
Fuzzy User Profile Modeling for Information Retrieval
Rim Fakhfakh, Anis Ben Ammar and Chokri Ben Amar
REGIM: REsearch Groups on Intelligent Machines,University of Sfax, ENIS, BP W, 3038 Sfax, Tunisia
Keywords: Fuzzy Logic, Personalized Search, Social Network.
Abstract: Given the continued growth in the number of documents available in the social Web, it becomes
increasingly difficult for a user to find relevant resources satisfying his information need. Personalization
seems to be an efficient manner to improve the retrieval engine effectiveness. In this paper we introduce a
personalized image retrieval system based on user profile modeling depending on user’s context. The
context includes user comments, rates, tags and preferences extracted from social network. We adopt a
fuzzy logic-based user profile modeling due to its flexibility in decision making since user preference are
always imprecise. The user has to specify his initial need description by rating concepts and contexts he is
interested in. Concepts and contexts are weighted by the user by associating a score and these scores will
infer in our fuzzy model to predict the preference degree related to each concept for such context and return
the preference degree. Relying on the score affected for each concept and context we deduce its importance
to apply then the appropriate fuzzy rule. As for as the experiments, the advanced user profile modeling with
fuzzy logic shows more flexibility in the interpretation of the query.
1 INTRODUCTION
Internet growth has trained various types of social
networks with big scale, which are now recognized
as an important means for the information diffusion.
With this social dimension that enriches the content
of web resources, user’s information needs have
been emerged for new contexts. But the classic
information retrieval does not seem to be suitable to
this dimension, involving users and their interactions
within social networks. The emergences of Social
Information Retrieval which is a recent approach
that take into account the information extracted from
social networks and adapt models and algorithms of
classical information retrieval to exploit the
convenient social information in the retrieval
process according to the conventional measures of
Recall and Precision.
Social information retrieval has the objective of
improving the information retrieval process by
exploiting social information and customizing the
user search according to its social context. The main
issues of this theme are to identify, exploit and
combine social information from social networks to
improve and possibly customize the information
retrieval. There are two approaches in the state of
the art related to social information retrieval. The
first category consists in exploiting social
information about the content like the annotations
(Gemmell et al., 2011) (Gemmell et al., 2010). The
second category combines this content with social
relations between users of social networks and then
the orientation towards personalized information
retrieval in which the relevant documents for a given
query may be different from one user to another
(Sharma et al., 2012)( Shen et al., 2005).
Therefore, we focus on the issues of the impact
of social information on information retrieval whose
purpose is to improve the classical information
results. Social information including social
relationships between users, annotations, clicks,
profiles etc. can be exploited in the process of
information retrieval in the step of the query analysis
and interpretation, the matching and finally in the
ranking of the results list.
In a personalized information retrieval system,
the user is the core of the entire system as the results
depend on his profile and his preferences hence the
importance of modeling the user profile which must
follow the changing in preferences and user interest
over the time. The user modeling can have different
representation, namely the representation of the user
profile can be a vector where the profile is composed
of one or more vectors defined in an indexing terms
431
Fakhfakh R., Ben Ammar A. and Ben Amar C..
Fuzzy User Profile Modeling for Information Retrieval.
DOI: 10.5220/0005156304310436
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval (KDIR-2014), pages 431-436
ISBN: 978-989-758-048-2
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

space , hierarchical where the characteristics of a
user are organized in a hierarchical structure of
concepts representing the fields of interest, or
multidimensional where the profile is represented by
a structured model of predefined dimensions such as
personal data, area of interest and preferences .
The static manipulation of user profile can affect
the decision making of the results in a wrong way. In
fact, this representation requires the processing of
data in a fixed manner ie a user can be endowed with
a precise theme or not while this logic does not
satisfy the human nature of the individual who can
change his mind across the time and context. In this
context, fuzzy logic provides a theoretical
framework for the representation and the processing
of these data with their imperfections. Its purpose is
to make the framework of representation and
knowledge processing flexible which is inspired
from human mental processes and therefore the
tendency for fuzzy modelling of the user profile
used for the improvement of personalized retrieval
systems, and systems recommendations.
2 RELATED WORK
User preferences discovery research aim to enhance
the effectiveness of personalized information
systems. User preferences are learnt by following
the user interaction with retrieval engine. This can
be reached either by asking the user his behaviors
directly in an explicit elicitation via filling out forms
or by observing their behaviors in implicit way by
extracting automatically his interaction with his
browser of from the social networks.
Discovering user preferences basing on implicit
elicitation requires less user involvement and this is
more efficient in retrieval process. Implicit
information can be extracted from social networks
and aims to find the importance of a user in the
social network and thus the importance of a
document in the collection database. The importance
of a user in social networks can be measured thanks
to social network analysis methods. In this context
researchers think on modeling information retrieval
system which can be enhanced by the document
relevance ranking based on centrality measures of
social networks. There are three elementary steps in
this model which are: social Network extraction,
social network analysis and document relevance
ranking (Kirchhoff, 2010). Enhancing retrieval
effectiveness using social networks is based on
finding structural information from the
documentation collection about social relationships
and exploiting it in retrieval process like
recommender systems, information filtering,
information retrieval, user modeling and
personalized agents (Pitsilis et al., 2009).
The richness of information that can be extracted
from social network has a grand impact for
enhancing the quality and the effectiveness of
multimedia information retrieval solutions. The new
trend of multimedia information retrieval is to
converge between multimedia content analysis and
social media which have a complementary role and
each one can affect the other. In (Hanjalic, 2012)
researchers show that social media complement
multimedia content analysis by expanding the
opportunities of the content access or also in
confirming or correcting the low-confidence of
multimedia content analysis techniques. This can be
done thanks to information extracted from social
networks through tags, ratings and comments
provided by the user. In other hand, multimedia
content analysis can be used to improve the
effectiveness and efficiency of the tagging process.
In fact, techniques of multimedia content analysis
can identify the content items and this latter can be
refined and enriched by the interaction of the user on
online social platforms through tagging, rating and
recommending of the items. Due to the complexity
of Information extracted from social networks, this
last can be structured in hypergraph structure. (Yang
et al., 2013) propose an hypergraph spectral hashing
for image retrieval with heterogeneous social
contexts. This hypergraph model the various
relationships among images and other contexts in
social media (tags, locations, users, communities).
3 FUZZY USER PROFILE
MODELING
3.1 Fuzzy Logic in Information
Retrieval
The uses of fuzzy logic in the field of information
retrieval have emerged due to its nature allowing the
bridge of the gap between the soft logic of human-
understandable and hard logic of machine readable.
Indeed, fuzzy logic is used in ontology which define
a new theoretical paradigm known as Fuzzy
Ontology that aim to improve the semantic
documents retrieval by handling the trade off
between the fixed definition of a term in the
ontology structure, and the actual meaning desired
by individuals. In (Silvia and Elie, 2007), Fuzzy
KDIR2014-InternationalConferenceonKnowledgeDiscoveryandInformationRetrieval
432

logic is used also as model of information retrieval
instead of the probabilistic model due to its
perfection shown by obtaining a comprehensive
treatment of imprecision and uncertainty pervading
the information retrieval process (Nowacka et al.,
2008) (Oussalah and Eltigani, 2005). With the
emergence of social networks and user profiling, in
the field of information retrieval the fuzzy logic is
used in the interpretation of the user profile like
(Ghaderi et al., 2012) who propose an approach that
aim to predict users' preferences and use it for movie
recommendation basing on the theory of the
representation of knowledge preferences discovery
by identifying types of subjectivity, vagueness and
uncertainty existing in the user preferences due to
developing a fuzzy model that provides a formalism
to quantify how much a user likes, dislikes or be
indifferent to an element given and its characteristics
based on the fuzzy set theory, it enriches the results
of discovered preferences including positive fuzzy
categories, negative, neutral and unknown
preferences.
The uses of fuzzy logic in information retrieval
have proven a great efficiency for various research
fields. In this context, we aim to apply fuzzy logic
for user profile modeling which is useful in the
process of information retrieval and go with the
characteristic of user preferences which are often
ambiguous and imprecise.
3.2 Fuzzy Logic for Profiling in
Information Retrieval
Our purpose is to reach a fuzzy user profile
modeling extracted from social network and operate
this profile for improving the information retrieval
process. Alike each information retrieval system, an
image retrieval system comprises four essential
modules: an image processor (Feki et al., 2013)
(Ksibi et al., 2013), a query processor (Fakhfakh et
al, 2012) (Fakhfakh et al 2013), a search and
matching function and a ranking capability (Feki et
al., 2012). As shown in Figure1, in an offline way
we construct an hypergraph that manage all
information extracted from the social network that
relate users, images and concepts. Information
related to each user are stocked in the hypergraph
structure and then used for query analysis step to
inform us about the user interest. The user profile is
used also in ranking process to sort the more
relevant images related to each user in first order.
In information retrieval, user profile is defined as a
collection of data about the user of the system,
which the system collects and maintains in order to
Figure 1: Fuzzy logic for information retrieval.
improve the quality of information access. These
data are divided in two major parts which are:
personal information like age, gender, location, etc
… and his interest known among his interaction on
the social network through commenting, sharing,
rating and other activities that can be done on the
resources available in the network. In addition to
user profile, there is another factor that can influence
the effectiveness of retrieval process which is the
context of research. We mean by context the
spatiotemporal data like location, time and devices
(laptop, mobile…) used for information search that
handle the user needs. Table1 shows how the search
context can impact the search result.
Table 1: Context influence on query interpretation.
Query Context User need suggestions
Food
Device: laptop
Location: at home
Recipes
Device: laptop
Location: at work
Online order for meal
Device: mobile
Location: in the car
Address of the nearest
restaurant, menu, prices …
In our case, the user interacts with the image
retrieval system in two ways: explicitly and
implicitly as shown in figure 2.
Explicit information based on rating technique:
the user gives his feedback after the evaluation
of system’s results and mention if he like or
dislike the results by giving a degree ranging
from 0 to 5.
FuzzyUserProfileModelingforInformationRetrieval
433
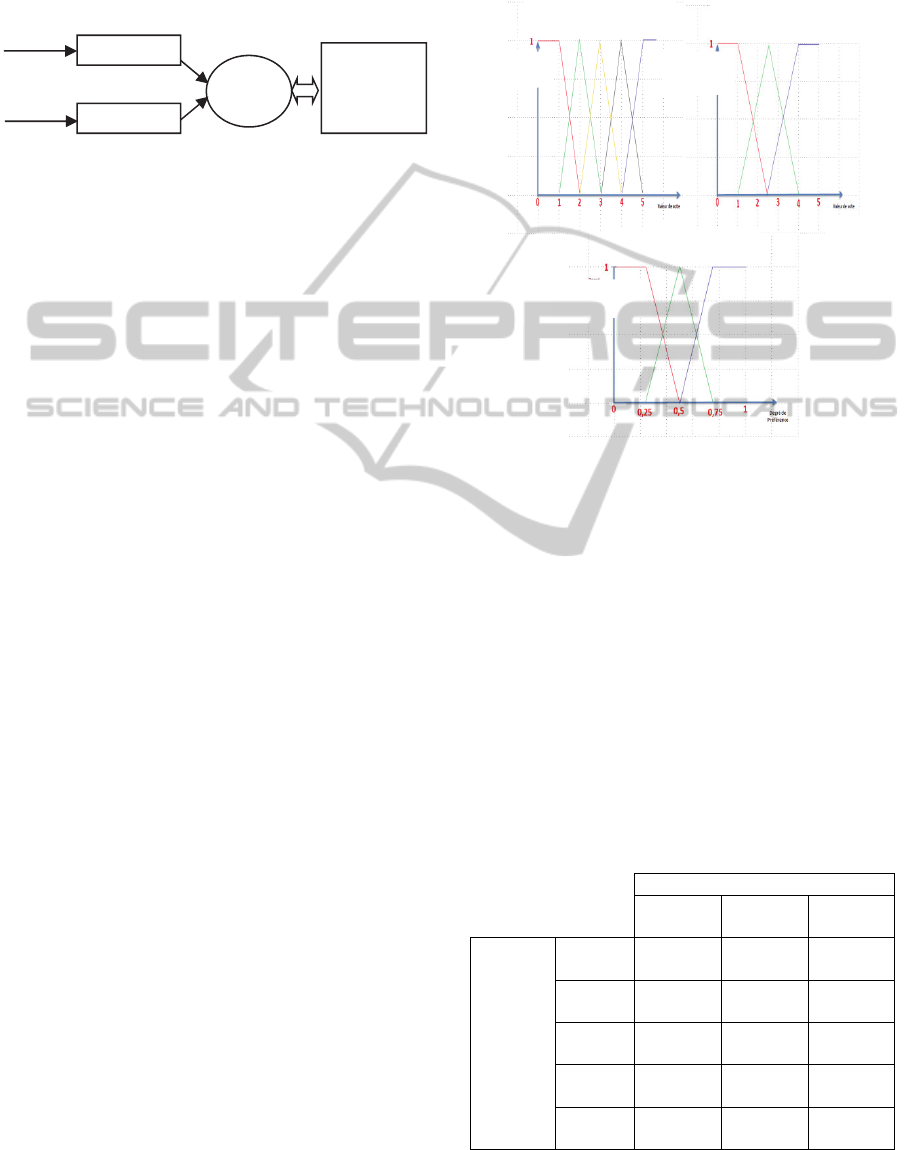
Implicit information extracted from the social
network. These data can be about personal
information (age, gender, occupation...) or about
user interest known through user interaction by
tagging, commenting or rating.
Figure 2: Data for user profile constriction.
With video search engine Youtube, the opinion
of a user about a video can only be: I like or I dislike
this video. This representation does not reflect the
reality of user preferences. There certainly
intermediate states between these two expressions.
Our contribution aims to give more flexibility in
the expression of user preference by choosing one of
the following classes of choice depending on the
rating value : Poor, Fair, Average, Good and
Excellent.
We adopt a multidimensional representation of
user interests and fuzzy logic approach to compute
the satisfaction degrees of the user rather than the
usual evaluation known as like or dislike (1 or
0) that represent the boolean logic. In our fuzzy user
model, we have two inputs and one output. As
inputs the user will be asked to give a value to
concepts and contexts he is interested in. The
relevant concepts and contexts will be rated as 4 or 5
value for example, against the disliked ones have a
score of 0 or 1.
Let’s denote:
n the value associated to concept’s rate where
∈ 05. The interpretation of this value
follows the next rules:Poor : if
∈
01
, Fair
: if
∈12, Average : if ∈23, Good :
if
∈34 and Excellent : if ∈45
m the value associated to the context’s rate
where
∈ 05. The interpretation of this
value is as follows: Not Relevant: if
∈
01
, average: if ∈14, Relevant: if
∈45.
The output of our user’ fuzzy logic model is the
preference degreep ∈ 01 that merge between the
concepts and contexts rated. The interpretation of
the preference degree can be as follows Not
Relevant: if p ∈ 00,25, Neutral: if p ∈
0,250,75, Relevant: if p ∈0,751
Figure 4 displays the representation of inputs and
the output of our fuzzy user preferences model.
Figure 3: Fuzzy representation of user preferences.
There are 15 fuzzy rules that identify our fuzzy
logic user preferences model due to the 15 possible
combinations that link the different value of inputs
representing concept rate and context rate.
To solve decision problems of the output we are
based on fuzzy inference system which is a way of
mapping an input space to an output space using
fuzzy logic. We try to formalize the reasoning
process of user preferences interpretation by means
of fuzzy logic. The fuzzy rule is presented as:
“IF (Concept rate is x ) AND (Context rate is y)
THEN (preference degree is z)”.
The different combination of x,y and z are
shown in Table2.
Table 2: Fuzzy rules of user preferences.
Context Rate
Not
Relevant
Average Relevant
Concept
Rate
Poor
Not
Relevant
Not
Relevant
Not
Relevant
Fair
Not
Relevant
Neutral Neutral
Average
Not
Relevant
Relevant Relevant
Good
Not
Relevant
Relevant Relevant
Excellent
Not
Relevant
Relevant Relevant
Rating
Social
Network
User
Profi
le
Personalized
image
retrieval
System
Ex
p
licit data
Im
p
licit data
Context
rate
Membership
degree
Not Relevant Neutral Relevant
Not Relevant Average Relevant
Concept
rate
Poor Fair Average Good Excellent
KDIR2014-InternationalConferenceonKnowledgeDiscoveryandInformationRetrieval
434
The different combination of x,y and z are shown in
Table2.
We used Mamdani’s method as inference method
to predict the preference degree. The conjunction
AND and the implication THEN are presented by
the operator “MIN. MAX is used as the fuzzy
aggregation operator. The defuzzification method
used is the Middle of Maximum.
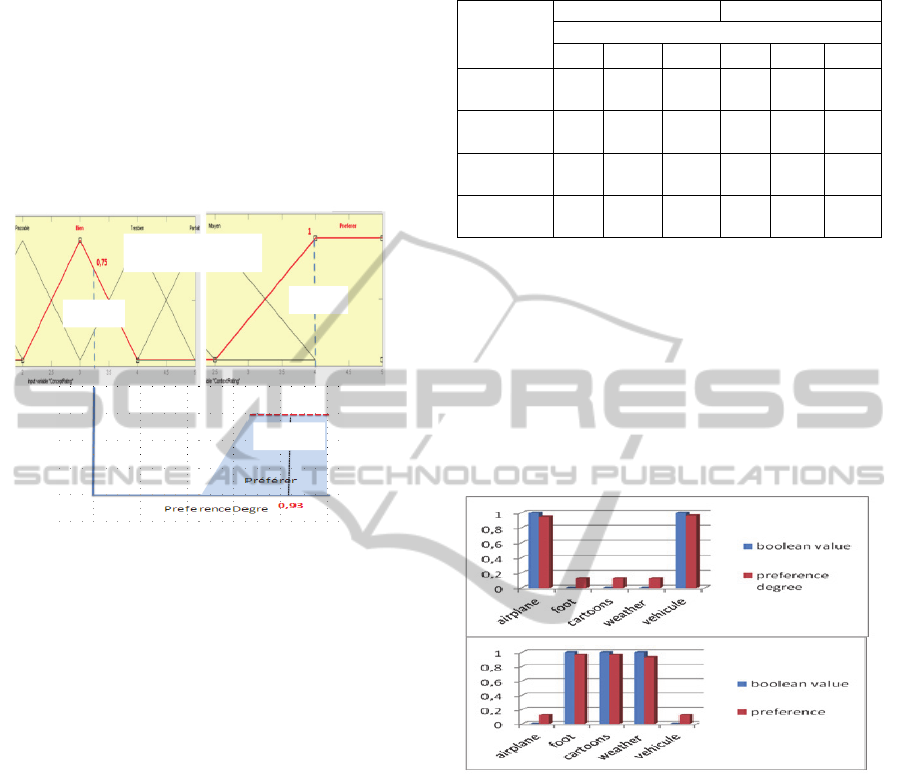
Figure 5 shows an example of defuzzification
where n=3.25 and m=1.
Figure 4: Preference degree prediction ( n=3.25, m=1).
4 EXPERIMENTS
Concepts used for user profile construction are 130
concepts extracted from the ontology LSCOM (
Large Scale Concept Ontology for Multimedia) like
actor, adult, airplane, animal, sports, plant ....
Based on the selected concepts we generate
randomly our queries. Example of queries: Adult
person, Olympic athlete, gift flower, ...
As for as the evaluation we are based on the
measurement P@5 and P@10 witch express the user
satisfaction related to the top 5 or 10 relevant
documents and MAP (Mean Average Precision) that
expresses the model ability in selecting relevant
documents in response to all tested queries.
We can observe from these results shown in
Table 3 that with the integration of fuzzy model user
preferences realize a significant improvement in
performance compared to standard Boolean model
(
Kalervo et al.,2002) especially in values clarification
P@5 and P@10 and consequently an improvement
in MAP.
The fuzzy user preference modeling has earned us
great flexibility with regard to the degree of
preference of a particular concept. For example: In
the context “at home”, the Boolean representation of
Table 3: result comparison for the context “At home”.
Query
Boolean model Fuzzy model
Precision
@5 @10 MAP @5 @10 MAP
Olympic
athlete
0.71 1 0,85 0,83 1 0,91
French bike
tour
0,38 0,769 0,57 0,45 0,9 0,67
Bird
singing
0,83 1 0,91 0,83 1 0,91
University
professor
0,5 1 0,75 1 1 1
user preferences will cause the elimination of
concepts preference values equal to 0 and will limit
choices only for concepts having rate 1. While in the
reality, we have the possibility of gradual and
flexible expression, for example by giving a
preference value equal to 0.7 which is allowed by
the fuzzy user preferences modeling is closer to the
user’s choices and this representation can eliminate
the rigid decision of the system. This is more
displayed in figure 6.
(a) standard boolean model (b) fuzzy model.
Figure 5: Boolean vs fuzzy modelling.
In our case, the context represents the
spatiotemporal representation of the user and the
equipment used for the research that can has an
impact on the result of the image retrieval system
depending on the characteristics of the used
hardware like the size of the screen, the ability of
memory, processor speed etc… Figure 7 shows the
impact of the context on the preferences decision
using the fuzzy interpretation. This representation
shows that the shape of the fuzzy preferences curve
(in green) is depending on the changes of context
rating (in Red). For example, when the concept has a
rate equal to 4.5 / 5 with a linguistic value: perfect),
the fuzzy preferences will 0.5 / 1 (Middle linguistic
value). This is due to the context score: less than 1.
n=
3
.
5
m=
1
p
=
0
,
93
(b) Fuzzy Model
Votingrate
Concept/context
(a) Boolean Model
FuzzyUserProfileModelingforInformationRetrieval
435
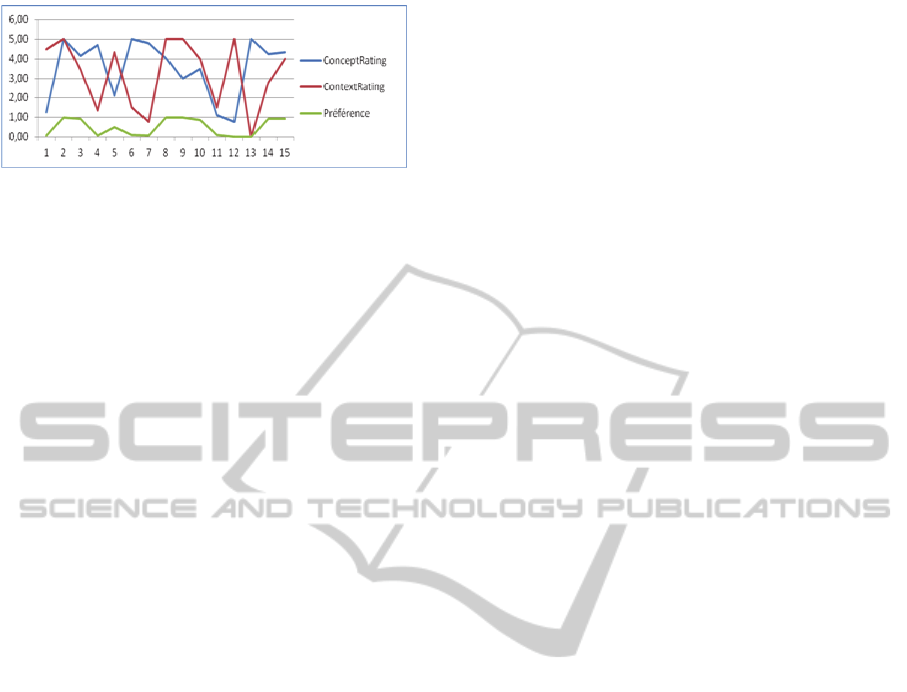
Figure 6: Context impact on user preferences decision.
5 CONCLUSION
In this paper we present our personalized image
retrieval system based on user profile modeling
depending on user’s context. We adopt a fuzzy
logic-based user profile modeling due to its
flexibility in decision making. This model work with
a list of concept and context where the user is asked
to rate them according to his interest and these rates
help in predicting the preference degree related to
each concept for such context. As for as the
experiments, the advanced user profile modeling
with fuzzy logic shows more flexibility in the
interpretation of the query compared with the
standard boolean model. For future work, we aim to
make the context detection automatic without user
intervention and the same thing for the concept
rating where the rate value will be deduced from the
user profile extracted from social network.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial
support of this work by grants from General
Direction of Scientific Research (DGRST), Tunisia,
under the ARUB program.
REFERENCES
Hanjalic.A, New grand challenge for multimedia
information retrieval:bridging the utility gap,
International Journal of Multimedia Information
Retrieval, 2012
Ksibi.A Feki.G, Ben Ammar.A, Ben Amar.C Effective
Diversification for Ambiguous Queries in Social
Image Retrieval. CAIP (2) 2013: 571-578.
Gemmell,J Schimoler,T. Mobasher,B. Burke,R. 2011.
Tag-Based Resource Recommendation in Social
Annotation Applications UMAP 2011, LNCS 6787,
pp. 111–122, 2011.
Gemmell, J., Schimoler, T., Mobasher, B., Burke, R.2010
Hybrid tag recommendation for social annotation
systems. In: 19th ACM International Conference on
Information and Knowledge Management, Toronto,
Canada (2010)
Pitsilis.G , Knapskog. Svein J, Social Trust as a solution
on address sparsity-inherent problems of
Recommender systems, ACM RecSys 2009,
Workshop on Recommender Systems & The Social
Web, New York, USA. 2009
Feki.G, Ksibi.A, Ben Ammar.A, Ben Amar.C. Improving
image search effectiveness by integrating contextual
information. CBMI 2013: 149-154.
Feki.G, Ksibi.A, Ben Ammar.A, Ben Amar.C. REGIMvid
at ImageCLEF2012: Improving Diversity in Personal
Photo Ranking Using Fuzzy Logic. CLEF 2012.
Kalervo Järvelin and Jaana Kekäläinen. 2002. Cumulated
gain-based evaluation of IR techniques. ACM Trans.
Inf. Syst. 20, 4 (October 2002), p422-446.
Nowacka.K, Zadrozny.S Kacprzyk.J, An experimental
comparison of various aggregation operators in a
fuzzy information retrieval model, In proceeding of:
Fuzzy Information Processing Society, 2008
Kirchhoff.L, 2010, Thesis: Applying Social Network
Analysis to Information Retrieval on the World Wide
Web: A Case Study of Academic Publication Space
,University of St. Gallen , Germany, 2010
Oussalah.M and Eltigani.A, Personalized Information
Retrieval system in the Framework of Fuzzy Logic,
2005
Ghaderi. M Ali, Yazdani.N, Moshiri.B, A Social Network-
based Meta Search Engine, Information Retrieval,
2010 , p744-749
Fakhfakh.R, Feki.G, Ksibi.A, Ben Ammar.A, Ben
Amar.C, REGIMvid at ImageCLEF2012: Concept-
based Query Refinement and Relevance-based
Ranking Enhancement for Image Retrieval, CLEF
(Online Working Notes/ Labs/ Workshop), 2012.
Fakhfakh.R, Ksibi.A, Ben Ammar.A, Ben Amar.C,
Enhancing query interpretation by combining textual
and visual analyses, International Conference on
Advanced Logistics and Transport (ICALT), 2013,
p170-175
Sharma,N. Sharma,M. Gupta,O. 2012. Search Engine
Personalization Using Concept Based User Profiles.
International Journal of Scientific Research
Engineering &Technology (IJSRET) Volume 1 Issue4
pp 084-087 July 2012
Shen X., Tan B., and Zhai C.2005. Implicit user modeling
for personalized search. In Proc. Int. Conf. on
Information and Knowledge Management, 2005, pp.
824–831.
Silvia.C and Elie.S , A Fuzzy Ontology-Approach to
improve Semantic Information Retrieval, Workshop
on Uncertainty Reasoning for the Semantic Web
Busan, Korea, November 12, 2007.
Yang.L , Jian.S, Jun.X, Fei.W, Yueting.Z, Hypergraph
Spectral Hashing for image retrieval with
heterogeneous social contexts, Neurocomputing 119
(2013) 49–58, 2013
KDIR2014-InternationalConferenceonKnowledgeDiscoveryandInformationRetrieval
436
