
The Comprehensive Modelling of BPMN Business Processes and
Business Rules using SBVR Profile
Egle Mickeviciute and Rimantas Butleris
Department of Information Systems, Kaunas University of Technology, Studentu g. 50, Kaunas, Lithuania
Centre of Information System Design Technologies, Kaunas University of Technology, Studentu g. 50, Kaunas, Lithuania
1 STAGE OF THE RESEARCH
In order to have the comprehensive business process
models we have to consider them together with
business rules, i.e., we must apply two different
modelling approaches that reflect two
complementary aspects of the problem domain. The
goal of this research is to embody the idea for the
comprehensive integration of BPMN processes with
SBVR business vocabulary and business rules in the
modelling environment of CASE tools, and keeping
the links among elements of these models. In order
to achieve the goal, the process was established how
to use the SBVR business vocabulary while creating
graphical BPMN process models, and the
transformation rules were defined that allow to
transform business process model to business
vocabulary and business rules representing BPMN
business process. Currently, the efforts are
concentrated on implementing transformations in the
QVT transformation language.
2 RESEARCH PROBLEM
Information system (IS) projects usually start from
defining business vocabulary and modelling
business processes that serve for the development of
further, more detailed IS models till their
implementation. The business vocabulary and
business processes help to reach the shared
understanding between domain experts and software
developers. However, CASE tools still lack means
for modelling business vocabulary, which often is
not properly documented.
Nowadays, modelling of
business processes is hard to imagine without the
business rules, which are closely related with
business vocabulary. Therefore, modelling of
business processes and business rules related with
business vocabulary are one of the most important
challenges in developing information systems.
Having such means in CASE tools, requirements can
be captured in the natural language and used to
create business process models, integrated with
business rules, which also are presented in the
limited natural language understandable for business
participants. So business experts are able not only to
present their requirements in the clear and precise
way, but also to validate created business process
models and ensure their compliance with actual
business rules.
The problem of modelling business processes
and business rules, related with business vocabulary,
has already interested many scientists and
practitioners. Current work is concentrated on
creating methodology and practical means for
achieving the comprehensive solution for this
problem. For doing this, it is necessary to answer the
following research questions:
1. How to make the right separation between
graphical business process models and
textual business rules models? This question
arises because processes also can be
modelled in a declarative way, as well as
business rules can be entangled into business
process models.
2. Is it possible to represent all business rules
related with modelling BPMN processes by
using standard SBVR vocabulary without
extensions?
3. How to precisely relate business vocabulary
with business process elements without
applying linguistic analysis, which is
appropriate to avoid?
4. Is it possible to define and implement
reversible and lossless transformations
between BPMN business process models
and SBVR business vocabulary and business
rules?
3 OUTLINE OF OBJECTIVES
The goal of this research is to allow creating the
57
Mickeviciute E. and Butleris R..
The Comprehensive Modelling of BPMN Business Processes and Business Rules using SBVR Profile.
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

comprehensive BPMN business process and
business rules models based on SBVR business
vocabulary implemented in CASE tools, linking
them to each other and eliminating the gaps that
occur due to the different modelling approaches, the
lack of integration and common modelling
environment.
For reaching this goal, the following tasks must
be fulfilled:
1. Analyse existing research works and
practices related with modelling
methodologies, languages, metamodels and
modelling tools for business processes,
business vocabularies and business rules.
2. Define the methodology, based on the
SBVR business vocabulary, for right
separation, formulation and linking business
rules, expressing process control flows that
should be represented by graphical models,
and business rules, representing structural
and behavioural constraints that should be
represented by the structured natural
language.
3. Define transformation rules and algorithms
that would allow obtain the complete SBVR
vocabulary describing BPMN process rules
and behavioural constraints.
4. Implement transformation between BPMN
and SBVR models based on SBVR profile,
and interface between business rules’
specifications in the chosen CASE tool and
SBVR Editor.
5. Carry out an experiment and evaluate the
results.
4 STATE OF THE ART
As business process modelling defines dynamic
aspects of business domain and business
vocabularies and rules define static aspects, these
two modelling approaches are giving us a challenge
to combine them and use together (Mickeviciute et
al., 2013). These two modelling approaches should
be kept together as complementary (Hohwiller et al.,
2011) to each other in order to have the
comprehensive representation of problem domain.
Analysis of combination of business process and
business rules revealed that there are various
proposals on this topic and there is a need to use
these two modelling approaches together. Some of
them are more theoretical then practical, other
proposals lack of implementations or comprehensive
information how to implement them. All of them
have their own advantages and disadvantages.
Analysis of Visual SBVR (Musham et al., 2008)
and the modelling method of Ross (Ross, 1997) has
shown that even if there is a possibility to express
business rules in a graphical notation, the method is
not practical, due to the large set of graphical
elements. Furthermore, there is no guidelines how to
link business rules to business process elements.
Sinur in Gartner group report (Sinur, 2009)
presented seven scenarios for using business rules in
business processes. Later, these seven scenarios
were critically reviewed and reduced to four key
patterns (Koehler, 2010) for using business rules.
The given thoughts of how business rules could be
used in business processes are of theoretical nature,
especially the last and the most complex scenarios.
The method for declarative business process
modelling was presented by Vanthienen et al.
(2007). However, business process models are better
understood when they are modelled in the
procedural manner (Schacker, 2006; Ceponiene et
al., 2009; Nemuraite et al., 2010; Knowgravity,
2012). Business rules templates (Milanovic et al.,
2011; Graml et al., 2008) allow improving graphical
business process modelling.
As BPMN and SBVR are based on different
metamodels, Agrawal (2011) has proposed to extend
SBVR metamodel to express business process
vocabularies, but such changes to SBVR metamodel
could cause problems for maintaining these changes
in future. Therefore, using the supplementary
mapping data between two metamodels was
proposed in (Skersys et al., 2012). Semi-automated
business vocabularies extraction from business
process models was proposed (Skersys et al., 2013),
however, it does not include business rules.
Automated method of BPMN business process
model to SBVR transformation (Malik et al., 2012;
Malik et al., 2013) was presented with a tool
implementation. The method covers just a few
BPMN elements. A bottom-up approach was
presented by Cheng et al. (Cheng et al., 2011).
Generation a natural language text from BPMN
business process models (Leopold et al., 2012) in
order to validate business process has shown that
this method requires sophisticated linguistic
processing techniques and does not guarantee
completeness and reliability. The reverse approach
was presented by Friedrich et al. (Friedrich et al.,
2011). These methods do not allow to link elements
from two different modelling approaches.
Summarizing the analysed works, it is possible to
conclude that the solution to the revealed problem
yet does not exist, and efforts are required for better
IC3K2014-DoctoralConsortium
58

alignment modelling of business processes and
business rules with business vocabularies and
business language understandable for business
participants.
5 METHODOLOGY
The current research is based on the methodology of
design science research adopted by Hevner et al. to
the field of Information Systems (Hevner et al.
2004). According to this methodology, new artefacts
methodology and transformations between BPMN
business process models and SBVR business
vovabulary and business rules will be created. The
relevance of research for solving business problems
and its validity regarding existing state of the art
were preliminary justified by analysing related
research literature, modelling languages and tools.
Experimental evaluation of the implemented
transformations will be carried out to validate its
correctness and applicability for the intended
purpose. The research will add new knowledge by
answering formulated research questions, which
have a practical significance for business
participants, experts and modellers, and information
system developers.
The research is related with the BPMN (Business
Process Modelling Notation) (OMG, 2013a) the
graphical notation that allows to model business
process models in a procedural way and is
developed by OMG (Object Management Group).
The SBVR (Semantics of Business Vocabulary and
Business Rules) (OMG, 2008; OMG, 2013b) has
given the most sophisticated formal knowledge
model for defining business vocabularies and
business rules. These two modelling approaches
were selected due to the recommendation of Zur
Muehlen and Indulska (2009) that the best
representation power of business processes and
business rules is given by combination of BPMN
with SBVR. The integration and transformation
between BPMN process models and SBVR business
vocabulary and business rules is based on SBVR
profile (Mickeviciute et al., 2014a), which can be
implemented in UML CASE tools (currently, in
CASE tool MagicDraw). Using the profile alows
extension of SBVR metamodel without changing its
original specification.
6 EXPECTED OUTCOME
The expected outcome of this research is the
methodology that allows modelling BPMN business
processes and business rules on the base of SBVR
business vocabulary, and transformation between
BPMN business process models and SBVR business
vocabulary and business rules. These capabilities
will be available in CASE tool MagicDraw using
SBVR Profile.
7 COMBINATION OF BUSINESS
PROCESS AND BUSINESS
VOCABULARY AND RULES
In this section we present the approach to integrate
BPMN with SBVR, the examples of BPMN to
SBVR transformation rules, a fragment of BPMN
process model, and an example of transformation
rules implemented in QVT transformation language.
7.1 The Analysis of Research Questions
The answer to the 1
st
research question “How to
make the right separation between graphical
business process models and textual business rules
models” was found on the base of analysis of related
works. Shortly, the answer is “to separate process
rules, initiating the process flow, from business
constraint rules, allowing or preventing execution of
activities, required by process flow rules”.
For finding the answer to the 2
nd
research
question “Is it possible to represent all business rules
related with modelling BPMN processes by using
standard SBVR vocabulary without extensions”, the
representative example of BPMN process was
created, typical situations were analysed and
transformation rules for all transformations were
tried to define. The conclusion was made that it is
possible to represent all business rules related with a
single BPMN process but there is no possibilities to
represent a process hierarchy; also, transformation
rules are quite complex, especially the reverse
transformation from SBVR business rules,
representing complex business process elements,
e.g., gates; it is impossible to identify activity types,
etc.
In order to obtain the complete set of business
rules representing complex hierarchical BPMN
process, the BPMN metamodel vocabulary was
proposed, which can be used for representing BPMN
concept types in SBVR business process vocabulary
and process rules. The BPMN metamodel
vocabulary allows explicitly represent process
structure and such complex elements as gates. The
TheComprehensiveModellingofBPMNBusinessProcessesandBusinessRulesusingSBVRProfile
59
specification of BPMN process vocabulary and
process rules as well as transformation between
BPMN and SBVR models becomes straightforward
with the usage of BPMN metamodel vocabulary.
However, BPMN process vocabulary and rules may
seem unconventional and even cumbersome for
business participants. Therefore, the priority is given
to standard SBVR vocabulary and rules though it is
limited to the scope of a single BPMN process.
The performed analysis also gave the answer to
the 3
rd
research question “How to precisely relate
business vocabulary with business process elements
without applying linguistic analysis, which is
appropriate to avoid”. For reaching this criterion,
two requirements were formulated for modelling
BPMN processes: 1) strict naming rules for BPMN
elements for aligning them with business
vocabulary; 2) using pools and lanes in process
models as otherwise it would be impossible
specifying verb concepts (Mickeviciute et al.,
2014b).
The 4
th
research question “Is it possible to define
and implement reversible and lossless
transformations between BPMN business process
models and SBVR business vocabulary and business
rules” will be answered after implementation and
experimental investigation of BPMN and SBVR
transformations, which currently are defined and
partially implemented MagicDraw CASE tool using
SBVR profile and QVT transformation language.
7.2 BPMN Process Example for
Investigating BPMN and SBVR
Transformation
To test this approach, we have created EU Rent
BPMN business process model based on EU Rent
business rules presented in SBVR specification
(OMG, 2008). The fragments of the overall process
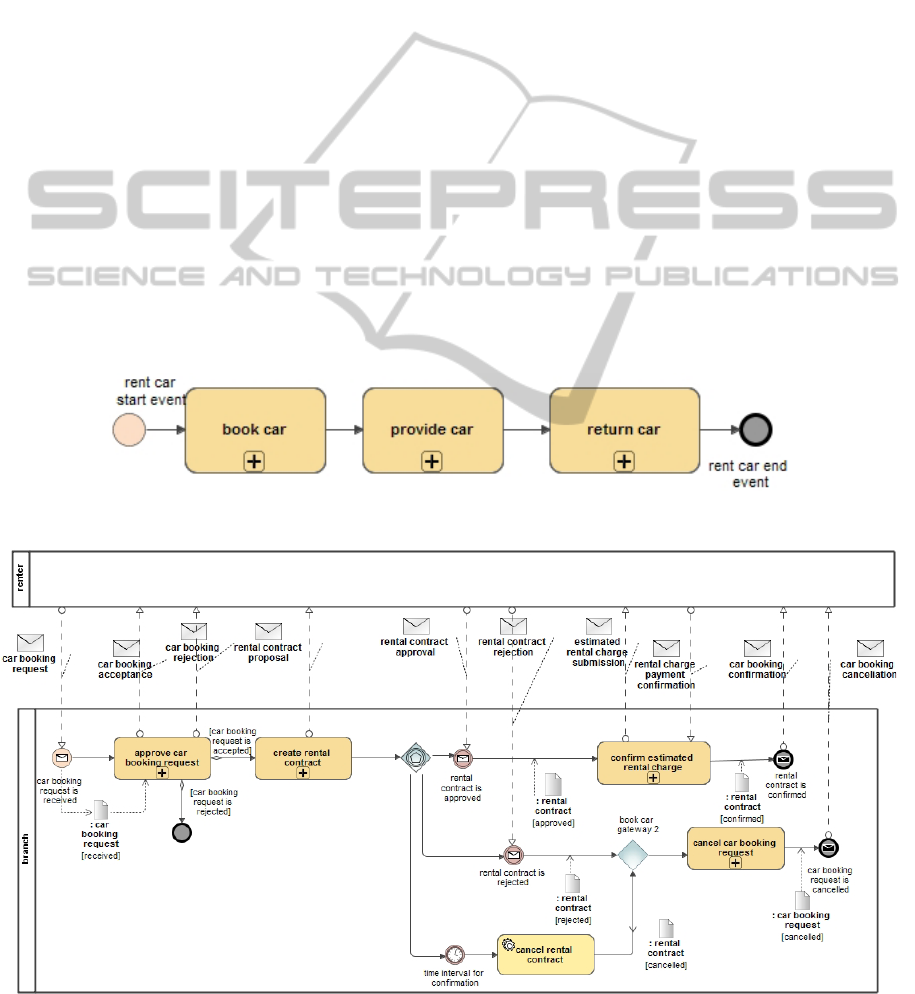
are presented in Figures 1 and 2.
Figure 1 represents the highest level of EU Rent
BPMN business process model. The subprocess
“book car”, represented in Figure 2, shows all
actions that are needed a client to book a car from a
branch. The model is related with SBVR business
vocabulary, created using SBVR Profile
(Mickeviciute et al., 2014a), based on the SBVR
specification (OMG, 2013). The implementation of
the SBVR profile is based on the DSL engine of
UML CASE tool MagicDraw.
Figure 1: BPMN business process “rent car”.
Figure 2: BPMN subprocess “book car”.
IC3K2014-DoctoralConsortium
60

7.3 Transformation Rules and
Their Implementation with QVT
In order to perform BPMN to SBVR transformation,
transformation rules were created. These rules were
grouped into 6 groups: BPMN elements to SBVR
general concepts; BPMN elements or their
combinations to verb concepts; BPMN combinations
of elements to SBVR business rules, which were
divided into four groups due to the target or initiator
of the rule: event, activity, message flow and data
object. The example of a transformation rule from
the first group is shown in Figure 3. The goal of this
transformation is to extract SBVR general concept
from BPMN message.
BPMN Message → SBVR General Concept
T
2
: transform(BPM, message: Message)
SBVR General Concept
e.g.:
transform(BPM, ‘rental contract
proposal‘)
rental_contract_proposal
Figure 3: Transformation rule from BPMN message to
SBVR general concept.
The example of a transformation rule from the
second group is shown in Figure 4. The goal of this
transformation is to extract the SBVR verb concept
from BPMN activity and pool or lane.
BPMN Activity → SBVR Verb Concept
T
9
: transform(BPM, pool|lane:
Pool|Lane, activity: Activity)→ SBVR
Verb Concept
e.g.:
transform(BPM, ‘branch‘, ‘approve car
booking request‘)
branch approve car booking request
Figure 4: Transformation rule from BPMN activity and
container to SBVR verb concept.
The example of a transformation rule from the
third-sixth groups is shown in Figure 5. The goal of
this transformation is to extract SBVR business rule
from elements combination of BPMN pool or lane
and two activities that are associated with sequence
flow.
To implement transformation rules, the QVT
transformation language was chosen, which is
developed by OMG group. The example of
transformation rule (Figure 3), implemented using
QVT, is shown in Figure 6.
Activity1 initiates Activity2
T
27
: transform(BPM, pool|lane:
Pool|Lane, activity
1
: Activity
1
,
sequence_flow(activity
1
, activity
2
):
SequenceFlow, activity
2
: Activity
2
)
SBVR Business Rule
e.g.: transform(BPM, ‘branch‘,
‘schedule pick up date time‘,
sequence_flow(‘schedule pick up date
time‘,‘schedule return date time‘),
‘schedule return date time‘)
It is obligatory that branch schedule
return_date_time if branch schedule
pick_up_date_time
Figure 5: Transformation rule from BPMN pool or lane
and two associated activities to SBVR business rule.
mapping
CentralBufferNode::Message2GeneralConcep
t():Class
when{self.isStereotypedBy('Common',
'Message')}‐‐mappingguard
{varste:Stereotype:=
prof.objectsOfType(Stereotype)![name=
"generalconcept"];
‐‐(2)Mappingresultmustbepartof
themodelbeforestereotypeapplication.
this.modelis.ownedType+=result;
‐‐
(3)Stereotypeapplicationonthe
resultingClasselement.
result.applyStereotype(ste);
name:=getNameWithNoSpace(self.name);
}
Figure 6: QVT code to transform BPMN element message
to SBVR general concept.
8 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORKS
Analysis of related works has shown that the
problem of modelling business processes and
business rules in CASE tool environment, related
with business vocabulary, is one of the most
important challenges for business analysts and
information system developers. This problem has
interested scientists and practitioners, especially for
integrating for this purpose the BPMN and SBVR
models. The main research questions were
investigated:
For making the right separation between
graphical business process models and textual
business rules, the solution was to separate process
rules, initiating the process flow, from business
TheComprehensiveModellingofBPMNBusinessProcessesandBusinessRulesusingSBVRProfile
61

constraint rules, allowing or preventing execution of
activities, required by process flow rules.
For analysing possibility to represent all business
rules related with modelling BPMN processes by
using standard SBVR vocabulary without
extensions, the representative example of EU Rent
BPMN process was created, typical situations were
analysed and transformation rules for all
transformations were defined. The conclusion was
made that it is possible to represent all business rules
related with a single BPMN process but there is no
possibilities to represent a process hierarchy; also,
transformation rules are quite complex, especially
the reverse transformation from SBVR business
rules, representing complex business process
elements, e.g., gates; it is impossible to identify
activity types, etc. The solution for representing the
complete BPMN processes, the BPMN metamodel
vocabulary was proposed for extending SBVR
metamodel without changing its original
specification.
For precisely relating business vocabulary with
business process elements without applying
linguistic analysis, which is appropriate to avoid,
two requirements were formulated for modelling
BPMN processes: 1) strict naming rules for BPMN
elements for aligning them with business
vocabulary; 2) using pools and lanes in process
models as otherwise it would be impossible
specifying verb concepts (Mickeviciute et al.,
2014b).
The possibility to implement reversible and
lossless transformations between BPMN business
process models and SBVR business vocabulary and
business rules will be investigated via experiments
after implementation of BPMN and SBVR
transformations, which currently are defined and
partially implemented in MagicDraw CASE tool
using created SBVR profile and QVT transformation
language.
The research will give the new knowledge and
the tool prototype, which have a practical
significance for business participants, experts and
modellers, and information system developers.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The work is supported by the project VP1-3.1-
ŠMM-10-V-02-008 „Integration of Business
Processes and Business Rules on the Basis of
Business Semantics" (2013-2015), which is funded
by the European Social Fund (ESF).
REFERENCES
Agrawal, A., 2011: Semantics of Business Process
Vocabulary and Process Rules. In: ISEC ’11
proceedings of the 4th India Software Engeneering
Conference, pp. 6168.
Ceponiene, L., Nemuraite, L., Vedrickas, G., 2009:
Separation of event and constraint rules in
UML&OCL models of service oriented information
systems. Information technology and control, 38(1),
29-37.
Cheng, R., Sadiq, S., Indulska, M., 2011: Framework for
Business Process and Rule Integration: A Case of
BPMN and SBVR. In: Business Information Systems,
LNBIP, vol. 87, pp. 1324.
Friedrich, F., Mendling, J., Puhlmann, F., 2011: Process
Model Generation from Natural Language Text. In:
Advanced Information Systems Engineering, LNCS,
vol. 6741, pp. 482496. Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Goedertier, S., Vanthienen, J., 2007: Declarative Process
Modeling with Business Vocabulary and Business
Rules. In: OTM 2007 Ws, Part I, LNCS, vol. 4805, pp.
603–612, Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg.
Graml, T., Bracht, R., Spies, M., 2008: Patterns of
Business Rules to Enable Agile Business Processes.
In: 11th IEEE International Enterprise Distributed
Object Computing Conference, vol. 2 (4), November
2008, pp. 385402.
Hevner, A.R.; March, S.T.; Park, J.; Ram, S. Design
Science in Information Systems Research. MIS
Quarterly, 2004, Vol. 28, No. 1, pp. 75–105.
Hohwiller, J., Schlegel, D., Grieser, G., Hoekstra, Y.,
2011: Integration of BPM and BRM. In: Dijkman, R.,
Hofstetter, J., Koehler, J. (eds.) BPMN 2011. LNBIP,
vol. 95, pp. 136–141. Springer, Heidelberg.
KnowGravity, 2012. KnowEnterprise. Version 1.7.,
http://www.knowgravity.com.
Leopold, H., Mendling, J., Polyvyanyy A., 2012:
Generating Natural Language Texts from Business
Process Models. In: Advanced Information Systems
Engineering, LNCS, vol. 7328, pp. 6479. Springer
Berlin Heidelberg.
Malik, S., Bajwa, S.I., 2013: Back to Origin:
Transformation of Business Process Models to
Business Rules. In: Business Process Management
Workshops, LNBIP, vol. 132, pp. 611622. Springer-
Verlag Berlin Heidelberg.
Malik, S., Jajwa, Sarwan, I., 2012: A Rule Based
Approach for Business Rule Generation from Business
Process Model. In: Business Process Management
Workshops, Rules on the Web: Research and
Applications, LNCS, vol. 7438, pp. 9299. Springer-
Verlag Berlin Heidelberg.
Mickeviciute, E., Butleris, R., 2013: Towards the
Combination of BPMN Process Models with SBVR
Business Vocabularies and Rules. In: Information and
software technologies: 19th International Conference,
ICIST 2013, Kaunas, Lithuania, October 10-11,
IC3K2014-DoctoralConsortium
62

Springer, 2013. CCIS, vol. 403, pp. 114-121. Springer
Berlin Heidelberg.
Mickeviciute, E., Nemuraite, L., Butleris, R., 2014b:
Applying SBVR Business Rules Vocabulary and
Business Rules for Creating BPMN Process Models.
In proceedings of International Conference on
Workshop on Applications of Knowledge-Based
Technologies in Business – AKTB 21-23 May, 2014,
Larnaca, Cyprus.
Mickeviciute, E., Pavalkis, S., Nemuraite, L., Butleris, R.,
2014a: Using SBVR Profile for Integrating Business
Vocabulary with BPMN Process Models. In
proceedings of International Conference on Advances
in Computing, Communication and Information
Technology – CCIT 01-02 June, 2014, London, UK.
Milanovic, M., Gaševic, D., Rocha, L., 2011: Modeling
Flexible Business Process with Business Rule
Patterns. In: 2011 15th IEEE International Enterprise
Distributed Object Computing Conference.
Musham, P., Singh, S., Bahal, R., Tv, P., 2008: Visual
SBVR. In: Digital Information Management, ICDIM
2008, pp. 676–683.
Nemuraite, L., Skersys, T., Sukys, A., Sinkevicius, E.,
Ablonskis, L., 2010: VETIS tool for editing and
transforming SBVR business vocabularies and
business rules into UML&OCL models. In:
Information Technologies’ 2010: Proceedings of the
16th International Conference on Information and
Software Technologies, IT 2010, Kaunas, Lithuania,
April 2123, pp. 377–384.
OMG, 2008: Semantics of Business Vocabulary and
Business Rules (SBVR) specification. Version 1.0.
OMG Document Number: formal/2008-01-02.
OMG, 2011: Query/View/Transformation (QVT), Version
1.1, OMG Document Number: formal/2011-01-01.
OMG, 2013b: Semantics of Business Vocabulary and
Business Rules (SBVR) specification. Version.1.1,
OMG Document Number: formal/2013-09-04.
OMG, 213a: Business Process Model and Notation
(BPMN), Version 2.0.1, OMG Document Number:
formal/2013-09-02.
Ross, R., G., 1997: The business Rule Book. Business
Rule Solutions, Houston, 2nd ed.
Schacher, M., 2006: Business Rules from an SBVR and an
xUML Perspective (Parts 1–3). Business Rules
Journal, 7(6–8).
Sinur, J., 2009: The art and science of rules vs. Process
flows. Research Report G00166408, Gartner.
Skersys, T., Butleris R., Kapocius, K., Vileiniskis, T.,
2013: An Approach for Extracting Business
Vocabularies from Business Process Models.
Information Technology and Control, 41(4), 178190.
Skersys, T., Tutkute, L., Butleris, R, Butkiene, R., 2012:
Extending BPMN Business Process Model with
SBVR Business Vocabulary and Rules. Information
Technology and Control, 41(4), 356-367.
Zur Muehlen, M., Indulska, M., 2009: Modeling
Languages for Business Processes and Business Rules:
A representational Analysis. Information Systems
Journal, 35(4), 379-390.
TheComprehensiveModellingofBPMNBusinessProcessesandBusinessRulesusingSBVRProfile
63
