
3-D Shape Matching for Face Analysis and Recognition
Wei Quan, Bogdan J. Matuszewski and Lik-Kwan Shark
Robotics and Computer Vision Research Laboratory, Applied Digital Signal and Image Processing (ADSIP) Research
Centre, University of Central Lancashire, Preston PR1 2HE, U.K.
Keywords: Face Recognition, Shape Matching and Modelling, Isometric Embedding Representation, Non-Rigid
Deformation Registration.
Abstract: The aims of this paper are to introduce a 3-D shape matching scheme for automatic face recognition and to
demonstrate its invariance to pose and facial expressions. The core of this scheme lies on the combination of
non-rigid deformation registration and statistical shape modelling. While the former matches 3-D faces
regardless of facial expression variations, the latter provides a low-dimensional feature vector that describes
the deformation after the shape matching process, thereby enabling robust identification of 3-D faces. In
order to assist establishment of accurate dense point correspondences, an isometric embedding shape
representation is introduced, which is able to transform 3-D faces to a canonical form that retains the
intrinsic geometric structure and achieve shape alignment of 3-D faces independent from individual’s facial
expression. The feasibility and effectiveness of the proposed method was investigated using standard
publicly available Gavab and BU-3DFE databases, which contain faces expressions and pose variations.
The performance of the system was compared with the existing benchmark approaches and it demonstrates
that the proposed scheme provides a competitive solution for the face recognition task with real-world
practicality.
1 INTRODUCTION
Human face is one of the widely used biometric
features. It is used for subject identification with
advantages, including: naturalness, non-contact and
non-intrusiveness. Face recognition and related
research have been for many years of great interest
to computer vision and image processing
communities, which has been exploited for
applications such as public security (Chellappa,
1995), fraud prevention (Jafri, 2009) and crime
prevention and detection (Kong, 2005). A fair
amount of efforts have been made on the
development of 2-D face recognition systems using
intensity images as input data in the past. Despite 2-
D face recognition systems have a capability to
achieve good performance under controlled
conditions, they are still facing great difficulties as
facial appearances can vary significantly even for
the same individual due to differences in pose,
lighting conditions and expressions (Lu, 2003).
By using 3-D face information, it is expected to
overcome the challenges faced by 2-D face
recognition systems and improve the performance of
face recognition, since the 3-D faces contain explicit
3-D geometry which can be used to handle the
variations of face pose and expressions (Lu, 2008).
Unlike simple image normalisation and alignment in
2-D face recognition, 3-D systems usually require
more sophisticated shape matching methodologies in
order to standardise data prior to feature extraction.
This is a major challenge in 3-D face recognition as
facial shapes of the same person can be very
different due to diverse expressions (Jenkins, 2011).
Face recognition based on range images has been
investigated by a number of researchers in order to
simplify 3-D face recognition and avoid the
complicated shape matching process (Pan, 2003),
(Chang, 2003; Huang, 2012). This type of method
does not use all the 3-D information available from a
face and often ignores the shape deformation caused
by the facial expression. Chua et al. (Chua, 2002)
introduced a modified version of Point Signature to
recognize 3-D face scans with facial expressions. A
method based on the integration of matching results
from multiple regions around the nose was presented
by Chang et al. (Chang, 2006). Bronstein et al.
(Bronstein, 2005) introduced an isometric model of
facial surfaces in order to derive an expression-
invariant face representation for 3-D face
45
Quan W., Matuszewski B. and Shark L..
3-D Shape Matching for Face Analysis and Recognition.
DOI: 10.5220/0005180300450052
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods (ICPRAM-2015), pages 45-52
ISBN: 978-989-758-077-2
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Figure 1: Examples of isometric embedding
transformation: (a) original faces from the same subject
across facial expressions; (b) transformed faces from row
(a); (c) original faces from different subjects; (d)
transformed faces from row (c).
recognition. The method relies on the assumption
that face is approximately isometric and the geodesic
distances among the points on the facial surface are
preserved under facial expressions. Lu et al. (Lu,
2008) proposed a 3-D deformation modelling
scheme that is capable of handling facial expression
variations. With assistance of automatically
extracted landmarks, a deformable model was built
linearly, and the method has been applied to the
problem of matching multiview facial scans to a
neutral facial model. Mpiperis et al. (Mpiperis,
2007) proposed a geodesic polar parameterisation of
the facial surface. With the parameterisation, the
intrinsic surface attributes do not change under the
isometric deformation caused by facial expressions.
A representation of patch geodesic moment for 3-D
face recognition was proposed by Hajati (Hajati,
2012). This patch-based local pattern combines local
and global geodesic paths with patches in a coarse to
fine hierarchical computation for each surface point.
One of the common approaches for 3-D face
recognition is to register a probe face to each gallery
face and then calculate the sum of the distances
between their points. This is computationally
expensive and sensitive to facial expresion
variations. To improve the efficiency,
Mohammadzade et al. (Mohammadzade, 2013)
introduced an iterative normal point method for
finding the corresponding points between a probe
face and gallery faces. The method can also cope
with the changes of facial expressions.
The statistical-model based face recognition has
been one of the most successful techniques over the
past few decades. In this paper, a 3-D shape
matching scheme is proposed, which works in
conjunction with statistical shape modelling to
complete the task of face recognition. An isometric
embedding shape representation is used for the
neutralisation of 3-D faces with facial expressions so
that the non-rigid deformation problem caused by
facial expressions can be handled and the locality
preserving projection (LPP) is used in the
dimensionality reduction process to construct the
statisitical shape model. One of the novel
contribution of the paper is the use of the isometric
embedding transformation. It not only enables the
shape representation of 3-D faces indepdenet from
individual’s facial expressions, but also reduces the
complexity of the dense point correspondence search
in the shape matching. Further more, the proposed
methods uses only 3-D point clouds with texture not
being used at all. The method is therefore inherently
invariant to variations in scenes illumination
conditions, background clutter and to some extent
angle of view. This is in striking contrast to the
method based on texture where these factors
severely limit their practical applicability.
The remainder of the paper is organised as
follows. Section 2 introduces the concept of the
isometric embedding shape representation. Then,
further shape alignment based on thin-plate spline
(TPS) surface warping is described in Section 3.
Section 4 explains the LLP dimensionality reduction
method. Section 5 describes the fitting approach for
new dataset. The experimental results are shown in
Section 6 with concluding remarks in Section 7.
2 ISOMETRIC EMBEDDING
SHAPE REPRESENTATION
Expression-invariance is of particular importance as
most of the face recognition systems have to cope
with various facial expressions. Isometric
embedding shape representation was proposed by
Elad and Kimmel (Elad, 2003), which provides a
possibility for expression-invariant face recognition.
In this work, the isometric embedding shape
representation is used to minimise the shape
ICPRAM2015-InternationalConferenceonPatternRecognitionApplicationsandMethods
46

(a)
(b)
Figure 2: Further shape alignment: (a) canonical faces
with 83 facial landmarks; (b) reference faces after
alignment.
variation across different 3-D faces from the same
individual, with the shape variations mainly caused
by facial expressions. Isometric embedding shape
representation assumes that different 3-D facial
scans from the same individual are isometric to
his/her 3-D facial scan of the neutral expression,
therefore they can be transformed to approximate the
shape of the neutral face. The new representation
provided by the isometric embedding transformation
is known as canonical form, which has the Euclidean
metric structure of the facial surface with the
geodesic replaced by Euclidean distance (Bronstein,
2007).
Figure 3: 3-D projection of LPP feature subspace for six
subjects with various facial expressions.
Multidimensional Scaling (MDS) is one of the
popular approaches for obtaining the canonical form
of faces (Bronstein, 2006). Given a smooth surface
that has been sampled at N points
1
{ ,..., }
N
,
(typically, N is approximately 3000 for a reasonable
surface description of a human face), with a matrix
of geodesic distance
[]
ij
between each pair of
surface points, each point
in the embedding space
3
is given by
12
(, )
kkk
. The geodesic distances
are calculated by some explicit or efficiently
approximated function
3
(, ) (, )
s
ij ij ij
dd
,
where
s
d
represents geodesic distance. MDS solves
the following optimisation problem
arg min ( , )
(1)
where
1
( ,..., )
N
is an
3N
matrix of
coordinates in
3
corresponding to points
1
{ ,..., }
N
on the surface, and
is an embedding error
criterion function, measuring the discrepancies
between the original geodesic distances and the
embedding space Euclidean distances. The most
common choices include the raw stress
2
(,) ( () )
raw ij ij
ij
d
(2)
and the normalised stress
2
2
(() )
(,)
()
ij ij
ij
norm
ij
ij
d
d
(3)
where
()
ij
d
is the short notation for
2
(, )
ij
d
. The
usual algorithms for solving the MDS problem are
Newton, Quasi-Newton and gradient-descent
optimisation (Bronstein, 2006). In this work, the
Newton optimisation approach is applied to achieve
the isometric embedding transformation. Figure 1
shows examples of 3-D faces before and after the
transformation. From Figure 1(b), it is seen that the
3-D shapes of the same subject with different facial
expressions appear to be similar after the
transformation, and this illustrates the goodness of
shape variance offered by the transformation for
recognition of a person independent from
individual’s facial expressions.
3 FURTHER SHAPE
ALIGNMENT
Alignment of 3-D faces in the training dataset is
essential for statistical model construction since
inappropriate alignment will result in erroneous
dense point correspondences. As the shape
deformation related to the facial expression is much
reduced by the isometric embedding transformation,
the remaining differences is the shape across the
faces of different subjects in the training dataset as
shown in Figures 1 (c) and (d). A further shape
alignment is achieved by Thin-Plate Spline (TPS)
surface warping (Quan, 2009). The alignment starts
3-DShapeMatchingforFaceAnalysisandRecognition
47

with the selection of a reference face from the
training dataset. The reference canonical face
usually contains a neutral facial expression. It is then
warped to align with other canonical faces in the
training dataset using the TPS transformation, which
is calculated based on the selected landmarks on the
faces. For the results reported here, 83 landmarks
provided in the BU-3DFE database (Yin, 2006),
were used for that purpose. For the Gavab database
(Moreno, 2004), the same 83 landmarks were
manually labelled on each training face. Figure 2
shows examples of the further shape alignment. It
can be seen that after the alignment the transformed
canonical reference faces of different subjects in
Figure 2(a) are closely matched to each other in
Figure 2(b). Thus the pair-wise dense point
correspondences between the warped canonical
reference face and other canonical faces from the
training dataset can be established by pairing points
based on the closest distance metric (Quan, 2009).
These corresponding points later provide the basis
for building a statistical shape model.
4 DIMENSIONALITY-
REDUCTION METHOD
Dimensionality-reduction is usually applied with
statistical shape modelling approaches. Principal
component analysis (PCA) and linear discriminant
analysis (LDA) are the popular choices, when data
lie in the linear subspace of a high dimensional
space. The locality preserving projection (LPP) is
able to handle a wider range of data variability while
preserving local structure, which often links the
structure of the manifold (He, 2005). Therefore it
suggests that LPP can perform well on the task of
face recognition even under the influence of facial
expressions.
LPP is a technique with isometric mapping from
the original data space to the reduced low
dimensional space (Hastie, 2001). The optimality
criterion to minimise,
() () 2
,
,
()
1
, , 1, 2,..., , 1, 2, ,
2
kk
ij
kij
ij
yy
s
ij N k d
(4)
where
()
=
k
T
j
k
j
y ax
describes the k-th coordinate of
vector
d
j
y
representing the j-th training face
n
j
x
in a lower dimensional space, dn
.
,
[]
ij
Ss is the adjacency matrix, which defines the
weighted similarity graph for all connected vertices,
and can be computed as,
2
,
exp( / 2 )
ij i j
sxx
(5)
where
is calculated as,
2
:
1
1
min
ij
N
ij
jx x
i
N
xx
(6)
To enforce a non-trivial solution to the problem
posed in Equation 4, vectors
i
a should fulfil the
following constraint,
1
TTT
ii
XDX aa. In this case, the
solution is given by solving the following
generalised eigenvalue problem:
TT
ii i
XLX XDXaa
(7)
where X contains all the training faces,
LDS
with
,
[]
ij
L
d
,
,,
1
N
ii i j
j
ds
,
,
0
ii
d
, for all
,ijdD
.
An example from the separability study of the
LPP-based method by reducing the dimensionality
for visualisation is provided in Figure 3, where the
LPP features of 150 faces from six persons with 25
expressions per person (taken from BU-3DFE
database) are projected to a 3-D space. As can be
seen, the output samples are well grouped in six
clusters corresponding to the six individuals and
exhibitings a good inter-person separability against
facial expressions even in a low dimensional space.
Figure 4: Rank-1 recognition accuracy versus feature
subspace dimensions.
5 NEW DATASET FITTING
After the eigenvectors of the constructed models are
extracted, the estimation of feature vectors can be
ICPRAM2015-InternationalConferenceonPatternRecognitionApplicationsandMethods
48
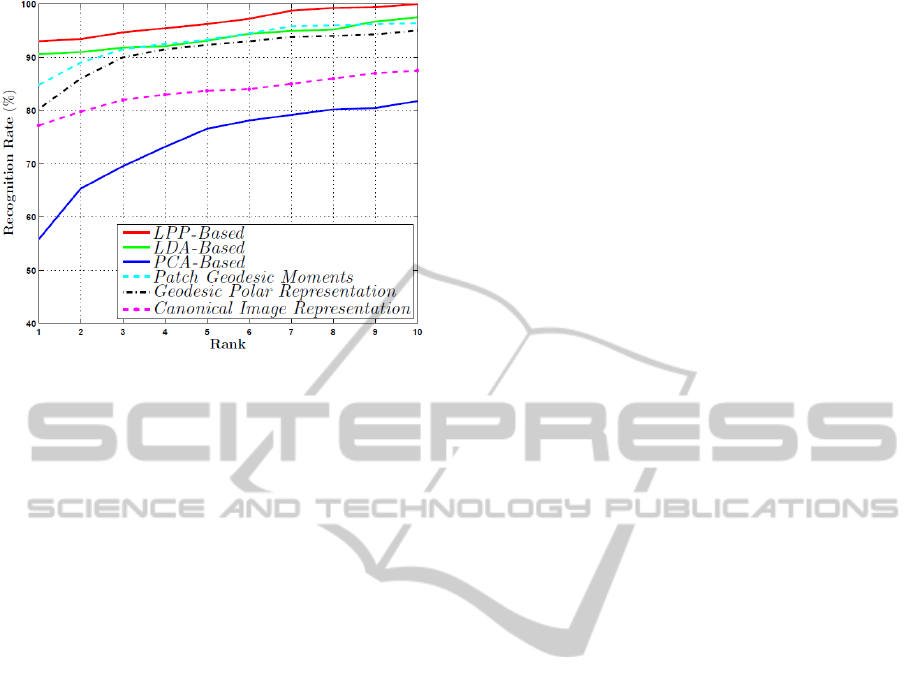
Figure 5: CMC curves of recognition accuracy for the
proposed and exiting benchmark methods.
undertaken in order to synthesize faces in a new set
of data. This is usually achieved by recursive data
registration, such as modified Iterative Closest Point
(ICP), in which the shape and pose parameters are
iteratively estimated in turn. While pose parameters
control the orientation and position of the model,
shape parameters encapsulate deformation of the
model. In order to solve all unknown parameters
effectively, the following standard optimisation
scheme is used:
1. Apply isometric embedding transformation to
the new face.
2. Align model and new face by using their
centroid point, to minimise translation
difference.
3. Apply isometric embedding transformation to
both model and new face.
4. Use ICP algorithm to estimate dense point
correspondences between transformed model
and new face.
5. Estimate feature vector
α for the new face
using back-projection based on the original
data, described as
T
opt
Aα x
(8)
where
x
is the estimated dense point
correspondences for a test face and A
opt
is the
matrix containing eigenvectors.
6. Generate a new instance of the statistical model
using the feature vector and repeat steps 2 to 5
until the pre-set convergence condition is
reached.
In this optimisation scheme, the isometric
embedding shape representation serves the similar
purpose as applied to the training dataset, which
reduces partial shape difference on both model and
new face. This potentially improves the dense point
correspondence search and provides better
estimation for the later stages of the optimisation.
Since vector
α controls the shape of the model, it
can be used as the feature vector for classifying face
identity.
6 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
To demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed
method for the purpose of face verification and
recognition, two public databases, BU-3DFE (Yin,
2006) and Gavab (Moreno, 2004), were utilised for
the evaluation in this work. While the former was
used for evaluating performance related to the
dimensions of feature subspace and facial expression
changes; the latter was used to further observe its
robustness to facial expression changes as well as
pose variations. For the sake of simplicity, the
nearest-neighbour classifier was chosen for the
feature classification in this study. The two popular
dimensionality-reduction methods, PCA and LDA,
are also compared along with other benchmark
approaches.
6.1 Experiments on BU-3DFE
Database
The BU-3DFE database consists of 2,500 3-D faces
from 100 subjects, ranging from 18 to 70 years old,
with a variety of ethnic origins including White,
Black, East-Asian, Middle East Asian, Indian and
Hispanic Latino. Each subject has seven
expressions, one neutral and six universal
expressions: anger, fear, disgust, happiness, sadness
and surprise. With the exception of the neutral
expression, each of the six universal expressions
includes four levels of intensity.
6.1.1 Feature Subspace Dimensions
The first experiment looks at the face recognition
performance against feature subspace dimension. All
2,500 faces available in BU-3DFE database were
used in the experiments. The faces were divided into
ten subsets with each subset containing the same 100
subjects and all seven kinds of expressions. For each
feature subspace dimension, one subset is selected
for testing while the remaining subsets were used for
training. Such experiments were repeated ten times
with a different subset selected for testing each time.
The faces in the training set are not used in testing.
3-DShapeMatchingforFaceAnalysisandRecognition
49
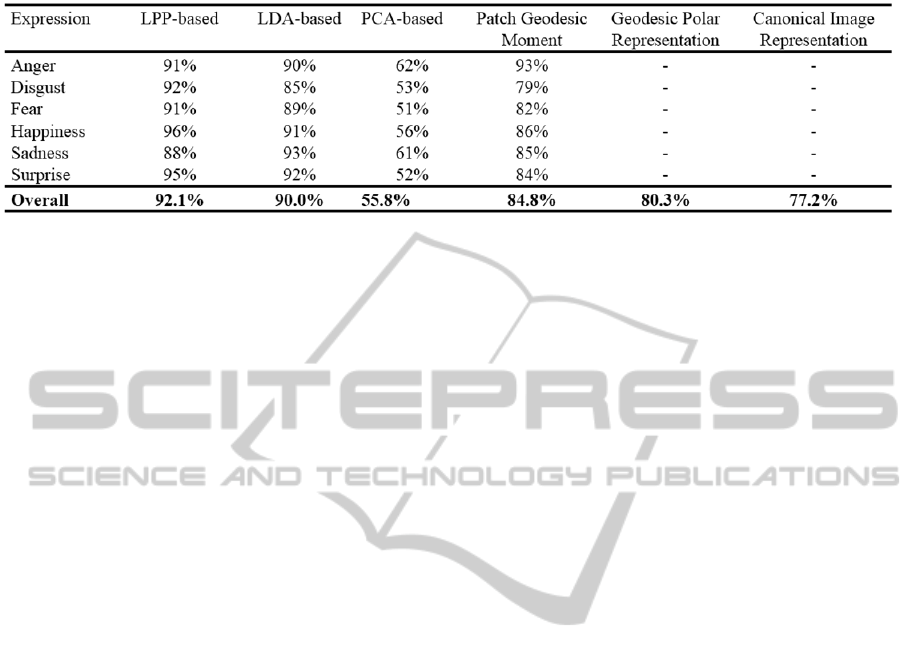
Table 1: Recognition comparison on BU-3DFE database.
Figure 4 shows the plots of rank-1 recognition rate
versus the dimensions of the feature-subspace. It is
seen that the LPP-based approach significantly
outperforms PCA and is able to achieve similar
results to LDA-based methods but with lower
dimensional subspace used. The highest recognition
rate for PCA is 79%, whereas both LDA and LPP
can reach 100% with 15 and 10 dimensional
subspace used, respectively.
6.1.2 Facial Expression
The robustness to facial expression variation is an
important aspect in the face recognition task. To see
how the proposed methods cope with this issue, a
comparison was made with that of the state-of-the-
art methods, including patch geodesic moments
(Mpiperis, 2007), geodesic polar representation
(Hajati, 2012) and canonical image representation
(Bronstein, 2005). The same experimental protocol
used in (Hajati, 2012) was applied in this work. The
performance was measured in terms of rank-1
recognition accuracy and the Cumulative Matching
Characteristics (CMC) (Rizvi, 1998). All the faces
with the neutral expression were used for training,
while the rest of database was used as the testing
faces. The rank-1 recognition rates were tabulated in
Table 1. From the table, it can be seen that among
the proposed methods the LPP-based approach
achieved the highest recognition rate with an
average accuracy of 92%, outperforming the other
state-of-the-art expression-invariant techniques by
around 8%. It is worth noticing that its recognition
rates for different expressions range from 88% to
96%. This shows that the proposed scheme can
handle facial expression changes well. The CMC of
the proposed methods together with those
benchmark methods are shown in Figure 5. From the
figure, it can be noticed that the recognition rate of
the LPP-based method is always higher.
6.2 Experiments on Gavab Database
The Gavab database is one of the most expression-
rich and noise-prone 3-D face datasets available to
the public (Moreno, 2004). It consists of 549 scans
from 61 different subjects. The subjects, of which 45
are male and 16 are female, are all Caucasian. Each
subject was scanned 9 times for different poses and
expressions, giving six neutral scans and three scans
with an expression. The scan with pose variations
contains one scan while looking up (+35
o
), one
while looking down (-35
o
), one for the left profile (-
90
o
), one for the right profile (+90
o
) as well as one
with random poses. The scans without pose changes
include two different frontal facial scans, one with
smile, and one with an accentuated laugh.
In order to evaluate the expression and pose
invariance, the proposed approach is compared with
the results achieved by the existing benchmark
methods reported in (Drira, 2010). The same
experimental protocol introduced in (Drira, 2010)
was used here. The benchmark methods include
sparse representation (Li, 2009), 3-D ridge images
(Mahoor, 2009), concave and convex regions
(Berretti, 2006) and elastic radial curves (Drira,
2010). In the experiment, one of the two frontal
scans with the neutral expression provided for each
person was taken as the training data. The rest of the
scans were used for testing. Since the proposed
approach is not designed for working on facial scans
with large part of missing data, the scans for the left
and right profiles were not included for testing.
Table 2 illustrates the results of the rank-1
recognition accuracy for different categories of
testing faces. From the table, it can be seen that the
proposed approach provides a high recognition
accuracy on both expression and pose variations,
and outperforms majority of the existing methods
with its performance very close to the best
recognition accuracy achieved by the elastic radial
curves (Drira, 2010).
ICPRAM2015-InternationalConferenceonPatternRecognitionApplicationsandMethods
50
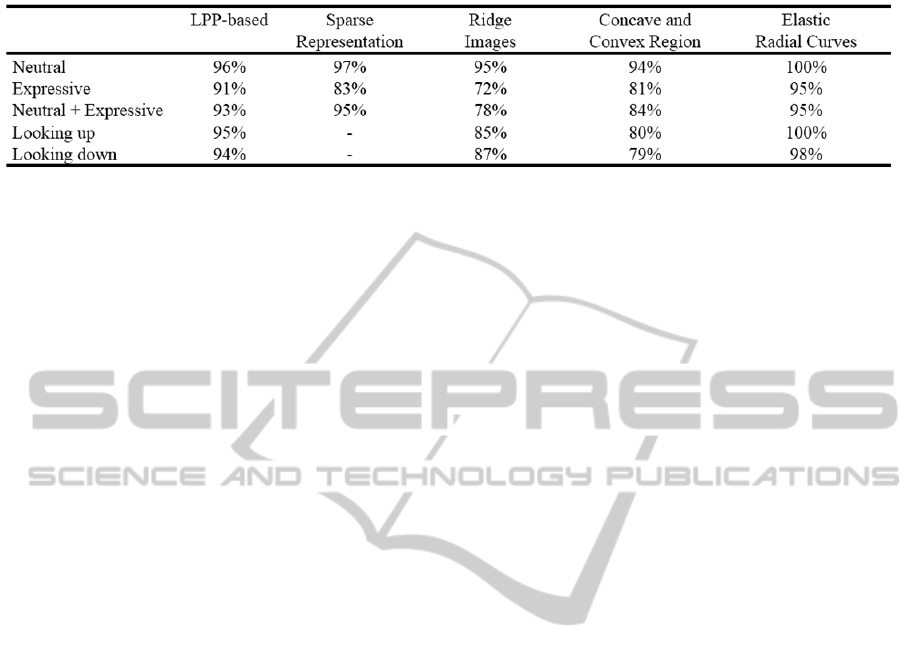
Table 2: Recognition comparison on Gavab database.
7 CONCLUSIONS
An effective 3-D shape matching scheme for pose
and expression-invariant face recognition has been
presented in this paper. The key contribution of the
proposed work is to use isometric embedding shape
representation and statistical modelling techniques to
achieve accurate dense point correspondences and
generate appropriate shapes for new 3-D face data.
From the experimental results on the Gavab and BU-
3DFE database, it can be concluded that the LPP-
based approach offers a recognition rate that can be
as high as nearly 100% and is more expression-
invariant compared with the existing benchmark
approaches. The research will be extended further by
taking into consideration more practical factors. One
possible extension for the work is to evaluate the
ability of the proposed algorithm using more
databases that are produced by different devices
operated under various acquisition environments.
The missing data problem can also be introduced
and dealt with by modifying the shape matching
scheme. Finally, more sophisticated pattern
recognition methods can be applied to increase the
overall performance of the proposed method.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The work presented in this paper was supported by
the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research
Council (Grant numbers EP/D077540/1 and
EP/H024913/1) and the EU FP7 Project
SEMEOTICONS.
REFERENCES
Berretti, S., Bimbo, A., Pala, P., 2006. 3D face recognition
by modelling the arrangement of concave and convex
regions. Adaptive Multimedia Retrieval, 108-118.
Bronstein, A., Bronstein, M., Kimmel, R., 2005. Three-
dimensional face recognition. International Journal of
Computer Vision, 64(1), 5-30.
Bronstein, A., Bronstein, M., Kimmel, R., 2007.
Expression-invariant representation of faces. IEEE
Transactions on Image Processing, 16(1), 188-197.
Bronstein, M., Bronstein, A., Kimmel, R., Yavneh, I.,
(2006). Multigrid multidimensional scaling.
Numerical Linear Algebra with Applications, 13, 149-
171.
Chang, K., Bowyer, K., Flynn, P., 2003. Multi-modal 2D
and 3D biometrics for face recognition. Proceeding of
IEEE Workshop Analysis and Modelling of Face and
Gestures, 187-194.
Chang, K., Bowyer, K., Flynn, P., 2006. Multiple nose
region matching for 3-D face recognition under
varying facial expression. IEEE Transactions on
Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 28(10),
1695-1700.
Chellappa, R., Wilson, C., Sirohey, S., 1995. Human and
machine recognition of faces: a survey. Proceeding of
IEEE, 83(5), 705-740.
Chua, C., Han, F., Ho, Y., 2002. 3-D Human face
recognition using point signature. Proceeding of
International Conference Automatic Face and Gesture
Recognition, 233-238.
Drira, H., Amor, B., Mohammed, D., Srivastava, A., 2010.
Pose and expression-invariant 3-D face recognition
using elastic radial curves. British Machine Vision
Conference.
Elad, A., Kimmel, R., 2003. On bending invariant
signatures for surfaces. IEEE Transactions on Pattern
Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 25(10), 1285-
1295.
Hastie, T., Tibshirani, R., Friedman, J., 2001. The
elements of statistical learning. Springer Series in
Statistic, Second Edition, Springer.
Hajati, F., Raie, A., Gao, Y., 2012. 2.5D face recognition
using patch geodesic moments. Pattern Recognition,
45(2012), 969-982.
He, X., Yan, S., Hu, Y., Niyogi, P., Zhang, H., 2005. Face
recognition using Laplacianfaces. IEEE Transactions
on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence. 27(3),
328-340.
Huang, D., Ardabilian, M., Wang, Y., Chen, L., 2012. 3-D
face recognition using eLBP-based facial description
and local feature hybrid matching. IEEE Transactions
3-DShapeMatchingforFaceAnalysisandRecognition
51

on Information Forensics and Security, 7(5), 1551-
1565.
Kong, S., Heo, J., Abidi, B., Paik, J., Abidi, M., 2005.
Recent advances in visual and infrared face
recognition – a review. Computer Vision and Image
Understanding, 97, 103-135.
Li, X., Jia, T., Zhang, H., 2009. Expression-insensitive 3D
face recognition using sparse representation.
Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern
Recognition. 2575-2582.
Lu, Y., Zhou, J., Yu, S., 2003. A survey of face detection,
extraction and recognition. Computing and
Informatics Pattern Recognition, 22(2), 163-195.
Lu, X., Jain, A., 2008. Deformation modeling for robust
3D face matching. IEEE Transactions on Pattern
Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 30(8), 1346-1356.
Mahoor, M., Abdel-Mottaleb, M., 2009. Face recognition
based on 3D ridge images obtained from range data.
Pattern Recognition. 42(3), 445-451.
Mohammadzade, H., Hatzinakos, D., 2013. Iterative
closest normal point for 3D face recognition. IEEE
Transaction on Pattern Analysis and machine
intelligence. 35(2), 381-397.
Moreno, A., Sanchez, A., 2004. GavaDB: a 3D face
database. COST Workshop on Biometrics on Internet:
Fundamentals, Advances and Applications. 77-82.
Mpiperis, I., Malassiotis, S., Strintzis, M., 2007. 3-D face
recognition with the geodesic polar representation.
IEEE Transaction on Information Forensic and
Security. 2(3), 537-547.
Pan, P., Wu, Z., Pan, Y., 2003. Automatic 3D face
verification from range data. Proceeding of
International Conference on Acoustic, Speech, and
Signal Processing (ICASSP 03), 3, 193-196.
Jafri, R., Ardabilian, H., 2009. A survey of face
recognition techniques. Journal of Information
Processing Systems, 53(2), 41-66.
Jenkins, R., White, D., Van-Montfort, X., Burton, A.,
2011. Variability in photos of the same face.
Cognition, 121, 313-323.
Rizvi, S., Philips, P., Moon, H., 1998. The FERET
verification test protocol for face recognition
algorithms. IEEE International Conference on
Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition.
Quan, W., Matuszewski, B., Shark, L., Ait-Boudaoud, D.,
2009. Facial expression biometrics using statistical
shape models. EURASIP Journal on Advances in
Signal Processing.
Yin, L., Weim, X., Sun, Y., Wang, J., Rosato, M., 2006. A
3D facial expression database for facial behavior
research. Proceeding of 7
th
International Conference
on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition, 221-216.
ICPRAM2015-InternationalConferenceonPatternRecognitionApplicationsandMethods
52
