T. The links beginning by "rc_"
looks functional but are not: in FL, multiple
destinations can be stated to indicate different
presentation possibilities. However, by convention,
such links override inherited links of the same types.
Table 8 shows how different kinds of "default
presentations" can be represented .in concise ways.
In a KRL that is perfectly regular with respect to a
particular kind of abstract/concrete term - e.g, the
concrete "operator based terms" (those that have an
operator in our approach) - allows the terms of this
kind to be (re-)presented in the same way.
Table 8: Important types of structured concrete terms (except for strings) and definition of their default presentation.
Structured_concrete_term_that_is_not_a_string //the examples in the comments below are in FL; with their delimiters a KRL
> exclusion // may have all these structures and still only requires an LALR(1) parser
{ (List_cTerm > Enclosed_list_cTerm /* e.g., .[A B C] */ Fct-like_list_cTerm /* e.g., A ..[B C] */ )
(Set_cTerm > Enclosed_set_cTerm /* e.g., .{A B C} */ Fct-like_set_cTerm /* e.g., A ..{B C} */ )
(Positional_cTerm //e.g., with operator "f" and parts/parameters A, B and C
rc_operator-name: "", rc_operator_begin_mark: "", rc_operator_end_mark: "", //link types listed in Table 3
rc_parts_begin-mark: "(", rc_parts_separator: "", rc_parts_end-mark: ")",
rc_infix-operator_position: 0, //when different from 0, this indicates the operator position within the parts
> exclusion { (Fct-like-cTerm
= exclusion { (Prefix_fct-like-cTerm rc_parts_begin-mark: "_(") //e.g.: f _(A B C)
(Postfix_fct-like-cTerm rc_parts_begin-mark: "(_") } ) //e.g.: (_ A B C)f
(List-like_fct_cTerm
= exclusion { (List-like_prefix-fct_cTerm rc_parts_begin-mark: ".(") //e.g.: .(f A B C)
(List-like_infix-fct_cTerm rc_parts_begin-mark: "(.",
rc_operator_begin_mark: ".") //e.g.: (. A B .f C)
(List-like_postfix-fct_cTerm rc_parts_begin-mark: "(..") } ) //e.g.: (.. A B C f)
} )
(Frame_cTerm //e.g., for the example below, with operator the type "f" and with parts two half-links of type r1 and r2
rc_operator-name: "", rc_operator_begin_mark: "", rc_operator_end_mark: "",
rc_parts_begin-mark: "{", rc_parts_separator: ",", rc_parts_end-mark: "}", //as in JSON-LD
rc_parts: 1..* Half-link_cTerm,
> exclusion { (Prefix_frame_cTerm rc_parts_begin-mark: "_{") //e.g.: f_{ r1: A, r2: B }
(List-like_frame_cTerm rc_parts_begin-mark: "{.",
> List-like_prefix-frame_cTerm //e.g.: {. f r1: A, r2: B}
List-like_infix-frame_cTerm ) //e.g.: {. r_id: f, r1: A, r2: B}
(Postfix_frame_cTerm rc_parts_begin-mark: "{_") //e.g.: {_ r1: A, r2: B } f
Alternating-XML_cTerm //Frame in the Alternating-XML style where concept nodes alternate
} ) // with link nodes, as in RDF/XML
Cterm_with_named_arguments //quite rare in KRLs, hence not detailed in this article
};
fc_prefix-fct-like_type _[?notationSet, ?operator_name, ?begin_mark, ?separator, ?end_mark] //call examples are in Table 9
:= ^(Prefix_fct-like-cTerm r_direct-or-indirect_part of: ?notationSet, rc_operator-name: ?operator_name,
rc_parts_begin_mark: ?begin_mark, rc_parts_separator: ?separator, rc_parts_end_mark: ?end_mark )
Phrase //any phrase has at least these presentations in these 2 kinds of notations (see Table 2), e.g., in RIF-PS and RIF-XML:
rc_type: ^(fc_prefix-fct-like_type _(.{Function-like_based_notation},"","(","",")") rc_annotation-position: -1)
^(fc_alternating-XML_type_(.{XML_based_notation},"") rc_annotation-position: 0 );
List rc_type: fc_list_type _( .{Notation}, "[", "," ,"]" ); //by default, in any notation, a list has for representation a
// comma separated list of element delimited by square brackets; note that fc_list_type has no argument for an operator name
KEOD2014-InternationalConferenceonKnowledgeEngineeringandOntologyDevelopment
104

A perfectly regular KRL is then one which is
perfectly regular for all the kinds of terms it allows.
The "Triplet notation" is perfectly regular. To be so, a
more expressive KRL would have to be fully based
on an ontology and be Nth-order logic based. Since
KIF re-uses the LISP notation, it is perfectly regular
with respect to "operator based concrete terms" and
"concrete terms for collections". Most KRLs have
some ad hoc abstract and concrete terms. E.g., in RIF-
XML the directives of a document are presented in
different ways: some via links, some via XML
attributes. In RIF-PS, they are presented as positional
terms but not links. Thanks to the fact that our general
model represents the directives both as parts and links
(see Table 5), these RIF predefined directives can be
represented within/via frames as well as via positional
terms. The first part of Table 9 shows how ad hoc
concrete terms of particular types of KRLs can be
specified in a concise way. The approach used to do
so for abstract terms (see the second part of Table 5)
is here re-used. Thus, the abstract and concrete terms
of a KRL - or a family of KRLs - can be specified at
the same time. This enables organized specifications
and thus eases the comparison of KRLs.
The second part of Table 9 shows how an ordered list
of concrete terms can be specified for a type of
abstract term, given a type of presentation and a list of
notation types. Since the function fc_r_parts is
recursive and, in turn, uses such specifications (links
of type rc_parts or, for non-structured terms, links of
Table 9: Ways to specify concrete terms for particular kinds of terms in particular notations, via our ontology.
//Thanks to the default values in our specifications for abstract and concrete terms, only the following lines are needed for
// defining the presentation in RIF-PS of the abstract terms shared by the KRLs of the RIF family. For instance, the order and
// operator names of the directives of a document can be found in Table 5. Since these directives follow the default presentation
// for phrases in RIF-PS, nothing needs to be specified about them here. The abstract term restrictions can be specified here (as
// illustrated below for "Frame" or separately, as illustrated by the second part of Table 5.
RIF r_only_such_part_of_that_type: //because of the default values, there is no need for more than the next lines
^(Phrase rc_type: fc_prefix-fct-like_type_(.{RIF-PS},"","(","",")") ) //by default, a phrase in RIF_PS follows this style
^(RIF_annotation rc_type: fc_list_type_(.{RIF-PS},"(*","","*)")) //this is overridden by some subtypes of Phrase, e.g., this one
^(Quantification_bound_list rc_type: fc_list_type_(.{RIF-PS},"","",""))
^(Rule rc_type: fc-like_infix-fct_type_(.{RIF-PS},":-","","",""))
^(Externally_defined_term rc_type: fc_prefix-fct-like_type_(.{RIF-PS},"External","(","",")"))
^(Equality_formula rc_type: fc_list-like_infix-fct_type_(.{RIF-PS},"=","","",""))
^(Subclass_formula rc_type: fc_list-like_infix-fct_type_(.{RIF-PS},"##","","","")) //e.g., "?t1 ## ?t2"; in FL: "?t1 < ?t2"
^(Class-membership_formula rc_type: fc_list-like_infix-fct_type_(.{RIF-PS},"#","","",""))
^(Frame > Minimal_frame, rc_type: fc_infix_list-like_frame_type_(.{RIF-PS},"","[","","]") ) //abstract+concrete specification
^(Half_link rc_type: fc_half-link_type_(.{RIF-PS},"","","->","",""))
^(Name-Termula_pair rc_type: fc_list_type_(.{RIF-PS},"","->",""))
^(Open_list rc_type: fc_prefix-fct-like_type_(.{RIF-PS},"List","(","|",")"))
^(Open-list_rest rc_type: fc_list_type_(.{RIF-PS},"","","",""))
^(Aggregate_function rc_type: fc_prefix-fct-like_type_(.{RIF-PS},"","{","|","}"))
^(Aggregate_function_bound_list rc_type: fc_fct-like_list_cTerm_(.{RIF-PS},"[","",]""));
RIF-FLD r_only_such_part_of_that_type: //only 1 example for RIF-XML: the concrete term for Document in RIF-FLD
^(Document rc_type: (1 fc_alternating-XML-cTerm_type_(.{RIF-XML},"Document") rc_annotation-position: 0,
rc_XML-attribute_type: r_dialect xml#base xml#prefix, //the last two are predefined in XML
rc_XML-link_types: .[rif#directive rif#payload] );
JSON-LD_model r_only_such_part_of_that_type: //the specifications of both the JSON-LD_model and the JSON-LD notation
^(Phrase rc_type: fc_list-like_infix-frame_type_(.{JSON-LD},"","{",",","}")) // except for the concrete terms
^(Half_link rc_type: fc_half-link_type_(.{JSON-LD},"",":","",""))
^(Module_header rc_type: fc_list-like_infix-frame_type_(.{JSON-LD},'"@context:"',"{",",","}"))
^(Module_body rc_type: fc_list_type_(.{JSON-LD},"","",",""))
^(Formula > ^(Minimal_frame r_operator: 1 Constant_gTerm)) //only 1 destination per link
^(Fterm_or_variable > Constant_or_set_or_closed_list)
^(Set rc_type: fc_list_type_(.{JSON-LD},"[",",","]")) //by default in JSON-LD (whereas in JSON, this would be for a list)
^(Closed_list > ^(Frame r_part: 1 .[r_container, Closed_list], //1st way to represent a list in JSON-LD
rc_type: fc_half-link_type_(.{JSON-LD},"","@container",":","@list","") )
^(Frame r_part: .[r_list, 1 Set], rc_type: fc_half-link_type_(.{JSON-LD},"","@list",":","","") ) ); //2nd way
^(Thing ?t rc_: (a Enclosed_list_cTerm ?c r_KRL-set: ^?notationSet)) //"^?" prefixes variables that are implicitly
rc_parts: f_remove_empty_elements_in_list _( .[ (^?cb rc_begin_mark of: ?c), // universally quantified
fc_r_parts_(?notationSet,(^?tp r_parts of: ?t),(^?cs rc_parts_separator of: ?c))
(^?cb rc_end_mark of: ?c) ] );
AnOntologyforSpecifyingandParsingKnowledgeRepresentationsStructuresandNotations
105

Table 10: Important links from Grammar_element, followed by an example of grammar head rule.
G
rammar_element //currently, the specifications are mainly only for EBNF-like grammars and Lex&Yacc-like grammars
r_part of: 1..* Grammar, //and conversely: Grammar r_part: 1..* Grammar_element;
> exclusion
{ (Phrase_of_a_grammar = exclusion{Non-lexical-grammar_rule Lexical-grammar_rule}, > Head_grammar-rule )
(Individual_gTerm_of_a_grammar = exclusion{ Lexical-grammar_individual-gTerm //what Lex grammars handle
Non-lexical-grammar_individual-gTerm } ) };
N
on-lexical-grammar_rule = NLG_rule, //this is a beginning but the representation of the whole grammar is similar
r_part: 1 NLG_rule_left-hand-side 1 NLG_expression 0..1 (Parsing_action_phrase < Phrase),
rc_: (1 fc_list_type_(.{W3C-EBNF,XBNF,Grammar},"","","") //like fc_prefix-fct-like-cTerm_type but without operator
rc_parts: .[NLG_rule_left-hand-side "::=" NLG_expression] ) //-> "A::=B" ("Grammar "-> default presentation)
(1 fc_list_type_(.{ISO-EBNF},"","","")
rc_parts: .[NLG_rule_left-hand-side "=" NLG_expression] ) //-> "A = B" in ISO-EBNF
(1 fc_list_type_(.{Yacc, Bison},"","","")
rc_parts: .[NLG_rule_left-hand-side ":" NLG_expression] ); //-> "A : B" in Yacc or Bison (without parsing actions)
Grammar_for_RIF_FLD_in_RIF-PS < Grammar, r_description of: 1..* (RIF-FLD < (KRL_model r_part of: 1..* KRL)),
r_part: 1 (fc_NLG_rule_type_( .{RIF-PS}, "RIF-FLD_document", .[ 0..1 Annotation "Document" "("
0..1 Dialect_directive 0..1 Base_directive 0..* Prefix_directive 0..* Import_directive
0..* Remote_module_directive 0..1 Group ")" ]
) < Head_grammar-rule );
type rc_), the specified ordered list only contains
strings. Finally, given the value of rc_separator
between tokens in the considered notation (i.e., the
kinds of space characters separating them), the kinds
of strings that can be associated to this collected list is
specified. Thus, the whole specification is fully
declarative. However, for concrete term generation
purposes, choices have to be made, e.g., about space
indentation. In our system, this is implemented via
generation functions (also included in our ontologies)
which recursively navigate the abstract and concrete
specifications to find the most precise relevant
specifications. Since our system rejects the entering of
ambiguous knowledge (e.g., different concrete term
specifications for a same type of abstract term and the
same type of notation), finding the most precise
relevant specifications was easy to implement.
Specifying parsing rules and generating them - for
a given abstract term and grammar notation - can be
represented using the same techniques. The first part
of Table 10 shows the beginning of an ontology for
grammars. The second part shows an example of
grammar rule (and its connection to a grammar but this
part actually needs not be generated). Once the
grammar rules are generated - in a way similar to
presentation generation - the generation of their
presentation is then done exactly as for any other
statement, according to the given grammar notation.
Our ontologies can be represented with OWL-2
based KRLs. E.g., r_parts links with "lists with
cardinalities" (e.g., .[0..1 Y, 1..* Z]) as destinations can
be replaced by lists without cardinalities (e.g., .[Y, Z])
as long as r_part links are also used for specifying the
cardinalities (e.g., X r_part: 0..1 Y, 1..* Z ). Functions
are not mandatory since their definitions can be
expanded whenever they are called.
Replicating our work does not require details on the
implementation of our system: our ontologies are the
required declarative code. The used inference engine
is irrelevant as long as it can handle the specifications.
However, some readers might be interested to know
that our translation server exploits the parser available
at http://goldparser.org while its inference engine was
implemented in Pascal Object (for portability
purposes) and exploits tableaux decision procedures
(Horrocks, 1997). This server and its inference engine
have recently been designed by Logicells/GTH
(http://www.mitechnologies.net/). This work on a
generic approach for handling KRLs comes from the
many problems encountered to handle various
versions of FL and other KRLs in the knowledge
sharing servers WebKB-1 (Martin and Eklund, 1999)
and WebKB-2 (Martin, 2002, 2011).
4 CONCLUSIONS
One contribution of this article is a generic model for
structured abstract or concrete terms. It is simple: only
a few types of links and a few distinctions (Tables 4
and 8). This operator+parameters based model
permits to define terms in a concise and flexible way,
and thus also their presentation and parsing.
KEOD2014-InternationalConferenceonKnowledgeEngineeringandOntologyDevelopment
106

A second contribution is the design of a KRL
model ontology by representing, aligning and
extending various KRL models, and defining their
elements via the above cited few links, as illustrated
by Tables 3 and 5-7. Thus, the merged models are
also easier to re-use.
A third one is the design of a KRL notation
ontology - to our knowledge, the first one - based on
the above two cited contributions, as illustrated by
Tables 8-10.
These three contributions permit to solve or reduce
the problems listed in the introduction: KRL syntactic
translations, KRL parser implementation, dynamic
extension of notations, etc. Thus, they provide an
ontology-based concise alternative to the use of XML
as a meta-language for easily creating KRLs following
KRL ontologies. Therefore, this also complements
GRDDL and can be seen as a new research avenue.
This avenue is important given the frequent need for
applications to i) integrate or easily import and export
from/to an ever growing number of models and
syntaxes (XML-based or not), and ii) let the users
parameter these processes.
Previous attempts (by the first author of this
article) based on directly extending EBNF - or directly
representing or generating concrete terms in a KRL or
transformation language - required much lengthier
specifications that were also more difficult to re-use.
Besides its translation server, the Logicells/GTH
company will use this work in its applications for
them to i) collect and aggregate KRs from the
knowledge bases they exploit, and ii) enable end-
users to adapt the input and output formats they wish
to use or see. The goal behind these two points is to
make these applications - and the ones they relate -
more (re-)usable, flexible, robust and inter-operable.
One theme of our future work on this approach will
be the generation of parsing actions in parsing rules,
given an implementation "data model". A second
theme will be the representation and integration of
more models and notations for KRLs as well as query
languages and programming languages. A third
theme will be the extension of our notation ontology
into a presentation ontology with concepts from style-
sheets and, more generally, user interfaces.
REFERENCES
Brophy, M., Heflin, J., 2009. OWL-PL: A Presentation
Language for Displaying Semantic Data on the Web.
Technical report, Department of Computer Science
and Engineering, Lehigh University.
Common Logic, 2007. Information technology - Common
Logic (CL): a framework for a family of logic-based
languages. ISO/IEC 24707:2007(E), JTC1/SC32.
Corby, O., Faron-Zucker, C, Gandon, F., 2014. SPARQL
Template: A Transformation Language for RDF. In
IC 2014, 25th Journées francophones d'Ingénierie des
Connaissances, Clermont-Ferrand, France.
Farquhar, A., Fikes, R., Rice, J., 1997. The Ontolingua
Server: a tool for collaborative ontology construction.
International Journal of Human-Computer Studies,
Volume 46, Issue 6, Academic Press, Inc., MN, USA.
Genesereth, M., Fikes R., 1992. Knowledge Interchange
Format, Version 3.0, Reference Manual. Technical
Report, Logic-92-1, Computer Science Dept., Stanford
University. http://www.cs.umbc.edu/kse/
GRDDL, 2007. Gleaning Resource Descriptions from
Dialects of Languages (GRDDL). W3C Recom-
mendation 11 September 2007. Editor: Connolly, D.
http://www.w3.org/TR/2007/REC-grddl-20070911/
Horrocks I., 1997. Optimising Tableaux Decision
Procedures for Description Logics. PhD thesis,
University of Manchester.
Martin Ph. and Eklund P., 1999. Embedding Knowledge in
Web Documents. Computer Networks: The International
Journal of Computer and Telecommunications
Networking, Vol. 31, Issue 11-16, pp. 1403-1419.
Martin Ph., 2002. Knowledge representation in CGLF,
CGIF, KIF, Frame-CG and Formalized-English.
Proceedings of ICCS 2002, LNAI 2393, pp. 77-91
Martin Ph., 2011. Collaborative knowledge sharing and
editing. International Journal on Computer Science and
Information Systems, Vol. 6, Issue 1, pp. 14-29.
OWL 2, 2009. OWL 2 Web Ontology Language Document
Overview (Second Edition). W3C Recommendation.
w3.org/TR/2012/REC-owl2-overview-20121211/
Pietriga, E., Bizer, C., Karger, D., Lee, R., 2006. Fresnel:
A Browser-Independent Presentation Vocabulary for
RDF. In ISWC 2006, 5th International Semantic Web
Conference, LNCS 4273.
Quan, D. 2005. Xenon: An RDF Stylesheet Ontology. In
WWW 2005, 14th World Wide Web Conference, Japan.
RIF-FLD, 2013. RIF Framework for Logic Dialects
(Second Edition). W3C Recommendation. Editors:
Boley, H., Kifer, M., http://www.w3.org/TR/2013/REC-
rif-fld-20130205/
RIF-FLD-OWL, 2013. RIF RDF and OWL Compatibility
(Second Edition). W3C Recommendation Feb. 5th 2013.
www.w3.org/TR/2013/REC-rif-rdf-owl-20130205/
SBVR, 2008. Semantics of Business Vocabulary and
Business Rules (SBVR), Version 1.0. OMG document
formal/08-01-02. http://www.omg.org/spec/SBVR/1.0/
Šváb-Zamazal, O., Dudás, M., Svátek, V., 2012. User-
Friendly Pattern-Based Transformation of OWL
Ontologies. In EKAW 2012, LNCS 7603.
AnOntologyforSpecifyingandParsingKnowledgeRepresentationsStructuresandNotations
107
