
Gunshot Classification from Single-channel Audio Recordings using a
Divide and Conquer Approach
H´ector A. S´anchez-Hevia, David Ayll´on, Roberto Gil-Pita and Manuel Rosa-Zurera
Department of Signal Theory and Communications, University of Alcal´a, Madrid 28805, Spain
Keywords:
Gunshot Acoustical Analysis, Pattern Recognition, Divide and Conquer, Feature Extraction.
Abstract:
Gunshot acoustic analysis is a field with many practical applications, but due to the multitude of factors in-
volved in the generation of the acoustic signature of firearms, it is not a trivial task, especially since the
recorded waveforms show a strong dependence on the shooter’s position and orientation, even when firing the
same weapon. In this paper we address acoustic weapon classification using pattern recognition techniques
with single channel recordings while taking into account the spatial aspect of the problem, so departing from
the typical approach. We are working with three broad categories: rifles, handguns and shotguns. Our ap-
proach is based on two proposals: a Divide and Conquer classification strategy and the inclusion of some
novel features based on the physical model of gunshot acoustics. The Divide and Conquer strategy is aimed
at improving the rate of success of the classification stage by using previously retrieved spatial information to
select between a set of specialized weapon classifiers. The minimum relative error reduction achieved when
both proposals are used, compared with a single-stage classifier employing traditional features is 38.7%.
1 INTRODUCTION
Gunshot acoustic analysis has practical applications
in many fields such as forensics, security, gun con-
trol or military tactics to name a few. The acoustic
signature produced by explosive propelled weapons,
particularly small firearms, has been the subject of
study for some decades (Weissler and Kobal, 1974;
Fansler et al., 1993; Maher, 2007). Nevertheless,
gunshot acoustic processing has become even more
important in recent years, mainly due to the devel-
opment of sniper detection systems (Kawalec et al.,
2006) aided by sensor fusion techniques.
Renewed interest in this topic has yielded multiple
approaches to gunshot detection over the last decade.
Most of the existing proposals use pattern recogni-
tion techniques such as Gaussian Mixture Models
(GMM) or Support Vector Machines (SVM) (Freire
and Apolin´ario Jr, 2010; Ahmed et al., 2013) in con-
junction with classic acoustic analysis features, al-
though there are also examples in the literature that
use different methodologies (Sergent and Winkler,
1995). On the other hand, acoustic weapon classi-
fication has not been widely studied yet, with only
a few available precedents (Khan et al., 2009; Sal-
lai et al., 2011). Other than detection itself, most of
the existing strategies to obtain additional information
from the recorded signals rely on physical measure-
ments taken at different locations. It is common to
employ temporal differences between the detection of
an event over a group of sensors to locate the shooter
or estimate the trajectory of the bullet by triangulation
(Millet and Baligand, 2006).
One of the main concerns in this field is the
strong dependence of the recorded waveforms on the
shooter’s position and orientation, mostly because the
acoustic disturbance created by the explosive pro-
peller is highly directional (Maher and Shaw, 2010).
This fact means that even when dealing with the same
weapon, the perceived sound has a strong spatial com-
ponent so that recordings from two distant locations
can be completely dissimilar.
In this paper, we tackle acoustic weapon classi-
fication from a novel approach. The main novelty
resides in the extraction of spatial information from
single-channel recordings,with the purpose of obtain-
ing better generalization.
We are working with three broad categories: rifles,
handguns and shotguns. Our approach is based on
a Divide and Conquer (D&C) strategy (Parvin et al.,
2011) aimed at minimizing the classification error by
taking advantage of less demanding problems to se-
lect between a set of specialized classifiers. The ob-
jective is to overcome the uncertainty produced by the
233
Sánchez-Hevia H., Ayllón D., Gil-Pita R. and Rosa-zurera M..
Gunshot Classification from Single-channel Audio Recordings using a Divide and Conquer Approach.
DOI: 10.5220/0005218302330240
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods (ICPRAM-2015), pages 233-240
ISBN: 978-989-758-077-2
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

lack of spatial references. As a way to balance out
the loss of information derived from the use of sin-
gle channel signals we have reformulated the spatial
problems addressed in this field to be able to solve
them without a multichannel setup. Weapon classi-
fication is aided by the solution of three additional
problems: detection of the shock wave produced by
supersonic projectiles, and a binary estimation of the
proximity both to the shooter and to the trajectory of
the bullet (range & alignment).
In our proposal, the shock-wave detection stage is
employed to extract a small set of novel features based
on its acoustic model, while range and alignment esti-
mators are responsible for performing spatial division
to select the most suitable classifier for the last stage.
2 ACOUSTIC MODEL
Before addressing the particularities of the presented
problem, it is worth making a brief overview of the
main elements that play a role in the composition of a
gunshot acoustic signature.
2.1 Muzzle Blast
Common firearms produce their characteristic sound
as a result of the sudden expansion of gases gener-
ated at the end of their barrel by the explosive charge
employed to propel the projectile, formally known as
muzzle blast.
A simple approach that can be used to understand
the acoustical excitation produced by this kind of phe-
nomenon is Weber’s spectrum model, accounted for
in ISO norm (ISO-CEN.17201-2, 2006). This model
gives us an estimation of the Fourier spectrum of a
blast wave on free air (Freytaga et al., 2006) as a func-
tion of the radius of the expanding gas sphere created
by the chargein the precise instant that its propagation
speed decreases enough to match the speed of sound
c. The energy of the explosion is directly related to
the volume of displaced gases, shifting the spectrum
to lower frequencies as the radius of the sphere in-
creases.
However, in the case of firearms, the constraining
effect of the barrel on the expansion of gases has a
big impact on the produced sound, making the muzzle
blast strongly directional. Applying Weber’s radius
model, this directionality can be explained as a result
of the divergence in the expelled gases shape from a
perfect sphere, implying a dependence between the
listener location and the perceived radius (Karl Wil-
hem Hirsch, 2013). Figure 1 shows the differences in
º
R
w1
R
w2
v
1
>c
v
2
=c
v
3<
c
Blast 1
Blast 2
Figure 1: Differences in blast wave radiation from an ellip-
soid volume at two points.
Bullet
trajectory
θ
M
Shock wave
front
t
0
t
0
+Δt
t
0
+2Δt
Δt
2Δt
c
V
Figure 2: Geometric model of shock wave propagation.
the blast waves created by an ellipsoid volume as a
function of the perceived radius.
2.2 Projectile Shock Wave
The second main component of a gunshot acoustic
signature is the shock wave produced by a projectile
traveling at supersonic speed.
For a projectile with a velocity V > c, and defin-
ing Mach number as M = V/c, the generated shock
wave propagates in conic shape forming an angle
θ
M
= arcsin(1/M) with the trajectory of the bullet,
as shown in Figure 2. This acoustic disturbance is
commonly referred as N-wave due to its characteristic
geometry resembling a capital letter “N”. Its most rel-
evant parameter, its duration T, can be approximated
by knowing the physical dimensions of the bullet, its
velocity and the closest distance between the micro-
phone and the projectile trajectory (Maher, 2006).
While the muzzle blast can be seen as a global
event, due to the extensive range reached by the gen-
erated acoustical excitation, the shock wave has a lo-
cal influence, since its appearance only takes place
for those positions close enough to the trajectory of
the bullet.
ICPRAM2015-InternationalConferenceonPatternRecognitionApplicationsandMethods
234

0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
50m
2m
Time (ms)
Muzzle blast
Muzzle blast
Shock wave
Muzzle blast reflection
Figure 3: Recorded pressure waveforms for a .45 caliber
handgun at two locations.
2.3 Additional Components
The aforementioned components are the main ingre-
dients of a gunshot acoustic signature. However in
a real scenario, the recorded waveform may be very
different from the ideal model. In the case of close
range recordings, ground reflections from both muz-
zle blasts and shock waves, along with the character-
istic sound produced by the firing mechanism of the
weapon are most likely to be present, which can be a
problem in the event that they overlap with the direct
signal. On the other hand, in the case of long range
recordings, the influence of the propagationpath has a
tremendous impact on the received sound, due to the
short duration of these waves that makes them act as
impulses, in addition to appearance of a vast range of
acoustical phenomena such as absorption, spreading,
attenuation, etc.
Other than these effects, non-idealities on the
recording equipment can also produce some artifacts,
the most notorious being saturation given the high
sound pressure levels created by muzzle blasts that
commonly exceed 140 dB.
Figure 3 illustrates various of this effects with two
recordings of the same weapon extracted from our
database.
It is worth mentioning that the uncertainty pro-
duced by the directivity of the muzzle blast and the
appearance of undesired acoustic phenomena, com-
monly make the differences between recordings of
a same weapon at two distant locations greater than
those of two distinct weapons captured at the same
position.
3 CLASSIFICATION SYSTEM
When approaching gunshot acoustic analysis there
are three main questions to be asked: which weapon
has been fired, where is the shooter and what is he/she
targeting. These problems can be reformulated, em-
ploying more adequate terms, into the problems of
weapon classification, shooter localization and bul-
let trajectory estimation. From these three problems
weapon classification is the only one that does not re-
quire some degree of spatial diversity, making it the
most suitable to tackle using single channel record-
ings.
Instead of focusing on differentiating between
particular gun models, weapon classification is being
performed by categories, namely handguns, rifles and
shotguns. In this way, the physical differences (barrel
length, caliber, propellant amount, etc.) between the
weapons inside each classification group are less sig-
nificative than those with the rest of the population.
By using broad categories, the usage of the database
is more effective since there is more available data on
each class and they are better balanced for the tests.
It is worth mentioning that proper detection is re-
quired in order to perform classification. Since we
are focusing on weapon classification, we work on
an assumption of perfect detection. As previously
stated, there are multiple gunshot detectors capable of
achieving good performance rates already available in
the literature.
The classification is performed using Least
Squares Linear Discriminant Analysis (LS-LDA) (Ye,
2007).
3.1 Feature Set
For the main feature set we are using a signal segment
of length 10.7 ms (1024 samples) containing the Muz-
zle blast. This segment is automatically selected by
the system, using a moving average of the energy of
the signal. Since the muzzle blast is always appear-
ing (perfect detection is assumed) and it is the main
source of energy, a secondary energy source preced-
ing it with a lower energy level has to be an N-wave.
(see Figure 4 for a visualization of this situation). The
moving average is computed using a moving square
window of length 64 samples over the squared input
signal and from it the starting point for the Muzzle
blast segment is selected from the absolute maximum.
0
50
100
20 40 60 80
0
50
100
Time (ms)
Figure 4: Energy moving average of two gunshots recorded
at the same position. (top) Rifle (bottom) Handgun.
GunshotClassificationfromSingle-channelAudioRecordingsusingaDivideandConquerApproach
235

Once the segment is selected, we estimate its spec-
tral density with a periodogram using the Fast Fourier
Transform (FFT). From this estimation, we compute
16 Mel-frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCCs)
(Hunt et al., 1980) to be used as features. By doing
this we obtain a perceptual representation of the spec-
tral characteristics of the signal compressed in a much
smaller number of values. MFCCs have demonstrated
that they are a valuable asset for general acoustic anal-
ysis on numerous occasions, and they are also used in
gunshot detectors from Freire et al. and Ahmed et
al. among many other applications. In addition to
MFCCs three additional features are extracted from
the stored peak values.
From the selected segment we calculate its energy
level in decibels and from the FFT we extract two
spectral descriptors namely kurtosis and roll-off.
The classification feature set is composed of 19 fea-
tures:
• 16 MFCCs
• Signal energy (in decibels)
• 2 Spectral descriptors:
Kurtosis
Roll-off
4 PROPOSED CLASSIFICATION
STRATEGIES
In this work we are addressing the problem of weapon
classification departing from a multichannel approach
in favor of single channel processing. Nonetheless,
this decision implies a significative reduction of the
available information on the events, specially since
we can no longer use triangulation based techniques
to solve the spatial problems that could help in the
classification stage. To address this issue we have
reformulated the initial problems, turning them into
simpler problems that do not require the use of multi-
ple information sources to be solved. However these
new objectives are notably influenced by the coverage
of the available database as we will later explain.
Recording at a single location suppresses the ca-
pability of triangulating the exact shooter’s position.
However we can still provide some vital information
on the event by making a classification of his prox-
imity to the sensor. In the current implementation,
we are discerning between close range (d < 20m) and
medium range (d > 20m) discharges, as the employed
database does not contain any long range recordings.
Nevertheless, the proposed methodology is valid for
any range.
1/1
0/1
1/0 0/0
Figure 5: Schematic representation of the spatial division
provided by the first classification stage (range/aligment).
Trajectory estimation also suffers from the lack of
spatial references. This estimation has been replaced
by the ability to classify the proximity of the sensor
with the trajectory followed by the bullet into two
broad alignment categories: on-axis and off-axis. On-
axis implies that the microphone location is inside a
30 degree cone within the actual trajectory of the bul-
let, while off-axis represents any other position.
In addition to these, we can obtain some ad-
ditional information from N-wave detection, since
shock-wave appearance is related both to the fired
weapon and to the relative range and aligment of the
recording. N-wavedetection does not present any par-
ticularity since it is commonly performed over sin-
gle channel signals even in distributed systems since
the detection usually takes place locally at each node.
However this stage is also employed to extract a small
set of features adapted to the particularities of the
problem.
Finally, we want to highlight that the different
problems described do not present the same level
of complexity: range estimation is the easiest and
weapon classification is the most difficult. Bearing
this in mind, it should be beneficial to employ the
most likely to be true knowledge on the signal, to aid
the decision making for the more likely to fail using
a Divide and conquer (D&C) strategy. D&C aims at
reducing the complexity of a problem by analyzing a
broken down version of itself, what in our case is per-
formed by employing the outcomes of the three easier
problems to aid in the solution of the most demand-
ing. N-wave detection is used to add new information
to the problem while range and alignment estimators
are used to divide the space in four regions, accord-
ing to Figure 5. Each of these regions are analyzed
independently with an specialized weapon classifier.
4.1 D&C Classifier Tree
We propose to use a D&C classification tree, by us-
ing the outcome of two spatial classifiers to select
between a set of specialized weapon classifiers that
ICPRAM2015-InternationalConferenceonPatternRecognitionApplicationsandMethods
236
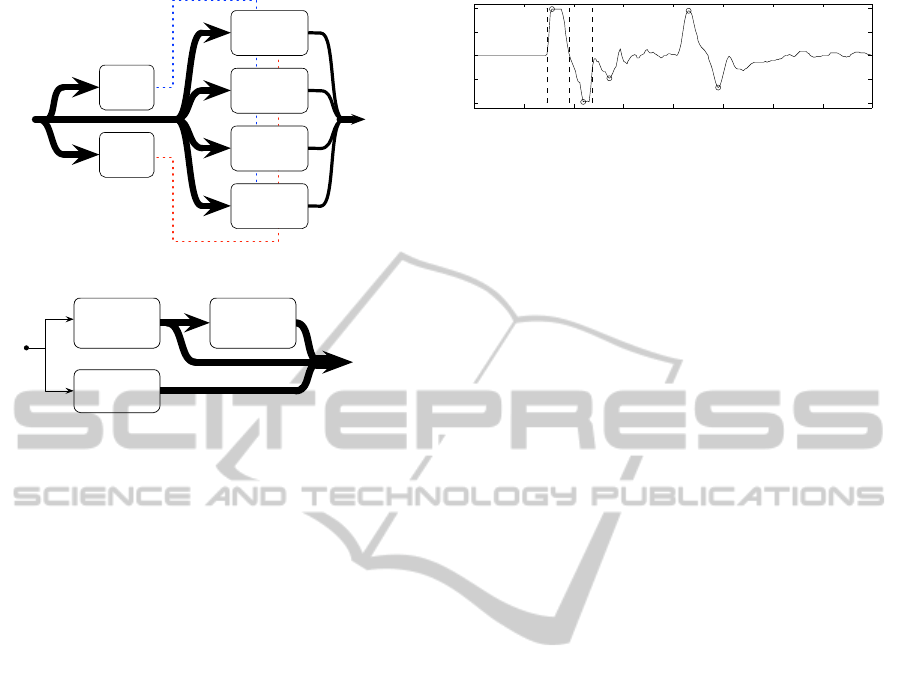
Set of
features
Weapon
class
Range
binary
estimator
Alignment
binary
estimator
Weapon
classifier
R=0/A=0
Weapon
classifier
R=0/A=1
Weapon
classifier
R=1/A=0
Weapon
classifier
R=1/A=1
Figure 6: Simplified diagram of the D&C Classifier tree.
Input
Signal
Proposed
set of
Features
N-wave
features
Standard
Features
N-wave
detector
Figure 7: Simplified diagram of the proposed feature ex-
traction system.
assume the veracity of the preceding decisions. The
first stage of the classifier tree is in charge of range
and alignment binary estimation, whereas the sec-
ond stage takes the decision on weapon category.
Each of the classifiers in the decision tree are im-
plemented with LS-LDA. The specialized classifiers
are designed using a specific subset of events, so that
they do not contemplate the existence of the other
branches. A simplified diagram of the D & C scheme
is shown in Figure 6. Notice that in the classification
tree only one specialized classifier is active at a time.
4.2 N-wave Based Features
The N-wave detector is not included in the decision
tree. Instead it is devised to extract some novel fea-
tures related to the shock wave that are later included
into the main feature set. In the same way as the clas-
sifier tree, the N-wave detector is implemented with
LS-LDA. This proposal relies on two feature sets, one
for the N-wave detector and one for the main classi-
fication, although some novel features are shared by
both sets. See Figure 7 for a schematic representation
of the feature integration between stages.
4.2.1 N-Wave Detector Features
For the N-wave detector feature set, we are using
a signal segment containing the first 10.7 ms (1024
samples) of the event that is automatically selected by
the system. This selection takes place using an algo-
rithm that scans the input signal to find all local peaks
larger than one-third of its absolute maximum. The
1 33 65 97 129 161 193 225 256
−1
−0.5
0
0.5
1
Figure 8: Selected signal segment (first half) and reference
points for feature extraction at the N-wave detector.
location of the first found peak sets the starting point
for the selected segment (with an offset of 50 sam-
ples). Additionally amplitude and index values for all
peaks are temporarily stored. From the selected seg-
ment we compute its FFT to obtain 16 MFCCs.
Since supersonic shock waves have a very relat-
able shape in the time domain (hence the name N-
wave) it should be advisable to employ some of their
temporal features to perform the detection. N-waves
typically range between 200 and 300 µs and have a
high degree of symmetry between their half cycles.
Other than that, in the event of existing, the N-wave is
always the first component to reach the microphone.
Knowing these facts and having already found the lo-
cal peaks of the signal we can use their values to com-
pute some shape descriptors to be used as features.
Notice that there are N-wave detectors that work with
this kind of temporal measurements alone without
resorting to advanced pattern recognition techniques
(Sallai et al., 2011).
Taking the index value of the first two peaks and
subtracting them we get a representative value of the
duration of the first wave, whether it is an N-wave or
not. From these same peaks we can also find the zero-
crossing points of the wave, that can be used to calcu-
late the half cycle duration ratio as a way of measuring
its symmetry. The last value extracted is the energy of
the alleged N-wave between its start and finish points
(zero-crossings). Figure 8 shows an N-wave segment
automatically selected by the algorithm and its differ-
ent reference points.
The complete N-wave detector feature set is com-
posed of 19 features:
• 16 MFCCs
• 3 N-wave descriptors:
Duration
Half cycle ratio
Energy
4.2.2 Proposed Feature Set
Instead of using the N-wave detector output to further
divide the classification tree, we propose to use it as
an additional feature. The raw output of the detector
GunshotClassificationfromSingle-channelAudioRecordingsusingaDivideandConquerApproach
237

(without thresholding) is added to the classification
feature set together with N-wave half cycle ratio and
duration previously obtained for the detector feature
set.
In addition to this, at the main feature extraction
stage, we calculate the temporal difference between
energy clusters (see Figure 4) since it represents the
Time Difference of Arrival (TDoA) between the N-
wave and the muzzle blast. The obtained TDoA is
used as a feature, however in the case that only one
source exists, this parameter is set to a default value
(zero).
The proposed classification feature set is composed of
23 features:
• 16 MFCCs
• Signal energy (in decibels)
• 2 Spectral descriptors:
Kurtosis
Roll-off
• 4 N-wave descriptors:
Time Difference of Arrival
Duration
Half cycle ratio
N-wave Detector output
5 EXPERIMENTAL WORK AND
RESULTS
In order to test the performance of the proposed sys-
tem and its generalization capability, we have per-
formed different experiments using various classi-
fier configurations, database divisions and resampling
strategies.
5.1 Database
Our database contains unprocessed recordings from
14 weapons, divided into 5 handguns, 5 rifles and 4
shotguns. Firing sounds for all the weapons are avail-
able at 10 distinct positions with 12 repetitions for
each weapon-position combination, adding up to a to-
tal of 1680 individuals registers.
Of the 10 unique positions, 4 are labeled as short-
range and 6 as medium range, whereas 6 are labeled
as on-axis and 4 as off-axis. N-waves only appear in
22.1% of the recordings, not appearing at all for 6 of
the weapons (2 handguns and all shotguns) since they
use subsonic ammunition.
All the signals are professionally recorded at
96000Hz using various high-quality microphones and
recording equipment.
5.2 Description of the Experiments
To design and test each classification system for the
experiments, the database is divided into two inde-
pendent subsets, a design set, used exclusively for de-
signing the classification system itself, and a test set,
used for evaluating its performance. It is important
to emphasize that under no circumstance is the same
pattern contained in both sets at the same time.
The results shown in Tables 1 and 2 are arranged
attending to the constraints imposed to the design set
in descending order. The term included used to de-
scribe different sets, refers only to the constraints ap-
plied to the design set as follows:
• Position & Gun not included: None of the sounds
of the tested gun, neither those recordings of the
remaining weapons at the tested position have
been employed for designing the classifiers.
• Position not included: The design set does not
contain any of the recordings at the tested posi-
tion.
• Gun not included: The design set does not contain
any sound of the tested weapon.
• Position & gun included: Only the tested sounds
have been excluded from the design set.
• 50/50 database division: The database is divided
in two equally sized random sets each containing
6 of the available events for each weapon-position
pair.
Table 1: Obtained weapon classification error for various
configurations and design constraints.
Standard
Classifier
Classifier
tree
Position & Gun not included
Standard feature set 56.9% 43.4%
Proposed feature set 45.6% 32.9%
Position not included
Standard feature set 46.5% 34.6%
Proposed feature set 36.5% 28.5%
Gun not included
Standard feature set 47.1% 29.3%
Proposed feature set 35.6% 21.4%
Position & Gun included
Standard feature set 39.9% 21.8%
Proposed feature set 29.5% 16%
50/50 database division
Standard feature set 35.6% 14.4%
Proposed feature set 20.9% 9%
ICPRAM2015-InternationalConferenceonPatternRecognitionApplicationsandMethods
238

Table 2: Obtained errors at the first classifying stage for
various design constraints.
Range Alignm. N-wave
Position & Gun
not included
3.5% 6.9% 8.9%
Position not
included
2.7% 6.7% 7.6%
Gun not
included
0.6% 2.3% 6.2%
Position & Gun
included
0.5% 2.2% 5.5%
50/50 database
division
0.5% 1.3% 2.9%
In the first four cases, we haveapplied a leave-one-out
cross-validation technique (LOOCV) (Efron, 1979).
The results were obtained averaging the outputs of
140 independent experiments, where the different test
sets are formed by the 12 repetitions available for ev-
ery weapon-position combination. The design set em-
ployed for each case is formed by all the remaining
sounds in the database not excluded by the imposed
constraints.
In the last case, all weapon-position pairs are
tested at the same time, the results were obtained aver-
aging 1024 random database divisions in two equally
sized sets.
Table 1 shows the effect of the adopted strategies
in the classification error. For each database division
there are 4 results, obtained with different configura-
tions. The first 2, labeled as Standard classifier were
obtained with a single classifier without the proposed
D&C scheme, while the other 2 labeled as Classifier
tree, take advantage of the suggested specialized clas-
sifier configuration. Additionally, for both configu-
rations 2 different sets of features were tested: Pro-
posed feature set including the novel features pre-
sented in this paper, and Standard feature set that ex-
cludes them.
Table 2 shows the errors obtained for the N-wave
detector and the first stage of the D & C Classifier
tree for the different database divisions when using
the proposed feature set.
5.3 Discussion of the Results
The obtained results show a strong dependence be-
tween the spatial resolution of the classifiers and the
obtained error, understandingspatial resolution in this
context, as the number of events contained in the de-
sign set with a unique spatial relationship between the
recording location and the shooter’s position and ori-
entation. However as it is clear from the results for
any of the tested constraints, the proposed strategies
help to greatly reduce the classification error, even
when used individually.
For the worst case-scenario in Table 1, when nei-
ther the tested gun nor the tested position were part of
the design set, the classification error of a single-stage
approach with traditional features reaches 56.9%.
This figure is reduced by 20% with the proposed
features and by 24% with the specialized classifier
scheme. When both proposals are used, the obtained
error is 32.9%, a 42% relative reduction over the ini-
tial error.
Notice how, even when the objective of the clas-
sification is to categorize the weapon, removing the
tested position from the design set (so that it does not
contain any previous references of that location) has
a greater impact than removing the gun itself. Al-
though the relevance of including the tested location
on the design set is more clearly shown on Table 2
under range and alignment errors.
We have chosen to use Linear Discriminant Anal-
ysis over more “capable” solutions, because non-
linear classifiers have shown an overfitting tendency
when dealing with the presented problems, specially
in the later weapon classification stage. Nevertheless,
the advantage of using specialized classifiers holds
true for any of the tested techniques.
6 CONCLUSIONS
In this work we have proposed a novel method for
extracting relevant information from single channel
gunshot recordings, departing from the typical mul-
tichannel approach.
We have shown that information retrieval from
single channel gunshot recordings is a feasible option,
specially when using an adequate feature set adapted
to the particularities of the scenario. We also show
how D&C strategies can be applied to simplify the
complexity of the problem. The minimum relative
error reduction achieved combining both proposals
when compared with a single-stage classifier with tra-
ditional features is 38.7%.
The next experiments should be conducted in-
creasing the spatial coverage of the database to in-
clude a broader spectrum of locations and orienta-
tions. Anyhow, further research is required to find
new solutions in order to address the variations on
the recorded waveformsproduced by the directivityof
the muzzle blast and the influence of the environment
since they represent the main source of uncertainty.
Despite the lower performance in comparison to
multichannel systems, single channel gunshot analy-
GunshotClassificationfromSingle-channelAudioRecordingsusingaDivideandConquerApproach
239

sis is a valuable tool for forensics and other applica-
tions where specialized hardware is no available, and
could also serve as a backup strategy for distributed
systems in case of a communication failure
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work has been funded by the Spanish Ministry
of Education and Science under project TEC2012-
38142-C04-02.
REFERENCES
Ahmed, T., Uppal, M., and Muhammad, A. (2013). Im-
proving efficiency and reliability of gunshot detection
systems. In Acoustics, Speech and Signal Process-
ing (ICASSP), 2013 IEEE International Conference
on, pages 513–517. IEEE.
Efron, B. (1979). Bootstrap methods: another look at the
jackknife. The annals of Statistics, pages 1–26.
Fansler, K. S., Thompson, W. P., Carnahan, J. S., and Pat-
ton, B. J. (1993). A parametric investigation of muzzle
blast. Technical report, DTIC Document.
Freire, I. L. and Apolin´ario Jr, J. A. (2010). Gunshot detec-
tion in noisy environments. In Proceeding of the 7th
International Telecommunications Symposium, Man-
aus, Brazil.
Freytaga, J. C., Begaultb, D. R., and Peltierc, C. A. (2006).
The acoustics of gunfire. In INTER-NOISE.
Hunt, M., Lennig, M., and Mermelstein, P. (1980). Ex-
periments in syllable-based recognition of continuous
speech. In Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing,
IEEE International Conference on ICASSP’80., vol-
ume 5, pages 880–883. IEEE.
ISO-CEN.17201-2 (2006). Acoustics noise from shooting
ranges part 2: Estimation of muzzle blast and projec-
tile sound by calculation.
Karl Wilhem Hirsch, W. B. (2013). Estimation of the direc-
tivity pattern of muzzle blasts. In AIA-DAGA.
Kawalec, A., Pietrasinski, J., and Danicki, E. (2006). Se-
lected problems of sniper acoustic localization. Tech-
nical report, DTIC Document.
Khan, S., Divakaran, A., and Sawhney, H. S. (2009).
Weapon identification using hierarchical classification
of acoustic signatures. In SPIE Defense, Security, and
Sensing, pages 730510–730510. International Society
for Optics and Photonics.
Maher, R. (2006). Modeling and signal processing of acous-
tic gunshot recordings. In Digital Signal Processing
Workshop, 12th-Signal Processing Education Work-
shop, 4th, pages 257–261. IEEE.
Maher, R. C. (2007). Acoustical characterization of gun-
shots. Proc. SAFE 2007 (Washington, DC, IEEE
Signal Processing Society, 11–13 April 2007), pages
109–113.
Maher, R. C. and Shaw, S. R. (2010). Directional aspects
of forensic gunshot recordings. In Audio Engineering
Society Conference: 39th International Conference:
Audio Forensics: Practices and Challenges. Audio
Engineering Society.
Millet, J. and Baligand, B. (2006). Latest achievements
in gunfire detection systems. Technical report, DTIC
Document.
Parvin, H., Alinejad-Rokny, H., and Parvin, S. (2011). Di-
vide and conquer classification. Australian Journal of
Basic & Applied Sciences, 5(12).
Sallai, J., Hedgecock, W., Volgyesi, P., Nadas, A., Balogh,
G., and Ledeczi, A. (2011). Weapon classification
and shooter localization using distributed multichan-
nel acoustic sensors. Journal of Systems Architecture,
57(10):869–885.
Sergent, E. W. and Winkler, J. C. (1995). Gunshot detector.
US Patent 5,455,868.
Weissler, P. G. and Kobal, M. T. (1974). Noise of police
firearms. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of
America, 56(5):1515–1522.
Ye, J. (2007). Least squares linear discriminant analysis. In
Proceedings of the 24th international conference on
Machine learning, pages 1087–1093. ACM.
ICPRAM2015-InternationalConferenceonPatternRecognitionApplicationsandMethods
240
