
Automatic Political Profiling in Heterogeneous Corpora
Hodaya Uzan
1
, Esther David
2
, Moshe Koppel
3
and Maayan Geffet-Zhitomirsky
4
1
Computer Science Dept. Bar-ilan Univeristy, Max & Anna Web st., Ramat-gan, Israel,
2
Computer Science Dept. Ashkelon Academic College, Yitzhak Ben-zvi st. 12, Ashkelon, Israel
3
Computer Science Dept. Bar-ilan univeristy, Max & Anna Web st., Ramat-gan, Israel
4
Information Science Dept. Bar-ilan univeristy, Max & Anna Web st., Ramat-gan, Israel
Keywords: Politics Classifying, Machine Learning, Text Classification, Automatic Profiling, Facebook.
Abstract: In this paper we consider automatic political tendency recognition in a variety of genres. To this end, four
different types of texts in Hebrew with varying levels of political content (manifestly political, semi-
political, non-political) are examined. It is found that in each case, training and testing in the same genre
yields strong results. More significantly, training on political texts yields classifiers sufficiently strong to
classify non-political personal Facebook pages with fair accuracy. This suggests that individuals’ political
tendencies can be identified without recourse to any tagged personal data.
1 INTRODUCTION
It is plainly of great utility to be able to
automatically determine the political orientation of
the author (or publisher) of a document by analyzing
the document’s statistical properties. In the case of a
document written or posted by an individual,
inferred political orientation can, for ex-ample, be
used for purposes of targeted messaging. In the case
of news items published by a public news source,
explicit or implicit political biased can be revealed.
Even in the case of politicians or political
organizations, for which political orientation is
usually explicitly declared and widely known, it can
be useful to consider the intensity of political
orientation expressed in particular documents.
In this paper, we explore the use of automated
text categorization methods to determine the
political orientation of documents in a variety of
genres. Such methods have been widely used for a
variety of author profiling tasks (Argamon et al.,
2009), typically for the purpose of identifying
authors' characteristics such as age, gender or native
language. The application of these methods for the
determination of political orientation is especially
challenging. First of all, unlike demographic
characteristics, an individual’s political orientation
may vary over time and is often complex and thus
not easily captured by a single simplistic label such
as left, right or center. Furthermore, conventions of
public expression often dictate that political views
be stated in a subtle manner, if at all. The problem is
especially difficult in contexts where the discussion
is not intended to be political at all.
A number of papers (see discussion below) have
considered the automatic identification of political
tendency for overtly political documents. In this
paper, we consider automated classification of
political preference in multiple genres, including
news articles, parliamentary speeches, political par-
ties’ Facebook pages and personal Facebook pages.
Clearly, the problem is a harder one when dealing
with personal Facebook pages than with overtly
political material such as parliamentary speeches or
political party Facebook pages. Thus, we consider,
inter alia, the possibility of training a classifier in a
genre for which labeled training data is easily
accessible (parliamentary speeches, political parties’
Facebook pages) and applying to a different genre
where such labeled data is difficult to obtain (per-
sonal Facebook pages) or a matter of dispute (news
articles).
We first use machine learning methods to show
the extent to which political preferences can be
discerned in manifestly political texts (political
parties’ Facebook pages, parliamentary speeches),
non-political texts (personal Facebook pages), and
semi-political texts (newspaper articles). Then we
study the extent to which the political preferences of
the author of a personal Facebook page can be
476
Uzan H., David E., Koppel M. and Geffet-Zhitomirsky M..
Automatic Political Profiling in Heterogeneous Corpora.
DOI: 10.5220/0005270104760481
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART-2015), pages 476-481
ISBN: 978-989-758-074-1
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

automatically determined using classifiers trained on
clearly identified political texts.
The texts we consider here are Hebrew texts
written by Israelis. This presents a number of
challenges and opportunities specific to this
linguistic and political context. Since we use only
lexical features, the morphological quirks of Hebrew
will not present any special challenges. However,
Israel’s purely proportional, single-region
parliamentary election system presents one
interesting opportunity. Unlike winner-take-all
regional elections, which typically result in only two
major parties, there are many medium-sized parties
in Israel. While each of these parties can rather
easily be identified as left, right or center, the parties
differ widely in terms of the demographic to which
they appeal.
The paper's outline is as follows. In the next
section, we describe related work. Then we present
the four corpora used in the paper and follow that
with an outline of our methodology and
experiments. The two sections after that include
detailed presentation of our results and some
conclusions.
2 RELATED WORK
Numerous studies have been performed in the area
of automatic recognition of an author’s demographic
profile. Text categorization methods have been used
to identify an anonymous author’s gender (Argamon
et al., 2003; Burger et al., 2011; Filippova, 2012),
age (Schler et al., 2006), native language (Koppel et
al., 2005) and personality (Pennebaker et al., 2003).
It has been shown that such demographic profiling
can also be done on personal Facebook pages
(Otterbacher, 2010; Popescu and Grefenstette, 2010;
Gosling et al., 2011). A survey of automated
demographic profiling is presented in (Argamon et
al., 2009).
Several studies have considered ways in which
additional available information can be used to
enhance purely text-based features to improve
demographic profiling. Thus, for example, it has
been found that text-based gender classification of
authors can be improved using additional
information such as names (Burger et al., 2011) and
social-network topology (Filippova, 2012). Similar
such methods have been used to improve automated
classification according to location and educational
level (Rao et al., 2010; Gillick, 2010) and age
(Rosenthal and McKeown, 2011). Others have
considered patterns of social network activity to
determine personality type (Bachrach et al., 2012;
Gosling et al., 2011; Ross et al., 2009).
A number of papers have considered the problem
of automatically determining an author’s political
preference (left, right). For example, (Laver et al.,
2003; Efron, 2004; Mullen and Malouf, 2006;
Hassanali and Hatzivassiloglud, 2010) use text
categorization methods for determining the political
orientation of political blogs. Grefenstette et al.,
(2004) explore the same problem for websites by
considering the aggregate of documents found on a
site. Rao et al., (2010) and Conover et al., (2011)
extend this work to Twitter accounts that are not
necessarily blatantly political. Kosinski et al., (2013)
have shown that political views, among other
personal characteristics, can be predicted from a
user’s "likes" on Facebook.
A variety of studies have applied supervised
learning for automatic perspective recognition of
politically-charged texts. To this end, Lin et al.,
(2006) classify articles from the Bitter-Lemons
website on the Palestinian-Israeli conflict using
lexical features. Beigman-Klebanov et al., (2010)
use the same corpus (and three other politically
polarized corpora) and showed that binary features
are not less effective than frequency-based features.
Similarly, Hasan and Ng, (2012) classify articles
taken from corpora concerning abortion and gun-
rights. Finally, Yu et al., (2008) classify U.S.
congressional speeches according to party
affiliation. In general, these studies deal with texts in
a genre in which labeled texts are relatively easy to
find.
In this study, we wish to classify texts in genres
for which examples labeled according to political
tendency are hard to come by. One possible way to
do this is to draw training data from other genres in
which documents are easy to label. An initial step in
this direction was originally proposed in a study by
Gentzkow and Shapiro, (2010) who identify a
newspaper’s political slant by measuring the
similarity of its language to that of congressional
Republicans and Democrats. To this end, they
counted the occurrences of the most frequent
political phrases semi-automatically selected from
Republicans and Democrats speeches in the U.S.
congress in the various newspapers. We use a
method similar to that of Gentzkow and Shapiro
(2010), but we use automated text categorization
methods rather than manual word counts.
Furthermore, we find that parliamentary speeches
are not as effective for training purposes as
Facebook pages of political parties.
AutomaticPoliticalProfilinginHeterogeneousCorpora
477

3 CORPORA
In this work, we will consider Hebrew texts, some of
which are explicitly political and some of which are
not. We will explore whether models learned on
political texts can be used to classify ostensibly non-
political texts.
We use the following four corpora:
(1) Posts on the Facebook pages of nine major
Israeli political parties. Each party is labelled as
left/ center /right, with three parties assigned to
each category. (While the assignments to
categories are uncontroversial, the parties in each
category are diverse in terms of their demo-
graphic appeal.) The corpus consists of 669
posts, including over 550,000 words. (Party
names and names of party leaders are omitted.).
(2) Transcripts of all Israeli parliament members'
speeches during a six-month period in 2011. This
corpus includes 119 articles (one for each
parliament member except for one member who
gave no speeches during that period of time).
Each speaker belongs to a political party and is
assigned to a category accordingly. As a result,
47% of the articles were labelled as right-wing,
26% as left-wing, and 27% as centrist.
(3) News stories from the five most popular Israeli
news websites during a four-month period in
2011. This corpus contains about 3,800 articles
including over 860,000 words. A survey of 272
random Israelis was conducted to assign each
news source a score on the left-right scale. Three
out of the five news websites were classified as
left-wing by the majority of the participants in
the survey, while one was assigned to the right-
wing and another to the center.
(4) Facebook pages of 300 random Israeli
individuals, half of whom self-identified as right-
wing and half of whom self-identified as left-
wing. Each individual’s text included all status
updates, personal details, as well as the titles of
“liked” pages. Although, these pages are not
inherently political, many of them refer to
politics.
4 METHODOLOGY
We begin by introducing the basic concepts from
text categorization that we use here. First, each text
in a set of labeled example texts is represented as a
numerical vector reflecting the frequencies in the
text of each feature in a specified feature set. Some
machine learning algorithm is then used to learn a
classifier that best distinguishes among training
examples in different classes. These classifiers can
then be used to classify new texts.
Specifically, here we aim to build a classifier that
distinguishes right-wing texts from left-wing texts.
Our primary machine learning method is Bayesian
Multinomial Regression (BMR) (Genkin et al.,
2007), a multivariate variant of logistic regression
that has been found in previous work (Argamon et
al., 2009) to be efficient and accurate. Similar results
were obtained using SVM and Winnow as learning
algorithms.
We consider two types of features: word
unigrams and word bi-grams. We choose the k most
frequent of these in each corpus. In some
experiments (as indicated below), we take from
among these the m words that discriminate best
between classes in the training corpus.
We measure the effectiveness of our methods by
applying a learned classifier to test texts for which
the correct answer is known. For some experiments,
we use k-fold cross-validation: we divide the
training set into k roughly equal parts, train on k-1
parts and test on the holdout set, repeating this k
times with a different part held out each time and
averaging the results.
5 EXPERIMENTS
5.1 Individual Corpora
For our initial experiments, we consider each corpus
individually. For each, we address the same
question: can we learn to distinguish texts assigned
to the class right-wing from those assigned to the
class left-wing. (Those in the center were ignored for
purposes of this experiment.)
To test the extent to which we can do so, we use
the same methodology for each. We use as our
feature set all word unigrams and bigrams that
appear in the corpus at least 3 times. We represent
each document as a vector indicating the frequency
of each feature in the document. We use Bayesian
logistic regression as our learning method.
We measure accuracy in 10-fold cross-validation
experiments. Results are shown in Figure 1.
ICAART2015-InternationalConferenceonAgentsandArtificialIntelligence
478
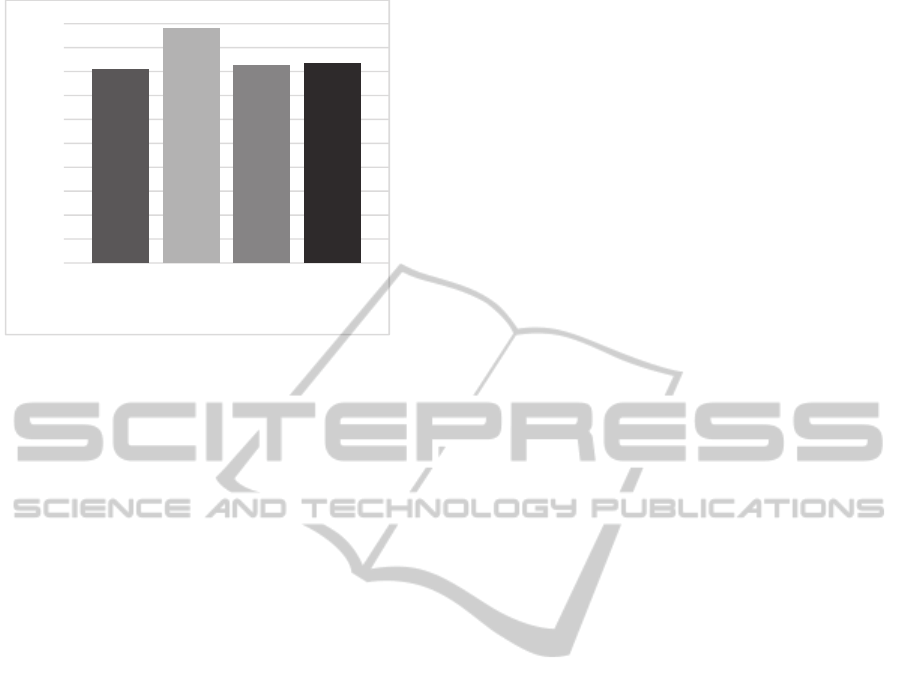
Figure 1: Accuracy in 10-fold cross-validation on each of
four corpora.
As can be seen, results in each case exceed 90%.
5.2 Distinguishing Features
Consideration of the main distinguishing features for
each experiment (as measured by Student’s t-test)
yields insight into why successful classification is
possible for each corpus. In general, we find that
across all experiments, texts associated with the left
are characterized by more frequent use of terms
related to social protest, as well as female pronouns
and third-person pronouns. On the other hand, texts
associated with the right are characterized by more
frequent use of terms reflecting positive attitudes,
references to religion and use of first-person
pronouns.
We now consider a more detailed comparison of
the key features per corpus. (All mentions of
“significant” differences are at p>.05.)
Parliamentary Speeches. Speeches by members of
right-wing parties are characterized by frequent
references to names of other parliament members
and frequent mention of various stages in the
legislation process (proposals, voting). This likely
reflects that the governing coalition at the time
consisted primarily of right-wing parties. In
addition, speeches by members of left-wing parties
include significantly more mentions of particular
political terms (freedom, rights, struggle, social,
welfare), as well as significantly more use of female
pronouns. On the other hand, members of right-wing
parties make significantly more frequent use of
terms reflecting positive attitudes (happy, good,
blessed) and religion (Jewish, sabbath, God).
News Websites. Since there are only three left-wing
news sites and a single right-wing news site,
differences are likely to include stylistic variations
not necessarily related to ideological differences.
Nevertheless, a considerable number of
ideologically loaded terms are prominent (e.g.,
Judea for the right, territories for the left).
Similarly, references to religious concepts are
significantly more frequent in right-wing news
stories, while certain politically loaded terms (social,
justice, rights, protest, Gaza) are significantly more
frequent in left-wing news stories. Interestingly,
right-wing news sites make significantly more
frequent use of first-person pronouns, while left-
wing news sites make significantly more frequent
use of third-person pronouns.
Party Facebook Pages. Right-wing party posts
make significantly more frequent mention of
religious concepts (rabbi, torah, God, sabbath),
while left-wing party posts make significantly more
frequent mention of particular politically-loaded
terms (freedom, rights, justice, territories, refugees,
poverty) and female pronouns.
Personal Facebook Pages. All the differences
found in the first three corpora are found even more
strongly in the personal pages. Self-identified right-
wingers use significantly more terms reflecting
positive attitudes (love, success, happy, good,
thanks, blessed) and religious terms, while self-
identified left-wingers use all the politically-loaded
terms associated with the left in the other corpora
(with the exception of the word freedom, which is
used more by right-wingers in this corpus). Left-
wingers also make many more references to
university life (education, university, college, test),
possibly reflecting demographic differences. In
addition, the right-wingers use more first-person
pronouns, while the left-wingers use more third-
person pronouns.
5.3 Learning across Corpora:
Facebook Pages
It is not always the case that individual Facebook
pages tagged for political orientation will be
available for training. However, public resources
self-identified with particular political orientations
are plentiful. Such, for example, are our
parliamentary speeches and political party pages.
Thus, we wish to examine whether these political
resources can be used to learn classifiers which can
in turn be used to classify individual Facebook
pages.
As above our feature set consists of all word
unigrams and bigrams that appear in the training
corpus at least 3 times. In this case, we filter the
50%
55%
60%
65%
70%
75%
80%
85%
90%
95%
100%
Parliament
speeches
Party
pages
News
stories
Facebook
pages
AutomaticPoliticalProfilinginHeterogeneousCorpora
479

feature set by considering a feature only if its
difference in frequency across classes (in the
training set) is significant at p=.05.
In Figure 2, we show accuracy results on
individual Facebook pages where the training set
consists of speeches only, party pages only and the
two together.
Figure 2: Accuracy results for training on indicated
corpora and testing on individual Facebook pages.
As can be seen, using only the Facebook party
pages as the training set obtained the highest
accuracy results for the individual Facebook pages.
Indeed, the combination of parliamentary Speeches
with the Party Facebook pages reduced the accuracy
by 6%.
This result can be explained by the relatively
high resemblance between the most characteristic
features in both the private and party Facebook
pages. In both corpora, the right is characterized by
references to religion and patriotism, as well as first-
person pronouns, while the left is characterized by
references to protests and third-person pronouns.
Parliamentary speeches prove to be less useful as
indicators of political sentiment because differences
in that corpus between left and right are actually
more indicative of differing political interests
between coalition members and opposition
members. These differences are not reflected in
individual Facebook pages.
The significance of this result is that it suggests
that using only inherently tagged data like party
pages can be used to classify non-political pages.
This spares us the need to gather personal pages
already labeled for political orientation as training
examples.
We note that when this learned classifier is
applied to individuals who self-identify as centrist,
70% are classified as right-wing. This might yield
some insight into the nature of political self-
identification.
5.4 Learning across Corpora: News
Sites
We now use the model trained on combination of
party pages and parliamentary speeches to classify
individual newspaper stories as right-wing or left-
wing. We wish to compare readers’ perception of the
orientation of a newspaper with the percentage of
stories identified as right-wing or left-wing by our
classifier. In Figure 3, we show a scatter plot
indicating for each of our five news sources its
orientation from left to right according to our
readers’ survey (x-axis) and the percentage of stories
classified as right-wing (y-axis).
Figure 3: Degree of right-wing orientation of news sites
according to survey (x-axis) and % articles classed as
right-wing (y-axis).
There is a clear, though non-linear, correlation
between reader perception and the classification of
individual articles by our learned classifier.
6 CONCLUSIONS
Profiling according to political orientation has
become an important element of targeted political
campaigns. Previous studies have focused on
specific genres and have shown that learning
classifiers can be useful for them. We have shown
that the same text categorization methods can be
used effectively in each of the four different genres
of varying degrees of political expressiveness.
Specifically, the findings demonstrate that in each
case, training and testing in the same genre yields
strong results.
More significantly, we show that so-called
"neutral" private Facebook pages may be classified
82,33%
65,00%
76,33%
50%
55%
60%
65%
70%
75%
80%
85%
90%
95%
100%
0%
10%
20%
30%
40%
50%
60%
0% 20% 40% 60% 80%
Party
pages
Knesset
Speeches
Speeches
+
Party pages
ICAART2015-InternationalConferenceonAgentsandArtificialIntelligence
480

into political orientation with a very high accuracy.
In particular, we show that using only the Facebook
party pages, which is publicly available, as the
training set, obtained the highest accuracy
classification results for the individual Facebook
pages. This result can be explained by the relatively
high resemblance between the most characteristic
features in both the private and party Facebook
pages. In both corpora, the right wing is
characterized by references to religion and
patriotism, as well as first-person pronouns, while
the left wing is characterized by references to
protests and third-person pronouns. The significance
of this result is that it suggests that using only
inherently tagged data like party pages can be used
to classify non-political pages. This saves the need
to gather personal pages already labeled for political
orientation as training examples.
Newspapers are commonly assumed neutral and
objective; however, seemingly the general
population perceives and associates each newspaper
with a certain political orientation. In this research,
we were able to confirm the general consensus
regarding the newspapers' political orientation by
applying the classifier we built using the corpora of
party pages and parliamentary speeches.
REFERENCES
Argamon, S., M. Koppel, J. Fine, and A. R. Shimoni,
2003, 'Gender, genre, and writing style in formal
written texts', Text, vol. 23, pp. 321-346.
Argamon, S., M. Koppel, J. W. Pennebaker & J. Schler,
2009, 'Automatically profiling the author of an
anonymous text', Communications of the ACM, vol.
52, no. 2, pp. 119-123.
Burger, J. D., J. Henderson, G. Kim & G. Zarrella, 2011,
'Discriminating gender on Twitter', Proc. of EMNLP-
11, pp. 1301-1309.
Bachrach, Y., Michal Kosinski, T. Graepel, Pushmeet
Kohli, & D. Stillwell, 2012, 'Personality and patterns
of Facebook usage'. Proceedings of the 3rd annual
ACM web science conference, June, 2012, Evanston,
US, pp. 24-32. ACM.
Efron, A., 2004: 'Cultural orientation: Classifying
subjective documents by co-citation [sic] analysis',
Proceedings of the AAAI Fall Symposium on Style and
Meaning in Language, Art, Music, and Design, pp. 41-
48.
Filippova, K., 2012: 'User Demographics and Language in
an Implicit Social Network', Proceedings of the 2012
Joint Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural
Language Processing and Computational Natural
Language Learning, pp. 1478-1488.
Genkin, A, D. D. Lewis, & D. Madigan, 2007, 'Large-
scale Bayesian logistic regression for text
categorization'. Technimetrics, vol. 49 no. 3, pp. 291-
304.
Gosling, S. D., A. A. Augustine, S. Vazire, N. Holtzman,
& S. Gaddis, 2011, 'Manifestations of Personality in
Online Social Networks: Self-Reported Facebook-
Related Behaviors and Ob-servable Profile
Information'. Cyber psychology, Behavior, and Social
Networking, vol. 14 no. 9, pp. 483-488.
Grefenstette, G, Y Qu, J G Shanahan, & D A Evans 2004,
'Coupling niche browsers and affect analysis for an
opinion mining application'. Proceedings of RIAO, pp.
186-194.
Hassanali K. N. & V Hatzivassiloglou, 2010, 'Automatic
Detection of Tags for Political Blogs'. Proceedings of
the NAACL HLT 2010 Workshop on Computational
Linguistics in a World of Social Media, pp. 21-22.
Koppel, M., J. Schler, & K. Zigdon, 2005, 'Deter-mining
an Author's Native Language by Mining a Text for
Errors', Proceedings of KDD, Chicago IL, pp. 624-
628.
Kosinski, M., D. Stillwell, & T. Graepel, 2013, 'Private
traits and attributes are predictable from digital records
of human behavior'. Proceedings of the National
Academy of Science of the United States of America
(PNAS), pp. 5802-5805.
Laver, M., K. Benoit & J. Garry, 2003, 'Extracting policy
positions from political texts using words as data'.
American Political Science Review, vol. 97 no. 2, pp.
311-331.
Mullen T., & R. Malouf, 2006, 'A preliminary
investigation into sentiment analysis of informal
political discourse'. Proceedings of the AAAI
Symposium on Computational Approaches to
Analyzing Weblogs, pp. 159-162.
Otterbacher, J., 2010, 'Inferring gender of movie
reviewers: Exploiting writing style, content and
metadata'. Proceedings of CIKM-10.
Popescu, A. & G. Grafenstette, 2010, 'Mining user home
location and gender from Flickr tags', Proceedings of
ICWSM-10, 369-378.
Pennebaker, J., W. Mehl & K. Niedehoffer, 2003, 'Effects
of age and gender on blogging'. Annual Review of
Psychology 2003, pp. 547-577.
Rao, D., D. Yarowsky, A. Shreevats, & M. Gupta, 2010,
'Classifying Latent User Attributes in Twitter'.
Proceedings of the 2nd international workshop on
Search and mining user-generated contents SMUC
'10, pp. 37-44.
Rosenthal, S., & K. McKeown, 2011, 'Age prediction in
blogs: A study of style, content, and online behavior in
pre- and post-social media generations'. Proceedings
of the 49th Annual Meeting of the Association for
Computational Linguistics: Human Language
Technologies, 1, pp. 763-772. ACM.
Schler, J., M. Koppel, S. Argamon & J. W. Pennebaker,
2006, 'Effects of age and gender on blogging'. AAAI
2006 Spring Symposium on Computational
Approaches to Analyzing Weblogs, Stanford, CA, pp.
199-206.
AutomaticPoliticalProfilinginHeterogeneousCorpora
481
