
Learning Dynamic Systems from Time-series Data
An Application to Gene Regulatory Networks
Ivo J. P. M. Timoteo and Sean B. Holden
University of Cambridge, Computer Laboratory,
William Gates Building, 15 JJ Thomson Avenue, Cambridge CB3 0FD, U.K.
Keywords:
Graphical Models, Local Search, Bioinformatics Application.
Abstract:
We propose a local search approach for learning dynamic systems from time-series data, using networks of
differential equations as the underlying model. We evaluate the performance of our approach for two scenarios:
first, by comparing with an l
1
-regularization approach under the assumption of a uniformly weighted network
for identifying systems of masses and springs; and then on the task of learning gene regulatory networks,
where we compare it with the best performers in the DREAM4 challenge using the original dataset for that
challenge. Our method consistently improves on the performance of the other methods considered in both
scenarios.
1 INTRODUCTION
We address the following general inference problem.
We have a partially observable system consisting of
many components, some of which may interact with
one-another. Our aim is to infer which components
interact, and possibly the nature of the interaction.
Such systems will typically be partially observable in
the sense that, while measurements over time of one
or more properties of the system are available, these
time series do not directly expose the underlying in-
teractions.
In studying problems of this kind we have in mind
the specific application of inferring gene regulatory
networks (GRNs). The action of a gene within an or-
ganism is often regulated and coordinated by its in-
teraction with other genes, and considerable effort is
invested in trying to discover exactly how genes in-
teract. It is hoped that a better understanding of the
network of interactions might lead to improvedunder-
standing of the basic processes occurring in a cell, and
thus of how specific traits or diseases develop. In turn
this might lead to new techniques to treat disease or
control cell development. Inferring such relationships
from observed data is, however, difficult because the
network is large and contains redundant paths, and be-
cause data is generally noisy due to the nature of the
experimental techniques used.
Biological processes are dynamic and we are in-
terested in interactions between molecules occurring
over time and in highly complex networks of interde-
pendent nodes. This suggests that in order to under-
stand a GRN it will be necessary to consider obser-
vations at multiple time instances, allowing us to ob-
serve temporal patterns and thus to better understand
causality and predict future behaviour. As a result re-
searchers have increasingly collected time-series gene
expression data—according to (Barrett et al., 2011),
the number of time-series datasets has been growing
exponentially.
Given the dynamic and temporal nature of the typ-
ically available data, it is natural to model gene ex-
pression networks using stochastic differential equa-
tions as suggested by (Ackers et al., 1982), (Gard-
ner and Collins, 2000) and (Marbach et al., 2010);
see also (Ly and Lipson, 2012) and (Voortman et al.,
2010) for further, related methods. Further, it seems
reasonable to assume that a similar model could
be used to learn the structure of the network it-
self, although we might expect this to be a compu-
tationally expensive process given the use of such
expressive models—for example, the one used by
GeneNetWeaver(Schaffter et al., 2011) and explained
in (Marbach et al., 2010).
In this paper we propose a simple approach for
the general problem of learning the structure of sys-
tems of differential equations. We demonstrate its
effectiveness first by comparing it to an existing l
1
-
regularization method using data for a system of
masses and springs. We then apply it to the prob-
324
J. P. M. Timoteo I. and B. Holden S..
Learning Dynamic Systems from Time-series Data - An Application to Gene Regulatory Networks.
DOI: 10.5220/0005282303240332
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods (ICPRAM-2015), pages 324-332
ISBN: 978-989-758-077-2
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

lem of inferring GRNs. We address the DREAM4
Challenge data (Dream4Challenge, 2009) and com-
pare our method against the methods that performed
best in the challenge. These methods did not take time
series data into account, and we find that our method
can improve on their performance by using them to
obtain an initial solution which it then develops fur-
ther using time series data.
2 INTERACTING DYNAMIC
SYSTEMS
2.1 General Model
We have a system of p time-dependent variables
x
T
(t) =
x
1
(t) ··· x
p
(t)
, and describe the evo-
lution of each variable using differential equations re-
lating it to other variables in the system. The evolu-
tion of the ith variable x
i
(t) is described by the expres-
sion
dx
i
(t) = F
i
(x(t))dt. (1)
The functions F
i
are selected from a family F of func-
tions defined as follows. Begin with a set of m ba-
sis functions f = { f
1
(·), f
2
(·),..., f
m
(·)}; these will be
chosen according to the domain of interest. Class F
consists of all functions of the form
F(x) =
p
∑
j=1
m
∑
k=1
a
jk
f
k
(x
j
(t)). (2)
where the parameters a
jk
define a specific F.
Given the set f of basis functions, define f
T
(x) =
f
1
(x) ··· f
m
(x)
and
f
T
(x) =
f
T
(x
1
) ··· f
T
(x
p
)
.
Then the full system of p variables can be described
by
dx(t) = Af(x(t))dt (3)
where A is a p× pm matrix containing p sets of pa-
rameters a
jk
.
Our goal is as follows: given the set f of basis
functions and an observed trajectory
X
0:T
≡ {x(0),x(η),...,x(T)} (4)
we wish to recoverthe structure of the system by iden-
tifying A. In (4), η is the interval between observed
values, and is assumed to be constant.
Example: Masses and Springs
Consider a dynamic system of masses connected by
springs. From the observation X
0:T
of the positions
of the masses over a time interval [0,T] we aim to in-
fer which masses are connected by springs. In this
case we know precisely which basis functions to use
as they follow directly from Newtonian mechanics.
Also, the matrix A now contains elements with val-
ues in {0,1} representing the presence or absence of
a spring.
Example: Gene Regulatory Networks
As noted in the introduction it is natural to model
gene expression networks using stochastic differen-
tial equations, and this is our central aim in what fol-
lows. Further, just as in the example of masses and
springs, we aim to infer useful information regarding
the structure of the network by inferring the matrix A.
2.2 Learning Algorithm
Since we observe a trajectory X
0:T
with interval η be-
tween consecutive values we should consider a dis-
crete model. The natural discretization of (3) is to
rewrite it as
x(t + 1) = x(t) + ηAf(x(t)) (5)
where x(t) and x(t + 1) are consecutive observations.
Assuming that our model is perturbed by Gaussian
noise we employ the least squares error function
Error(A) =
p
∑
i=1
n−1
∑
t=0
[x
i
(t + 1) − x
i
(t) − ηA
i
f(x(t))]
2
.
(6)
Where A
i
is the ith row of A. This error function
has been shown to be convex when A is real-valued
(Banerjee et al., 2008).
Our proposed algorithm assumes that A has ele-
ments A
i, j
∈ W where W is a finite set. This assump-
tion is not too restrictive as in many interesting prob-
lems the existence of an edge and its nature are all
we are looking for. For example, in addressing gene
interactions we are mainly interested in identifying
whether a gene inhibits, enhances or does not influ-
ence other genes. In this case W = {−1,0, 1} would
be an appropriate choice provided we have an ade-
quate set f of basis functions. Also, determining the
structure of the system in this way can form a first
step making the edge weights easier to estimate after-
wards.
Even though (6) is convex for a real-valued A, our
choice to restrain A
i, j
to W entails the loss of that
guarantee. Nevertheless, we show that restraining the
search space according to the domain of interest, de-
spite the loss of convexity, can lead to improved per-
formance (Experiment 1).
LearningDynamicSystemsfromTime-seriesData-AnApplicationtoGeneRegulatoryNetworks
325

We use a local search strategy to avoid searching
all |W|
p
2
m
possible structures. We start with an arbi-
trary structure—perhaps chosen according to the spe-
cific domain to reduce the search time—and gener-
ate new candidates by selecting an edge and altering
the value among the possibilities in W. If the change
results in a decrease in the error, we keep the new
structure and restart. When we cannot generate new
candidates that decrease the error we stop the search.
This strategy can no longer guarantee that we achieve
a global minimum so we consider additional strate-
gies that may help us avoid local minima. For con-
venience, we will refer to this approach as flip-edge
throughout the paper due to the way new structures
are generated.
It is of interest to note that the error function used
is decomposable, in the sense that is familiar from
probabilistic graphical models (Koller and Friedman,
2009). This leads to a simple method for quickly eval-
uating the error. The error function is a sum of p sum-
mands, one for each variable and each itself having
limited dependencies. The total error is a sum of in-
dividual node errors
Error(A) =
p
∑
i=1
nodeError
i
(A) (7)
where
nodeError
i
(A) =
n−1
∑
t=0
[x
i
(t + 1) − x
i
(t) − ηA
i
f(x(t))]
2
.
(8)
This is useful as our algorithm, from an initial struc-
ture, generates neighbouring structures based on one
edge flip, and we want to minimise the error func-
tion. Let e
( j,k),i
be the edge from variable j to vari-
able i associated with f
k
. We are seeking the value
w ∈ W for e
( j,k),i
that minimises the error function.
Since e
( j,k),i
is only associated with row A
i
we know
that minimising the error of A is equivalent to min-
imising nodeError
i
(A). Let δ(e) be a function that re-
turns the w minimising Error(A) when flipping edge
e. This function can easily be cached as it will only
change when some other element of the relevant A
i
is
changed.
3 EXPERIMENTS
3.1 Masses and Springs
We first compare the flip-edge algorithm with a l
1
-
regularised least squares (l
1
-rls) algorithm in a masses
and springs scenario as presented in (Bento et al.,
2010) and introduced above. We will assume rest dis-
tances, masses and elastic coefficients are equal to 1
and focus on inferring which masses are connected.
The general equations that model the dynamics of
such a system are
dq(t) = v(t)dt
dv(t) = −∇U(q(t))dt + σdW(t)
U(q
i
(t)) =
1
2
∑
j
A
i, j
(||q
i
− q
j
|| − D
i, j
)
2
(9)
where q is the position, v is the velocity, D
i, j
is the
resting distance, dW(t) denotes the Wiener process
and σ
2
is the noise variance. The simulation is per-
formed using the Euler-Maruyama method for a time
step of 0.01. We sample using η = 0.1 and use
σ = 0.2 unless explicitly stated.
The same dynamic system was previously used as
an example by (Bento et al., 2011) though with a dif-
ferent target structure. (Bento et al., 2010) propose
the l
1
-rls algorithm for the recovery of the structure of
a network of stochastic differential equations
1
. The
idea is to recover each row of the support matrix A
independently by solving a convex optimisation prob-
lem. For each row i, A
i
is estimated by minimising
L(A
i
;X
0:T
) + λ||A
i
||
1
(10)
where
L(A
i
;X
0:T
) =
1
2η
2
n
T
∑
t=0
[x
i
(t + 1) − x
i
(t) − ηA
i
f(x(t))]
2
.
(11)
We used the CVX package (Grant and Boyd, 2008;
Grant and Boyd, 2012) to describe and solve the con-
vex program.
Our experiments used the following protocol: a
network is generated, the behaviour of this network
over an interval of time is simulated, and the result-
ing data is supplied to the algorithms. Each network
is generated as an N × M grid of masses, separated
along each axis by a unit of distance and connected
to all eight neighbours where possible. To generate
different structures, masses and springs are removed
with probability 0.1. We guarantee that all the springs
in the final structure are connected to two masses.
In the experiments a 5 × 5 initial grid is used except
when explicitly studying the performance under dif-
ferent network sizes.
Our goal was to compare our method against
an optimally tuned instance of l
1
-rls. We therefore
started by running preliminary experiments to study
the response of the l
1
-rls algorithm to different values
1
Though their focus is on the theoretical bounds of the
recovery rather than on performance.
ICPRAM2015-InternationalConferenceonPatternRecognitionApplicationsandMethods
326

of its parameters λ and τ (a threshold above which
we consider the existence of an edge). The prelim-
inary study led to the following approach: we run
the algorithm for λ ∈ {0,0.05,0.10,...,0.90,0.95}
and τ ∈ {0,0.1,0.2,. ..,1.8,1.9} and use the best pair
(λ,τ), chosen by direct comparison against the results
obtained with the known correct structure, to extract
the structure for comparison with our algorithm. Fur-
thermore, we guaranteed that the chosen pair was a lo-
cal minimum by 8-neighbour comparison in the λ× τ
space considered.
In a realistic setting, we would not be able to tune
l
1
-rls using the correct structure. Nevertheless, we
wanted to compare our suggested flip-edge algorithm
with the best possible l
1
-rls results.
Figure 1 shows the results from these experiments.
These results suggest that flip-edge, while undoubt-
edly a straightforward algorithm, performs very well
in uniform weight networks. In fact, in our ex-
periments it surpasses the l
1
-regularization approach
common in the literature in its ability to recover the
structure of the network. Specifically, it proved more
resistant to noise, small trajectories of observed data,
and size of the network (for the same length of tra-
jectory). Furthermore, the fact that it does not require
tuning of the parameters, for which there seems to be
no obvious method in the l
1
-rls algorithm, makes it a
more straightforward method to use.
3.2 Learning Gene Regulatory
Networks from Time-series
Knockout Data
We assessed our algorithm in the context of identify-
ing GRNs by employing data from the DREAM4 In
Silico Network Challenge (Dream4Challenge, 2009)
(see also (Marbach et al., 2010; Marbach et al., 2009;
Prill et al., 2010)). This allowed us to assess our al-
gorithm against many other methods—at least 25 in
the challenge itself—evaluated under the same condi-
tions.
Time-series data are especially useful if gathered
after applying perturbations to the regulatory equilib-
rium of the cell, as the relationships are then more
apparent than in a stable cell where the expression of
each gene remains reasonably constant. A common
experiment is to knock out a gene, that is, to com-
pletely block its expression, and observe the system
as it re-adapts. With this in mind, the DREAM4 chal-
lenge involves inferring the structure of five gene reg-
ulatory networks, each with 100 genes. Two were ex-
tracted from E. coli and three from Yeast. We are pro-
vided with data on the steady-state expression levels
of the wild-type, and after the knockout and knock-
down of every gene. (Knockdowns reduce the expres-
sion of some gene to half of that in the wild-type.) We
are also provided with 10 time-series of 21 time points
where an unknown perturbation is applied at the start
and released half way through the time-series.
We used the three best-performing methods from
the DREAM4 Challenge as comparisons for our
method. Pinna et al. (Pinna et al., 2010) presented
the best method by applying a pruning procedure on
top of z-score to remove potentially redundant edges.
This algorithm has a parameter—denoted t in the
original paper and renamed to θ in the following—
used to decide when an edge should be included. The
z-score method of Prill et al. (Prill et al., 2010) was
placed second and the TRANSWESD method of Klamt
et al. (Klamt et al., 2010) achieved the third best per-
formance with a variant of transitive reduction for
weighted signed digraphs.
It is of interest to note that the three top scorers in
the DREAM4 Challenge did not make any use of the
time-series data, as it seems clear that it might provide
interesting insights into the correct structure. Figure
2 shows an example of three genes (P: dotted line,
D: dashed line and S: solid line) where there are in-
hibitory relationships from P to S, P to D and S to D.
However, from the observation of the initial and final
states only, it would be impossible to infer anything
more than the inhibitory relationship from P to S.
We applied the flip-edge algorithm to this data.
Our method relies on time-series data to improve the
inferences made by the existing static methods. Un-
like in the example using masses and springs we do
not in this case know a correct set of basis functions.
Bonneau et al. (Bonneau et al., 2006) suggest the use
of the logistic sigmoid (while ultimately using a lin-
ear approximation) and this agrees with our initial in-
tuition. The model thus becomes, for some general
gene i,
dx
i
(t) = [−x
i
(t) + F(A
i
,β, x(t))]dt + σdW(t) (12)
where
F(A
i
,β, x(t)) =
max
eq
(x
i
)
1+ exp
−
∑
j
A
i, j
β
j
x
j
(t)
. (13)
Here, dW(t) is a Wiener process, β
j
denotes the
weight the expression of the jth gene would have on
the activation of the other genes, and and max
eq
(x
i
)
denotes the maximum observed value of x
i
in an equi-
librium state. We added the scaling factor max
eq
(x
i
)
since the observed maximum expression values may
vary considerably for each variable. However, this re-
sults in a need to estimate β. With the above model,
LearningDynamicSystemsfromTime-seriesData-AnApplicationtoGeneRegulatoryNetworks
327

Figure 1: Identification of systems of masses and springs. We plot the number of incorrectly classified edges against, respec-
tively: noise variance, size of the observed time-series, and size of the structure being learnt. Each data point was obtained by
running the algorithm 10 times; the bars correspond to one standard deviation.
Figure 2: Example of the evolution of the expression of
three genes where time-series data, rather than just the ob-
servation of the initial and final state, is crucial to infer all
three relationships.
the error function becomes
Error(A,β) =
p
∑
i=1
∑
t
x
i
(t + 1) − x
i
(t)
η
+ x
i
(t)−
max
eq
(x
i
)
1+ exp
−
∑
j
A
i, j
β
j
x
j
(t)
!
2
(14)
We used W = {−1, 0,1} as we are interested in
whether a gene is inhibiting, enhancing or just unre-
lated to the expression of some other gene. We ran all
experiments with η = 0.001 after observing the gene
expression changes, from step to step, in the time se-
ries data.
The flip-edge algorithm was modified as follows
to incorporate the estimation of β:
1. Generate an initial network structure.
2. Use the current structure to estimate β.
3. Run flip-edge using the estimated β.
In step 1 of the algorithm we generated prior struc-
tures using the two most successful methods from the
DREAM4 Challenge, and using different values for
θ. After this step we have the first candidate A.
In step 2 we estimate β by performing ordinary
least squares multivariate regression. Note that in this
algorithm β
i
is constant—it does not itself vary with
time. The motivation for this assumption was that β
would be modelling transcription rates rather than the
effectiveness of the resulting protein in influencing
the transcription of the other genes. For the estimation
of β we only consider the gene expressions at stable
states such as the wild-type—that is, the expression
values of the non-perturbed network—and the stable
states after the knockout of a single gene. In a gen-
eral stable state s we have ds
i
(t)/dt = 0, along with
s
i
= F(A
i
,β,s) and
A
i
◦ s
T
β = −log
max
eq
(s
i
)
s
i
− 1
= g(s
i
) (15)
where ◦ denotes the Hadamard product. That is, the
expression of the gene s
i
is regulated by its parents
(A
i
◦s
T
) weighted by β. Let S be the square matrix of
stacked s
T
and define g
T
(s) =
g(s
1
) ··· g(s
p
)
such that
g(s) = (A◦ S)β. (16)
Finally let y be a vector of stacked g(s) and X a matrix
of stacked A◦S so that we can estimate β using all the
instances of stable states available. We have
y = Xβ (17)
and we want to estimate β by least squares
argmin
β
k
∑
i=1
(y
i
− X
i
β)
T
(y
i
− X
i
β) (18)
where k denotes the number of stable state data in-
stances, y
i
corresponds to the ith g(s) and X
i
corre-
sponds to the ith (A◦ S), which gives us
β = (X
T
X)
−1
X
T
y. (19)
In step 3 we use A from step 1 and β from step 2,
and run flip-edge gradient descent using (14) which is
also decomposable. When applying flip-edge we de-
cided to use only the second half of the time-series
data provided; that is, from the point when the pertur-
bation is lifted, as we do not know the exact nature of
the perturbation.
ICPRAM2015-InternationalConferenceonPatternRecognitionApplicationsandMethods
328

Table 1: Comparison of the results of other methods with
our method run for three rounds of estimation and flip-edge
with different values of θ.
overall auroc aupr
Pinna et al 71.589 40.110 103.068
z-score 71.297 39.737 102.857
TRANSWESD 64.715 37.324 92.106
θ = 2.5 78.232 48.684 107.779
θ = 3 79.116 49.278 108.953
θ = 3.5 82.962 52.707 113.217
θ = 4 80.955 50.584 111.326
θ = 4.5 77.892 49.051 106.732
The DREAM4 Challenge evaluated performance
using the p-values for the area under the ROC curve
(AUROC) and area under the precision-recall curve
(AUPR) measures for each network—see (Schaffter
et al., 2011) and (Dream4Challenge, 2009) for a com-
plete description. The p-values provide an indication
of the probability that random predictions would be
of equal or better quality than those produced by the
method of interest. Let p
AUROC
and p
AUPR
be the ge-
ometric means of the corresponding p-values for the
five networks of the dataset. The scores are given by
auroc score = − log
10
(p
AUROC
)
aupr score = −log
10
(p
AUPR
)
overall score = −0.5log
10
(p
AUROC
× p
AUPR
).
(20)
Figure 3 (a) shows the performance of our method
alongside that of the top three methods presented at
DREAM4. (As pointed out in (Schaffter et al., 2011),
the best performer in the DREAM3 Challenge (Yip
et al., 2010) did not repeat its previous success. The
method presented in (Yip et al., 2010) uses an ap-
proach similar to ours in trying to learn first from
knockout and then from time-series data using differ-
ential equation models.)
Figure 3 (b) shows how the performance of our
algorithm is affected by using different methods to
choose the initial structure. Clearly the use of z-score
or the method of Pinna et al. has little effect on the
score achieved by our algorithm. This suggests that
our algorithm is improving due to the time series data,
independently of the initial structure and most likely
improving on different features than those targeted by
Pinna et al.’s pruning step. The average difference in
the score over the values of θ considered is 0.052 in
favour of Pinna et al., which is considerably smaller
than the original difference before the application of
our method (see Table 1).
Unfortunately, comparison using only the data
of the DREAM4 Challenge does not allow us to
have statistical confidence in the performance of
our method, since we address only one prediction
task. However, the GeneNetWeaver distribution in-
cludes the kinetic models of the networks used in the
DREAM4 Challenge. This allows us to generate new
data from the same networks. We ran our method
as described above with θ = 3.5. We used 10 new
datasets from each individual network and we com-
pared our score with the score obtained by our im-
plementation of Pinna et al.’s method, in this case us-
ing θ ∈ {2, 2.5, 3,3.5} and finding that θ = 3.0 max-
imised its average score over the set of 50 prediction
tasks (ten datasets drawn from five networks). In Fig-
ure 4, we present the percentage improvement of our
method over Pinna et al. with θ = 3.0 for the ten
datasets for each of the five DREAM4 Challenge net-
works. In Figure 4 we see a box plot where the whole
boxes and whiskers are above zero. Furthermore, the
p-values for the t-test on the improvement for the dif-
ferent networks are 0.00064, 1.43057e-09, 0.00637,
1.88231e-05, and 6.6216e-10 meaning that the im-
provement of our method over the best scorer at the
DREAM4 Challenge is strongly significant. In fact,
it boasts quite surprising improvement in some net-
works suggesting it is considerably more efficient at
discovering particular graphical features.
4 FURTHER REFINEMENTS
Since the local search approach cannot guarantee to
end at the global minimum of the error function it is
interesting to consider some strategies to try to avoid
finishing the search in local minima. Many differ-
ent possibilities are presented in the literature, such
as random restarts, tabu searches and annealing meth-
ods, among others. Given the characteristics of our
problem we were led to exploring data perturbation
methods.
The idea is that it might be possible to escape lo-
cal minima if we slightly change the weight given to
each data point. Intuitively, we want to change the
weights of the data in the error function enough to es-
cape local minima while keeping the general shape of
the error function unaltered. A common approach is
to consider a probability distribution over the weights
and make it converge to the uniform distribution so
that we get closer and closer to the original dataset
over time.
Looking back at (14) we can see that the error
function can be decomposed as a sum of terms each
corresponding to a pair i,t.
Error(A,β) =
p
∑
i=1
∑
t
error(i,t,A,β) (21)
to which we can add a matrix of weights
LearningDynamicSystemsfromTime-seriesData-AnApplicationtoGeneRegulatoryNetworks
329
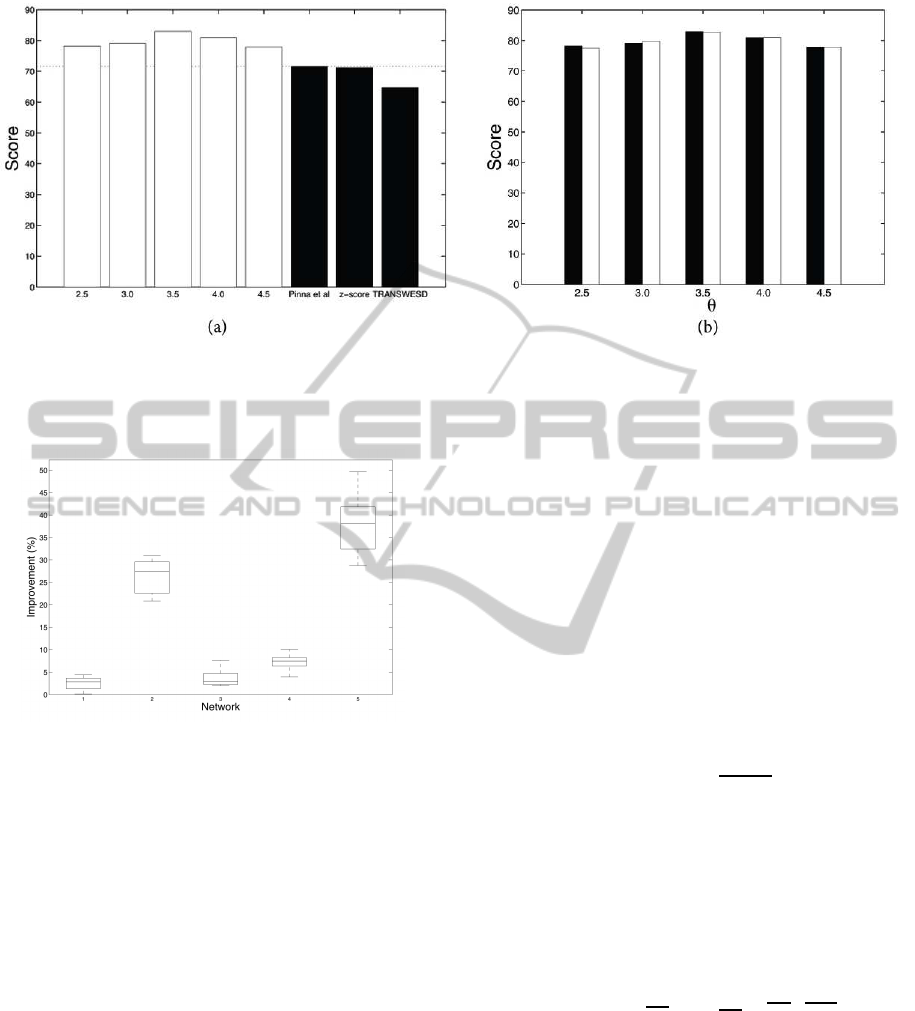
Figure 3: (a) Comparison of the scores of our method (white), for different values of θ, and the top three scorers (black) in the
DREAM4 Challenge. The horizontal dotted line represents the score of the best method at the DREAM4 Challenge.
(b) Comparison of the scores achieved by our method from different starting structures and using different values for θ. Black
bars: using the method of Pinna et al. as initial structure; white bars: using z-score as initial structure.
Figure 4: Percentage improvement of flip-edge with θ = 3.5
and three rounds, over our implementation of the method
of Pinna et al. with θ = 3.0 (the best score from θ ∈
{2,2.5,3,3.5}) for ten new datasets generated from each
original DREAM4 network. The p-values for the t-test on
the improvement for the different networks are 0.00064;
1.43057e-09; 0.00637; 1.88231e-05; 6.6216e-10.
Error(A,β,w) =
p
∑
i=1
∑
t
w
i,t
error(i,t,A,β) (22)
4.1 Random Perturbation
For the random perturbation we sample each w
i,t
from
a Gamma distribution (as it is non-negative)
w
i,t
∼ Gamma(1/τ,τ) (23)
where τ is a “temperature” variable that decreases
over time. The above distribution has mean equal to
one and variance proportional to τ therefore forcing
w
i,t
to approach one over time.
4.2 Adversarial Perturbation
With the aim of escaping a possible local minimum, it
is possible to employ a more informed strategy when
choosing the weights used to perturb the data. The
general idea, as presented by (Elidan et al., 2002), is
as follows. We aim to modify the error function such
that the current minimum becomes less desirable. In
this way the optimization is able potentially to escape
from the minimum, should it be local. This means that
instead of randomly generating a new weight vector,
we will iteratively update it. In general one can con-
sider:
w
n+1
i,t
= w
n
i,t
+ ζ
∂Error
∂w
i,t
(24)
so that we increase the relevance of the weights that
contribute more towards an increased value of the er-
ror function. (Elidan et al., 2002) further developsthis
idea to ensure convergence towards the uniform dis-
tribution and avoid negative weight values. Follow-
ing their results we have the following weight update
equation
w
n+1
i,t
= α
n+1
w
0
i,t
κ
κ+λ
(w
n
i,t
)
λ
κ+λ
e
−
ζ
κ+λ
∂Error
∂w
i,t
|
w
n
i,t
(25)
where α
n+1
is a normalisation constant and both κ and
λ are inversely proportional to the temperature τ.
In both the random and adversarial approaches,
we start with uniform weights and allow our algo-
rithm to converge to a (possibly local) minimum. We
then select a new set of weights using the appropri-
ate update equation and temperature, and optimise
again starting from the previously found minimum.
This process is repeated several times, updating the
ICPRAM2015-InternationalConferenceonPatternRecognitionApplicationsandMethods
330

temperature at each iteration, and the best minimum
found is returned.
We further extended our method by checking
whether the best solution was in a plateau, and if so
continuing the search in case we were able to escape
the plateau.
4.3 Results
All the experiments were run for ten temperature up-
dates where the temperature was reduced by a factor
of a (τ ← aτ). For the random perturbation, where
w
i,t
∼ Gamma(1/τ,τ), we used an initial τ = 1, a =
0.9 for five runs. For adversarial perturbation we used
initial τ = 0.001, a = 0.9, ζ = 1 and κ,λ = 1/τ unless
otherwise stated. Note that adversarial perturbation is
a deterministic procedure so only one run per param-
eter configuration was performed.
81.5
82
82.5
83
83.5
Random Adversarial (1) Adversarial (2) Adversarial (3)
Figure 5: Score of different runs after including data pertur-
bation. The horizontal line marks the best score achieved
without data perturbation. The first box refers to random
perturbation and the following three refer to adversarial per-
turbation: (1) for different ζ = [0.7,0.8,... , 1.3]; (2) for dif-
ferent initial τ = [10,1,... , 1e − 05]; (3) for different tem-
perature fall rates a = [0.1,0.2,... , 0.9]. Also plotted are
the actual values for each value of ζ, τ and a.
Figure 5 presents the results obtained using the re-
finements proposed above. We can see that they do
not consistently improve on the results obtained us-
ing non-perturbed data though some configurations of
parameters and some runs using random perturbation
indeed improved on the score. Checking for the ex-
istence of plateaus produced no improvement on the
score. On the rare occasions it lead to an escape the
search ended on a minimum equivalent to one found
for another temperature.
In terms of the value of the error functions, instead
of the DREAM4 score, data perturbation was consis-
tently reaching lower values. Also of note is the fact
that the correct network, with the data given, has a
higher value on the error function than the structures
found by those methods, meaning that our method
would discard it in favour of the networks it even-
tually found. This could be due to the noise in the
data or to the unavoidable misrepresentation of the
phenomenon by our chosen basis function. Neverthe-
less, all the alternatives studied here are clear win-
ners when compared to the best methods that tackled
the DREAM4 challenge, strongly suggesting that the
use of time series data and these simple, yet effective,
methods is beneficial.
5 FINAL REMARKS
It is important to note that some of the data provided
in the DREAM4 Challenge datasets—namely, infor-
mation on the steady-state expression after the knock
out of each gene in the network—is very unrealistic.
However that data was only used in the creation of
an appropriate prior structure, and all subsequent im-
provement was made using time-series perturbation
data from ten experiments. This data is considerably
more realistic in terms of what might be produced in a
laboratory environment, especially since we were not
informed of the exact characteristics of the perturba-
tion.
It might be argued that with the release of the
information concerning GeneNetWeaver (Schaffter
et al., 2011)—the in silico simulator used to gener-
ate the datasets—and the datasets themselves with the
gold standard, we would have an unfair advantage.
Note, however, that our method is completely inde-
pendent from the design of GeneNetWeaver and all
the parameters apart from θ—used to create the ini-
tial structure before the time series dataset is used—
are estimated using only the initial dataset.
In terms of application to a real-world scenario, it
is fair to assume that there would be prior knowledge
concerning the organism being studied, and that the
experiments themselves would have a specific goal.
In such a scenario we feel that the prior knowledge
could help in the construction of an appropriate prior
structure (a fairly sparse but high-confidence prior
seems to be favourable to flip-edge). Flip-edge would
then be run on time-series data from appropriately de-
signed experiments. We also feel that knowing the
characteristics of the perturbation could help in mak-
ing the method more efficient.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Ivo Timoteo is supported by an FCT Individual Doc-
toral Fellowship, number SFRH/BD/88466/2012.
LearningDynamicSystemsfromTime-seriesData-AnApplicationtoGeneRegulatoryNetworks
331

REFERENCES
Ackers, G. K., Johnson, A. D., and Shea, M. A.
(1982). Quantitative model for gene regulation by
lambda phage repressor. Proceedings of the National
Academy of Sciences, 79(4):1129–1133.
Banerjee, O., Ghaoui, L., and D’Aspremont, A. (2008).
Model selection through sparse maximum likelihood
estimation for multivariate Gaussian or binary data.
Journal of Machine Learing Research, 9:485–516.
Barrett, T., Troup, D. B., Wilhite, S. E., Ledoux, P., Evan-
gelista, C., Kim, I. F., Tomashevsky, M., Marshall,
K. A., Phillippy, K. H., Sherman, P. M., Muertter,
R. N., Holko, M., Ayanbule, O., Yefanov, A., and
Soboleva, A. (2011). NCBI GEO: archive for func-
tional genomics data set - 10 years on. Nucleic Acids
Research, 39:D1005–D1010.
Bento, J., Ibrahimi, M., and Montanari, A. (2010). Learn-
ing networks of stochastic differential equations. In
Lafferty, J. D., Williams, C. K. I., Shawe-Taylor, J.,
Zemel, R. S., and Culotta, A., editors, NIPS, pages
172–180. Curran Associates, Inc.
Bento, J., Ibrahimi, M., and Montanari, A. (2011). Infor-
mation theoretic limits on learning stochastic differ-
ential equations. In Kuleshov, A., Blinovsky, V., and
Ephremides, A., editors, ISIT, pages 855–859. IEEE.
Bonneau, R., Reiss, D. J., Shannon, P., Facciotti, M., Hood,
L., Baliga, N. S., and Thorsson, V. (2006). The infer-
elator: an algorithm for learning parsimonious regula-
tory networks from systems-biology data sets de novo.
Genome Biology, 7(5).
Dream4Challenge (2009). DREAM4, Chal-
lenge 2 – In Silico Network Challenge.
http://wiki.c2b2.columbia.edu/dream/index.php?title=D4c2.
Elidan, G., Ninio, M., Friedman, N., and Schuurmans, D.
(2002). Data perturbation for escaping local maxima
in learning. In In AAAI, pages 132–139.
Gardner, T. S. and Collins, J. J. (2000). Neutralizing noise
in gene networks. Nature, 405(6786).
Grant, M. and Boyd, S. (2008). Graph implementations
for nonsmooth convex programs. In Blondel, V.,
Boyd, S., and Kimura, H., editors, Recent Advances in
Learning and Control, volume 371 of Lecture Notes
in Control and Information Sciences, pages 95–110.
Springer London.
Grant, M. and Boyd, S. (2012). CVX: Matlab software
for disciplined convex programming, version 2.0 beta.
http://cvxr.com/cvx.
Klamt, S., Flassig, R., and Sundmacher, K. (2010). TRAN-
SWESD: inferring cellular networks with transitive
reduction. Bioinformatics, 26(17):2160–2168.
Koller, D. and Friedman, N. (2009). Probabilistic graphical
models: principles and techniques. MIT Press.
Ly, D. L. and Lipson, H. (2012). Learning symbolic rep-
resentations of hybrid dynamical systems. Journal of
Machine Learning Research, 13:3585–3618.
Marbach, D., Prill, R. J., Schaffter, T., Mattiussi, C., Flo-
reano, D., and Stolovitzky, G. (2010). Revealing
strengths and weaknesses of methods for gene net-
work inference. Proceedings of the National Academy
of Sciences.
Marbach, D., Schaffter, T., Mattiussi, C., and Floreano,
D. (2009). Generating realistic in silico gene net-
works for performance assessment of reverse engi-
neering methods. Journal of Computational Biology,
16(2):229–239.
Pinna, A., Soranzo, N., and de la Fuente, A.
(2010). From knockouts to networks: estab-
lishing direct cause-effect relationships through
graph analysis. PLoS ONE 5(10): e12912.
doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0012912.
Prill, R. J., Marbach, D., Saez-Rodriguez, J., Sorger, P. K.,
Alexopoulos, L. G., Xue, X., Clarke, N. D., Altan-
Bonnet, G., and Stolovitzky, G. (2010). Towards a
rigorous assessment of systems biology models: The
DREAM3 challenges. PLoS ONE, 5(2):e9202.
Schaffter, T., Marbach, D., and Floreano, D. (2011).
GeneNetWeaver: in silico benchmark generation and
performance profiling of network inference methods.
Bioinformatics, 27(16):2263–2270.
Voortman, M., Dash, D., and Druzdzel, M. (2010). Learn-
ing why things change: The difference-based causal-
ity learner. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Sixth An-
nual Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelli-
gence (UAI).
Yip, K., Alexander, R., Yan, K., and Gerstein, M.
(2010). Improved reconstruction of In Silico
gene regulatory networks by integrating knockout
and perturbation data. PLoS ONE 5(1): e8121.
doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0008121, 5(1):e8121.
ICPRAM2015-InternationalConferenceonPatternRecognitionApplicationsandMethods
332
