
Robot Local Navigation with Learned Social Cost Functions
No
´
e P
´
erez-Higueras
1
, Rafael Ram
´
on-Vigo
1
, Fernando Caballero
2
and Luis Merino
1
1
School of Engineering, Pablo de Olavide University, Crta. Utrera km 1, Seville, Spain
2
Dpt. of System Engineering and Automation, University of Seville, Camino de los Descubrimientos s/n, Seville, Spain
Keywords:
Robot Navigation, Social Robots, Inverse Reinforcement Learning, Learning from Demonstrations.
Abstract:
Robot navigation in human environments is an active research area that poses serious challenges. Among
them, human-awareness has gain lot of attention in the last years due to its important role in human safety and
robot acceptance. The proposed robot navigation system extends state of the navigation schemes with some
social skills in order to naturally integrate the robot motion in crowded areas. Learning has been proposed as a
more principled way of estimating the insights of human social interactions. To do this, inverse reinforcement
learning is used to derive social cost functions by observing persons walking through the streets. Our objective
is to incorporate such costs into the robot navigation stack in order to “emulate” these human interactions. In
order to alleviate the complexity, the system is focused on learning an adequate cost function to be applied at
the local navigation level, thus providing direct low-level controls to the robot. The paper presents an analysis
of the results in a robot navigating in challenging real scenarios, analyzing and comparing this approach with
other algorithms.
1 INTRODUCTION
The Fun Robotic Outdoor Guide (FROG) FP7
project
1
aims to deploy a guiding robot in touristic
sites. While robot guides has been developed for more
than a decade (Thrun et al., 2000; Siegwart et al.,
2003), the project considers as new contributions the
development of social behaviors and a wining robot
personality by integrating social feedback, as well as
the robust operation in outdoors crowded scenarios.
The project aims to demonstrate the operation of the
robot in the Lisbon City Zoo and the Royal Alcazar
in Seville (see Fig. 1). Acting in these crowded sce-
narios (the Royal Alcazar may have around 5000 vis-
its per day, totaling 1.5 million-visitors per year) in-
volves not only ensuring a safe and efficient naviga-
tion but also social interaction and social awareness
when performing the robot tasks.
The creation of motion plans for robots that share
space with humans in dynamic environments is a
subject of intense investigation in the robotics field.
Robots must respect human social conventions, guar-
antee the comfort of surrounding persons, and main-
tain legibility, so humans can understand the robots
intentions (Kruse et al., 2013). This human aware
navigation involves different fields as human percep-
1
http://www.frogrobot.eu
Figure 1: The FROG project aims to deploy a guiding robot
with a fun personality, considering social feedback, in the
Royal Alcazar of Seville and the Zoo of Lisbon. A typical
situation of the first scenario is presented here.
tion, cognitive models and motion planning. Fur-
thermore, these considerations have to be taken into
account in the entire robot planning and navigation
stack, from task planning (Alili et al., 2009), task su-
pervision and execution (Clodic et al., 2008) to path
planning and execution (Sisbot et al., 2007; Tipaldi
and Arras, 2011; Trautman and Krause, 2010).
Social awareness requires that a robot is able to
detect persons, estimate their poses and differenti-
ate them from static and dynamic obstacles. Laser
rangefinders have been used for person detection and
tracking (Arras et al., 2008; Carballo et al., 2010).
Other common approach is the use of vision. In the
618
Pérez-Higueras N., Ramón-Vigo R., Caballero F. and Merino L..
Robot Local Navigation with Learned Social Cost Functions.
DOI: 10.5220/0005120806180625
In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics (ICINCO-2014), pages 618-625
ISBN: 978-989-758-040-6
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

FROG robot, in addition to laser rangefinders, a stereo
vision system is able to provide persons positions
and orientations in real time (Enzweiler and Gavrila,
2008; Keller et al., 2011).
Once the robot has information about the sur-
rounding persons, the navigation stack should con-
sider them in a different way than other obstacles in
the environment to achieve a socially normative nav-
igation. Current path planners will not solve the so-
cial navigation problem, as planners try to minimize
time or length, which does not translate to social paths
in general. This requires determining costs related to
social compliance. Some authors (Sisbot et al., 2007;
Kirby et al., 2010) have included costs and constraints
related to human-awareness into planners to obtain
socially acceptable paths, but these costs are pre-
programmed. However, hard-coded social behaviours
may be inappropriate (Feil-Seifer and Mataric, 2011).
Thus, learning these costs and models from data
seems a more principled approach. In the last years,
several contributions have been presented in this di-
rection: supervised learning is used in (Trautman and
Krause, 2010) to learn appropriate human motion pre-
diction models that take into account human-robot in-
teraction when navigating in crowded scenarios. Un-
supervised learning is used by (Luber et al., 2012)
to determine socially-normative motion prototypes,
which are then employed to infer social costs when
planning paths.
A potential approach is learning from demonstra-
tions (Argali et al., 2009): an expert indicates the
robot how it should navigate among humans. One
way to implement it is through inverse reinforcement
learning (Abbeel and Ng, 2004), in which a reward (or
cost) function is recovered from the expert behavior,
and then used to obtain a corresponding robot policy.
While a direct policy from state to actions may be also
learned from the examples, learning a reward function
allows to transfer the task to other situations.
In (Henry et al., 2010), the authors present a path
planner based on inverse reinforcement learning. As
the planner is learned for exemplary trajectories in-
volving interaction, it is also aware of typical social
behaviors. In this paper we also consider inverse re-
inforcement learning for social navigation. However,
while in (Henry et al., 2010) the costs are used to path
plans, here they are employed to learn local execution
policies, thus providing direct control of the robot.
This can be combined with other planning techniques
at higher levels, while alleviating the complexity as-
sociated to learning. Furthermore, a dataset of person
motion is employed here to learn the cost functions.
In the paper, we analyze and compare this approach
with several other possibilities.
The structure of the paper is as follows: next sec-
tion describes the robotic platform used and explains
the navigation stack implemented in the robot. Then,
Section 3 is where the learning approach is detailed.
Section 4 deals with the evaluation through experi-
ments, finishing with the conclusions and future open
lines.
2 ROBOT NAVIGATION
2.1 FROG Robot
Figure 2 shows a picture of the FROG robot. It
consists of a skid-steering platform, with 4 wheels
adapted to the scenarios considered in the project.
The platform has been developed by the Portuguese
company IDMind. It has an autonomy of two to four
hours depending on the type of ground and the num-
ber of embedded PCs running, up to three. The robot
weights 80Kg approximately and its maximum veloc-
ity is 1.6 m/s (software limited to 0.8 m/s).
Figure 2: Robot platform, placement and field of view of
the sensors. Green planes denote the front and rear laser
scanner planes. Orange plane stands for the 45
◦
tilted laser
scanner. Red fields denote the field of view of the front
stereo camera and back camera. Blue areas stand for sonar
sensing areas.
The robot is equipped with a wide range of sen-
sors for safety, localization and navigation. Among
them, the following sensors are considered for person
detection and navigation:
• Odometry is computed by reading encoders and
angular velocities from an MTi-G IMU from
XSens.
• Three laser rangefinders are considered. Two de-
ployed horizontally in the rear and in the front
of the robot, employed for localization, obstacle
avoidance and person detection. The third laser
RobotLocalNavigationwithLearnedSocialCostFunctions
619

is placed in front of the robot and tilted 45
◦
, it is
used for 3D obstacle avoidance.
• A stereo camera pair is employed for person de-
tection, pose estimation and 3D perception.
• An additional camera is used for low-range affec-
tive computing of the interacting persons.
• A sonar ring surrounding the robot for obstacle
detection.
In the FROG robot the sensors are disposed in
order to cover as much area as possible around it.
The frontal and real lasers cover a total angle of 360
◦
around the robot. Moreover, the sonars are employed
to detect obstacles in the lateral areas of the robot
which the lasers can not cover as well as elements at
different height than the lasers.
A tilted laser was also installed in the robot in
order to detect short range obstacles not visible by
the frontal lasers (obstacles upper or below their scan
plane). The laser is placed right below the screen and
tilted 45
◦
approximately. This configuration allows
for detecting close objects in front of the robot.
Regarding the key-aspect of person detection, the
main sensor considered is the stereo camera pair
which is used by the People Detection algorithm (En-
zweiler and Gavrila, 2008; Keller et al., 2011). This
algorithm has demonstrated to be flexible and accu-
rate enough to detect persons in front of the robot.
However, the limited field of view of the stereo cam-
eras used as image input for this algorithm limits the
amount of information served to the navigation stack
and, more importantly, do not provide person infor-
mation in the back of the robot.
A second source of information has been added
to increase the detection area for persons, a 2D laser-
based algorithm for persons detection (Arras et al.,
2008). This algorithm is not as accurate as the vision
algorithm but it is reliable enough to provide good es-
timations of persons around the robot. We use the
front and rear lasers as inputs for this algorithm, so we
are able to detect persons in 360
◦
around the robot.
2.2 Structure of the Navigation Stack
The navigation stack of the FROG robot follows the
classical separation between a global path planner and
a local path execution module (see Fig. 3). The global
planner employs the robot global pose and global
models of the obstacles (and potentially other mod-
els) in order to determine a path to the goal. The lo-
cal planner receives the global path and tries to fol-
low it, by considering the most up to date sensorial
information on the robot frame. This local planner
generates the controls (angular and linear velocities)
commanded to the robot platform.
Figure 3: The navigation stack consists of a global planner,
acting on global models; and a local planner acting on the
most up to date information at a higher frequency.
The current implementation of the navigation
stack extends the Robot Operating System (ROS)
(Marder-Eppstein et al., 2010) navigation architec-
ture. In this paper we are mainly concerned with
adapting the local planner, although significant mod-
ifications have been carried out to adapt the global
planner to the FROG requirements. The global path
planner is based on a Dijkstra’s algorithm to search
through the available working area and find the best
path. As future work we plan to consider also social
constraints at this level.
We consider as local planner an extension of the
Trajectory Rollout algorithm (Gerkey and Konolige,
2008). The algorithm has been almost reimplemented
considering computational efficiency as a major con-
straints. This controller predicts possible trajectories
with a discrete-time simulation over a receding hori-
zon. To ensure safe and feasible motion, the robot’s
kinodynamic constrains and accelerations have to be
indicated correctly. The controller choses the best tra-
jectory among the predicted trajectories by evaluating
different cost functions such as distance to the global
path, distance to local goal or obstacle cost among
others. These different cost functions are combined
by using a convex combination and allow to balance
the robot different goals. We modify this technique
to include additional cost terms considering social
awareness and the position of the persons, which are
then learned from data.
To compute the global path and to evaluate the
different trajectories to follow the path locally, two
2D grid maps are used. Each map cell of the grid
map contains relevant information for motion, such
as the presence of an obstacle, or membership in a
recognized path. For global planning, the grid map is
built from the information of the predefined naviga-
tion map along with the sensors data. For local plan-
ning, another 2D grid map is built just from sensors
data. This is a rectangular grid map around the robot.
ICINCO2014-11thInternationalConferenceonInformaticsinControl,AutomationandRobotics
620
3 LEARNING THE SOCIAL COST
FUNCTION
As indicated above, it is hypothesized that learning
the mentioned cost functions by observing how hu-
mans navigate among themselves will lead to socially
normative behaviors.
The learning of the cost function is accom-
plished by using inverse reinforcement learning (IRL,
(Abbeel and Ng, 2004)). IRL assumes that the expert
from which we want to learn is modeled by a Markov
Decision Process (MDP). Formally, a discrete MDP is
defined by the tuple hS,A,T,R,D,γi. The state space
is the finite set of possible states s ∈ S; the action
space is defined as the finite set of possible actions
a ∈ A. At every step, an action is taken and a reward
is given (or cost is incurred). After performing an ac-
tion a, the state transition is modeled by the condi-
tional probability function T (s
0
,a, s) = p(s
0
|a, s). At
every time instant then the state is observed. The re-
ward obtained at each step is denoted R(s,a). A func-
tion a = π(s) that maps an state to an action is called
a policy. A policy that maximizes the sum of ex-
pected rewards, or value, earned during D time steps
E[
∑
D
t=0
γ
t
R(s, a)] is called an optimal policy. To en-
sure that the sum is finite when D → ∞, rewards are
weighted by a discount factor γ ∈ [0,1).
The objective of IRL is to determine the reward
function R(s,a) that the expert is following by ob-
serving the expert acting in the real world, assuming
that it is executing a policy according to the given
MDP. In many cases, the reward function can be as-
sumed to depend on a set of features θ(s), which are
functions of the state.
The idea of using IRL for robot navigation has
been proposed by Henry et al., (Henry et al., 2010) to
estimate cost functions for robot path planning. Here,
there are several differences with respect to this ap-
proach, that will be described in the next sections.
3.1 Models
The most relevant aspect of the approach is to define
the MDP model, and, in particular, the state space and
the features on which the reward function is depend-
ing on. This constitute the main hypothesis consid-
ered here.
In addition, in order to alleviate the complexity of
the problem, we use two models. One just consider-
ing features concerning pairwise relative motions be-
tween two persons, and another one, based on high
level features like person densities in different regions
in front of the robot. We evaluate the models in sec-
tion 4.
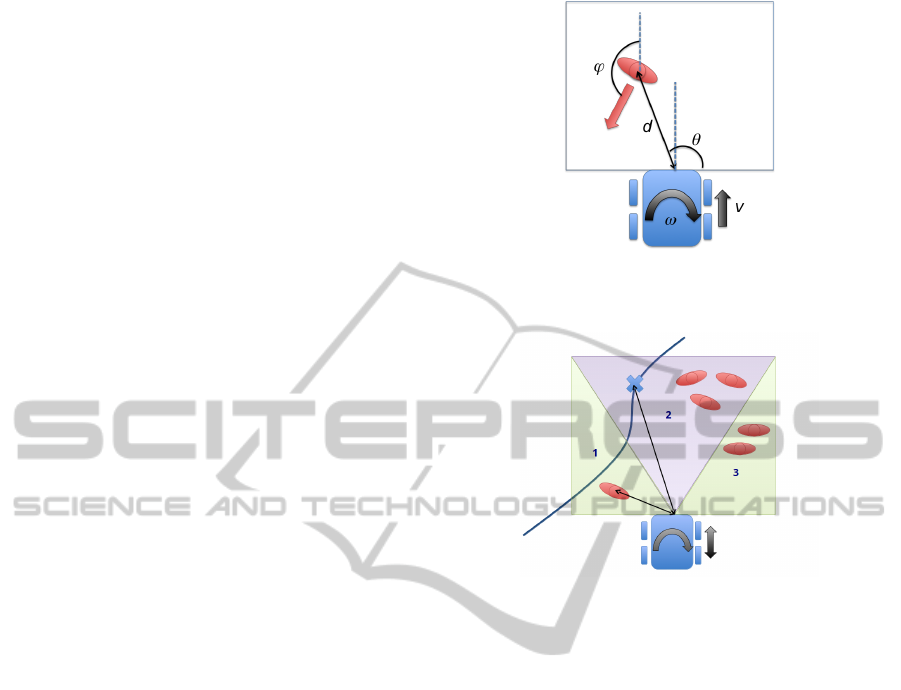
Figure 4: The state of model 1 is defined as the relative pose
of the person with respect to the robot. The actions (linear
and angular speeds) affect how this state evolves.
Figure 5: The state in the model 2 is defined with the densi-
ties (persons/m
2
) in the three regions in front of the robot.
3.1.1 Model 1
In principle, the actions of a person (or robot) navigat-
ing among other people will depend on the state of all
the persons close to the robot, plus many other factors,
like obstacles and the person goal. However, consid-
ering all the persons will lead to a large (and time-
variant in size) state space. In (Henry et al., 2010),
this is tackled by considering the density and flow di-
rection as features, and using them at the path plan-
ning level.
Here, the model considers the generation of the
velocity controls of the vehicle. Contrary to (Henry
et al., 2010), we parameterize the state on the local
robot/expert frame. This allows reducing the com-
plexity of the problem. Furthermore, in the model
we consider just pairwise relative motions between
two persons (a robot and a person). The state is
then defined by the relative position and orientation
of the person with respect to the robot, encoded as
s =
d θ ϕ
T
(see Fig. 4). As the parameteriza-
tion is local, the pose of the robot is not considered
into the state. The effects of the actions on the state
are modeled by using simple kinematic equations, and
are considered to be deterministic. Uncertainties are
added on the person motion part, sampling several
RobotLocalNavigationwithLearnedSocialCostFunctions
621

variations on the linear and angular velocities of the
person and determining its future position. This way,
the transition function T (s
0
,a, s) is determined. One
hypothesis that will be analyzed in this paper is if the
model can be extrapolated to cases with more persons
by means of the cost function learned applied to all
the persons present in the scene.
3.1.2 Model 2
The second MDP model proposed is based on high
level features to define the reward function. In partic-
ular, the person densities in different regions in front
of the robot are considered to parametrize the state on
the robot frame. We use the same area as in model
1, but in this case, we divide it in three independent
regions; one in front of the robot and two on the left
and right sides (see Fig. 5).
Therefore, the state is encoded as
s =
ρ
1
ρ
2
ρ
3
T
. The density value for each
region is divided in 5 bins of range 0.25 persons/m
2
,
except the first bin that corresponds to value 0 of
density. Then, the transition function T (s
0
,a, s) is
determined by considering how the densities in the
regions are affected by the robot motion. In this case,
the uncertainties are introduced in the new density
values due to the inflow motion of persons and the
outflow of persons in the regions.
The development of this model aims at comple-
menting the first model in a simple way. The idea is
to capture other navigation behaviors in crowded en-
vironments that the first model does not consider, as it
only considers the closest pedestrian. We alleviate the
complexity of the IRL problem and the computational
cost by dividing the learning process into different re-
ward functions. Thus, we do not add the new densi-
ties features into the previous model state in order to
obtain a more complete (and complicated) model. In-
stead, we develop a new model considering only the
densities features, and then obtaining the correspond-
ing reward function. Then, we can use the reward
function learned for model 1 and mix it with the new
reward function obtained for the model of densities,
model 2. The results will be showed in Sections 4.
3.1.3 Learning
We consider the algorithm Gaussian Process IRL
(GPIRL) (Levine et al., 2011) for solving the IRL
problem. The main difference with respect to other
approaches is that it employs a Gaussian Process to
learn a non-linear reward function over the feature
space. Thus, the GP allows to extrapolate the learnt
reward function to other state spaces within the do-
main of the features considered.
Figure 6: Example image of the pedestrian dataset used for
learning. See (Pellegrini et al., 2009) for more details.
As a source of examples, the BIWI Walking
Pedestrians dataset
2
has been used (Pellegrini et al.,
2009). This dataset consists of a bird view of a out-
doors urban environment, and is annotated with the
positions and velocities of all persons and the corre-
sponding timestamps (see Fig. 6).
In our case, we employ the dataset to gather
the examples from experts in the task of navigating
among persons. A set persons are selected as ”ex-
perts” among the pedestrians that are moving in the
dataset. For each point in the trajectory followed by
the person we extract:
• The state for model 1 s
i
=
d θ ϕ
T
of the
closest person within the local planning zone (6
meters in front and 2 meters at each side of the
robot).
• In case of model 2. The state s
i
=
ρ
1
ρ
2
ρ
3
T
.
• The action performed by the expert at the same
time instant. In particular, the linear and angular
velocities a
i
=
v ω
T
, in order to easily transfer
them to the robot.
Thus, for each expert the trajectory {s
i
,a
i
}
N
i=1
is
stored as one episode for the learning phase. The
GPIRL algorithm uses a discrete MDP as model.
Therefore, the state and actions spaces are discretized
considering how experts and pedestrians behave in the
dataset.
Finally, by using the previous examples extracted
from the dataset as an input to the IRL algorithm, a
reward (cost) function R(s, a) is obtained as a result,
which associates a scalar value to each state (Ramon-
Vigo et al., 2014). We use this value as a new cost in
the local planning algorithm and its weight is tuned
by hand.
2
http://www.vision.ee.ethz.ch/datasets/
ICINCO2014-11thInternationalConferenceonInformaticsinControl,AutomationandRobotics
622

4 EXPERIMENTS
In this section we show actual experiments performed
with the robotic platform, integrating the subsystems
described above. In these experiments, the robot au-
tonomously navigates from a starting point to a given
waypoint, encountering persons in his path during the
execution.
The experiments will evaluate the approach by
comparing a classic local planner (Gerkey and Kono-
lige, 2008) with the same planer augmented with the
learned costs and the costs based on a classic Prox-
emics aproach (Hall, 1990; Kirby et al., 2009).
The results are compared using as metrics the to-
tal distance traveled towards the goal (TD), the time
to execute the path and the minimum and average dis-
tances to the persons (Min PD and Mean PD respec-
tively) along the path. They are shown along with
their standard deviations. By computing the execu-
tion time and total distance traveled we can assess the
effectiveness to reach the goal, while the distances to
persons let us know how the personal space is con-
served.
4.1 Experiments with Static Controlled
Pedestrians
In this set of experiments, the robot had to cross a
controlled scenario with pedestrian standing, talking
to each other. It is assumed an static scenario in the
sense that people do not move from their initial posi-
tion. We performed 4 runs for each approach, keeping
the same configuration between the different runs.
We show the results for the basic navigation with-
out ”social component” (No social), results for the
proxemics approach (Proxemics), results with the so-
cial cost obtained with the model 1 (One Ped), results
with the model 1 generalization from one pedestrian
to all (All Ped), results for model 2 (Densities) and
finally, results taking into account the costs derivated
for model 1 and model 2 (One Ped + Dens). Table 1
summarizes the metrics for each approach:
• No social: the navigation without the social com-
ponent tries to optimize time and distance trav-
eled. It can be seen how the average and mean
distances to pedestrians are the lowest of all the
approaches.
• Proxemics: this classical approach improves a bit
the results of the ”No social” navigation, in the
sense that the robot keeps itself farther from the
personal space of the persons. Anyway, it per-
forms a too significant avoidance when the robot
is close to pedestrian which is consider unneces-
sary.
Table 1: Experimental results in a static scenario.
T (s) TD (m) Mean PD (m) Min PD (m)
No social 50.65 ± 0.21 21.76 ± 0.29 2.82 ± 0.06 0.82 ± 0.03
Proxemics 71.00 ± 1.55 21.09 ± 1.04 3.69 ± 1.69 1.05 ± 0.18
One Ped 54.28 ± 3.39 20.50 ± 0.22 5.19 ± 1.06 1.29 ± 0.18
All Ped 58.85 ± 0.21 22.68 ± 0.19 5.22 ± 1.69 1.69 ± 0.04
Densities 51.05 ± 0.92 24.53 ± 0.01 4.50 ± 0.21 0.87 ± 0.02
OnePed + Dens 53.27 ± 3.17 21.19 ± 1.56 4.00 ± 1.82 1.01 ± 0.29
• One pedestrian (model 1). The proxemics re-
sults are improved by this approach. It keeps a
longer distance to the pedestrians than in the no
social case, but the avoiding maneuvers are per-
formed more in advance than in the proxemics
case, which can be suitable for no-crowded sce-
narios. But the performance can degrade if there
are several people surrounding the robot.
• All pedestrian. According to the results, taking
into account all the pedestrian instead of just the
closest, has a similar performance as in the pre-
vious case. These results can be different in ex-
periments with more people. Anyway, we think
that this generalization can not retrieve the neces-
sary key aspects for a good navigation in crowded
environments.
• Densities (model 2). In this case, the distances to
the pedestrians are lower than the case of model 1
and its generalization. However, aspects like the
orientation or the direction of motion of the pedes-
trian are not taken into account, which can lead to
unwanted avoiding behaviors.
• One pedestrian + Densities (model 1 and model
2). This approach performs the avoiding ma-
neuvers before than in the proxemics case with-
out performing excessive avoidance. Moreover,
it keeps a shorter distance to the pedestrians than
just model 1 without being uncomfortable for
them. We consider that this behavior can be suit-
able for crowded environments.
4.2 Experiments with Dynamic
Controlled Pedestrians
To perform these experiments we used the same sce-
nario than before, but, in this case, the pedestrians
were moving and crossing the area. As before, we
performed 4 runs for each navigation approach, try-
ing to repeat the pedestrians movement.
The setup of the controlled experiment is like fol-
lows: Two pedestrians walk opposite to robot direc-
RobotLocalNavigationwithLearnedSocialCostFunctions
623

Table 2: Experimental results in a dynamic scenario.
T (s) TD (m) Mean PD (m) Min PD (m)
No social 59.22 ± 0.06 20.38± 0.29 2.31 ± 0.15 0.20 ± 0.09
Proxemics 68.44 ± 0.02 20.99 ± 0.68 2.59 ± 0.10 0.38 ± 0.04
One Ped 69.45 ± 7.01 21.85 ± 1.89 4.46 ± 0.19 0.20 ± 0.17
All Ped 61.20 ± 0.0 20.50 ± 0.0 2.49 ± 0.16 0.60 ± 0.12
Densities 65.26 ± 10.08 20.75 ± 0.24 2.56 ± 0.17 0.47 ± 0.16
OnePed + Dens 60.20 ± 1.81 20.36± 0.35 2.46 ± 0.10 0.33 ± 0.02
tion forcing it to avoid them. Then, other pedestrian
cross in diagonal in front of the robot. Finally, two
new pedestrians pass the robot on the left walking in
the same direction as it.
The results are presented in Table 2. They are very
similar to the results obtained in case of static pedes-
trians. Again, all the ”social” approaches suggested
improve the ”no social” behavior. In this case, the
model 1 (One Ped) seems to make some excessive
avoiding maneuvers. However, the mixed approach
of model 1 and model 2 seems to keep an acceptable
distance to pedestrians in crowded environments and
makes smooth avoiding maneuvers.
4.3 Experiments in Target Scenarios:
Royal Alcazar of Seville
Another set of experiments were performed in the
Alcazar of Seville, where the final demo of FROG
project will take place. In this case, the social costs
obtained from model 1 and 2 were employed (see Fig.
7).
The guided tour has a distance of 435 meters ap-
proximately, including the return path to the initial
point, which involves a different route. During a week
of testing, the tour was performed satisfactory twice
a day, which gives a total of almost 4.5 kms of au-
tonomous navigation in a very crowded scenario.
The social behavior of the robot was showed to
be suitable in several cases. The robot is able to an-
ticipate its movements performing smooth avoiding
maneuvers when it detects people walking in the op-
posite direction.
5 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
The paper summarized the robot navigation system
developed in the framework of the FROG project.
An efficient and safe navigation system has been im-
plemented according to the FROG system specifica-
Figure 7: Example of people detection system. On the left:
typical situation at Royal Alcazar, with lot of people around
the robot. On the right: localization of the robot, with 360
◦
people detection (green cylinders).
tions, paying special attention to the social interac-
tion aspects of this navigation. We have presented
an approach that uses inverse reinforcement learning
to learn cost/reward functions from examples for the
task of navigating among persons. Two simple mod-
els and the use of a public dataset to extract the learn-
ing samples are described.
All the different approaches are compared be-
tween them and the Proxemics approach. The re-
sults show that IRL can be used to transfer some
human navigation behaviors into the low-level navi-
gation controllers of a mobile robot. The robot lo-
cal controller improves lightly the Proxemics perfor-
mance and is able to anticipate smooth avoiding ma-
neuvers when people is walking in opposite or almost
parallel directions. However, the improvement is not
very significant and the social costs do not retrieve
all the key-insight involved in a social navigation in
crowded environments. This may indicate that the lo-
cal planner used is no able to find the best action in
these cases.
As future work, we plan to record our own dataset
which includes a richer variety of crossing behaviors
between persons and other social constrains. Further-
more, new features can be added to the models like
the persons flow direction. We will consider random-
ized planners, like RRTs (Rios-Martinez et al., 2011),
as local planner. We will reason about social costs in
the global path planning level. Besides, we plan to
carry out a qualitative evaluation on the perception
of the pedestrian regarding the different navigation
modes described in the experimental section.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work is partially funded by the European
Commission 7th Framework Programme under grant
agreement no. 288235 (FROG) and the project PAIS-
MultiRobot, funded by the Junta de Andaluc
´
ıa (TIC-
ICINCO2014-11thInternationalConferenceonInformaticsinControl,AutomationandRobotics
624

7390). The authors also thank the Lisbon Zoo and the
Royal Alc
´
azar in Seville for allowing to perform the
experiment at their facilities.
REFERENCES
Abbeel, P. and Ng, A. Y. (2004). Apprenticeship learning
via inverse reinforcement learning. In Proceedings of
the twenty-first international conference on Machine
learning, ICML ’04, pages 1–, New York, NY, USA.
ACM.
Alili, S., Warnier, M., Ali, M., and Alami, R. (2009). Plan-
ning and plan-execution for human-robot cooperative
task achievement. In 19th International Conference
on Automated Planning and Scheduling.
Argali, B., Chernova, S., Veloso, M., and Browning, B.
(2009). A survey of robot learning from demonstra-
tions. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 57:469–
483.
Arras, K. O., Mozos, O. M., and Burgard, W. (2008). Us-
ing boosted features for the detection of people in
2d range data. In Proc. International Conference on
Robotics and Automation, ICRA.
Carballo, A., Ohya, A., and Yuta, S. (2010). People detec-
tion using range and intensity data from multi-layered
laser range finders. In Proc. International Conference
on Intelligent Robots and Systems, IROS, pages 5849–
5854.
Clodic, A., Cao, H., Alili, S., Montreuil, V., Alami, R.,
and Chatila, R. (2008). SHARY: A Supervision Sys-
tem Adapted to Human-Robot Interaction. In Khatib,
O., Kumar, V., and Pappas, G. J., editors, Experi-
mental Robotics, The Eleventh International Sympo-
sium, ISER 2008, July 13-16, 2008, Athens, Greece,
volume 54 of Springer Tracts in Advanced Robotics,
pages 229–238. Springer.
Enzweiler, M. and Gavrila, D. (2008). Integrated pedes-
trian classification and orientation estimation. In Proc.
of the IEEE Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern
Recognition.
Feil-Seifer, D. and Mataric, M. (2011). People-aware navi-
gation for goal-oriented behavior involving a human
partner. In Proceedings of the IEEE International
Conference on Development and Learning (ICDL).
Gerkey, B. and Konolige, K. (2008). Planning and control
in unstructured terrain. In Workshop on Path Planning
on Costmaps, Proceedings of the IEEE International
Conference on Robotics and Automation.
Hall, E. T. (1990). The Hidden Dimension. Anchor.
Henry, P., Vollmer, C., Ferris, B., and Fox, D. (2010).
Learning to navigate through crowded environments.
In ICRA’10, pages 981–986.
Keller, C., Enzweiler, M., Rohrbach, M., Llorca, D.-F.,
Schn
¨
orr, C., and Gavrila, D. (2011). The benefits of
dense stereo for pedestrian detection. IEEE Trans. on
Intelligent Transportation Systems, 12(4):1096–1106.
Kirby, R., J. Forlizzi, J., and Simmons, R. (2010). Affec-
tive social robots. Robotics and Autonomous Systems,
58:322–332.
Kirby, R., Simmons, R. G., and Forlizzi, J. (2009). Com-
panion: A constraint-optimizing method for person-
acceptable navigation. In RO-MAN, pages 607–612.
IEEE.
Kruse, T., Pandey, A. K., Alami, R., and Kirsch, A. (2013).
Human-aware robot navigation: A survey. Robot. Au-
ton. Syst., 61(12):1726–1743.
Levine, S., Popovic, Z., and Koltun, V. (2011). Nonlin-
ear inverse reinforcement learning with gaussian pro-
cesses. In Neural Information Processing Systems
Conference.
Luber, M., Spinello, L., Silva, J., and Arras, K. (2012).
Socially-aware robot navigation: A learning ap-
proach. In IROS, pages 797–803. IEEE.
Marder-Eppstein, E., Berger, E., Foote, T., Gerkey, B. P.,
and Konolige, K. (2010). The Office Marathon: Ro-
bust Navigation in an Indoor Office Environment. In
International Conference on Robotics and Automa-
tion.
Pellegrini, S., Ess, A., Schindler, K., and van Gool, L.
(2009). You’ll never walk alone: Modeling social be-
havior for multi-target tracking. In International Con-
ference on Computer Vision.
Ramon-Vigo, R., Perez-Higueras, N., Caballero, F., and
Merino, L. (2014). Transferring human navigation be-
haviors into a robot local planner. In RO-MAN. In
Press.
Rios-Martinez, J., Spalanzani, A., and Laugier, C. (2011).
Understanding human interaction for probabilistic au-
tonomous navigation using risk-rrt approach. In In-
telligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 2011 IEEE/RSJ
International Conference on, pages 2014–2019.
Siegwart, R., Arras, K. O., Bouabdallah, S., Burnier, D.,
Froidevaux, G., Greppin, X., Jensen, B., Lorotte,
A., Mayor, L., Meisser, M., Philippsen, R., Piguet,
R., Ramel, G., Terrien, G., and Tomatis, N. (2003).
Robox at Expo.02: A large-scale installation of per-
sonal robots. Robotics and Autonomous Systems,
42(3-4):203–222.
Sisbot, E. A., Marin-Urias, L. F., Alami, R., and Sim
´
eon, T.
(2007). A Human Aware Mobile Robot Motion Plan-
ner. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 23(5):874–883.
Thrun, S., Beetz, M., Bennewitz, M., Burgard, W., Cremers,
A. B., Dellaert, F., Fox, D., and Hahnel, C. (2000).
Probabilistic algorithms and the interactive museum
tour-guide robot minerva. The International Journal
of Robotics Research, 19:972–999.
Tipaldi, G. D. and Arras, K. O. (2011). Planning Problems
for Social Robots. In Proceedings fo the Twenty-First
Internacional Conference on Automated Planning and
Scheduling, pages 339–342.
Trautman, P. and Krause, A. (2010). Unfreezing the robot:
Navigation in dense, interacting crowds. In IROS,
pages 797–803. IEEE.
RobotLocalNavigationwithLearnedSocialCostFunctions
625
