
Company Mention Detection for Large Scale Text Mining
Rebecca J. Passonneau
1
, Tifara Ramelson
2
and Boyi Xie
3
1
Center for Computational Learning Systems, Columbia University, New York, NY, U.S.A.
2
Brandeis University, Waltham, MA, U.S.A.
3
Department of Computer Science, Columbia University, New York, NY, U.S.A.
Keywords:
Text Mining For Financial News, Financial Analytics, Coreference Resolution, Named Entity Recognition.
Abstract:
Text mining on a large scale that addresses actionable prediction needs to contend with noisy information
in documents, and with interdependencies between the NLP techniques applied and the data representation.
This paper presents an initial investigation of the impact of improved company mention detection for financial
analytics using Named Entity recognition and coreference. Coverage of company mention detection improves
dramatically. Improvement for prediction of stock price varies, depending on the data representation.
1 INTRODUCTION
Given that it is easy to access vast amounts of on-
line news, it becomes possible to mine news on a
large scale to automatically discover information rel-
evant for human decision making. For example, the
ability to detect conflict among political entities, as
in (O’Connor et al., 2013), could potentially inform
policy decisions. Text mining could also affect deci-
sions by individual analysts who track entities of other
sorts, such as corporate entities. Our work inves-
tigates the problem of mining online financial news
sources in order to learn about the fundamental mar-
ket value of publicly traded companies. The ability to
automatically discover aspects of the market through
news has broad significance. It could be used by in-
dividual investors who want to make informed invest-
ment decisions, by corporations that want to under-
stand public perception of the market, by government
entities that regulate markets, or by intelligence agen-
cies that monitor the market for unusual events. Given
a company whose stock price has changed on a given
day, the general task we address is to predict whether
the price went up or down, based on the news. The
specific focus of this paper is to test the benefit of find-
ing more mentions of companies in the news through
Named Entity detection and coreference.
Our goal is to study the impact of a high preci-
sion, high recall approach to mining news for men-
tions of entities of interest. In the financial domain,
we currently restrict our attention to publicly traded
companies. The two issues we address are 1) to
resolve variant names to the same company (e.g.,
Eli Lilly and Company, Eli Lilly, Eli Lilly & Co.,
Lilly & Co.), and 2) to resolve coreferent expres-
sions consisting of noun phrases and pronouns (e.g.,
Eli Lilly and Company is an American global phar-
maceutical company with headquarters in Indianapo-
lis, Indiana. The company also has offices in Puerto
Rico and 17 other countries. Their products are sold
in 125 countries. It was founded in 1876.). We refer
to this task as company mention detection.
Improved company mention detection will not
necessarily improve price prediction from news. This
is an extremely challenging prediction problem with
many confounding factors. For example, news items
that provide novel information about a company po-
tentially have more impact on price than news items
that provide old information. Accurate company
mention detection might incorporate a higher propor-
tion of sentences that provide old information, which
could hurt rather than benefit prediction of price
change. Given the complexity of factors involved in
testing whether more accurate company mention de-
tection improves prediction of stock price change, it
is possible that results would vary, depending on the
type of feature representation used. To make our test
more general, we use an existing framework that com-
pares alternative document representations in this do-
main (Xie et al., 2013). Because this framework com-
pares several kinds of vector and tree space represen-
tations, it serves as a more general test of the impact
of improved company mention detection.
One of the challenges in mining financial informa-
512
J. Passonneau R., Ramelson T. and Xie B..
Company Mention Detection for Large Scale Text Mining.
DOI: 10.5220/0005174405120520
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval (SSTM-2014), pages 512-520
ISBN: 978-989-758-048-2
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

Company name: Baker Hughes Inc
Ticker: BHI
Company divisions: Baker Hughes Drilling Fluids, Baker Oil Tools, Baker Petrolite, etc.
———————————– Example sentence 1 (a company found by named entity recognition) ————————–
<company ticker=‘BHI’ type=‘SP500’ sector=‘energy’>Baker Hughes Inc</company> lowered estimates in mid-July
to $1.12-$1.14 per share.
———————————– Example sentence 2 (company divisions found by named entity recognition) —————-
Wall, 54, comes from <company ticker=‘BHI’ type=‘SP500’ sector=‘energy’>Baker Hughes</company>, where he
served since 2005 as group president, completion & production, responsible for the combined activities of <company
ticker=‘BHI’ type=‘SP500’ sector=‘energy’>Baker Oil Tools</company> and <company ticker=‘BHI’ type=‘SP500’
sector=‘energy’>Baker Petrolite</company> divisions.
———————————– Example sentence 3 (company found by coreference resolution) ——————————
<company ticker=‘BHI’ type=‘SP500’ sector=‘energy’>Baker Hughes</company> said <company ticker=‘BHI’
type=‘SP500’ sector=‘energy’>it</company> supplied products to customers in Myanmar. ... Although <company
ticker=‘BHI’ type=‘SP500’ sector=‘energy’>it</company> did not have an office or operations there, <company
ticker=‘BHI’ type=‘SP500’ sector=‘energy’>it</company> was constantly reviewing <company ticker=‘BHI’
type=‘SP500’ sector=‘energy’>its</company> presence in nations around the globe.
Figure 1: Example company and news sentences.
tion from news is that the domain of publicly traded
corporate entities is extremely heterogeneous. For ex-
ample, the features that prove predictive in (Xie et al.,
2013) vary markedly across sectors, and can even pre-
dict opposite direction of price change in different
sectors, such as retail versus industrials. It is also
well known that the performance of NLP techniques
varies across domains. Domain adaptation has been
addressed in parsing (Ravi et al., 2008; McClosky
et al., 2010; Roux et al., 2012) and language mod-
eling (Bulyko and Ostendorf, 2003; Sarikaya et al.,
2005). Sensitivity to domain is undoubtedly true as
well of NER and coreference. This suggested to us
that to evaluate the effect on performance of existing
NLP tools for improving company mention detection,
it is important to assess performance sector by sector.
We find that extension of the NER component of the
framework in (Xie et al., 2013) and integration of a
coreference toolkit dramatically improves recall, but
much more so for one sector in particular. Manual
assessment of samples of the data suggests that pre-
cision remains high. The impact on prediction, how-
ever, is not uniform. Predictive accuracy improves
primarily for one of the three sectors, using the more
expressive tree space representation. Improving pre-
diction is not necessarily dependent on the number
of mentions captured, but rather on the quality of the
content surrounding company mentions.
2 MOTIVATION
Company mention detection is a challenging task.
Consider the example in Figure 1. Baker Hughes Inc
is a company that provides oil and gas services in the
Energy sector. Example sentence 1 mentions the full
name of the company and an exact match can iden-
tify it. The challenges occur when companies men-
tioned in the articles are referred to by a more ab-
breviated version of their full name, such as Baker
Hughes or Baker, as in example sentence 2. Further
problems lie in the fact that some of these abbrevi-
ated mentions name other entities, such as a person,
or are generic words, such as the word baker, when
it introduces a person of that occupation. We had to
consider if increasing the recall to capture these cases
would outweigh the negative effect of a decrease in
precision. Accordingly, we looked at how frequently
abbreviated name strings are in fact used to refer to a
company versus a different entity. Additionally, there
are instances where sub-branches of a company are
mentioned, and it is questionable as to whether these
are important instances to capture. Baker Hughes,
in example sentence 2, has divisions Baker Oil Tools
and Baker Petrolite, which are mentioned in the same
news article, but an exact match by full name can-
not capture these mentions. The question of whether
news reports about subsidiary units affect the main
company’s price requires is a complex one that we do
not address here.
Further improvement of company mention detec-
tion requires coreference resolution, especially to de-
tect mentions in different sentences, as shown in ex-
ample sentence 3 of Figure 1. Coreference resolu-
tion was not used in many previous studies on finan-
cial news analytics, including (Rosenfeld and Feld-
man, 2007; Feldman et al., 2011; Xie et al., 2013).
We found that the Stanford CoreNLP coreference
parser (Lee et al., 2013), a state-of-art coreference res-
olution toolkit that works well on the CoNLL Shared
Task, does not lead to good results when directly ap-
CompanyMentionDetectionforLargeScaleTextMining
513

Table 1: Description of news data.
GICS C N S T
10 40 5,373 109,277 2,014,085
15 26 2,295 53,595 953,133
20 58 8,325 238,570 3,780,129
plied. It introduces many mention chains that are
irrelevant to the company entities, and some chains
contain heterogeneous noun phrases that are not ap-
propriate for our company mention annotation task.
However, it has a modular design that supports rela-
tively easy re-design, as described in Section 6.
Text mining in the financial domain with shallow
techniques has shown some success (Tetlock, 2007;
Gentzkow and Shapiro, 2010; Engelberg and Parsons,
2011). Recent work has applied NLP techniques to
various financial media (conventional news, tweets)
to detect sentiment in conventional news (Devitt and
Ahmad, 2007; Haider and Mehrotra, 2011) or mes-
sage boards (Chua et al., 2009), or to discriminate
expert from non-expert investors in financial tweets
(Bar-Haim et al., 2011). (Kogan et al., 2009) an-
alyzed quarterly earning reports to predict stock re-
turn volatility and to predict whether a company will
be delisted. (Luss and d’Aspremont, 2008) used text
classification to model daily price movements that are
above a predefined threshold. (Xie et al., 2013) pro-
posed a semantic tree structure for data representa-
tion and used tree kernel for support vector learning
to predict the price change based on financial news.
This work is related to the above studies that explore
richer NLP techniques for company driven financial
news analysis. However, most of the existing research
focuses on task specific modeling, such as price pre-
diction or fraud detection. Little attention is paid to
the best ways to integrate fundamental text process-
ing methodologies such as named entity recognition
and coreference resolution.
3 RELATED WORK
This paper focuses on improving the text processing
pipeline to improve the overall financial news knowl-
edge discovery framework. Capturing named entities
is essential for making accurate predictions because
we rely on named entity recognition to select com-
pany relevant news information for price modeling.
Named entity recognition is a major area of interest
in text mining. A large resource that supports this
task is the Heidelberg Named Entity Resource, a lex-
icon that links many proper names to named entities
(Wolodja Wentland and Hartung, 2008). It is not used
in our study because its coverage is limited: it fails
to capture enough mentions for our targeted company
list, which is based on the S&P 500.
1
As a result, we
require a more general and comprehensive method. In
addition to named entity recognition, we also incorpo-
rated a coreference resolution step to further improve
the performance of text mining procedure. There are
coreference parsers that use various approaches in at-
tempts to attain optimal performance. The corefer-
ence resolution model that our method builds on is
the Stanford CoreNLP parser (Manning et al., 2014).
Named entity recognition and coreference resolution
are the two key components in our company mention
detection task. We leverage state-of-art tools to maxi-
mize compatibility and stock market predictability for
the financial news domain.
4 DATA
We work with a large dataset for doing extensive news
analysis, where publicly available Reuters news data
for the year 2007 are used for this study. The Global
Industry Classification Standard (GICS) is an indus-
try taxonomy developed by Standard & Poors (S&P)
for use by the global financial community. The GICS
structure consists of 10 sectors, 24 industry groups,
68 industries and 154 sub-industries into which S&P
has categorized major public companies. We concen-
trated on the first three sectors in GICS: 40 compa-
nies in GICS 10 of Energy such as Hess and Exxon
Mobile, 26 companies in GICS 15 of Materials such
as Du Pont, and 58 companies in GICS 20 of Indus-
trials such as Boeing and General Electric. Table 1
describes our data. C is number of companies in each
sector; N is the number of news items; S is the num-
ber of sentences; and T is the number of words.
5 FRAMEWORK
Our framework to capture news impact on the finan-
cial market consists of three main components, as
shown in Figure 2: (1) text processing, (2) data in-
stance formation, and (3) model learning and evalua-
tion. In the text processing component, a four-stage
NLP pipeline is used. The title and full text of the
news article are first extracted from the HTML docu-
ments from Reuters News Web Archive. The sentence
segmentation stage splits the full text into sentences.
The company mention detection stage then identifies
1
S&P 500 is an equity market index that includes 500
publicly traded companies in leading industries.
KDIR2014-InternationalConferenceonKnowledgeDiscoveryandInformationRetrieval
514
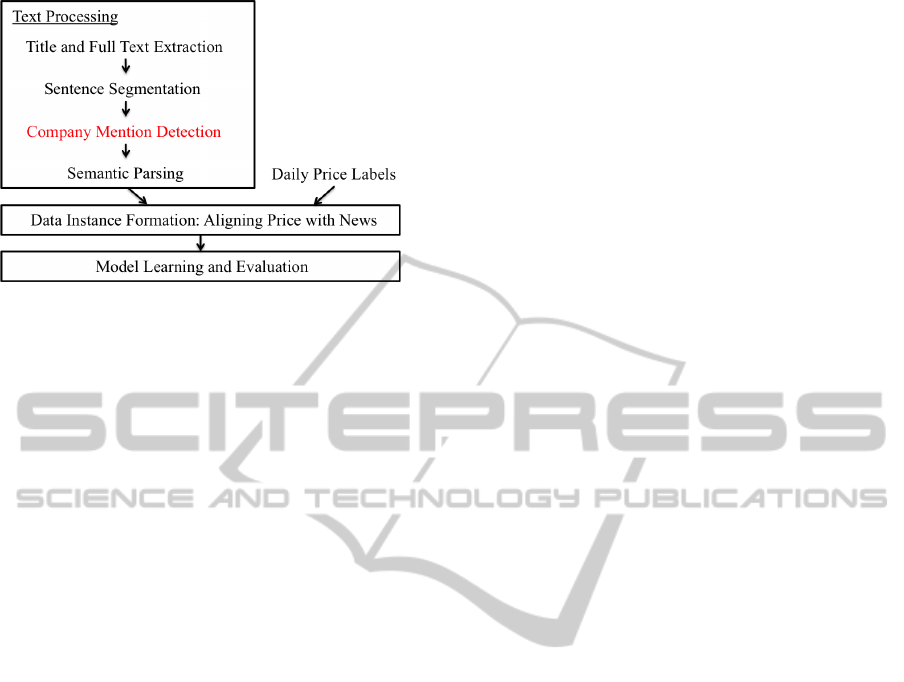
Figure 2: Framework of the text mining on financial news
for stock market price prediction.
if any company of interest is mentioned in the sen-
tence. In this study, we focus on a finite list of compa-
nies in the S&P 500. The remaining framework relies
on the implementation described in (Xie et al., 2013).
The sentences with at least one S&P 500 company
mention are parsed and used for text mining. There-
fore, the company mention detection task provides the
data foundation for the whole framework. How to im-
prove the coverage of the company mention detection
in a way that improves prediction is the main focus in
this study.
After text processing, we align public available
daily stock price data from Yahoo Finance with the
textual news data following the method in (Xie et al.,
2013). Recall that the task is to predict the change in
price of a company on a date based on the analysis of
the preceding day’s news. A data instance is all the
news associated with a company on a given day, and
consists of the companies whose price changed above
a threshold between the closing price on the day of
the news and the closing price on the following day.
In the learning and evaluation component, rich
vector space models are used to test the price pre-
diction performance. These vector space models in-
clude bag-of-words models, semantic frame features,
and part-of-speech based word affective features. A
model that encodes rich structured semantic informa-
tion, SemTreeFWD of (Xie et al., 2013), is also used
for model learning and evaluation. It is an enriched
hybrid of vector and tree space models that contains
semantic frames, lexical items, and part-of-speech-
specific affective features trained with Tree Kernel
SVM (Moschitti, 2006).
6 COMPANY MENTION
DETECTION
Our Company Mention Detection module attempts to
identify all named entities, variants of these names,
and coreferential expressions, then replaces the origi-
nal strings with a unique identifier. For the identifiers,
we use the company tickers, character codes between
length of one to five, to identify publicly traded com-
panies. The NLP pipeline in (Xie et al., 2013) used
a rule-based method for partial matching on the full
company names that only recognized a limited num-
ber of the variant names for a company. We have ex-
panded its NER (Named Entity Recognition) rules to
capture a much wider range of name variants. We
also tested the Stanford CoreNLP coreference parser,
and modified it to achieve optimal performance for
our domain. This section describes the original and
our new NER module, and the changes we made to
Stanford coreference parser.
To obtain a lower bound for NER, we used an
Exact Match method, defined as matching the exact
string to the official names of the S&P 500 compa-
nies. This ensures 100% precision, but recall is low.
The approach in (Xie et al., 2013) for NER relies on a
few conservative rules. These rules focus on the struc-
ture of the company names, which can consist of two
types of tokens. The words that make up the unique
name of the company are the general name elements.
The second type are the generic endings, a predefined
set of possible suffixes that are optionally included in
company names. A generic ending, when included,
will be the last token of a company name. It uses the
generic endings Company, Corporation, Incorpora-
tion, and Limited, as well as their abbreviations.
The NER module in (Xie et al., 2013) applies
three rules, Exact Match to the company official
name, a rule for the generic endings in the Exact
Match, and one for the name elements. The second
rule applies if there is a generic ending: the program
substitutes, one at a time, each generic element in our
predefined list for the original generic element, and
finally a null element, and searches for each of these
new candidate name strings in the text; note that if
the null element is substituted, then the new search
string consists only of a sequence of name elements
with no generic ending. The third rule, which trig-
gers after the second, truncates the sequence of name
elements by iteratively removing the last name ele-
ment unless the sequence of name elements is length
two. After each truncation step, the second rule is re-
applied. The process terminates at the first word of a
company name.
Our Company Mention Detection module incor-
CompanyMentionDetectionforLargeScaleTextMining
515

porates the NER from (Xie et al., 2013) described
above, but extends the set of rules so that it does
not terminate when the sequence of name elements
is length one. Through random sampling and visual
inspection, we found that it would be beneficial to
include the first word. To maintain high precision,
we hard-coded rules for companies where there was
a strong possibility that the first token of their names
could be mistaken for another entity.
Our Company Mention Detection module also in-
corporates the Stanford CoreNLP parser, which out-
puts lists of entities that corefer, called coreference
chains (Manning et al., 2014). The Stanford parser
was trained on various copora where the average F-
measure was about 60%, which is considered a high
score for this task. Furthermore, this parser was in-
tended to be easy for others to modify, either by re-
moving or adding methods to capture coreference pat-
terns. Initially, the Stanford parser seemed ineffective
for our dataset due to some inaccuracies in the results.
It captured many more instances than it should have,
thus decreasing precision. By observing the list of en-
tities in the coreference chains, we noticed that there
were some incorrect linkings. First, distinct compa-
nies were sometimes linked with each other, such that
an incorrect ticker was assigned to one of the compa-
nies. Second, the parser captured predicate nomina-
tive instances, which are not relevant for our purposes.
Third, there were general incorrect linkings between
company names and other words in the text.
To address these issues, we re-structured the com-
ponents of the Stanford CoreNLP coreference parser.
The original algorithm goes through ten passes, or
sieves, to capture different kinds of coreference phe-
nomena for each iteration (Lee et al., 2013). By
exploring the sieves in the coreference toolkit, we
were able to identify the ones causing problems in
our data, and to manually tune the parser to meet our
needs. The three passes that decreased the accuracy
of the mention detection algorithm are called Precise
Constructs, Strict Head Match 3 and Relaxed Head
Match. There are a few rules incorporated into Pre-
cise Constructs, but the main one causing issues in our
data was the predicate nominative condition, which,
when capturing an entity, also captures the text fol-
lowing a linking verb (Lee et al., 2013). For example,
a sentence that mentions the ConocoPhillips company
says, ConocoPhillips is an international, integrated
petroleum company with interests around the world.
Precise Constructs gives the output ConocoPhillips is
ConocoPhillips.
Strict Head Match 3 removes a word inclusion
constraint used in Strict Head Match 1, where all the
non-stop words of one entity must match the non-stop
words that appear in the previous one. By remov-
ing this sieve and thereby imposing this constraint,
our program avoids generating incorrect linkages be-
tween entities. Strict Head Match 3 removes this
constraint since the score for the dataset the Stanford
team tested it on improved. Relaxed Head Match al-
lows any word in the main entity to match with enti-
ties in other coreference chains. As a result, for the
company Air Products, the original algorithm incor-
rectly recognized these products to be the company
entity. Once these three sieves were eliminated, we
observed a significant improvement.
The passes that remained in the coreference parser
include Speaker Identification, Exact String Match,
Relaxed String Match, Strict Head Match 1, Strict
Head Match 2, Proper Head Word Match and Pro-
noun Match. The Speaker Identification sieve detects
the speakers in the text and captures any pronouns that
refer to them. In Exact String Match, the parser cap-
tures the exact string of entities, similar to the idea
of our Exact Match method, but with the additional
property of including modifiers and determiners. Re-
laxed String Match removes the text following the
head words of two entities, and links them together
if the remaining strings match. Strict Head Match 1
uses the heads of the entities and imposes contraints to
determine if the mentions are coreferent. Strict Head
Match 2 eliminates a restriction used in Strict Head
Match 1, where in this property, modifiers in one en-
tity must match the modifiers in the previous entity in
order to be linked together. Proper Head Word Match
links proper nouns that have the same head word, but
also has specific restrictions imposed on these enti-
ties. Pronoun Match focuses on pronominal rules and
imposes agreement constraints to capture the entities
that are compatible. These seven sieves (Lee et al.,
2013) provided the results we needed for capturing
additional correct instances.
7 EXPERIMENT
Before conducting our experiment with the Company
Mention Detection module, we did some probes on
the data to shape our expectations for performance
gains. Taking a randomly selected company, and ten
randomly selected documents that mention the com-
pany, we counted how many company mentions were
captured by each of the three methods: Exact Match,
the Initial NER from (Xie et al., 2013) and our Com-
pany Mention Detection (CMD). Percentage results
for the 54 mentions this yielded are displayed in Ta-
ble 2. As shown, CMD yielded greatly improved
recall at a reasonable sacrifice in precision, and an
KDIR2014-InternationalConferenceonKnowledgeDiscoveryandInformationRetrieval
516

Table 2: A manual evaluation for company detection in a
preliminary experiment.
Methods Precision Recall F-measure
Exact Match 100.0% 17.0% 29.0%
Initial NER 100.0% 57.4% 72.9%
CMD 90.0% 76.6% 82.8%
overall increase in F-measure of 13.6%, compared to
the Initial NER. Interestingly, the incorrect instances
for CMD were not entirely wrong: they all referred
to units within the company. We count them as in-
correct, however, because of our focus on predicting
stock price for the S&P 500 (parent) companies. As
noted above, what happens to one unit of a company
may not necessarily affect public perception of the
company as a whole. We, therefore, do not regard
sub-companies as correct instances for the purposes
of our experiment.
The Exact Match method has a very low F-
measure since it only captures the full name of a com-
pany. Except for the first time it is mentioned in a
news article, a company is usually not referred to by
its full name. Instead, variations of company names
are frequently used. Clearly, the Initial NER method
from (Xie et al., 2013) far outperforms this baseline,
yet leaves much room for improvement in recall.
As described in section 6, CMD further expanded
the NER so as to search for abbreviated name strings
that include only the first word of the full named en-
tity string of the companies. For the company Baker
Hughes Inc., this would lead to the inclusion of men-
tions by the single name Baker. Although in the gen-
eral case, this could introduce imprecision, if a doc-
ument already contains the full company name, it is
likely that use of the first name token in the full name
(e.g., Baker) would be a company mention. In ad-
dition, CMD also captures many coreferential expres-
sions for company mentions. For example, one article
says, Baker Hughes said it supplied products to cus-
tomers; where the original NER rules capture Baker
Hughes. CMD also captures it. As shown in Table 3,
CMD captures many additional instances of company
mentions. This also leads to some gains in stock price
prediction, as will be reported in the next section.
The full experiment uses as input the data de-
scribed in Table 1 consisting of all the news in three
Table 3: Counts of company mentions by sentence.
GICS Initial NER CMD Increase
10 8,646 11,252 30.14%
15 5,445 6,336 16.36%
20 15,286 17,865 16.87%
Total 29,377 35,453 20.68%
market sectors from Reuters news archive for 2007.
Recall, we use the framework described in Section 5
because it allows us to test the impact of improved
F-measure for CMD across multiple document rep-
resentations. The five document representations we
test in the experiment are: 1) BOW, which refers
to bag-of-words with unigram counts; 2) BOW (n-
gram), for BOW with unigram, bigram and trigram
counts; 3) FW which is like BOW (n-gram) but also
includes Frame Semantic elements (see next para-
graph); 4) FWD consists of FW plus a prior polar-
ity on words from the Dictionary of Affect in Lan-
guage (DAL score; see next paragraph); 5) and lastly,
SemTreeFWD, which is a tree structure that uses the
FWD features combined with a tree kernel.
Three of the five document representations make
use of features from frame semantics (Fillmore,
1976). Frame semantics aims for a conceptual rep-
resentation that generalizes from words and phrases
to abstract scenarios, or frames, that capture explicit
and implicit meanings of sentences. The three ba-
sic feature types from frame semantics are frame
name, frame target, and frame element. Each frame is
evoked by a frame target, or lexical unit, for example,
sue or accuse evoke the Judgement Communication
frame, which describes a lawsuit scenario. Its frame
elements, or semantic roles, are Communicator, Eval-
uee, and Reason. FW and FWD uses bag-of-frames
(including frame names, frame targets, and frame ele-
ments) features in a vector space representation, while
SemTreeFWD encodes relational structures between
the company entity and the semantic frame features
in a tree representation, in addition to FWD. The se-
mantic parsing we use to extract frame features is
SEMAFOR
2
(Das and Smith, 2011; Das and Smith,
2012), a statistical parser that uses a rule-based frame
target identification, a semi-supervised model that ex-
pands the predicate lexicon of FrameNet for semantic
frame classification, and a supervised model for argu-
ment identification.
FWD and SemTreeFWD contain word affect fea-
tures based on DAL, the Dictionary of Affect in Lan-
guage (Whissel, 1989). It is a psycholinguistic re-
source designed to quantify the undertones of emo-
tional words that includes 8,742 words annotated for
three dimensions: pleasantness, activation, and im-
agery. We use the average scores, in terms of the three
dimensions, for all words, verbs, adjectives, and ad-
verbs in a vector space for feature representation.
The experiments assess the performance of pre-
dicting the direction of price change across companies
in a sector. Recall that a data instance in our experi-
ment is all the news associated with a company on a
2
http://www.ark.cs.cmu.edu/SEMAFOR
CompanyMentionDetectionforLargeScaleTextMining
517

Table 4: Averaged test accuracy for each company by sector that uses 80% of the data for training 20% for testing. Boldface
identifies a higher CMD mean and ∗ identifies the CMD that is significantly better than the Initial NER with p-value < 0.05.
GICS Sector type BOW BOW (n-gram) FW FWD SemTreeFWD
10 Energy
Initial NER 59.94±16.38 61.18±15.43 59.99±14.46 59.05±16.58 64.26±14.95
CMD 58.54±17.32 61.11±15.34 58.67±15.76 58.44±18.40 64.87±15.04
15 Materials
Initial NER 58.23±15.53 59.74±14.33 62.10±14.24 62.69±15.28 68.62±14.72
CMD 61.82±15.18 60.63±15.33 63.23±13.71 63.12±15.01 67.18±13.37
20 Industrials
Initial NER 56.70±14.81 55.47±13.86 53.86±13.43 54.29±14.31 57.25±16.88
CMD 60.13±14.04∗ 58.19±13.44∗ 55.37±13.31 55.75±13.54 56.36±18.38
given day, and consists of the companies whose price
changed above a threshold between the closing price
on the day of the news and the closing price on the fol-
lowing day. In this experiment, we use the threshold
of 2% that corresponds to a moderate fluctuation. A
binary class label {-1, +1} indicates the direction of
price change on the next day after the data instance
was generated from the news. For each company,
80% of the data is used for training and 20% for test-
ing. We report the averaged accuracy and standard
deviation of the test data for both the Initial NER, as a
benchmark, and our CMD on a sector-by-sector basis.
8 RESULTS
The experiment addresses two questions: 1) Does
CMD improve the coverage of company mentions in
the domain of interest? 2) Does our Company Men-
tion Detection improve accuracy of prediction on the
task to identify the direction of price change? Based
on our probe of the data where we could manually
assess precision (Table 2 in section 7), we expected
a large increase in coverage. Projecting from the re-
sults of this manual probe, we assume that an increase
in recall comes with an acceptable (small) degrada-
tion in precision. Yet, because there is no gold stan-
dard data set, we cannot assess precision of CMD for
the full dataset. Prediction accuracy is the true test
of performance on the benefit of increased coverage
of company mentions using CMD, but is only a very
indirect measure of precision. As noted above, stock
price prediction from news is a challenging task with
a great deal of noise in the input. Results presented
here show a substantial increase in coverage, and sta-
tistically significant increases in prediction accuracy
for some but not all of the experimental conditions.
As background to interpret the results, it is im-
portant to consider the relation between the increased
number of mentions versus the number of data in-
stances per company, and the differences across sec-
tors in the average number of data instances per com-
pany. Again, each data instance consists of all the
news for a given company on a given day. Therefore,
new data instances will be added only if CMD identi-
fies news for a given company on a day that was not
identified before. If new sentences for a given day
are identified, however, then we expect that BOW and
BOW (n-gram) are very likely to be enriched, and pre-
diction could improve in these two cases. If new men-
tions in an existing sentence are identified, this should
not improve BOW and BOW (n-gram) because all the
relevant feature positions in the vector (unigram, n-
gram) will already have had values, and the values
will not change. In contrast, if new mentions occur
not in the same sentence but in new clauses within or
across sentences, the representations that use seman-
tic frame parsing (FW, FWD, SemTreeFWD) could
be enriched if the new clauses contain words that trig-
ger new frames, and the new mentions fill their roles.
We found that CMD did not increase the num-
ber of data instances. This result suggests that if
a news item mentions a relevant company, at least
one mention will be either an exact match to the full
name string, or a near match based on the conserva-
tive NER rules in (Xie et al., 2013). On the other
hand, there were substantial gains in the total number
of sentences. Table 3 reports the absolute numbers
of sentences with company mentions from the origi-
nal NER module in (Xie et al., 2013) compared with
those for the Company Mention Detection module. At
increases of between 16% and 17%, the Materials and
Industrials sectors already show large increases; the
increase for the energy sector is nearly double that
of the two other sectors. This difference between the
GICS 15 and 20 versus GICS 10 reflects the under-
lying domain differences from sector to sector, which
accounts to some degree for the difficulty of the pre-
diction task. We further note that the number of data
instances per company differs substantially across the
three sectors. The mean and standard deviation for
each sector are as follows, respectively: GICS 10, µ =
24.37, σ = 15.80; GICS 15 µ = 20.80, σ = 15.52;
GICS 20: µ = 16.16, σ = 18.96. Based on these fig-
ures, we expect the gains for GICS 15 and 20 to be
similar, and the gains for GICS 10 to be larger for the
semantic frame representations.
Table 4 gives the average accuracy per sector of
KDIR2014-InternationalConferenceonKnowledgeDiscoveryandInformationRetrieval
518

the CMD combined with the five document repre-
sentation methods introduced in the previous section.
(Note: None of these results significantly beat the
baseline accuracy given by the average over the ma-
jority class for each company, but the standard devi-
ations for this baseline–as for the results in Table 4–
are quite high. This does not diminish the compari-
son of the different representations, and the question
of whether CMD can improve performance.) Pre-
diction accuracy improved for the BOW representa-
tions. The numbers in boldface are the cases where
the average accuracy for CMD is higher than for the
original NER, and the cells with an asterisk indicate
cases where a t-test of the difference is statistically
significant. As shown, the two cases where there is
a statistically significant improvement are for the two
BOW representations for the sector with the fewest
average data instances per company, namely Indus-
trials. When using NER, the BOW representations
already had very competitive performance, and CMD
increases their performance. This suggests that the
new sentences that are identified with CMD add new
vocabulary that is predictive. The two vector-based
representations with frames also have higher accu-
racy, but the increase is not statistically significant.
For the tree-based representation (SemTreeFWD), the
performance degrades somewhat. The performance
of the frame-based representations suggests that the
new sentences for Industrials do not add new frames,
or possibly add new frames that have semantic con-
flicts with the frames that were found earlier. The
same general pattern holds for the Materials sector.
The one case where the SemTreeFWD perfor-
mance improves is for the Energy sector, but the
improvement is not statistically significant. We can
only speculate that this sector is the only one where
SemTreeFWD shows greater accuracy because this is
the sector where the number of additional sentences
is substantially larger.
The two questions posed by our experiment can
be answered briefly as follows: 1) CMD improves
the coverage of company mentions dramatically at the
sentence level: the number of additional sentences per
sector increases on average by over 20%. This does
not, however, increase the number of data instances;
2) CMD has a statistically significant impact on pre-
dictive accuracy only for the Industrials sector, for the
two BOW reprsentations. In the next section we dis-
cuss the ramifications of these results.
9 CONCLUSION
Evaluation of coreference performance generally in-
volves assessment of the accuracy of coreference as
an independent module. Here we provide an evalua-
tion of coreference as an independent module (intrin-
sic), and as part of an end-to-end system that aims at
a real world prediction task (extrinsic). The results
presented in the preceding section provide a very dra-
matic and concrete demonstration that large gains for
coreference as a stand-alone module do not necessar-
ily result in system gains. They also demonstrate the
importance of considering the overall integration of
information for data representation.
Of the fifteen conditions in Table 4, the two condi-
tions where we find statistically significant improve-
ments from CMD pertain to the two data representa-
tions that are relatively less rich, BOW and BOW (n-
gram), for the sector with the fewest data instances.
There are marginal improvements that are not statisti-
cally significant for FW and FWD, and a degradation
for SemTreeFWD. This indicates to us that the new
sentences added for the Industrials sector add new
features to the BOW feature vector, but do not add as
much in the way of frame features. Continuing with
this sector, the differences between the five document
representations are not as great for NER as they are
with CMD, and the unigram BOW representation in
the CMD condition ends up with the highest accuracy
for the ten conditions. The same general trend for the
vector representations holds in Materials as for Indus-
trials, but without statistical significance. For Materi-
als, however, SemTreeFWD remains the representa-
tion with the highest accuracy among all five.
Energy, which had a much more substantial gain
in number of sentences, has a different pattern. There
are no gains for the vector based representations. En-
ergy is also the sector with the greatest number of data
instances per company. Here we speculate that the
addition of new sentences does not add new vocabu-
lary: with such a large number of data instances per
company already, vocabulary coverage was perhaps
already high. SemTreeFWD shows a small gain in
accuracy that is not statistically significant.
In our view, rich semantic and pragmatic data min-
ing for large scale text mining should aim for informa-
tion that supports more informed decision making, or
in other words, is actionable. To summarize the re-
sults of the experiment presented here, a substantial
increase in coverage for the task of detecting men-
tions of relevant entities on a large scale prediction
task does not necessarily translate to gains in the ac-
tionable value of the information gained. Further, the
experiment demonstrates the interdependence of se-
mantic and pragmatic data mining with feature rep-
resentation, and with the end goals of the data min-
ing task. For future work, a detailed post hoc anal-
CompanyMentionDetectionforLargeScaleTextMining
519

ysis of results across sectors, and across companies
within sectors, should yield insights that could inform
a more sophisticated processing architecture, as well
as a more effective document representation.
REFERENCES
Bar-Haim, R., Dinur, E., Feldman, R., Fresko, M., and
Goldstein, G. (2011). Identifying and following ex-
pert investors in stock microblogs. In Proceedings of
the 2011 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural
Language Processing, pages 1310–1319, Edinburgh,
Scotland, UK.
Bulyko, I. and Ostendorf, M. (2003). Getting more mileage
from web text sources for conversational speech lan-
guage modeling using class-dependent mixtures. In
Proc. HLT-NAACL 2003, pages 7–9.
Chua, C., Milosavljevic, M., and Curran, J. R. (2009). A
sentiment detection engine for internet stock message
boards. In Proceedings of the Australasian Language
Technology Association Workshop 2009, pages 89–93,
Sydney, Australia.
Das, D. and Smith, N. A. (2011). Semi-supervised frame-
semantic parsing for unknown predicates. In Proceed-
ings of the 49th Annual Meeting of the ACL, HLT ’11,
pages 1435–1444, Stroudsburg, PA, USA.
Das, D. and Smith, N. A. (2012). Graph-based lexicon
expansion with sparsity-inducing penalties. In HLT-
NAACL, pages 677–687.
Devitt, A. and Ahmad, K. (2007). Sentiment polarity iden-
tification in financial news: A cohesion-based ap-
proach. In Proceedings of the 45th Annual Meeting
of the ACL, pages 984–991, Prague, Czech Republic.
Engelberg, J. and Parsons, C. A. (2011). The causal impact
of media in financial markets. Journal of Finance,
66(1):67–97.
Feldman, R., Rosenfeld, B., Bar-Haim, R., and Fresko,
M. (2011). The stock sonar - sentiment analysis of
stocks based on a hybrid approach. In Proceedings of
the Twenty-Third Conference on Innovative Applica-
tions of Artificial Intelligence, August 9-11, 2011, San
Francisco, California, USA.
Fillmore, C. J. (1976). Frame semantics and the nature of
language. Annals of the New York Academy of Sci-
ences, 280(1):20–32.
Gentzkow, M. and Shapiro, J. M. (2010). What drives media
slant? Evidence from U.S. daily newspapers. Econo-
metrica, 78(1):3571.
Haider, S. A. and Mehrotra, R. (2011). Corporate news
classification and valence prediction: A supervised
approach. In Proceedings of the 2nd Workshop on
Computational Approaches to Subjectivity and Senti-
ment Analysis (WASSA 2.011), pages 175–181, Port-
land, Oregon.
Kogan, S., Levin, D., Routledge, B. R., Sagi, J. S., and
Smith, N. A. (2009). Predicting risk from financial re-
ports with regression. In Proceedings of Human Lan-
guage Technologies: The 2009 Annual Conference of
the North American Chapter of the ACL, NAACL ’09,
pages 272–280, Stroudsburg, PA, USA.
Lee, H., Chang, A., Peirsman, Y., Chambers, N., Surdeanu,
M., and Jurafsky, D. (2013). Deterministic coref-
erence resolution based on entity-centric, precision-
ranked rules. Computational Linguistics, 39(4).
Luss, R. and d’Aspremont, A. (2008). Predicting abnor-
mal returns from news using text classification. CoRR,
abs/0809.2792.
Manning, C. D., Surdeanu, M., Bauer, J., Finkel, J.,
Bethard, S. J., and McClosky, D. (2014). The Stanford
CoreNLP natural language processing toolkit. In Pro-
ceedings of 52nd Annual Meeting of the ACL, pages
55–60.
McClosky, D., Charniak, E., and Johnson, M. (2010). Auto-
matic domain adaptation for parsing. In Human Lan-
guage Technologies: The 2010 Annual Conference of
the North American Chapter of the ACL, HLT ’10,
pages 28–36, Stroudsburg, PA, USA.
Moschitti, A. (2006). Making tree kernels practical for nat-
ural language learning. In In Proceedings of the 11th
Conference of the European Chapter of the ACL.
O’Connor, B., Stewart, B. M., and Smith, N. A. (2013).
Learning to extract international relations from politi-
cal context. In Proceedings of the 51st Annual Meet-
ing of the ACL, pages 1094–1104, Sofia, Bulgaria.
Ravi, S., Knight, K., and Soricut, R. (2008). Automatic pre-
diction of parser accuracy. In Proceedings of the 2008
Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Lan-
guage Processing, pages 887–896, Honolulu, Hawaii.
Rosenfeld, B. and Feldman, R. (2007). Using corpus statis-
tics on entities to improve semi-supervised relation
extraction from the web. In ACL 2007, Proceedings
of the 45th Annual Meeting of the ACL, June 23-30,
2007, Prague, Czech Republic.
Roux, J. L., Foster, J., Wagner, J., Samad, R., Kaljahi, Z.,
and Bryl, A. (2012). DUC-Paris13 systems for the
SANCL 2012 shared task.
Sarikaya, R., Gravano, A., and Gao, Y. (2005). Rapid
language model development using external resources
for new spoken dialog domains. In International
Congress of Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing
(ICASSP), pages 573–576, Philadelphia, PA, USA.
IEEE, Signal Processing Society.
Tetlock, P. C. (2007). Giving Content to Investor Sentiment:
The Role of Media in the Stock Market. The Journal
of Finance.
Whissel, C. M. (1989). The dictionary of affect in lan-
guage. Emotion: Theory, Research, and Experience,
39(4):113–131.
Wolodja Wentland, Johannes Knopp, C. S. and Hartung, M.
(2008). Building a multilingual lexical resource for
named entity disambiguation, translation and translit-
eration. In (ELRA), E. L. R. A., editor, Proceedings of
the Sixth International Language Resources and Eval-
uation (LREC’08), Marrakech, Morocco.
Xie, B., Passonneau, R. J., Wu, L., and Creamer, G. (2013).
Semantic frames to predict stock price movement. In
Proceedings of the 51st Annual Meeting of the ACL,
pages 873–883, Sofia, Bulgaria.
KDIR2014-InternationalConferenceonKnowledgeDiscoveryandInformationRetrieval
520
