
Neural Control using EEG as a BCI Technique for Low Cost
Prosthetic Arms
Shyam Diwakar
1
, Sandeep Bodda
1
, Chaitanya Nutakki
1
, Asha Vijayan
1
,
Krishnashree Achuthan
2
and Bipin Nair
1
1
Amrita School of Biotechnology, Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham (Amrita University),
Clapana P.O., Amritapuri, Kollam, Kerala, India
2
Amrita School of Engineering, Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham (Amrita University),
Clapana P.O., Amritapuri, Kollam, Kerala, India
Keywords: Brain Computer Interface, Prosthetic Arm, Kinematics, EEG, Iterative Algorithm, Machine Learning.
Abstract: There have been significant advancements in brain computer interface (BCI) techniques using EEG-like
methods. EEG can serve as non-invasive BMI technique, to control devices like wheelchairs, cursors and
robotic arm. In this paper, we discuss the use of EEG recordings to control low-cost robotic arms by
extracting motor task patterns and indicate where such control algorithms may show promise towards the
humanitarian challenge. Studies have shown robotic arm movement solutions using kinematics and machine
learning methods. With iterative processes for trajectory making, EEG signals have been known to be used
to control robotic arms. The paper also showcases a case-study developed towards this challenge in order to
test such algorithmic approaches. Non-traditional approaches using neuro-inspired processing techniques
without implicit kinematics have also shown potential applications. Use of EEG to resolve temporal
information may, indeed, help understand movement coordination in robotic arm.
1 INTRODUCTION
Brain Computer Interfaces (BCI) is a novel fast
evolving technology connecting the brain to a
computing devices (Birbaumer, 2006; Wolpaw et al.,
2002), now seen as a ubiquitous detection and
diagnostics tool. The domain of EEG-based BCIs
include several applications like controlling a cursor
on the screen (Yuanqing Li et al., 2008), selecting
letters from keyboard playing games (Donchin et al.,
2000), controlling a prosthetic arm (Bi et al., 2013;
Muller and Blankertz, 2006). BCI devices are used
in multiple modes including invasive or non-
invasive (Leuthardt et al., 2004; Owen and Coleman,
2008; Pfurtscheller et al., 2010), synchronous and
asynchronous (Md Norani et al., 2010) modes in
current BCI applications. Prosthetic articulators
based on EEG play a vital role in the area of haptics
and sensorimotor control (Wolpert and Flanagan,
2010). In this position paper, we discuss the
evolution of EEG-based BCI techniques for control
of neuro-prosthetic articulators and include our case
study on a low-cost robotic arm model.
Electroencephalography (EEG) is a widely used
neuroimaging technique, owing to its high temporal
resolution, low cost, high portability and has become
a practical choice for BCI. The quality of EEG
signals are usually affected by noise from scalp,
skull and a significant contribution from
background noise (Nicolas-Alonso and Gomez-Gil,
2012). Various EEG-based BCIs differ based on
user intent to extract neuro-electrical activity.
Techniques commonly used are based on
recognition of specific pattern in EEG to a particular
task (Millán et al., 2002; Pfurtscheller et al., 2003;
Wolpaw et al., 2002), identification of characteristic
waveforms in EEGs which follow an event
(Birbaumer et al., 2003; Farwell and Donchin,
1988), and the presence of periodic waveforms in
EEGs in the range of frequencies of an oscillatory
signal corresponding to a light flash stimulus
(Friman et al., 2007). EEG signals, based on
specific responses related to a task-related stimulus,
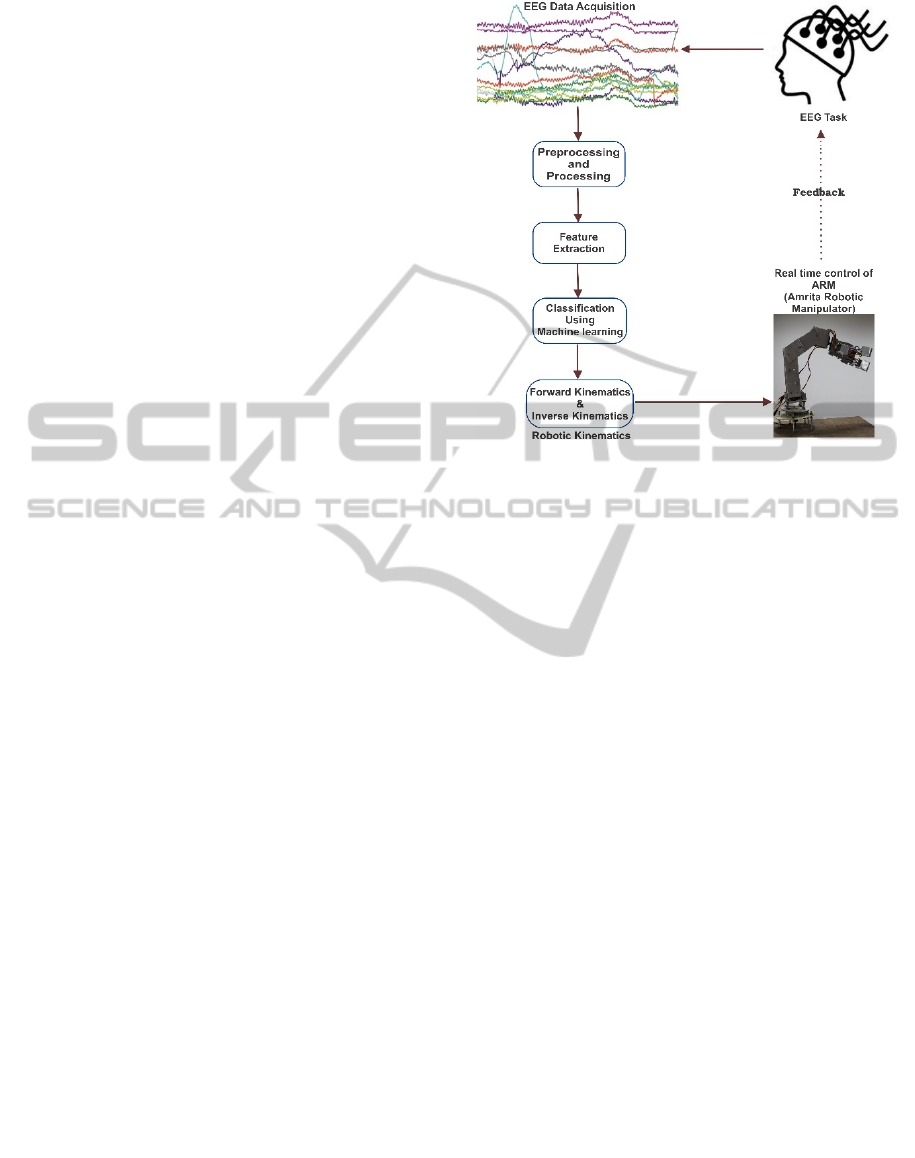
serve as an input for BCI systems to control
prosthetic arms (Figure 1). EEG patterns can be
extracted using Sensory Motor Rhythms (SMR).
Motor movement or imaginary movement changes
the oscillatory patterns of EEG, resulting in
270
Diwakar S., Bodda S., Nutakki C., Vijayan A., Achuthan K. and Nair B..
Neural Control using EEG as a BCI Technique for Low Cost Prosthetic Arms.
DOI: 10.5220/0005134802700275
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Neural Computation Theory and Applications (NCTA-2014), pages 270-275
ISBN: 978-989-758-054-3
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
suppression of amplitude (ERD) or enhancement in
amplitude (ERS) for mu or beta rhythms.
(McFarland et al., 2000; Pfurtscheller et al., 2006;
Wolpaw et al., 2002).
1.1 Implementation Issues regarding
EEG Based Techniques
Although EEG is portable (Nicolas-Alonso and
Gomez-Gil, 2012; Tanaka et al., 2005) and cost
effective (Bi et al., 2013; Vespa et al., 1999) for
research purposes, poor signal to noise ratio or
artefacts are recorded during signal acquisition. For
statistical significance, EEG analysis require
complex data analytics and significantly large
dataset with a fair number of subjects (Schlögl et al.,
2002). Due to low spatial resolution, EEG signals
need elaborate interpretation in order to functionally
hypothesize on areas activated by particular
response (Srinivasan, 1999). Pre-recording setup
times are also significantly long.
Noise in the signals plays an important role in
EEG signal analysis and interpretation of data
(Repovs, 2010). There is a necessity for efficient
strategies towards noise prevention and removal.
1.2 Neurological Mechanisms Used in
BCI
Control signals generated by BCI methods
correspond into 5 main categories namely
sensorimotor activity (ERD/ERS), VEP, P300, SCP,
activity of neural cell (Wolpaw et al., 2002), and
furthermore into two additional categories, mental
arithmetic tasks (non-movement) and multiple
neural mechanisms (Anderson, 1995; Gysels et al.,
2005).
Previous studies (Anderson, 1995; Choi, 2012;
Craig and Nguyen, 2007; Leeb et al., 2007; Pires et
al., 2008; Tanaka et al., 2005) have shown that these
neurological mechanisms were used in different
motor-related tasks. A previous work (Tanaka et al.,
2005) had extracted ERD/ERS neurological
phenomena for pattern classification of turn-left and
turn-right events concerning a BCI-enabled wheel
chair. Similar methods were employed for moving-
forward and moving-backward tasks but used SVM
(Choi, 2012), Linear classifier (Leeb et al., 2007),
Artificial Neural Network(ANN) (Craig and
Nguyen, 2007). Methods using EEG-based
techniques involved low-pass filtering(7 Hz) of the
P300 wave and feature-extraction using windowing
or normalization (Pires et al., 2008).
Figure 1: Schematic representation of a BCI-controlled
low-cost robotic upper arm model.
Datasets were then classified using Bayesian
classifier for categorizing multi-class movement
data. A motor–task study using SSVEP-based
methods (Middendorf et al., 2000), employed feature
extraction using Welch periodogram (512 FFT
points) and involved SVM-based classification of
turning right/going forward and stopping (Dasgupta
et al., 2010). Neural Networks with back-
propagation learning have been shown to classify
arithmetic calculation task features, extracted using
Burg method/Levison algorithm (auto-regression
models) (Anderson, 1995). Studies on word-
generation and motor activity used Butterworth filter
(1-40 Hz) coefficients and phase locking
values(PLV) (Lachaux et al., 1999) as features and
classified the dataset using SVM (Gysels et al.,
2005). Laplacian algorithms have also been used for
movement-related tasks (McFarland et al., 2000).
1.3 Prosthesis & Control with EEG
Signal
Brain computer interface (BCI) have been employed
to control prosthetic arms (Wolpert and Flanagan,
2010) in order to do specialized tasks, namely,
reaching the target with an optimal feedback
(Mitrovic et al., 2010), examining the different
parameters of an object (Saal and Vijayakumar,
2010). Prosthetic or robotic arms consist of a series
of links which were equipped by an end-effector to
move in a 3D space (AbuQassem, 2010; Wolpert
and Flanagan, 2010). Links were driven by motors
NeuralControlusingEEGasaBCITechniqueforLowCostProstheticArms
271

changing the orientation of the manipulator
(Megahed, 2013).
Modeling of robotic arm behavior for prosthetic
devices involved kinematics of the robotic links
(Kay, 2005). Different algorithms have been
proposed to solve the robotic kinematics; DH
method (Iqbal et al., 2012), homogenous method
(Mitra, 2012) for forward kinematic model and
analytical method (Iqbal et al., 2012) for inverse
kinematics model. Analytical methods are
subcategorized into geometric and algebraic
approaches. Geometric approach has been applied to
simple robotic structures with few DOF, whereas
algebraic approach were used for greater DOF
(Kucuk and Bingul, 2006). Triangulation and CCD
(Cyclic Coordinate Descent) algorithms (Muller-
Cajar and Mukundan, 2007) have been used to solve
inverse kinematics with a scalable number of links.
Quaternion algebraic approach (Sahu et al., 2008)
has been shown to be computationally cost-effective
compared to homogenous methods.
A feedback system was shown to control grip
force of a gripper/ grasper (Westling and Johansson,
1984). Controllers like PID (open loop
optimization), OFC (closed loop optimization) have
been used to optimize the motor commands with the
help of cost functions like iterative linear quadratic
Gaussian (ILQG) which use trajectory planning and
execution in multiple steps (Mitrovic et al., 2010)
instead of using sensors. Stochastic optimal control
is another application which is now widely being
used for planning and controlling of robotic systems
(Rawlik et al., 2012). It has been demonstrated that
Kullback-Leibler divergence minimization algorithm
could present a solution towards stochastic optimal
control (Rawlik et al., 2012).
1.4 Non-Traditional BCI Methods
Models of spiking neural networks (SNN) take
advantage of precise timing of spikes to produce rich
dynamic behavior(Kasabov et al., 2013). The study
of enriched cognitive systems embodied interaction
with environment could be achieved by employing
SNN. Futuristic design of hybrid architecture
inspired by the working human brain have led to
complex structures and significant models of
internal dynamics has seen in representation of the
model kinematics structures such as the cerebellum
(Furber et al., 2014; Shepherd et al., 1998).
The key contribution to this direction of study
will be a method for simulating a spiking neural
network with high parallelism relying on data
organization has seen in internal representation
mimicking the motor circuit in the brain. An
evaluation of user configurable structures resemble
primary circuit of movement coordination such as
the cerebellum or the V1 motor cortex may suggest
discrete spike based transformation models
generating responses appropriate to kinematic
algorithms via data classification technique such
circuits may have ranges modified by nature of input
and delays configuring the plasticity of adaptive
responses as seen in biological neural circuit.
CMAC (Albus, 1975) had proposed a pattern
separation algorithm based on internal representation
model of the cerebellar neurons that perform
movement coordination tasks. While spiking neuron
models of CMAC-like algorithms are being
elaborated, benchmark nonlinear tests have shown to
function using simple neural microcircuit models
(Joshi and Maass, 2005).Such neural circuits may
perform indifferently to the kind of feedback
received compared to the control performance of
traditional techniques. A trend of novel spiking
neural circuit based methods for SLAM techniques
may help bridge the gap for the BCI devices and
such low-cost articulator models.
1.5 Implementation Issues for Low
Cost Prosthetic Devices
For sensorimotor control, the primary aim was to
accomplish a task of reaching a specified target.
Targets for low economic cost prosthetic arms
include an ability of generalization of tasks (say
grasp task) without significant precision or high
accuracy. Adapting variability models in kinematic
algorithms and using learning methods, some of the
issues may be overcome (Vijayan et al., 2013).
Position feedback is measured in some robotic arms
using sensors (Mitrovic et al., 2010). In devices
without sensor-based feedback of real-time
localization, effective prediction-correction schemes
may be needed (Kalanovic et al., 2000).
Although a major humanitarian necessity, the
major challenges faced when designing a low cost
prosthetic devices include the economic cost for
research and development, local availability of
components, device functionality, prediction of time
of failure, design simplicity (D’Apuzzo et al., 2012).
Avoiding sensory feedback decreased cost but
increased the localization variability in models.
However, with a low-cost prosthesis implementation
issues such as position control, simultaneous
localization models and power management pose
additional challenges post-design. We have however
regarded a task-based control model in the context
of this paper.
NCTA2014-InternationalConferenceonNeuralComputationTheoryandApplications
272

2 CASE STUDY: LOW-COST
PROSTHETIC ARM CONTROL
USING EEG
In our study, we used a indigenously designed
robotic ARM (Amrita Robotic Manipulator), a part
of remotely-triggered experiments available online
(Vijayan et al., 2013) with 6 DOF as a prototype for
a prosthetic upper arm. We tested the kinematic
behavior of the manipulator with DH method and
algebraic method (AbuQassem, 2010) for forward
kinematics and triangulation algorithm (Muller-
Cajar and Mukundan, 2007) for inverse kinematics.
We used F3 and F4 channels data for extracting
movement patterns. Signal pre-processing was done
using band-pass filtering from 6 to 30 Hz to obtain
Mu and beta rhythms.
To extract features, we used power spectral
density and cross-correlation analysis from
preprocessed signal data (Hosni et al., 2007).
Movement of the arm to left or right directions were
categorized as two classes. We used classification
(Vijayan et al., 2013) for translating imagery to
robotic articulation (Figure 2). In our study,
prosthetic arm had a localization variability of ±5
cm variability. Mapping and localization of end-
effector positions were corrected using error
minimization algorithms (work in progress).
Previous studies on pattern classification of
signals related to motor tasks used to train prosthetic
devices like wheelchairs have shown a high level of
accuracy (~80%) (Tanaka et al., 2005).The
scalability of similar techniques on high-end devices
like the DLR JUSTIN arm or DARPA ARM may
need detailed studies and outreach modifications.
Figure 2: Accuracy of robotic arm dataset for different
classification algorithms.
3 CONCLUSIONS
The paper aims to highlight the current progress in a
humanitarian challenge of redesigning a low
economic cost neuro-prosthetic arm that could be
controlled using EEG-based signal re-classification.
Usual techniques include applications of machine
learning and adaptive feature extraction methods to
process EEG real-time and using a learned system to
control the arm using kinematic techniques. Such
methods have their performance and training issues.
While data reliability and over-learning can cause
issues, the device variability requires prediction-
correction or other iterative approaches. The issues
may be solved using feedback via sensors but that
would add considerable financial and computational
overload to the design and implementation. To keep
the low-cost target, internal representation models
may be needed to help the prediction-correction
process. Our case-study using a home developed
(<$50 ARM) suggests the common issues seen with
any low-cost project while allowing us to use the
platform for testing the potential solutions. The
suggestions are as follows: Firstly, while EEG based
tests are reliable for some event-related tasks, a
learned feature extraction approach may help reduce
the noise in the dataset. Secondly, classification has
to have simple mechanisms such as testing using
SVM or ANNs. Thirdly, better approximations are
to be favored over precision. Iterative processing of
kinematics movements may substitute the sensory-
motor feedback model. Spiking neural network
based internal representation models may help
overcome some of the internal representation issues.
While traditional approaches have their own
performance and implementation issues, a novel
non-traditional approach seems inevitable.
As a final word, we indicate that control
mechanisms using BCI may change the design of
kinematics for robotic articulators. It may, therefore,
need a dual-styled approach of classification and
interpretation from EEG to the arm and an internal
representation model to predict the kinematics of the
arm based on the feature-triggered categorization of
movement dynamics.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work derives direction and ideas from the
chancellor of Amrita University, Sri Mata
Amritanandamayi Devi. This work is partially
supported by grants SR/CSI/49/2010 and
SR/CSI/60/2011 and Indo-Italy POC 2012-13 from
DST, BT/PR5142/MED/30/764/2012 from DBT and
by Sakshat Virtual Labs, NMEICT, MHRD,
Government of India. Authors would like to thank
Hareesh Singanamala and Dhanush Kumar for their
help with the robotic arm.
NeuralControlusingEEGasaBCITechniqueforLowCostProstheticArms
273

REFERENCES
AbuQassem, M.R., 2010. Simulation and Interfacing of 5
DOF Educational Robot Arm. Islamic University of
Gaza.
Albus, J.S., 1975. A New Approach to Manipulator
Control: The Cerebellar Model Articulation
Controller(CMAC). J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control.
Anderson, C., 1995. EEG signal classification with
different signal representations. In: Neural Networks
for Signal Processing. IEEE, Cambridge, MA, pp.
475–483.
Bi, L., Fan, X.-A., Liu, Y., 2013. EEG-Based Brain-
Controlled Mobile Robots: A Survey. IEEE Trans.
Human-Machine Syst. 43, 161–176.
Birbaumer, N., 2006. Breaking the silence: brain-computer
interfaces (BCI) for communication and motor control.
Psychophysiology 43, 517–32.
Birbaumer, N., Hinterberger, T., Kübler, A., Neumann, N.,
2003. The thought-translation device (TTD):
neurobehavioral mechanisms and clinical outcome.
IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 11, 120–3.
Choi, K., 2012. Control of a vehicle with EEG signals in
real-time and system evaluation. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol.
112, 755–66.
Craig, D.A., Nguyen, H.T., 2007. Adaptive EEG thought
pattern classifier for advanced wheelchair control. In:
Annual International Conference of the IEEE
Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. pp.
2544–7.
D’Apuzzo, M., Liccardo, A., Bifulco, P., Polisiero, M.,
2012. Metrological issues concerning low cost EMG-
controlled prosthetic hand. In: 2012 IEEE
International Instrumentation and Measurement
Technology Conference Proceedings. IEEE, pp. 1481–
1486.
Dasgupta, S., Fanton, M., Pham, J., Willard, M.,
Nezamfar, H., Shafai, B., Erdogmus, D., 2010. Brain
controlled robotic platform using steady state visual
evoked potentials acquired by EEG. In: 2010
Conference Record of the Forty Fourth Asilomar
Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers. IEEE,
pp. 1371–1374.
Donchin, E., Spencer, K.M., Wijesinghe, R., 2000. The
mental prosthesis: assessing the speed of a P300-based
brain-computer interface. IEEE Trans. Rehabil. Eng.
8, 174–179.
Farwell, L. a, Donchin, E., 1988. Talking off the top of
your head: toward a mental prosthesis utilizing event-
related brain potentials. Electroencephalogr. Clin.
Neurophysiol. 70, 510–23.
Friman, O., Volosyak, I., Gräser, A., 2007. Multiple
channel detection of steady-state visual evoked
potentials for brain-computer interfaces. IEEE Trans.
Biomed. Eng. 54, 742–50.
Furber, S.B., Galluppi, F., Temple, S., Plana, L.A., 2014.
The SpiNNaker Project. Proc. IEEE 102, 652–665.
Gysels, E., Renevey, P., Celka, P., 2005. SVM-based
recursive feature elimination to compare phase
synchronization computed from broadband and
narrowband EEG signals in Brain–Computer
Interfaces. Signal Processing 85, 2178–2189.
Hosni, S.M., Gadallah, M.E., Bahgat, S.F., AbdelWahab,
M.S., 2007. Classification of EEG signals using
different feature extraction techniques for mental-task
BCI. 2007 Int. Conf. Comput. Eng. Syst. 220–226.
Iqbal, J., Islam, R., Khan, H., 2012. Modeling and
Analysis of a 6 DOF Robotic Arm Manipulator. Can.
J. Electr. Electron. Eng.
Joshi, P., Maass, W., 2005. Movement generation with
circuits of spiking neurons. Neural Comput. 17, 1715–
1738.
Kalanovic, V.D., Popoviic, D., Skaug, N.T., 2000.
Feedback Error Learning Neural Network for Trans-
femoral Prosthesis. IEEE Trans. Rehabil. Eng. 8, 71–
80.
Kasabov, N., Dhoble, K., Nuntalid, N., Indiveri, G., 2013.
Dynamic evolving spiking neural networks for on-line
spatio- and spectro-temporal pattern recognition.
Neural Netw. 41, 188–201.
Kay, J., 2005. Introduction to Homogeneous
Transformations & Robot Kinematics.
Kucuk, S., Bingul, Z., 2006. Robot Kinematics: Forward
and Inverse Kinematics. In: Industrial-Robotics-
Theory-Modelling-Control. pp. 117–148.
Lachaux, J.P., Rodriguez, E., Martinerie, J., Varela, F.J.,
1999. Measuring phase synchrony in brain signals.
Hum. Brain Mapp. 8, 194–208.
Leeb, R., Friedman, D., Müller-Putz, G.R., Scherer, R.,
Slater, M., Pfurtscheller, G., 2007. Self-paced
(asynchronous) BCI control of a wheelchair in virtual
environments: a case study with a tetraplegic. Comput.
Intell. Neurosci. 79642.
Leuthardt, E.C., Schalk, G., Wolpaw, J.R., Ojemann, J.G.,
Moran, D.W., 2004. A brain-computer interface using
electrocorticographic signals in humans. J. Neural
Eng. 1, 63–71.
McFarland, D.J., Miner, L. a, Vaughan, T.M., Wolpaw,
J.R., 2000. Mu and beta rhythm topographies during
motor imagery and actual movements. Brain Topogr.
12, 177–86.
Md Norani, N.A., Mansor, W., Khuan, L.Y., 2010. A
review of signal processing in brain computer
interface system. In: 2010 IEEE EMBS Conference on
Biomedical Engineering and Sciences (IECBES).
IEEE, pp. 443–449.
Megahed, S.M., 2013. Mechanical Design & Production
Department.
Middendorf, M., McMillan, G., Calhoun, G., Jones, K.S.,
2000. Brain-computer interfaces based on the steady-
state visual-evoked response. IEEE Trans. Rehabil.
Eng. 8, 211–4.
Millán, J., Franzé, M., Mouriño, J., Cincotti, F., Babiloni,
F., 2002. Relevant EEG features for the classification
of spontaneous motor-related tasks. Biol. Cybern. 86,
89–95.
Mitra, A.K., 2012. Joint Motion-based Homogeneous
Matrix Method for Forward Kinematic Analysis of
Serial Mechanisms. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Adv. Eng.
2, 111–122.
NCTA2014-InternationalConferenceonNeuralComputationTheoryandApplications
274

Mitrovic, D., Nagashima, S., Klanke, S., Matsubara, T.,
Vijayakumar, S., 2010. Optimal Feedback Control for
Anthropomorphic Manipulators. In: Int. Conf. Robot.
Autom. 2010). Alaska, USA.
Muller, K.-R., Blankertz, B., 2006. Toward noninvasive
brain-computer interfaces. IEEE Signal Process. Mag.
23, 128–126.
Muller-Cajar, R., Mukundan, R., 2007. Triangulation : A
new algorithm for Inverse Kinematics. In:
Proceedings of Image and Vision Computing New
Zealand. pp. 181–186.
Nicolas-Alonso, L.F., Gomez-Gil, J., 2012. Brain
computer interfaces, a review. Sensors (Basel). 12,
1211–79.
Owen, A.M., Coleman, M.R., 2008. Using neuroimaging
to detect awareness in disorders of consciousness.
Funct. Neurol. 23, 189–94.
Pfurtscheller, G., Allison, B.Z., Brunner, C., Bauernfeind,
G., Solis-Escalante, T., Scherer, R., Zander, T.O.,
Mueller-Putz, G., Neuper, C., Birbaumer, N., 2010.
The hybrid BCI. Front. Neurosci. 4, 30.
Pfurtscheller, G., Brunner, C., Schlögl, A., Lopes da Silva,
F.H., 2006. Mu rhythm (de)synchronization and EEG
single-trial classification of different motor imagery
tasks. Neuroimage 31, 153–9.
Pfurtscheller, G., Neuper, C., Müller, G.R., Obermaier, B.,
Krausz, G., Schlögl, A., Scherer, R., Graimann, B.,
Keinrath, C., Skliris, D., Wörtz, M., Supp, G.,
Schrank, C., 2003. Graz-BCI: state of the art and
clinical applications. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst.
Rehabil. Eng. 11, 177–80.
Pires, G., Castelo-Branco, M., Nunes, U., 2008. Visual
P300-based BCI to steer a wheelchair: a Bayesian
approach. In: Conference Proceedings : ... Annual
International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in
Medicine and Biology Society. IEEE Engineering in
Medicine and Biology Society. Conference. pp. 658–
61.
Rawlik, K., Toussaint, M., S, V., 2012. On Stochastic
Optimal Control and Reinforcement Learning by
Approximate Inference. In: Robotics: Science and
Systems Conference.
Repovs, G., 2010. Dealing with Noise in EEG Recording
and data analysis. Inform. Medica Slov. 15, 18–25.
Saal, H.P., Vijayakumar, S., 2010. Active estimation of
object dynamics parameters with tactile sensors. In:
2010 IEEE/RSJ Int. Conf. Intell. Robot. Syst. IEEE,
pp. 916–921.
Sahu, S., Biswal, B.B., Subudhi, B., 2008. Computational
Intelligence , Control and Automation A Novel
Method for Representing Robot Kinematics using
Quaternion Theory A Novel Method for Representing
Robot Kinematics using Quaternion Theory. IEEE
Spons. Conf. Comput. Intell. Control Comput. Vis.
Robot. Autom.
Schlögl, A., Slater, M., Pfurtscheller, G., 2002. Presence
research and EEG Properties of EEG recordings.
Shepherd, G.M., Mirsky, J.S., Healy, M.D., Singer, M.S.,
Skoufos, E., Hines, M.S., Nadkarni, P.M., Miller, P.L.,
1998. The Human Brain Project: neuroinformatics
tools for integrating, searching and modeling
multidisciplinary neuroscience data. Trends Neurosci.
21, 460–468.
Srinivasan, R., 1999. Methods to Improve the Spatial
Resolution of EEG. Int. J. Bioelectromagn. 1, 102–
111.
Tanaka, K., Matsunaga, K., Wang, H.O., 2005.
Electroencephalogram-Based Control of an Electric
Wheelchair. IEEE Trans. Robot. 21, 762–766.
Vespa, P.M., Nenov, V., Nuwer, M.R., 1999. Continuous
EEG monitoring in the intensive care unit: early
findings and clinical efficacy. J. Clin. Neurophysiol.
16, 1–13.
Vijayan, A., Nutakki, C., Medini, C., Singanamala, H.,
Nair, B., 2013. Classifying Movement Articulation for
Robotic Arms via Machine Learning. J. Intell.
Comput.
Westling, G., Johansson, R.S., 1984. Factors influencing
the force control during precision grip. Exp. brain Res.
53, 277–84.
Wolpaw, J.R., Birbaumer, N., McFarland, D.J.,
Pfurtscheller, G., Vaughan, T.M., 2002. Brain-
computer interfaces for communication and control.
Clin. Neurophysiol. 113, 767–91.
Wolpert, D.M., Flanagan, J.R., 2010. Q&A: Robotics as a
tool to understand the brain. BMC Biol. 8, 92.
Yuanqing Li, Chuanchu Wang, Haihong Zhang, Cuntai
Guan, 2008. An EEG-based BCI system for 2D cursor
control. In: 2008 IEEE International Joint Conference
on Neural Networks (IEEE World Congress on
Computational Intelligence). IEEE, pp. 2214–2219.
NeuralControlusingEEGasaBCITechniqueforLowCostProstheticArms
275
