
HIDE: Hybrid Symmetric Key Algorithm for Integrity Check, Dynamic
Key Generation and Encryption
Jayagopal Narayanaswamy, Raghav V. Sampangi and Srinivas Sampalli
Faculty of Computer Science, Dalhousie University, Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada
Keywords:
Dynamic Key Generation, Chained Key Generation, Encryption, Integrity Check.
Abstract:
This paper proposes a hybrid encryption technique that generates a key dynamically, along with integrity check
parameters. Our approach generates the key stream using a chained approach, beginning with an initial pre-
shared key. Subsequent keys are derived using logical operations on intermediate cipher texts and intermediate
keys generated in each stage. This is an improvement over chaining techniques, which use a cipher text to
derive successive keys. We validate our algorithm by proof-of-concept implementation and security analysis.
1 INTRODUCTION
Block ciphers split a message into blocks of identical
sizes, which are encrypted with key blocks. A key for
a block cipher remains the same or is derived from an
initial key using functions such as the Feistel function
(Knudsen, 1994). In contrast, stream ciphers encrypt
a stream of bits from a message with a key bit-by-bit
using the logical exclusive-OR (XOR) operation. The
key stream is generated by a PRNG through a fixed
size input called the seed.
In stream ciphers, the encryption operation is sim-
ple but vulnerable to attacks such as distinguishing
and key recovery attacks (Hell et al., 2009). Stream
ciphers generate a continuous stream of key bits us-
ing a Linear Feedback Shift Register (LFSR) that re-
quire an n-bit seed value. A drawback with a LFSR is
that an n-bit pattern may repeat in the key stream be-
fore completing all 2
n
possible patterns (Zeng et al.,
1991). To avoid this issue a Non-Linear Feedback
Shift Register (NLFSR) has been proposed, but there
are no generic designs for a NLFSR (Dubrova et al.,
2008) (Bardis et al., 2004). In addition, in both block
and stream ciphers, the key is derived from an ini-
tial key or a seed, therefore, knowledge of the initial
key reveals information about the original message.
To overcome this issue, we use multiple keys that are
generated dynamically.
Recently, an algorithm called Hummingbird was
proposed as a hybrid of the stream and block ci-
pher approaches that was designed for resource-
constrained devices, such as, Radio Frequency Iden-
tification (RFID) systems (Engels et al., 2010). Hum-
mingbird follows the traditional encryption process of
block ciphers such as substitution and looping; while
a key is derived through the stream cipher principle.
The key generation and encryption process in Hum-
mingbird is computationally expensive. However, we
compare our algorithm with Hummingbird as an ex-
ample. We don’t inherit any property of the Humming
algorithm in our approach.
After the encryption process, any encrypted mes-
sage is hashed to offer integrity. Hashing is a one-way
mathematical function, which converts the variably
sized messages into a fixed size output called a Mes-
sage Digest (MD). The receiver verifies the integrity
of received message by hashing it and then compares
it with the received MD.
In this paper, we propose a hybrid encryption al-
gorithm that requires a simple (Exclusive-OR) XOR
operation. We use the stream cipher approach to de-
rive a key, while the block cipher approach is adopted
in the encryption process. In our approach, a key
stream is generated from a previous key block and
an intermediate cipher text block, which is encrypted
with a message block-by-block using the XOR op-
eration. In addition to encryption, a fixed-size fi-
nal key in each round is used as the MD that pro-
vides the integrity to the message. Since we use only
the XOR operation throughout the encryption process
and provide the integrity check parameter without us-
ing any external hashing algorithm, we expect that
our approach will reduce the computational complex-
ity as well as increase performance. We have imple-
mented the algorithm and we show that our algorithm
can withstand such potential attacks as differential,
124
Narayanaswamy J., V. Sampangi R. and Sampalli S..
HIDE: Hybrid Symmetric Key Algorithm for Integrity Check, Dynamic Key Generation and Encryption.
DOI: 10.5220/0005273901240131
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy (ICISSP-2015), pages 124-131
ISBN: 978-989-758-081-9
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

known cipher text, known plain text, distinguishing
and key recovery attacks. We also conducted stan-
dard security analysis tests (such as, entropy analysis,
periodicity check, frequency test, poker test, run test,
serial test etc.) and have included the results in the
security analysis section.
2 BACKGROUND AND
LITERATURE REVIEW
In stream ciphers, an LFSR plays an important role
in the generation of a key stream. One possible im-
plementation of a Pseudo Random Number Genera-
tor (PRNG) is using an LFSR. An LFSR can be con-
structed by the consecutive assembly of shift regis-
ters. An n-bit LFSR produces a continuous bit stream
from an n-bit seed. One of the drawbacks of an LFSR
is that it will form a cycle on or before reaching 2
n
patterns for a given n-bit seed (i.e. the same sequence
of bits will be generated on or before reaching 2
n
pat-
terns) (Zeng et al., 1991).
To overcome this drawback, an NLFSR was in-
troduced (Dubrova et al., 2008) (Bardis et al., 2004).
NLFSRs avoid the linearity problem and extend the
cyclic period. A common way of constructing an
NLFSR is to use more than one LFSR connected
through logic gates. Logic gates are used to choose
the current LFSR output from a list of connected LF-
SRs. Thus, linearity can be broken easily and the
cyclic period will be extended. Even though NLFSR
acts as an alternative to LFSR, there is no NLFSR
that guarantees a long cyclic period. Furthermore,
a general technique for constructing NLFSRs has
been an open problem (Lv et al., 2012) (Rachwalik
et al., 2012) (Hu and Gong, 2011) (Mandal and Gong,
2012).
Block ciphers offer better security over stream ci-
phers, however the latter are computationally more
efficient. Hybrid approaches that combine the ben-
efits of both have been the focus of recent research.
Trivium (De Canni
`
ere, 2006) is the stream cipher that
uses the block cipher principle for the key genera-
tion process. The Hummingbird algorithm encrypts
the message block-by-block and uses internal regis-
ters to update the key stream. It has a small block size
of 64-bits, which is further divided into four smaller
blocks of 16-bits each that are equivalent to the num-
ber of bits in the internal state register. Initially, the
internal state register is loaded with random bits. Fur-
thermore, the LFSR and the cipher text are used to re-
generate the internal state register bits. It uses a 256-
bit key that is split into four 64-bit keys to encrypt
the message. Two more secret keys, namely, K5 and
K6, are introduced and these are derived from the ini-
tial four keys. The Hummingbird algorithm has four
rounds of substitution and permutation and uses four
keys on each round to encrypt the message. In the
fifth round, the output is encrypted with key K5 fol-
lowed by a final substitution and then encryption with
key K6. This approach is more suitable for resource-
constrained devices such as RFID systems. It is re-
sistant to differential as well as linear attacks (Engels
et al., 2010). However, we use this algorithm as an
example of a hybrid approach and our algorithm does
not inherit any properties used in Hummingbird.
Kutuboddin and Krupa (Jinabade and Rasane,
2013) have extended the research on the Humming-
bird algorithm to increase its computational effi-
ciency. They propose an approach, which replaces the
traditional Hummingbird modulo operation by intro-
ducing Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA). As
the proposed approach uses XOR operation, compu-
tational efficiency is better compared to the original
version.
Integrity is an important component of network
security that prevents an anonymous entity from data
manipulation. The Integrity of the message can be
achieved through hashing algorithms, such as, MD5,
SHA1, SHA2, SHA3, etc. Traditional hashing is a
mathematical one-way function, which encrypts the
message but decryption is not possible. It converts
any variable size message to a fixed size output called
the Message Digest (MD). A collision between two
MD is possible after hashing 2
n
messages. How-
ever, as the encryption (or decryption) and hashing
are disjoint operations, the use of hashing will lead to
computational overhead on the system (Kumar et al.,
2011) (Hu and Wang, 2009) (Li et al., 2012).
In recent years, a hybrid approach called Authen-
ticated Encryption (AE) has provided integrity as well
as authenticity for short messages (Jeddi et al., 2013).
However, it requires a Message Authentication Code
(MAC), which is derived from the hashing technique.
This creates further computational overhead. For ex-
ample, Signcryption was proposed for the asymmet-
ric key algorithm (Zheng, 1997)(Wang et al., 2013),
which replaced a traditional encrypt and sign practice
by integrating message signatures (similar to MD) as
a part of an encryption process. Zheng et al.’s (Zheng,
1997) work on the signcryption scheme is based on
the theory that a combined computational cost of a
signature (using hashing) and encryption will be less
than their individual costs. In signcryption, part of
the key is generated using a hashing algorithm to pro-
vide the integrity, and the same key is used to en-
crypt (using an asymmetric key algorithm) the mes-
sage to offer confidentiality, integrity and authentica-
HIDE:HybridSymmetricKeyAlgorithmforIntegrityCheck,DynamicKeyGenerationandEncryption
125

tion (Zheng, 1997).
Our literature review concludes that existing algo-
rithms are weak in generating a key or the encryp-
tion process leads to computational overhead. To fill
a gap between computational overhead and to support
a strong dynamic key generation process to encrypt
the message, we propose a new approach that uses
a simple XOR operation for better computation, and
Intermediate Cipher Text (ICT) to generate the key
dynamically.
3 PROPOSED APPROACH
3.1 Overview
Table 1 contains a list of notations that are used in the
proposed approach.
In block ciphers, common modes of encryption
such as Cipher Block Chaining (CBC), Propagating
Cipher Block Chaining (PCBC) and Cipher Feedback
(CFB) use the cipher text as part of the encryption.
This may lead to some information about the original
message being revealed to an attacker. To avoid this
issue, our approach uses an Intermediate Cipher Text
(ICT) to generate a dynamic key. Since the dynamic
key is used on each block of the message encryption,
the cipher text bits are completely random.
Table 1: Notations.
K
a
Keys to encrypt in Round One
K
b
Keys to encrypt in Round Two
n Last block
l Current block
i
x
Prediction bit
M Message to be encrypted
m
1
, m
2
...m
l
Message blocks
XOR Logical bit-by-bit XOR operation
δ() Derivation function
ρ() Prediction function
γ() Inversion function
M
x
Message block x
K
ax
Round One key block x
K
bx
Round Two key block x
ICT
x
Intermediate Cipher Text block x
CT
x
Cipher Text block x
C
α,β
Chunk β of component α (α can be
M
x
, ICT
x
, K
ax
, K
bx
, CT
x
)
KG1 Key generation for Round One
KG2 Key generation for Round Two
Figure 1: Overview of the encryption process.
A hybrid encryption algorithm is proposed, which
includes both stream cipher and block cipher features.
This approach consist of two parts: a key generation
part (based on stream ciphers) and two rounds of en-
cryption (or decryption) using a basic XOR opera-
tion (employing message blocks as in block ciphers).
The message is encrypted block-by-block with differ-
ent (block) keys on each message block. The size of
one block in the message is 128-bits in sixteen 8-bit
chunks.
Figure 1 illustrates the overall encryption process.
This approach requires two initial keys that encrypt
the first block in each round. Except for the initial key,
every successive key (to encrypt each block) is de-
rived from the bits in the current key block and an ICT
block. In general, blocks of message are encrypted
using blocks of keys generated using the stream ci-
pher scheme. Key generation and encryption follows
a chained approach, with the current (block) keys and
ICTs used to generate (block) keys for the encryption
of the subsequent message blocks. The encryption
and key generation processes are described later in
this section.
3.2 Assumptions
It is assume that the initial key used to encrypt the first
block of the message in each round is generated by the
sender and securely transmitted to the receiver. The
key used to encrypt the message is randomly chosen
from a set of strong keys.
3.3 Design
3.3.1 Key Generation
Since it is assumed that the key is known only to the
sender and the receiver, we generate successive keys
from the previous keys with the help of an intermedi-
ate cipher text (ICT). The term “intermediate cipher
text” represents an encrypted message after Round
1, whereas the actual cipher text is generated after
Round 2 (as will be discussed in detail in the encryp-
ICISSP2015-1stInternationalConferenceonInformationSystemsSecurityandPrivacy
126
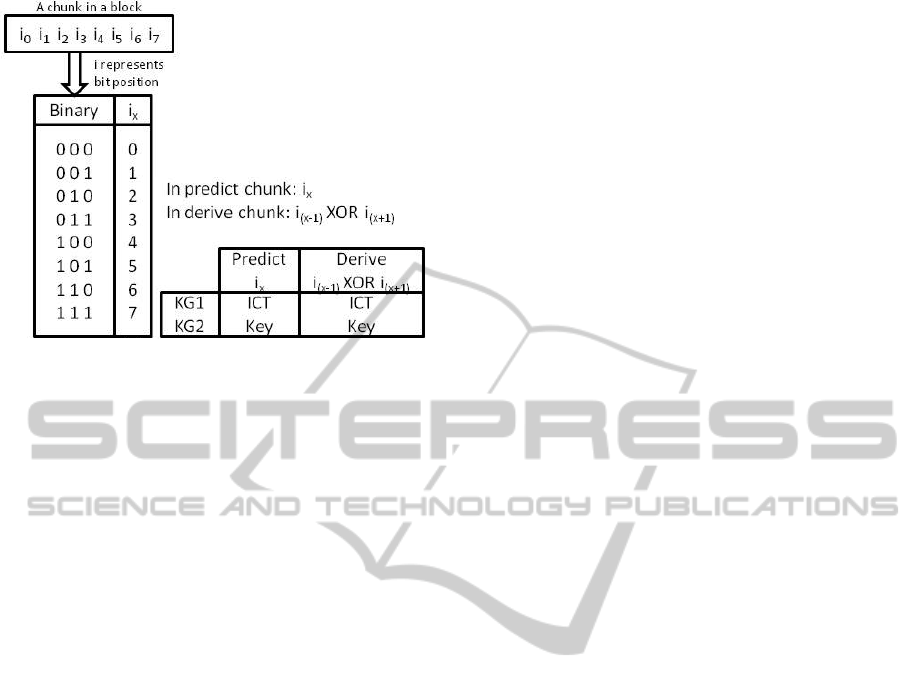
Figure 2: Key Generation Process Overview.
tion section). The key generation process in this ap-
proach is different for both rounds. Each round uses a
different initial key (K
a0
& K
b0
) to encrypt the first
block in the message. To encrypt each successive
block in the message, we introduce a combination of
prediction and derivation techniques to generate suc-
cessive keys (K
a1...n
for Round 1 and K
b1...n
for Round
2) from a previous key block and an ICT block.
In prediction, three bits in every chunk per block
are used to choose the i
th
x
bit within the respective
chunk. The value of i
x
is based on the three binary
bits chosen in the chunk. The value of i
x
is a decimal
representation of the 3-bit binary. In a chunk, 3-bits
are selected in a clockwise direction starting from the
most significant bit (MSB) in the chunk to the least
significant bit (LSB) to choose one out of eight pos-
sible values for i
x
, which is repeated 8 times starting
from the MSB to the LSB. The value of i represents
the position of the binary bit in the chunk. Each value
of i
x
predicts a new bit that is used to generate chunks
per block in every successive key. As shown in Fig-
ure 2, three bits are rotated in a clockwise direction to
yield one out of eight possible values for i
x
.
In derivation, the successive key is generated by
XORing the (i
x
− 1)
th
position of the binary bit with
the (i
x
+ 1)
th
position of the binary bit to form a new
bit. The same process is repeated in every chunk per
block to generate a whole key for encrypting the suc-
cessive block in the message. The whole process of
key generation offers a randomness in the key stream
without forming a cycle.
The process for applying prediction and
derivation in combination to generate a key is as
follows. In Round 1, the key is derived from key
K
a
series based on the ICT block’s prediction. In
contrast, Round 2’s successive keys are derived from
the ICT block based on the key block’s prediction.
To generate a key, the prediction and derivation
combination is applied alternatively on an ICT block
and a key block over two rounds.
3.3.2 Encryption (or Decryption)
Initially, in Round 1, four out of eight bits (say
0, 2, 3, 5) in every chunk in a key K
a0
are inverted.
The first chunk in the initial key K
a0
is XORed with
the first chunk in the first block of the message, which
produces the first chunk in ICT
0
(which represents the
ICT first block). Again, four out of eight bits (say
2, 4, 5, 7) in every chunk in ICT
0
are inverted (this pro-
cess is common throughout the ICT blocks), which is
followed by successive key generation operations (al-
ready discussed in detail earlier). The output of the
key generation operation will be the first chunk in the
key K
a1
to encrypt the first chunk of the next mes-
sage block. The first chunk of key K
a1
is XORed with
the second chunk of key K
a0
that will be used to en-
crypt the second chunk in the first block of the mes-
sage. In conclusion, every first chunk in each block
of the message is directly XORed with the first chunk
of the respective key, whereas the successive chunks
in each block in the message are encrypted with the
XORed output of the successive chunk in the present
key and the currently derived chunk for the next key.
For example, the 4
th
chunk in message C
M
2
,4
will be
encrypted with the XORed output of the 4
th
chunk in
the current key C
K
a2
,4
and the 3
rd
chunk in the next
key C
K
a3
,3
.
Round 2 follows the same procedure as Round 1,
except that the message and initial key K
a0
will be re-
placed by the ICT and key K
b0
respectively. In addi-
tion, the inversion operation is applied on bits 1, 4, 6, 7
and 0, 1, 3, 6 for the key and the ICT respectively. The
output of Round 2 is the final cipher text. Every block
in a message is XORed with the key block to gener-
ate a cipher text. Figure 3 illustrates the encryption
process.
A decryption process is symmetric with encryp-
tion in reverse manner.
3.3.3 Integrity Check
The final keys (say K
a(n+1)
and K
b(n+1)
) in each round
of encryption will act as the integrity check param-
eter. In this approach, the 128-bit key K
a(n+1)
will
be concatenated with the 128-bit key K
b(n+1)
to form
a 256-bit message digest, which is used for integrity
check.
HIDE:HybridSymmetricKeyAlgorithmforIntegrityCheck,DynamicKeyGenerationandEncryption
127
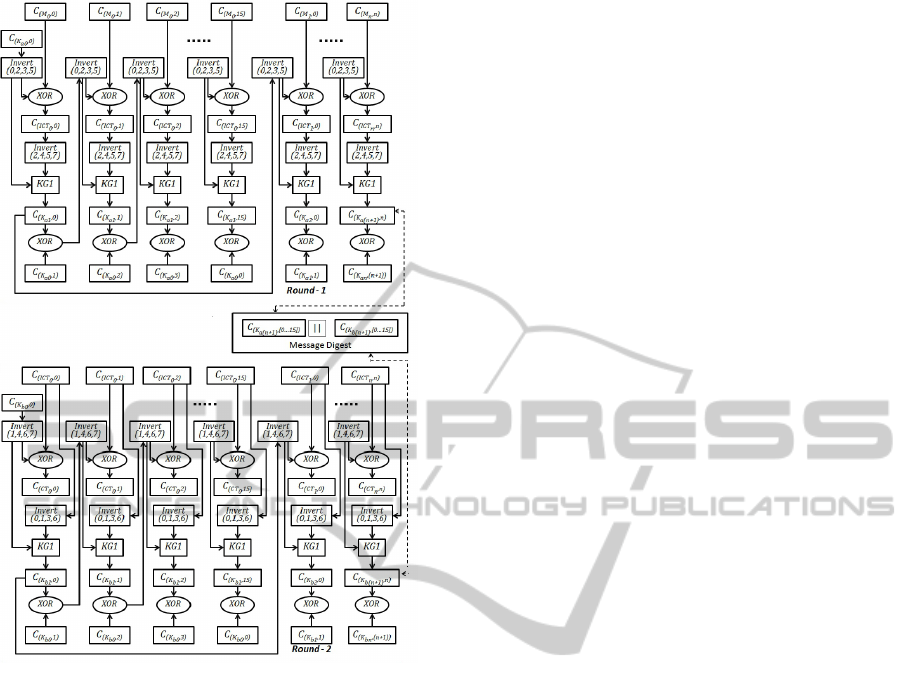
Figure 3: Encryption Process.
3.4 Example
3.4.1 Encryption and Key Generation
In this section the two rounds of the encryption pro-
cess will be explained with a generic example. Each
round used different initial key (K
a0
and K
b0
). Further,
the message (M) is segmented into different blocks.
The first block of the plain text message is encrypted
with a key combination of K
a0
(the present key) and
K
a1
(the currently derived key) at Round 1 that gener-
ates the first ICT block.
Let the message blocks be:
M = M
0
, M
1
, M
2
, M
3
, ..., M
n
(1)
Round − 1 : Encrypting the first block of the mes-
sage: The message block will be encrypted chunk
by chunk. Before the XOR operation, bit positions
0, 2, 3, 5 will be inverted in the first chunk of an initial
key. Then, the first chunk in the first block of the mes-
sage will be XORed with the initial key’s first chunk
(which is after the inversion).
C
0
K
a0
,0
= γ(C
K
a0
,0
) (2)
C
ICT
0
,0
= E
C
0
K
a0
,0
(C
M
0
,0
) (3)
Once again, bits 2, 4, 5 and 7 in the ICT will be in-
verted before the key generation process and the out-
put will be used to generate a key to encrypt the next
chunk as well as the block.
C
0
ICT
0
,0
= γ(C
ICT
0
,0
) (4)
Each bit of the key, C
K
a1
,0
, is generated from the
previous key, C
0
K
a0
,0
, whereas, n bits in C
0
ICT
0
,0
chooses
a bit in C
0
K
a0
,0
to produce the new key, C
K
a1
,0
. In
general, a current key, K
al
, is generated from the
prediction of a previous ICT block, ICT
l−1
, and the
derivation of the previous key, K
a(l−1)
, in Round 1.
Every first chunk in the message block is directly
XORed with the inversion of the first chunk in the key,
whereas the 2
nd
to 15
th
chunk in the message will be
encrypted with an inversion of the XORed value of
the next chunk key with next block’s chunk’s key.
Key Generation: for initial chunks only
C
K
al
,0
= ρ(C
0
ICT
l−1
,0
[δ(C
0
K
a(l−1)
,0
)]) (5)
For the 2
nd
to 15
th
chunks
C
K
al
,1
= [C
K
al
,1
]XOR[C
K
a(l+1)l
,0
] (6)
...
C
K
al
,15
= [C
K
al
,15
]XOR[C
K
a(l+1)l
,14
] (7)
The generic equation for encryption in Round 1 is as
follows:
ICT
0
= E
K
a0
(M
0
), ICT
1
= E
K
a1
(M
1
), ..., ICT
n
= E
K
an
(M
n
)
(8)
Figure 4 is an example diagram for the encryp-
tion and integrity check processes. For this exam-
ple, it is assume that the message contains only two
blocks and that each one has only two chunks (the
typical block size used in this example is 16-bits,
which is composed of two 8-bit chunks). The initial
key, K
a0
(10011010 11011011), is encrypted with the
message (00101101 00110011 10111011 01000011)
which produces, in Round 1, the ICT (00000011
11010010 10000001 01001111). Then, in Round 1,
the ICT block is used to predict a derivation bit in a
key block, whereas in Round 2 a key block predicts
the derivation bit in the ICT block. Further, in Round
2, the cipher text (11110011 01000111 00111000
10111101) will be obtained by encrypting the ICT
with the key block K
b0
(10111011 00101100). Fi-
nally, the concatenation of the last derived keys, K
a2
and K
b2
, will act as the message digest (01000111
11100010 10111001 11001111).
Round − 2 : In this Round, the encryption process
is the same as in Round 1. But in the key generation
ICISSP2015-1stInternationalConferenceonInformationSystemsSecurityandPrivacy
128

Figure 4: An example of the Encryption and Integrity Check
Process.
process, the prediction and derivation functions are
interchanged between an ICT block and a key. An ini-
tial key (K
b0
) encrypts the first block of the ICT block.
To encrypt subsequent blocks, a current key (K
bl
) is
generated from the prediction of a previous Key block
(K
b(l−1)
) and the derivation of a previous ICT block
(ICT
l−1
). In Round 2, the bits chosen to invert are dif-
ferent form Round 1. For a key bits 1, 4, 6 and 7 are
inverted before encryption, whereas bits 0, 1, 3 and 6
are inverted for the ICT chunks (after the encryption,
but before the key generation process).
Encrypting first block of the message:
C
0
K
b0
,0
= γ(C
K
b0
,0
) (9)
C
CT
0
,0
= E
C
0
K
b0
,0
(C
ICT
0
,0
) (10)
C
0
ICT
0
,0
= γ(C
ICT
0
,0
) (11)
Key Generation: for initial chunks only
C
K
bl
,0
= ρ(C
0
K
b(l−1)
,0
[δ(C
0
ICT
l−1
,0
)]) (12)
For the 2
nd
to 15
th
chunks
C
K
bl
,1
= [C
K
bl
,1
]XOR[C
K
b(l+1)l
,0
] (13)
...
C
K
bl
,15
= [C
K
bl
,15
]XOR[C
K
b(l+1)l
,14
] (14)
The generic equation for encryption in Round 2 is as
follows:
CT
0
= E
K
b0
(ICT
0
), CT
1
= E
K
b1
(ICT
1
), ..., CT
n
= E
K
bn
(ICT
n
)
(15)
3.4.2 Message Digest
The final keys generated from each round will be con-
catenated to yield the 256-bit Message Digest.
MD = K
a(n+1)
||K
b(n+1)
(16)
4 ANALYSIS AND DISCUSSION
This proposal has successive key derivation function,
which uses both a key as well as a message to choose
the next key dynamically. Every message block is en-
crypted with a different key chosen from the 2
128
pos-
sible combination keys for a given 128-bits in the key
space. As successive keys are generated based on a
message and a key in any one process of either pre-
diction or derivation, the generated key is completely
dynamic. Thus, it guarantees that there would be no
regular cycle in a key bit stream. The algorithm is a
very simple, which uses XOR operations to generate
keys as well as encrypt a message. It can withstand
a variety of attacks (chosen-plain text attack, chosen-
cipher attack, differential attack, linear attack and dis-
tinguishing attack) (Hell et al., 2009) (Zulkifli, 2008)
(Northwood, online).
4.1 Cryptanalysis
A short description of possible attacks and their anal-
yses are explained in this section. Chosen-plain text
and chosen-cipher text attacks are targeted on sym-
metric key encryption schemes. Both attacks work
on the principle of choosing a piece of information
for retrieving an original message for a given cipher
text or to reach a cipher text for a given plain text.
In this approach, since the key is changed for every
block encrypted, chosen-plain text and chosen-cipher
text attacks are hard to launch. A differential attack
compares an input value with an output value to ob-
tain a possible key. Since this proposal relies on both
a key and an ICT, and the key is chosen from a strong
key, a differential attack is difficult to implement. In
HIDE:HybridSymmetricKeyAlgorithmforIntegrityCheck,DynamicKeyGenerationandEncryption
129
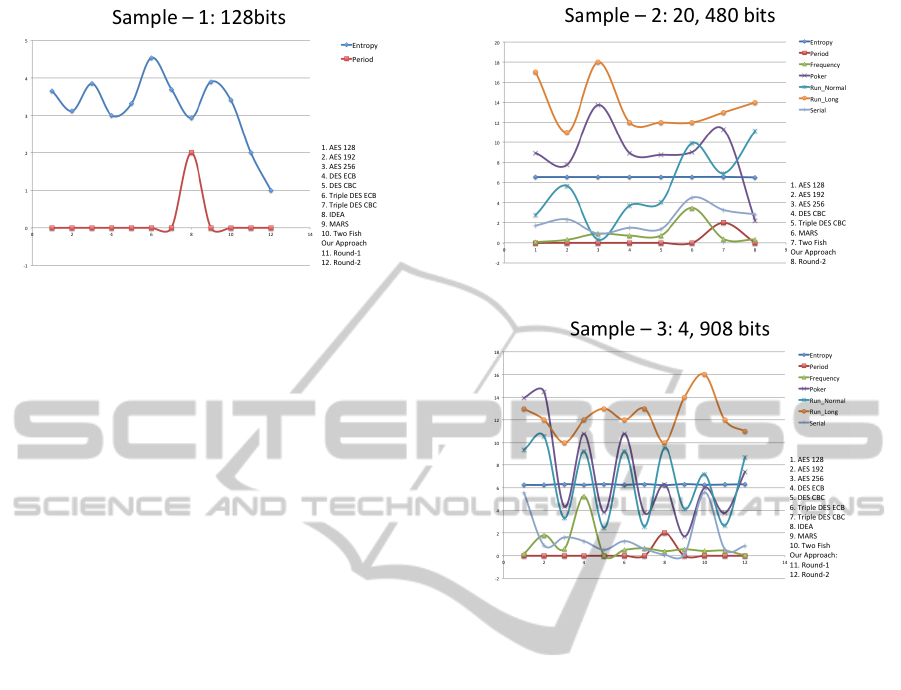
Figure 5: Sample 1.
linear cryptanalysis, an equation is formed from plain
text and cipher text, which is equated to possible key
bits to reveal some information about the message. To
avoid this issue, the key generation process i switched
between prediction and derivation techniques. A dis-
tinguishing attack focuses on stream ciphers that com-
pare a given sequence of values to check the random-
ness. A dynamically generated key ensures that there
will be no relation between the current and previous
keys, so launching a distinguishing attack is difficult.
4.2 Security
In addition to the attacks mentioned above, tests were
done using a cryptanalysis tool called Cryptool (url,
2014). As mentioned earlier, though the key genera-
tion part is in the nature of a stream cipher, the actual
encryption process adopts a block cipher approach.
The security analysis of the proposed approach was
compared with existing block cipher algorithms such
as AES, DES, IDEA, MARS, Twofish etc. (the imple-
mentation of which is available as a built in option in
Cryptool). Graphs are presented below with five dif-
ferent scenarios, which are based on the cryptanaly-
sis tests (entropy test, periodicity test, frequency test,
poker test, run test and serial test) (Wu et al., 2011)
(Biebighauser, 2000) (Soto, online). The results from
this analysis show that our algorithm passes the above
mentioned tests and that the security level is no lower
than the pool of example algorithms used. Figures 5,
6, 7 display the sample graphs that were taken from
the security analysis with different sample inputs.
The proposed algorithm provides non-linearity in
the key cycle, which is achieved by using an interme-
diate cipher text block. However, using cipher text
to encrypt a message is vulnerable, so two rounds of
encryption were designed with an ICT as the second
round key generator instead of the cipher text. Ap-
plying key generation from a key for the first round
and an ICT for the second round ensures a dynamic
property in successive keys.
Figure 6: Sample 2.
Figure 7: Sample 3.
4.3 Performance
The performance of our approach has yet to be
tested, but it is expected to be computationally effi-
cient, which is our contention based on the following
claims. Initially, the computation is required only for
the encryption part, but the integrity check does not
require any additional computation. As the key gen-
eration process is a bitwise operation, it is the only
difficulty in this approach. The number of operations
required per bit is only fourteen, which includes en-
cryption (or decryption), an integrity check and key
generation. We identified from our research that an
increase in performance would require an increase in
the hardware component, which may not be appropri-
ate depending on the requirements of the application.
However, we are currently working on the key gener-
ation part.
5 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORK
In this paper, a hybrid encryption algorithm is pro-
posed with increased security. In our approach,
blocks of message are encrypted using the blocks of
ICISSP2015-1stInternationalConferenceonInformationSystemsSecurityandPrivacy
130

keys generated by a stream cipher scheme. Key gen-
eration and encryption follows a chained approach in
which current (block) keys and ICTs are used to gen-
erate (block) keys for the encryption of subsequent
message blocks. This approach is feasible for en-
crypting a message using a hybrid stream cipher and
block cipher approach. The novelty of our approach
is its dynamic key generation from an intermediate ci-
pher text with an the integration of an integrity check.
We are currently extending our research to optimize
the computational efficiency of our approach.
REFERENCES
(2014). The cryptool portal @ONLINE. http://www. cryp-
tool.org/en.
Bardis, N., Markovskyy, A., and Andrikou, D. (2004).
Method for designing pseudorandom binary se-
quences generators on nonlinear feedback shift reg-
ister(nfsr). WSEAS Transactions on Communications,
3(2):758–763.
Biebighauser, D. (2000). Testing random num-
ber generators @ONLINE. http://www-users.
math.umn.edu/vgarrett/students/reu/pRNGs.pdf.
De Canni
`
ere, C. (2006). Trivium: A stream cipher con-
struction inspired by block cipher design principles.
In Information Security, pages 171–186. Springer.
Dubrova, E., Teslenko, M., and Tenhunen, H. (2008). On
analysis and synthesis of (n, k)-non-linear feedback
shift registers. In Design, Automation and Test in Eu-
rope, 2008. DATE’08, pages 1286–1291. IEEE.
Engels, D., Fan, X., Gong, G., Hu, H., and Smith, E. M.
(2010). Hummingbird: ultra-lightweight cryptog-
raphy for resource-constrained devices. In Finan-
cial Cryptography and Data Security, pages 3–18.
Springer.
Hell, M., Johansson, T., and Brynielsson, L. (2009). An
overview of distinguishing attacks on stream ciphers.
Cryptography and Communications, 1(1):71–94.
Hu, H. and Gong, G. (2011). Periods on two kinds of non-
linear feedback shift registers with time varying feed-
back functions. International Journal of Foundations
of Computer Science, 22(06):1317–1329.
Hu, M. and Wang, Y. (2009). The collision rate tests of two
known message digest algorithms. In Computational
Intelligence and Security, 2009. CIS’09. International
Conference on, volume 2, pages 319–323. IEEE.
Jeddi, Z., Amini, E., and Bayoumi, M. (2013). A novel au-
thenticated encryption algorithm for rfid systems. In
Digital System Design (DSD), 2013 Euromicro Con-
ference on, pages 658–661. IEEE.
Jinabade, K. and Rasane, K. (2013). Efficient implemen-
tation of hummingbird cryptographic algorithm on
a reconfigurable platform. In International Journal
of Engineering Research and Technology, volume 2.
ESRSA Publications.
Knudsen, L. R. (1994). Practically secure feistel ciphers. In
Fast Software Encryption, pages 211–221. Springer.
Kumar, Y., Munjal, R., and Sharma, H. (2011). Compari-
son of symmetric and asymmetric cryptography with
existing vulnerabilities and countermeasures. Interna-
tional Journal of Computer Science and Management
Studies, 11(03).
Li, X., Zhang, W., Wang, X., and Li, M. (2012). Novel con-
vertible authenticated encryption schemes without us-
ing hash functions. In Computer Science and Automa-
tion Engineering (CSAE), 2012 IEEE International
Conference on, volume 1, pages 504–508. IEEE.
Lv, H., Xie, J.-X., Fang, J.-C., and Qi, P. (2012). Generating
of a nonlinear pseudorandom sequence using linear
feedback shift register. In ICT Convergence (ICTC),
2012 International Conference on, pages 432–435.
IEEE.
Mandal, K. and Gong, G. (2012). Probabilistic generation
of good span n sequences from nonlinear feedback
shift registers. University of Waterloo.
Northwood, C. Cryptography, attacks and countermeasures
@ONLINE. http://www.pling.org.uk/cs/cry.html.
Rachwalik, T., Szmidt, J., Wicik, R., and Zablocki, J.
(2012). Generation of nonlinear feedback shift reg-
isters with special-purpose hardware. In Communi-
cations and Information Systems Conference (MCC),
2012 Military, pages 1–4. IEEE.
Soto, J. Statistical testing of random number gen-
erators @ONLINE. http://infosec.pku.edu.cn/
vtly/oldversion/nist-nissc-1999/papers/p24.pdf.
Wang, Y., Manulis, M., Au, M. H., and Susilo, W. (2013).
Relations among privacy notions for signcryption and
key invisible sign-then-encrypt. In Information Secu-
rity and Privacy, pages 187–202. Springer.
Wu, Y., Noonan, J. P., and Agaian, S. (2011). A novel infor-
mation entropy based randomness test for image en-
cryption. In Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC),
2011 IEEE International Conference on, pages 2676–
2680. IEEE.
Zeng, K., Yang, C.-H., Wei, D.-Y., and Rao, T. (1991).
Pseudorandom bit generators in stream-cipher cryp-
tography. Computer, 24(2):8–17.
Zheng, Y. (1997). Digital signcryption or how to
achieve cost (signature & encryption) łcost (signa-
ture) + cost(encryption). In Advances in Cryptology-
CRYPTO’97, pages 165–179. Springer.
Zulkifli, M. Z. W. M. (2008). Attack on crypto-
graphy @ONLINE. https://idazuwaika.files.word
press.com/2008/06/attack-on-cryptography.pdf.
HIDE:HybridSymmetricKeyAlgorithmforIntegrityCheck,DynamicKeyGenerationandEncryption
131
