
Naive Bayes Classifier with Mixtures of Polynomials
J. Carlos Luengo
1
and Rafael Rumi
2
1
IES Alyanub, Almer´ıa, Spain
2
Dept. of Mathematics, University of Almeria, Almer´ıa, Spain
Keywords:
Mixtures of Polynomials, Naive Bayes classifier, Graphical Models.
Abstract:
We present in this paper a methodology for including continuous features in the Naive Bayes classifier by
estimating the density function of the continuous variables through the Mixtures of Polynomials model. Three
new issues are considered for this model: i) a classification oriented parameter estimation procedure ii) a
feature selection procedure and iii) the definition of new kind of variable, to deal with those variables that are
in theory continuous, but their behavior makes the estimation difficult. These methods are tested with respect
to classical discrete and Gaussian Naive Bayes, as well as classification trees.
1 INTRODUCTION
Classification problems are present in all science
fields, and deal with many real-world problems ev-
eryday. That is why they have caught the attention of
the statistics, artificial intelligence or machine learn-
ing community. In a classification problem there is
a qualitative (discrete) variable, called class, whose
value we want to predict given some other variables,
called features. If the class value is known for a data
sample, it is called supervised classification, but if it
is unknown, it is called unsupervised classification
or clustering. We focus in this paper on supervised
classification. There are several techniques available
that try to solve this problem, as for example neu-
ral networks, classification trees, logistic regression,
or probabilistic graphical models. Bayesian networks
(BNs) (Pearl, 1988; Jensen and Nielsen, 2007) are a
specific type of probabilistic graphical models that are
widely used in classification, mainly due to their mix-
ture of model-complexity and accuracy results (Fried-
man et al., 1997). In fact there is a wide variety in the
BN-models for classification that can be used, ranging
from the simplest one, called Naive Bayes (NB) (Min-
sky, 1963), to the most complex one, a BN with no
restrictions. The election of the appropriate model de-
pends on the complexity of the problem and the data
available. However, the NB model is probably the
most used model, because of its simplicity and good
results (Domingos and Pazzani, 1997). Originally,
BN models were defined only for categorical vari-
ables, however in the last decades several frameworks
have emerged for dealing with hybrid BNs, in which
discrete and continuous variables coexist. The main
goal of this paper is to present a new NB-classifier
based on the Mixtures of Polynomials (MoP) model,
which we will note by NB-MoP, able to deal simul-
taneously with discrete and continuous features. This
model was already presented in (L´opez-Cruz et al.,
2013), howeverit was introduced as an example of ap-
plication of a more general model. We include in this
paper some improvements, such as a feature selection
procedure, a specific classification-oriented parame-
ter estimation scheme, and the definition of a pseudo-
continuous type of variables in order to make the most
of the ability of the model to work with a hybrid set
of variables.
Section 2 presents the basics of BNs in classifi-
cation, Section 3 presents two preprocessing steps to
apply in the learning procedure, Section 4 presents
the MoP model and the parameter estimation algo-
rithm designed specifically for classification. Section
5 shows an experimental evaluation of the proposed
algorithms, and finally in Section 6 conclusions and
future work are outlined.
2 BAYESIAN NETWORKS FOR
CLASSIFICATION
A BN is composed by two components: a qualitative
part and a quantitative part:
1. The qualitative part is a directed acyclic graph in
14
Luengo J. and Rumi R..
Naive Bayes Classifier with Mixtures of Polynomials.
DOI: 10.5220/0005166000140024
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods (ICPRAM-2015), pages 14-24
ISBN: 978-989-758-076-5
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

which every node represents a random variable,
and the presence of an edge between two variables
shows a dependence relation between them.
2. The quantitative part is the definition of a set
of conditional probabilities, in particular one for
each variable given its parents in the graph,
p(x
i
|pa(x
i
)) ∀i = 1. . . , n
BNs have traditionally been used only for discrete
data. In the presence of continuous data, most of the
researchers and practitioners discretize the data, using
some common techniques such as equal width, equal
frequency or k-means (Dougherty et al., 1995), more
sophisticated algorithms that dynamically discretize
the distributions according to the evidence (Kozlov
and Koller, 1997), or using specific algorithms for
classification problems that relate every continuous
feature variable to the class variable (Fayyad and
Irani, 1993). However, discretizing the data imply
some loss of information and cause problems of ac-
curacy, so alternative solutions have been proposed
in the literature. The first approach is to define the
continuous variables as Gaussians, which leads to
the Conditional Gaussian model (Lauritzen and Wer-
muth, 1989; Cowell et al., 1999). It is the alternative
solution most widely used, however it has some dis-
advantages, as for example that discrete nodes cannot
have continuous nodes as parents in the graph, and
that the distribution of the continuous variables must
be Gaussian, which does not hold for every contin-
uous variable. Following this idea appears the Mix-
tures of Truncated Exponentials model (MTE) (Moral
et al., 2001), in which any probability distribution
can be approximated and there is no restriction in the
topology of the network. This model has been suc-
cessfully applied in recent years to classification and
regression problems (Aguilera et al., 2010; Fern´andez
and Salmer´on, 2008; Morales et al., 2007) and in gen-
eral to hybrid BNs (Rum´ı et al., 2006; Romero et al.,
2006). The Mixtures of Polynomials model (MoP)
(Shenoy and West, 2011; Shenoy, 2011) is similar, in
the sense that it can also approximate any probability
distribution, but uses polynomials as the basis func-
tions, gaining fitting power just increasing the degree.
They have mostly been applied to approximate spe-
cific known distributions, as in (Shenoy et al., 2011),
but not to include them as a tool to approximate any
dataset. There are some recent publications that deal
with this problem using different properties of the
polynomials (Langseth et al., 2013; L´opez-Cruz et al.,
2013).
For classification problems it is usual to restrict
the structure of the network in order to obtain simpler
but effective models. The simplest BN model for clas-
sification is the NB model, in which all the features
C
X
2
X
1
X
n−1
···
X
n
Figure 1: Structure of Naive Bayes classifier.
are assumed to be independent given the class (see
Fig. 1). Even though this assumption is not always
true, NB is known to be an accurate classifier with a
relatively small computational complexity. The lack
of independence affectsto the estimation of the proba-
bility of the classes, but the class with maximum prob-
ability is still correct (Domingos and Pazzani, 1996).
Some other Bayesian classifiers have been proposed,
such as the Tree Augmented Network model (Fried-
man et al., 1997), the kdB model (Sahami, 1996) or
the FAN model (Lucas, 2002) but all of them increase
the complexity of the model adding more links to the
structure.
NB was first proposed to deal only with discrete
variables, however, there are some approaches in
which continuous variables are allowed as features,
representing them as Gaussian distributions (Domin-
gos and Pazzani, 1997), kernel density estimations
(John and Langley, 1995; P´erez et al., 2009) or MTEs
(Morales et al., 2007). Since MoPs are a novel and
efficient way to represent and compute with continu-
ous variables in BNs, the aim of this paper is to intro-
duce this representation framework in the NB model
together with some preprocessingsteps in order to im-
prove its applicability.
3 PREPROCESSING STEPS
Prior to the specific procedure of estimating the pa-
rameters of the network, we will also investigate in
this paper the effect of two different pre-processing
methods, a classical filter-wrapper feature selection,
and some partial discretization of the variables.
3.1 Discretization
The discretization of continuous variables is usual in
classification tasks, but it means that some informa-
tion from the dataset will be lost.
Nevertheless, there are some variables that cannot
be considered as discrete neither continuous because
of the great number of factors or the difficulty for fit-
ting a polynomial. In this paper we have considered
three kinds of features:
NaiveBayesClassifierwithMixturesofPolynomials
15

• Discrete: Character or string features as well as
numeric features that have less than 20 different
values.
• Pseudo-Continuous: numeric features which have
more than 20 different values but less than the 5%
of the total number of observations of the dataset.
• Totally-Continuous: numeric features which are
not pseudo-continuous
Pseudo-Continuous variables are mainly found in
large databases (more than 400 observations). For in-
stance, in a database composed by 1000 observations,
a variable will be pseudo continuous if it has between
20 and 50 different values (which is the 5% of 1000)
In the Adult dataset there are two examples of
what we have called pseudo-continuous variables.
They are capital-gain and capital-loss. The number
of different values are 118 and 90, respectively, and,
more importantly, 91 and 95% of those values, respec-
tively, are zeroes, due to the fact that they represent
the purchases or sales that a person does in one year,
which frequently are none. Usually these variables
are processed as continuous, however such a variable
is difficult to represent by means of a continuous dis-
tribution.
Keeping those three kinds of variables in mind, we
have designed two different alternatives for the NB
- MoP algorithm and tested them in the experiments
section:
• Process each variable as it originally is, discrete
variables are processed as discrete and continuous
variables, both pseudo-continuous and totally-
continuous, as continuous.
• Process discrete and pseudo-continuous variables
as discrete, i. e., discretize those variables that are
not clearly neither discrete nor continuous.
In the last case the discretization procedure used
is the Fayyad-Irani method (Fayyad and Irani, 1993).
3.2 Feature Selection
It is known that selecting the appropriate feature vari-
ables in a classification problem may lead to an in-
crease of accuracy in the model, as well as to avoid
overfitting and noise in the model (Dash and Liu,
1997). A filter-wrapper approach for feature selec-
tion has been implemented, in which, firstly, the mu-
tual information between the class and each variable
is computed, and different models are learned, start-
ing with one feature variable and adding variables fol-
lowing the order of the previous ranking, until no im-
provement in terms of accuracy is achieved.
The mutual information is defined as
MI(X;C) =
n
∑
i=1
m
∑
j=1
p(x
i
, c
j
)log
p(x
i
, c
j
)
p(x
i
)p(c
j
)
(1)
in the case of X being a discrete feature variables, and
as
MI(X;C) =
m
∑
j=1
Z
Ω
x
f(x, c
j
)log
f(x, c
j
)
f(x)p(c
j
)
(2)
in the case of X being a continuous feature vari-
able where f(x) is obtained using a MoP.
Note that, a filter-wrapper approach as this one
is not properly a pre-processing step, since it is per-
formed during the learning of the model, not before.
However, we decided to include it in this Section for
a better reading of the paper.
4 LEARNING THE MODEL
Given the structure of the NB, to learn this model it is
needed to estimate the probability distribution of the
class, and the conditional distribution of every feature
variable given the class.
These conditional distributions will be a condi-
tional probability table (CPT) in the case of discrete
features, and a MoP density function for each value of
the class variable, in the case of continuous features.
Once the model is learnt, it is able to predict the
class value (c
i
) of a given observation x = (x
1
, . . . , x
n
)
using the following formula:
c
∗
= argmax
c
i
∈Ω
C
p(c
i
|x) (3)
where each p(c
i
|x) is computed as
p(c
i
|x) = p(c
i
|x
1
, . . . , x
n
) ∝ p(c
i
)
n
∏
j=1
p(x
j
|c
i
) (4)
In the following sections the process of estimating
a MoP density from data will be deeply explained.
4.1 Mixtures of Polynomials
The Mixtures of polynomials (MoPs) framework is
able to approximate any continuous distribution by a
piecewise function which has in each piece a polyno-
mial function. This allows to work directly with the
continuous variables without the need of discretizing
them. A MoP function is defined as follows (Shenoy
and West, 2011):
Definition 1. A one-dimensional function f : R → R
is said to be a mixture of polynomials function if it is
a piecewise function of the form
f(x) =
(
a
0i
+ a
1i
x+ · ·· + a
ni
x
n
for x ∈ A
i
, i = 1, . . . , k
0 otherwise
(5)
ICPRAM2015-InternationalConferenceonPatternRecognitionApplicationsandMethods
16

where A
1
, . . . , A
k
are disjoint intervals in R and
a
0i
, . . . , a
ni
are real constants for all i.
There are some variants to this definition, in
(Shenoy, 2011) Shenoy et al re-defines the MoP
function to include multivariate functions in which
A
1
, . . . , A
k
may be also hyper-rhombuses. This re-
definition makes MoP functions richer because now
they can deal with deterministic functions, however
it makes computations more complex (Shenoy et al.,
2011; Rum´ı et al., 2012). We do not use this variant
because, in the NB model, there is no need of estimat-
ing multivariate continuous MoPs.
The main reason for using MoPs is that they have
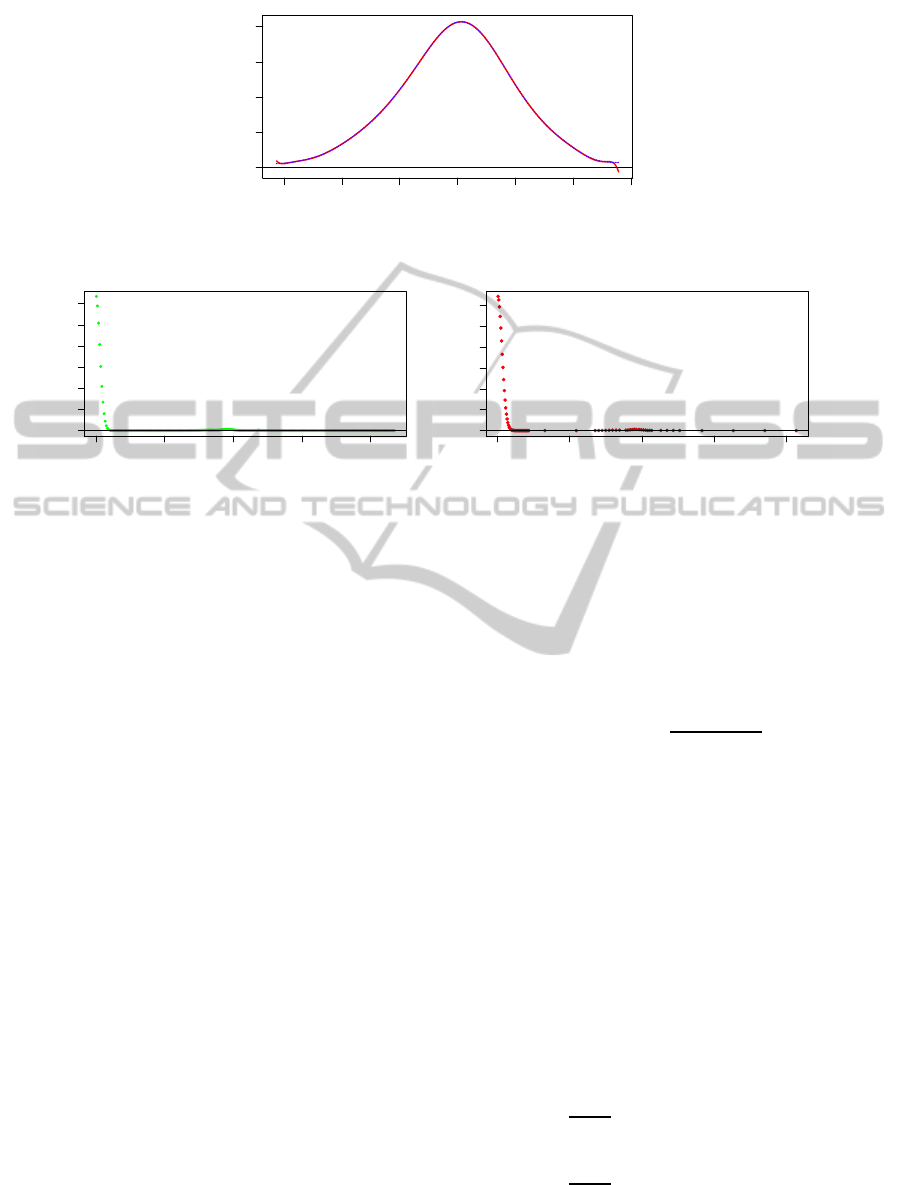
a great fitting power, as we can see in Fig. 2 in which
we show a Gaussian distribution and the correspond-
ing MoP approximation, according to the parameter
estimation procedure explained in Section 4.2.
4.2 Learning Mixtures of Polynomials
from Data
In previous papers, MoPs were designed to approxi-
mate known distributions, such as Gaussian or Chi-
square, taking advantage of some properties of the
functions, like symmetry or inflection points (L´opez-
Cruz et al., 2013). In this paper we design a method-
ology for learning MoP distributions from a sample
(dataset), without knowing the true underlying distri-
bution. This approach is similar to the one shown
in (Langseth et al., 2013), but different in some de-
tails and focused on a posterior application to the NB
model.
To obtain a univariate MoP density from a dataset
we have applied the mean squared error (MSE) pa-
rameter estimation procedure, by means of the lm
method implemented in software R (R Core Team,
2013). An outline of the most important steps is:
1. Input: A sample (x
1
, . . . , x
n
) from variable X.
2. Output: a function f : R → R expressed as in Def.
1.
3. Obtain the pairs (x
∗
i
, y
∗
i
), i = 1, . . . , m where x
∗
i
is
a value in the support set of X and y
∗
i
is the as-
sociated density value estimated through a kernel
density estimator (Simonoff, 1996).
4. Set the degree to i = 1
5. Estimate the parameters of the polynomial of de-
gree i (p
i
(x)) by minimizing the MSE in the pairs
(x
∗
i
, y
∗
i
).
6. p
i
(x) may be negative in some points of the do-
main. Select only the most important positive
part, in terms of weight or size (detailed in Sec-
tion 4.4)
7. Normalize the polynomial so that its integral is
equal to the proportion of points of the sample in-
cluded in the selected subinterval.
8. If a part of the domain of p
i
(x) has been removed
because of the negative values, add the necessary
tails to extend the domain of the polynomial to in-
clude the whole domain of X (in this case, a piece-
wise function is obtained as seen in Section 4.4)
9. Compute the corresponding MSE
10. If i < 15 then i := i+ 1 and repeat from step 5.
11. Select the best out of the 15 different polynomials,
according to the criteria explained in Section 4.4.
Using this procedure, we end up with a MoP fol-
lowing Def. 1, that may be defined in pieces (at most
in three), and at most with degree 15 (in the central
piece, and 0 in the tails, if there are any). See Section
4.4 for more details.
We will briefly expand some of the steps of the
above algorithm.
4.3 Kernel Density Estimator
To be able to apply the MSE procedure, we need
as input data a grid of x
∗
and y
∗
points (Step 3).
They are obtained through a kernel density estimator
with the reflection boundary effect correction (Schus-
ter, 1985). Initially 500 kernel points equally spaced
are selected
1
and the domain is then divided in 10
subintervals of equal length. These points are fil-
tered in such a way that more importance is given to
those subintervals of the domain with more sample-
frequency. In those intervals that actually contain
less than 10% sample, the number of kernel points
is reduced until they represent the same proportion
as the sample-frequency (these points are chosen to
be also equally spaced within the correspondent in-
terval). The selection of the number of initial kernel
points (500) was done after trying several other sizes.
In Fig. 3, it can be seen an example of the ker-
nel points selection. In this case we used the variable
hours-per-week from the dataset Adult (see Section 5
for more information). In the first plot it is shown an
equally spaced griddata representing the kernel den-
sity estimations for that variable, while in the sec-
ond plot the points are selected following the method
described above, that is the reason why there some
subintervals of the domain with fewer data. In this
way, some subintervals with small sample frequency
will have less importance in the polynomial fitting
than other subintervalswith a great proportion of sam-
ple points.
1
The use of more points has been dismissed because its
lack of influence in the results
NaiveBayesClassifierwithMixturesofPolynomials
17
−3 −2 −1 0 1 2 3
0.0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4
x
Density
Figure 2: MoP approximation (red) to the standard Gaussian distribution (blue).
0 1000 2000 3000 4000
0.000 0.006 0.012
x
y
(a) Original kernel points
0 1000 2000 3000 4000
0.000 0.006 0.012
x
y
(b) Selected kernel points
Figure 3: Difference between the original Kernel Smooth Density and the selection of points according to the sample fre-
quency.
4.4 Parameter Estimation
Once we have the points x
∗
1
, . . . , x
∗
m
and y
∗
1
, . . . , y
∗
m
ob-
tained from X, we can calculate the polynomial that
best fits the grid-data through minimizing the MSE
(Step 5). However, this procedure has two main dis-
advantages: the degree of the polynomial has to be set
in advance and the returned function may have nega-
tive values.
The solution for the first problem is to design an
iterative procedure (see Sect. 4.2) in which several
different degrees are checked.
The solution for the second problem is to keep
only the positive part of the function, omitting the
negative one (Step 6). Also, an increase in the degree
of the polynomial implies an increase in the number
of roots, which may lie within the domain of the vari-
able. Two different approaches were observed in or-
der to select the subinterval of the domain to keep:
1. The most distant roots, i.e., the longest interval
that can be considered included in the minimum
and maximum value of X
i
for which the function
is positive.
2. The couple of roots which include the higher pro-
portion of points x
∗
i
, y
∗
i
between them, for which
the function is positive.
It is usual that the longest interval also includes
the major number of points, however there are some
exceptions in which there are lots of points in a small
interval and the rest are disperse.
(Step 7) It is necessary to normalize it so that the
integral of the function between the roots is 1. If r
min
and r
max
are the selected roots, the polynomial p
norm
is:
p
norm
(x) =
p(x) ∗ prob
R
r
max
r
min
p(x)
(6)
where prob stands for the proportion of points of the
sample in (r
min
, r
max
).
(Step 8) After defining the initial domain
(r
min
, r
max
) where the polynomial p
norm
(x) will be de-
fined, it is necessary to extend it to include the re-
moved negative parts. This means to include (if nec-
essary) one or two tails to p
norm
(x). The probability
of each tail will be the proportion of sample points
that lie on it (p
j
, j = 1, 2). This way p(x) will become
an actual density function. Let p
1
is the probability
of the left side of r
min
and p
2
the probability of the
right side of r
max
, and let range
1
= r
1
− min(x) and
range
2
= max(x) − r
2
the MoP will be:
p(x) =
p
1
range
1
for x < r
min
p
norm
(x) for r
min
< x < r
max
p
2
range
2
for x > r
max
(7)
In Figure 4 there is an example of a polynomial
fitted to a sample from Adult dataset, in which we can
ICPRAM2015-InternationalConferenceonPatternRecognitionApplicationsandMethods
18
0 200000 600000 1000000 1400000
0e+00 3e−06
x
Density
Kernel points
Initial MoP estimation
Final MoP estimation
Figure 4: Initial and final MoP estimation from a sample.
see the inclusion of a right tail to the initial MoP esti-
mation.
4.5 Related Work
Some other approaches for estimating parameters in
MoPs densities include constraints in the MSE prob-
lem in order to asure non-negative functions (L´opez-
Cruz et al., 2013; Langseth et al., 2013), however
we followed a different approach due to several rea-
sons: i) If the restrictions were included in the algo-
rithm, the calculations would get more complex and
the whole algorithm less stable due to the fact that it
would be an optimization problem, possibly linked to
numerical instability ii) The estimation is carried out
splitting the domain and fitting a polynomial in each
subinterval, leading probably to a more heavier poly-
nomial, in terms of parameters to estimate iii) Despite
the fact that the estimation of the parameters can be
appropriate, it is also possible that the approximation
in the tails is not so good. In a classification prob-
lem as the studied in this paper, it can be a key point,
as the choice of the class may depend on a value ly-
ing on a tail. That is the reason why we decided to
estimate the tails using a piecewise function with a
constant for each tail instead of including some con-
straints in order not to have negative values. In this
case, the estimation will be at least as accurate as the
discretization.
A MoP parameter estimation based on splines in-
terpolation was used in a NBclassifier in (L´opez-Cruz
et al., 2013). However, they only deal with totally
continuous problems. We focus more on hybrid prob-
lems. Also, the R-package provided in (L´opez-Cruz
et al., 2013) only estimates the parameters of the MoP
distributions, not the NB model. For these two rea-
sons, we do not include this model in the experimental
set up.
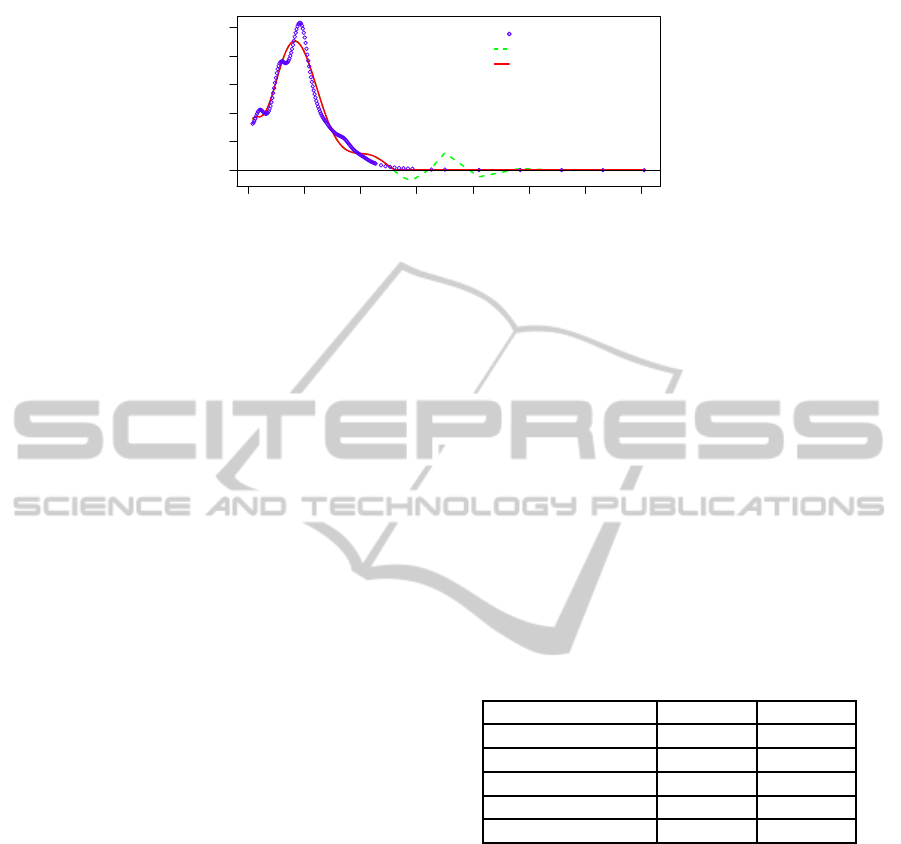
However, in order to briefly compare this estima-
tion procedure with the one proposed here, the same
distribution mentioned in the former Section (see fig-
ure 4) was learnt using the algorithm proposed in
(L´opez-Cruz et al., 2013) and displayed together with
our proposal in Figure 5 and the histogram for the
original data. As we can see, the two MoP distri-
butions are quite similar. The B-Splines based MoP
is defined in 16 different intervals, with a 3-degree
polynomial fitted on each one, requiring a total of 64
parameters to estimate. However, the MoP estimation
procedureproposedhere yields a MoP density defined
on two pieces, one with a 12-degree polynomial fitted
on it, and a tail in which a uniform (constant) distri-
bution is fitted, requiring a total of 14 parameters to
estimate.
In table 1 we can also observe some statistics for
a more detailed comparison between both approaches
for this variable.
Table 1: Statistics for comparison between the B-splines
based MoP estimation (B-Spline) and our proposal (MoP).
Statistic B-Spline MoP
Mean 182989.4 184519.6
1st quartile 170859.4 175907.3
Median 211942.9 219630.9
3rd quartile 311405.6 322937.7
Standard deviation 94595.7 95474.4
As we can see in figure 5, most of the intervals
defined in the B-Splines based MoP are included in
the tail of the MoP proposed here, so we get a similar
MoP distribution but much simpler.
However, the main goal of this paper is not a
comparison between different MoP estimation proce-
dures, but to check the validity of the proposed pro-
cedure as a competitive classifier, so the experiments
we will show in the next section will be devoted to
that aim.
5 EXPERIMENTS
The aim of the paper is to validate the MoP-NB
model, in terms of accuracy of the predictions. This
NaiveBayesClassifierwithMixturesofPolynomials
19

0 500000 1000000 1500000
0e+00 3e−06
X
Density
0
B−Splines estimation
MoP estimation
Figure 5: Comparison between proposed estimation and B-Splines estimation. Vertical dashed lines represent the limits of
the intervals of the B-Splines MoP density function.
is done through a k-fold cross validation process, in
which overfitting is avoided because all the available
data is used, both for learning and testing the model.
The proposed model is compared to an implemen-
tation of the CART methodology, available through
the package rpart in R (R Core Team, 2013) and
some Naive Bayes classifiers used to manage contin-
uous variables (Bouckaert, 2004), such as the Gaus-
sian, Kernel and Discrete NB models implemented in
WEKA (Hall et al., 2009). The comparison of the
different accuracies is carried out by means of a sta-
tistical test.
A total of 13 different datasets have been selected
for the experiments from the UCI Machine Learn-
ing Repository (Bache and Lichman, 2013) and the
KEEL repository (Alcal´a-Fdez et al., 2011). They
all have both discrete and continuous features, with
a wide range of number of cases (from 61 to 30162),
number of features (from 3 to 39) and number of cat-
egories for the class variable (from 2 to 5). In the
case of missing values, the corresponding cases were
removed from the dataset.
From the experiments several issues are to be con-
sidered i) The improvement of the results due to to the
Feature selection scheme ii) The improvement of the
results when pseudo-continuous variables are taken
into account iii) The validity of the MoP-NB model
in comparison, as mentioned above, to well-known
classifiers, in particular the classical discrete NB, the
Gaussian NB, the Kernel NB (P´erez et al., 2009) and
Classification Trees (Breiman et al., 1984).
The algorithms for learning and classification the
different models proposed in this paper were imple-
mented in R (R Core Team, 2013).
The results of the different classifiers over the se-
lected datasets are depicted in Table 3. No discretiza-
tion and Pseudo-discretizationrefers to the NB mod-
els listed in Section 3.1, whilst Classification Tree
refers to the CART classification tree models, Gauss
NB refers to the Gaussian Naive-Bayes model, Kernel
NB refers to the Kernel Naive-Bayes model and Disc.
NB refers to the Multinomial version of the Naive-
Bayes model.
Each method has been tested using a 10-fold cross
validation method, therefore, the Accuracy is the
mean of the accuracy of every fold. # Variables rep-
resents, for the proposed algorithms the mean number
of features included in the model for each fold, and
for the state-of-the-art algorithms the number of vari-
ables of the final model after performing feature se-
lection. For Gauss, Kernel and Discrete NB models, a
Wrapper Feature Selection procedure was performed
to reduce the size of the model.
Table 3 also shows, in those datasets that contain
pseudo-continuous variables (abbreviated as P-C fea-
tures in the table), that are Adult, Australian, Credit
and German, the mean number of pseudo-continuous
variables included in the model for each fold, whether
they have been discretized or treated as continuous
features. Notice that this part does not make sense in
those datasets where there are not pseudo-continuous
features.
To answer hypothesisi), whether or not the feature
selection makes a difference, a Wilcoxon paired rank
test was perform, returning a p-valueof 0.001221, and
so rejecting the hypothesis of equal performance be-
tween Feature Selection and No Feature Selection.
In order to answer ii), wether results improve
when discretizing pseudo-continuous variables, no
statistical test was carried out, since only four dataset
contain this kind of variables. However, in 3 out of
these 4 datasets the accuracy when discretizing these
P-C variables is higher. The reason for this may be
double i) the pseudo-continuous variable is not se-
lected in the feature selection procedure, because its
probability distribution was not properly estimated ii)
it was included, but added extra-noise to the model,
because of the wrong estimation of the probability
ICPRAM2015-InternationalConferenceonPatternRecognitionApplicationsandMethods
20

Table 2: Databases used in experiments.
Datasets Discrete Pseudo-Continuous Totally-Continuous Class Instances
Features Features Features Categories
Adult 9 4 1 2 30162
Australian 8 1 5 2 690
Band 25 0 14 2 277
Cleveland 8 0 5 5 297
Credit 9 1 5 2 653
Echocardiogram 4 0 8 2 61
German 21 1 2 2 1000
Haberman 1 0 2 2 306
Hepatitis 13 0 6 2 80
Hungarian 6 0 4 2 261
Ionosphere 2 0 32 2 351
Liver 1 0 5 2 345
Switzerland 7 0 3 5 105
Table 3: Results of the experiments. Proposed algorithms are shown firstly: without any discretization (with and without
feature selection) and discretizing only pseudo-continuous variables. For each dataset the best accuracy result is boldfaced.
Feature selection is included in all methods except for the first one, which is specified in the table.
Proposed algorithms State of the art algorithms
Datasets
No Disc. No Pseudo- Class. Gauss Kernel Discrete
No FS Disc. Disc. Tree NB NB NB
Adult Accuracy 0.7750 0.7648 0.7496 0.7140 0.8287 0.8487 0.8381
# Var (# P-C) 14 (4) 2.2 (0.5) 1 (0) 3 14 14 10
Australian Accuracy 0.7898 0.7942 0.8246 0.8507 0.8550 0.8550 0.8565
# Var (# P-C) 14 (1) 4.9 (0.9) 5.1 (1) 4 1 1 12
Band Accuracy 0.4055 0.6063 0.6462 0.6857 0.7400 0.6823
# Var (# P-C) 39 (0) 2.5 2 10 10 11
Cleveland Accuracy 0.5244 0.5721 0.5420 0.5690 0.5993 0.5757
# Var (# P-C) 13 (0) 2.2 7 8 7 3
Credit Accuracy 0.7909 0.8032 0.8092 0.8468 0.8637 0.8637 0.8652
# Var (# P-C) 15 (1) 5.2 (0.8) 5.4 (0.7) 5 1 1 13
Echocardiogram Accuracy 0.7928 0.9660 0.9344 0.9180 0.9344 0.9180
# Var (# P-C) 12 (0) 5.6 1 6 2 3
German Accuracy 0.7490 0.7430 0.7610 0.7380 0.7610 0.7510 0.7320
# Var (# P-C) 24 (1) 3.5 (0.9) 3.6 (0.2) 7 16 16 5
Haberman Accuracy 0.7400 0.7488 0.7287 0.7483 0.7614 0.7287
# Var (# P-C) 3 (0) 1.8 3 2 2 1
Hepatitis Accuracy 0.6250 0.7000 0.6500 0.7875 0.7125 0.7875
# Var (# P-C) 19 (0) 3.2 4 3 2 3
Hungarian Accuracy 0.6894 0.8277 0.7509 0.8390 0.8199 0.8160
# Var (# P-C) 10 (0) 4 5 5 7 3
Ionosphere Accuracy 0.7918 0.9230 0.8831 0.9031 0.9202 0.9088
# Var (# P-C) 34 (0) 6.1 5 4 29 5
Liver Accuracy 0.4299 0.5505 0.6579 0.6086 0.6753 0.5623
# Var (# P-C) 6 (0) 1.4 6 5 5 1
Switzerland Accuracy 0.2433 0.3766 0.4666 0.3809 0.4380 0.3809
# Var (# P-C) 10 (0) 3.1 3 3 3 1
distribution. These two issues are partially avoided
by the discretization of these variables.
So, we select the pseudo-Disc model (column #3
from table 3) as the optimal proposed one, and com-
pare it with some state-of-the-art algorithms (Class.
Tree and Gauss, Kernel and Discrete NB from Ta-
ble 3) performing a Friedman’s test with signifi-
cance level 0.05. The result indicated a statisti-
cally significant difference (p-value of 0.0059), but
a post-hoc comparison using Wilcoxon-Nemenyi-
NaiveBayesClassifierwithMixturesofPolynomials
21

1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
−0.10 0.00 0.10 0.20
Figure 6: Boxplot of the difference in accuracy for all pairwise comparisons of the algorithms for the different datasets. The
colored box indicate a significant difference. The labels in the plot correspond to: 1 - Discrete NB vs. Class. Tree, 2 - Gauss.
NB vs. Class. Tree, 3 - Kernel NB vs. Class. Tree, 4 - MoP-NB vs. Class. Tree, 5 - Gauss. NB vs. Discrete NB, 6 - Kernel
NB vs. Discrete NB, 7 - MoP-NB vs. Discrete NB, 8 - Kernel NB vs. Gauss. NB, 9 - MoP-NB vs. Gauss NB, 10 - MoP-NB
vs. Kernel NB. The MoP-NB model refers to the pseudo-Disc model in table 3.
McDonald-Thompson’s post-hoc test (Hollander and
Wolfe, 1999) yields that the only significative differ-
ences (marked in green in figure 6) is between the
Kernel NB and the Classification trees. There are no
differences between the MoP-NB proposed method
and the rest of the algorithms.
It is also important to note that the inclusion of
continuous variables leads to more compact mod-
els, according to the number of variables included.
The mean number of variables included is obviously
very similar for the No discretization and pseudo-
discretization versions of the MoP-NB model (they
only vary in 4 datasets) 3.51 and 3.46 respectively,
however, this mean number of variables movesto 4.23
for the classification trees(recall that CART method-
ology does a feature selection internally when select-
ing the variables to split). The mean number of vari-
ables for the Gaussian, Kernel and Discrete NB mod-
els are 6, 7.61 and 5.46 respectively.
6 SUMMARY AND
CONCLUSIONS
We have presented in this paper a novel classifier,
based on Naive Bayes and modeling the distribution
of the continuous variables through the MoP model.
This work differs from other models using MoP in
several senses, we have included a feature selection
procedure, as well as a classification-oriented param-
eter estimation procedure in which tails are given im-
portance. From a more general point of view, we
have defined a new kind of variables, called pseudo-
continuous which seem to be continuous, but have a
behavior that makes them appropriate for discretizing.
The experiments designed show that this new
kind of classifier is competitive with respect to
other classifiers such as Gaussian, Kernel and Dis-
crete Naive Bayes and CART classification trees.
These results also indicate an improvement when the
pseudo-continuous variables are differentiated from
the totally-continuous and discretized.
There are more complex BN classification mod-
els, such as the TAN model, the kDb model or the
AODE model. They require more computations in
their learning stage, as well as a general inference al-
gorithm to perform the final predictions. We plan to
continue the application of MoPs in these more so-
phisticated models, as well as emphasizing the idea
of the pseudo-continuous variables with a definition
ad-hoc for each different problem.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work has been supported by the Span-
ish Ministry of Science and Innovation, through
project TIN2010-20900-C04-02, by Junta de An-
daluca through project P12-TIC-2541 and by ERDF
(FEDER) funds.
REFERENCES
Aguilera, P. A., Fern´andez, A., Reche, F., and Rum´ı, R.
(2010). Hybrid Bayesian network classifiers: Appli-
cation to species distribution models. Environmental
Modelling & Software, 25:1630–1639.
Alcal´a-Fdez, J., Fernandez, A., Luengo, J., Derrac, J.,
Garc´ıa, S., S´anchez, L., and Herrera, F. (2011).
Keel data-mining software tool: Data set repository,
integration of algorithms and experimental analysis
ICPRAM2015-InternationalConferenceonPatternRecognitionApplicationsandMethods
22

framework. Journal of Multiple-Valued Logic and Soft
Computing, 17:255–287.
Bache, K. and Lichman, M. (2013). UCI machine learning
repository. http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml.
Bouckaert, R. (2004). Naive bayes classifiers that per-
form well with continuous variables. In Proc. of the
17th Australian Conference on Artificial Intelligence,
pages 1089 – 1094.
Breiman, L., Friedman, J. H., Olshen, R. A., and Stone, C. J.
(1984). Classification and regression trees. Chapman
& Hall/CRC.
Cowell, R. G., Dawid, A. P., Lauritzen, S. L., and Spiegel-
halter, D. J. (1999). Probabilistic Networks and Ex-
pert Systems. Statistics for Engineering and Informa-
tion Science. Springer.
Dash, M. and Liu, H. (1997). Feature selection for classifi-
cation. Intelligent Data Analysis, 1(3):131 – 156.
Domingos, P. and Pazzani, M. (1996). Beyond indepen-
dence: Conditions for the optimality of the simple
bayesian classifier. In Proceedings of the Interna-
tional Conference on Machine Learning.
Domingos, P. and Pazzani, M. (1997). On the optimality
of the simple bayesian classifier under zero-one loss.
Machine Learning, 29:103 – 130.
Dougherty, J., Kohavi, R., and Sahami, M. (1995). Super-
vised and unsupervised discretization of continuous
features. In y S. Russell, A. P., editor, Machine Learn-
ing: Proceedings of the Twelfth International Confer-
ence, pages 194–202. Morgan Kaufmann, San Fran-
cisco.
Fayyad, U. M. and Irani, K. B. (1993). Multi-interval dis-
cretization of continuous-valued attributes for classi-
fication learning. In Proceedings of the 13th Inter-
national Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence
(IJCAI-93), pages 1022 – 1027.
Fern´andez, A. and Salmer´on, A. (2008). Extension of
Bayesian network classifiers to regression problems.
In Geffner, H., Prada, R., Alexandre, I. M., and David,
N., editors, Advances in Artificial Intelligence - IB-
ERAMIA 2008, volume 5290 of Lecture Notes in Arti-
ficial Intelligence, pages 83–92. Springer.
Friedman, N., Geiger, D., and Goldszmidt, M. (1997).
Bayesian network classifiers. Machine Learning,
29:131–163.
Hall, M., Frank, E., Holmes, G., Pfahringer, B., Reutemann,
P., and Witten, I. H. (2009). The weka data min-
ing software: An update. SIGKDD Explor. Newsl.,
11(1):10–18.
Hollander, M. and Wolfe, D. A. (1999). Nonparametric
Statistical Methods. Wiley, 2nd edition edition.
Jensen, F. V. and Nielsen, T. D. (2007). Bayesian Networks
and Decision Graphs. Springer.
John, G. H. and Langley, P. (1995). Estimating continuous
distributions in bayesian classifiers. In Proceedings
of the Eleventh conference on Uncertainty in Artificial
Intelligence, pages 338 – 345.
Kozlov, D. and Koller, D. (1997). Nonuniform dynamic
discretization in hybrid networks. In Geiger, D. and
Shenoy, P., editors, Proceedings of the 13th Confer-
ence on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence, pages
302–313. Morgan & Kaufmann.
Langseth, H., Nielsen, T. D., P´erez-Bernab´e, I., and
Salmer´on, A. (2013). Learning mixtures of truncated
basis functions from data. International Journal of
Approximate Reasoning.
Lauritzen, S. and Wermuth, N. (1989). Graphical mod-
els for associations between variables, some of which
are qualitative and some quantitative. The Annals of
Statistics, 17:31–57.
L´opez-Cruz, P. L., Bielza, C., and Larra˜naga, P. (2013).
Learning mixtures of polynomials of multidimen-
sional probability densities from data using b-spline
interpolation. International Journal of Approximate
Reasoning, In Press.
Lucas, P. J. (2002). Restricted Bayesian network structure
learning. In G´amez, J. and Salmer´on, A., editors, Pro-
ceedings of the 1st European Workshop on Probabilis-
tic GraphicalModels (PGM’02), pages 117–126.
Minsky, M. (1963). Steps towards artificial inteligence.
Computers and Thoughts, pages 406–450.
Moral, S., Rum´ı, R., and Salmer´on, A. (2001). Mixtures
of Truncated Exponentials in Hybrid Bayesian Net-
works. In Benferhat, S. and Besnard, P., editors, Sym-
bolic and Quantitative Approaches to Reasoning with
Uncertainty, volume 2143 of Lecture Notes in Artifi-
cial Intelligence, pages 156–167. Springer.
Morales, M., Rodr´ıguez, C., and Salmer´on, A. (2007). Se-
lective na¨ıve Bayes for regression using mixtures of
truncated exponentials. International Journal of Un-
certainty, Fuzziness and Knowledge Based Systems,
15:697–716.
Pearl, J. (1988). Probabilistic Reasoning in Intelligent Sys-
tems. Morgan-Kaufmann. San Mateo.
P´erez, A., Larra˜naga, P., and Inza, I. (2009). Bayesian
classifiers based on kernel density estimation: Flex-
ible classifiers. International Journal of Approximate
Reasoning, 50(2):341 – 362.
R Core Team (2013). R: A Language and Environment for
Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical
Computing, Vienna, Austria. ISBN 3-900051-07-0.
Romero, V., Rum´ı, R., and Salmer´on, A. (2006). Learning
hybrid Bayesian networks using mixtures of truncated
exponentials. International Journal of Approximate
Reasoning, 42:54–68.
Rum´ı, R., Salmer´on, A., and Moral, S. (2006). Estimating
mixtures of truncated exponentials in hybrid Bayesian
network. Test, 15:397–421.
Rum´ı, R., Salmer´on, A., and Shenoy, P. P. (2012). Tractable
inference in hybrid bayesian networks with determin-
istic conditionals using re-approximations. In Pro-
ceedings of the Sixth European Workshop on Proba-
bilistic Graphical Models (PGM’2012), pages 275 –
282.
Sahami, M. (1996). Learning limited dependence Bayesian
classifiers. In KDD96: Proceedings of the second in-
ternational Conference on Knowledge Discovery and
Data Mining, pages 335–338.
Schuster, E. F. (1985). Incorporating support constraints
into nonparametric estimators of densities. Commu-
NaiveBayesClassifierwithMixturesofPolynomials
23

nications in Statistics, Part A. Theory and Methods,
14:1123 – 1136.
Shenoy, P. P. (2011). A re-definition of mixtures of
polynomials for inference in hybrid Bayesian net-
works. In Liu, W., editor, Symbolic and Quantitative
Approaches to Reasoning with Uncertainty, Lecture
Notes in Artificial Intelligence 6717, pages 98–109.
Springer.
Shenoy, P. P., Rum´ı, R., and Salmer´on, A. (2011). Some
practical issues in inference in hybrid bayesian net-
works with deterministic conditionals. In Proceed-
ings of the Intelligent Systems Design and Applica-
tions (ISDA).
Shenoy, P. P. and West, J. (2011). Inference in hy-
brid Bayesian networks using mixtures of polynomi-
als. International Journal of Approximate Reasoning,
52:641–657.
Simonoff, J. (1996). Smoothing methods in Statistics.
Springer.
ICPRAM2015-InternationalConferenceonPatternRecognitionApplicationsandMethods
24
