
A Block-based Approach for Malignancy Detection within the Prostate
Peripheral Zone in T2-weighted MRI
Andrik Rampun
1
, Paul Malcolm
2
and Reyer Zwiggelaar
1
1
Department of Computer Science, Aberystwyth University, Aberystwyth SY23 3DB, U.K.
2
Department of Radiology, Norfolk & Norwich University Hospital, Norwich NR4 7UY, U.K.
Keywords:
Prostate Cancer Detection, MRI, Block-based approach, Grey Levels Appearance.
Abstract:
In this paper, a computer-aided diagnosis method is proposed for the detection of prostate cancer within the
peripheral zone. Firstly, the peripheral zone is modelled according to the generic 2D mathematical model from
the literature. In the training phase, we captured 334 samples of malignant blocks from cancerous regions
which were already defined by an expert radiologist. Subsequently, for every unknown block within the
peripheral zone in the testing phase we compare its global, local and attribute similarities with training samples
captured previously. Next we compare the similarity between subregions and find which of the subregion has
the highest possibility of being malignant. An unknown block is considered to be malignant if it is similar
in comparison to one of the malignant blocks, its location is within the subregion which has the highest
possibility of being malignant and there is a significant difference in lower grey level distributions within the
subregions. The initial evaluation of the proposed method is based on 260 MR images from 40 patients and we
achieved 90% accuracy and sensitivity and 89% specificity with 5% and 6% false positives and false negatives,
respectively.
1 INTRODUCTION
Prostate cancer is the most commonly diagnosed can-
cer among men and remains the second leading cause
of cancer death in men. In 2013, there were ap-
proximately 240,000 and 40,000 cases reported in
the United States and United Kingdom respectively,
and is estimated to reach 1.7 million cases globally
by 2030 (Howlader et al., 2013; Chou et al., 2010;
PCUK, 2014). In the last decade, prostate cancer
screening has been receiving more attention because
it can help to detect cancer at an early stage before
there are any symptoms. Nowadays, clinical diag-
nostic tools are very popular and globally used de-
spite their inconsistency (60% - 90%) in producing
accurate results (Yu and Hricak, 2000). Many fac-
tors causing this inconsistency such as random biopsy
tests (hence, higher chance of cancerous tissues being
missed), less sensitivity to detect slow-growing and
non-aggressive tumors (as a result tumors often de-
tected in the late age (above 70 years old)), inaccurate
results (e.g. an elevated level of PSA in the blood does
not necessarily indicate cancer), etc.
Computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) of prostate mag-
netic resonance imaging (MRI) has the potential to
improve the results of clinical diagnostic tools. Un-
fortunately, prostate MRI requires a high level of
expertise and suffers from observer variability (Vos
et al., 2010). CAD systems can be of benefit to im-
prove the diagnostic accuracy of clinical methods, re-
duce variability and speed up the reading time of clin-
icians (Vos et al., 2010). In contrast to segmentation
algorithms, detection algorithms only try to decide if
tumor is present and output the approximate tumor
location instead of providing a complete segmenta-
tion. Therefore, the main goal of our research is to
develop CAD methods which automatically delineate
and localise malignant regions, leading to a reduction
of search and interpretation errors, as well as a re-
duction of the variation between and within observers
(Vos et al., 2010). In this paper, we propose a block-
based approach to find malignant regions within the
prostate peripheral zone. A block-based approach is
chosen due to its efficiency in comparison to a pixel
by pixel sliding window approach (see section 4). The
key idea of this method is, a block or patch is con-
sidered being malignant if its grey levels distribution
is similar with our training samples. We use specific
metrics to measure similarity for malignancy detec-
tion which will be explained in section 3.3.
56
Rampun A., Malcolm P. and Zwiggelaar R..
A Block-based Approach for Malignancy Detection within the Prostate Peripheral Zone in T2-weighted MRI.
DOI: 10.5220/0005179000560063
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Bioimaging (BIOIMAGING-2015), pages 56-63
ISBN: 978-989-758-072-7
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
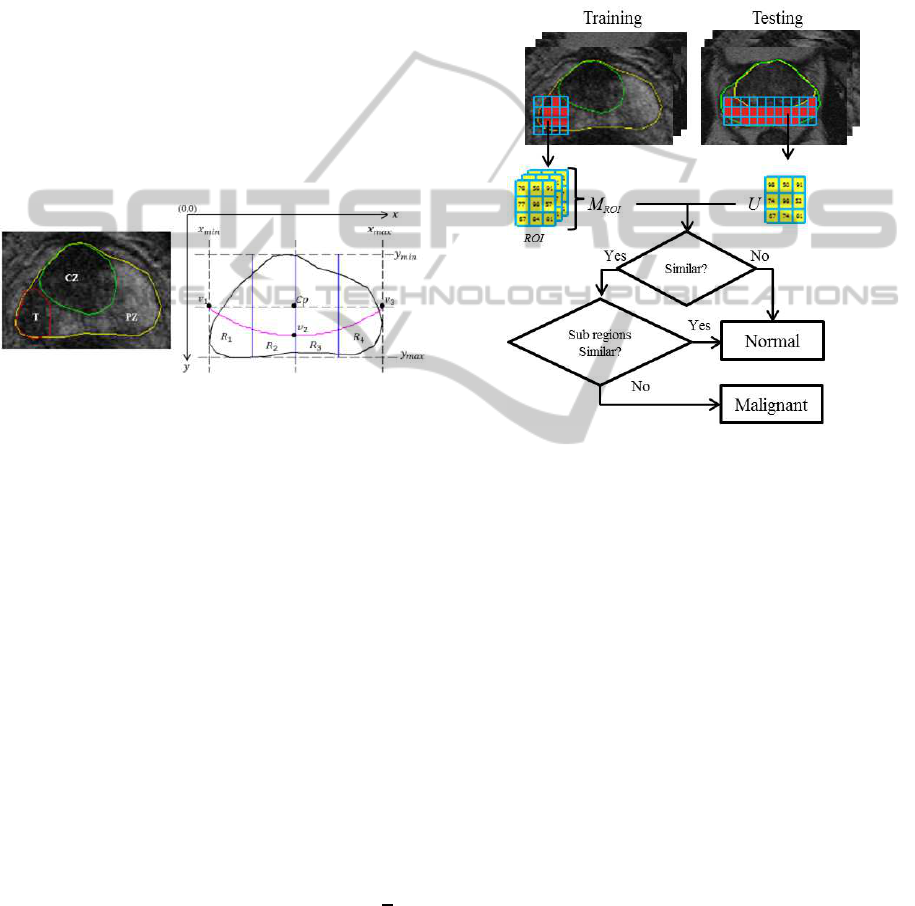
2 PERIPHERAL ZONE MODEL
Pathologically, 80%− 85% of the cancers arise in the
Peripheral Zone (PZ) and the rest are within the cen-
tral zone (Edge et al., 2010). Since the percentage oc-
currence of abnormality in the peripheral zone is high,
we aim to detect prostate abnormality within that re-
gion similar to studies in (Artan and Yetik, 2012), (Ito
et al., 2003) and (Ocak et al., 2007). We did not
perform prostate segmentation because all prostates
were already delineated by our expert radiologist (the
same in (Artan and Yetik, 2012)). To automatically
capture the PZ, we used a generic 2D mathematical
model proposed in (Rampun et al., 2014c; Rampun
et al., 2013). Figure 1 shows an example of prostate
MRI with its ground truth and the generic 2D prostate
model.
Figure 1: Prostate gland (yellow), peripheral zone (PZ), tu-
mor (T) in red and central zone (CZ) in green. Prostate
gland (black) and the defined PZ boundary y = ax
2
+bx+c
(magenta) which goes through v
1
,v
2
and v
3
.
The prostate’s PZ is defined using the quadratic equa-
tion y = ax
2
+bx+c based on three crucial coordinate
points of the prostate which are v
1
,v
2
and v
3
. They are
determined by the outmost x and y coordinates of the
prostate boundary which are x
min
,x
max
,y
min
,y
max
(see
Figure 1). For example, x
min
and y
max
can be deter-
mined by taking the minimum x and maximum y co-
ordinates along the prostate boundary. Moreover, the
x coordinates of v
1
and v
3
are captured from x
min
and
x
max
and their y coordinate is determined by taking
the y coordinate between y
min
and y
max
. Mathemati-
cally, these can be represented equations (1), (2), (3)
and (4).
C
p
= ((x
min
+ x
max
)/2,(y
min
+ y
max
)/2) (1)
v
1
= (x
min
,(y
min
+ y
max
)/2) (2)
v
2
= ((x
min
+ x
max
)/2,y
min
+ ((y
max
− y
min
) ×
3
4
))
(3)
v
3
= (x
max
,(y
min
+ y
max
)/2) (4)
where C
p
is the central coordinate of the prostate
gland. Once the coordinates of v
1
,v
2
and v
3
are
defined, we can determine the boundary of the PZ.
Finally, the PZ region is divided into four subre-
gions (R
1
, R
2
, R
3
and R
4
) according to the prostate
anatomy in the European consensus guidelines divi-
sion of prostate gland (Dickinson et al., 2011).
3 METHODOLOGY
Figure 2: An overview of the proposed methodology.
Figure 2 shows the summary of the proposed method-
ology. In the training phase, we capture region of in-
terests (ROI, also known as a block) from tumor re-
gions. In Figure 2, M
ROI
contains many collections of
ROIs which basically represents different patterns of
grey level distribution within malignant regions. Sub-
sequently, in the testing phase each unknown block
(U) within the PZ is compared with every block in
M
ROI
. Based on the comparison results, if U is simi-
lar (measured using specific metrics) with any blocks
in M
ROI
, then we assume U is most likely being ma-
lignant.
3.1 Preprocessing
Similar to the study in (Artan and Yetik, 2012), each
image MRI is median filtered to reduce noises as well
as to preserve sharp regional boundaries (in our case
we want to preserve the information-bearing struc-
tures such as tumor’s edge boundaries).
3.2 Training
In training phase, we captured 334 number of ma-
lignant blocks (334 of ROIs as illustrated in 2) sized
ABlock-basedApproachforMalignancyDetectionwithintheProstatePeripheralZoneinT2-weightedMRI
57

7× 7 (this size gives the best quantitative experimen-
tal results, see experimental results) from 5 patients
(50 malignant regions of 50 MRI slices/images). Note
that, each malignant region is already delineated by
an expert radiologist. For every malignant region in
MRI image, we divide it into blocks (ROI) and only
take ROI if all of its elements are within the tumor re-
gion (red in figure 2). This means ROI is excluded if
one or more of the pixels within the block is outside
the tumor boundary to ensure reliability in our train-
ing samples (we want to make sure that our training
samples are purely taken from malignant tissues). At
the end of this process, M
ROI
contains 334 number of
malignant blocks as shown in equation (5).
M
ROI
(i) = {ROI
1
,ROI
2
,ROI
3
....ROI
i
} (5)
where i is the i
th
block in M
ROI
.
3.3 Testing
In the testing phase, for each unknown block (U)
we compare its similarity with every block in M
ROI
(hence there will be 334 comparisons for every U). If
U is similar with one of the blocks in M
ROI
, we as-
sume that the PZ has higher possibility of being ma-
lignant. Note that for block´s size selection, we per-
formed exactly the same in the training phase within
the prostate gland and PZ boundaries. On the other
hand, we used the following metrics to measure sim-
ilarity between U and M
ROI
: global similarity, local
similarity and attribute similarity which have the min-
imum and maximum values of 0 and 1.0, respectively.
In all cases we use a default threshold 0.5 which
means if the similarity is more than half of its max-
imum similarity value (1.0), U is considered being
malignant. According to (Ali et al., 2005) the human
eye is less sensitive in perceiving a change in shape
and texture if the similarity percentage between two
objects is less than 50% (hence studies in (Ali et al.,
2005; Hasan et al., 2009; Hasan et al., 2012) have
used a default threshold 0.5 in measuring similarity
between two textures). In fact, a study conducted
by (Chen et al., 2006) discussed the use of decision
threshold (minimum and maximum are 0 and 1, re-
spectively) adjustment in classification for cancer pre-
diction concluded that when the sample sizes are sim-
ilar (in our case each U and ROI are the same size),
they suggested that the optimal decision threshold and
balanced decision is approximately 0.5 as their exper-
imental results show high concordance with a balance
between sensitivity and specificity. When estimating
string similarity, (Elita et al., 2007) considers the se-
quence of common elements have to be at least 50%
in both strings to be considered similar.
3.3.1 Global Similarity
Global similarity (G) measures the number of ele-
ments (#U) in U within the range of i
th
block in
M
ROI
. This metric does not concern about the indi-
vidual grey level value in ROI
i
but the overall range.
To calculate the global similarity:
1. Calculate the mean (ROI
mean
i
) and standard devia-
tion (ROI
std
i
)
2. Calculate its lower (ROI
Lrange
i
) and upper
(ROI
Urange
i
) ranges using equation (6) and (7)
3. Calculate G using equation (8)
ROI
Lrange
i
= ROI
mean
i
− ROI
std
i
(6)
ROI
Urange
i
= ROI
mean
i
+ ROI
std
i
(7)
G
i
=
ROI
Lrange
i
≤ #U ≤ ROI
Urange
i
n× m
(8)
where n and m are the size of the block. Equation (8)
calculates similarity based on the number of elements
inU within the range of i
th
block in M
ROI
. This means
the more elements in U within the range of i
th
block,
the more similar they are (leads to higher possibility
being malignant).
3.3.2 Local Similarity
Local similarity (L) measures the amount of overlap-
ping information between two blocks. In comparison
to global similarity, this metric compares correspond-
ing elements in U and ROI
i
. For every U we measure
its L using equation (9).
L
i
=
∑
min{U(z),ROI
i
(z)}
∑
max{U(z),ROI
i
(z)}
(9)
where z represents every single element in a block. In
this measure, the higher the overlapping value means
the more similar the blocks (between U and ROI
i
).
3.3.3 Attribute Similarity
Attribute similarity (A) measures the number of oc-
currences of unique overlapping grey levels between
two blocks. This means only grey levels appear in
both blocks will be taking into account. This metric
can be calculated using the following steps:
1. Find unique elements in U and ROI
i
, let say
U
unique
and ROI
unique
i
2. Count the number of grey level occurrences in
U
unique
and ROI
unique
i
, let say f
U
unique
and f
ROI
unique
i
3. Find the overlapping elements in U
unique
and
ROI
unique
i
, let say U
unique
∩ ROI
unique
i
BIOIMAGING2015-InternationalConferenceonBioimaging
58

4. Count the number of occurrences for ev-
ery element in U
unique
and ROI
unique
i
, let say
f
U
unique
∩ROI
unique
i
5. Use equation (10) to calculate A
A
i
=
∑
f
U
unique
∩ROI
unique
i
∑
f
U
unique
∪ROI
unique
i
(10)
where f
U
unique
∪ROI
unique
i
represents the number of grey
levels occurrences in both U and ROI
i
(the same as
the number of grey levels in U and ROI
i
).
3.4 Subregion Similarity
In addition to the metrics in section 3.3, we use his-
togram intersection distance (d) to measure the simi-
larity between two subregions’ histograms (e.g. his-
togram from R
1
and R
3
in Figure 1) by measuring
their distance in the intersection space (Rubner et al.,
2000). Previous studies (Rampun et al., 2014b; Ram-
pun et al., 2014a) have shown that the peripheral
zone has higher chance of being malignant if one
of the subregions contains a significant number of
lower grey levels (e.g. below 120) in comparison
to the other subregions. For example, R
1
contains
80% lower grey levels whereas R
2
, R
3
and R
4
are
dominated by upper grey levels (this makes R
1
looks
darker in T2-Weighted-MRI image in comparison to
the other subregions). Several studies suggested that
prostate cancer tissue tends to appear darker on T2-
weighted MRI images (Garnick et al., 2012; Ginat
et al., 2009; Taneja, 2004; Mohamed et al., 2003).
Moreover, radiologists also tend to use regions in-
tensity (e.g. darker region is more likely to be ma-
lignant) to identify abnormality within the peripheral
zone (Edge et al., 2010). Therefore, the main ob-
jective of this metric is to find subregion which has
the highest possibility of being malignant. We chose
this metric because of its capability to handle partial
matches when the areas of two regions are different
(Rubner et al., 2000). In our case, every area of sub re-
gion is different (due to PZ and prostate boundaries).
For each subregion (e.g. R
1
), we contsruct grey level
histogram (255 bins) by assigning every pixel to its
appropriate grey level and normalise it to sum equal to
1. After normalisation, we calculate the histogram’s
mean value to roughly identify which subregion has
the highest number of lower grey levels. The same
process applied to the other subregions (R
2
, R
3
and
R
4
). Subsequently, we take histograms with the low-
est and highest histogram mean values and calculate
d using equation (11).
d = 1 − (
∑
j=1
min{H
max
( j),H
min
( j)}/
∑
j=1
H
max
( j))
(11)
where j represents each bin in the histogram and H
max
and H
min
are subregions’ histograms which have the
highest and lowest histogram mean values, respec-
tively. In contrast to the metrics in section 3.3, smaller
d indicates higher similarity as it means smaller dis-
tance separates two histograms in the intersection dis-
tance (hence lower possibility of the PZ being malig-
nant).
3.5 Malignancy Detection
An unknown sample/block (U) is considered to be
malignant if all of the following conditions are true:
1. If its G, L and A are greater than 0.5 and
2. If d > 0.5 and
3. If the location of U is within the subregion with
the lowest histogram mean value
Figure 3 shows the flow chart decision rules for ma-
lignancy detection in the proposed method. Note that
the selected R is the subregion with the lowest his-
togram mean value. If the location of the segmented
region is not within the subregion which has the low-
est histogram mean value, we do not consider U as
malignant because previous studies (Rampun et al.,
2014b; Rampun et al., 2014a) shows that in many
cases cancerous region has lower intensity as previ-
ously mentioned in (Garnick et al., 2012; Ginat et al.,
2009; Taneja, 2004; Mohamed et al., 2003). Note that
Figure 3: Flow chart decision rule.
the threshold 0.5 is selected based on the studies con-
ducted by (Chen et al., 2006; Ali et al., 2005; Hasan
et al., 2009; Hasan et al., 2012; Elita et al., 2007) in
ABlock-basedApproachforMalignancyDetectionwithintheProstatePeripheralZoneinT2-weightedMRI
59

different applications. Hence, we did not perform ex-
periments to determine a new threshold value due to
the extensive experiments have been done in the liter-
ature.
4 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
For evaluation, our database contains 260 MRI im-
ages (118 images are identified as malignant and 142
are benign/normal) from 40 different patients aged 54
to 74 collected from the Norfolk and Norwich Univer-
sity Hospital. The prostates, cancers and central zones
were delineated by an expert radiologist on each of
the MRI images and all malignant lesions are biopsy
proven. Each image was analysed and classified as
to whether the prostate contains malignancy (and seg-
ment the approximate tumor location) based on the
decision rules explained in section 3.5. Subsequently,
we compared the result with the ground truth whether
the prostate contains malignancy or not. The pro-
posed method achieved 90% accuracy and sensitivity
and 89% specificity with 5% and 6% false positives
and false negatives, respectively. Note that the term
accuracy here means correct classification rate (CCR)
which means if an image is classified as containing
malignancy and the ground truth is malignant then the
image is classified correctly. The first two examples
in Figure 4 shows the results of two MR images con-
taining malignant region in each of them.
Figure 4: Examples of malignant cases.
The ground truth of malignant regions are within the
red lines and green blocks are blocks identified as ma-
lignant. For every case, we use a generic PZ mathe-
matical model in section 2 to define the PZ bound-
ary (magenta line) and divide the PZ model into four
subregions (partitioned by the blue lines). As we can
see in image 1 and 2 the segmented blocks are within
the malignant regions indicating correct classification
and approximate location. In image 1, a small block
segmented within R
3
(false positive) which indicates
malignancy. However, since the subregion R
1
has the
lowest average grey level value (and d > 0.5), we con-
sider the segmented region in R
1
has higher possibil-
ity of being malignant and only consider blocks in R
1
.
Similarly in image 2, segmented blocks in R
3
are con-
sidered having higher possibility of being malignant
because subregion R
3
has the lowest grey level aver-
age value (and d > 0.5), hence a segmented block in
R
4
are considered to have lower possibility of being
malignant.
Figure 5: Examples of cases with two malignant regions.
Figure 5 shows examples of MR images containing
two malignant regions. In both image 3 and 4, sub-
region R
1
has the lowest grey level mean value and
d > 0.5. The results show that most malignant blocks
were found to be malignant within the cancerous re-
gions (red lines). We also can see some segmented
blocks within the second malignant regions in both
images. On the other hand, Figure 6 shows examples
of segmentation results using different window sizes.
In image 5, there is no segmented region using 9 × 9
window size but we can clearly see several regions
were segmented in image 6 using 7× 7 window. This
indicates bigger window size decreases the sensitivity
rate and increases the specificity rate.
Figure 6: Examples of segmentation results using different
window sizes.
We tested the accuracy, sensitivity and specificity of
the proposed method using different window sizes of
3× 3, 5× 5, 7 × 7, 9× 9 and 11× 11. Based on the
results shown in Figure 7, sensitivity increases using
a small size of window 3× 3 and gradually decreases
as the window size is getting bigger. On the other
hand, specificity decreases using a small window and
increases when a bigger window size is used (e.g.
9× 9). A balanced results in terms of accuracy, sen-
sitivity and specificity were achieved using a medium
window size of 7× 7.
Various methods using different frameworks, modali-
ties and features have been proposed in the literature
and our method achieved similar results. Neverthe-
less, it is extremely difficult to make a quantitative
comparison due to the differences in datasets (differ-
ent modalities such as T2-weighted MRI, diffusion-
weighted MRI, etc) and frameworks (e.g. combining
different modalities) used in the other studies. In fact,
absence of public datasets also makes a quantitative
BIOIMAGING2015-InternationalConferenceonBioimaging
60

Figure 7: Accuracy, sensitivity and specificity using differ-
ent window sizes.
comparison of methodologies in the literature is im-
possible. However, to have an overall qualitative es-
timate of the functioning of our method we compared
with some of the previous studies in Table 1.
Table 1: Results are ordered based on accuracy, sensitivity
and specificity, respectively (all measured in %).
Authors Cases Acc Sen Spe
Our method 40 90 90 89
(Sung et al., 2011) 42 89 89 89
(Vos et al., 2010) 29 89 - -
(Ampeliotis et al., 2007) 10 87 - -
(Tiwari et al., 2010) 19 84 - -
(Rampun et al., 2014c) 25 82 81 84
(Artan and Yetik, 2012) 15 82 76 86
(Tabesh et al., 2007) 29 81 - -
(Kim et al., 2006) 20 75 73 77
(Han et al., 2008) 46 - 96 92
(Engelbrecht et al., 2003) 36 - 93 -
(Shimofusa et al., 2005) 60 - 93 -
(Ito et al., 2003) 111 - 87 74
(Litjens et al., 2011) 188 - 83 -
(Niaf et al., 2012) 30 - 82 -
(Futterer et al., 2006) 6 - 83 83
(Miao et al., 2007) 30 - 76 70
(Ocak et al., 2007) 50 - 73 88
(Llobet et al., 2007) 303 - 57 61
(Schlemmer et al., 2004) 28 - - 68
From the qualitative comparisons in Table 1, the pro-
posed method achieved similar results with the state
of the arts in all metrics (accuracy, sensitivity and
specificity). Note that some of the authors did not
report one or two of their results. In terms of ac-
curacy and sensitivity, our method achieved the best
result in comparison to the other methods in Table
1. However, the proposed method of (Sung et al.,
2011) achieved similar results in all metrics of 89%.
(Vos et al., 2010) and (Ampeliotis et al., 2007) did
not report sensitivity and specificity of but their pro-
posed methods achieved similar results 89% and 87%,
respectively. For sensitivity, (Han et al., 2008) re-
ported their proposed method achieved 96% which is
the highest in Table 1 where the proposed methods of
(Engelbrecht et al., 2003) and (Shimofusa et al., 2005)
achieved 93% followed by our method 90%. (Llobet
et al., 2007) achieved 57% sensitivity based on 303
number of cases where (Litjens et al., 2011) achieved
83% in 188 number of cases. Finally, in terms of
specificity, the proposed method of (Han et al., 2008),
once again achieved the highest result of 92% where
our proposed method achieved 89% similar with the
methods proposed by (Sung et al., 2011), and (Ar-
tan and Yetik, 2012). (Llobet et al., 2007) once again
achieved the lowest result of 61% but evaluated based
on the largest dataset in Table 1.
These comparisons are subjective as results are highly
influenced by the number of datasets, different modal-
ities and methods frameworks. For example although
the method proposed of (Llobet et al., 2007) produced
the lowest sensitivity and specificity but the evalua-
tion is based on 303 prostates. On the other hand, al-
though (Han et al., 2008) achieved the highest sensi-
tivity and specificity (based on Table 1 ) but was eval-
uated with smaller dataset contains 46 ultrasound im-
ages (46 patients). Similarly, although the proposed
method achieved 90% for both accuracy and sensitiv-
ity, these are based on a specific window size (7× 7).
The performance of the proposed method vary ac-
cording to window sizes (e.g accuracy 72% and 80%
with 3 × 3 and 5 × 5 window size, respectively, see
7). In terms of computationally complexity, the pro-
posed method took approximately 3 hours 30 minutes
in both training and testing phases (310 MRI images,
Matlab 2013, Windows 7 Intel core i5). On the other
hand using a pixel by pixel sliding window approach
took approximately 30 hours for the entire experiment
with 7× 7 window size. Using smaller window size
(e.g. 5× 5) took even longer. Therefore we chose
block based approach due to its speed performance.
5 DISCUSSIONS
In contrast to the earlier methods, our method is dif-
ferent in the sense that:
1. We only used a single modality for abnormal-
ity detection which is T2-Weighted MRI whereas
(Engelbrecht et al., 2003) used multimodality
such as diffusion MRI and MR Spectroscopy.
2. The method in (Han et al., 2008) used additional
clinical knowledge (e.g. shape of the region) to
discriminate cancer regions in addition of image
features while our method only used the informa-
tion of grey level distributions between two sam-
ples to achieve similar results.
ABlock-basedApproachforMalignancyDetectionwithintheProstatePeripheralZoneinT2-weightedMRI
61

3. The methods in (Ocak et al., 2007; Sung et al.,
2011) used various perfusion parameters on a sin-
gle modality while our method is purely based
on the information of grey level distributions to
achieve similar results.
This paper makes three contributions:
1. A novel approach of CAD diagnosis method
which is based on similarity measure between un-
known and sample blocks.
2. The development of the proposed method and its
application in prostate cancer detection and local-
isation using a single MRI modality with compa-
rable results to the state-of-the-art methods in the
literature.
3. We introduced a simple approach in measuring
similarity based on the occurrences of overlapping
grey levels between two samples (section 3.3.3).
6 CONCLUSIONS
The proposed method could help clinicians to perform
targeted biopsies which ought to be better and poten-
tially improve the accuracy of prostate cancer diagno-
sis. In conclusion, we have presented a novel method
of prostate cancer detection and localisation within
the PZ. In this paper we have showed the potential
of grey level information (G, L and A) in predicting
malignancy by comparing each unknownsample with
malignant samples. In addition to that, we also have
used statistical grey levels information (mean value)
to find subregion which has the most possibility of be-
ing malignant. By combining these information, we
achieved promising and similar results with the state
of the arts in the literature. Nevertheless, the best
results were achieved using 7 × 7 window size and
achieved lower accuracy and specificity in smaller
window sizes.
REFERENCES
Ali, M. A., Dooley, L. S., and Karmakar, G. C. (2005). Au-
tomatic feature set selection for merging image seg-
mentation results using fuzzy clustering. In Inter-
national Conference on Computer and Information
Technology.
Ampeliotis, D., Antonakoudi, A., Berberidis, K., and
Psarakis, E. Z. (2007). Computer aided detection of
prostate cancer using fused information from dynamic
contrast enchanced and morphological magnetic res-
onance images. In IEEE International Conference
on Signal Processing and Communications(ICSPC
2007). IEEE Xplore.
Artan, Y. and Yetik, I. S. (2012). The digital rectal exami-
nation (dre) remains important outcomes from a con-
temporary cohort of men undergoing an initial 12-18
core prostate needle biopsy. Can J Urol, 16(6):1313
–1323.
Chen, J. J., Tsai, C., Moon, H., Ahn, H., Young, J. J., ,
and Chen, C. (2006). The use of decision threshold
adjustment in classification for cancer prediction.
http://www.ams.sunysb.edu/∼hahn/psfile/papthres.pdf.
Accessed 19-June-2014.
Chou, R., Croswell, J. M., Dana, T., Bougatsos, C., Blaz-
ina, I., Fu, R., Gleitsmann, K., Koenig, H. C., Lam,
C., Maltz, A., Rugge, J. B., and Lin, K. (2010). A
review of the evidence for the u.s. preventive services
task force. http://www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.
org/uspstf1 2/prostate/prostateart.htm/. Accessed 15-
November-2013.
Dickinson, L., Ahmed, H. U., Allen, C., Barentsz, J. O.,
Carey, B., Futterer, J. J., Heijmink, S. W., Hoskin,
P. J., Kirkham, A., Padhani, A. R., Persad, R., Puech,
P., Punwani, S., Sohaib, A. S., Tombal, B., Villersm,
A., v. der Meulen, J., and Emberton, M. (2011). Mag-
netic resonance imaging for the detection, localisa-
tion, and characterisation of prostate cancer: recom-
mendations from a european consensus meeting. Eur
Urol, 59(4):477–494.
Edge, S. B., Byrd, D. R., Compton, C., Fritz, A. G., Greene,
F. L., and Trotti, A. (2010). AJCC Cancer Staging
Manual. Springer, Chicago, 7th edition.
Elita, N., Gavrila, M., and Cristina, V. (2007). Experiments
with string similarity measures in the ebmt frame-
work. In Proceedings of the RANLP 2007 Conference.
Engelbrecht, M. R., Huisman, H. J., Laheij, R. J., Jager,
G. J., van Leenders, G. J., Kaa, C. A. H.-V. D., de la
Rosette, J. J., Blickman, J. G., and Barentsz, J. O.
(2003). Discrimination of prostate cancer from nor-
mal peripheral zone and central gland tissue by using
dynamic contrast-enhanced mr imaging. Radiology,
229:248–254.
Futterer, J. J., Heijmink, S. W. T. P. J., Scheenen, T. W. J.,
Veltman, J., Huisman, H. J., Vos, P., de Kaa, C.
A. H., Witjes, J. A., Krabbe, P. F. M., Heerschap,
A., and Barentsz, J. O. (2006). Prostate cancer lo-
calization with dynamic contrast-enhanced mr imag-
ing and proton mr spectroscopic imaging. Radiology,
241(2):449–458.
Garnick, M. B., MacDonald, A., Glass, R., and Leighton,
S. (2012). Harvard Medical School 2012: Annual Re-
port on Prostate Diseases. Harvard Medical School.
Ginat, D. T., Destounis, S. V., Barr, R. G., Castaneda, B.,
Strang, J. G., and Rubens, D. J. (2009). Us elastog-
raphy of breast and prostate lesions. Radiographics,
29(7):2007–2016.
Han, S., Lee, H., and Choi, J. (2008). Computer-aided
prostate cancer detection using texture features and
clinical features in ultrasound image. J. Digital Imag,
21(1):121–133.
Hasan, M. M., Ali, M. A., Kabir, M. H., and Sorwar, G.
(2009). Object segmentation using block based pat-
terns. In TENCON 2009 -2009 IEEE Region 10 Con-
ference, pages 1–6.
BIOIMAGING2015-InternationalConferenceonBioimaging
62

Hasan, M. M., Sharmeen, S., Rahman, M. A., Ali, M. A.,
and Kabir, M. H. (2012). Block based image segmen-
tation. Advances in Communication, Network, and
Computing, 108:15–24.
Howlader, N., Noone, A. M., Krapcho, M., Garshell, J.,
Neyman, N., Altekruse, S., Kosary, C., Yu, M., Ruhl,
J., Tatalovich, Z., Cho, A., Mariotto, H., Lewis, D.,
Chen, H., Feuer, E., and Cronin, K. (2013). Seer can-
cer statistics review,1975-2010, national cancer insti-
tute. http://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975 2010/. Accessed
16-October-2013.
Ito, H., Kamoi, K., Yokoyama, K., Yamada, K., and
Nishimura, T. (2003). Visualization of prostate can-
cer using dynamic contrast-enhanced mri: compari-
son with transrectal power doppler ultrasound. British
Journal of Radiology, 76(909):617–624.
Kim, K. C., Park, B. K., and Kim., B. (2006). Localiza-
tion of prostate cancer using 3t mri: comparison of
t2-weighted and dynamic contrast-enhanced imaging.
J Comput Assist Tomogr, 30:7–11.
Litjens, G. J. S., Vos, P. C., Barentsz, J. O., Karssemeijer,
N., and Huisman, H. J. (2011). Automatic computer
aided detection of abnormalities in multi-parametric
prostate mri. In Proc.SPIE 7963, Medical Imaging
2011: Computer-Aided Diagnosis. SPIE.
Llobet, R., Juan, C., Cortes, P., Juan, A., and Toselli, A.
(2007). computer-aided detection of prostate can-
cer. International Journal of Medical Informatics,
76(7):547–556.
Miao, H., Fukatsu, H., and Ishigaki, T. (2007). Prostate
cancer detection with 3-t mri: comparison of diffu-
sionweighted and t2-weighted imaging. Eur J Radiol,
61:297–302.
Mohamed, S., El-Saadany, E. F., Abdel-Galil, T., Shen, J.,
Salama, M. M. A., Fenster, A., Downey, D. B., and
Rizkalla, K. (2003). Region of interest identification
in prostate trus images based on gabor filter. In IEEE
46th Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems,
volume 1, pages 415–419.
Niaf, E., Rouviere, O., Mege-Lechevallier, F., Bratan, F.,
and Lartizien, C. (2012). Computer-aided diagnosis
of prostate cancer in the peripheral zone using multi-
parametric mri. Phys Med Biol, 57:3833–3851.
Ocak, I., Bernardo, M., Metzger, G., Barrett, T., Pinto, P.,
Albert, P. S., and Choyke, P. L. (2007). Dynamic
contrast-enhanced mri of prostate cancer at 3 t: a study
of pharmacokinetic parameters. American Journal of
Roentgenology, 189(4):W192–W201.
PCUK (2014). Prostate cancer key facts.
http://www.cancerresearchuk.org/cancer-
info/spotcancerearly. Accessed 15-April-2014.
Rampun, A., Malcolm, P., and Zwiggelaar, R. (2013). De-
tection and localisation of prostate abnormalities. In
3rd Computational and Mathematical Biomedical En-
gineering (CMBE’13), pages 204–208.
Rampun, A., Malcolm, P., and Zwiggelaar, R. (2014a).
Computer aided diagnosis method for mri-guided
prostate biopsy within the peripheral zone using grey
level histograms. In 7th International Conference on
Machine Vision (ICMV’14).
Rampun, A., Malcolm, P., and Zwiggelaar, R. (2014b).
Detection and localisation of prostate cancer within
the peripheral zone using scoring algorithm. In 16th
Irish Machine Vision and Image Processing Confer-
ence (IMVIP’14).
Rampun, A., Malcolm, P., and Zwiggelaar, R. (2014c).
Detection of prostate abnormality within the periph-
eral zone using local peak information. In 3rd Inter-
national Conference on Pattern Recognition Applica-
tions and Methods (ICPRAM’14). SCITEPRESS.
Rubner, Y., Tomasi, C., and Guibas., L. J. (2000). The earth
movers distance as a metric for image retrieval. Inter-
national Journal of Computer Vision, 40(2):99–121.
Schlemmer, H. P., Merkle, J., and Grobholz, R. (2004). Can
preoperative contrast-enhanced dynamic mr imaging
for prostate cancer predict microvessel density in
prostatectomy specimens? Eur Radiol, 14:309–317.
Shimofusa, R., Fujimoto, H., Akamata, H., Motoori, K., Ya-
mamoto, S., Ueda, T., and Ito, H. (2005). Diffusion-
weighted imaging of prostate cancer. J Comput Assist
Tomogr, 29:149–153.
Sung, Y. S., Kwon, H.-J., Park, B. W., Cho, G., Lee,
C. K., Cho, K.-S., and Kim, J. K. (2011). Prostate
cancer detection on dynamic contrast-enhanced mri:
Computer-aided diagnosis versus single perfusion pa-
rameter maps. American Journal of Roentgenology,
197(5):1122–1129.
Tabesh, A., Teverovskiy, M., Pang, H. Y., Kumar, V. P.,
Verbel, D., Kotsianti, A., and Saidi, O. (2007). Mul-
tifeature prostate cancer diagnosis and gleason grad-
ing of histological images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imag.,
26(10):1366–1378.
Taneja, S. S. (2004). Imaging in the diagnosis and man-
agement of prostate cancer. Reviews in Urology,
6(3):101–113.
Tiwari, P., Kurhanewicz, J., Rosen, M., and Madabhushi, A.
(2010). Semi supervised multi kernel (sesmik) graph
embedding: identifying aggressive prostate cancer via
magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy. In
Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted In-
tervention MICCAI. Springer.
Vos, P. C., Hambrock, T., Barentsz, J., and Huisman, H.
(2010). Computer-assisted analysis of peripheral zone
prostate lesions using t2-weighted and dynamic con-
trast enhanced t1-weighted mri. Physics in Medicine
and Biology, 55:1719–1734.
Yu, K. K. and Hricak, H. (2000). Imaging prostate cancer.
Radiol Clin North Am, 38(1):59–85.
ABlock-basedApproachforMalignancyDetectionwithintheProstatePeripheralZoneinT2-weightedMRI
63
