
Spatio-temporal Comparison between ERD/ERS and MRCP-based
Movement Prediction
Anett Seeland
1
, Laura Manca
2
, Frank Kirchner
1,3
and Elsa Andrea Kirchner
1,3
1
Robotics Innovation Center (RIC), German Research Center for Artificial Intelligence (DFKI GmbH),
Robert-Hooke-Straße 1, 28359 Bremen, Germany
2
Faculty of Biology and Chemistry, University of Bremen, Leobener Str., 28359 Bremen, Germany
3
Robotics Group, Faculty of Mathematics and Computer Science, University of Bremen,
Robert-Hooke-Straße 1, 28359 Bremen, Germany
Keywords:
Movement Prediction, ERD/ERS, MRCP, Brain-computer Interface, BCI.
Abstract:
In brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) based on electroencephalography (EEG), two distinct types of EEG pat-
terns related to movement have been used for detecting the brain’s preparation for voluntary movements: a)
event-related patterns in the time domain named movement related cortical potentials (MRCPs) and b) patterns
in the frequency domain named event-related desynchronization/synchronization (ERD/ERS). The applicabil-
ity of those patterns in BCIs is often evaluated by the classification performance. To this end, the known
spatio-temporal differences in EEG activity can be of interest, since they might influence the classification
performance of the two different patterns. In this paper, we compared the classification performance based
on ERD/ERS and MRCP while varying the time point of prediction as well as the used electrode sites. Em-
pirical results were obtained from eight subjects performing voluntary right arm movements. Results show:
a) classification based on MRCP is superior compared to ERD/ERS close to the movement onset whereas the
opposite results farther away from the movement onset, b) the performance maximum of MRCP is located at
central electrodes whereas it is at fronto-central electrodes for ERD/ERS. In summary, the results contribute to
a better insight into the spatial and temporal differences between ERD/ERS and MRCP in terms of prediction
performance.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the event-related brain activity, two patterns are
commonly associated with movement, the move-
ment related cortical potentials (MRCPs) and the
event related desynchronization and synchronization
(ERD/ERS) (Pfurtscheller and Lopes da Silva, 1999).
Each of these patterns has components in the prepara-
tory phase of movements (Pfurtscheller and Lopes da
Silva, 1999; Shibasaki and Hallett, 2006).
The MRCPs are slow changes in the amplitude of
the recorded brain activity elicited by movement plan-
ning and execution. Among the pre-movement MR-
CPs several components can be distinguished. The
early readiness potential (RP) starts about 2-1.5 s be-
fore voluntary movement (Stanc
´
ak et al., 2000; Par-
adiso et al., 2004; Shibasaki and Hallett, 2006). It is
followed by a steep increase in negativity about 500-
400 ms before movement onset (Deecke et al., 1976;
Stanc
´
ak et al., 2000; Shibasaki and Hallett, 2006),
called late RP. The term pre-motor positivity (PMP)
commonly indicates a positive increase of potential
occurring between 100 and 50 ms before movement
onset (Deecke et al., 1976; Shibasaki and Hallett,
2006; Santucci and Balconi, 2009), which is between
the late RP and the motor potential (MP). The latter
is a steep increase in negativity starting shortly be-
fore movement onset (∼ 50 ms) (Deecke et al., 1976;
Stanc
´
ak et al., 2000).
The ERD/ERSs are the reflection of changes in
the oscillatory activity of neural networks in form
of an attenuation/increase in the power of specific
frequency bands, which correspond to a desynchro-
nization/synchronization of neural populations in re-
sponse to an event. The brain rhythms commonly
associated with movement, including pre-movement
components, are the µ (8-13 Hz), β (13-30 Hz) and
γ (over 30 Hz) rhythms (Pfurtscheller and Lopes da
Silva, 1999; Pfurtscheller, 1981; Pfurtscheller and
Neuper, 1992; Pfurtscheller et al., 1993; Bai et al.,
219
Seeland A., Manca L., Kirchner F. and Kirchner E..
Spatio-temporal Comparison between ERD/ERS and MRCP-based Movement Prediction.
DOI: 10.5220/0005214002190226
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing (BIOSIGNALS-2015), pages 219-226
ISBN: 978-989-758-069-7
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

2005). The µ ERD has been reported having its onset
about −2 s with respect to movement onset (Stanc
´
ak
et al., 2000; Shibasaki and Hallett, 2006). The onset
of the ERD in the β-band has been reported between 2
and 1 s before movement onset (Stanc
´
ak et al., 2000;
Bai et al., 2005; Shibasaki and Hallett, 2006). Con-
cerning the γ-band a pre-movement ERS has been
reported starting about 1 s before movement onset
(Pfurtscheller and Lopes da Silva, 1999).
Being able to recognize and correctly classify
these pre-movement components allows to predict
forthcoming movements. Exploiting the temporal ad-
vantage offered by brain signals over normal output
pathways can for instance result in an earlier per-
ceived response of brain computer interfaces (BCIs)
(Morash et al., 2008), thus making BCIs more user
friendly. Furthermore the detection of motor intention
may be relevant for neuro-rehabilitation by promoting
activity-dependent brain plasticity (Niazi et al., 2011).
Motivated by these possibilities, BCI-researchers
often used the two patterns for the classification of
movement intention (e.g. Wang et al., 2004; Li et
al., 2004; Morash et al., 2008; Bai et al., 2011; Fol-
gheraiter et al., 2011; Lew et al., 2012; Seeland et
al., 2013; Ibanez et al., 2014; Jiang et al, 2014).
Some studies used MRCP or ERD/ERS separately
(e.g. Mller-Gerking et al., 1999; Morash et al., 2008;
Wang and Wan, 2009; Bai et al., 2011; Niazi et al.,
2011; Lew et al., 2012; Seeland et al., 2013; Jiang et
al., 2014), others combined them (e.g. Wang et al.,
2004; Li et al., 2004; Ibanez et al., 2014). . However
in only a few studies the reasons behind the choice of
the applied pattern are discussed—a choice that may
rather derive from experience than having a solid the-
oretical basis. Hence, one aim of this work is to em-
pirically compare the two patterns concerning their
efficiency for movement prediction.
For such a comparison the time point of predic-
tion as well as the used electrode sites can be rel-
evant, since one of the most observed differences
between the two patterns is their spatio-temporal
evolution. The ERD/ERS has a contralateral on-
set and evolves to a bilateral spread around move-
ment onset (Pfurtscheller and Berghold, 1989; Ba-
biloni et al., 1999; Leocani et al., 2001), while MRCP
starts as bilateral spread and shifts to the contralat-
eral hemisphere as the onset of movement approaches
(Shibasaki and Hallett, 2006). Our intent was to in-
vestigate whether this difference has an impact on the
prediction of voluntary movements in order to get a
better insight into the two EEG patterns that are com-
monly applied for movement prediction. Found dif-
ferences between ERD/ERS and MRCP can be ad-
vantageous for the applicability of movement predic-
Figure 1: Experimental Setup: During the experiment, sub-
jects performed 120 similar movements with their right arm
from a push button to a buzzer.
tion systems. For example they may help in selecting
electrode setups or choosing the target pattern for de-
tection, depending on the application at hand.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
The comparison of the two signals is based on an
empirical analysis of a previously conducted study
(Tabie and Kirchner, 2013). Data and methods used
in this analysis are described in the following.
2.1 Data Description
EEG data were recorded via 128 electrodes (acti-
CAP Brain Products GmbH, Munich, Germany) lo-
cated according to the extended international 10-20
system. The predefinded sampling frequency of the
hardware (four BrainAmp DC amplifiers; Brain Prod-
ucts GmbH, Munich, Germany) was 5 kHz. The elec-
trode FCz was used as reference and the data were fil-
tered between 0.1 and 1000 Hz. Simultaneously, eight
bipolar channels placed on the right arm of the partic-
ipant were used to record the electromyogram (EMG)
in order to monitor muscular activity (amplified with
BrainExG MR; Brain Products GmbH, Munich, Ger-
many). Moreover, a motion capturing system (ProRe-
flex 1000, three cameras; Qualisys AB, Gothenburg,
Sweden) was used at 500 Hz to mark the mechanical
movement onset in the EEG.
Eight healthy subjects (29.9 ± 3.3 years) partic-
ipated in the study. Handedness and gender were
fixed to right-handed males to avoid an influence of
these factors on the experimental results of the rather
small number of subjects. Subjects sat comfortably at
a table in a shielded room and performed three ses-
sions interleaved with breaks of 10 min. They were
BIOSIGNALS2015-InternationalConferenceonBio-inspiredSystemsandSignalProcessing
220

instructed to perform voluntary self-paced right arm
movements from a push button to a buzzer (see Fig-
ure 1). A resting time of 5 s between two consecutive
movements had to be maintained for a valid move-
ment. A visual feedback was shown to subjects when
the resting time was shorter. Each session was con-
sidered as completed when 40 valid movements were
performed. For a detailed description of data and
paradigm it is referred to (Tabie and Kirchner, 2013).
2.2 Physiological Movement Onset
The point in time when the muscles get the electri-
cal signal to move is defined as physiological move-
ment onset. Commonly in neurobiological studies
the physiological movement onset, derived from the
EMG, is used to define the timescale, i.e., time point
zero corresponds to the point in time when an increase
in electric activity is measured at the muscles. Here,
in an offline procedure the EMG data of M. biceps
brachii and M. brachioradialis, which contained the
highest signal-to-noise-ratios, were used to label the
physiological movement onset (EMG onset) of each
trial. First, each trial was normalized by subtracting
the mean and dividing by the standard deviation of
the resting period [−2500, −500 ms] preceding the
release of the push button at 0 ms, respectively. Then,
these two normalized EMG channels were averaged.
Next, a variance filter (Nikolic and Krarup, 2011;
Tabie and Kirchner, 2013) with a window length of
20 ms was applied. Finally, the physiological move-
ment onset was set to the first point in time where the
data value exceeded a threshold T for at least 30 ms.
This threshold was defined as
T = m
[−2500,−500]
+ 5 ∗ s
[−2500,−500]
(1)
with mean m and standard deviation s computed for
the resting period from −2500 to −500 ms with re-
spect to the release of the push button.
2.3 Mechanical Movement Onset
The electromechanical delay (Cavanagh and Komi,
1979; Zhou et al., 1995) describes the time between
the physiological movement onset and the produc-
tion of force that yields to an actually visible move-
ment. The latter onset, here named mechanical move-
ment onset, can also be of interest for applications.
Hence, its relation to the physiological movement on-
set shall be given. For that, EEG/EMG and tracking
data streams were synchronized. After calculation of
the speed per sample from the tracking data, the data
were analyzed beginning from the release of the push
button backwards in time. Whenever the speed went
below a threshold of 0.15 mm/sample, which corre-
sponds to the accuracy of the tracking system, a me-
chanical movement onset was marked in the EEG.
The median distance between physiological and
mechanical movement onset across trials was 70 ms
(interquartile range 69 ms).
2.4 EEG Processing
Signal processing and classification of the EEG data
were performed with the open source software frame-
work pySPACE (Krell et al., 2013).
Both processing chains, one to detect MRCP and
one to detect ERD/ERS, were provided with the same
training and testing data. The training data contained
supposedly clearly distinguishable instances for the
two classes: instances close to or short after the EMG
onset for the movement preparation class (positive
class) and instances far away from the EMG onsets for
the rest class (negative class). Accordingly, 1 s win-
dows ending at −100 and 50 ms with respect to EMG
onset belonged to the movement preparation class,
and windows of the same length cut every 200 ms, if
no movement occurred 3 s before and 2 s after them,
belonged to the rest class. For the testing data of the
rest class the same extraction rules were applied, but
in order to investigate the temporal evolution of the
performance to detect a pre-movement pattern, the
testing data for the movement preparation class had
to be varied (see Section 2.5).
After window extraction the data were standard-
ized channel-wise (subtraction of mean and division
by standard deviation). Then, the data were processed
differently, depending on the type of patterns (MR-
CPs or ERD/ERSs) that should be detected. This dif-
ferent processing, including dimensionality reduction
and feature extraction, was required due to the differ-
ent properties of the pattern types.
2.4.1 Processing for MRCP
The processing used to detect MRCP pre-movement
components has already be described (Kirchner et al.,
2013a; Kirchner et al., 2013b; Seeland et al., 2013).
Since the RP is a low-frequency component, a first
noise reduction step comprised a decimation of the
sampling rate to 20 Hz together with an anti-alias fi-
nite impulse response filter. Subsequently, another
band pass filter was applied to reduce the frequen-
cies contained in the signal to 0.1-4 Hz. After this
preprocessing, the 1 s window was reduced to the
last 200 ms. A second noise reduction step was ac-
complished by training the spatial filtering algorithm
xDAWN (Rivet et al., 2009), that is specifically de-
signed to enhance evoked potentials. Then, the am-
Spatio-temporalComparisonbetweenERD/ERSandMRCP-basedMovementPrediction
221

plitude values of four channels retained from xDAWN
were extracted as features.
2.4.2 Processing for ERD/ERS
The data were decimated to 125 Hz since higher
frequencies are of importance for detection of
ERD/ERS. Accordingly, the signal was filtered in the
broad band from 8 to 40 Hz, which has been chosen
from previous investigations. Broad bands are often
employed for ERD/ERS classification in the literature
(Wang et al., 2004; Li et al., 2004; Bai et al., 2011).
The window was then reduced to the last 800 ms and a
common spatial pattern filter (Blankertz et al., 2008)
was applied with 16 retained pseudo-channels. The
mean and variance of each channel were used as fea-
tures, which has been suggested before (Liao et al.,
2007).
2.4.3 Classification and Postprocessing
Each feature dimension was normalized to have zero
mean and a standard deviation of one on the training
data, before a linear support vector machine (SVM)
was trained on the data (Chang and Lin, 2011). The
complexity parameter of the SVM was optimized
for each split using a grid search strategy (grid val-
ues: 10
0
,10
−1
,...,10
−6
) together with a nested 5-
fold cross validation on the training data. Further,
to account for the class imbalance and to emphasize
the importance of the movement preparation class, the
weight parameter of the SVM for the positive class
was set to 2. Finally, an optimal decision criterion
(threshold), that maximizes the performance on the
training data, was determined to assign a class label
based on the SVM score.
2.5 Evaluation
For evaluation, the data of each subject (three ses-
sions) were merged and results were obtained with a
stratified 10-fold cross-validation. Accordingly, 108
trials labeled as movement preparation were used in
each cross-validation split for training and 12 trials
for testing. The total number of trials for the rest class
varied across subjects between 140 and 647 since
there was no upper limit of the resting time between
two consecutive movements. As for the movement
preparation class, training in each cross-validation
split was based on 90 % of the trials and the remaining
10 % were used for evaluation.
The balanced accuracy was used as metric, i.e.,
the average of true positive and true negative rate
(BA = (TPR + T NR)/2). The BA compensates for
Figure 2: Electrode locations of a 128-channel actiCAP sys-
tem. Used electrodes in this analysis are numbered. The
number denotes the cluster (1–15) to which the electrode
was grouped.
the different unbalanced ratios of the number of trials
for the positive and negative class (Straube and Krell,
2014).
To investigate the spatio-temporal differences in
performance of the two brain patterns, the end time of
the windows for the movement preparation class and
the electrode locations used for classification were
varied. 68 electrodes, that cover a broad area around
the motor cortex, were considered in this analysis.
Electrodes were grouped into 15 different spatial clus-
ters of four or five electrodes to account for the nois-
iness of a single EEG channel (Figure 2). In the time
dimension, time points from −2.5 to 0.2 s with re-
spect to the EMG onset were analyzed. In addition,
the performances based on all 68 channels as well
as the performance of a random classifier were com-
puted and served as baselines.
3 RESULTS & DISCUSSION
The results are structured into two parts. First,
the movement prediction performance of MRCP and
ERD/ERS components was compared in the temporal
and spatial domain by analyzing the performance at
different electrode groups and time points. However,
a suboptimal performance was expected in this anal-
ysis since only four or five electrodes were used to
train each classifier. Hence, the second part presents a
comparison of the two patterns using all electrodes
BIOSIGNALS2015-InternationalConferenceonBio-inspiredSystemsandSignalProcessing
222
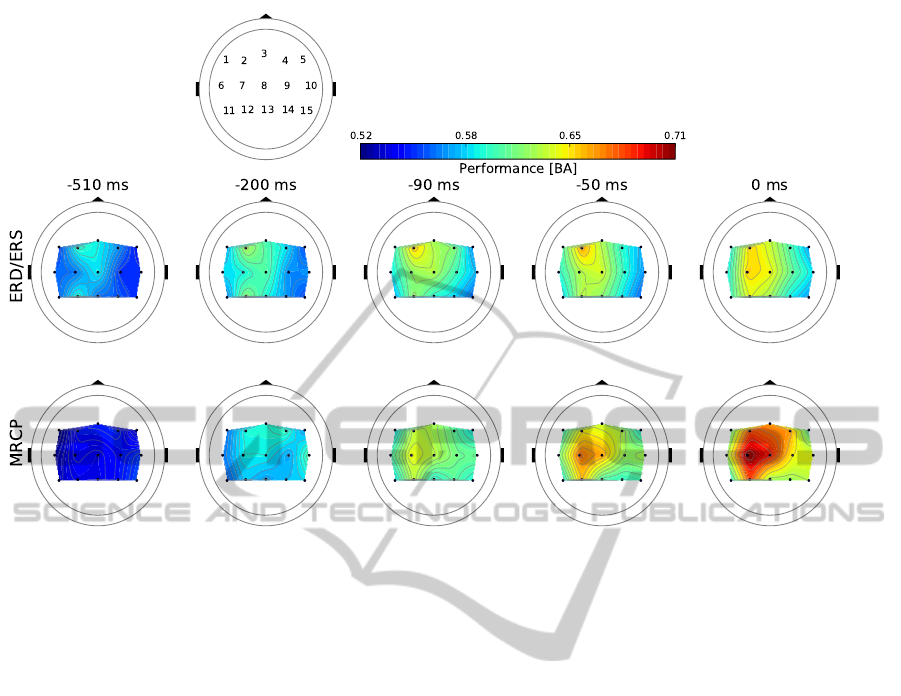
Figure 3: Spatio-temporal evolution of movement prediction performance in terms of averaged balanced accuracy (BA)
across splits and subjects based on ERD/ERS (top) and MRCP (bottom). Topologies are displayed for 15 electrode clusters
(each black dot indicates the center of a cluster). Time points, relative to the EMG onset at zero, were selected to illustrate
exemplarily the different spatial stages for each pattern as well as the main spatial differences.
for training, i.e., only the time dimension is var-
ied. Additionally, this second analysis gives a more
application-oriented view, since one common objec-
tive in an application is to maximize classification
performance.
3.1 Spatio-temporal Comparison
The averaged performance results of MRCP and
ERD/ERS showed differences in their spatio-
temporal evolution as illustrated for selected time
points in Figure 3. The performance of ERD/ERS
exceeded the baseline (0.5 BA) earlier than that of
MRCP (ERD/ERS at about −1.5 s, MRCP at about
−1.0 s).
Furthermore, the performance increase for
ERD/ERS emerged as a recurrent process consisting
of a local maximum at cluster 2 and partly also
cluster 12, as well as a spread of this maximum to
surrounding clusters 8, 3 and sometimes 4 and 7.
For example, 0.09 s before EMG onset the highest
performance is obtained at cluster 2 (Figure 3 third
column). On the other hand the stage of a more
distributed performance can be seen, e.g., 0.51 s
before movement onset (Figure 3 first column).
Compared with this, accuracy of MRCP detection
increased simultaneously, i.e., being widespread over
clusters even 0.46 s before EMG onset. Then, a local
maximum emerged at −0.43 s at cluster 2 that spread
to clusters 3 and 4 during the following 200 ms. The
next increase in performance is obtained at −0.24 s
at cluster 4 that spread again widely over clusters 3,
7, 8, and 2 within 0.23 and 0.18 s before movement
onset (Figure 3 second column). Finally, a maximum
occurred at cluster 7 that expanded to clusters 8 and
12 (Figure 3 at −0.09 and −0.05 s).
Optimal classification accuracies for ERD/ERS
and MRCP were observed at time point −0.04 s and
zero, respectively, whereby classification of MRCP
outperformed detection of ERD/ERS (average BA
± standard error; ERD/ERS: 0.67 ± 0.01, MRCP:
0.71 ± 0.01).
3.2 Comparison using All Channels
As expected, the overall classification performance
increased for both brain signals when all 68 chan-
nels were used during training. A possible rea-
son for this increase could be that performance of
MRCP and ERD/ERS is at least partly distributed
over electrodes, as indicated by the results explained
above (Section 3.1 and Figure 3). Thus, adding
more electrodes for training might reveal more rel-
evant information for the detection of the specific
Spatio-temporalComparisonbetweenERD/ERSandMRCP-basedMovementPrediction
223
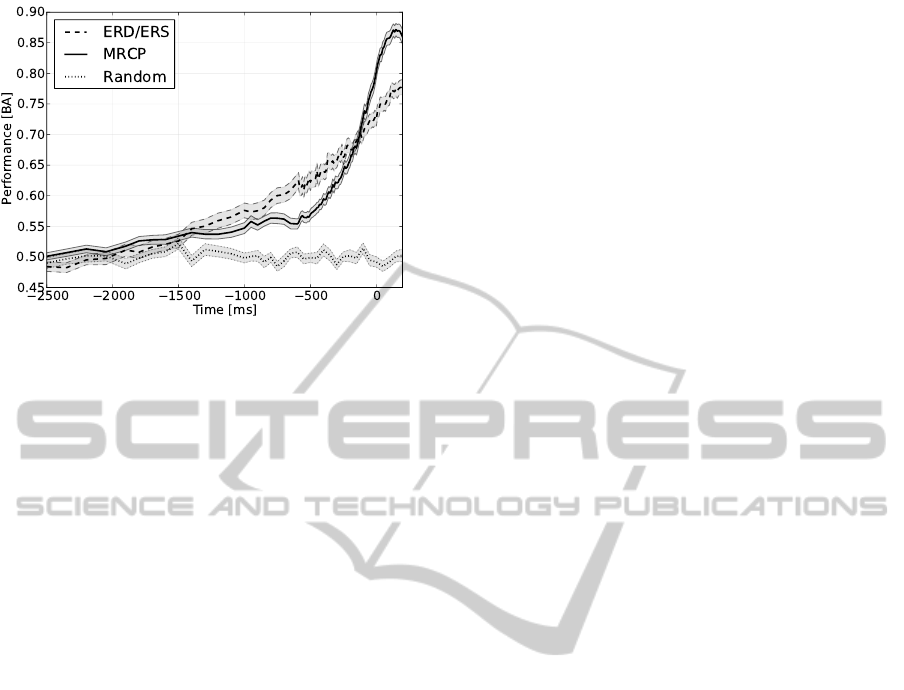
Figure 4: Averaged classification performance across splits
and subjects over time for classifiers based on ERD/ERS
(dashed line) and MRCP (solid line). As baseline per-
formance of a random classifier is depicted. Shaded area
around curves represent the standard error.
brain pattern. The increase was slightly weaker
for ERD/ERS than for MRCP, e.g., at EMG onset
(ERD/ERS: 0.65 ± 0.014 BA with electrodes in clus-
ter 2 and 0.72 ±0.012 BA with 68 electrodes, MRCP:
0.71±0.014 BA with electrodes in cluster 7 and 0.8±
0.012 BA with 68 electrodes).
Figure 4 shows the time course of performance for
the classification of MRCP and ERD/ERS, respec-
tively. In addition, the performance of a classifier
that randomly assigns a class label with equal prob-
ability is depicted. The classification performance of
both, MRCP and ERD/ERS, performed clearly better
than random after −1.5 s. Further, both performance
curves can be subdivided into three slopes with differ-
ent timings: For MRCP a slow raise in performance
up to −500 ms was observed followed by a steeper in-
crease from −500 to −200 ms, that was even steeper
from −200 ms until the movement approached. In
comparison, accuracy of ERD/ERS detection also
slowly raised up to −900 ms, but already then in-
creased more steeply from −900 to −150 ms, having
the strongest increase from −150 ms until movement
onset. However, this last slope was weaker than the
corresponding one of the MRCP performance curve.
Therefore the two curves intersect at around −130 ms.
After EMG onset the raise in performance for both
patterns continued, resulting for example at the aver-
aged mechanical movement onset (70 ms after EMG
onset) in an accuracy of 0.85 for MRCP and 0.75 for
ERD/ERS.
4 CONCLUSION & OUTLOOK
In this work, we compared the classification perfor-
mance of pre-movement components based on MRCP
and ERD/ERS at different time points and differ-
ent electrode groups. This comparison allows to in-
vestigate if the reported neurobiological differences
(Pfurtscheller and Berghold, 1989; Leocani et al.,
2001; Babiloni et al., 1999; Shibasaki and Hal-
lett, 2006) have an influence on the effectiveness of
movement prediction. Indeed, we obtained spatio-
temporal differences for ERD/ERS and MRCP in the
performances which indicate a higher effectiveness
of ERD/ERS far away from the movement onset,
whereas MRCP performed better near the movement
onset. In the spatial domain, ERD/ERS performance
peaked rather locally at fronto-central electrodes
(contra-medial to the side of movement). This peak
spread to central electrodes. On the contrary, MRCP
performance distribution was more widespread, peak-
ing at central electrodes (contra-medial to the move-
ment side). These findings do not map one-to-one to
the neurobiological literature, but this is not expected
since methodology (average analysis vs. single trial
processing) and independent variable (voltages differ-
ences vs. classification performance) differed.
As outlined in the introduction, ERD/ERS and
MRCP are used separately or sometimes combined.
However, there is no consistent opinion in the litera-
ture on whether ERD/ERS and MRCP should be com-
bined or not. Some authors are in favor of a combi-
nation (Wang et al., 2004; Li et al., 2004) while some
others believe that there is no benefit from the extrac-
tion of features from both patterns (Wang and Wan,
2009). Our results, i.e., the obtained spatio-temporal
differences, indicate that an improvement by combin-
ing features from both patterns may also depend on
the time point of classification and the used electrode
sites. Taking a closer look at these two aspects (time
point and sites) may help to resolve existing contro-
versies. Furthermore, knowledge about the spatio-
temporal differences can facilitate the design of novel
combining strategies.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by the German Bundes-
ministerium f
¨
ur Wirtschaft und Technologie (BMWi,
grant FKZ 50 RA 1012 and grant FKZ 50 RA 1011).
The authors like to thank Marc Tabie for providing us
with the data.
BIOSIGNALS2015-InternationalConferenceonBio-inspiredSystemsandSignalProcessing
224

REFERENCES
Babiloni, C., Carducci, F., Cincotti, F., Rossini, P. M., Neu-
per, C., Pfurtscheller, G., and Babiloni, F. (1999). Hu-
man movement-related potentials vs desynchroniza-
tion of EEG alpha rhythm: a high-resolution EEG
study. Neuroimage, 10(6):658–65.
Bai, O., Mari, Z., Vorbach, S., and Hallett, M. (2005).
Asymmetric spatiotemporal patterns of event-related
desynchronization preceding voluntary sequential fin-
ger movements: a high-resolution EEG study. Clin.
Neurophysiol., 116(5):1213–1221.
Bai, O., Rathi, V., Lin, P., and Huang, D. (2011). Prediction
of human voluntary movement before it occurs. Clin.
Neurophysiol., 122(2):364–372.
Blankertz, B., Tomioka, R., Lemm, S., Kawanabe, M., and
M
¨
uller, K.-R. (2008). Optimizing spatial filters for ro-
bust EEG single-trial analysis. IEEE Signal Process-
ing Magazine, pages 41–56.
Cavanagh, P. R. and Komi, P. V. (1979). Electromechanical
delay in human skeletal muscle under concentric and
eccentric contractions. European Journal of Applied
Physiology and Occupational Physiology, 42(3):159–
163.
Chang, C.-C. and Lin, C.-J. (2011). LIBSVM:
A library for support vector machines. ACM
Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Tech-
nology, 2:27:1–27:27. Software available at
http://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/ cjlin/libsvm.
Deecke, L., Gr
¨
ozinger, B., and Kornhuber, H. H. (1976).
Voluntary finger movement in man: Cerebral poten-
tials and theory. Biol. Cybern., 23(2):99–119.
Folgheraiter, M., Kirchner, E., and Seeland, A. (2011). A
multimodal brain-arm interface for operation of com-
plex robotic systems and upper limb motor recovery.
In BIODEVICES 2011 - International Conference on
Biomedical Electronics and Devices, pages 150–162.
Ibanez, J., Serrano, J. I., del Castillo, M. D., Monge-
Pereira, E., Molina-Rueda, F., Alguacil-Diego, I.,
and Pons, J. L. (2014). Detection of the onset of
upper-limb movements based on the combined anal-
ysis of changes in the sensorimotor rhythms and slow
cortical potentials. Journal of Neural Engineering,
11(5):056009.
Jiang, N., Gizzi, L., Mrachacz-Kersting, N., Dremstrup, K.,
and Farina, D. (2014). A brain-computer interface for
single-trial detection of gait initiation from movement
related cortical potentials. Clin Neurophysiol.
Kirchner, E. A., Albiez, J., Seeland, A., Jordan, M., and
Kirchner, F. (2013a). Towards assistive robotics for
home rehabilitation. In Chimeno, M. F., Sol
´
e-Casals,
J., Fred, A., and Gamboa, H., editors, Proceedings of
the 6th International Conference on Biomedical Elec-
tronics and Devices (BIODEVICES-13), pages 168–
177, Barcelona. ScitePress.
Kirchner, E. A., Kim, S. K., Straube, S., Seeland, A.,
W
¨
ohrle, H., Krell, M. M., Tabie, M., and Fahle, M.
(2013b). On the applicability of brain reading for pre-
dictive human-machine interfaces in robotics. PLoS
ONE, 8(12):e81732.
Krell, M. M., Straube, S., Seeland, A., W
¨
ohrle, H., Teiwes,
J., Metzen, J. H., Kirchner, E. A., and Kirchner, F.
(2013). pySPACE - a signal processing and classifica-
tion environment in Python. Frontiers in Neuroinfor-
matics, 7(40). https://github.com/pyspace.
Leocani, L., Toro, C., Zhuang, P., Gerloff, C., and Hallett,
M. (2001). Event-related desynchronization in reac-
tion time paradigms: a comparison with event-related
potentials and corticospinal excitability. Clin. Neuro-
physiol., 112(5):923–30.
Lew, E., Chavarriaga, R., Silvoni, S., and Mill
´
an, J. D. R.
(2012). Detection of self-paced reaching movement
intention from EEG signals. Front. Neuroeng., 5:13.
Li, Y., Gao, X., Liu, H., and Gao, S. (2004). Classifica-
tion of single-trial electroencephalogram during finger
movement. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng., 51(6):1019–
1025.
Liao, X., Yao, D., Wu, D., and Li, C. (2007). Combining
spatial filters for the classification of single-trial EEG
in a finger movement task. IEEE Trans. on Bio-med.
Eng., 54(5):821–31.
Morash, V., Bai, O., Furlani, S., Lin, P., and Hallett, M.
(2008). Classifying EEG signals preceding right hand,
left hand, tongue, and right foot movements and motor
imageries. Clin. Neurophysiol., 119(11):2570–2578.
M
¨
uller-Gerking, J., Pfurtscheller, G., and Flyvbjerg, H.
(1999). Designing optimal spatial filters for single-
trial EEG classification in a movement task. Clin.
Neurophysiol., 110(5):787–798.
Niazi, I. K., Jiang, N., Tiberghien, O., Nielsen, J. r. F. k.,
Dremstrup, K., and Farina, D. (2011). Detection
of movement intention from single-trial movement-
related cortical potentials. J Neural Eng, 8(6).
Nikolic, M. and Krarup, C. (2011). EMGTools, an adaptive
and versatile tool for detailed EMG analysis. Biomed-
ical Engineering, IEEE Transactions on, 58(10):2707
–2718.
Paradiso, G., Cunic, D., Saint-Cyr, J. a., Hoque, T., Lozano,
A. M., Lang, A. E., and Chen, R. (2004). Involve-
ment of human thalamus in the preparation of self-
paced movement. Brain, 127(Pt 12):2717–2731.
Pfurtscheller, G. (1981). Central beta rythm during senso-
rimotor activities in man. Electroencephalogr. Clin.
Neurophysiol., 51(3535):253–264.
Pfurtscheller, G. and Berghold, a. (1989). Patterns of corti-
cal activation during planning of voluntary movement.
Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol., 72(3):250–
258.
Pfurtscheller, G. and Lopes da Silva, F. H. (1999). Event-
related EEG/MEG synchronization and desynchro-
nization: basic principles. Clin. Neurophysiol.,
110(11):1842–1857.
Pfurtscheller, G. and Neuper, C. (1992). Simultaneous EEG
10Hz desynchronization and 40 Hz synchronization
during finger movements. Neuroreport, 3:1057–1060.
Pfurtscheller, G., Neuper, C., and Kalcher, J. (1993). 40-Hz
oscillations during motor behavior in man. Neurosci.
Lett., 164(1-2):179–182.
Rivet, B., Souloumiac, A., Attina, V., and Gibert, G. (2009).
xDAWN algorithm to enhance evoked potentials: ap-
Spatio-temporalComparisonbetweenERD/ERSandMRCP-basedMovementPrediction
225

plication to brain-computer interface. IEEE Trans. on
Bio-med. Eng., 56(8):2035–2043.
Santucci, E. and Balconi, M. (2009). The multicompo-
nential nature of movement-related cortical potentials:
functional generators and psychological factors. Neu-
ropsychol. Trends.
Seeland, A., Woehrle, H., Straube, S., Kirchner, E. A., and
W
¨
ohrle, H. (2013). Online Movement Prediction in a
Robotic Application Scenario. In Proc. 6th Int. IEEE
EMBS Conf. Neural Eng., pages 41–44, San Diego.
Shibasaki, H. and Hallett, M. (2006). What is
the Bereitschaftspotential? Clin. Neurophysiol.,
117(11):2341–2356.
Stanc
´
ak, A., Feige, B., L
¨
ucking, C. H., and Kristeva-Feige,
R. (2000). Oscillatory cortical activity and movement-
related potentials in proximal and distal movements.
Clinical neurophysiology : official journal of the In-
ternational Federation of Clinical Neurophysiology,
111(4):636–50.
Straube, S. and Krell, M. M. (2014). How to evaluate an
agent’s behaviour to infrequent events? – reliable per-
formance estimation insensitive to class distribution.
Frontiers in Computational Neuroscience, 8(43).
Tabie, M. and Kirchner, E. A. (2013). EMG onset detec-
tion – comparison of different methods for a move-
ment prediction task based on EMG. In Alvarez,
S., Sol
´
e-Casals, J., Fred, A., and Gamboa, H., ed-
itors, In Proceedings of the 6th International Con-
ference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Process-
ing (BIOSIGNALS-13), pages 242–247, Barcelona.
SciTePress.
Wang, B. and Wan, F. (2009). Classification of Single-Trial
EEG based on support vector clustering during finger
movement. Adv. Neural NetworksISNN 2009, pages
354–363.
Wang, Y., Zhang, Z., Li, Y., Gao, X., Gao, S., and Yang, F.
(2004). BCI Competition 2003–Data set IV: an algo-
rithm based on CSSD and FDA for classifying single-
trial EEG. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng., 51(6):1081–6.
Zhou, S., Lawson, D. L., Morrison, W. E., and Fairweather,
I. (1995). Electromechanical delay in isometric mus-
cle contractions evoked by voluntary, reflex and elec-
trical stimulation. European Journal of Applied Phys-
iology and Occupational Physiology, 70(2):138–145.
BIOSIGNALS2015-InternationalConferenceonBio-inspiredSystemsandSignalProcessing
226
