
PEGASO Fit for Future
Renata Guarneri and Giuseppe Andreoni
Politecnico di Milano – Design Dept., Via Durando 38/A, 20158 Milano, Italy
{mariarenata.guarneri, giuseppe.andreoni}@polimi.it
Abstract. Challenging teen-agers in their own fields and areas of interest,
PEGASO – Fit 4 Future - aims at promoting a sustainable behavior change
towards healthy lifestyles, with a holistic and multidisciplinary approach.
PEGASO is based on a mobile, social and networked gaming platform,
considered as a powerful tool to actively engage the younger population in
activities that will stimulate healthier choices in their daily lives to counterfeit
sedentariness, overweight up to obesity. To support this action, in the platform,
represented by the smartphone, three main functionalities are implemented: an
individual & environmental monitoring through wearable devices, a feedback
system for providing a feedback in terms of “health status” changes, the Social
connectivity and engagement to support motivation.
1 Overview and Rationale
The rapidly increasing prevalence of overweight and obesity among children and
adolescents reflects a global ‘epidemic’ worldwide. Recently the US Center for
Disease Control and Prevention has evidenced that “Childhood obesity has more than
doubled in children and quadrupled in adolescents in the past 30 years.”[1, 2].
Fig. 1. The WHO web page on the priority to overweight and obesity prevention in children
(last accessed march 18, 2015).
Andreoni G. and Guarneri R.
PEGASO Fit for Future.
DOI: 10.5220/0006156800770096
In European Project Space on Computational Intelligence, Knowledge Discovery and Systems Engineering for Health and Sports (EPS Rome 2014), pages 77-96
ISBN: 978-989-758-154-0
Copyright
c
2014 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
77

Also WHO recognized prevention of juvenile overweight and obesity as a priority
for future health being in 2014 and in the WHO European region 1 on 3 11-years old
children in this condition.
The following histogram represents the dramatic situation and dimension of the
problem at European and worldwide level.
Fig. 2. Measured overweight (including obesity) among children aged 5-17 in 2010 or nearest
year.
Due to the associated serious medical conditions, it is estimated that obesity
already accounts for up to 7% of healthcare costs in the EU, as well as costs to the
wider economy associated with lower productivity, lost output and premature death.
Obesity in younger age groups has been recognized as an alarming key predictor for
obesity in adulthood, but also entails a number of short term health complications in
juvenile age such as hypertension, type 2 diabetes, metabolic syndrome, fatty liver
disease, sleep disturbances along with greater risk of social and psychological
problems [3, 4].
78
EPS Rome 2014 2014 - European Project Space on Computational Intelligence, Knowledge Discovery and Systems Engineering for Health
and Sports
78

Sedentariness and over-consumption of high calorie foods and beverages are a
priori determinants of overweight/obesity and poor health status also in adolescents,
according to well-grounded evidences.
“Prevention is of obvious importance and there is an urgent need for further
research into how physical activity and training, in addition to nutrition, can
prevent the steadily increasing average body mass index of Europeans. This
proposal includes a vision that integrates a lifestyle of healthy habits with an
environment that promotes healthy living by encouraging exercise and making
healthy food affordable.” (Visions for Horizon 2020) [3].
Healthy lifestyle habits, including healthy eating and physical activity, can lower the
risk of becoming obese and developing related diseases. The dietary and physical
activity behaviors of children and adolescents are influenced by many sectors of
society, including families, communities, schools, child care settings, medical care
providers, faithbased institutions, government agencies, the media, and the food and
beverage industries and entertainment industries.
2 Methodological Approach and Concept of the PEGASO Project
Juvenile obesity is a complex disorder with many interrelated consequences.
Addressing the obesity issues requires a comprehensive approach taking into account
the individual's physical-physiological characteristics, personality as well as the
social and psychological environments influencing decisions and habits in their
everyday life. Challenging teen-agers in their own fields and areas of interest,
PEGASO – Fit 4 Future - aims at promoting a sustainable behavior change towards
healthy lifestyles, with a holistic and multidisciplinary approach. The approach of
PEGASO is based on three level of intervention enabling teen-agers to become co-
producers of their wellbeing:
1. Generating self-awareness (acknowledgement of risks associated to unhealthy
behaviors),
2. Enhancing and sustaining motivation to take care of their health with a
short/medium/long term perspective,
3. Changing behavior towards a healthy lifestyle based on healthy diet and adequate
physical activity.
In order to achieve the above targets PEGASO applies behavior change techniques to
prevention and will develop a mobile-based Behavior Change Platform that can
effectively address teen-agers.
The solution proposed by PEGASO comes from the convergence of the need to
address through appropriate preventative measures the rapidly increasing prevalence
of obesity among children and adolescents on one side and the rapid development of
ICT, and in particular mobile technologies, together with their increasing diffusion
among the EU population, on the other side.
Indeed the capabilities of ICT technologies (i.e. mobile phones, digital tablets)
together with the possibility to integrate them with the new and fashionable additional
technologies for data acquisition (e.g. wearable sensors) offer the opportunity to
develop an effective behavior change platform. The solution proposed by PEGASO is
79
PEGASO Fit for Future
79
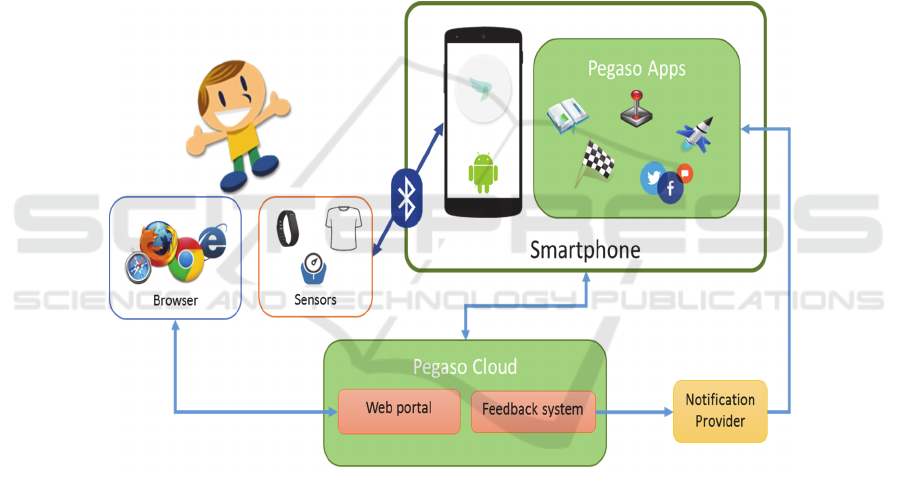
therefore based on a mobile, social and networked gaming platform, considered as
a powerful tool to actively engage the younger population in activities that will
stimulate healthier choices in their daily lives.
From the technology point of view, cloud computing, and convergence towards
mobile are the key enablers.
The central element of the PEGASO platform is the smartphone. Europe‘s
smartphone penetration is already amongst the highest in the world, with projections
indicating a target of 55% in 2015. The smartphone indeed offers unique
characteristics that ensure to achieve a cost-effective and scalable solution and may
favour its adoption by the target audience.
In addition to the smartphone, wearable sensors - that can be added with a
modular approach and a cloud based service offering based on a behavior and
situation recognition system - represent the basic elements of the PEGASO platform
architecture.
The Figure 3 provides an overview of the PEGASO architecture.
Fig. 3. Key elements of PEGASO architecture and their inter-relations.
2.1 PEGASO Key Functions
The PEGASO system framework is addressing prevention, by offering to teenagers –
the primary target of PEGASO - three main functionalities:
1. Individual & Environmental Monitoring - This dimension consists of the
environmental, behavioral and physiological analysis of young users, through a
high level-monitoring platform including wearable sensors and mobile phone as
80
EPS Rome 2014 2014 - European Project Space on Computational Intelligence, Knowledge Discovery and Systems Engineering for Health
and Sports
80
well as multimedia diaries for the acquisition of physical, behavioral and
emotional attitude of adolescent.
2. Feedback System - This second functionality is aimed at providing a feedback in
terms of “health status” changes, required actions to undertake and so on. This
function will also propose personalized healthy modification of the lifestyle (in
terms of diet and/or physical activity), thus promoting the active involvement of
adolescents in changing their behaviors.
3. Social Connectivity and Engagement - The third dimension extends to include a
social network where the user can share experiences with a community of peers
concerning e.g. physical activity, food consumptions and everyday habits through
different gaming strategies.
PEGASO has adopted a User Centred Design approach (UCD) by considering the
target population (i.e. teenagers) at the centre of the system in a palingenetic process
[5]. The UCD approach integrates three main elements: user involvement in all stages
of the problem solving process; multidisciplinary research and development team; and
iterative design process to refine the solution set. The main target users in PEGASO
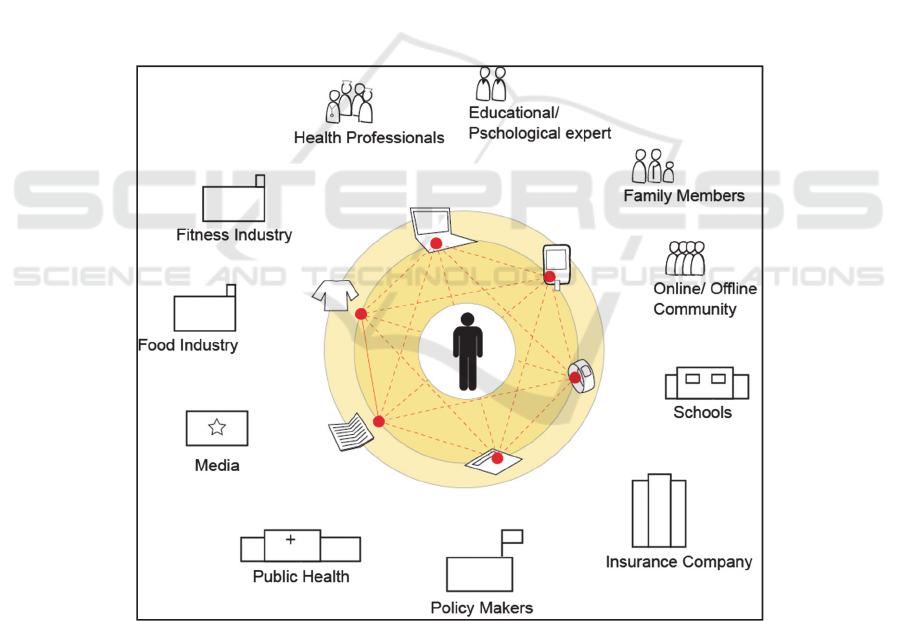
project are teenagers; however there are also several actors (who are also secondary
users – see Figure 4) and products (as shown by the inner circle in Figure 4) involved.
Fig. 4. PEGASO Stakeholders’ System.
The ecosystem of stakeholders and enablers is composed of three main parts that
are integrated in the user centred PEGASO system: technological frame (multimedia
81
PEGASO Fit for Future
81

diaries, embedded sensors systems, mobile & web platform), services frame
(stakeholders services to provide answers to users’ needs and desires in real time/not
real time, from the health companion to the serious gaming and social experiences)
and experts layer (which are knowledgeable groups of people from different
disciplines - medical/psychological/educational – able to interact with the system,
who provide them with filtered accurate and needed information to reach their
PEGASO objective).
Technological Frame. Teens are familiar with Internet, social networks, mobile
phones and apps, video gaming and, in general, with all the ICT platforms.
Smartphones also assures the highest level of technology acceptance. This key issues
are assumed as technological starting point to define the PEGASO architecture and to
define a successful strategy to empower the teen-agers awareness about healthy
lifestyle. The huge amount of personal and social exchanged and/or stored data
includes also health records, thus posing severe reliability and security requirements
that will be effectively managed through a cloud platform. Finally, PEGASO apps
and games from the software layer, as well as wearable sensor and other more
traditional systems (balance board for instance) complete the PEGASO technology
frame.
Services Frame. Social is the key word for service development: the services created
by stakeholders in PEGASO Project promote an individual and social healthier
lifestyle through motivating and engaging multiuser serious games. Nevertheless
individual support is provided both for data entry through multimedia apps that
simplify and engage the users (for instance through multimedia diary compilation or
through the health companion interaction). The health companion, developed by
PEGASO, constitutes the interface on the smartphone between the guidance system
and the teenager. All the stakeholders (including the Food Industry, Public and
Private Health Policy actors, Fitness industries, Media, Schools, and Insurance
companies) at different levels will offer to users the infrastructure to motivate (and
promote) the adoption a healthy behavior.
Experts Layer. in PEGASO motivation and engagement by means of gaming
strategies will be integrated with healthier lifestyle. All the information from the users
must be “handled” and processed and the corresponding feedback provided. This
means building an expert layer that is able to analyse all the data and deliver the
resulting answers to the teenagers. A part of this layer will be composed by automatic
algorithm (for real-time processing and feedback provision when applicable); a
second building block will be the experts’ team who will integrate the previous
assessment to better stimulate the teenagers’ consciousness about obesity and their
motivation to adopt a healthy lifestyle. The role of experts in PEGASO project is
assumed to be twofold: 1) to personalize information for each individual’s physical
and psychological models (i.e. personalized care) in order to reach the full acceptance
by each teenager and guarantee a correct interpretation; and 2) to follow up of each
teenager healthy status.
82
EPS Rome 2014 2014 - European Project Space on Computational Intelligence, Knowledge Discovery and Systems Engineering for Health
and Sports
82
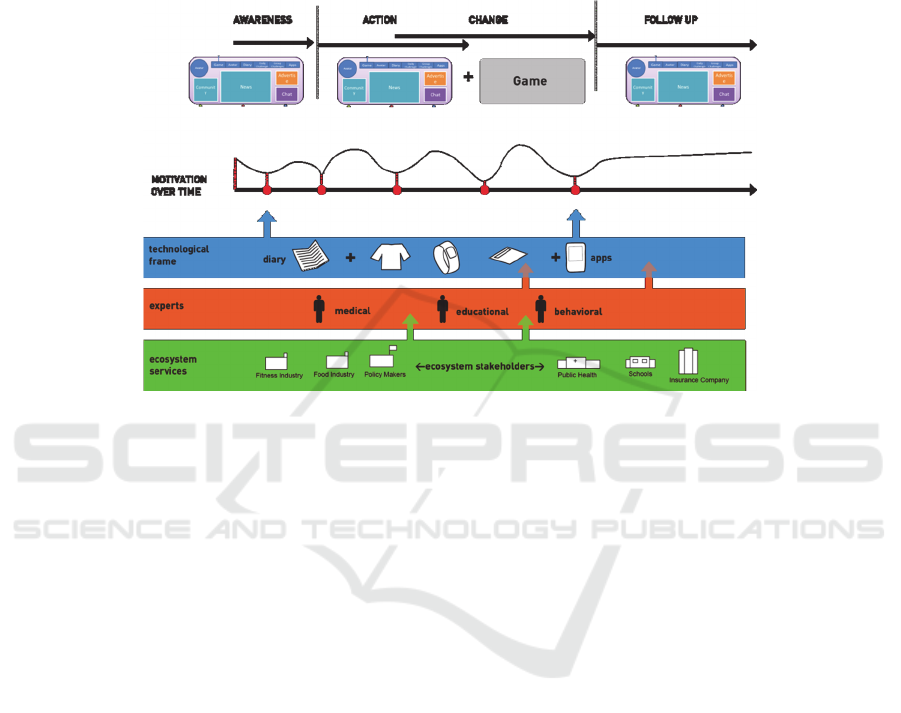
2.2 The Elements of Behavior Change
PEGASO considers four levels of engagement towards persuasion for user (the teen-
agers) empowerment in healthcare [6]: awareness of obesity risks, motivation,
affective learning and finally behavior change.
Fig. 5.
Various types of expertise / knowledge and technologies feed these levels of
engagement towards healthier lifestyle and empower the teen-agers to take decisions
accordingly.
Develop Awareness: teenagers need to be aware of what they are doing; what is right
and what is wrong for their healthy living. Some of them are unconsciously and
automatically acting, and often under estimate or have no clear notion about
information they receive. Monitoring lifestyle of teen’s activity, collecting parameters
and integrating their own data will enable self-awareness on their current situation.
Through developing self-awareness and self-reflection, the user can frame the
problem or the opportunity area to act upon or intervene.
Affective Learning is the “highest” learning goal. The learner should trust in
something that happens in several years. That is also a good argument in a new
“learning level” to use a constructivist learning model and special media like “social
games” are adequate to reach this goal. Giving teenagers information through tools
they are affectionate is a strategy to reach their behavioral change.
Create Motivation: it is important to motivate teenagers to change their behavior and
keep this activity in a long-term period. The actors in the ecosystem offer healthier
benefits and services in the users’ environment towards satisfying their needs or
desires.
This part is quite challenging, since the motivation depends on many factors as
well as emotions, psychological environment and personality of teens. The system
needs to provide constant different layouts of motivational activities where experts,
83
PEGASO Fit for Future
83

technological frame monitoring and stakeholders services come into the scene.
Enable Behavior Change: once teenagers have the awareness and the motivation, it
is important to involve experts and use PEGASO system to support the behaviour
change process and reinforce existing virtuous behaviors. The turn from old unhealthy
behaviors into healthier new ones has to be monitored through technology on a longer
period.
In order to create prevention, it is important to change or stop old unhealthy habits
and develop new healthier habits. In this respect, PEGASO takes a holistic approach
involving the teenager’s environment and specifically the families, by means of an
education process empowered by training that will be provided on location (schools)
and on line. The expert team will give feedbacks to the users allowing them to change
their behavior on a long-term basis. The overall system takes advantage of gaming
strategies to persuade users to change their behavior.
2.3 PEGASO Evaluation Strategy
PEGASO will be validated by secondary school students with the support of their
schools and families. The reason for involving these students as sample population
lies on the assumption that around the age of 14 years old the teen-agers acquire more
independency and have increasingly the opportunity to make own and independent
decisions. It is therefore important that at this stage they become aware of the
consequences of inappropriate, unhealthy lifestyles.
Four validation studies will be carried out in Italy (Lombardy), Spain (Catalonia)
and United Kingdom (England/Scotland).
The validation activities will assess the following aspects of the PEGASO
Behavior Change Platform:
‐ System and Technology acceptance, usability and long-term use: these will
constitute also a secondary assessment of motivation and engagement;
‐ Reliability in assessing the teen-agers lifestyles and their changes (with focus on
the eating habits and on physical activities) and related efficacy of the sensing
platform (i.e. smartphone and wearable sensors’ system);
‐ Efficacy of the system in encouraging lifestyle change;
‐ Subjective assessment for awareness;
‐ System’s compliance to Stakeholders’ needs.
Further studies are required, and are currently out of PEGASO’s scope, to be able to
evaluate the longer term outcomes of the intervention, and to perform in particular the
evaluation of the user risk awareness regarding the development of obesity and
related comorbidities, the evaluation of user environmental factors (family and
school), the potential harms and costs, all of them assessable involving the same
target groups few years after the project completion.
3 Activities and Results
PEGASO Fit for Future has been running for over a year, with the first year being
84
EPS Rome 2014 2014 - European Project Space on Computational Intelligence, Knowledge Discovery and Systems Engineering for Health
and Sports
84

dedicated mostly to the consolidation of requirements from the user viewpoint and the
general architecture of the platform.
3.1 The Comprehensive Virtual Individual Model
The PEGASO project aims at pushing this concept further introducing the feature of
dynamically selecting the opportune tailored interventions based on the user’s
individual characteristics and interaction context [7]. Tailoring the intervention
involves modeling the user’s characteristics and for this purpose it has been
developed the Virtual Individual Model, which comes from the concept of the Virtual
Physiological Human. The latter is a methodological and technological framework for
integrated modeling of a living human body that describes the interaction of all the
physiological components of individuals from molecular to apparatus level [8]. The
Virtual Individual Model aims to include individual’s characterization composed of
physiological, physical, and psychological determinants. This allows integrating
biological aspects of human functioning with lifestyle behaviors and psychosocial
externalities that are crucial for the determination of the adoption of a certain life-
style. This model is integrated in the system through an ontology-based virtualization.
This process allows turning the information contained in the Virtual Individual Model
into a structured knowledge that can be dynamically updated and elaborated by the
computer to select the best interventions for each individual. Tailored interventions
make the information personally relevant and researches demonstrated that computer-
tailored health education is more effective in motivating people to make dietary
changes [9] and that it could be also a good practice to promote physical activity [10].
3 Tailored Intervention Forms The Virtual Individual Model characterizes the user’s
nutritional habits, physical status, and psychological status to provide personalized
intervention to foster the adoption of a healthy life-style. Obviously, the interaction
between the system and the user plays a crucial role in the tailoring process and to
facilitate the effectiveness of the intervention. Since the teenagers are the targets of
the PEGASO project, the smartphone has been chosen as the mediator of the
interaction. Indeed, the smartphones are already perceived as a companion and it is
most likely that this relationship between user and smartphone will strengthen in the
future [11]. The smartphone is the perfect companion because it is personal and it is
ubiquitous. It will provide the possibility of interacting directly with the user asking to
enter some information or in a discreet and implicit manner allowing monitoring the
user activity. The sensed data referring to the parameters that concern the selected
characteristics modeled for the tailoring will be updated constantly in the Virtual
Individual Model. Moreover, with the many connection possibilities, the smartphone
can allow accessing the information stored in the cloud and can connect to other
devices, such as wearable accessories that can improve the physical activity
monitoring. Since it is ubiquitous, it can always provide the appropriate trigger, as
tailored messages, to influence the user’s behavior. This is very important, since Fogg
observed that “without an appropriate trigger, behavior will not occur even if both
motivation and ability are high” [6]. Moreover, the many sensors integrated in the
smartphone allow capturing the contextual information, which can help to generate
the trigger at the opportune moment maximizing its effectiveness. Moreover, the
smartphone allows installing many applications as media services and games that will
85
PEGASO Fit for Future
85

motivate the teenagers to interact with the system. The mobile game will be designed
to promote physical exercise. The integration with social networks will add the social
aspect of the users’ life to the parameters for the tailoring of the interventions and,
most importantly, the social factor represents a very effective motivator. Another
mobile application will be a sort of personal food diary, where the user will be able to
note his/her alimentary behavior. This diary will help to understand the alimentary
behavior of the user in order to provide the right feedback. For example, some data
suggest that breakfast consumption is associated with higher intakes of
micronutrients, fruit and vegetables and less frequent use of soft drink [12]. This
means that the breakfast consumption habit can help to adopt a healthy dietary
behavior. The diary allows following this behavior and to intervene through an alarm
in order to remind to the teenager to have breakfast. The eating behavior is not only
related to homeostatic reasons. In fact, an important factor that influences people’s
need and choice of food is represented by the emotional state [13]. The diary will
allow noting also the mood in order to include the emotional state in the recognition
of behavioral patterns. In fact, this information can be used to find some specific
behavioral pattern related to emotional eating in order to generate the best
intervention.
The introduction of biological models empowering technological actions for the
promotion of citizen's health and well-being is considered to lead to a higher user
centricity producing a more individualized strategy of health management and a
stronger empowerment and engagement of the user [14].
The concepts supporting the PEGASO Virtual Individual Model (VIM) stem from
a background of European experiences based on the vision of the individual as a
unique multiple organ system, overtaking the traditional approach - in force in the
medical practice - of the human body as a set of independent sections. The current
modelling of a living human, such as the Physiome model [8], relies on different body
functions incorporating knowledge from several biological disciplines and converges
into a holistic integrative architecture. However, such an approach does not account
for the behavioral and social externalities, which are known to interfere with and
determine the biological balance of functions in health and disease.
By contrast, the PEGASO VIM's ambition is to provide a definition of individual's
characteristics relevant for the condition of overweight/obesity, including both
biological specifications and alimentary and exercise behavior factors, along with
their psycho-social drives, specifically analyzed for young people, in a defined age
range of 13-16. To this aim, the contribution of experts from different Europe
countries has been integrated into a comprehensive view joining competences
including medical, exercise physiology and nutritional knowledge, together with
psycho-social expertise.
The PEGASO VIM overall structure is depicted in Figure 6 and considers the
individual's health and well-being as resulting from the balance between components
of physical, functional and psycho-social domains, according to the World Health
Organization founding definition [15].
The model is based on elements relevant for overweight/obesity among
adolescents. It considers health and well-being as primarily settled on a balance
between physical body structure, body functionalities and psycho-social factors
which, on turn, influence dietary and exercise behaviors and their possible changes.
Alimentary and physical activity habits are key life-styles for preserving good
86
EPS Rome 2014 2014 - European Project Space on Computational Intelligence, Knowledge Discovery and Systems Engineering for Health
and Sports
86
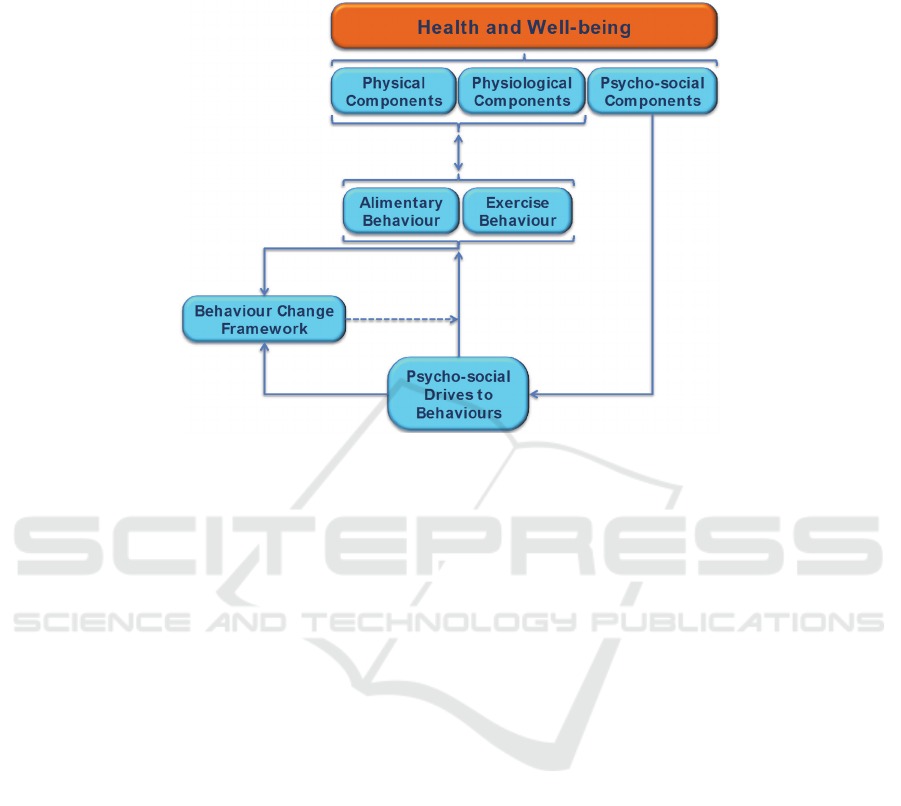
physical conditions and a well-functioning organism.
Fig. 6. Overall PEGASO Virtual Individual Model.
Dietary and physical activity behaviors are important life-styles affecting health
and well-being through the preservation of optimal physical conditions and functional
order. The model thus involves also concepts related to behavioral and psycho-social
domains which are only partially covered by current vocabularies and ontologies.
Since healthy life-style awareness, motivation and engagement among adolescents are
the principal objectives of the PEGASO system, a particular emphasis is given in
VIM to the aspects related to behavior change strategies and their relation with
psycho-social components driving alimentary and exercise behaviors, especially if
liable to be modified.
It is important to consider the psychosocial aspects of overweight and obesity in
adolescents because problems associated to these aspects (E.g. peer pressure, low
confidence, low self-esteem, depression and attitudes towards food) are likely to have
an impact upon their lives and contribute towards differences in physical activity
patterns and weight fluctuations. The following sections describe the social and
psychological aspects of obesity in adolescents, using a behavioral model based on
the analysis of Capability, Opportunity and Motivation as main components of
behavior (COM-B). Where relevant in relation to the target behaviors selected for
PEGASO adolescents, examples will be given with details.
At the core of the Virtual Individual Model analysis of behaviors is a
psychological model of human behavior incorporating the psychological components
associated with behavior change. COM-B components are applicable to all human
behaviors and are the starting point for developing new behavior change
interventions. Each component in the COM-B model directly influences behavior, and
interacts with the other components. In combination they can provide the rationale for
why the target behavior is not engaged in, and this then identifies the appropriate
87
PEGASO Fit for Future
87
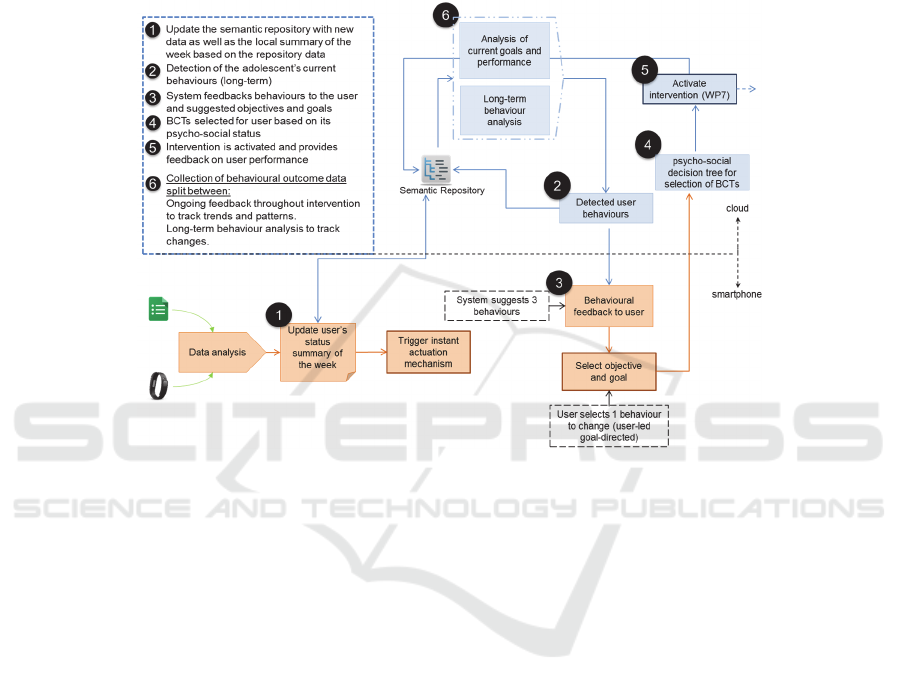
components to be addressed to bring about a change in that behavior. In this way all
the components of the COM-B model are interdependent, and work in unison to help
change a target behavior, or support the maintenance of a target behavior once an
individual has adopted it into their regular pattern of behavior. Each component of the
COM-B model is divided into sub-components which are used to capture the more
refined details of the COM-B components that are specific to the target behavior.
Fig. 7. The functional flow-chart of the PEGASO intervention.
Designing the PEGASO products and service systems the co-design methodology
was adopted as key strategy. This is relevant for the specific target population to
achieve high acceptance and compliance.
Smartphone, Wearable sensors and Multimedia Diaries have been categorized as
sensors of the PEGASO system, and their acceptance and use by the end-user is the
first essential requirement for the project success. Together with the sensors two other
main fundamental categories constitute the PEGASO system architecture: the Social
level of the platform, and the gamification of teens’ life.
In this project, Social Network is intended as the creation of a social community
that shares the same objective, i.e. healthy lifestyle habits. The End-User
requirements aimed at retrieving opinion about the Information Sharing, in particular
what teenagers want to share, people they’d prefer to be connected with, how they
would like to share those information (feedback system and notification)
Finally, the Social platform represents also the gamification of teens’life and the
role of experts is to monitor results from physiological data and to send specific
feedback information on the health status of the user through the Health Companion.
Schools play a particularly critical role by establishing a safe and supportive
environment with policies and practices that support healthy behaviors. Schools also
provide opportunities for students to learn about and practice healthy eating and
88
EPS Rome 2014 2014 - European Project Space on Computational Intelligence, Knowledge Discovery and Systems Engineering for Health
and Sports
88
physical activity behaviors. For this reason we involved and collaborated with schools
in organizing the focus groups and recruiting teenagers in the user requirements
definition phase. 16 focus groups in three nations were carried out with about 200
teenagers to gather this information and to iteratively design services and devices,
according to the identified directions of PEGASO interventions.
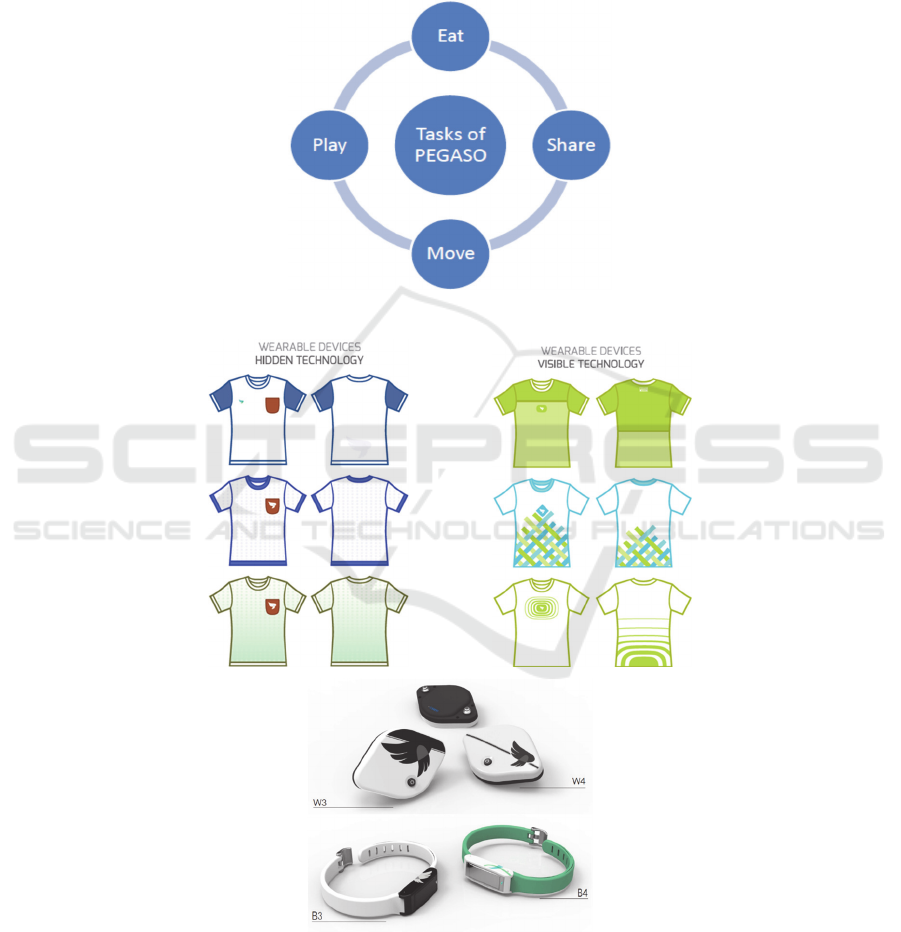
Fig. 8. PEGASO interventions assets.
Fig. 9. The prototypes of garments and wearable devices.
89
PEGASO Fit for Future
89
This is a sort of life compass that the PEGASO project aims at helping teenagers
to build, through a positive message and tool dedicated to teenagers, for improving
their lives. The identified 4 pillars/directions are: a) move, i.e. the adoption of an
active lifestyle, b) play, i.e. the serious game sustains engagement and motivation in
the choice, c) eat, i.e. food education and pleasure, and d) share, a community and
social approach to mutually engage in the actions.
The initial systems have been designed and prototyped and are currently
undergoing pre-pilot tests.
A key feature is the PEGASO companion. The smart companion is a Personal
Digital “Friend” acting as a daily-life guide for Coaching, Caring for, and
Empowering teenagers in their activities toward healthy habits. From this definition
the companion has multiple facets fostering behavior change.
• Digital: the companion exists in the smartphone
• Personal: the companion is customized to the single user
• Friend: the companion would establish an affective relationship with the user
• Daily-life guide: the companion accompanies the user (coaching, caring and
empowering) during her daily activity
• Toward healthy habits: supporting behavior change to promote healthy lifestyles
is the main goal of the companion and PEGASO project in general
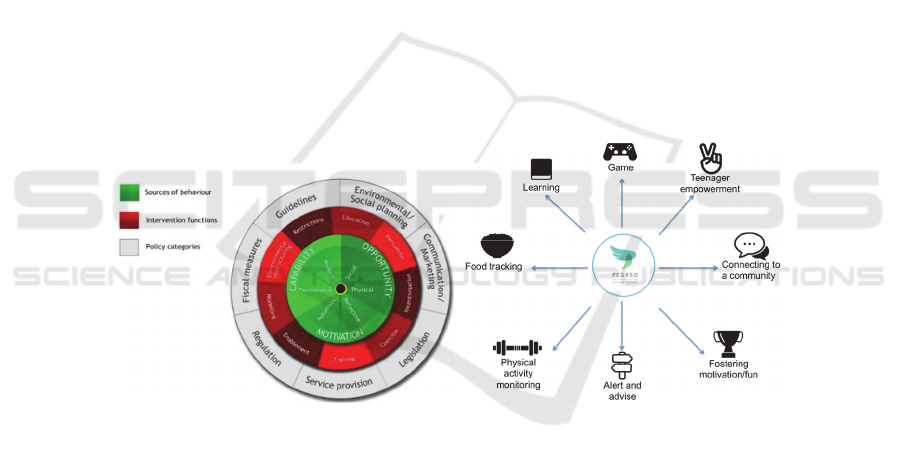
Figure 10 highlights the most relevant services that the companion, represented by the
circle in the center, should offer to the user in relation to the COM-B model.
Fig. 10. The reference COM-B model and related services for Companion design.
The main goal of the Companion is to support teenagers’ behavior change
increasing Capacity, Opportunity and Motivation to achieve a set of target behaviors.
As we can see from the previous definition, the COM-B model of behavior is at
the base of the design of the companion. In particular, the target behaviors have been
selected in collaboration with PEGASO experts and taking into account the results of
the focus groups. The selected target behaviors are:
• Physical activity: 10.0000 steps, 60 minutes of physical activity per day,
Community sports teams, School sports teams, Screen viewing duration, Sleep
duration & quality, Walk or cycle to school;
• Alimentation: Breakfast eating, Fruit consumption, Vegetable consumption, Sugar
sweetened drinks.
90
EPS Rome 2014 2014 - European Project Space on Computational Intelligence, Knowledge Discovery and Systems Engineering for Health
and Sports
90

Fig. 11. The first conceptualization of the PEGASO Companion.
Fig. 12. The first draft PEGASO Companion.
4 Conclusions and Expected Impact
PEGASO believes that we are at a key turning point in the history of the Internet.
Convergence of major trends is occurring which is driving changes in people behavior
and expectations. These trends include the exponential rise in use of smartphones and
91
PEGASO Fit for Future
91

tablets, increased Internet access speeds, new business models driven by online
commerce and app stores, the impact of social online communication, and software
delivery transitioning from prior PC/internet models to cloud-based services accessed
with touch-based devices (smartphones and media tablets).
With more than five billion mobile users worldwide and a massive global
network, for the first time in history mobility is attracting significant attention among
the healthcare and life sciences community.
Integrating mobility, gamification and life science has the potential to motivate
individuals to adopt healthy lifestyles, with personalization techniques and incentives
that will be delivered through the PEGASO system.
The following key issues however have to be adequately addressed and are at the
center of the PEGASO rationale:
‐ Knowledge of how to stay healthy is ubiquitous; however, obesity and lifestyle-
related illness are still among the top healthcare challenges in Europe.
‐ Although clinical content and health information have been available through the
Internet for years, there has been no improvement in overall health in Europe.
‐ Motivating individuals to change behavior is not just a clinical issue. Successful
programs include incentives along with personalized programs and, increasingly,
the inclusion of behavioral science.
‐ Gamification has emerged as a recognizable trend that can have a significant
positive impact on all businesses and is yet to be leveraged by wellness and
healthcare.
‐ Because gamification's goal is to change human behaviors, PEGASO as a
wellness player will confront both opportunities and risks, requiring a clear vision
of the value of the system.
The strategy proposed by PEGASO, based on behavior changes, is expected to have
favorable effects in reducing overweight/obesity and associated diseases and social
costs in proportion to the national prevalence of body mass excess in this age class
taking advantage of the possibilities offered by innovative ICT and of teens’ affection
to mobile and social network.
4.1 Enhancing Self-awareness of Younger People for Health Issues, by
Means of Inclusive Approach Integrating Individuals into a
Community Context, and Promoting Behavioral Changes in Favour
of Physical Activity and Healthy Diets
Recommendations specific for children and young people have been released in 2005
also by the Commission of European Communities in the Green Paper on healthy
diets and physical activity for the prevention of obesity among EU citizen [16].
Reducing the risks deriving from unhealthy diets and physical inactivity and
increasing awareness and understanding of the influences of diet and physical activity
on health are the core objectives of the global strategy dictated by the World Health
Organization (WHO) against non-communicable disease and changes in behavior has
been indicated by WHO among the outcome indicators for assessing actions
fostering such a global strategy [17, 18]. The relationship between diet, physical
92
EPS Rome 2014 2014 - European Project Space on Computational Intelligence, Knowledge Discovery and Systems Engineering for Health
and Sports
92

activity and health is based on strong scientific evidence. Studies using motion
sensors have shown that children who spend less time in physical activity are at
higher risk to become obese during childhood and adolescence [19, 20]. Television
and video games contribute to more sedentary leisure activities and are reported to
favour concurrent consumption of energy-dense snacks and beverages [21]. In the
greatest majority, behavioral aspects related to lifestyle and diet (with a relevant
interference of socioeconomic factors) play an important causative role. The findings
from the 2009/2010 survey in EU countries from Health Behavior in School-aged
Children (HBSC) international report indicate that young people who are
overweight/obese are more likely to exhibit unhealthy alimentary patterns, are less
physically active and watch television more [22].
4.2 Preventing Juvenile Overweight/Obesity and Reducing Morbidities
Associated to Juvenile Overweight/Obesity in the Short Time, and
Long Term Health Consequences, including Adult Obesity, and
Associated Medical, Social and Personal Costs
According with the 2007 report of the EU Public Health Program Project "Global
Report on the Status of Health in the European Union - EUGLOREH", the number of
EU children affected by overweight and obesity is estimated to be rising by more than
400,000 a year, adding to the over 14 million of the EU population who are already
overweight (including at least 3 million obese children) [23]. Overall, across the
entire EU, overweight affects almost 1 out of 4 school age children/adolescents.
Childhood obesity has physical, psychosocial and economic consequences.
Overweight and obesity in the juvenile age are associated with a number of serious
medical conditions such as sleep-related breathing disorders and asthma, fatty liver
disease, poor glucose tolerance, increased risk of non-insulin-dependent diabetes,
hypertension, and can lead to increased rates of non-communicable disease in
adulthood such as cerebro-vascular disease, diabetes, certain types of cancer,
osteoarthritis, gall bladder and endocrine disorders, in relation with the high
probability for obese children to become obese adults [24]. Recent estimates indicate
that more than 27 000 children in the EU have type 2 diabetes and more than 400.000
have impaired glucose tolerance. About 1.1 million suffer from hypertension and 1.2
million suffer from metabolic syndrome (consisting in a clustering of hypertension,
abnormalities of lipid metabolism, and raised blood glucose levels)[23]. Moreover,
body mass excess in the juvenile age leads to low self-esteem, depression and social
exclusion, with immediate consequences in the psychological and social domain,
possibly leading also to concurrent or subsequent psychiatric pathology. Specifically,
social exclusion in childhood has been associated with reduced psychological
functioning in adulthood [19].
4.3 Reducing Medical, Social and Personal Costs Associated to Juvenile
and Adult Overweight/Obesity
The economic impact of overweight and obesity on health care and social systems is
definitely sizable. Such an economic burden has been recognized in terms of direct
93
PEGASO Fit for Future
93

medical costs (including preventive, diagnostic, and treatment services related to
obesity), indirect costs (attributable the value of income lost from decreased
productivity, restricted activity, absenteeism, and bed days), and intangible costs
(which can be referred to as the social and personal costs or losses associated with
obesity) [25, 26]. In recent years, health costs deriving from obesity among adults in
different Western European countries have been conservatively estimated to amount
up to over 10 billion Euros with relative economic burdens ranging from 0.20% to
0.61% of each country's gross domestic product [25]. A fairly higher economic load,
although scarcely definable with accuracy, can be considered to arise from the impact
of obesity on the wider economy in terms of loss of productivity [26]. It is even more
difficult to estimate the overall cost of obesity among children and young people. In
the perspective of health care costs, in fact, it has been assessed that overweight and
obese children exhibit significantly higher expenditures for outpatient visits, drug
prescriptions, and emergency room admissions, and have a higher probability of
being high utilizers of health care services [27]. Additionally, in the personal context,
it has determined by different studies that individuals who were obese, as adolescents
become adults with lower educational attainment, earning less money, experiencing
higher rates of poverty and having a lower likelihood of marriage, compared with
thinner peers [28]. Furthermore, as childhood obesity is a risk factor for adult
diseases, mortality costs in terms of the value of future income lost by premature
death in adulthood, should be considered.
4.4 Developing a System Suitable for Interventions based on Equity and
Inclusivity
The PEGASO system, integrating state of the art technologies within an holistic
approach including social and human aspects, fully complies with WHO guidelines
indicating the priority of comprehensive and coordinated multiple-strategy
interventions across the whole population promoting behavioral changes in favor of
physical activity and healthy diets in order ensue an effective obesity prevention in
childhood [4]. An increased prevalence of overweight/obesity is also significantly
associated with low family affluence [23]. The principles of the intervention included
in the present proposal, based on a "virtual individual" model considering as basic
features also social status and social behaviors, are in accordance with the main
outcomes from the 2009/2010 HBSC report recommending to address not only health
and health behavior issues, but also the social context in which young people live,
providing equal opportunities for all [22].
4.5 Providing a Transnational Opportunity for a Coordinated Effort to
Tackle a Transnational Issue
The transnational relevance of the growing prevalence of overweight/obesity among
younger population in industrialized and developing countries worldwide, prompt
also to an EU co-ordinated effort in research and industrial development to face such
an epidemic in member countries, which is another main feature entailed in the
present proposal. Indeed, the promotion of research for the prevention and control of
94
EPS Rome 2014 2014 - European Project Space on Computational Intelligence, Knowledge Discovery and Systems Engineering for Health
and Sports
94

non-communicable diseases (which include overweight/obesity) is one of the main
objectives recently focused by the WHO 2008/2013 Action Plan, proposing for
international partners the action of work jointly on "research on socioeconomic
determinants, lifestyle and behavior modification as well as community-based
interventions" [29].
Acknowledgements. This paper is based on the discussions and on the material
produced during the preparation and the activities of the PEGASO project to which
all project partners have contributed. The PEGASO project is co-funded by the
European Commission under the 7
th Framework Programme. PEGASO is part of the
cluster of projects in the ICT for health area, it has started in December 2013 and will
run for 42 months.
The authors wish to thank all the project partners for their contribution to this
work.
References
1. Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Kit BK, Flegal KM. Prevalence of childhood and adult obesity in
the United States, 2011-2012. Journal of the American Medical Association 2014; 311(8):
806-814.
2. National Center for Health Statistics. Health, United States, 2011: With Special Features on
Socioeconomic Status and Health. Hyattsville, MD; U.S. Department of Health and Human
Services; 2012.)
3. Visions for Horizon 2020 - Copenhagen Research Forum, 2012.
4. World Health Organization. Population-based prevention strategies for childhood obesity:
report of a WHO forum and technical meeting, Geneva, 15–17. December 2009.
5. Sanders, E. B., (2002). From User-Centered To Participatory Design Approaches. Design,
1-7. Taylor &Francis.
6. Fogg, B.J., (2009). A Behavior Model for Persuasive Design, Proceedings of the 4th
International Conference on Persuasive Technology Persuasive 09, ISBN: 9781605583761.
7. Caon M, Carrino S, Guarnieri R, Andreoni G, Lafortuna CL, Abou Khaled O, and
Mugellini E. A Persuasive System for Obesity Prevention in Teenagers: a Concept. Second
International Workshop on Behavior Change Support Systems (BCSS 2014) pp 17-20,
http://ceur-ws.org/Vol-1153/Paper_2.pdf)
8. Fenner JW, Brook B, Clapworthy G, Coveney PV, Feipel V, Gregersen H, Hose DR, Kohl
P, Lawford P, McCormack KM, Pinney D, Thomas SR, Van Sint Jan S, Waters S,
Viceconti M. The EuroPhysiome, STEP and a roadmap for the virtual physiological human.
Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2008; 366: 2979-2999.
9. Brug J., Oenema A., and Campbell M., Past, present, and future of computer-tailored
nutrition education., Am. J. Clin. Nutr., vol. 77, no. 4 Suppl, p. 1028S–1034S, Apr. 2003.
10. den Akker HO, Moualed LS, Jones VM, and Hermens HJ, A self-learning personalized
feedback agent for motivating physical activity, Proc. 4th Int. Symp. Appl. Sci. Biomed.
Commun. Technol. - ISABEL ’11, pp. 1–5, 2011.
11. Carrino, S., Caon, M., Abou Khaled, O., Andreoni, G., Mugellini, E. (2014). PEGASO:
Towards a Life Companion, in the Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on
Human-Computer Interaction, 22 - 27 June 2014, Heraklion, Crete, Greece.
12. Merten MJ, Williams AL, Shriver LH. Breakfast consumption in adolescence and young
adulthood: parental presence, community context, and obesity. Journal of the American
Dietetic Association, 2009, 109(8):1384-1391
13. C. Science, A. Kapoor, P. Johns, K. Rowan, E. A. Carroll, M. Czerwinski, and A.
95
PEGASO Fit for Future
95

Roseway, “Food and Mood : Just-in-Time Support for Emotional Eating,” ACII2013, pp.
252–257, 2013.
14. Honka A, Kaipainen K, Hietala H, Saranummi N. Rethinking Health: ICT-Enabled
Services to Empower People to Manage Their Health. IEEE Rev Biomed Eng. 2011; 4
:119-139.
15. World Health Organization, 1948. Preamble to the Constitution of the World Health
Organization as adopted by the International Health Conference, New York, 19-22 June,
1946; signed on 22 July 1946 by the representatives of 61 States (Official Records of the
World Health Organization, no. 2, p. 100) and entered into force on 7 April 1948. Available
at: http://www.who.int/about/definition/en/print.html.
16. Commission of European Community. Green Paper - Promoting healthy diets and physical
activity: a European dimension for the prevention of overweight, obesity and chronic
diseases. COM(2005) 637, Brussels, December 2005.
17. World Health Organization. Global Strategy on Diet, Physical Activity and Health, Geneva,
2004.
18. World Health Organization. Global Strategy on Diet, Physical Activity and Health. A
framework to monitor and evaluate implementation, Geneva, 2006.
19. Consensus statement: Childhood Obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005; 90: 1871-87.
20. Lobstein T et al. Obesity in children and young people: a crisis in public health. Obes Rev.
2004; 5 Suppl 1:4-104.
21. Rey-López JP et al. Food and drink intake during television viewing in adolescents: the
Healthy Lifestyle in Europe by Nutrition in Adolescence (HELENA) study. Public Health
Nutr. 2011;14(9):1563-9.
22. Currie C et al. eds. Social determinants of health and well-being among young people.
Health Behavior in School-aged Children (HBSC) study: international report from the
2009/2010 survey. Copenhagen, WHO Regional Office for Europe, 2012 (Health Policy for
Children and Adolescents, No. 6).
23. EUGLOREH2007 project The Status of Health in the European Union: Towards a
Healthier Europe, available at: http://euglorehcd.eulogos.it
24. World Health Organization. Obesity: Preventing and Managing the Global Epidemic.
Report of a WHO Consultation. WHO Technical Report Series no. 894. WHO: Geneva,
2000.
25. Müller-Riemenschneider F et al. Health-economic burden of obesity in Europe. Eur J
Epidemiol. 2008; 23: 499-509.
26. Dent M. The economic burden of obesity. Oxford: National Obesity Observatory, 2010.
27. Trasande L & Chatterjee S. The impact of obesity on health service utilization and costs in
childhood. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2009; 17: 1749-54.
28. Gortmaker SL et al. Social and economic consequences of overweight in adolescence and
young adulthood. N Engl J Med 1993; 329: 1008–1012.
29. World Health Organization. 2008-2013 Action plan for the global strategy for the
prevention and control of noncommunicable diseases. Geneva, 2008.
96
EPS Rome 2014 2014 - European Project Space on Computational Intelligence, Knowledge Discovery and Systems Engineering for Health
and Sports
96
