
Engineering Implantable Microfluidic Drug Delivery Device for
Individualized Cancer Chemotherapy
Peiyi Song, Danny Jian Hang Tng, Rui Hu and Ken-Tye Yong
School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore 639798, Singapore
Keywords: Cancer Drug Delivery, Implantable Device, Biocompatibility, in Vitro, in Vivo.
Abstract: Cancer patients nowadays suffer from serious side effects and unpleasant experiences when treated with
anti-cancer drugs. Conventional drug delivery methods including drug pills/capsules, topical drug gels/drops
and drug injections are too simple, incapable of providing controllable and efficient tumour drug delivery in
cancer treatment. Implantable drug delivery devices open a new horizon for drug treatment. Through device
implantation locally onto disease site, high efficiency drug delivery can be achieved. Utilizing techniques
from microfluidics, precise manipulation of drug fluids by these devices offer great advances for treatment.
In our study, an electrochemical actuated microfluidic drug delivery device was fabricated and studied in
vitro and in vivo. Cultured pancreatic cancer cell colonies were successfully inhibited by programmable
Doxorubicin treatments controlled by devices. Further, 12 devices were implanted into 12 Kunming mice
for evaluation of biocompatibility and drug delivery performance. Tissue biopsy and blood sample analyses
indicated all 12 mice remaining healthy after devices implantation. Adrenaline was delivered to the
abdominal cavity of the mice by using the implanted device and compared with conventional injection as a
positive control. Both approaches have shown that they are able to precisely control and manipulate the
increment rate of blood pressure in the small animals.
1 INTRODUCTION
Chemotherapy is an important method in treating
cancer. However, nowadays cancer patients suffer
from serious side effects and unpleasant treatment
experiences during chemotherapy with anti-cancer
drugs, which are usually highly toxic in order to
inhibit the rapid growth of cancer tumors (Song et
al., 2013, Song et al., 2014, Gensler et al., 2010b).
Conventional drug delivery methods including drug
pills/capsules, topical drug gels/drops and drug
injections have either low efficiency, wasting most
of the drug formulation during transportation via
systemic circulation, or invasive; which causes pain
and cellular damage (Li et al., 2010, Li et al., 2009,
Li et al., 2008, Tsai and Sue, 2007). Also only
simple drug profiles can be achieved by
conventional methods (Elman and Upadhyay, 2010).
The application of conventional drug delivery
methods has reached its limit in terms of
controllability and efficiency for chemotherapeutic
treatment of tumours. Recent developments in drug
delivery devices enable drug carrying devices to be
implanted locally at disease sites, providing an
unprecedented efficiency in drug delivery (Gensler
et al., 2012, Meng and Hoang, 2012, Saati et al.,
2010b, Song et al., 2013, Farra et al., 2012).
Leveraging on microfluidic technologies, precise
manipulation of drug fluids by these devices offer
great advances in treatment. These devices present
enormous capabilities; allowing the tailoring of drug
dosages, drug delivery profiles, as well as localized
and targeted delivery of drugs to the disease sites.
Through the optimization of these parameters,
effective treatment fitting the needs of every
individual patient can be realized. This approach
will minimize the side effects of drugs formulation
to the body while maintaining the desired
therapeutic concentration for effective therapy of
illnesses.
Currently, there is one type of implantable drug
delivery devices that has a chip-like structure,
consisting of an array of micro-reservoirs (10 –
200nL capacity). By selectively open those micro-
reservoirs, designed drug formulations will diffuse
to disease site. These devices have been tested in
vitro (Chen et al., 2009, Chung et al., 2009, Elman et
al., 2009, Yang et al., 2011), in vivo (LaVan et al.,
37
Song P., Tng D., Hu R. and Yong K..
Engineering Implantable Microfluidic Drug Delivery Device for Individualized Cancer Chemotherapy.
DOI: 10.5220/0005202900370043
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Biomedical Electronics and Devices (BIODEVICES-2015), pages 37-43
ISBN: 978-989-758-071-0
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

2003, Prescott et al., 2006) and in human(Farra et al.,
2012). However, these drug delivery microchips are
unsuitable for cancer chemotherapies due to their
limited reservoir volume, necessitating periodic re-
implantations to achieve the long term drug
treatment effects (Santini Jr et al., 2000). New
studies proposed to solve this challenge by
employing an implantable drug delivery device with
a single reservoir system instead of relying on
multiple micro-reservoirs. The device system is
integrated with a MEMS micropump actuator for
driving the fluid out from the large reservoir (Tsai
and Sue, 2007). The localized delivery of drugs is
then achieved by using a cannula connected to the
drug reservoir and thereby allowing the drugs to be
delivered to the targeted tumor site. It is
demonstrated that these devices can be implanted
subcutaneously (Shobo et al., 2011) thereby
allowing one to easily refill the system with drugs
using a specialized port or via a syringe (Po-Ying et
al., 2010, Tng et al., 2013). For cancer treatment, the
significance of refilling serves not only to extend the
drug therapy period, but more importantly, the
capability to amend the formulations used,
especially when drug resistance is encountered
(Song et al., 2013, Gottesman, 2002). Single
reservoir drug delivery devices have been
extensively tested for in vitro (Gensler et al., 2012,
Shobo et al., 2011, Gensler et al., 2010b, Lo et al.,
2009b), ex-vivo(Li et al., 2008) and in vivo (Saati et
al., 2010a, Gensler et al., 2010a, Ambati et al., 2000).
Here, we demonstrate an electrochemically
actuated, single reservoir implantable microfluidic
drug delivery device for cancer treatment studies.
Fabrication was achieved using MEMS
microfabrication techniques with biocompatible
materials. The use of the microfluidic drug delivery
device for cancer chemotherapy in vitro is presented
and the experimental results highlights the drug
delivery device’s capability of customizing specific
drug delivery profiles for treating different types of
pancreatic cancer cell lines. Furthermore, working
towards usage in clinical settings, the impact and
biocompatibility of these devices implanted in the
body were carefully studied in vivo. We carefully
examine the impacts and biocompatibility of the
implantable microfluidic drug delivery device by
subcutaneously implanting them into 12 Kunming
mice for a 28 days observation. In addition, we also
demonstrate the device can be successfully used for
drug delivery therapy under implantation settings
upon comparing its effectiveness with the
conventional intravenous injection method.
2 DESIGN
The microfluidic drug delivery device is constructed
by three parts: the Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS)
drug reservoir, the Polyolefin cannula and the metal
electrode actuator (Figure 1). PDMS and Polyolefin
were chosen as construction materials for their
proven bio-compatibility. PDMS has an attractive
resealing feature thus the singular drug reservoir
constructed of PDMS can be filled/refilled using
syringe and needle without damage its structure(Lo
et al., 2009a). The metal electrode actuator contains
a pair of interdigitated Pt/Ti fingers as anode and
cathode. When supplying bias voltage on the
electrodes, Hydrogen (H
2
) and oxygen (O
2
) gases
were generated by water electrolysis. The formation
of the gases quickly increases the pressure within the
drug reservoir, and then pushes drug solution within
the reservoir to be released through the long cannula,
reaching to the disease site. This single reservoir
together with long cannula design negates the
requirement to implant the entire device at the
disease site. This is a major advantage as diseases
are hard to be reached by implantable chips due to
spatial and physiological constraints at the disease
site can now be treated with implantable devices.
For example, Ambati et al. have reported the
subcutaneous implantation of an osmotic pump
between the scapulars with a long cannula delivering
drug into the choroid and retina of rabbit eye, where
it was hard to implant an entire drug delivery chip
(Ambati et al., 2000).
Figure 1: Design of the microfluidic drug delivery device.
In the traditional design of metal electrodes, a 2-
layer electrode design was used (Song et al., 2013,
Li et al., 2008). Titanium served as adhesive layers
for platinum/gold onto substrate, which resists
oxidation in the electrolysis reaction. However,
metal electrode structure delamination was
frequently observed when the actuator was designed
to be miniaturized for implantation into small
BIODEVICES2015-InternationalConferenceonBiomedicalElectronicsandDevices
38

animals. And the delamination would negatively
affect the actuation performance as well as lifetime
(Hang Tng et al., 2014). Facing this challenge, we
invented a nanosandwiched Pt/Ti multi-layer
electrode design. The multilayered design of the
electrode was constructed with several repeating
units of thin Ti/Pt layers instead of one. All unites
are bonded together to withstand forces from water
electrochemical reaction. A relatively thick layer of
Ti at the top of metal structure provides additional
protection for the electrode (Figure 2). In our study,
the new metal electrode actuator design has shown
to enhance the lifetime up to 400% more than
conventional, despite its smaller feature size (<
20μm) than before.
Figure 2: Cross section SEM images of nanosandwiched
multilayer electrodes (a) An overview of a metal electrode.
(b) An enlarged electrode marked by measurements.
Images are reprinted with permission from Royal Society
of Chemistry (RSC).
3 FABRICATION
Nanosandwiched Pt/Ti multi-layer electrode actuator
was fabricated through photolithography, electron
beam metal evaporation and lift off processes.
AZ5214 photoresist was spun coated onto the Si
substrate at 4000 rpm for 45 s followed by a pre-
exposure bake (105 ˚C, 2 min). The electrode pattern
was generated by photolithography. Five metal
layers of titanium and platinum were then deposited
respectively (Ti-Pt-Ti-Pt-Ti) by electron beam
evaporation to create the nanosandwich structure.
The wafer was rinsed with acetone to lift-off the
remaining AZ photoresist and release electrodes.
Two thin copper wires were bonded to electrodes
with silver conductive adhesive paint. The Pt/Ti
multilayer electrode actuator measures 5mm long,
5mm wide and 0.5mm thick. The actuator was
integrated as the base of the drug reservoir.
Drug reservoir was fabricated through soft-
lithography processes. SU-8 photoresist was spun
coated onto the Si substrate at 1000 rpm for 60 s
followed by a pre-exposure bake (110 ˚C, 4 hour).
Device mold pattern was generated by exposure
(420 W, 90 s, hard contact). A post exposure bake
(95 ˚C, 1 hour) and developing was performed to
release the SU-8 mold. Polydimethylsiloxane
(PDMS) was poured into the SU-8 mold and then
degassed with in a vacuum oven. The PDMS was
then cured at 120 °C for 20 min and was
subsequently removed from the mold to get drug
reservoir pattern. Electrode actuator and drug
reservoir were assembled using PDMS. The PDMS
drug reservoir measures 10mm long, 10mm wide
and 2mm thick. A polyolefin cannula measuring 30
mm long and 0.5mm inner diameter and 0.8mm
outer diameter was then bonded to drug reservoir
using PDMS. Subsequently, the whole device was
baked at 120 ˚C for curing.
4 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Device Characterization
The delivery performance of our electrochemical
actuated microfluidic drug delivery device was
studied. Drug flow rates versus supplied voltages
were measured. Characterization results are shown
in figure 3.
Figure 3: Characterization of drug delivery flow rates at 5,
6, 7, 8 and 9 V (n = 4, mean ± SD).
The result showed that flow rates from 1 μl/s to
2.3 μl/s can be achieved with supplied voltage from
5 V to 9 V. An approximately linear trend was
observed. The controllability of actuator on delivery
drug flow rates offers great advances in treatment,
providing flexible treatment profiles (flow rates,
drug volume and treatment timing) on demands. By
using the reliable nanosanwiched metal electrode
actuator, devices showed great reliability and
consistency during drug delivery as shown by the
relatively small standard deviation. No fluid leakage
occurred during the whole test. It is worth to
mention that long-time operation of electrolysis
actuation with high voltage may lead to temperature
EngineeringImplantableMicrofluidicDrugDeliveryDeviceforIndividualizedCancerChemotherapy
39

rising. In the characterization of our devices, no
significant raise in temperature occurred during a
reasonable operation time.
4.2 Individualized Cancer Treatment
Study in Vitro
Experiment setting is shown in figure 4a. Two types
of pancreatic cancer cell (MiaPaCa-2 and Panc-1)
were cultured in petri dish for 10 days until they
have grown into colonies (Figure 4b). Cancer
chemotherapy drug doxorubicin (Dox) was delivered
to cultured cancer cell colonies using our
microfluidic drug delivery device automatically for
8 days. Gaining from the device’s controllability on
drug delivery profiles, two customized drug dose
profiles (program I: 6μg of doxorubicin delivery in
day 0, day 1 and day 2, program II: 9μg of
doxorubicin delivery in day 0 and day 3) were
conducted onto the two types of pancreatic cancer
cells. The cancer cell colonies size changes were
monitored during the 8 days treatment. Our results
have shown that cancer colonies lost their viability
after chemotherapy (Figure 4c) and the growth of
cancer cell colonies was successfully inhibited as
compared with control group (Figure 5). It is
important to notice that, the MiaPaCa-2 group and
Panc-1 group have demonstrated different response
under each customized treatment profile. Under the
treatment profile “program II”, the treatment effects
occurred at DAY 3 when the drug concentration
reached 18μg for both MiaPaCa-2 and Panc-1.
However, under the treatment profile “program I”,
the timing when inhibition of growth occurred was
different in each group (DAY 1 and DAY 2), which
Figure 4: Pancreatic cancer chemotherapy using
microfluidic drug delivery device in vitro: a. Drug
delivery device is placed in cell culture dish powered with
a 9 volt battery. b. Microscopy image of pancreatic cancer
cell colonies after 10 days culturing. c. Cancer cell
colonies after chemotherapy.
means 12μg of DOX delivery would be sufficient to
inhibit MiaPaCa-2 pancreatic cancer. Thus treatment
profile “program II” may not be suitable for treating
MiaPaCa-2 cancer for possibly overdosing the drug
amount. Therefore, using the implantable device for
an controlled drug delivery treatment, it is possible
for designing and conducting individualized
treatment profiles to treat and cure cancers towards
each patient’s needs, in the meanwhile to avoid side
effects of chemotherapies.
Figure 5: Pancreatic cancer cell colonies size changes
under programmed treatment profiles. Pictures are
reprinted with permission from Royal Society of
Chemistry. Images are reprinted with permission from
Royal Society of Chemistry (RSC).
4.3 Device Implantation in Vivo Study
with Kunming Mice
In Vivo study has been conducted for evaluating the
biocompatibility and overall performance of our
microfluidic drug delivery device. In total 12
devices were implanted subcutaneously in 12
Kunming mice where the long cannula was inserted
into the animal abdominal cavity for drug delivery
purpose. The microfluidic drug delivery device can
be easily implanted through minimally invasive
surgery procedures by creating 2 separate small
incisions in the small animal (Figure 6a, b). All 12
BIODEVICES2015-InternationalConferenceonBiomedicalElectronicsandDevices
40
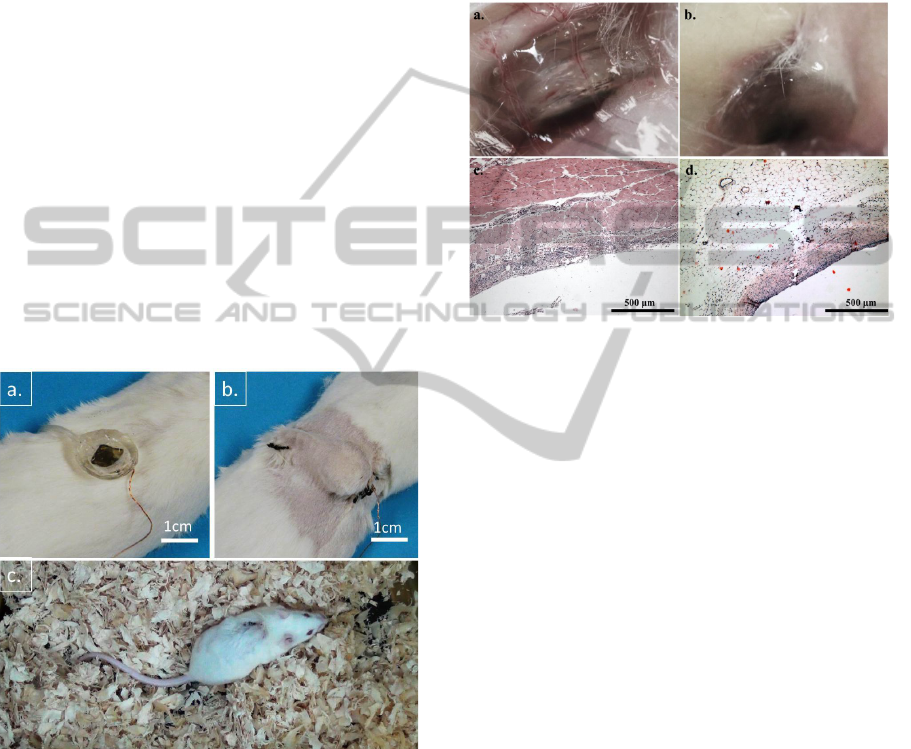
mice remained alive and healthy after surgery
throughout the 28 days experiment. 9 mice carrying
devices were involved into biocompatibility test and
other 3 mice were in implanted drug delivery study.
Figure 6c shows the representation of a device
implanted in a mouse. From the basic observations,
we concluded that the device implantation did not
cause major adverse impacts to the implanted mice.
Furthermore we carefully examined the
biocompatibility of our device by blood analysis and
tissue histology. At DAY 2, DAY 4 and DAY 28, 3
mice were sacrificed and their 1 ml blood samples as
well as tissues samples surrounding implanted
devices were acquired. Blood markers including
haemoglobin (Hb), total bilirubin (TBILI), direct
bilirubin (DBILI), red blood cell (RBC) count,
neutrophils (NE), monocytes (MO), lymphocytes
(LY), and white blood cell (WBC) showed no
abnormal variance indicating no severe infection and
adverse immune response generated from the
implantation for 28 days. Alanine aminotransferase
(ALT), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), creatinine
(CRE), and uric acid (UA) level indicated the
healthy liver and kidney functions of tested mice.
Figure 6: Device implanting into Kunming mice: a. Before
implantation. b. After implantation. c. Photography of
Kunming mouse 10 days after device implantation.
Surrounding tissue samples showed a normal
wound healing process on tested mice from DAY 2
to DAY 28 (Figure 7a, b). Implanted devices were
fully encapsulated by fibrous tissues at DAY 28
(Figure 7b). Further we have done microscopy of
haematoxylin-eosin (H&E) stained paraffin-
embedded fixed tissue sections. The observations
showed that, in DAY 4 (Figure 7c), a slight
inflammation and edema occurred at device
implantation area, but in DAY 28 (Figure 7d)
surrounding tissues returned to normal with newly
capillaries and fibrous cells formed. The results
strongly suggested that there is no rejection of the
implanted devices showing in tested animals. Our
microfluidic drug delivery device presented great
biocompatibility during the implantation with
Kunming mice.
Figure 7: Biocompatibility studies of microfluidic drug
delivery device implantation: a. Photography of device 2
days after implantation surgery. b. Photography of device
28 days after implantation surgery. c. Microscope photos
of subcutaneous tissue surrounding implanted device,
haematoxylin-eosin (H&E) stain, day4 with 10X
magnification. d. H&E stained tissue sample, photo taken
at Day28 with 10X magnification.
4.4 Implanted Drug Delivery
3 microfluidic drug delivery devices carrying 50 μl
of adrenaline were implanted into 3 Kunming Mice.
After implantation, devices were switched on for 25
seconds to deliver the adrenaline formulation into
abdominal cavities of mice. The changes of systolic
blood pressure (SBP) and diastolic blood pressure
(DBP) were measured before/5-minute after
adrenaline delivery. As comparison, 50 μl adrenaline
formulations were intraperitoneal injected to 3
Kunming mice without implant as control group.
The result showed that the SBP and DBP of both
control and experimental groups increased as the
same trend after drug delivery (Figure 8a, b). We
concluded that the microfluidic drug delivery device
is functioning properly under the implantation
setting. As the adrenaline formulation worked
similarly in both groups, we assume that in the
application of microfluidic drug delivery device for
cancer treatment, chemotherapy drug activity would
not be affected by the new delivery method.
EngineeringImplantableMicrofluidicDrugDeliveryDeviceforIndividualizedCancerChemotherapy
41
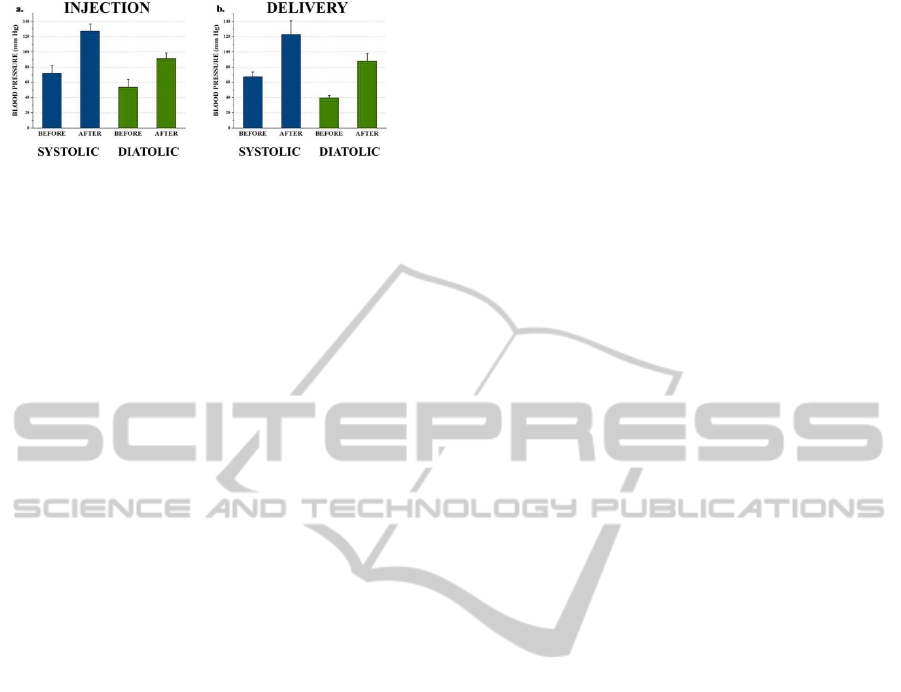
Figure 8: Blood pressure measurement data: a. Drug
delivery by syringe injection. b. Drug delivery by devices.
Both SBP and DBP were measured for every mouse.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Implantable microfluidic drug delivery devices have
been shown to have great potentials in futuristic
cancer treatment. Their controllability and ability to
leverage on the strengths of anti-cancer drugs has
made them an attractive option for overcoming the
present challenges faced in medicine. Demonstrated
with the in vitro pancreatic cancer model, we
concluded that through the programing of these
devices, chemotherapy could potentially be
individualized for every individual to gain better
treatment effects. The biocompatibility and drug
delivery performance of the device were
demonstrated with Kunming mice model in vivo.
Future researches on the microfluidic drug delivery
device will be focused on treatment effects of
different cancer tumor models on small animals, and
further clinical trials.
REFERENCES
Ambati, J., Gragoudas, E. S., Miller, J. W., You, T. T.,
Miyamoto, K., Delori, F. C. & Adamis, A. P. 2000.
Transscleral Delivery Of Bioactive Protein To The
Choroid And Retina. Investigative Ophthalmology &
Visual Science, 41, 1186-1191.
Chen, J., Chu, M., Koulajian, K., Wu, X. Y., Giacca, A. &
Sun, Y. 2009. A Monolithic Polymeric Microdevice
For Ph-Responsive Drug Delivery. Biomedical
Microdevices, 11, 1251-1257.
Chung, A. J., Huh, Y. S. & Erickson, D. 2009. A Robust,
Electrochemically Driven Microwell Drug Delivery
System For Controlled Vasopressin Release.
Biomedical Microdevices, 11, 861-867.
Elman, N. M., Ho Duc, H. L. & Cima, M. J. 2009. An
Implantable Mems Drug Delivery Device For Rapid
Delivery In Ambulatory Emergency Care. Biomedical
Microdevices, 11, 625-631.
Elman, N. M. & Upadhyay, U. M. 2010. Medical
Applications Of Implantable Drug Delivery
Microdevices Based On Mems (Micro-Electro-
Mechanical-Systems). Current Pharmaceutical
Biotechnology, 11, 398-403.
Farra, R., Sheppard, N. F., Mccabe, L., Neer, R. M.,
Anderson, J. M., Santini, J. T., Cima, M. J. & Langer,
R. 2012. First-In-Human Testing Of A Wirelessly
Controlled Drug Delivery Microchip. Science
Translational Medicine, 4, 122ra21.
Gensler, H., Sheybani, R., Li, P.-Y., Lo, R., Zhu, S., Yong,
K.-T., Roy, I., Prasad, P. N., Masood, R. & Sinha, U.
K. Implantable Mems Drug Delivery Device For
Cancer Radiation Reduction. Micro Electro
Mechanical Systems (Mems), 2010 Ieee 23rd
International Conference On, 2010a. Ieee, 23-26.
Gensler, H., Sheybani, R., Li, P. Y., Lo Mann, R. & Meng,
E. 2012. An Implantable Mems Micropump System
For Drug Delivery In Small Animals. Biomedical
Microdevices, 14, 483-496.
Gensler, H., Sheybani, R., Li, P. Y., Lo, R., Zhu, S. T.,
Yong, K. T., Roy, I., Prasad, P. N., Masood, R., Sinha,
U. K., Meng, E. & Ieee 2010b. Implantable Mems
Drug Delivery Device For Cancer Radiation
Reduction. Mems 2010: 23rd Ieee International
Conference On Micro Electro Mechanical Systems,
Technical Digest.
Gottesman, M. M. 2002. Mechanisms Of Cancer Drug
Resistance. Annual Review Of Medicine, 53, 615-627.
Hang Tng, D. J., Song, P., Hu, R., Yang, C. & Yong, K.-T.
2014. High Reliability Nanosandwiched Pt/Ti
Multilayer Electrode Actuators For On-Chip
Biomedical Applications. Analyst, 139, 407-415.
Lavan, D. A., Mcguire, T. & Langer, R. 2003. Small-Scale
Systems For In Vivo Drug Delivery. Nature
Biotechnology, 21, 1184-1191.
Li, P. Y., Sheybani, R., Gutierrez, C. A., Kuo, J. T. W. &
Meng, E. 2010. A Parylene Bellows Electrochemical
Actuator. Journal Of Microelectromechanical Systems,
19, 215-228.
Li, P. Y., Sheybani, R., Kuo, J. T. W. & Meng, E. A
Parylene Bellows Electrochemical Actuator For
Intraocular Drug Delivery. Solid-State Sensors,
Actuators And Microsystems Conference, 2009.
Transducers 2009. International, 21-25 June 2009
2009. 1461-1464.
Li, P. Y., Shih, J., Lo, R., Saati, S., Agrawal, R., Humayun,
M. S., Tai, Y. C. & Meng, E. 2008. An
Electrochemical Intraocular Drug Delivery Device.
Sensors And Actuators A-Physical, 143, 41-48.
Lo, R., Li, P.-Y., Saati, S., Agrawal, R., Humayun, M. &
Meng, E. 2009a. A Passive Mems Drug Delivery
Pump For Treatment Of Ocular Diseases. Biomedical
Microdevices, 11, 959-970.
Lo, R., Li, P. Y., Saati, S., Agrawal, R. N., Humayun, M.
S. & Meng, E. 2009b. A Passive Mems Drug Delivery
Pump For Treatment Of Ocular Diseases. Biomedical
Microdevices, 11, 959-970.
Meng, E. & Hoang, T. 2012. Mems-Enabled Implantable
Drug Infusion Pumps For Laboratory Animal
Research, Preclinical, And Clinical Applications.
Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 64, 1628-1638.
BIODEVICES2015-InternationalConferenceonBiomedicalElectronicsandDevices
42

Po-Ying, L., Sheybani, R., Gutierrez, C. A., Kuo, J. T. W.
& Meng, E. 2010. A Parylene Bellows
Electrochemical Actuator. Microelectromechanical
Systems, Journal Of, 19, 215-228.
Prescott, J. H., Lipka, S., Baldwin, S., Sheppard, N. F.,
Maloney, J. M., Coppeta, J., Yomtov, B., Staples, M.
A. & Santini, J. T. 2006. Chronic, Programmed
Polypeptide Delivery From An Implanted,
Multireservoir Microchip Device. Nature
Biotechnology, 24, 437-438.
Saati, S., Lo, R., Li, P.-Y., Meng, E., Varma, R. &
Humayun, M. S. 2010a. Mini Drug Pump For
Ophthalmic Use. Current Eye Research, 35, 192-201.
Saati, S., Lo, R., Li, P. Y., Meng, E., Varma, R. &
Humayun, M. S. 2010b. Mini Drug Pump For
Ophthalmic Use. Current Eye Research, 35, 192-201.
Santini Jr, J. T., Richards, A. C., Scheidt, R., Cima, M. J.
& Langer, R. 2000. Microchips As Controlled Drug-
Delivery Devices. Angewandte Chemie International
Edition, 39, 2396-2407.
Shobo, M., Yamada, H., Koakutsu, A., Hamada, N., Fujii,
M., Harada, K., Ni, K. & Matsuoka, N. 2011. Chronic
Treatment With Olanzapine Via A Novel Infusion
Pump Induces Adiposity In Male Rats. Life Sciences,
88, 761-765.
Song, P., Hu, R., Tng, D. J. H. & Yong, K.-T. 2014.
Moving Towards Individualized Medicine With
Microfluidics Technology. Rsc Advances, 4, 11499-
11511.
Song, P., Tng, D. J. H., Hu, R., Lin, G., Meng, E. & Yong,
K.-T. 2013. An Electrochemically Actuated Mems
Device For Individualized Drug Delivery: An In Vitro
Study. Advanced Healthcare Materials, 2, 1170-1178.
Tng, D. J. H., Song, P., Hu, R., Lin, G. & Yong, K.-T. A
Sustainable Approach To Individualized Disease
Treatment: The Engineering Of A Multiple Use Mems
Drug Delivery Device. Nanoelectronics Conference
(Inec), 2013 Ieee 5th International, 2-4 Jan. 2013 2013.
153-156.
Tsai, N.-C. & Sue, C.-Y. 2007. Review Of Mems-Based
Drug Delivery And Dosing Systems. Sensors And
Actuators A: Physical, 134, 555-564.
Yang, X. Q., Moosa, B. A., Deng, L., Zhao, L. & Khashab,
N. M. 2011. Ph-Triggered Micellar Membrane For
Controlled Release Microchips. Polymer Chemistry, 2,
2543-2547.
EngineeringImplantableMicrofluidicDrugDeliveryDeviceforIndividualizedCancerChemotherapy
43
