
Action Preparation and Replanning in Manipulation
Hisashi Hayashi
1
and Hideki Ogawa
2
1
Corporate Research & Development Center, Toshiba Corporation, 1 Komukai-toshiba-cho, Saiwai-ku, Kawasaki, Japan
2
Corporate Manufacturing Engineering Center, Toshiba Corporation, 33 Sin-isogo-cho, Isogo-ku, Yokohama, Japan
Keywords:
Speculative Action Preparation, Replanning, Manipulation, Robotics.
Abstract:
In order to pick (place) a target object from (on) a shelf, a service robot moves to the front side of the shelf,
removes obstacles, and reaches out a hand. If the robot prepares for the next arm manipulation while moving
to the shelf, it is possible to save time for plan execution. The robot also needs to replan if, for example, a
person removes obstacles for the robot. After replanning, the robot might need to suspend the current action
execution or next action preparation before executing the updated plan. This paper introduces a method to
integrate planning, action execution, speculative next action preparation, replanning, and action suspension
based on Hierarchical Task Network (HTN) planning. We also show that this method is effective for pick-and-
place manipulation in dynamic environments.
1 INTRODUCTION
Pick-and-place manipulation in dynamic environ-
ments is an important research theme in robotics.
Typically, a service robot moves around the environ-
ment, picks an object from a shelf, and places the ob-
ject on the target shelf. The robot needs to use a right
or left hand to pick or place the object without colli-
sion with obstacles or removes the obstacles before-
hand.
In order to implement service robots of this
type, combinations (Cambon et al., 2009; Choi and
Amir, 2009; Haspalamutgil et al., 2010; Hauser and
Latombe, 2009; Kaelbling and Lozano-Perez, 2010;
Wolfe et al., 2010) of a high-level general-purpose
task planner and a low-level motion planner such as
RRT (LaValle and Kuffner, 2001) have played impor-
tant roles. Given a manipulation task, the high-level
task planner decides which object to move and where
to bring the object. The low-level motion planner con-
trols the arm, considering kinematic constraints and
geometric map information. Manipulation planning
“among movable obstacles” is also implemented by
combinations (Nieuwenhuisen et al., 2008; Ota, 2009;
Stilman et al., 2007; Zacharias et al., 2006) of a high-
level algorithm and a low-level motion planner.
A typical task plan is “move to table1”, “pick ob-
ject1”, “move to table2”, and “place object1”. The
execution times of these actions are long. In order to
shorten the execution time of the plan, it is effective
to move an arm while moving to a shelf and prepare
for the next pick (or place) action.
On the other hand, a service robot working in the
real world needs to replan when the environment un-
expectedly changes. For example, before the robot
removes an obstacle, a person might remove it for the
robot before the robot arrives in front of the shelf. In
this case, the robot no longer needs to remove the ob-
stacle. Therefore, the robot needs to replan and cancel
the action preparation for removing the obstacle.
In order to adapt to a dynamic environment, we
understand that replanning is necessary. In addition,
the following new functions are necessary:
• Integration of action preparation and replanning;
• Suspension of preparing/executing actions.
In this paper, we extend an online Hierarchi-
cal Task Network (HTN) planning agent Dyna-
gent
1
(Hayashi et al., 2006) so that it integrates ac-
tion preparation and suspension of action prepara-
tion/execution. We also show that these new functions
of online planning are effective for service robots
that pick and place objects in dynamic environments.
Note that in the previous work of Dynagent the ef-
fects of replanning and suspension of action execu-
tion/preparation in the pick-and-place manipulation
have not been investigated.
1
Dynagent is a registered trademark of Toshiba Corpo-
ration.
109
Hayashi H. and Ogawa H..
Action Preparation and Replanning in Manipulation.
DOI: 10.5220/0005152101090116
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART-2015), pages 109-116
ISBN: 978-989-758-073-4
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

The rest of this paper is organized as follows: Sec-
tion 2 discusses related work. Section 3 briefly ex-
plains the online HTN planning algorithm that we use
in this work. Section 4 briefly explains our heuris-
tics for object manipulation. Section 5 shows how
to prepare for future action executions using existing
online HTN planners. Section 6 shows how to report
the result of an action execution and update the plans.
Section 7 shows how to suspend current action execu-
tion/preparation after replanning. Section 8 presents
the result of an experiment. Section 9 presents the
result of another experiment. Section 10 is the con-
clusion.
2 RELATED WORK
Some research on replanning in robotics has been re-
ported. In (Philip et al., 2009), a motion planner
makes plans to control a humanoid robot. Using vi-
sion information, this planner dynamically updates
the path. In another paper (Hayashi et al., 2009), an
HTN planner is used to compute the path of a mobile
robot. While executing a plan, the planner controls
the sensing target in the background to obtain new in-
formation that might hinder the plan execution. How-
ever, in none of this research, do the robots prepare
for the next action execution while executing another
action.
Motion planning among moving obstacles or hu-
mans is an important research topic. In (Mainprice
and Berenson, 2014), prediction of human motions,
replanning, and execution are interleaved. At the re-
planning step, the next motion plan is made while the
robot is moving, which is important for saving time.
Because humans move, their locations are predicted
before planning to avoid collisions. In another ap-
proach (Park et al., 2013), GPU is used to compute
the trajectory of the robot in parallel. They also inter-
leave planning and execution. Because the planning
times become short, the robot can quickly respond to
the dynamic environment. In none of this research,
however, is the next action executed in parallel with
the current action. In addition, unlike in the present
work, unnecessary action execution is not suspended
after replanning. Furthermore, they do not use real
robots for evaluation.
Replanning has a long history of research in ar-
tificial intelligence. A well-known planner, STRIPS
(Fikes and Nilsson, 1971), uses a triangle table (Fikes
et al., 1972) to check the preconditions of actions in
the plan. As explained in (Russell and Norvig, 1995),
the first partial-order online planner that smoothly in-
tegrates planning, replanning, and execution is IPEM
(Ambros-Ingerson and Steel, 1988), which uses “pro-
tected links” for precondition checking. Protected
links were first introduced in NONLIN (Tate, 1977)
and used in many partial-order planners, including
TWEAK (Chapman, 1987) and SNLP (McAllester
and Rosenblitt, 1991). However, unlike in the present
work, these techniques are not used to suspend unnec-
essary action execution after replanning.
Parallel plan execution is closely related to next
action preparation since multiple actions are executed
in both approaches. In (Jacobs et al., 2012), motion
plans are executed in parallel. They do not use a high-
level planner such as an HTN planner. In (Einig et al.,
2013), an architecture of parallel plan execution for
mobile service robots is presented. They use a partial-
order HTN planner called JSHOP2 (Nau et al., 2003).
They also claim that they can extend their system so
that the robot can replan when action execution fails.
Our motivation is the same in that both parallel action
execution and replanning would reduce the total plan
execution time in manipulation. However, they have
not yet evaluated the effect of replanning.
3 ONLINE HTN PLANNING
We use Dynagent (Hayashi et al., 2006), a general-
purpose forward-chaining HTN planning agent work-
ing in a dynamic environment. Although we use it for
pick-and-place manipulation, it can also be used for
other purposes. Forward-chainingHTN planners such
as Dynagent and SHOP (Nau et al., 1999) make plans
by incrementally decomposing an abstract task into
more detailed tasks in the same order that they will be
executed, and search for an optimal/suboptimal plan
by best-first search. Rule programmers of HTN plan-
ners can express domain control heuristics using task
decomposition rules.
The agent does not have to decompose an abstract
task till the agent needs to execute the task. (This is
called “lazy evaluation” or “lazy planning”.) How-
ever, the first task in each plan must be an executable
action before selecting the plan for execution.
It keeps and modifies several alternative plans
while executing a plan. Therefore, it can change the
plan to an alternative plan when the current plan be-
comes invalid or another plan becomes more attrac-
tive in terms of costs.
After successfully executing an action, the agent
updates the belief based on the effect of the action,
and removes the executed action from each plan if the
first action in the plan is unifiable
2
with the executed
2
Two actions are unifiable if and only if they become
ICAART2015-InternationalConferenceonAgentsandArtificialIntelligence
110

action. When the agent fails to execute an action, it
removes each plan such that the first action in the plan
is unifiable with the action that could not be executed.
Invalid plans can be found by rechecking the (pro-
tected) precondition of each action in the plans. Some
preconditions must be protected if they might become
unsatisfiable when the belief is updated. Even if the
precondition of an action is unsatisfiable when plan-
ning initially, it might become satisfiable later be-
cause of a belief update. Therefore, the agent keeps
such invalid plans as well.
4 MANIPULATION STRATEGY
This section briefly explains our heuristics for object
manipulation that was shown in our previous paper
(Hayashi et al., 2013) in more detail. We express the
heuristics using the task decomposition rules of HTN
planning. The top-level task is to bring object1 from
shelf1 to shelf2. In order to execute this task, we ex-
ecute the following plan (a sequence of subtasks): 1.
move to shelf1; 2. pick object1 with the right (left)
hand; 3. move to shelf2; 4. place object1 with the
right (left) hand.
In order to pick or place the object with the right
(left) hand, the robot stretches the arm diagonally
from the right (left) front of the shelf. Therefore, all
the obstacles on the right (left) front of the shelf have
to be removed before stretching the arm to avoid colli-
sions. In order to place an object on a shelf, the robot
places the object as far as possible from the robot so
that the robot can place many objects on the shelf.
There are many ways to remove or avoid obsta-
cles. Best-first search finds a low-cost plan. In other
words, it tries to minimize the number of obstacle re-
movals.
5 ACTION PREPARATION
In order to prepare for the next manipulation while
moving to a shelf, it is necessary to know the next
actions to execute after the current action execution.
For this purpose, we add an argument for each action
so that it can record the list of next actions.
For example, suppose that the agent makes the fol-
lowing plan:
1. goto(shelf1);
2. pickL(object1,shelf1).
syntactically the same by substituting some variables.
In this plan, the robot goes to shelf1 and picks object1
with the left hand.
The agent first tells the lower-level module to ex-
ecute goto(shelf1). However, the lower-level module
does not know the next action after goto(shelf1). For
this reason, we modify the task-decomposition rules
of Dynagent so that the following plan is made:
1. goto(shelf1,[pickL(object1,shelf1)]);
2. pickL(object1,shelf1.[]).
In this case, the agent tells the lower-level module
to execute goto(shelf1,[pickL(object1,shelf1)]). Now,
the lower-level module can prepare for the execution
of pickL(object1,shelf1) while executing goto(shelf1).
In this way, we do not have to change the framework
or the source code of Dynagent.
In general, this strategy is summarized as follows:
Strategy 1. (Planning for action preparation)
Consider the following plan:
1. a
1
(t
1
, ..., t
i
1
)
2. a
2
(t
1
, ..., t
i
2
)
.
.
.
3. a
n−1
(t
1
, ..., t
i
n−1
)
4. a
n
(t
1
, ..., t
i
n
)
In order to give the information of the next two
actions to the lower-levelaction execution module, we
modify the task-decomposition rules of Dynagent so
that the following plan is made:
1. a
1
(t
1
, ..., t
i
1
, [a
2
(t
1
, ..., t
i
2
)])
2. a
2
(t
1
, ..., t
i
2
, [a
3
(t
1
, ..., t
i
3
)])
.
.
.
3. a
n−1
(t
1
, ..., t
i
n−1
, [a
n
(t
1
, ..., t
i
n
)])
4. a
n
(t
1
, ..., t
i
n
, [])
In this strategy, each action records only the next
action. In the same way, it is possible to record mul-
tiple actions if necessary.
6 REPORTING RESULTS
Strategy 1 in the previous section works as long
as the plan is not modified in the middle of the
action execution. However, if we need to re-
plan, we have another problem. In the example
of the previous section, after the robot moves to
shelf1, the low-level action executor reports to Dy-
nagent that goto(shelf1,[pickL(object1,shelf1)]) has
been successfully executed. Then, Dynagent re-
moves goto(shelf1,[pickL(object1,shelf1)]) from the
plan. However, Dynagent cannot remove the first ac-
tion from the following alternative plan:
ActionPreparationandReplanninginManipulation
111

1. goto(shelf1, [pickR(object2,shelf1)])
2. pickR(object2,shelf1,
[placeR(object2,shelf1,cell7)])
3. placeR(object2,shelf1,cell7,
[pickL(object1,shelf1)])
4. pickL(object1,shelf1, [])
In this alternative plan, the robot goes to shelf1, picks
object2 with the right hand, places object2 at cell7 on
shelf1 with the right hand, and picks object1 with the
left hand.
Here, the first action is the same as
goto(shelf1,[pickL(object1,shelf1)]) except that
the next action is different. Because Dynagent is a
general-purpose planning agent, it recognizes that
goto(shelf1,[pickL(object1,shelf1)]) and goto(shelf1,
[pickR(object2,shelf1)]) are different actions because
they are not unifiable.
This problem can be avoided if the low-level ac-
tion executor reports to Dynagent that it has executed
goto(shelf1,
) where is a new variable. In this
way, both goto(shelf1,[pickL(object1,shelf1)]) and
goto(shelf1, [pickR(object2,shelf1)]) become unifi-
able with goto(shelf1,
). Therefore, these first actions
are removed from both of the plans.
Similarly, when failing to execute this action, if
the low-level action executor reports to Dynagent that
it has failed to execute goto(shelf1,
), then Dynagent
removes these two invalid plans.
In general, this strategy is summarized as follows:
Strategy 2. (Reporting the action execution result)
After executing the first action:
a
1
(t
1
, ..., t
i
1
, [a
2
(t
1
, ..., t
i
2
)])
of the plan that was made by Strategy 1, it reports the
execution result (success or failure) of the following
form of the action:
a
1
(t
1
, ..., t
i
1
,
)
where
is a new variable
In this way, we do not have to change the frame-
work or the source code of Dynagent.
7 ACTION SUSPENSION
Dynagent changes the plan as the situation changes.
Sometimes it becomes unnecessary to finish the cur-
rent action execution if the current plan becomes in-
valid. In robotics, the execution time of one action
is long and it is better to suspend such unnecessary
action execution to save time. Sometimes the robot
might find a new obstacle while picking or placing an
object. In this case, it is necessary to stop stretching
the arm to avoid collision with the obstacle.
Similarly, the current action preparation might be-
come unnecessary after modifying the plan. In this
case, we would like to stop the current action prepa-
ration as well.
From these view points, we suspend unnecessary
action execution and action preparation as follows:
Strategy 3. (Replanningand suspension of action ex-
ecution/preparation)
When the belief is updated, plans are modified and
the action execution/preparation is suspended as fol-
lows:
1. Belief
3
update instruction is given as an input.
2. Update the belief as instructed.
3. If a plan is being executed, do the following pro-
cedure:
(a) If the current action execution/preparationcan-
not be suspended, wait until the current action
execution/preparation finishes.
(b) Modify the plans
4
including alternative plans.
(c) Choose a plan for execution from alternative
plans.
(d) If an action is being executed or prepared and
it becomes unnecessary, do the following pro-
cedure:
i. Send an instruction to suspend the current ac-
tion execution/preparation to the lower-level
action execution module.
ii. Update the belief considering the effect
of the suspension of the action execu-
tion/preparation.
iii. Remodify the plans including alternative
plans.
iv. Rechoose a plan for execution from alterna-
tive plans.
(e) Resume the plan execution.
8 EXPERIMENT 1
As shown in Figure 1, in the initial state, there exist
the objects A, B, and C respectively at cells 1, 5, and
6 on shelf1. Each object has an RFID tag and rough
location on the shelf is recognized through the RFID
reader attached underneath.
3
Belief is the knowledge that is used for planning.
4
Although we use the replanning algorithm of Dyna-
gent, any replanning algorithm can be used in this strategy.
ICAART2015-InternationalConferenceonAgentsandArtificialIntelligence
112

1
4
7 8 9
6
32
5
A
B
C
C
shelf1
(Side Table)
2. Right Hand
3. Left Hand
Robot
1. Approach
Figure 1: Initial Plan.
We used a service robot called SmartPal V
5
(Yaskawa Electric Corporation, 2007). SmartPal V
is a mobile robot equipped with two hands/arms. The
robot can recognize an object through a stereo camera
and pick the recognized object.
We installed a forward-chaining HTN planning
agent, Dynagent on a PC (Windows XP), and con-
nected it with other modules on SmartPal V through
the middleware called OpenRTM-aist 1.0.0.
In the following subsections, we first explain the
three scenarios that were used for experiments and
then show the results of the experiments.
8.1 Static Scenario 1
6
Given the task of picking B, the robot first approaches
shelf1. While approaching shelf1, the robot raises
the right arm to prepare for the next action execution.
When the robot stops in front of cell 6, it recognizes
C with the stereo camera, picks C, and places it at
cell 7 with the right hand avoiding collision with B.
The robot then recognizes B and picks B with the left
hand. When the environment does not change, we
confirmed that the robot works as expected as shown
in Figure 1.
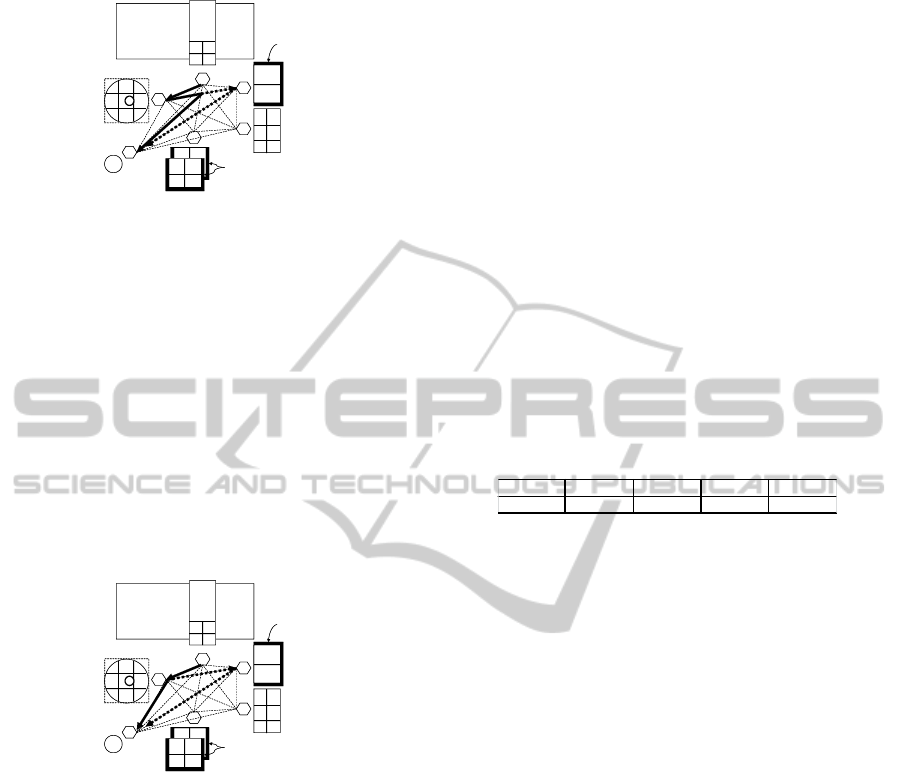
8.2 Dynamic Scenario 1
This scenario is the same as static scenario 1 in
the previous subsection except that the environment
changes in the middle of the plan execution. There-
fore, this scenario includes replanning in the middle
of action execution.
In this scenario, while the robot is stretching the
right arm to try to pick obstacle C, a person removes
the obstacle on behalf of the robot as shown in Fig-
ure 2. After the robot finds that the obstacle has been
removed through the RFID reader attached under the
table, it replans, stops picking C, and directly picks
the target object B with the left hand.
5
SmartPal is a registered trademark of Yaskawa Electric
Corporation.
6
Similar static scenario is reported in more detail in our
previous paper (Hayashi et al., 2013).
Figure 2: Replanning and Action Suspension.
8.3 Dynamic Scenario 2
This scenario is similar to dynamic scenario 1 in the
previous subsection. The difference is the timing of
the help by a person. In addition, this scenario in-
cludes replanning in the middle of action execution
and the speculative next action preparation. Note that
dynamic scenario 1 in the previous subsection does
not include replanning in the middle of the “specula-
tive next action preparation”.
Figure 3: Replanning and Action Preparation Suspension.
In this scenario, a person removes the obstacle
while the robot is approaching shelf1 as shown in Fig-
ure 3(a) Note that the robot is raising the right arm
while moving to prepare for the next action. After
the robot finds that the obstacle has been removed,
it replans, stops preparing for picking C, and starts
preparing for picking the target object B while mov-
ing to shelf1. Therefore, in Figure 3(b), the robot is
putting the right arm down and raising the left arm
while moving to shelf1.
8.4 Result
This subsection shows the experimental results of the
previous subsections. We conducted experiments in
the following six patterns:
ActionPreparationandReplanninginManipulation
113

• Pattern 1a: Static scenario 1
• Pattern 2a: Dynamic scenario 1
• Pattern 3a: Dynamic scenario 2
• Pattern 1b: Same as Pattern 1a except that the
robot does not prepare for the next picking action
while approaching shelf1.
• Pattern 2b: Same as Pattern 2a except that the
robot does not prepare for the next picking action
while approaching shelf1.
• Pattern 3b: Same as Pattern 3a except that the
robot does not prepare for the next picking action
while approaching shelf1.
In Patterns 1a, 2a, and 3a, the robot prepares for the
next picking action while approaching shelf1. On the
other hand, it does not in Patterns 1b, 2b, and 3b.
We measured the execution times of the plans for
the robot to approach shelf1 and pick up the target
object B. However, the time for vision-recognition is
not included. Table 1 shows the results of the experi-
ments.
By comparing the results for patterns 1a and 1b (or
the patterns 2a and 2b, or the patterns 3a and 3b), we
understand that the robot saves 5 seconds by prepar-
ing for the next pick action while approaching shelf1.
By comparing the results for patterns 1a and 2a (or
the patterns 1b and 2b), we understand that the robot
saves 40 seconds by suspending the pick action of C
and omitting the place action of C.
By comparing the results for patterns 1a and 3a (or
the patterns 1b and 3b), we understand that the robot
saves 53 seconds by omitting the pick action and the
place action of C.
From these results, we can confirm that action
preparation, replanning, and suspension of unnec-
essary action execution/preparation are effective not
only for adapting to dynamic environments but also
for saving plan execution time.
Table 1: Time for Moving and Picking the Target Object.
324585274080Time (sec)
3b2b1b3a2a1aPattern
324585274080Time (sec)
3b2b1b3a2a1aPattern
9 EXPERIMENT 2
In this experiment, we use the same robot and envi-
ronment as in Experiment 1. The robot moves around
the room shown in Figure 4. The side table in Figure
1 that was used in Experiment 1 is also used in this
experiment as shown in Figure 4. In the initial state,
the robot is at node 1. The object A exists at cell 5 on
the side table. No other objects exist.
1
2
bookcase
rack
fridge with two shelves
side table
bed table
bed
2
12
34
5
6
1
2
3
4
1
2
3
4
1 2 3
4 5 6
7 8 9
1
2
3
4
5
1
wall
wall
1
trash can
6
A
Figure 4: Static Scenario 2 and Dynamic Scenario 3.
In the following subsections, we first explain the
four scenarios that were used for experiments and
then show the results of the experiments.
9.1 Static Scenario 2
As shown in Figure 4, given the task to bring A from
the side table to the bookcase, the robot makes a plan,
moves from node 1 to node 2, picks A with the right
hand, moves from node 2 to node 5, places A at cell
1 in the bookcase, and finishes the task. Soon after-
wards, the robot is given another task to move A from
the bookcase to the trash can. The robot makes a plan,
picks A with the right hand, moves from node 5 to
node 6, puts A into the trash can, and finishes the sec-
ond task. In this scenario, the robot plans and com-
pletes two tasks consecutively. However, the robot
does not replan.
9.2 Dynamic Scenario 3
This scenario is similar to static scenario 2. However,
the timing of receiving the second task is different.
While placing A at cell 1 in the bookcase to com-
plete the first task, the robot is requested to put A into
the trash can. In other words, the destination of A is
changed. Now the robot does not need to place A in
the bookcase. The robot replans, suspends the action
execution, moves from node 5 to node 6, puts A into
the trash can, and finishes the second task.
9.3 Dynamic Scenario 4
This scenario is similar to static scenario 2 and dy-
namic scenario 3. However, the timing of receiving
the second task is different. While the robot is mov-
ing from node 2 to node 5 to approach the bookcase,
as shown in Figure 5, the robot is requested to put A
into the trash can. Now the robot does not need to go
to the bookcase. The robot replans, suspends the ac-
tion execution, moves to node 6, puts A into the trash
can, and finishes the second task.
ICAART2015-InternationalConferenceonAgentsandArtificialIntelligence
114
1
2
rack
fridge with two shelves
side table
bed table
bed
2
12
34
5
6
1
2
3
4
1
2
3
4
1 2 3
4 5 6
7 8 9
1
2
3
4
5
1
wall
wall
1
trash can
6
A
bookcase
Figure 5: Dynamic Scenario 4.
9.4 Dynamic Scenario 5
This scenario is similar to static scenario 2, dynamic
scenario 3, and dynamic scenario 4. However, the
timing of receiving the second task is different. While
the robot is moving from node 1 to node 2 to approach
the side table, as shown in Figure 6, the robot is re-
quested to put A into the trash can. Now the robot
does not need to start the action to go to the bookcase.
The robot replans, continues to go to node 2, picks
A with the right hand, moves from node 5 to node 6,
puts A into the trash can, and finishes the second task.
1
2
rack
fridge with two shelves
side table
bed table
bed
2
12
34
5
6
1
2
3
4
1
2
3
4
1 2 3
4 5 6
7 8 9
1
2
3
4
5
1
wall
wall
1
trash can
6
A
bookcase
Figure 6: Dynamic Scenario 5.
9.5 Result
This subsection shows the experimental results of the
previous subsections. We conducted experiments in
the following four patterns:
• Pattern 4: Static scenario 2
• Pattern 5: Dynamic scenario 3
• Pattern 6: Dynamic scenario 4
• Pattern 7: Dynamic scenario 5
The purpose of these experiments is to evaluate how
much time can be saved by replanning and action/plan
suspension. We expect that the robot can save time by
suspending unnecessary movements between nodes.
We measured the execution times for the robot in the
case of starting from node 1 and putting A into the
trash can. However, the time for vision-recognition is
not included. Table 2 shows the results of the experi-
ments.
By comparing the results for patterns 4 and 5, we
understand that the robot saves 33 seconds by sus-
pending the place action of A in the bookcase. By
comparing the results for patterns 4 and 6, we under-
stand that the robot saves 55 seconds by suspending
the move action from node 2 to node 5. By compar-
ing the results for patterns 4 and 7, we understand that
the robot saves 64 seconds by omitting the move ac-
tion from node 2 to node 5. From these results, we
understand that the robot saves tens of seconds by re-
planning and action/plan suspension. We also under-
stand that the sooner the robot replans, the shorter the
total plan execution time becomes. The robot saved
much time not only by skipping unnecessary pick-
and-place actions but also by omitting unnecessary
move actions.
Table 2: Time for Moving the Object to the Trash Can.
Pattern 4 5 6 7
Time(Sec) 143 110 88 79
10 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we have integrated planning, action
preparation, replanning, and suspension of action ex-
ecution/preparation. We have shown that this inte-
gration is effective not only for adapting to dynamic
environments but also for saving plan execution time
in manipulation. We implemented this integration by
the three strategies shown in this paper. We have
also shown that this integration method is effective
for pick-and-place manipulation in dynamic environ-
ments using a real mobile robot with two arms.
In future, we would like to explore more possi-
bilities of speculative action preparations, replanning,
and action/plan suspensions in other scenarios. When
the robot has nothing to do, the robot might be able to
prepare for future tasks. However, this is not simple
because the speculative action preparation might pre-
vent or delay future plan execution if the speculation
is wrong.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
A part of this work is supported by a grant from the
Intelligent Robot Technology (RT) Software Project
of the New Energy and Industrial Technology Devel-
opment Organization (NEDO) of Japan. We would
ActionPreparationandReplanninginManipulation
115

like to thank the researchers of Yaskawa Corporation
who cooperated with us in conducting experiments.
REFERENCES
Ambros-Ingerson, J. and Steel, S. (1988). Integrating plan-
ning, execution and monitoring. In AAAI88, pages
735–740.
Cambon, S., Alami, R., and Gravot, F. (2009). A hybrid
approach to intricate motion, manipulation and task
planning. Journal of Robotics Research, 28(1):104–
126.
Chapman, D. (1987). Planning for conjunctive goals. Arti-
ficial Intelligence, 32(3):333–377.
Choi, J. and Amir, E. (2009). Combining planning and mo-
tion planning. In ICRA09, pages 4374–4380.
Fikes, R., Hart, P., and Nilsson, N. (1972). Learning and
executing generalized robot plans. Artificial Intelli-
gence, 3(4):251–288.
Fikes, R. and Nilsson, N. (1971). STRIPS: A new approach
to the application of theorem proving to problem solv-
ing. Artificial Intelligence, 2(3-4):189–208.
Haspalamutgil, K., Palaz, C., Uras, T., Erdem, E., and
Patoglu, V. (2010). A tight integration of task plan-
ning and motion planning in an execution monitoring
framework. In AAAI10 Workshop on Bridging The
Gap Between Task And Motion Planning (BTAMP).
Hauser, K. and Latombe, J. (2009). Integrating task and
PRM motion planning: Dealing with many infeasible
motion planning queries. In ICAPS09 Workshop on
Bridging the Gap between Task and Motion Planning
(BTAMP).
Hayashi, H., Ogawa, H., and Matsuhira, N. (2013).
Htn planning for pick-and-place manipulation. In
ICAART13, pages 383–388.
Hayashi, H., Tokura, S., Hasegawa, T., and Ozaki, F.
(2006). Dynagent: An incremental forward-chaining
HTN planning agent in dynamic domains. In Declar-
ative Agent Languages and Technologies III, number
3904 in LNAI, pages 171–187. Springer.
Hayashi, H., Tokura, S., Ozaki, F., and Doi, M. (2009).
Background sensing control for planning agents work-
ing in the real world. International Journal of Intel-
ligent Information and Database Systems, 3(4):483–
501.
Jacobs, S. A., Manavi, K., Burgos, J., Denny, J., Thomas,
S., and Amato, N. M. (2012). A scalable method
for parallelizing sampling-based motion planning al-
gorithms. In ICRA12, pages 2529–2536.
Kaelbling, L. P. and Lozano-Perez, T. (2010). Hierarchi-
cal task and motion planning in the now. In ICRA10
Workshop on Mobile Manipulation.
Einig, L., Klimentjew, D., Rockel, S., Zhang, L., and
Zhang, J. (2013). Parallel plan execution and re-
planning on a mobile robot using state machines with
HTN Planning Systems. In ROBIO13, pages 151–157.
LaValle, S. M. and Kuffner, J. J. (2001). Rapidly-exploring
random trees: Progress and prospects, pages 293–
308. A K Peters.
Mainprice, J. and Berenson, D. (2014). Motion planning
for human-robot collaborative manipulation tasks us-
ing prediction of human motion. In RSS14 Workshop
on Human-Robot Collaboration for Industrial Manu-
facturing.
McAllester, D. and Rosenblitt, D. (1991). Systematic non-
linear planning. In AAAI91, pages 634–639.
Nau, D., Cao, Y., Lotem, A., and M˜unoz-Avila, H. (1999).
SHOP: simple hierarchical ordered planner. In IJ-
CAI99, pages 968–975.
Nau, D., Ilghami, O., Kuter, U., Murdock, W. J., Wu, D.,
and Yaman, F. (2003). SHOP2: an HTN planning
system. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research,
20:379–404.
Nieuwenhuisen, D., van der Stappen, A. F., and Overmars,
M. H. (2008). An effective framework for path plan-
ning amidst movable obstacles. In Algorithmic Foun-
dation of Robotics VII, pages 87–102.
Ota, J. (2009). Rearrangement planning of multiple mov-
able objects by a mobile robot. Advanced Robotics,
23(1-2):1–18.
Park, C., Pan, J., and Manocha, D. (2013). Real-
time optimization-based planning in dynamic environ-
ments using GPUs. In ICRA13, pages 4090–4097.
Philip, M., Chestnutt, J., Kagami, S., Nishiwaki, K.,
Kuffner, J., and Kanabe, T. (2009). Humanoid nav-
igation planning using future perceptive capability. In
Digital Human Symposium.
Russell, S. and Norvig, P. (1995). Artificial Intelligence: A
Modern Approach. Prentice Hall.
Stilman, M., Schamburek, J.-U., Kuffner, J., and Asfour, T.
(2007). Manipulation planning among movable obsta-
cles. In ICRA07, pages 3327–3332.
Tate, A. (1977). Generating project networks. In IJCAI77,
pages 888–893.
Wolfe, J., Marthi, B., and Russel, S. (2010). Combined
task and motion planning for mobile manipulation. In
ICAPS10, pages 254–257.
Yaskawa Electric Corporation. (2007). YASKAWA devel-
ops a service robot “SmartPal V (SmartPal Five)”-
Additional waist area unit expands the allowable op-
erating range -, http://www.yaskawa.co.jp/en/topics/
071128
01/index.html, (Accessed on 10 June 2014).
Zacharias, F., Borst, C., and Hirzinger, G. (2006). Bridging
the gap between task planning and path planning. In
IROS06, pages 4490 – 4495.
ICAART2015-InternationalConferenceonAgentsandArtificialIntelligence
116
