
Building Emotional Agents for Strategic Decision Making
Bexy Alfonso
1
, Emilio Vivancos
1
, Vicente Botti
1
and Pen´elope Hern´andez
2
1
Departamento de Sistemas Inform´aticos y Computaci´on, Universitat Polit`ecnica de Val`encia, Valencia, Spain
2
ERI-CES and Departamento de An´alisis Econ´omico, Universidad de Valencia, Valencia, Spain
Keywords:
Agents, Emotional Architecture, Simulation, Prisoner Dilemma, Trust Game.
Abstract:
Experimental economics has many works that demonstrate the influence of emotions and affective issues on
the process of human strategic decision making. Personality, emotions and mood produce biases on what
would be considered the strategic solution (Nash equilibrium) to many games. Thus considering these issues
on simulations of human behavior may produce results more aligned with real situations. We think that
computational agents are a suitable technology to simulate such phenomena. We propose to use O3A, an
Open Affective Agent Architecture to model rational and affective agents, in order to perform simulations
where agents must take decisions as close as possible to humans. The approach evaluation is performed
trough the classical ‘prisoner dilemma’ and ‘trust’ games.
1 INTRODUCTION
There is enough evidence about the behavioral issues
of the decision-making process (Lerner et al., 2004;
Elbanna, 2006; Seo et al., 2010). Phenomena like the
individual “risk aversion” (how tolerant is an individ-
ual to risk) (Loewenstein et al., 2001), or the “illusion
of control” (overestimationof individualsof their abil-
ity to control events) (Schwenk, 1984), also involve
the affect of the decision-maker. Thus, for example,
an owner of a property that has benefited from it for
many years, and has affective bonds with it, would try
to sell the property at a higher price than an investor
that has not relation with the property. Bearing all
this in mind one may assume that when performing
experiments with human that must make strategic de-
cisions, it is very likely to get individual biased action
profiles regarding to what should be a rational solu-
tion. Therefore, when simulating human behavior in
scenarios of strategic decision-making, the representa-
tion of the individual affect may become an important
parameter in order to get results better aligned with a
real situation. Computational agents could be a suit-
able technology for creating such simulations. This
field has evolved enough to build rational entities with
a human-like practical reasoning (Weiss, 1999). The
BDI architecture is a widely accepted conceptualiza-
tion for agents that includes on its definition represen-
tative elements of human characteristics. Neverthe-
less one of the biggest challenges in this area is to pro-
vide the agents with the necessary structures in order
to reach an accurate representation of the human affec-
tive side. Some steps have been taken inspired on psy-
chological and/or neurological grounds (Marsella and
Gratch, 2009; Becker-Asano and Wachsmuth, 2010),
nevertheless a bigger effort must be done to offer less
disperse approaches and to follow an incremental line
of research (Marsella et al., 2010).
With this work we want to address some impor-
tant questions: is it possible to build a scenario with
entities representing humans that can take decisions
as humans do? How can an affective component bias
results from the rationally optimal solution? How to
model this to properly simulate the strategic decision-
making process in humans? We want to give an an-
swer to these and other questions. Our aim is to model
entities able to behave as humans do by integrating ra-
tional and emotional components, and offer them as
what-if tools than can behave as and interact with hu-
man in situations of strategic decision making. We
propose an instantiation of the Open AffectiveAgents’
Architecture. Our approach is grounded on strong
psychological and neurological fundaments.
In order to validate our proposal we have imple-
mented it, and we have used classical games of exper-
imental economy (as the prisoner’s dilemma, dictator,
ultimatum and trust games). This what-if tool allows
to tune human affective characteristics in multi-agent
systems and analyze how they influence the decision-
making process in classical games.
390
Alfonso B., Vivancos E., Botti V. and Hernández P..
Building Emotional Agents for Strategic Decision Making.
DOI: 10.5220/0005204703900397
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART-2015), pages 390-397
ISBN: 978-989-758-074-1
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

The rest of the paper is organized as follows. A re-
view of the related literature is presented in section 2.
The main components of the supporting architecture
of the approach are described in section 3. Assump-
tions, considerations as well as the main architecture
components are described in section 4. In section 5
the experiments performed as well as their results are
offered. Finally, section 6 offers a discussion and the
conclusions of the work.
2 RELATED WORK
2.1 Psychological and Neurological
Background
Psychology uses various concepts to describe the af-
fective characteristics of humans. At first there are
individual intrinsic traits that influence motivations
and behavior known as personality (Ryckman, 2007).
Then we found approaches about emotions whose
definitions vary depending on researchers and disci-
plines, but researchers generally agree on the notion
of reactions as a consequence of events, actions of
other agents, and/or objects (Ortony et al., 1988). An-
other issue considered in psychological literature is
that, regardless of the emotions experienced after an
event, humans keep a kind of temperament or mood,
which has less intensity than emotions, isalso an expe-
riential component but lasts longer and is not necessar-
ily associated to a cause (Mehrabian, 1997). Personal-
ity and emotions have been addressed from different
perspectivesby important psychologists and scientists
(Cornelius, 2000; Ryckman, 2007). The cognitive
perspective stands out among the others for compu-
tational applications. On the other hand neurological
experiments use advanced technology to find out the
way the brain works on linking the human emotions
mechanism and cognition processes (Pessoa, 2008).
A. Dam´asio and J. E. Ledoux works have been very
relevant on the study of the emotions and the brain
(LeDoux, 1998; Dam´asio, 1994). Dam´asio argued
that in some situations affective factors, as power-
ful heuristics of the brain to solve complex prob-
lems, may get better decisions than rational factors
(Bechara et al., 1997), in that they alleviate individ-
uals of the overloads that may come by using only
cognitive processes when facing complex choices.
2.2 Computational Approaches
In this section we review some approaches that ad-
dress the main processes related to the affective side
of individuals from a cognitive perspective. These
processes include the appraisal, the affect internal dy-
namics and the affect consequences. The way they
dial with the different processes as well as the main
psychological concepts related to affect is often par-
tial and domain specific. There are interdisciplinary
approaches that are continuously used (Ortony et al.,
1988; Mehrabian and Russell, 1974; Ekman, 1999b).
They have become widely accepted alternatives due
to their suitability for computational applications.
The BDI architecture has commonly been a start-
ing point to model rational agents. This is the case of
(Jiang et al., 2007). The authors propose a practical
reasoning separated from the emotions mechanism,
and primary (infant-like emotions such as “angry”,
“happy” or “surprised”) as well as secondary emo-
tions (prospect-based and directly related to expecta-
tions and past experiences) receive a differentiated at-
tention when they influence the process of decision-
making of a traditional BDI architecture. The emo-
tional state of the agent is represented through a set of
emotion intensities. This state influences the way be-
liefs are acquired from communication or contempla-
tion and also the prioritization of the agents desires.
All emotions, beliefs, desires and intentions are as-
signed a priority. Emotions prioritize desires and they
also help to decide intentions. In this architecture in-
dividual differences associated to emotions are deter-
mined by the specific model used on each agent to
deal with emotions. The dynamic change of the affec-
tive state is not considered and there is no feedback
from previous situation that allows to learn from emo-
tional states.
S. C. Marsella and J. Gratch created EMA, which
stands for “EMotion and Adaption” (Marsella and
Gratch, 2009). They describe a computational model
for the dynamic of emotional appraisal, and provide
a framework based on a domain independent archi-
tecture for emotional agents. In EMA a computa-
tional model of appraisal uses the interpretation of
a person-environment relationship (causal interpreta-
tion), and this interpretation is done in terms of a set
of appraised variables and is altered by a set of “cop-
ing strategies” (processes that manipulate this repre-
sentation to respond to the appraised interpretation).
The appraised variables have some values for each
proposition extracted from the environment which
are stored in the Appraisal frames. These variables
are: relevance, perspective, desirability, likelihood,
expectedness, causal attribution, controllability and
changeability. A two-level notion of emotional state
is modeled: appraisal and mood. The first determines
the agent coping response, and the second has an in-
direct effect on appraisal in that it is applied a mood
BuildingEmotionalAgentsforStrategicDecisionMaking
391

adjustment to individual appraisal frames. Symbolic
labels of emotions (like fear, joy or hope) are assigned
to appraisal frames, but the agent coping responses
are determined by the appraisal variables. Mood is
represented through a set of emotion labels with some
intensity. Again in this approach individual differ-
ences are not clearly modeled and the emotions com-
ponent cannot be easily detached from the practical
reasoning of the agent to allow its improvement or
modification.
C. Becker-Asano and I. Wachsmuth built
WASABI (Becker-Asano and Wachsmuth, 2010).
WASABI is an architecture for affect simulation
whose model of core affect is based on the PAD
theory (Mehrabian, 1997), and its appraisal process
is inspired by Scherer’s sequential-checking theory
(Scherer, 2001). This model distinguishes primary
and secondary emotions. It is based on (Dam´asio,
1994), (LeDoux, 1998), (Ekman, 1999a) and (Ortony
et al., 2005) theories. Mood is modeled as a back-
ground state whose value moves in a bipolar scale
of positive versus negative. Other issues added to
this proposal are the memory and emotion dynamics
components. This work was used for simulating
emotions capabilities in a virtual player. The sig-
nificance of primary and secondary emotions was
evaluated. Specific structures for dealing with each
virtual character personality and individual traits are
not explicitly defined in the architecture. Its range of
domain applications moves around virtual characters
and robotics, since it has embedded elements for
physical behavior like facial expressions as manifes-
tation of emotions. Nevertheless in order to achieve
complex cognitive behaviors its integration in other
domains like multi-agent simulations is difficult.
R. Santos et al. describe a group decision-support
system that combines personality, emotion and mood.
The approach is based on the Five Factor Model
(FFM) to represent the personality (McCrae and John,
1992), and the PAD space to model mood (Mehra-
bian, 1996b). The emotional system uses the Ortony’s
improved version of the OCC model of emotions
(Ortony, 2003). Emotions then influence the argu-
mentation process after being mapped to the PAD
space (following (Gebhard, 2005)), and also person-
ality is considered in the argumentation phase. Al-
though many affective concepts are considered in this
architecture it is specific for a scenario of negotiation
with argumentation in a group and it is difficult to sep-
arate the overall practical reasoning of the agent.
A. Fagundes et al. develop an architecture for
emotional agents. Again the affective components
emotions, personality and mood are integrated in a
BDI architecture. The results of the ALMA project
Personality
Current mood
Emotion
reactive
Mood
component
Coping
component
Results
Previous
Beliefs
Percepts
Percepts
influenced
by mood
Emotion
deliberative
Appraisal
Intentions
Options
Beliefs
component
component
component
Primary
emotions
Secondary
emotions
Figure 1: Main components of the O3A architecture.
(Gebhard, 2005) are used, and hence the OCC, PAD
and the FFM theories. Although the focus of the ap-
proach is on the cognitive state and it is easy to be
applied to various situations, it makes strong assump-
tions such as the “discarding” of percepts or elements
of the memory if they don’t rise intense emotional
states or if they don’t lead to a desirable emotional
state. Also there is not a possibility for adapting the
way emotions and mood influence the cognitive pro-
cesses for particular requirements.
In (Alfonso et al., 2014) we propose “O3A” (an
Open Affective Agent Architecture). It mainly pur-
sues to be open enough to allow different implemen-
tations of its components in order to be adapted to dif-
ferent situations. It also integrates the most important
concepts addressed on psychological theories about
affect and emotions on humans in a BDI architecture.
This way the practical reasoning and affective issues
converge in a single representation where the respon-
sibilities of each component are well defined and in-
teract to produce diverse, adaptive, and believable be-
haviors on agents. It will be better described in sec-
tion 3.
3 SUPPORTING ARCHITECTURE
Based on the appraisal theory, O3A combines men-
tal, cognitiveand motivational issues with an affective
component (Alfonso et al., 2014). O3A is build over
a BDI architecture, what allows it to reuse all the ma-
chinery of the widely accepted BDI structure. More-
over O3A brings some of the most important and ac-
cepted theories in psychology and neurology related
to emotions.
3.1 Main Components
The O3A basic structure is depicted in figure 1. Four
main components are in charge of regulating the emo-
tional processes: appraisal, emotions dynamics, and
the influence of emotions on beliefs and on intentions.
ICAART2015-InternationalConferenceonAgentsandArtificialIntelligence
392

Appraisal Component. Controls how emotions are
derived from the environment and also from the cur-
rent agent state. This task is performed by two sub-
components: the emotion reactive component and
the emotion deliberative component. The former
derives primary emotions, which follows the idea
of “onto-genetically earlier emotions” (Becker-Asano
and Wachsmuth, 2010) like those experienced by an
infant. The later determines secondary emotions con-
sidering that they are the result of more complex
chains of reasoning.
Beliefs Component. Depending on the agent cur-
rent mood, percepts may trigger different effects. The
judging of the value and importance of objects and
events is influenced by the affective valence and
arousal; for example the likelihood of seeing a poten-
tial trait increases when experiencing fear (Zadra and
Clore, 2011).
Mood Component. It is in charge of deriving a
global temperament or mood on the basis of the per-
ceived emotions and the previous mood. Personality
determines which is the mood of the agent when it is
in a neutral or “equilibrium” state. This component
also controls the way mood returns to this “equilib-
rium” state.
Coping Component. It has a close relation with the
agent intentions since it determines how the current
mood finally influences the selection of the next ac-
tion to perform through the prioritization of its inten-
tions.
4 COMPONENTS DESIGN AND
CONSIDERATIONS
4.1 Components Design
O3A is open on its definition which allows to use dif-
ferent theories in order to determine how each one of
its processes must be performed. Hence, for character-
izing the way in which some of the architecture com-
ponents specifically works, we were inspired by pre-
vious works that fit to each component definition, and
simultaneously we offer our own vision of the not cov-
ered issues. The main theories used to instantiate the
O3A Components are based on the works of (Ortony
et al., 1988), (Mehrabian, 1996b) and (Marsella and
Gratch, 2009). These works have proven to produce
relevant results in the area and are versatile enough to
be reused in new approaches.
In our design the emotion reactive component as-
sumes that percepts are labeled with the “more com-
mon emotions” to be experienced given these percept.
So for example the percept “hurricane” may have an
associated “fear” label that becomes the correspond-
ing primary emotion after been processed by the emo-
tion reactive component. The emotion deliberative
component, as stated on its own definition, performs
a more complex processing and considers more fac-
tors in order to derive secondary emotions. In our
design secondary emotions are derived from events
of any nature. They can be internal events (like the
beginning of a new intention) or external (a percept).
Events are characterized according to five variables:
desirability, likelihood, expectedness, causal attribu-
tion, and controllability. The definition of each one of
these characteristics is similar to the variables of the
appraisal frames presented in (Marsella and Gratch,
2009). From this work it was also used the mapping
from the appraisal pattern to emotion labels, which
are secondary emotions in our design. The variables
characterizing the appraisal frames are linked to the
agent mental state and they are:
desirability: linked to the agent general standards or
preferences of the event consequences. For example
if an agent is given a possibility to play in one of two
lotteries and the minimum to pay in both is higher that
the prize, the desirability of the event “time to play”
will be very low. On the other hand, even if the prize
is lower, but the collected money goes to charity, and
it is significant for the agent, the desirability will be
high. We have called this property “personal benefit”,
and is applicable to each possible option to carry out
the intention triggered by the event.
likelihood: this variable is linked to the likelihood of
outcomes. It considers the existence of past or future
states. Currently our implementation of the emotion
deliberative component only considers present propo-
sitions so the value for this variable is always 1.
expectedness: linked to the agent expectations asso-
ciated to the event. Whether the expectations are ful-
filled or violated may produce emotive reactions and
hence changes in the agent mood.
causal attribution: whether the event was produced
by the agent or by other agent or source.
controllability: linked to the capacity of the agent to
react in some way to the event. If there are no actions
defined to respond to the event its controllability will
be low.
On the other hand, the Mood component is in
charge of keeping the “current mood” updated. We
used the PAD dimensional approach (Mehrabian and
Russell, 1974) for representing the mood. The initial
mood is defined by the agent personality (it is spec-
ified in the agent definition). For representing the
personality we used the Five Factor Model (McCrae
and John, 1992). The FFM is able to accurately de-
BuildingEmotionalAgentsforStrategicDecisionMaking
393
scribe individual traits through five dimensions (open-
ness, conscientiousness, extraversion, agreeableness,
and neuroticism). The current mood will be updated
as soon as the emotions are appraised in such a way
that with a positive mood, the agent is less likely to ex-
perience a negative mood and vice versa. In particular
the mapping from the agent five dimensions of per-
sonality to the three dimensions of the PAD space to
establish the initial mood is done according to Mehra-
bian’s work (Mehrabian, 1996a). On the other hand,
the transformation of the set of emotions appraised
into the PAD mood follows the result of P. Gebhard in
(Gebhard, 2005). The Coping component then feeds
on the current mood in order to establish a priority
for the agent intentions. This requires to represent a
proper measure for each intention indicating benefits,
risks and other factors that may be biased by the agent
current mood. Currently we limit this measure to the
intention risk, that is, a measure of possible losses or
undesirable states for the agent, having in mind the
widely treated issue of risk aversion in the behavioral
economic literature (Loewenstein et al., 2001; Harri-
son and Rutstr¨om, 2008; Demaree et al., 2009). In
particular some works demonstrate that the influence
of the trait Dominance of the PAD space is a signif-
icant indicator of the risk of the decision (Demaree
et al., 2009).
5 EXPERIMENTS AND RESULTS
5.1 General Design and Integration in
Jason
We have used the BDI algorithm of Jason (Bordini
et al., 2007) to integrate the O3A emotional compo-
nents in a BDI architecture. This algorithm offers all
the necessary elements to carry out the proposed de-
sign. Table 1 shows the main elements of the model
and how they are inserted in the Jason inner structure.
Current mood, and primary and secondary emotions
are modeled as internal objects of the Jason architec-
ture. The agent personality is specified in the agent
definition and it is stored on its correspondinginternal
structure. On the other hand, to perform an intention,
each plan must have a set of necessary “personal ben-
efit arguments” in order to evaluate the “benefits” of
each possible option of the agent according to its pref-
erences and standards. The “associated risk” is in line
with the global preferability of each possible option.
The process of derivation of the primary emotions
uses perceptions from the ‘Perceive’ process of Jason.
Secondary emotions are determined through the GET-
SECONDARY-EM process and takes the event to be
processed on each reasoning cycle deriving, if it is ap-
propriate, the secondary emotions. This process feeds
on Beliefs and on the Desires derived in the Jason
‘Get
option’ process. The initial mood is set on the
process of agent initialization and the current mood is
updated each time new emotions are appraised. After
selecting an event to process, the possible options for
an agent are the Jason “applicable plans”. Then the Ja-
son ‘Filter’ process is customized in order to consider
also the agent current mood.
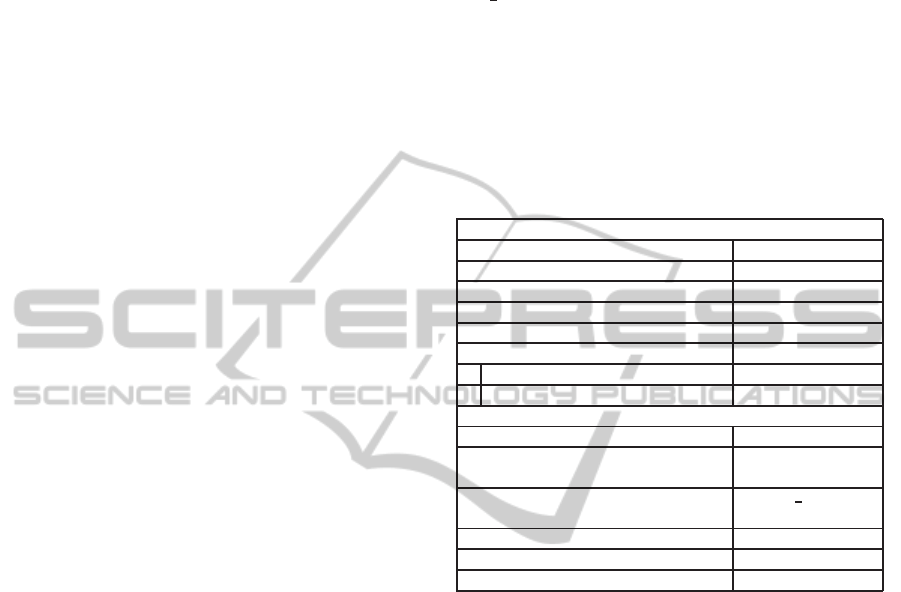
Table 1: Integration of the affective components in the Jason
platform.
VARIABLES
Description Jason element
Current Mood (M) Internal Object
Primary Emotions (PEm) Internal Object
Secondary Emotions (SEm) Internal Object
Personality (P) Agent definition
Plans attributes
Associated risk Plan annotation
Personal Benefit args. Agent rule
PROCESSES
Description BDI integration
GET-PRIMARY-EM Perceive
input: Labeled perc. | output: PEm
GET-SECONDARY-EM Get option
input: Events | output: SEm Beliefs
SET-INITIAL-MOOD Initialization
UPDATE-MOOD
FILTER-APPLICABLE-PLANS Filter
5.2 Two Classical Games and Results
Strategic games are an important tool in experimental
economy to evaluate how individuals behave in situ-
ations where a single decision must be taken (Swope
et al., 2008). In many of these games there are gen-
erally two players involved, and there is also a stable
equilibrium concept called “Nash equilibrium”: situa-
tion where no player can obtain more benefits by tak-
ing a different decision. Nevertheless, what happens
in real situations is that individuals take decisions bi-
ased by emotions. Our proposal aims to model the
behavior of individuals in real situations where deci-
sions are taken considering rational and emotional as-
pects. We have chosen the Prisoner dilemma and the
Trust Game in order to evaluate if the decisions influ-
enced by emotions in our system are similar to the
decisions of individuals in a real context.
Prisoner Dilemma (PD)
This game offers a model of cooperation that empha-
sizes how individual and collective interests coexist
ICAART2015-InternationalConferenceonAgentsandArtificialIntelligence
394

(Axelrod and Hamilton, 1981). The participants rep-
resent two prisoners. Each one has the opportunity to
declare that the other committed the crime and hence
to betray him, or otherwise cooperate with him and
remain silent. For each possible situation the conse-
quences are (Tucker, 1983): i) both prisoners betray
the other: 2 years in prison for both, ii) prisoner 1
betrays prisoner 2 and prisoner 2 remains silent: pris-
oner 1 gets free and prisoner 2 gets 3 years of prison,
iii) both prisoners remain silent (cooperate): both get
1 year of prison. The most rational option according
to economic theory would be that they both betray
each other (Sewell, 2010), nevertheless a systematic
behavior in humans is to have a silent participant side
what is an evidence of cooperation between them.
The code of figure 2 is an extract of the agentA
implementation. It expects that agentB is not going
to betray (line 1). The expectation is represented
through a rule with an “EventFunctor” (the event that
triggers the expectation verification), a fulfillment
condition (that belief that makes the expectation
to become fulfilled) and a violation condition (a
belief that is the opposite of the fulfillment belief)
1
.
The personal benefit of the agent for each option
is determined trough the rule of line 2. The agent
basically looks for an option that reports to him the
lower value of the maximum possible years in prison
after selecting the corresponding option. This value
is stored on the ‘PB’ variable and ‘Max’ and ‘Min’
are the maximum and minimum possible values for
‘PB’. The fourth parameter of the rule is a list with the
properties (in form of literals) of the plan to consider
in the calculus. Lines 4 and 5 contain the possible
options after the event, that is the plans with this
triggering event. The plans annotations correspond
to the parameters to determine the “personal benefit”
and the risk associated. Risk values are two numbers
arbitrarily selected. What is important is the relative
relation between plans risks (the ‘p
silence’ plan is
more risky considering the best solution according to
Nash equilibrium). Another issue to add is that the
triggering event (‘+decide’), is acquired as a percept:
decide(cooperationpayoff(2), defectpayoff(1),
delatorpayoff(0),temptationpayoff(3) [emotions
(fear,hope,joy)]
2
that has the most common
emotions we have considered for this situation. The
agentB is similar to agentA, but in this case he doesn’t
have expectations.
1
Both the fulfillment and violation conditions are ex-
plicitly modeled on expectations because we take an “open
world” assumption so if a negation of a belief is not explic-
itly declared, then the agent has no information about if it is
true or false.
2
Values extracted from (Ashlock and Rogers, 2008)
1
expect__("silence",FullfilCond ,
ViolateCond ,EventFunctor):-
FullfilCond =silence(decision)
[source(agentB)] &
ViolateCond =betray(decision)[
source(agentB)] & EventFunctor="+
decide".
2
pb_max(PB, Max, Min, [max_years(MY)])
:- (not .ground(MY)|MY>0) & Max=3
& Min=0 & PB=Max/MY.
3
4
@p_betrayal[max_years(2),risk(0.3)]
+!decide (...) <- (...)
5
@p_silence[max years(3),risk(0.5)]
+!decide (...) <- (...)
Figure 2: Appearance of the Jason implementation of the
agentA agent in the prisoner dilemma.
The values for the parameters of the personal-
ity profiles were defined according to (Santos et al.,
2010). A set of four combination of values were
used. These four personality types are: social, trou-
bleshooter, negotiator, and realistic. Some combina-
tion of these personality profiles produced the follow-
ing results:
A social, B troubleshooter: A silence, B betrayal
A social, B negotiator: A silence, B silence
A social, B realistic: A silence, B betrayal
A social, B social: A silence, B silence
Coherently with the personality types chosen, in
this experiment the social agent tends to be coopera-
tive (keeping silence). The troubleshooter and realis-
tic tend to be more pragmatic betraying the other pris-
oner and the negotiator takes risks looking for benefits
and remains in silence (cooperates).
Trust Game (TG)
Another important sequential game is the the trust
game (Berg et al., 1995). In this game a proposer (or
trustor) is being given an amount of endowment to be
split and shared with the trustee. The amount shared
is multiplied by a factor (usually three) and then the
trustee decides to give back any amount. This way
the trustor hopes to receive something back related to
it’s initial offer trusting in the intentions of the other.
In real situations both players tend to share more than
what would be predicted in the game perfect equilib-
rium: “no trust” (Bracht and Feltovich, 2008).
The game was implemented similar
to PD. In this case, the trustor perceives
decide(endowment(10))[emotions(hope)]
from
the environment, expects a fair offer from the trustee
(around the half) and his personal benefit is max-
BuildingEmotionalAgentsforStrategicDecisionMaking
395

1 Trustor
2 @p 1st [ r e s t ( 75) , r i s k (0 .3 ) ]+! decide ( . . . )
3 @p 2nd[ r e s t ( 60) , r i s k (0 .4 ) ]+! decide ( . . . )
4 @p 3rd [ r e s t ( 4 5 ) , r i s k (0 .5 ) ]+! decide ( . . . )
5 @p 4th [ r e s t ( 30) , r i s k (0 .5 ) ]+! decide ( . . . )
6 Trustee
7 @p 1st [ o f f e r (2 0 ) , r i s k (0 .1 ) ]+! o f f e r ( . . . )
8 @p 2nd[ o f f e r ( 30) , r i s k (0 .2 ) ]+! o f f e r ( . . . )
9 @p 3rd [ of f er (40) , r i s k (0 .4 ) ]+! o f f e r ( . . . )
10 @p 4th [ o f f e r (5 0 ) , r i s k (0 .6 ) ]+! o f f e r ( . . . )
Figure 3: Appearance of the Jason implementation of the
trustor and trustee agent in a trust game.
imized when he gives a fair offer. Moreover the
trustee has no labeled percepts or expectations, and
his personal benefit is maximized if he offers as less
as possible. The possible options for both players are
shown in figure 3. The parameters for the trustor are
what he keeps in percent after sharing (rest) and risk,
and for the trustee are what he offers from the triplied
endowment received in percent, and risk. Again the
values have no real meaning but the relative relation
between them. The combination of some personality
profiles and the configuration described previously
produced the following results:
A social, B troubleshooter: A 55%, B 40%
A social, B negotiator: A 55%, B 40%
A social, B realistic: A 55%, B 40%
A social, B social: A 55%, B 50%
A troubleshooter, B social : A 35%, B 50%
A negotiator, B social: A 55%, B 50%
A negotiator, B realistic: A 55%, B 40%
A troubleshooter, B realistic: A 35%, B 30%
Similarly to the PD, in the TG the social agent be-
haves in a cooperative way and offers a high quantity
(55% as trustor or 50% as trustee). The troubleshooter
and realistic are prudent showing a pragmatic behav-
ior (35-40% and 30-40% respectively), and the nego-
tiator takes risks offering always more than the mini-
mum allowed (55-40%), but remaining prudent.
6 DISCUSSION AND
CONCLUSIONS
In this work we used an open agent affective archi-
tecture to build emotional agents that must simulate
situations of strategic decision-making influenced by
affective issues. We have used several widely ac-
cepted supporting psychological theories in order to
contribute to an incremental line of research in the
field of emotional computing. We have also made our
own propositions and assumptions to fill uncovered
gaps overlooking a final implementation. These ini-
tial results demonstrate in first place that there are ev-
idences that we can reach a diverse, believable and
closer to humans behavior when including an emo-
tion mechanism in an agent. The behavior of O3A
agents in some classical games is more like the behav-
ior of humans in real situations compared to agents
that doesn’t include emotions. Between the affective
issues modeled, personality seems to produce more
variability on results, what is quite consistent with a
real situation. Nevertheless using iterated versions of
the games may change the result and would help to
better tune the overall design. In the proposed de-
sign the influence of agents interactions on emotions
is given by the use of ‘expectations about others’ and
‘personal benefits’ related to others, which produces
emotional reactions associated to interactions. Never-
theless we aim to improve existing structures and to
create new ones in order to offer more realistic simu-
lations of the human decision process.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by the Spanish government
grant MINECO/FEDER TIN2012-36586-C03-01and
HUMBACE (Human and Social Behavior Models
for Agent-Based Computational Economics) project.
Thanks also to the Research and Development Sup-
port Programme of the Universidad Polit´ecnica de Va-
lencia PAID-06-11 Project.
REFERENCES
Alfonso, B., Vivancos, E., and Botti, V. J. (2014). An Open
Architecture for Affective Traits in a BDI Agent. In In
Proceedings of the International Conference on Evolu-
tionary Computation Theory and Applications (ECTA-
2014), pages 320–325.
Ashlock, D. and Rogers, N. (2008). A model of emotion in
the prisoner’s dilemma. In IEEE Symposium on Com-
putational Intelligence in Bioinformatics and Compu-
tational Biology, 2008. CIBCB’08, pages 272–279.
Axelrod, R. and Hamilton, W. D. (1981). The evolution of
cooperation. Science, 211(4489):1390–1396.
Bechara, A., Damasio, H., Tranel, D., and Dam´asio, A. R.
(1997). Deciding advantageously before knowing
the advantageous strategy. Science, 275(5304):1293–
1295.
Becker-Asano, C. and Wachsmuth, I. (2010). Affective
computing with primary and secondary emotions in
a virtual human. AAMAS ’10, 20(1):32–49.
ICAART2015-InternationalConferenceonAgentsandArtificialIntelligence
396

Berg, J., Dickhaut, J., and McCabe, K. (1995). Trust, reci-
procity, and social history. Games and economic be-
havior, 10(1):122–142.
Bordini, R. H., H¨ubner, J. F., and Wooldridge, M. (2007).
Programming multi-agent systems in AgentSpeak us-
ing Jason. Wiley.
Bracht, J. and Feltovich, N. (2008). Efficiency in the trust
game: an experimental study of precommitment. In-
ternational Journal of Game Theory, 37(1):39–72.
Cornelius, R. R. (2000). Theoretical approaches to emotion.
In ISCA Tutorial and Research Workshop (ITRW) on
Speech and Emotion.
Dam´asio, A. R. (1994). Descartes’ error: emotion, reason,
and the human brain. Quill.
Demaree, H. A., DeDonno, M. A., Burns, K. J., Feldman,
P., and Everhart, D. E. (2009). Trait dominance pre-
dicts risk-taking. Personality and Individual Differ-
ences, 47(5):419–422.
Ekman, P. (1999a). Basic Emotions, pages 45–60. John
Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Ekman, P. (1999b). Facial expressions, chapter 16, pages
301–320. The Handbook of Cognition and Emotion.
John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Elbanna, S. (2006). Strategic decision-making: Process per-
spectives. International Journal of Management Re-
views, 8(1):1–20.
Gebhard, P. (2005). ALMA: a layered model of affect. In
Proceedings of the fourth international joint confer-
ence on Autonomous agents and multiagent systems,
pages 29–36, NY, USA. ACM.
Harrison, G. W. and Rutstr¨om, E. E. (2008). Risk aversion
in the laboratory. Research inexperimental economics,
12:41–196.
Jiang, H., Vidal, J. M., and Huhns, M. N. (2007). EBDI:
An Architecture for Emotional Agents. In Proceed-
ings of the 6th International Joint Conference on Au-
tonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems, pages 11:1–
11:3. ACM.
LeDoux, J. E. (1998). The emotional brain: the mysterious
underpinnings of emotional life. A Touchstone book.
Simon & Schuster.
Lerner, J. S., Small, D. A., and Loewenstein, G. (2004).
Heart strings and purse strings: Carryover effects of
emotions on economic decisions. Psychological Sci-
ence, 15(5):337–41.
Loewenstein, G., Weber, E. U., Hsee, C. K., and Welch,
N. (2001). Risk as Feelings. Psychological Bulletin,
127(2):267–286.
Marsella, S. C. and Gratch, J. (2009). EMA: A process
model of appraisal dynamics. Cognitive Systems Re-
search, 10(1):70–90.
Marsella, S. C., Gratch, J., and Petta, P. (2010). Computa-
tional models of emotion. In A Blueprint for Affective
Computing: A Sourcebook and Manual, Affective Sci-
ence, pages 21–46. OUP Oxford.
McCrae, R. R. and John, O. P. (1992). An introduction to
the five-factor model and its applications. Journal of
personality, 60(2):175–215.
Mehrabian, A. (1996a). Analysis of the big-five personality
factors in terms of the pad temperament model. Aus-
tralian Journal of Psychology, 48(2):86–92.
Mehrabian, A. (1996b). Pleasure-arousal-dominance: A
general framework for describing and measuring indi-
vidual differences in Temperament. Current Psychol-
ogy, 14(4):261–292.
Mehrabian, A. (1997). Comparison of the PAD and PANAS
as models for describing emotions and for differentiat-
ing anxiety from depression. Journal of Psychopathol-
ogy and Behavioral Assessment, 19(4):331–357.
Mehrabian, A. and Russell, J. A. (1974). An approach to
environmental psychology. MIT Press.
Ortony, A. (2003). On Making Believable Emotional
Agents Believable. In Trapple, R. P., Petta, P., and
Payer, S., editors, Emotions in Humans and Artifacts,
chapter 6, pages 189–212. MIT Press.
Ortony, A., Clore, G. L., and Collins, A. (1988). The Cog-
nitive Structure of Emotions. Cambridge University
Press.
Ortony, A., Norman, D. A., and Revelle, W. (2005). Af-
fect and Proto-Affect in Effective Functioning. In Who
needs emotions. The brain meets the machine., pages
173–302. J.M. Fellous & M.A. Arbib.
Pessoa, L. (2008). On the relationship between emotion and
cognition. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 9(2):148–
158.
Ryckman, R. M. (2007). Theories of Personality. PSY 235
Theories of Personality Series. Thomson/Wadsworth.
Santos, R., Marreiros, G., Ramos, C., Neves, J., and Bulas-
Cruz, J. (2010). Using personality types to support
argumentation. In Argumentation in Multi-Agent Sys-
tems, pages 292–304. Springer.
Scherer, K. R. (2001). Appraisal considered as a process of
multilevel sequential checking. Appraisal processes
in emotion: Theory, methods, research, 92:120.
Schwenk, C. R. (1984). Cognitive simplification processes
in strategic decision-making. Strategic management
journal, 5(2):111–128.
Seo, M.-G., Goldfarb, B., and Barrett, L. F. (2010). Af-
fect and the framing effect within individuals over
time: Risk taking in a dynamic investment simulation.
Academy of Management Journal, 53(2):411–431.
Sewell, M. (2010). Emotions Help Solve the Prisoner’s
Dilemma. In Behavioural Finance Working Group
Conference: Fairness, Trust and Emotions in Finance,
London, pages 1–2.
Swope, K. J., Cadigan, J., Schmitt, P. M., and Shupp, R.
(2008). Personality preferences in laboratory eco-
nomics experiments. The Journal of Socio-Economics,
37(3):998–1009.
Tucker, A. (1983). The mathematics of Tucker: A sam-
pler. The Two-Year College Mathematics Journal,
14(3):228–232.
Weiss, G. (1999). Multiagent systems: a modern approach
to distributed artificial intelligence. MIT press.
Zadra, J. R. and Clore, G. L. (2011). Emotion and percep-
tion: The role of affective information. Wiley Interdis-
ciplinary Reviews: Cognitive Science, 2(6):676–685.
BuildingEmotionalAgentsforStrategicDecisionMaking
397
