
Salient Parts based Multi-people Tracking
Zhi Zhou
1
, Yue Wang
2
and Eam Khwang Teoh
1
1
School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore 639798, Singapore
2
Visual Computing Department, Institute for Infocomm Research (I2R), Singapore 138632, Singapore
Keywords:
Multi-people Tracking, Salient Parts, Tracking by Detection, Saliency Detection.
Abstract:
The saliency of an object or area is the quality to stand out from its neighborhood, it is an important component
when we observe objects in the real world. The detection of saliency has been studied for years and has
already been applied in many areas. In this paper, salient parts based framework is proposed for multi-people
tracking. The framework follows tracking-by-detection approach and performs multi-people tracking from
frame to frame. Salient parts are detected inside the human body area by finding high contrasts to their local
neighborhood. Short-term tracking of salient parts are applied to help locating targets when the association
with detections fails. And supporting models are on-line learnt to indicate the locations of targets based on the
tracking results of salient parts. Experiments are carried out on PETS09 and Town Center datasets to validate
the proposed method. The experimental result shows the promising performance of the proposed method and
comparison with state-of-the-art works is provided.
1 INTRODUCTION
Multi-people tracking has been studied for a long
time. It is an important research topic which can be
applied to many areas such as people tracking in pub-
lic places, abnormal action/event detection. It faces
many serious problems including occlusion by back-
ground object, mutual occlusion between targets, ID
switch and so on. Traditional methods (Checka et al.,
2003; Storms and Spieksma, 2003; Oh et al., 2004)
depend on short-term tracking from frame to frame.
Kalman filtering or data association were common
methods used. Andriluka (Andriluka et al., 2008)
introduced a way to solve people tracking problem
by combining detection and tracking. Since then,
the task of multi-people tracking has benefited a lot
from the powerful human detectors (Dalal and Triggs,
2005; Felzenszwalb et al., 2010), which provide pos-
sible locations of human existence in images. Meth-
ods in recent years consider multi-people tracking as
an optimization problem of data association over a pe-
riod of time. With the assistance of human detection
in each frame, Dynamic Programming (Fleuret et al.,
2008) or Linear Programming (Jiang et al., 2007)
methods are used to associate detections in different
frames. The aim is to reach the global optimum and
form consecutive trajectories.
In this paper, we propose a multi-people tracking
method by tracking salient parts concurrently. Meth-
ods pursuing global optimization are always applied
on a batch of frames. Usually the number of frame
is from tens to hundreds, thus it causes time delay
which is not preferred in real application. The pro-
posed method performs frame to frame tracking and
estimates locations of targets in current frame only
based on the previous frame. Saliency detection is in-
troduced into multi-people tracking in this paper. For
human visual perception, saliency is a very important
component when we observe objects in real world. It
was first introduced to computer vision area by (Itti
et al., 1998). Now many techniques have been devel-
oped to detect salient regions/objects (Cheng et al.,
2011; Perazzi et al., 2012; Yeh et al., 2014). And
Saliency has been used in many areas in computer vi-
sion, such as object segmentation (Li et al., 2014; Tian
et al., 2014) and people re-identification (Zhao et al.,
2013; Iodice and Petrosino, 2013). As far as we know,
saliency has not been applied to multi-people tracking
yet, so this is the first work to introduce saliency to the
multi-people tracking task. For each target, we con-
struct a salient parts based model by extracting salient
regions inside the human body area. Salient regions
are detected by using color and orientation informa-
tion, respectively. These salient parts will be tracked
concurrently along with the tracking of target people.
They will provide relative spatial information with the
231
Zhou Z., Wang Y. and Teoh E..
Salient Parts based Multi-people Tracking.
DOI: 10.5220/0005262202310240
In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications (VISAPP-2015), pages 231-240
ISBN: 978-989-758-091-8
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

whole body to help locating the target. Experimental
results show the satisfying performance of the pro-
posed method in multi-people tracking.
The rest of the paper is constructed as follows.
Section 2 gives a brief review on existing methods
on multi-people tracking. Section 3 presents the
overview of the proposed method, followed by de-
tailed description in Section 4. Experimental results
are addressed in Section 5. Finally, conclusion and
future work are given in Section 6.
2 RELATED WORKS
Multi-people tracking problem is mainly the combi-
nation of two tasks: inference of people locations
and data association. Some of existing works fol-
low frame to frame tracking by detection approach.
Andriluka (Andriluka et al., 2008) combined people
detector and tracker for frame to frame multi-people
tracking. A hierarchical Gaussian Process Latent
Variable Model (hGPLVM) is used to model the hu-
man walking cycle with prior knowledge, which helps
to improve the accuracy of articulation based people
detection. Breitenstein (Breitenstein et al., 2011) ap-
plied tracking by detection on a single camera. Par-
ticle filter is used for tracking. Person-specific clas-
sifiers are on-line learnt and used to detect people.
Zhang (Zhang et al., 2012) proposed a multi-people
tracking framework by tracking with an ensemble of
on-line updated templates. Both mean-shift tracking
and Kalman filtering are included to perform track-
ing. The birth and death of Trackers are controlled to
eliminate unwanted false detections. Wu (Wu et al.,
2012) combined a sparsity-driven people detection
and network-flow data association method for multi-
people tracking. It is performed in a 3D grid formed
by three simultaneously-recorded cameras.
Recently, data association approaches focusing
on pursing the global optimization become popular.
Some methods perform adding, merging and split-
ting of tracklets recursively to obtain a minimal global
cost function. These methods are processed over a
large batch of frames. Cost functions are defined
individually. In Ge’s work (Ge and Collins, 2008),
Markov Chain Monte Carlo Data Association (MCM-
CDA) is used to estimate a varying number of tra-
jectories, based on tracklets extracted from the video.
Benfold (Benfold and Reid, 2011) also used MCM-
CDA for data association. HOG detections along with
KLT tracking are used. Estimations on head loca-
tions are provided for maintaining target IDs when
occlusion or false detection is encountered. In Se-
gal’s work (Segal and Reid, 2013), Latent Data As-
sociation parametrization and inference algorithm are
introduced to multi-people tracking. Associations be-
tween observations are implicit, rather than being ex-
plicitly sought as in most traditional formulations,
thus the number of tracks can be determined auto-
matically during inference. In (Fleuret et al., 2008),
a Probabilistic Occupancy Map (POM) is estimated
based on images from multiple cameras with differ-
ent viewing angles. Locations of people are deter-
mined based on POM, then a Dynamic Programming
method is applied to form trajectories over sequences
of frames. Andriyenko (Andriyenko and Schindler,
2011) proposed a multi-people tracking method based
on global optimization method. An energy function
is constructed with consideration of detection of peo-
ple, target dynamic, collision avoidance, persistence
of tracklet and regularization. The objective is to find
the set of trajectories which achieves minimum global
energy function. Milan (Milan et al., 2014) extended
Andriyenko’s work by including additional appear-
ance component into the energy function, in order to
improve the performance against mutual occlusion.
Those methods pursuing global optimization with
large batch of frames usually require complicated
model and heavy calculation. Therefore, some re-
searchers find reliable tracklets in a smaller batch
of frames first. Concatenation is later performed to
form longer trajectories. Kuo (Kuo et al., 2010)
proposed an on-line learning appearance model for
multi-people tracking. Reliable tracklets linking de-
tection responses are first formed, followed by the
linking of tracklets based on the appearance mod-
els. Yang (Yang and Nevatia, 2012a) extended Kuo’s
work by introducing on-line learned Conditional Ran-
dom Field (CRF) model. Multi-people tracking is
transformed into an energy minimization problem,
and CRF model is used to differentiate pairs of track-
lets. Pirsiavash (Pirsiavash et al., 2011) proposed
a greedy algorithm based tracking method to track
a variable number of people from a single camera.
Multi-people tracking is considered as an Integer Lin-
ear Programming problem and follows the min-cost
flow method. Birth and death of trackers are estimated
by evaluating the cost function. Pursuing a global
optimization, Berclaz (Berclaz et al., 2011) applied
K-shortest Paths algorithm on Direct Acyclic Graphs
(DAGs), which is formed based on the POM from
(Fleuret et al., 2008). Shitrit (Shitrit et al., 2013) ex-
tended the work in (Berclaz et al., 2011) by introduc-
ing sparse appearance information of people. This is
used to prevent ID switches when the trajectories of
two targets have intersects.
Besides data association, some approaches focus
on occlusion reasoning. Tang (Tang et al., 2012) tried
VISAPP2015-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
232

to solve the occlusion by targets during multi-people
tracking. Based on Deformable Part Model (DPM),
he built a double-person detector. Several compo-
nents are included to solve different level of occlu-
sion problem. A joint detector is further formed by
combining DPM and double-person detector. Ouyang
(Ouyang and Wang, 2013) proposed a probabilistic
approach which incorporated single pedestrian detec-
tor and multi-pedestrian detector. A mixture model of
multi-pedestrian detectors is trained by using DPM.
Tracking parts of human body can always help
improving the accuracy of the tracker. Wu (Wu and
Nevatia, 2006) used the human body part detection in
static images to help the tracking of human. Part de-
tectors are only used when data association is failed.
Izadinia (Izadinia et al., 2012) proposed a multi-
people tracking method with the assistance of fixed
human parts tracking concurrently. In Yangs work
(Yang and Nevatia, 2012b), discriminative part-based
appearance model (DPAM) is proposed to deal with
occlusion problem and help tracking multiple humans
in real scenes. DPAM explicitly finds unoccluded
parts by occlusion reasoning and can be on-line up-
dated.
3 OVERVIEW
An overview of the proposed methods is presented in
Figure 1. Deformable Part Model (DPM) (Felzen-
szwalb et al., 2010) is used for human detection in
each frame. Locations detected are further used for
data association. Before a tracker is confirmed, a
tracker initialization step is performed to remove tran-
sitory false positive detections from DPM. For each
following frame, the tracker is first associated with
detections from DPM. If matching fails, short-term
tracking of salient parts and head part are applied. The
tracking results of salient parts and head are used to
confirm the location of target person. Trackers are
updated after the determination of targets locations.
Those trackers have not been updated for a certain
period of time are removed to keep computing effi-
ciently. More details are presented in next section.
4 MULTI-PEOPLE TRACKING
4.1 Tracking Model Representation
The objective of the proposed multi-people tracking
method is to maximize the joint posterior probability
of all people trajectories χ
t
based on the observations
I
t
in current frame
Figure 1: Overview of the proposed method.
χ
t
= argmax
χ
t
P(χ
t
|I
t
) (1)
During the tracking process, a model is constructed
for each target person. Use χ = {θ
i
} to represent a
set of people trajectories in a video, where θ
i
= {x
i,t
}
is one trajectory containing locations across frames.
x
i,t
= (l
i,t
, p
i,t
, s
i,t
, c
i,t
, h
i,t
, SP
i,t
) is the model of tra-
jectory i at frame t, containing label l
i,t
, position
of human p
i,t
, scale of human s
i,t
, human appear-
ance (represented in color histogram) c
i,t
, head part
h
i,t
and salient parts SP
i,t
= {sp
i,t,k
}. For head part
h
i,t
= (p
h
i,t
, s
h
i,t
, c
h
i,t
, r
h
i,t
, rp
h
i,t
) and salient parts sp
i,t,k
=
(p
SP
i,t,k
, s
SP
i,t,k
, c
SP
i,t,k
, r
SP
i,t,k
, rp
SP
i,t,k
), they all contain position
p
i,t,k
, scale s
i,t,k
, color histogram (represents the ap-
pearance of the part) c
i,t,k
, ratio of the part to the hu-
man patch r
i,t,k
and the relative position inside the hu-
man body rp
i,t,k
, respectively.
4.2 People Detection
As an important part in tracking by detection, the ac-
curacy of human detection has a great impact on the
performance of multi-people tracking. Fortunately,
recent works on human detection (Dalal and Triggs,
2005; Felzenszwalb et al., 2010) show promising re-
sults. In this paper, the human detection method
Deformable Part Model (DPM) (Felzenszwalb et al.,
2010) is employed in each frame. DPM is an object
detection method based on mixtures of multi-scale
star-structured deformable part models. The model
usually is constructed with a root filter which captures
the global shape information, plus a set of part filters
SalientPartsbasedMulti-peopleTracking
233

Figure 2: Deformal part model.
with relatively constrained locations capturing local
shape information. The model of DPM used in this
paper is shown in Figure 2, which is trained by INRIA
Person dataset (Dalal and Triggs, 2005). Locations of
full body and head obtained from DPM detection are
kept for further processing.
4.3 Salient Parts Detection
In this section, the method used in this paper to ob-
tain salient parts is described. These salient parts are
further used to assist people tracking.
Salient regions of human body can be considered
as important properties if an appearance model is con-
structed. They are highly contrast to the local or
global neighborhood. Therefore, it could stand out
from the background, or be representative for the hu-
man body.
From Itti (Itti et al., 1998), we learn that using the
differences with local neighborhood is a good way to
detect saliency. It is computational efficient as well.
To detect the salient parts, the most common used
features–color and orientation are selected in the pro-
posed method.
A bottom up method is first used to form the
saliency map, as shown in Figure 3. The human patch
is first smoothed by using Gaussian pyramids with 8
different scales. Then 4 contrast maps are obtained by
subtracting patches smoothed with larger scales from
patches smoothed with smaller scales. These con-
trast maps denote the difference between pixels and
their neighborhood in different scales. They are com-
bined to form the saliency map. A sliding window
with fixed size will be applied to find areas with top
saliency scores. Saliency score in a window is calcu-
lated as the average saliency value of pixels inside the
window. Those windows with saliency score Sal
i
ex-
Figure 3: Flow chart of salient map formation.
ceed the threshold τ
sal
= 0.9Sal
max
are kept. Among
them, spatially close windows are combined together
by weight to decide the location of this salient part.
Weight of window is calculated as
Weight
i
=
Sal
i
− τ
sal
∑
j
(Sal
j
− τ
sal
)
(2)
Windows with higher salient score receives higher
weight. Then the location of salient part is decided
as
p
SP
=
∑
Weight
i
× p
i
(3)
where p
i
is the location of a window.
In this paper, color and orientation salient maps
are not combined together. Instead, we detect the
color salient parts and orientation salient parts sepa-
rately. For color salient map, it is a combination of
local contrast maps from different color planes, while
orientation salient map is a combination of different
local contrast maps from different orientations. Ex-
amples of salient parts detection are shown in Figure
4. Color and orientation are used separately to detect
salient regions. In Figure 4 (d), yellow boxes are parts
extracted from color saliency detection, while green
boxes are parts extracted from orientation saliency de-
tection.
4.4 People Tracking along with Salient
Parts Tracking
4.4.1 Data Association
The proposed method follows the tracking by detec-
tion approach. Therefore, after locations of human
are detected by DPM, data association is used to link
detection results with existing trajectories. Hungar-
ian Algorithm (Kuhn, 1955) is applied in this paper
to associate detections in current frame with loca-
tions of trackers in previous frame. For one obser-
VISAPP2015-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
234

Figure 4: Examples of salient parts detection. (a) is the orig-
inal image. (b) and (c) are saliency maps formed by color
and orientation respectively. (d) is the result of detected
salient parts.
vant y
j,t
= (p
j,t
, s
j,t
, c
j,t
), the cost of linking this ob-
servant to a tracker location in previous frame x
i,t−1
=
(p
i,t−1
, s
i,t−1
, c
i,t−1
) considers the difference on spa-
tial location, scale size and appearance. It is calcu-
lated as
cost(y
j,t
, x
i,t−1
) = cost
p
(p
y
j,t
, p
x
i,t−1
)
+ cost
s
(s
y
j,t
, s
x
i,t−1
)
+ cost
c
(c
y
j,t
, c
x
i,t−1
)
(4)
cost
p
(p
y
j,t
, p
x
i,t−1
) = 1 −
Area(p
y
j,t
T
p
x
i,t−1
)
Area(p
y
j,t
S
p
x
i,t−1
)
(5)
cost
s
(s
y
j,t
, s
x
i,t−1
) = 1 −
min(s
y
j,t
, s
x
i,t−1
)
max(s
y
j,t
, s
x
i,t−1
)
(6)
cost
c
(c
y
j,t
, c
x
i,t−1
) = 1 −
∑
b
min(c
y
j,t,b
, c
x
i,t−1,b
) (7)
Observant receives higher cost are those with smaller
overlap area, larger size change and lower appearance
similarity. For those costs larger than thresholds of
cost
p
, cost
s
or cost
c
are set to be infinite.
4.4.2 Tracker Initialization
In a video, the number of people in frames is usu-
ally varying, people entering or leaving the scene is
quite common. Therefore, a flexible way to handle
the number of people tracker should be applied. The
initialization and termination of trackers are included
in the proposed method, they can also help to exclude
false positive detections from DPM.
With DPM, locations with high probability of
people existence are detected. New detections are
recorded as tracker candidates, and they are updated
in following frames by matched detections with small
spatial distance and high appearance similarity. Here
the appearance similarity is simply calculated by
color histograms, no specific appearance model is in-
volved. After the existence of a tracker candidate in
frames reaches the threshold, the tracker candidate is
transited to a tracker.
4.4.3 Tracking of Salient Parts and Head Part
Salient parts tracking along with head part tracking
are used when the tracker fails to associate with de-
tections. As representative parts of the human body,
locations of salient parts and head part can provide
reliable information indicating the whole body loca-
tion. Only those salient parts or head part updated in
previous frame are used for tracking, otherwise it will
deteriorate the performance of tracking. Median Flow
(Kalal et al., 2010) is used for parts tracking from pre-
vious frame to current frame. Then the location of
the tracker in current frame can be obtained by us-
ing a supporting model P
t
(p
i
|SP
i
) similar in (Grabner
et al., 2010). The supporting model indicates the lo-
cation of human p
i,t
based on information from head
and salient parts observed
P(p
i,t
|I) ∝ P
t
(p
i
|SP
i
)P(SP
i,t
|I) (8)
Some examples of the salient parts tracking are shown
in Figure 5. The first two pairs come from Town
Center dataset and the last pair comes from PETS09
dataset. Blue boxes are head parts, yellow boxes are
color salient parts and green boxes are orientation
salient parts.
Figure 5: Examples of salient parts tracking.
4.4.4 Tracker Update
Either by detection association or by salient parts
tracking, the tracker is updated after the current lo-
cation of tracker is determined. Contents to be up-
dated include the location of the human, human ap-
pearance represented as color histogram. Information
about head and salient parts are updated as well if
these parts are detected or tracked validly, satisfying
appearance similarity and spatial overlap conditions
∑
b
min(c
SP
i,t,k,b
, c
x
i,t−1,k,b
) > τ
c
(9)
SalientPartsbasedMulti-peopleTracking
235

Area(p
SP
i,t,k
T
p
SP
i,t−1,k
)
Area(p
SP
i,t,k
S
p
SP
i,t−1,k
)
> τ
p
(10)
where τ
c
and τ
p
are thresholds.
Besides, the supporting model is updated for those
updated salient parts. The exponential forgetting prin-
ciple is used to achieve on-line updating:
P
t
(p
i
|SP
i
) ∝ αP
t−1
(p
i
|SP
i
) + (1 − α)p(p
i,t
|SP
i,t
)
(11)
where p(p
i,t
|SP
i,t
) indicates the spatial relation be-
tween salient parts and human location.
4.4.5 Tracker Termination
As the number of frames increase, the number of
tracker could increase as well. The computation keeps
increasing if no deletion of unused tracker is made.
Therefore, those trackers have not been updated for a
period of time are terminated and no longer consid-
ered in the tracking process.
5 EXPERIMENTS AND RESULTS
There are four parts in this section. First, brief in-
troduction of datasets and evaluation criterion used is
given. Then, performances of the proposed method
are compared with method of data association and
method of head tracking. Thirdly, performances of
the proposed method by using different features are
compared. Finally, the proposed method is compared
with state-of-the-art works.
5.1 Introduction of Datasets and
Evaluation Criterion
5.1.1 Datasets
The proposed method has been carried out on
PETS09 (Ferryman and Shahrokni, 2009) and Town
Center (Benfold and Reid, 2011) to evaluate its per-
formance.
Sequence S2L1 from PETS09 is one of the most
used sequences in multi-people tracking. It was cap-
tured outdoor with an elevated viewpoint. People in
the video perform usual walking as well as some ir-
regular non-linear motions. The sequence also in-
cludes occlusions by object and mutual occlusions be-
tween people.
Town Center dataset contains a video capturing
a street in a town center. It includes mid-level peo-
ple density with some severe mutual occlusion condi-
tions. In addition, the scale of people changes as they
walk through the image.
5.1.2 Evaluation Criterion
As other methods in multi-people tracking, this pa-
per follows the CLEAR MOT (Kasturi et al., 2009) to
evaluate the performance of the proposed method. By
comparing the tracking result with Ground Truth pro-
vided by datasets, two important metrics are obtained.
The Multiple Object Tracking Accuracy (MOTA)
evaluates three types of errors: False Positive (de-
noted as f p
t
), False Negative (called miss detected
target and denoted as m
t
) and ID switch (called mis-
matches and denoted as mme
t
).
MOTA = 1 −
∑
t
(m
t
+ f p
t
+ mme
t
)
∑
t
g
t
(12)
where g
t
is the number of ground truth at frame t.
The Multiple Object Tracking Precision (MOTP)
evaluates the ability of the tracker to estimate pre-
cise object positions to the Ground Truth. The higher
score is, the smaller distance has between tracking re-
sult and ground truth.
MOT P =
∑
i,t
d
i
t
∑
t
c
t
(13)
where c
t
is the number of matches between tracking
result and ground truth at frame t. And d
i
t
is the dis-
tance between matches, which can be calculated as
overlap of bounding boxes.
5.2 Performance Evaluation of Salient
Parts Tracking
Since in the proposed method, salient parts tracking
are used along with data association and head part
tracking. In this section, to prove the impact of salient
parts tracking, comparison is given between the per-
formance of the proposed method and performances
using only data association or using data association
with head part tracking.
Some quantitative comparisons are provided in
Table 1. As can be observed, with salient parts track-
ing, the performance of multi-people tracking im-
proves.
Some qualitative analysis is provided in Figure 6.
First rows in Figure 6 (a) and Figure 6 (b) are results
from DPM detection, while second rows are the re-
sults from the proposed method. In Figure 6 (a), the
woman in blue is not tracked due to miss detection.
Also, in frame 157 and frame 192, a person at the
right top corner fails to be tracked by data association
VISAPP2015-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
236
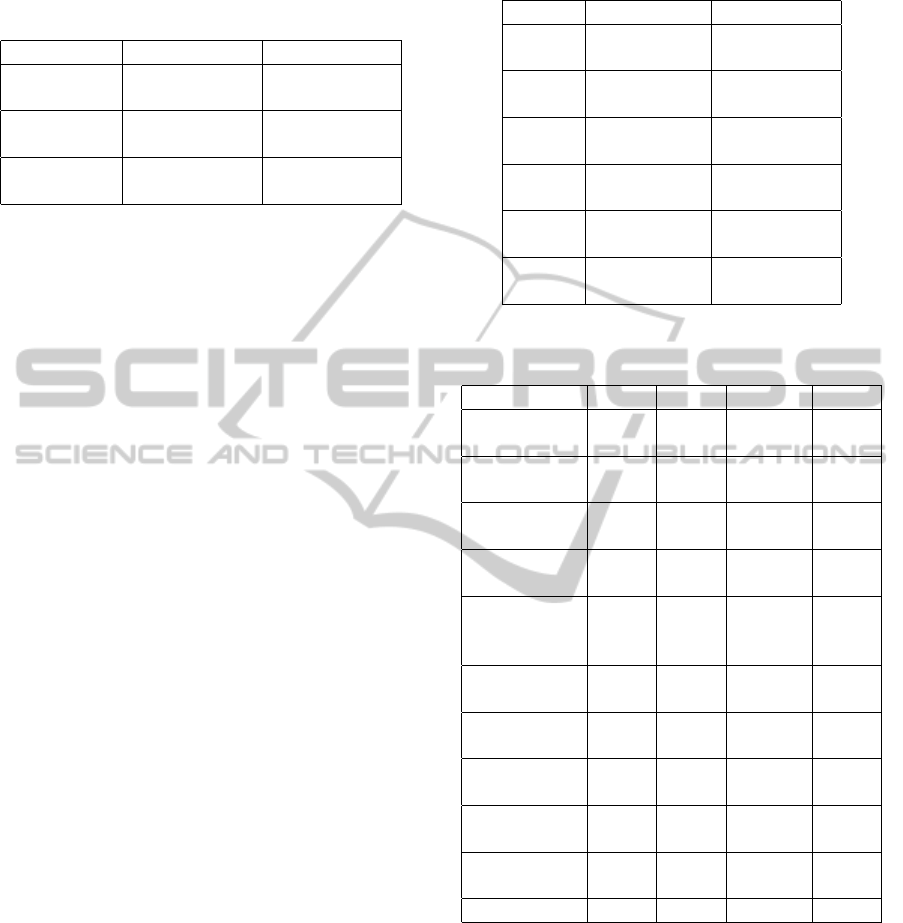
Table 1: Comparison of the proposed Salient Parts based
Tracking (DA+HP+SP) with Data Association (DA) and
Data Association with Head Part Tracking (DA+HP). The
best is shown in bold.
Method PETS09 Town Center
DA
MOTP=75.69
MOTA=74.37
MOTP=73.71
MOTA=70.80
DA+HP
MOTP=75.68
MOTA=87.18
MOTP=72.05
MOTA=72.80
DA+HP+SP
MOTP=75.45
MOTA=90.84
MOTP=71.75
MOTA=74.07
method. The proposed method tracked the woman
in blue in most of frames, it also keeps tracking of
the man at the right top corner. In Figure 6 (b), the
woman with pram is not detected by DPM, therefore
she can not be tracked by data association method. In
frame 933 and frame 957, some people on the edge of
frame are not tracked by data association method as
well. While the proposed method accurately tracked
the woman with pram and those people on the edge of
frame. Overall, when human detection fails, salient
parts could be a good complementary to the tracking
of targets.
5.3 Evaluation of the Performances of
Different Features
Salient detection result may vary with different fea-
ture used. In this section, the performances of the
proposed method are evaluated with different saliency
detection settings.
From the Table 2, it can be observed that us-
ing combination of several color channels performs
slightly better than using single color channels in
saliency detection. In addition, we compared HSV
color space, RGB color space, as well as combination
of 4 color channels RGBY, which is similar in Ittis
work (Itti et al., 1998). The result shows that detect-
ing salient parts in HSV color space outperforms the
other two color spaces for multi-people tracking. Be-
sides, we compared two different sets of scales when
performing Gaussian pyramids. Smaller scale used,
the salient region detected is more contrast to local
neighborhood, while salient region detected by using
larger scale is more contrast to the neighborhood with
a wider range. Table 2 shows smaller scale is more
helpful to salient parts based multi-people tracking.
5.4 Comparison with State-of-the-Art
Methods
In this section, the proposed method is compared with
some state-of-the-art works on PETS09 (Ferryman
Table 2: Comparison of tracking performance with different
salient detection settings. The best is shown in bold.
Feature Large Scale Small Scale
H
MOTP=75.7
MOTA=88.2
MOTP=75.5
MOTA=90.3
S
MOTP=75.6
MOTA=88.4
MOTP=75.6
MOTA=90.5
V
MOTP=75.7
MOTA=88.2
MOTP=75.4
MOTA=89.8
HSV
MOTP=75.7
MOTA=88.3
MOTP=75.4
MOTA=90.8
RGB
MOTP=75.7
MOTA=88.1
MOTP=75.5
MOTA=89.8
RGBY
MOTP=75.6
MOTA=89.6
MOTP=75.4
MOTA=88.2
Table 3: Comparison on PETS09 dataset. The best is shown
in bold.
Method MOTP MOTA Precision Recall
(Berclaz
et al., 2011)
62 78 78 62
(Breitenstein
et al., 2011)
59 74 89 60
(Pirsiavash
et al., 2011)
73.7 84.6 96.8 93.2
(Izadinia
et al., 2012)
76 90.7 96.8 95.2
(Yang and
Nevatia,
2012b)
- - 94.8 97.8
(Zhang
et al., 2012)
68.17 93.27 97.14 96.52
(Milan et al.,
2013)
74.3 90.3 - -
(Segal and
Reid, 2013)
75 92 - -
(Shitrit
et al., 2013)
- 81 - -
(Milan et al.,
2014)
80.2 90.6 98.4 92.4
Proposed 75.45 90.8 96.89 95.68
and Shahrokni, 2009) and Town Center (Benfold and
Reid, 2011) datasets.
Table 3 shows the comparison of the proposed
method with other methods on PETS09 dataset, while
Table 4 shows the comparison with other methods on
Town Center dataset. As can be observed, there is no
one method shows overwholming performance on all
evaluation parameters. In PETS09 dataset, the pro-
posed method achieves comparable performance on
all evaluation parameters with most of the state-of-
the-art works. And in Town Center dataset, the pro-
SalientPartsbasedMulti-peopleTracking
237

Figure 6: Comparison of results from the proposed method and DPM detections.
Table 4: Comparison on Town Center dataset. The best is
shown in bold.
Method MOTP MOTA Precision Recall
(Benfold
and Reid,
2011)
80.3 61.3 82 79
(Leal-Taix
´
e
et al., 2011)
71.5 67.3 71.6 67.6
(Pirsiavash
et al., 2011)
68.8 63.5 84.9 78.9
(Yamaguchi
et al., 2011)
70.9 63.3 71.1 64
(Izadinia
et al., 2012)
71.6 75.7 93.6 81.8
(Zhang
et al., 2012)
68.75 73.61 91.06 82.19
Proposed 71.75 74.07 87.23 88.36
posed has comparable score on MOTA with the best
performance, and outperforms other methods on Re-
call score.
It should be noted that the proposed method do
not use any information in following frames to avoid
time delay. Those methods with data association over
a period of time have the advantage that they can lo-
cate the missing targets by linking tracklets over a pe-
riod of time, therefore improving the tracking perfor-
mance. However, such methods would cause some
delay on the tracking performance which sometimes
may not be desired in real application.
6 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORK
In this paper, we introduced salient parts into multi-
people tracking. Following the tracking-by-detection
approach, salient parts tracking can be a good comple-
mentary to data association and head tracking. Sup-
porting models are constructed and on-line updated
to indicate the spatial relations between salient parts
and target locations. Experimental results validate the
improvement of performance by adding salient parts
tracking. Furthermore, it shows the comparable per-
formance of the proposed method with state-of-the-
art methods.
In the future work, there are a lot of works can
be done to improve the performance. In this paper,
only RGB and HSV color space and orientation of
edges are tested for salienty detection, more features
or combination of features could be tested in future to
exploit better performance. Besides, salient regions
VISAPP2015-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
238

used in this paper are square boxes with fixed size.
However, salient areas usually are in irregular shapes.
A method to detect regions in their own shapes might
improve the short term tracking performance. In addi-
tion, salient parts outside the human body area could
also be considered to help the tracking of people.
REFERENCES
Andriluka, M., Roth, S., and Schiele, B. (2008).
People-tracking-by-detection and people-detection-
by-tracking. In Computer Vision and Pattern Recog-
nition, 2008. CVPR 2008. IEEE Conference on, pages
1–8. IEEE.
Andriyenko, A. and Schindler, K. (2011). Multi-target
tracking by continuous energy minimization. In Com-
puter Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2011
IEEE Conference on, pages 1265–1272. IEEE.
Benfold, B. and Reid, I. (2011). Stable multi-target tracking
in real-time surveillance video. In Computer Vision
and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2011 IEEE Confer-
ence on, pages 3457–3464. IEEE.
Berclaz, J., Fleuret, F., Turetken, E., and Fua, P. (2011).
Multiple object tracking using k-shortest paths opti-
mization. Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,
IEEE Transactions on, 33(9):1806–1819.
Breitenstein, M. D., Reichlin, F., Leibe, B., Koller-Meier,
E., and Van Gool, L. (2011). Online multiper-
son tracking-by-detection from a single, uncalibrated
camera. Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,
IEEE Transactions on, 33(9):1820–1833.
Checka, N., Wilson, K., Rangarajan, V., and Darrell, T.
(2003). A probabilistic framework for multi-modal
multi-person tracking. In Computer Vision and Pat-
tern Recognition Workshop, 2003. CVPRW’03. Con-
ference on, volume 9, pages 100–100. IEEE.
Cheng, M.-M., Zhang, G.-X., Mitra, N. J., Huang, X., and
Hu, S.-M. (2011). Global contrast based salient region
detection. In Computer Vision and Pattern Recogni-
tion (CVPR), 2011 IEEE Conference on, pages 409–
416. IEEE.
Dalal, N. and Triggs, B. (2005). Histograms of oriented gra-
dients for human detection. In Computer Vision and
Pattern Recognition, 2005. CVPR 2005. IEEE Com-
puter Society Conference on, volume 1, pages 886–
893. IEEE.
Felzenszwalb, P. F., Girshick, R. B., McAllester, D., and
Ramanan, D. (2010). Object detection with discrim-
inatively trained part-based models. Pattern Analy-
sis and Machine Intelligence, IEEE Transactions on,
32(9):1627–1645.
Ferryman, J. and Shahrokni, A. (2009). Pets2009: Dataset
and challenge. In Winter-PETS.
Fleuret, F., Berclaz, J., Lengagne, R., and Fua, P. (2008).
Multicamera people tracking with a probabilistic oc-
cupancy map. Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelli-
gence, IEEE Transactions on, 30(2):267–282.
Ge, W. and Collins, R. T. (2008). Multi-target data associa-
tion by tracklets with unsupervised parameter estima-
tion. In BMVC, volume 2, page 5.
Grabner, H., Matas, J., Van Gool, L., and Cattin, P. (2010).
Tracking the invisible: Learning where the object
might be. In Computer Vision and Pattern Recogni-
tion (CVPR), 2010 IEEE Conference on, pages 1285–
1292. IEEE.
Iodice, S. and Petrosino, A. (2013). Person re-identification
based on enriched symmetry salient features and
graph matching. In Pattern Recognition, pages 155–
164. Springer.
Itti, L., Koch, C., and Niebur, E. (1998). A model of
saliency-based visual attention for rapid scene anal-
ysis. IEEE Transactions on pattern analysis and ma-
chine intelligence, 20(11):1254–1259.
Izadinia, H., Saleemi, I., Li, W., and Shah, M. (2012). 2t:
Multiple people multiple parts tracker. In Computer
Vision–ECCV 2012, pages 100–114. Springer.
Jiang, H., Fels, S., and Little, J. J. (2007). A linear
programming approach for multiple object tracking.
In Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2007.
CVPR’07. IEEE Conference on, pages 1–8. IEEE.
Kalal, Z., Mikolajczyk, K., and Matas, J. (2010). Forward-
backward error: Automatic detection of tracking fail-
ures. In Pattern Recognition (ICPR), 2010 20th Inter-
national Conference on, pages 2756–2759. IEEE.
Kasturi, R., Goldgof, D., Soundararajan, P., Manohar, V.,
Garofolo, J., Bowers, R., Boonstra, M., Korzhova, V.,
and Zhang, J. (2009). Framework for performance
evaluation of face, text, and vehicle detection and
tracking in video: Data, metrics, and protocol. Pat-
tern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, IEEE Trans-
actions on, 31(2):319–336.
Kuhn, H. W. (1955). The hungarian method for the as-
signment problem. Naval research logistics quarterly,
2(1-2):83–97.
Kuo, C.-H., Huang, C., and Nevatia, R. (2010). Multi-target
tracking by on-line learned discriminative appearance
models. In Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition
(CVPR), 2010 IEEE Conference on, pages 685–692.
IEEE.
Leal-Taix
´
e, L., Pons-Moll, G., and Rosenhahn, B. (2011).
Everybody needs somebody: Modeling social and
grouping behavior on a linear programming multiple
people tracker. In Computer Vision Workshops (ICCV
Workshops), 2011 IEEE International Conference on,
pages 120–127. IEEE.
Li, Y., Hou, X., Koch, C., Rehg, J., and Yuille, A. (2014).
The secrets of salient object segmentation. CVPR.
Milan, A., Roth, S., and Schindler, K. (2014). Continuous
energy minimization for multi-target tracking.
Milan, A., Schindler, K., and Roth, S. (2013). Detection-
and trajectory-level exclusion in multiple object track-
ing. In Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition
(CVPR), 2013 IEEE Conference on, pages 3682–
3689. IEEE.
Oh, S., Russell, S., and Sastry, S. (2004). Markov chain
monte carlo data association for general multiple-
target tracking problems. In Decision and Control,
SalientPartsbasedMulti-peopleTracking
239

2004. CDC. 43rd IEEE Conference on, volume 1,
pages 735–742. IEEE.
Ouyang, W. and Wang, X. (2013). Single-pedestrian detec-
tion aided by multi-pedestrian detection. In Computer
Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2013 IEEE
Conference on, pages 3198–3205. IEEE.
Perazzi, F., Krahenbuhl, P., Pritch, Y., and Hornung, A.
(2012). Saliency filters: Contrast based filtering for
salient region detection. In Computer Vision and Pat-
tern Recognition (CVPR), 2012 IEEE Conference on,
pages 733–740. IEEE.
Pirsiavash, H., Ramanan, D., and Fowlkes, C. C. (2011).
Globally-optimal greedy algorithms for tracking a
variable number of objects. In Computer Vision and
Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2011 IEEE Conference
on, pages 1201–1208. IEEE.
Segal, A. V. and Reid, I. (2013). Latent data association:
Bayesian model selection for multi-target tracking.
In Computer Vision (ICCV), 2013 IEEE International
Conference on, pages 2904–2911. IEEE.
Shitrit, B. H., Berclaz, J., Fleuret, F., and Fua, P. (2013).
Multi-commodity network flow for tracking multiple
people.
Storms, P. P. and Spieksma, F. C. (2003). An lp-based
algorithm for the data association problem in multi-
target tracking. Computers & Operations Research,
30(7):1067–1085.
Tang, S., Andriluka, M., and Schiele, B. (2012). Detection
and tracking of occluded people. International Jour-
nal of Computer Vision, pages 1–12.
Tian, Y., Li, J., Yu, S., and Huang, T. (2014). Learning
complementary saliency priors for foreground object
segmentation in complex scenes. International Jour-
nal of Computer Vision, pages 1–18.
Wu, B. and Nevatia, R. (2006). Tracking of multiple, par-
tially occluded humans based on static body part de-
tection. In Computer Vision and Pattern Recogni-
tion, 2006 IEEE Computer Society Conference on,
volume 1, pages 951–958. IEEE.
Wu, Z., Thangali, A., Sclaroff, S., and Betke, M. (2012).
Coupling detection and data association for multi-
ple object tracking. In Computer Vision and Pat-
tern Recognition (CVPR), 2012 IEEE Conference on,
pages 1948–1955. IEEE.
Yamaguchi, K., Berg, A. C., Ortiz, L. E., and Berg, T. L.
(2011). Who are you with and where are you going?
In Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR),
2011 IEEE Conference on, pages 1345–1352. IEEE.
Yang, B. and Nevatia, R. (2012a). An online learned crf
model for multi-target tracking. In Computer Vision
and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2012 IEEE Confer-
ence on, pages 2034–2041. IEEE.
Yang, B. and Nevatia, R. (2012b). Online learned dis-
criminative part-based appearance models for multi-
human tracking. In Computer Vision–ECCV 2012,
pages 484–498. Springer.
Yeh, H.-H., Liu, K.-H., and Chen, C.-S. (2014). Salient
object detection via local saliency estimation and
global homogeneity refinement. Pattern Recognition,
47(4):1740–1750.
Zhang, J., Presti, L. L., and Sclaroff, S. (2012). Online
multi-person tracking by tracker hierarchy. In Ad-
vanced Video and Signal-Based Surveillance (AVSS),
2012 IEEE Ninth International Conference on, pages
379–385. IEEE.
Zhao, R., Ouyang, W., and Wang, X. (2013). Unsupervised
salience learning for person re-identification. In Com-
puter Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2013
IEEE Conference on, pages 3586–3593. IEEE.
VISAPP2015-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
240
