
LS
2
C – A Platform to Design, Implement and
Execute Social Computations
Flavio S. Correa da Silva
1
, David S. Robertson
2
and Wamberto W. Vasconcelos
3
1
Dept. of Computer Science, University of Sao Paulo, Sao Paulo, Brazil
2
School of Informatics, University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, U.K.
3
Dept. Computing Science, University of Aberdeen, Aberdeen, U.K.
Keywords:
Interaction Models, Social Computation Models, Social Interaction Protocols.
Abstract:
Social computers have been characterised as goal oriented complex systems comprised of humans as well as
computational devices. Such systems can be found in natura in a variety of scenarios, as well as designed to
tackle specific issues of social and economic relevance. In the present article we introduce the Lightweight
Situated Social Calculus (LS
2
C) as a language to design executable specifications of interaction protocols for
social computations. Additionally, we describe a platform to process these specifications, giving them a com-
putational realisation. We argue that LS
2
C can be used to design, implement and execute social computations.
1 INTRODUCTION
Social computers have been characterised as complex
systems that harness the innate problem solving, ac-
tion and information gathering powers of humans and
the environments in which they live to tackle large
scale social and economic problems (Giunchiglia and
Robertson, 2010):
• The “hardware” of a social computer is supplied
by humans (taken as individuals as well as collec-
tively in the form of human-powered institutions)
and the environment where these humans live, in-
cluding all relevant artifacts which can be natural
or man-made, as well as computational devices.
• The “software” of a social computer is comprised
of human capabilities, organisational and social
rules and norms, social conventions, as well as
computer software.
• The “algorithms” of social computation are de-
fined by socially accepted goals and correspond-
ing actions which can be taken to achieve local as
well as global goals.
• Finally, the “processing” of algorithms in so-
cial computers are collective, decentralised, goal-
oriented actions whose emergent results can be
iteratively evaluated and steered towards active
goals.
Evidently, one cannot program a social computer
the way conventional computational devices are pro-
grammed. Social computers are evolving social sys-
tems, whose components (i.e. their “hardware”, “soft-
ware”, “algorithms” and “processing”) are dynami-
cally and evolutionarily designed together with their
goals and available resources. The analysis and de-
sign of social computers require novel methodologi-
cal practices, blending existing techniques and experi-
ences from applied social sciences and computational
sciences (Correa da Silva et al., 2013).
In order to design, implement and continuously
monitor and steer the behaviour of social computers,
specialised languages are required to build specifica-
tions, and corresponding computational platforms are
required to support, manage and provide a computa-
tional realisation of social computations. An essential
aspect to be represented in such languages is inter-
action between components of social computers, so
that the internal behaviour of these components can
be abstracted and the resulting systems can be anal-
ysed as a whole. Additionally, since these languages
should be used to communicate specifications as well
as processing results to participants in social comput-
ers (i.e. humans who behave as components in so-
cial computers), they should be concise and simple to
understand. Finally, in order to build social comput-
ers whose behaviour can be verified with respect to
desired requirements and attributes, these languages
196
Correa Da Silva F., Robertson D. and Vasconcelos W..
LS2C – A Platform to Design, Implement and Execute Social Computations.
DOI: 10.5220/0005237101960203
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART-2015), pages 196-203
ISBN: 978-989-758-074-1
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

should have a formal underpinning and the corre-
sponding specifications and processing results should
be formally verifiable.
In the present article we present the ongoing de-
velopment of a language and a platform for social
computers. The proposed language and companion
computational platform – coined the Lightweight Sit-
uated Social Calculus (LS
2
C) is a fusion of two previ-
ously existing languages, respectively the Lightweight
Social Calculus (LSC) and the JamSession platform.
In section 2 we present some related work and the
preliminary concepts that have guided the develop-
ment of the LS
2
C language and platform. In section
3 we introduce in detail the LS
2
C language. In section
4 we briefly describe the platform in which this lan-
guage shall be used. In section 5 we illustrate how this
platform can be used in practice. Finally, in section
6 we present some conclusions and proposed future
work.
2 RELATED WORK AND
PRELIMINARY CONCEPTS
The LS
2
C platform is a fusion of the Lightweight
Social Calculus (LSC) and the JamSession platform.
LSC, in turn, is an extension of the Lightweight Coor-
dination Calculus (LCC). In the following paragraphs
we briefly introduce these languages and platforms.
The LCC is an executable specification language
grounded on the notions of process algebras and ini-
tially proposed for the specification and processing
of interaction models for distributed software compo-
nents (Robertson, 2004). It has been extended in a
variety of ways, e.g. for contextual reasoning about
distributed software systems (Sindhu et al., 2006), for
the specification and execution of choreographies for
web services (Bai et al., 2012) and, more recently,
for the specification of social computers, under the
name of Lightweight Social Calculus – LSC (Murray-
Rust and Robertson, 2014). It has also been success-
fully implemented using the logic programming lan-
guage Prolog, the object oriented programming lan-
guage Java and the object-functional programming
language Scala.
LCC and its variations – particularly LSC – ful-
fill most of the requirements to be a language for the
specification, implementation and processing of so-
cial computations. LSC is a compact formal language
that can be used to specify and to mediate ongoing so-
cial interaction protocols. The syntax of LSC (as well
as all other variations of LCC), however, can lead to
lengthy specifications which can be difficult for hu-
man reading and understanding. Moreover, the exten-
sion of LCC to manage contexts (coined Ambient LCC
(Sindhu et al., 2006)) departs from the lightweight
approach and becomes more complex than the other
variations of LCC, resulting in a not so concise and
effective platform for the specification and execution
of interaction protocols by human system designers.
The explicit management of contexts can be a
powerful technique to help in the analysis and de-
sign of social interactions, given that many of these
interactions are context-dependent (e.g. business ne-
gotiations must occur in adequately equipped meet-
ing rooms, to ensure privacy and the availability of
required communication resources; healthcare must
occur in hospitals and clinics, to ensure the avail-
ability of required specialised equipment and person-
nel; bank transactions must occur over the appropri-
ate counters; the automated interactions among com-
municating portable devices in an Internet of Things
scenario must be context sensitive to ensure privacy
and reliability of interactions; and so on). Therefore,
a useful feature in a language for social computers is
the explicit representation and management of con-
texts, which can be abstracted as locations in which
certain interactions are allowed to occur.
The JamSession platform is a language developed
for purposes similar to those of LSC. It was initially
conceived as an executable specification language to
manage the interactions between human controlled
and synthetic characters in Second Life-style virtual
worlds and multiplayer computer games, and later
employed to mediate business interactions between
organisations in cross-organisational workflows (Cor-
rea da Silva, 2011; Correa da Silva et al., 2012). A
simplified prototype of JamSession has been imple-
mented in Prolog, and a cloud-based prototype of
JamSession has been implemented using the func-
tional language F], based on which sample demos of
applications have been developed (David, 2012). The
fundamental concept in JamSession is the notion of
situated interaction protocols, which determine how
and where agents can interact with each other and
with the environment. The semantics of situated in-
teraction protocols can be formally characterised in
terms of Nested Petri Nets, which are an extension
of coloured Petri nets to handle recursion (Fernan-
dez Venero and Correa da Silva, 2013a). Nested Petri
Nets, in turn, can be translated into the specifica-
tion language Promela and verified using the model
checker SPIN with respecto to properties of their op-
erational behaviour (such as liveness and termina-
tion) (Fernandez Venero and Correa da Silva, 2013b).
There have been initiatives by other authors to
analyse social interactions based on formal languages
capable of capturing the dynamics of interactions,
LS2C-APlatformtoDesign,ImplementandExecuteSocialComputations
197

in many cases grounded on the notions of dynamic
modal logics, preference logics and public announce-
ment logics (Christoff and Hansen, 2013; Hansen,
2014; Seligman et al., 2011; Zhen and Seligman,
2011). Our work distinguishes from these initiatives
in two relevant senses:
1. We focus on systems design as well as analysis,
whereas those initiatives focus primarily on anal-
ysis of existing social networks grounded on for-
mal theories.
2. Since we are interested in the design of sys-
tems for goal-oriented social interactions, we have
taken into account scalability and computational
performance issues, as well as interaction design
issues. Previously existing initiatives have mostly
focused on theoretical issues, accounting for com-
putational and system level performance as sec-
ondary issues. Scalability in LS
2
C shall be en-
sured by the appropriate use of asynchronous state
management based on Linda-style tuple spaces
(Gelernter, 1985), following the implementation
practices used in JamSession.
3 THE LS
2
C LANGUAGE
The Lightweight Situated Social Calculus (LS
2
C) is
based on the notion of situated social interactions.
A situated social interaction is comprised of actions
which are permitted to occur if performed by spe-
cific agents at specific locations, together with mes-
sages exchanged among agents in order to enable and
trigger further actions, and with migrations of agents
across locations. In LS
2
C, locations are an abstraction
used to represent a variety of concepts, such as:
• Actual physical locations, e.g. the counter in a
bank where financial transactions are permitted to
occur.
• Contextual information, e.g. characterising the
collective acceptance of interaction protocols by
agents in a business transaction (buy, sell, le-
gal procedures, and so on) so that it is common
knowledge that the transaction can be carried out
as long as all actions in all protocols – the “set-
ting” for the transaction – are fulfilled.
Locations are represented as nodes in a directed
graph, in which edges represent accessibility rela-
tions, characterising allowed transitions between lo-
cations or contexts. We denote the set of nodes in a
graph of locations as S = {s
1
,...,s
r
}
1
.
1
We abuse notation and also refer to the graph of loca-
tions itself as S.
Each location can host an unlimited number of
agents. An agent is capable of:
• Moving between directly connected locations.
• Performing allowed actions while in specific loca-
tions.
• Reading, writing or deleting messages in loca-
tions.
We have a set of agents A = {a
1
,...,a
m
} whose
behaviour is constrained and determined by each role
that they adopt, according to each location to which
they move. Actions and message types are available
only to agents bearing specific roles at specific loca-
tions. The positioning of agents in locations is the
way to control the processing of algorithms in social
computers represented using LS
2
C.
Actions can be enabled by and influence or trans-
form objects that can be found in the environment. We
have a set of objects B = {b
1
,...,b
n
}, which are sub-
ject to the actions of agents. Objects can be physical
objects as well as their digital counterparts.
We build mappings pointing to agents and objects,
so that we can refer to them indirectly through built
connections between them (such as FatherOf(X) to re-
fer to an agent by naming another agent). For this
reason, we also include in the language a set F of n-
ary functions, 0 < n < ∞, such that if f ∈ F has arity
j, it can be used to build or point to an element of
A ∪ B given j elements of A ∪ B ∪ S . In other words,
f : (A ∪ B ∪ S )
j
7→ A ∪B.
In order to be able to build terms as in first order
logics, we also include a countable set of variables
X = {x
1
,...}. Every formula built in this calculus is
assumed to be existentially closed, i.e. free variables
are implicitly bound to existential quantifiers.
We build relations involving agents and objects,
representing information that can be known by agents
and action statements. We have three sets of n-ary
predicates to represent each of these relation types:
• P : set of n-ary knowledge predicates, 0 ≤ n < ∞.
• Q : set of n-ary action predicates, 0 ≤ n < ∞.
• R : set of n-ary protocol names, 0 ≤ n < ∞.
Predicates are prefixed by modal operators as fol-
lows, in which p ∈ P ,q ∈ Q , r ∈ R ,s ∈ S and a ∈ A:
• [k]
s
a
p denotes a knowledge modality – agent a
knows fact p ∈ P at location s.
• [e]
s
a
q denotes an engagement modality – agent a
performs action q ∈ Q at location s.
• [i]
s
q denotes a location-specific computation
modality – action q ∈ Q is processed at location
s.
ICAART2015-InternationalConferenceonAgentsandArtificialIntelligence
198

• [i]
s
r denotes a location-specific interaction proto-
col – protocol r ∈ R can be started from location
s.
In order to avoid unnecessary complications in our
proposed language, we allow modal operators to only
prefix a single predicate, i.e. no nesting of modali-
ties is allowed, nor it is allowed to have a modality
prefixing arbitrary formulae.
Communicative actions are defined as follows, in
which p ∈ P ,a,a
0
∈ A and s,s
0
∈ S :
• null: a void message.
• [e]
s
a
write(p,a
0
): agent a writes message in loca-
tion s, which is then stored as predicate p known
by agent a
0
in s, i.e. [k]
s
a
0
p. In other words, agent
a tells p to a
0
in s.
• [e]
s
a
del(p, a
0
): agent a deletes message which was
previously stored in location s as predicate p
known by a
0
in s, i.e. the piece of knowledge
[k]
s
a
0
p is retracted from location s.
In order to continue with the definition of LS
2
C,
we need to define two connectives:
• Non-commutative conjunction: given two exis-
tentially closed formulae ϕ and ψ, the conjunction
ϕ u ψ is evaluated as > if:
1. ϕ is evaluated as > AND
2. the variable bindings performed during the
evaluation of ϕ are used to bind the values of
variables in ψ, producing the instatiated for-
mula
ˆ
ψ AND
3.
ˆ
ψ is also evaluated as >.
Otherwise, the conjunction ϕ u ψ is ⊥.
• Non-commutative disjunction: given two existen-
tially closed formulae ϕ and ψ, the disjunction
ϕ t ψ is evaluated as > if:
1. ϕ is evaluated as >, in which case ψ is never
evaluated OR
2. ϕ is evaluated as ⊥, and ψ is evaluated as >. In
this case, the variable bindings performed dur-
ing the evaluation of ϕ are not used to bind the
values of variables in ψ.
Otherwise, the disjunction ϕ t ψ is ⊥.
We define an atomic event AE as one of the fol-
lowing expressions, in which p ∈ P , q ∈ Q ,r ∈ R ,a ∈
A and s,s
i
,s
j
∈ S :
• [k]
s
a
p.
• [e]
s
a
q.
• [i]
s
q.
• [i]
s
r.
• [i]
s
i
→s
j
a
mv, in which the special predicate mv is
used to state that agent a is being moved from lo-
cation s
i
to location s
j
.
• a communicative action M.
We define an event E as a conjunction of atomic
events, i.e. E = u
i
AE
i
.
Finally, we define an interaction protocol as a pair
h[i]
s
r,t
i
E
i
i, in which [i]
s
r is a location-specific inter-
action protocol and t
i
E
i
is a non-commutative dis-
junction of events.
The interaction protocol h[i]
s
r,t
i
E
i
i is triggered
by a formula that unifies with the left hand side ex-
pression [i]
s
r. Variable bindings are applied to the
right hand side expression t
i
E
i
, which is then com-
puted. Each event E
i
is an alternative course of ac-
tions that can be tested. If one of the events E
i
re-
turns >, then the interaction protocol succeeds and
the corresponding variable bindings are presented. If
all alternatives in tE
i
return ⊥, then the interaction
protocol fails and variable bindings are discarded.
It should be observed that, since location-specific
interaction protocol expressions [i]
s
i
r
i
can occur as
atomic events in the right hand side of interaction pro-
tocols, recursive interaction protocols are allowed in
LS
2
C.
LS
2
C is a coordination language. Knowledge is
encoded in the platform using communicative actions
that update knowledge predicates p ∈ P , and action
predicates are expected to be evaluated by external
actors, which can include human as well as compu-
tational agents.
4 THE LS
2
C PLATFORM
We are working on a robust implementation for the
LS
2
C language, benefitting from existing implemen-
tations of LCC and of JamSession, that shall be freely
deployed as the LS
2
C platform. In this software plat-
form, the graph of locations, the list of pairs hs, ai, s ∈
S,a ∈ A for each predicate indicating where and by
whom it can be evaluated, and the state of each loca-
tion are managed in a centralised cloud server.
Interaction protocols are stored in distributed
hosts. The processing of these protocols may require
human intervention, this way characterising the LS
2
C
Platform as a tool to support and manage social inter-
actions. The physical location where interaction pro-
tocols can be found is stored in the centralised cloud
server as an address catalog. This catalog can be re-
arranged locally according to private ranking crite-
ria, defined by priority policies used in different sites
which can be used to rank interaction protocols.
LS2C-APlatformtoDesign,ImplementandExecuteSocialComputations
199
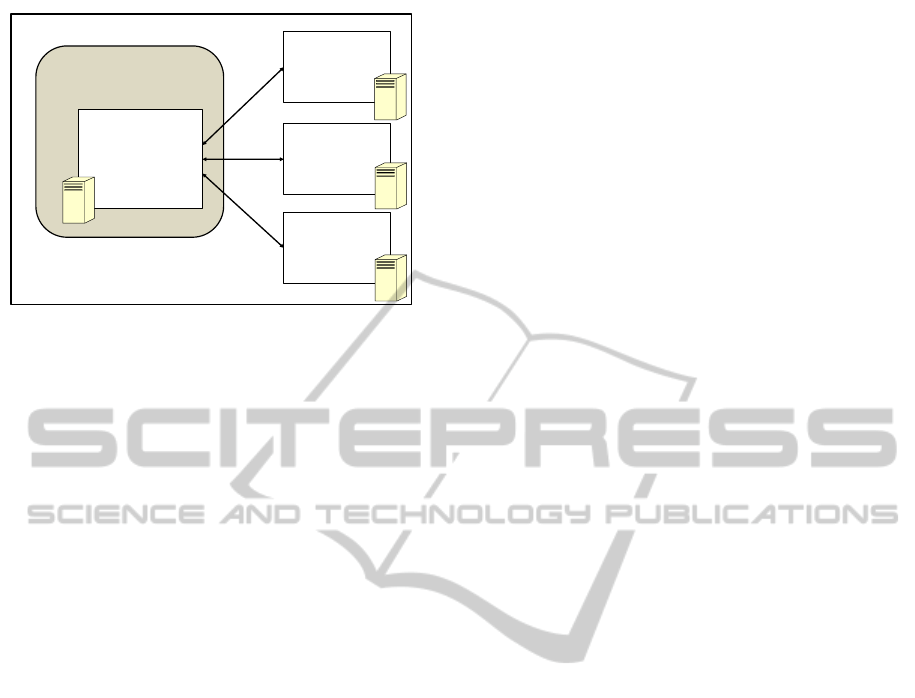
CLOUD
LS
2
C client:
• Predicates
• Protocols
LS
2
C client:
• Predicates
• Protocols
LS
2
C client:
• Predicates
• Protocols
LS
2
C server:
• Graph of sites
• State of each site
• Location of agents
• Messages
Figure 1: The architecture of the LS
2
C Platform.
The locations of agents are also managed in the
centralised server, characterising the notions of vir-
tual worlds as featured in the JamSession literature
(Correa da Silva, 2011) and mirror worlds as fea-
tured in the LSC literature (Murray-Rust and Robert-
son, 2014).
The definitions of predicates – including action
predicates, which can capture the input-output ex-
pected behaviour of human actions – are stored in the
distributed hosts. The locations of interaction proto-
cols and their corresponding predicates are stored in
the centralised server.
The architecture of the LS
2
C Platform is depicted
in Figure 1.
Protocols can be triggered concurrently and asyn-
chronously by several users. As a consequence, the
verification of properties related to distribution and
concurrency is important to ensure an expected be-
haviour in a system whose interactions are specified
using LS
2
C. We are working on the characterisation of
LS
2
C protocols using Nested Petri Nets, based on our
experience using the same formalism to characterise
JamSession protocols. Nested Petri Nets can be used
to formally verify properties such as fairness, liveness
and termination. Given that Nested Petri Nets can also
be translated as Promela programs to be verified using
the model checker SPIN (Fernandez Venero and Cor-
rea da Silva, 2013b), we will be able to verify such
properties also for LS
2
C social interaction protocols.
Similarly to LCC and to what can be observed
in business process modeling (Correa da Silva et al.,
2012; Robertson, 2004), social interaction protocols
can be considered at specification time and at run
time. Specification time refers to the design of so-
cial computers, while run time can refer to the a
posteriori analysis of the actual execution of social
computations, in which e.g. specific protocols are
used to enact concrete interactions. Such analysis
can reveal social network properties involving inter-
acting peers, such as centrality of a location, and co-
hesiveness and density of location-related interactions
(Jackson, 2008), whose interpretation can be relevant
to understand features of specific domains.
5 AN EXAMPLE – LS
2
C FOR S
3
In this section we mention some potential applications
for the LS
2
C platform, and sketch how some interac-
tion protocols can be encoded for one of these appli-
cations.
The LS
2
C platform has been conceived to design
and implement social computations in which situ-
ated interactions are most relevant. Social comput-
ers of this sort can be found in urban computing
and in intelligent city environments, which are ur-
ban landscapes augmented with digital communica-
tion and processing devices and applications (Jiang
et al., 2013; Komninos, 2006; Schaffers et al., 2011;
Zheng et al., 2011).
Urban computing refers to requesting citizens to
carry (most likely within their smartphones) software
applications that track their activities, interact with
them and provide information to service managers,
so that the quality of service provisioning can be im-
proved in issues such as traffic monitoring, public
transportation and emergency relief.
Intelligent cities are urban settings which have
been augmented with ubiquitous computing devices,
in such way that existing services can become more
effective and novel services can be offered to citizens,
businesses and governments. A representative exam-
ple of what can be achieved under the concept of in-
telligent cities is the structuring of effective business
clusters supported by digital services. In the follow-
ing paragraphs we detail this possibility.
An important well known factor for regional eco-
nomic development is innovation. Innovative en-
trepreneurship is frequently associated with start-up
companies, which in most cases are small companies
which hold deep knowledge and skills over a narrow
and specialised domain. One factor that has proven
to be influential for the survival of these companies is
their ability to cooperate with other companies, pos-
sibly forming or entering a network of cooperating
organisations. Local and regional governments have
taken notice of that and have created programmes
to support and incentive the blooming of such net-
works, as well as studied how these networks should
be structured in order to minimise the risk of failure of
participating companies and maximise the economic
efficiency of the networks (Feldman and Audretsch,
1999; Lazzarini et al., 2001; Mesquita and Lazzarini,
ICAART2015-InternationalConferenceonAgentsandArtificialIntelligence
200

2007; Pedrozo and Pereira, 2006).
Business clusters are emergent agglomerations of
companies which benefit from the proximity of each
other to grow. Smart Specialisation Strategies (S
3
)
have been proposed recently as means for policy mak-
ers to build “smart clusters”, in which the use of
knowledge and resources is optimised and coopera-
tion among companies is brought to be most effective
(EU, 2012; EU, 2013). S
3
can be seen as an effort to
design business clusters, instead of simply providing
appropriate means for them to emerge.
Business relations are partially constrained by ra-
tionality rules (such as profit maximisation and risk
minimisation). On the other hand, companies are
human-powered and human controlled institutions,
and therefore – especially small companies – are in-
fluenced by human decision making, which takes into
account rules beyond those that can be captured by
simplified models of pure rationality (e.g. brand fi-
delity, intuition driven trust relations, aesthetic con-
siderations and cultural affinity). Company relations
are diversified and include customer-supplier rela-
tions as well as cooperative relations involving sim-
ilar companies (Lazzarini et al., 2001; Pedrozo and
Pereira, 2006; Mesquita and Lazzarini, 2007). Hence,
we suggest that business networks can be treated as
social computers, and that the LS
2
C Platform can be
a useful tool to design, implement, run, monitor and
iteratively refine Smart Specialisation Strategies.
In order to illustrate how this can be done, we
show a simplified version of interaction rules that
could be relevant in a customer-supplier relationship
involving two companies. In this example, company
A asks company B to provide a service that is required
to carry on production activities within company A
2
.
Company A may wish to minimise risk in its op-
erations by limiting the number of open requests sent
to company B to a fixed value N: once A has sent N
requests to B, it will only send a new request after B
has fulfilled at least one of the queued requests.
In order to model this small example, the graph
consists of two locations s
A
and s
B
, and edges con-
necting these two locations in both directions (Figure
2). Agents, in this example, represent orders: when
company A places an order, an agent is sent from s
A
to s
B
, and when this order is delivered by company B
the agent is sent back from s
B
to s
A
. In Figure 2 we
depict agents as black dots. In that figure, company
A accepts to have seven simultaneous open orders at
2
This example is borrowed and adapted from (Correa da
Silva et al., 2012). Evidently, we are exhibiting only a very
small fraction of a model for S
3
using this example. Our
goal is simply to illustrate how rules that could be used to
model a S
3
would look like.
s
A
s
B
Figure 2: The two locations and corresponding agents for
the customer-supplier example.
most (i.e. N = 7), as shown by the seven agents that
are inside s
A
.
The following three small interaction protocols
implement this interaction
3
:
• Protocol 1:
1. h[i]
s
A
req1(X,Order),
2. [i]
s
A
→s
B
X
mv u[e]
s
B
X
write(message(Order),X) u
3. [i]
s
B
supply(X ,Order)
4. i.
• Protocol 2:
1. h[i]
s
B
supply(Y,W ),
2. [e]
s
B
Y
message(W ) u [e]
s
B
Y
prOrder(W ) u
3. [i]
s
A
req2(Y,W )
4. i.
• Protocol 3:
1. h[i]
s
A
req2(Z,U),
2. [e]
s
B
Z
del(message(U),Z) u [i]
s
B
→s
A
Z
mv u
3. [k]
s
A
Z
orderEnd(U) u [e]
s
A
Z
contProd(U)
4. i.
Interaction protocols 1 and 3 reside in a host
managed by company A, and interaction proto-
col 2 resides in a host managed by company B.
[i]
s
A
req1(X,Order) triggers the interactions, by ask-
ing an agent X in location s
A
to start interaction req1,
in which order Order will be requested to company B.
This is performed by moving the agent to location s
B
,
where it registers the order and triggers protocol 2.
By pattern matching on the right hand side of pro-
tocol 2, the message stored in location s
B
containing
the specification of the order is verified as being part
of the knowledge of Z while in s
B
, based on which the
3
We adopt the Prolog convention that variables begin
with capital letters, and all other terms begin with small let-
ters.
LS2C-APlatformtoDesign,ImplementandExecuteSocialComputations
201

order is processed (by triggering the action predicate
prOrder) and finally protocol 3 is triggered.
By pattern matching on the right hand side of pro-
tocol 3, the message is deleted and the agent is moved
back to location s
A
, then it is checked whether the or-
der has been properly delivered (using the knowledge
predicate orderEnd) and the protocol returns the con-
trol back to company A internal actions (using the ac-
tion predicate contProd).
This is a simplified example, in which suc-
cess/failure verifications of performed operations and
security issues are not taken into account. Additional
features can be implemented by extending these pro-
tocols and/or by adding special purpose protocols, to-
wards the design of interaction rules that can specify
and characterise successful relations between compa-
nies in a supply chain.
Other protocols can be designed to compete with
these protocols, and protocols can also be designed
to characterise cooperative behaviour of suppliers
to provide combined services to customers, towards
the design of interaction rules that can specify and
characterise relations between companies in a net-
work. Hence, the relations involving companies in a
netchain, i.e. a network of relations mixing supply
chains and cooperative/competitive relations (Laz-
zarini et al., 2001) can be designed.
Based on theoretical analysis of properties of the
interaction protocols, as well as empirical analysis of
actual relations that can result from the use of these
protocols, iterative refinements and adjustments can
be made.
6 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORK
In this article we have introduced the LS
2
C platform to
design, implement and execute social computations,
and sketched how it can be used to model and sup-
port a complex system of economic relevance, namely
the organisation of companies in a business cluster ac-
cording to S
3
.
A platform for social computations should present
features such as:
• The possibility to empower domain experts and
end users to build specifications and execute them,
• Technology-agnosticism, meaning that imple-
mentations can be built based on various and di-
verse software platforms, operating systems and
programming languages,
• Explicit account of participants in social interac-
tions and their possible behaviours,
• Resources for the design of interaction protocols
as well as for the analysis of existing protocols,
including formal analysis based on algebraic and
logical concepts.
The design and implementation of the LS
2
C plat-
form is work in progress. Since it inherits features and
properties of LCC/LSC as well as of JamSession, we
claim that this platform addresses all these features.
Our immediate future work concerns the imple-
mentation of the LS
2
C platform, and its field test in
the development of realistic social computers.
The specification of social interactions as charac-
terised in the LS
2
C platform can be used at least in
three different ways:
1. As a design tool to specify desired features of in-
teraction protocols in a decentralised way,
2. As a platform for the execution of social compu-
tations, and
3. As a tool to reason about specifications, including
strategic reasoning (e.g., given alternative proto-
cols that can be built, what is best for me/my com-
pany?), whereby participants may try out certain
behaviours “in vitro” before these can be actually
enacted.
LSC has been combined with an existing so-
cial network platform (Murray-Rust and Robertson,
2014), and JamSession has been combined with an ex-
isting workflow management platform (David, 2012).
We envisage that a full LS
2
C Platform can be imple-
mented as the combination of a novel implementation
of the LS
2
C language, a workflow management sys-
tem (e.g. Bonita
4
) and a social network platform (e.g.
elgg
5
or eXo
6
). The implementation of the LS
2
C lan-
guage shall benefit from previous experience imple-
menting LSC and JamSession.
We are particularly interested in the characterisa-
tion of Smart Specialisation Strategies (S
3
) as a disci-
pline to steer the emergency of networks of social in-
teractions involving human-powered agencies aiming
at regional economic efficacy. We believe that this ap-
proach can be appropriate to implement S
3
effectively,
and that the LS
2
C platform can be useful to support
the design and operation of business clusters follow-
ing S
3
. In future work, we shall explore these views,
hopefully through the analysis of empirical data re-
sulting from the actual structuring of clusters of inno-
vation as goal-oriented social interaction networks.
4
http://www.bonitasoft.com/
5
http://elgg.org/
6
http://www.exoplatform.com/
ICAART2015-InternationalConferenceonAgentsandArtificialIntelligence
202

ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work has been partially supported by FAPESP
and CNPq.
REFERENCES
Bai, X., Klein, E., and Robertson, D. (2012). Choreograph-
ing web services with semantically enhanced script-
ing, pages 583–587. Web Intelligence and Intelligent
Agent Technology.
Christoff, Z. and Hansen, J. U. (2013). A two-tiered formal-
ization of social influence. In Logic, Rationality, and
Interaction, volume 8196 of Lecture Notes in Com-
puter Science – Springer LNCS 8196, pages 68–81.
Correa da Silva, F. S. (2011). Knowledge-based interac-
tion protocols for intelligent interactive environments.
Knowledge and Information Systems, 30:1–24.
Correa da Silva, F. S., Fernandez Venero, M. L., David,
D. M., Saleem, M., and Chung, P. W. H. (2012). Inter-
action protocols for cross-organisational workflows.
Knowledge Based Systems, 37:1–16.
Correa da Silva, F. S., Robertson, D., and Vasconcelos, W.
(2013). Experimental interaction science. Artificial
Intelligence and Simulation of Behaviour - Annual
Convention 2013: Workshop on Social Coordination
– Principles, Artifacts and Theories.
David, D. M. (2012). Protocolos de interacao baseados em
conhecimento : implementacao da plataforma Jam-
Session (in Portuguese). MSc dissertation, University
of Sao Paulo, Brazil, Brazil.
EU, E. C. (2012). Guide to Research and Innovation Strate-
gies for Smart Specialisation. European Union, Brus-
sels.
EU, E. C. (2013). The role of clusters in smart specialisa-
tion strategies. European Union, Brussels.
Feldman, M. P. and Audretsch, D. B. (1999). Innovation
in cities: science-based diversity, specialization and
localized competition. European Economic Review,
43:409–429.
Fernandez Venero, M. L. and Correa da Silva, F. S. (2013a).
Modelling and simulating interaction protocols using
Nested Petri Nets. Workshop on Formal Methods in
the Development of Software.
Fernandez Venero, M. L. and Correa da Silva, F. S. (2013b).
On the use of SPIN for studying the behavior of nested
Petri nets. 16th Brazilian Symposium on Formal
Methods.
Gelernter, D. (1985). Generative communication in linda.
ACM Transactions on Programming Languages and
Systems, 7:80–112.
Giunchiglia, F. and Robertson, D. S. (2010). The social
computer - combining machine and human computa-
tion. University of Trento Technical Report, DISI-10-
036.
Hansen, J. U. (2014). Reasoning about opinion dynamics in
social networks. In Proceedings of the eleventh con-
ference on logic and the foundations of game and de-
cision theory (LOFT 11).
Jackson, M. O. (2008). Social and Economic Networks.
Princeton University Press, USA.
Jiang, S., Fiore, G. A., Yang, Y., Ferreira Jr, J., E., F., and
Gonzalez, M. C. (2013). A review of urban computing
for mobile phone traces: current methods, challenges
and opportunities. In Urban Computing 2013.
Komninos, N. (2006). The architecture of intelligent cities:
integrating human, collective, and artificial intelli-
gence to enhance knowledge and innovation. In In-
telligent Environments 2006.
Lazzarini, S. G., Haddad, F. R., and Cook, M. (2001). Inte-
grating supply chain and network analyses: the study
of netchains. Journal of Chain and Network Science,
1(1):7–22.
Mesquita, L. M. and Lazzarini, S. G. (2007). Horizontal and
vertical relationships in developing economies: impli-
cations for smes access to global markets. Academy
of Management Journal, 51(2):359–380.
Murray-Rust, D. and Robertson, D. (2014). LSCitter: build-
ing social machines by augmenting existing social net-
works with interaction models. International World
Wide Web Conference Committee.
Pedrozo, E. A. and Pereira, B. A. D. (2006). Empreende-
dorismo coletivo e possivel? uma analise do pro-
cesso de constituicao de relacionamentos cooperativos
em rede. Revista de Administracao (in Portuguese),
12(4).
Robertson, D. (2004). Multi-agent coordination as dis-
tributed logic programming, pages 416–430. Proceed-
ings 20th International Conference on Logic Program-
ming – Springer LNCS 3132.
Schaffers, H., Komninos, N., Pallot, M., Trousse, B., Nils-
son, M., and Oliveira, A. (2011). Smart cities and the
future internet: towards cooperation frameworks for
open innovation, pages 431–446. Future Internet As-
sembly – Springer LNCS 6656.
Seligman, J., Liu, F., and Girard, P. (2011). Logic in the
Community, pages 178–188. Logic and Its Applica-
tions – Springer LNCS 6521.
Sindhu, J., Perreau De Pinninck, A., Robertson, D., Sierra,
C., and Walton, C. (2006). Interaction model lan-
guage definition. Open Knowledge Project – technical
reports, UK.
Zhen, L. and Seligman, J. (2011). A logical model of the
dynamics of peer pressure. Electronic Notes in The-
oretical Computer Science, 278:275–288. Proceed-
ings of the 7th Workshop on Methods for Modalities
(M4M2011) and the 4th Workshop on Logical As-
pects of Multi-Agent Systems (LAMAS2011).
Zheng, Y., Liu, Y., Yuan, J., and Xie, X. (2011). Urban
computing with taxicabs. In UbiComp 2011.
LS2C-APlatformtoDesign,ImplementandExecuteSocialComputations
203
