
A Time-location-Based Itinerary Visualization
Florian Haag
1
, Thomas Schlegel
2
and Thomas Ertl
1
1
Institute for Visualization and Interactive Systems, University of Stuttgart,
Universit
¨
atsstraße 38, 70569 Stuttgart, Germany
2
Junior Professorship Software Engineering of Ubiquitous Systems, Technische Universit
¨
at Dresden,
N
¨
othnitzer Straße 46, 01178 Dresden, Germany
Keywords:
Timetable Visualization, Itinerary Visualization, Transportation.
Abstract:
With the advent of linked data sources, transportation information systems are no longer limited to indicating
how to get from one location to another. They can suggest where to go shopping on the way or plan several
synchronized itineraries for groups of travelers. Along with these developments, information about stopovers
evolves from mere additional data to a crucial part of the itinerary. However, current time-based visualizations
of itineraries cannot adequately convey the stopovers contained in an itinerary. We propose a time-location-
based itinerary visualization that can be used when planning trips, which allows for the easy comparison of
itineraries with different routes, and for aligning itineraries of several travelers in collaborative scenarios. We
describe the visualization concept and report on a user study that confirms the basic ideas and provides a
number of insights on how the visualization can be developed further.
1 INTRODUCTION
Automated travel planning systems for public trans-
portation have become commonplace in many coun-
tries. Instead of transportation company employees,
software searches for the appropriate itineraries based
upon the user’s wishes. In particular, such travel in-
formation systems are increasingly used on mobile
devices (Heimonen, 2009), and a multitude of efforts
to cater to mobile users of transportation information
systems have been undertaken (Arikawa et al., 2007;
Ferris et al., 2010).
With the increased integration of linked data into
services for general audiences, different kinds of in-
formation and data from several sources can be au-
tomatically combined (Gahleitner and W
¨
oß, 2004;
Walther et al., 2009). This is particularly promising
in the field of transportation, where the raw data from
travel itineraries can be cross-linked with information
about shopping opportunities or points of interest for
tourists (Alves et al., 2009; Husain and Dih, 2012).
An additional aspect to consider is that informa-
tion systems get integrated into and start supporting
our social lives (Khalil and Connelly, 2005). Systems
that support not only single users, but groups of users
in their mutual lives are being developed (Boti
ˇ
cki
et al., 2011). Travelling is one of these social activi-
ties; groups of people join each other for common legs
of a journey or meet each other while underway (Gar-
cia et al., 2011).
As a result, trip planning systems of the future will
do more than just find an itinerary that brings a trav-
eler from one place to another. They will suggest
an itinerary that lets users run errands without mak-
ing detours, or choose routes so they can meet friends
who are underway at roughly the same time. Conse-
quently, the current ways to display itineraries are not
sufficient for that kind of trip planning, as they were
designed with single trips for single or homogenous
groups of travelers in mind. Instead, new visualiza-
tions are required to provide an overview of the avail-
able itineraries, with information about possible ac-
tivities at stopovers or about itineraries of other trav-
elers.
2 RELATED WORK
A very widespread approach for displaying itinerary
suggestions is a tabular display. This is offered by
systems such as the website of the German railroad
operator Deutsche Bahn AG (DB, 2014) and provides
a basic, text-based overview of the available trips.
Other services have enhanced such a table-based
view so that the vertical axis indicates time. Sev-
77
Haag F., Schlegel T. and Ertl T..
A Time-location-Based Itinerary Visualization.
DOI: 10.5220/0005199600770084
In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Information Visualization Theory and Applications (IVAPP-2015), pages 77-84
ISBN: 978-989-758-088-8
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

eral alternative trip suggestions are placed next to
one another, similar to Gantt charts (overview by
Wilson (2003)) or the LifeLines approach (Plaisant
et al., 1996). Sometimes, detailed information can be
made available upon request (Batrinca et al., 2013).
On the other hand, displaying the relevant informa-
tion side by side allows for a direct comparison be-
tween timelines (Havre et al., 2000; Zhao et al., 2012).
This time-based approach has become widespread in
practice, in the context of passenger traffic (Daimler,
2014; Schildbach, 2014) as well as transport logis-
tics (NETRONIC, 2013) or work scheduling (Chau
et al., 2004). Additional information such as the es-
timated walking time at stops (if travelers have to
bridge a distance to get to the connecting vehicle) can
be integrated into this kind of visualization. However,
the described timeline approaches do not provide an
easy way to get an idea of the different routes used by
the trip suggestions.
Map-based views are based upon the geographic
properties of the transportation network and dis-
play the temporal aspect only as an additional fac-
tor (Cherry et al., 2006) or in a separate view (Stewart
et al., 2013). While they provide a good overview
of the available routes and the whereabouts of the re-
spective stopovers, they do not allow for a quick com-
parison of departure and arrival times or durations of
waiting phases at stopovers. Related approaches pro-
vide chances for integrating additional information
into the maps, but do not propose a complete possi-
ble solution that displays the full itineraries (B
¨
ottger
et al., 2008). When spatial and temporal informa-
tion are combined, visualizations tend to focus on the
exact representation of the spatial aspect without al-
lowing for a direct comparison of times and durations
in overlapping itineraries (Thudt et al., 2013; Ventura
and McGuffin, 2014). If both aspects are represented,
comparing itineraries at the same or at overlapping
locations becomes problematic (Hewagamage et al.,
1999), or—when using three dimensions—times can-
not always be clearly seen at a glance (Kraak, 2003).
Alternatively, place-time-charts have been pro-
posed as a visualization base rather than a geograph-
ical map. They are not only used for transportation
or logistics planning (VIA, 2013; Goverde and Meng,
2011; Regmi and Hanaoka, 2012), but have also been
proposed for passenger information, however without
integrating any extended information on the transfers
directly in the visualization (Masoodian and Budd,
2004).
A schematic graph-based and a matrix-based view
have been presented, as well (Keller et al., 2011).
While both provided an overview of the number of
routes and the travel time, the graph-based visualiza-
tion did not allow for an intuitive comparison of the
travel times, while the matrix-based visualization re-
quired memorizing the mapping of colors to various
aspects of the itineraries.
Therefore, none of the existing visualizations
gives a good idea of where several itineraries coincide
or differ in terms of location, while also conveying
an adequate comparison of the arrival and departure
times at each stop.
3 TIME-LOCATION-BASED
ITINERARY VISUALIZATION
We propose a timetable visualization for trip plan-
ning that provides an overview of both the time and
the location in the course of the journey, and that al-
lows for a side-by-side comparison of several alter-
native itineraries. Locations are abstracted to logi-
cal places, such as named stops in a public trans-
portation network, rather than the physical (geograph-
ical) location. The respective information can be re-
trieved from linked data sources that provide meta-
information on businesses and facilities near public
transportation stops (Ruta et al., 2012).
3.1 Basic Itinerary Layout
As a basis for our visualization, we chose a grid-
based approach, comparable to the small multiple
paradigm (Tufte, 1983, p. 48): Rows in the grid rep-
resent single stops that appear in any of the displayed
itineraries, while each itinerary occupies one column
in the grid. Each cell of the grid indicates a stop (ori-
gin, destination, or intermediate transfer).
Figure 1: Depiction of four grid cells in the time-location-
based visualization. They contain an excerpt of two
itineraries (columns) at two stops (rows). Three transfers
are shown (the different colors of the wide bars represent
different transportation lines). The left itinerary does not
require a transfer at the second shown stop.
Figure 1 shows four exemplary cells in the
itinerary grid. In keeping with the aforementioned
placement, the two columns belong to two distinct
IVAPP2015-InternationalConferenceonInformationVisualizationTheoryandApplications
78
itineraries, and the two rows indicate how two dif-
ferent locations are integrated in those two itineraries.
The lower left cell only shows a thin connecting line,
meaning that there is no transfer required at the given
location in that itinerary. The other cells each feature
a wide bar indicating—by its height—the time spent
at the location, as well as two tall bars symbolizing
the means of transportation used to get to and to de-
part from the location. The colors of these tall bars
match the line colors from the transit map for a good
visual correspondence here, though other color map-
pings are conceivable.
3.2 Transfer Information
The time spent at each location is represented by the
height of the wide white bar. At its upper and lower
edge, a thin bar represents the arrival and the depar-
ture time, respectively. These times are also written
as text above and below the according lines. Thus,
the vertical dimension represents time.
The same scaling is used across the whole grid.
Each grid row has its own time axis, so arrival and
departure times at one location can be compared vi-
sually across all itineraries.
Finally, the white area may partially be filled with
two semi-transparent rectangles. One rectangle ex-
tends from the arrival time downward and indicates
the estimated walking time at the location. The other
rectangle extends from the left border of the cell to
the right as an indicator for the walking distance—
the further the cell is filled horizontally, the closer the
walking distance gets to the maximum distance dis-
played in the bottom right corner of the screen (cf.
Figure 2).
Figure 2: A single grid cell displays some information on
a transfer. On the vertical time axis, the times of arrival
and departure at the location are shown. About half of the
area between the arrival and departure is filled with a grey
bar, implying that about half of the stopover time will be
required for walking. A yellow bar fills the area horizontally
by about
2
3
, which, with respect to the total distance of 90m
shown in the lower right corner, points to a walking distance
of approximately 60m.
3.3 Static Example
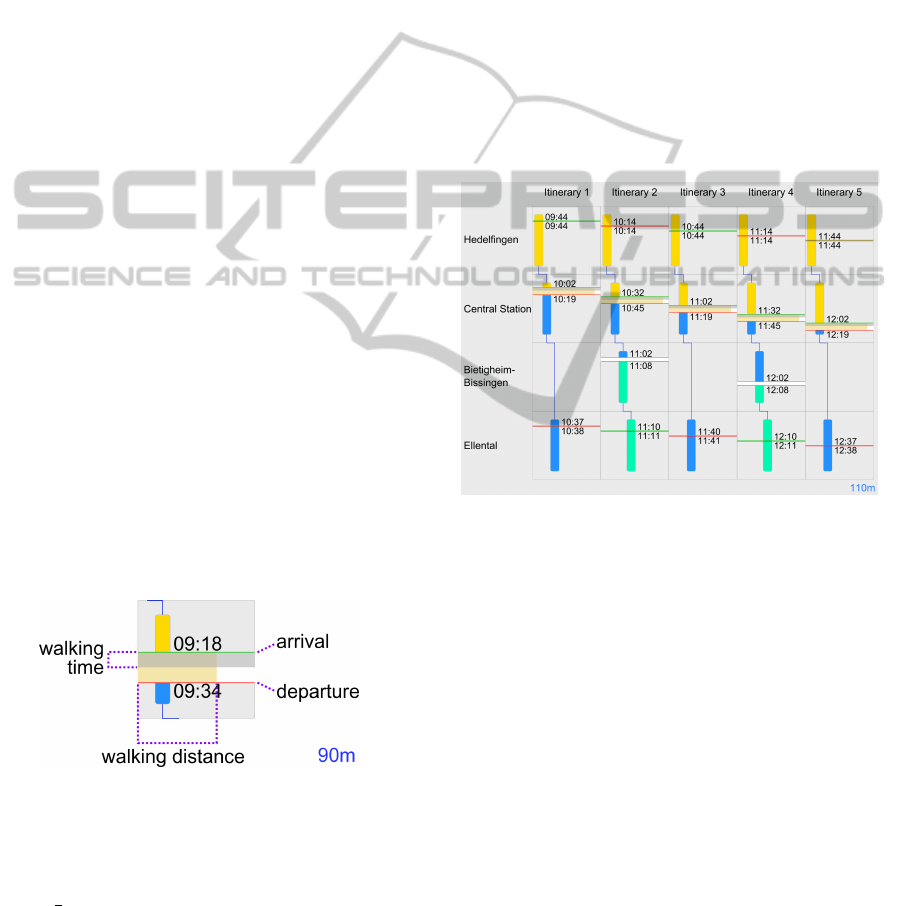
Figure 3 shows an exemplary timetable that displays
five itineraries to travel from the stop Hedelfingen
to the stop Ellental. It is evident at a single glance
that only itineraries 2 and 4 require a transfer in
Bietigheim-Bissingen. By comparing the relative ver-
tical placement of arrival and departure lines, users
can also recognize that all itineraries in this case take
about the same time, and that no two stopovers at any
of the stops overlap even by a short amount of time.
The stop at Central Station inevitably requires bridg-
ing a distance of about 100 meters, as the horizontal
walking distance indicator almost completely fills up
the stopover area at that location and the reference is
indicated as 110 meters in the lower right corner of
the screen.
Figure 3: A complete screen showing five itineraries with
the time-location-based approach. Two of the itineraries
require two intermediate transfers, the other three do not
require a transfer at stop Bietigheim-Bissingen. Three dif-
ferent colors are used for the vertical bars, which means
that three different transportation lines are used in these
itineraries (cf. Section 3.1).
3.4 Order of Locations
The order of the locations in the time-location-based
approach is not fixed. As different itineraries might
include the same locations, but in opposite orders,
there is no single optimal ordering for all displayed
locations. Instead, the order of rows can be changed.
Figure 4 shows two itineraries, where locations
have been ordered based on Itinerary 1. For Itiner-
ary 2, the order of stopovers is still recognizeable: A
thin connection line links the colored tall bars in the
order the transfers happen, and moreover, that order
is reflected by the horizontal displacement of the tall
bars.
ATime-location-BasedItineraryVisualization
79

Figure 4: Two itineraries in the time-location-based visu-
alization that visit a bookstore and an electronics store in
different orders. The stops are sorted to match the order
found in Itinerary 1. The order of stops in Itinerary 2 is
still recognizeable both by the horizontal displacement of
the thick bars and by the thin blue connection lines.
4 USER STUDY
We have conducted a small user study to gather some
comments by possible users and gain some insight
into how they react to and use our visualization. Our
study had two goals: On the one hand, we wanted
to compare the performance of users in traditional
time-based timetable visualizations with that in our
time-location-based approach. On the other hand, we
wanted to test whether the additional information con-
tained in our timetable visualization approach would
be correctly recognized by users.
For the comparative goal, we chose to present
screenshots of the free mobile app
¨
Offi (Schildbach,
2014), shown in Figure 5, which is widely used in
Germany and provides public transit data for many
European cities. It serves as a typical example for the
class of transportation information services that dis-
play itineraries with a standard time-based visualiza-
tion (Victor, 2012; Upbin, 2012; Voyages-sncf.com,
2014; Daimler, 2014).
4.1 Participants
Eleven participants between 20 and 30 years of age
took part in our user study. All participants thought
of themselves as frequent users of public transporta-
tion, though only four of them had used mobile ap-
plications to retrieve related information. Participants
were recruited with a public ad and were not affiliated
with the authors.
Figure 5: A screenshot of
¨
Offi’s (Schildbach, 2014) time-
based visualization as shown in the user study.
4.2 Materials
Written descriptions of the featured visualizations
were prepared to warrant providing each participant
with the same initial information. Trial descriptions,
along with a brief presentation of the scenario, were
prepared on paper, as well.
The prototypical application, which was installed
and configured before the user study on a Samsung
Galaxy S4 Android smartphone (cf. Figure 6), in-
cludes two major features:
• It displays static screenshots of itineraries output
by the comparison application that were retrieved
from actual requests to the transportation informa-
tion system.
• It displays itineraries based upon our time-
location-based approach. The displayed itiner-
aries were hard-coded based on the task defini-
tions for the study. Column headers could be
tapped to reorder stops based on the respective
itinerary (cf. Section 3.4).
Only actual itineraries from the public transit system
of the city and region of Stuttgart were used. This
use of real data ensured that the itineraries were re-
alistic. Moreover, none of the participants could rely
on extensive prior knowledge about Stuttgart’s transit
system as the study was conducted with inhabitants of
Dresden, about 400 kilometers away.
4.3 Design
The study was broken up into four tasks, each of
which consisted of three to six trials. Trials were al-
ways conducted in the same order to warrant compa-
IVAPP2015-InternationalConferenceonInformationVisualizationTheoryandApplications
80

Figure 6: The application used in the study, showing the
time-based (left) (Schildbach, 2014) and the time-location-
based (right) visualization on devices of the type used in
the study. Various itineraries with different stopovers can
be seen well on the right-hand device here.
rable results, and because tasks and trials would grad-
ually increase in difficulty.
4.3.1 General Information (Departure and
Arrival Times, Number of Routes ...)
The first task aimed at a comparison of our visu-
alization with the traditional time-based approach.
Each participant was shown three sets of itineraries
with the time-based visualization and three sets of
itineraries with the time-location-based visualization.
Stop names were shown as locations. Based upon that
on-screen output, some general information about the
itineraries had to be determined—in detail, the origin
and destination of the itineraries, the earliest shown
departure time and the latest shown arrival time after
and before a given time, respectively, the minimum
and maximum number of vehicle changes, as well as
the displayed number of distinct routes.
4.3.2 Available Time at Stopovers, Walking
Distance
In the second task, three sets of itineraries were shown
in connection with a scenario where a user needs to
run several errands on their way to a destination. Lo-
cations were mapped to stop names; some stops were
marked to contain special facilities (such as particu-
lar stores). Users were asked to identify the itinerary
from each set that leaves a maximum amount of time
for the errands, and the itinerary that requires the least
amount of walking, based on the distance.
4.3.3 Order of Stopovers
For the third task, instead of concrete stops, the lo-
cations were labeled bank, supermarket, etc., and
did not necessarily refer to the physically same place
across all itineraries. Each itinerary would visit the
locations in a different order, and users were asked to
identify the itinerary in each set that visits the facili-
ties in a specific order (e.g. fetching money from the
bank before buying something in the supermarket).
4.3.4 Aligning with other Itinerary
The fourth task dealt with a short encounter between
two acquaintances at a stopover. Therefore, each of
three sets of itineraries was combined with an addi-
tional highlighted itinerary that had a different origin
and destination than the others (cf. Figure 6, right).
Users were asked to identify the itinerary that pro-
vided the best opportunity to meet the other person
(using the highlighted itinerary) underway.
4.4 Procedure
Participants took part in the study one at a time in a
closed room, with one supervisor of the study present.
The printed information was handed out to them.
Participants were provided with the mobile device
on which the application was running. They had some
time to get acquainted with both visualizations based
on two sample sets of itineraries before starting the
tasks. While it was made clear to them that the whole
study would be recorded on video, the time measure-
ment in task 1 was not mentioned in order to avoid
any feeling of time pressure.
After completing the tasks, participants were
asked to provide some comments on the two visual-
izations, which were noted down by the study super-
visor. Each participant concluded the study within 30
to 40 minutes and received a small financial reward.
4.5 Results
While we were primarily interested in user comments
on the time-location-based itinerary visualization, we
did check the correctness of the responses. This was
done in order to determine whether the study partic-
ipants had correctly understood how to read the vi-
sualizations in question. Overall, participants could
answer most questions on both visualizations cor-
rectly, though error rates—and the distribution of er-
rors among participants—varied considerably. Most
answers were given in a timespan between 3 and 20
seconds for both visualizations. Table 1 provides an
overview of the correctness of answers.
ATime-location-BasedItineraryVisualization
81

Table 1: Correctness of responses in the user study: For
each task (T), the questions, the visualization (time-based
(t) or time-location-based (tl)) and the total number of re-
sponses is shown, along with the number of incorrect re-
sponses and the number of subjects who responded incor-
rectly to at least one question.
T Question Vis.
Total
Resp.
Incorrect
Resp. Subj.
1
origin/
destination
t 33 0 0
tl 33 13 6
earliest
departure
t 33 1 1
tl 33 0 0
latest
arrival
t 33 2 2
tl 33 6 3
no. of
changes
t 33 3 3
tl 33 12 5
number
of routes
t 33 12 10
tl 33 9 4
2
av. time
tl
33 18 10
min. dist. 33 5 4
3 order 33 6 3
4 meeting 33 1 1
4.5.1 Task 1: General Information
Most of the questions about the general information
were correctly solved. Several users, however, had
some difficulties recognizing the destination depend-
ing on the order of locations in the time-location-
based visualization. Determining the number of ve-
hicle changes sometimes proved difficult for a few
users especially in the time-location-based approach,
whereas this posed no problem to the other six partic-
ipants. Likewise, seven of the users could correctly
distinguish the numbers of routes among the dis-
played itineraries in the time-location-based model.
Using the time-based visualization, in contrast, ten
out of the eleven participants failed to determine the
number of different routes in one of the trials.
A few participants were discontented with aspects
of the time-location-based visualization such as the
reordering of locations, the coloring of the tall bars
(though there were also positive remarks about these
colors matching different lines in the transit system)
and the lack of any directly visible information on the
concrete lines to use (for instance, a bus number).
4.5.2 Task 2: Available Time at Stopovers,
Walking Distance
Exactly recognizing the available time at stopovers
proved difficult for most participants, even though
eleven of the incorrect answers were still partially cor-
rect. In the question about walking distances, seven of
the participants did not commit any mistakes.
Several of the participants raised concerns about
the time necessary to get used to the time-location-
based visualization. Also, they found the time re-
quired for walking to be irrelevant. Other partici-
pants commented, however, that the displayed infor-
mation was overall important; that the time available
at stopovers was easily recognizable by the vertical
time scales and that the indication of the walking
distance was useful. Two participants explicitly re-
marked that they liked the large amount of informa-
tion shown at a time.
4.5.3 Tasks 3 & 4: Order of Stopovers, Aligning
with other Itinerary
As comments on the tasks focusing on the correct or-
der of stopovers and on aligning one’s itinerary with
that of an acquaintance were very similar, the results
will be presented together.
Tasks 3 and 4 were correctly answered by almost
all participants. Only three participants made any
mistakes at all in the order-related task. An additional
participant corrected their initial erroneous answers
for one of the trials in each task 3 and task 4.
Several participants stated that they liked the
scenarios presented in these tasks. Two partici-
pants spoke favorably of the option to sort the time-
location-based view based upon each itinerary. Three
participants remarked that they considered the thin
connection line across cells unclear especially when
locations were not sorted in the order of the exam-
ined itinerary, with one of the participants explicitly
describing the line as “necessary, but confusing”.
Further comments dealt with issues in our pro-
totypical implementation that were not inherent to
the visualization concept, such as a lack of feedback
about the current location sort order, the fact that the
highlighted reference itinerary in task 4 was not fixed
to the viewport and would thus sometimes become in-
visible, and the missing support for zooming.
5 DISCUSSION
We have gathered a number of insights on what could
be considered successful and what still needs to be
changed for our time-location-based approach to be-
come useful. In general, the study participants were
able to solve the tasks by using the time-location-
based visualization. In tasks with high error rates
for the time-location-based visualization, all mistakes
were committed by about half of the participants,
while the others solved the respective task correctly.
Still, in the comparative task, users mostly performed
IVAPP2015-InternationalConferenceonInformationVisualizationTheoryandApplications
82

better in the time-based visualization. One exception
is the question about the number of different routes,
which reflects that routes cannot be compared in the
time-based visualization.
The basic grid layout appeared to be welcomed by
users. The side-by-side comparison of the itineraries
with different routes and the uniform time-scale
across the whole view were pointed out to be good
ideas. The same applies to the general amount of in-
formation, though differing statements by users im-
ply that some details—such as the estimated walk-
ing time—should be made optional. The possibility
to align one’s itinerary with that of another traveler
was positively noted, but it also evoked the question
whether the system could automatically determine the
best opportunity for a meeting. Travelers may, how-
ever, possess some additional knowledge about a par-
ticular stop, which is not available to the system and
thus could not be factored into such a decision.
The capability to reorder the locations was partly
praised, partly criticized. Much of the critique was
related to users being unsure about the current sort-
ing, which points to a lack of visible feedback in our
implementation. The observed difficulties in recog-
nizing the point of origin and the destination of the
trips could be mitigated by giving the respective cells
more visual distinctiveness compared to the stopover
cells. Moreover, using diagonal lines for the connec-
tion lines across cells could further enhance the visi-
bility of the current sorting order and make the con-
nection lines more dissimilar to the grid lines.
Some of the users made remarks about a lack of
information, such as the concrete bus or tram lines to
use, and expressed that they are used to time-based
visualizations. Therefore, a combination of the time-
location-based and the time-based visualizations ap-
pears to be promising, where the time-location-based
view is used during the planning phase and users are
free to switch to the time-based view when starting
their journey. This, along with explanatory interac-
tive clues displayed upon request, could also help
solve the perceived effort to learn how to use the time-
location-based visualization.
6 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORK
We have discussed the state of the art for visually
comparing itineraries. Based upon related work and
the requirements resulting from multi-user scenarios,
we have defined a novel way to visualize itineraries
that can be easily compared both based on tempo-
ral and local aspects, and that is suited for the syn-
chronization of trips across travelers. We have imple-
mented a prototypical mock-up of our visualization
and have conducted a small user study. Users could
solve most tasks correctly and various aspects of the
visualization were praised as useful ideas. However,
some users also committed a high number of mistakes
in some tasks, which have helped identify flaws in
some aspects of our initial time-location-based visual-
ization concept. In the discussion of the study results,
we have assembled a list of suggestions for the further
development of the time-location-based visualization
and some open issues that need to be solved.
We are confident that the time-location-based
itinerary visualization is a promising approach that
should receive further attention. The optimizations
hinted at in the study results discussion, zooming fea-
tures for the time axis, cosmetic changes such as the
user suggestion to express certain locations with icons
rather than texts, and the integration of real-time in-
formation for the displayed itineraries will require
some further user experiments. Ultimately, the results
may be applicable to other fields as the time-location-
based visualization can be generalized for other types
of event-related information—event logs of software
systems that communicate and exchange data among
each other, as well as the planning of shared resources
that can be reserved and used by the staff of an enter-
prise come to mind.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We would like to thank Steffen Huber and Bianca
Zimmer of TGU interaktion.biz (unit of TTI GmbH)
for their fine-tuning and practical execution of the
user study. Also, we would like to thank our stu-
dent research assistant Dang Huynh for his imple-
mentation of the Android prototype. This research
was funded through the IP-KOM-
¨
OV project (Ger-
man Ministry of Economy and Technology (BMWi)
grant number 19P10003N).
REFERENCES
Alves, A. O., Pereira, F. C., Biderman, A., and Ratti, C.
(2009). Place enrichment by mining the web. In AmI
’09, volume 5859 of LNCS, pages 66–77, Heidelberg,
Germany. Springer.
Arikawa, M., Konomi, S., and Ohnishi, K. (2007). Nav-
itime: Supporting pedestrian navigation in the real world.
IEEE Pervasive Comput., 6(3):21–29.
Batrinca, L., Khan, M. T., Billman, D., Aydemir, B., and
Convertino, G. (2013). A timeline visualization for
ATime-location-BasedItineraryVisualization
83

multi-team collaborative planning. In EA CHI ’13, pages
157–162, New York, NY, USA. ACM.
Boti
ˇ
cki, I., Looi, C.-K., and Wong, L. H. (2011). Supporting
mobile collaborative activities through scaffolded flexi-
ble grouping. Educ. technol. soc., 14(3):190–202.
B
¨
ottger, J., Brandes, U., Deussen, O., and Ziezold, H.
(2008). Map warping for the annotation of metro maps.
IEEE CG&A, 28(5):56–65.
Chau, K., Anson, M., and Zhang, J. (2004). Four-
dimensional visualization of construction scheduling and
site utilization. ASCE J. Constr. Eng. M., 130(4):598–
606.
Cherry, C., Hickman, M., and Garg, A. (2006). Design of
a map-based transit itinerary planner. Journal of Public
Transportation, 9(2):45–68.
Daimler AG (2014). moovel. My A to B. .
https://www.moovel.com.
DB Vertrieb GmbH (2014). DB Bahn: bahn.de. .
http://www.bahn.de.
Ferris, B., Watkins, K., and Borning, A. (2010). OneBus-
Away: Results from providing real-time arrival informa-
tion for public transit. In Proc. CHI ’10, pages 1807–
1816, New York, NY, USA. ACM.
Gahleitner, E. and W
¨
oß, W. (2004). Enabling distribution
and reuse of ontology mapping information for semanti-
cally enriched communication services. In Proc. Work-
shop on DEXA 04, pages 116–121, Piscataway, NJ, USA.
IEEE.
Garcia, I., Sebastia, L., and Onaindia, E. (2011). On the
design of individual and group recommender systems for
tourism. Expert Syst. Appl., 38(6):7683–7692.
Goverde, R. M. and Meng, L. (2011). Advanced monitoring
and management information of railway operations. J.
Rail Transp. Plann. Manage., 1(2):69–79.
Havre, S., Hetzler, B., and Nowell, L. (2000). ThemeRiver:
Visualizing theme changes over time. In Proc. InfoVis
’00, pages 115–123, Piscataway, NJ, USA. IEEE.
Heimonen, T. (2009). Information needs and practices of
active mobile internet users. In Proc. Mobility ’09, pages
50:1–50:8, New York, NY, USA. ACM.
Hewagamage, K., Hirakawa, M., and Ichikawa, T. (1999).
Interactive visualization of spatiotemporal patterns using
spirals on a geographical map. In Proc. VL ’99, pages
296–303, Piscataway, NJ, USA. IEEE.
Husain, W. and Dih, L. Y. (2012). A framework of a person-
alized location-based traveler recommendation system in
mobile application. IJMUE, 7(3):11–18.
Keller, C., Korzetz, M., K
¨
uhn, R., and Schlegel, T. (2011).
Nutzerorientierte Visualisierung von Fahrplaninforma-
tionen auf mobilen Ger
¨
aten im
¨
offentlichen Verkehr. In
Mensch & Computer 2011, Munich, Germany. Olden-
bourg.
Khalil, A. and Connelly, K. (2005). Improving cell phone
awareness by using calendar information. In INTERACT
2005, volume 3585 of LNCS, pages 588–600. Springer,
Heidelberg, Germany.
Kraak, M. (2003). The space-time cube revisited from a
geovisualization perspective. In Proc. ICC ’03, pages
1988–1996, Durban, South Africa. ICA.
Masoodian, M. and Budd, D. (2004). Visualization of travel
itinerary information on pdas. In Proc. AUIC ’04, pages
65–71, Darlinghurst, Australia. ACS.
NETRONIC Software GmbH (2013). Gantt Dia-
gramm – Visuelles Steuern von Produktion- Projekten-
Ressourcen. http://www.netronic.de/produkte/varchart-
xgantt/ueberblick.html.
Plaisant, C., Milash, B., Rose, A., Widoff, S., and Shnei-
derman, B. (1996). LifeLines: Visualizing personal his-
tories. In Proc. CHI ’96, pages 221–227, New York, NY,
USA. ACM.
Regmi, M. B. and Hanaoka, S. (2012). Assessment of in-
termodal transport corridors: Cases from north-east and
central asia. RTBM, 5(0):27–37. Intermodal Freight
Transport and Logistics.
Ruta, M., Scioscia, F., Ieva, S., Loseto, G., and Di Sciascio,
E. (2012). Semantic annotation of OpenStreetMap points
of interest for mobile discovery and navigation. In Proc.
MS ’12, pages 33–39, Piscataway, NJ, USA. IEEE.
Schildbach, A. (2014).
¨
Offi. http://oeffi.schildbach.de.
Stewart, K., Fan, J., and White, E. (2013). Thinking about
space-time connections: Spatiotemporal scheduling of
individual activities. Trans. GIS, 17(6):791–807.
Thudt, A., Baur, D., and Carpendale, S. (2013). Visits: A
spatiotemporal visualization of location histories. In Eu-
roVis – Short Papers, pages 79–83, Leipzig, Germany.
Eurographics Association.
Tufte, E. R. (1983). The Visual Display of Quantitative In-
formation. Graphics Press, Cheshire, CT, USA.
Upbin, B. (2012). Why Hipmunk is the world’s best travel
site. .
http://www.forbes.com/sites/bruceupbin/2012/06/29/
why-hipmunk-is-the-worlds-best-travel-site/.
Ventura, Q. and McGuffin, M. J. (2014). Geo-topo Maps:
Hybrid visualization of movement data over building
floor plans and maps. In Proc. GI ’14, pages 159–166,
Toronto, Ont., Canada. CIPS.
VIA Consulting & Development GmbH (2013). LUKS
2.3.5 wurde im April 2013 ver
¨
offentlicht. .
http://www.via-con.de/luks-2-3-5-released/1921.
Victor, B. (2012). BART Widget. .
http://worrydream.com/bartwidget/.
Voyages-sncf.com (2014). Mytripset – vos itin
´
eraires en
europe. http://mytripset.voyages-sncf.com.
Walther, M., Schuster, D., and Schill, A. (2009). Federated
product search with information enrichment using het-
erogeneous sources. In BIS 2009, volume 21 of LNBIP,
pages 73–84. Springer, Heidelberg, Germany.
Wilson, J. M. (2003). Gantt charts: A centenary apprecia-
tion. Eur. J. Oper. Res., 149(2):430–437.
Zhao, J., Drucker, S. M., Fisher, D., and Brinkman, D.
(2012). TimeSlice: Interactive faceted browsing of time-
line data. In Proc. AVI ’12, pages 433–436, New York,
NY, USA. ACM.
IVAPP2015-InternationalConferenceonInformationVisualizationTheoryandApplications
84
